Assessing the Performance of Water Vapor Products from ERA5 and MERRA-2 during Heavy Rainfall in the Guangxi Region of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data Description
2.1.1. Reanalysis Dataset
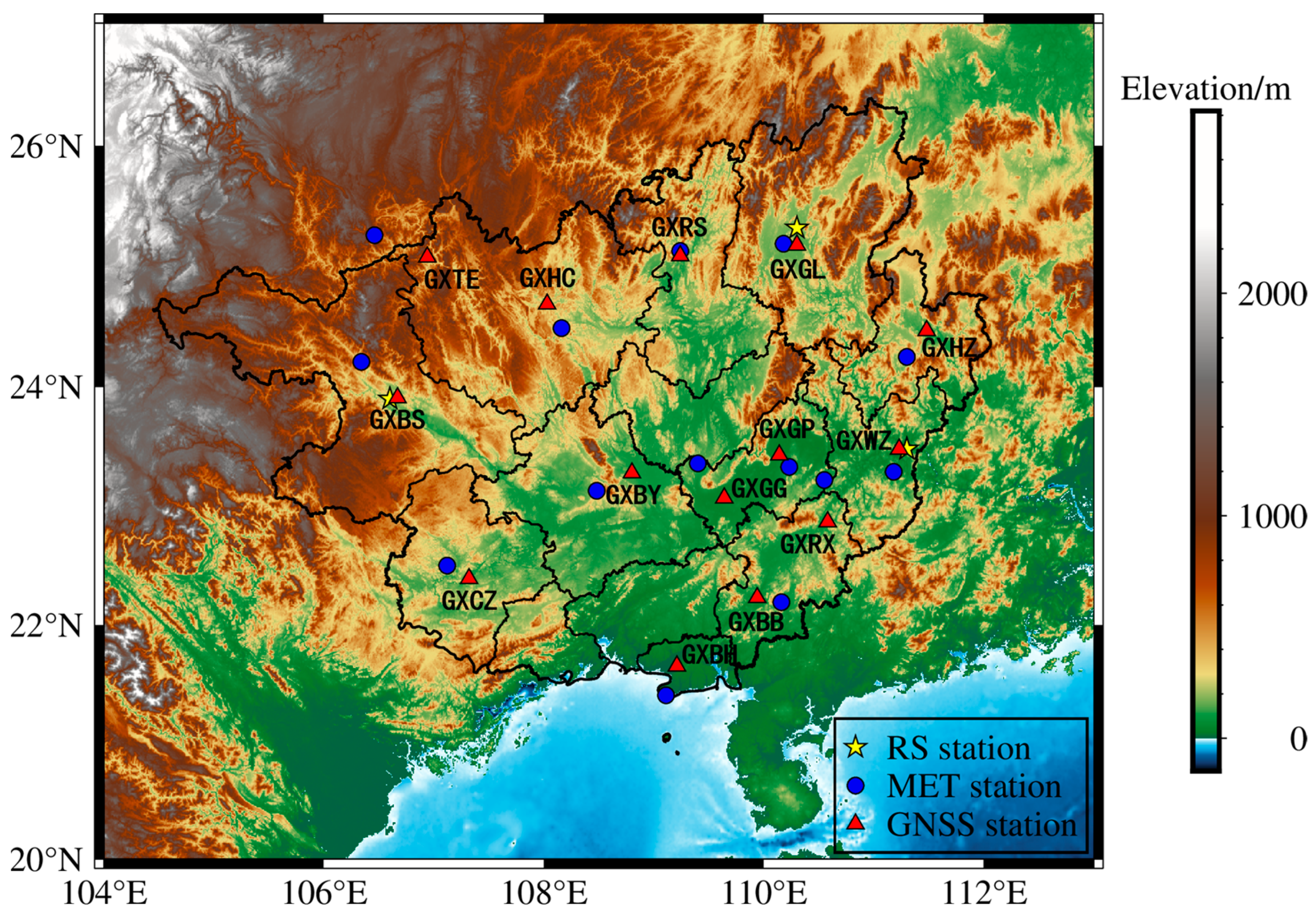
2.1.2. Meteorological Data
2.1.3. Radiosonde Data
2.1.4. GNSS Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. GNSS PWV Inversion Method
2.2.2. Preprocessing of MERRA-2 and ERA5 Data to Be Evaluated
2.2.3. Accuracy Assessment
2.2.4. Rainfall Intensity Levels Defined by the China Meteorological Administration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of PWV between Radiosonde and GNSS
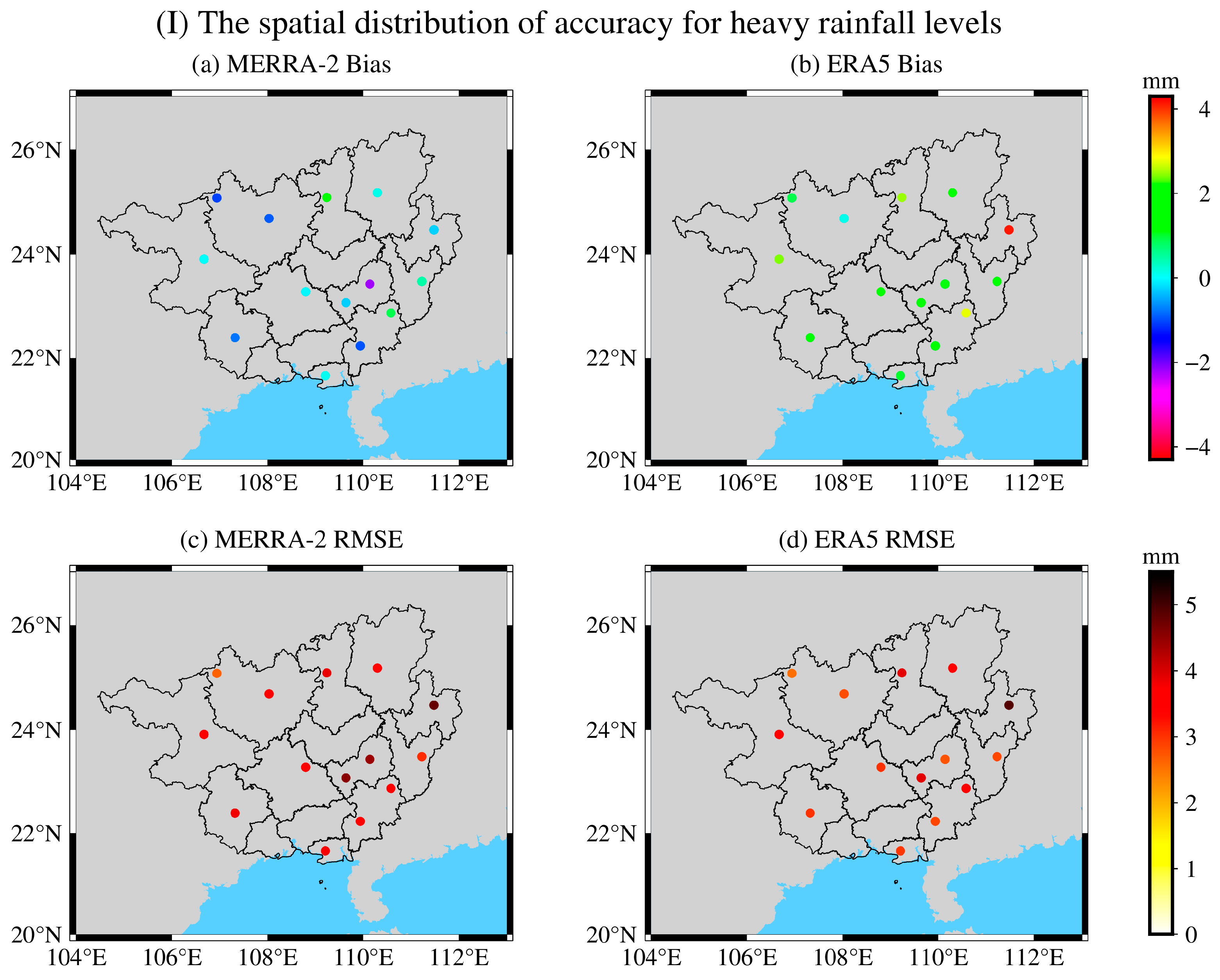
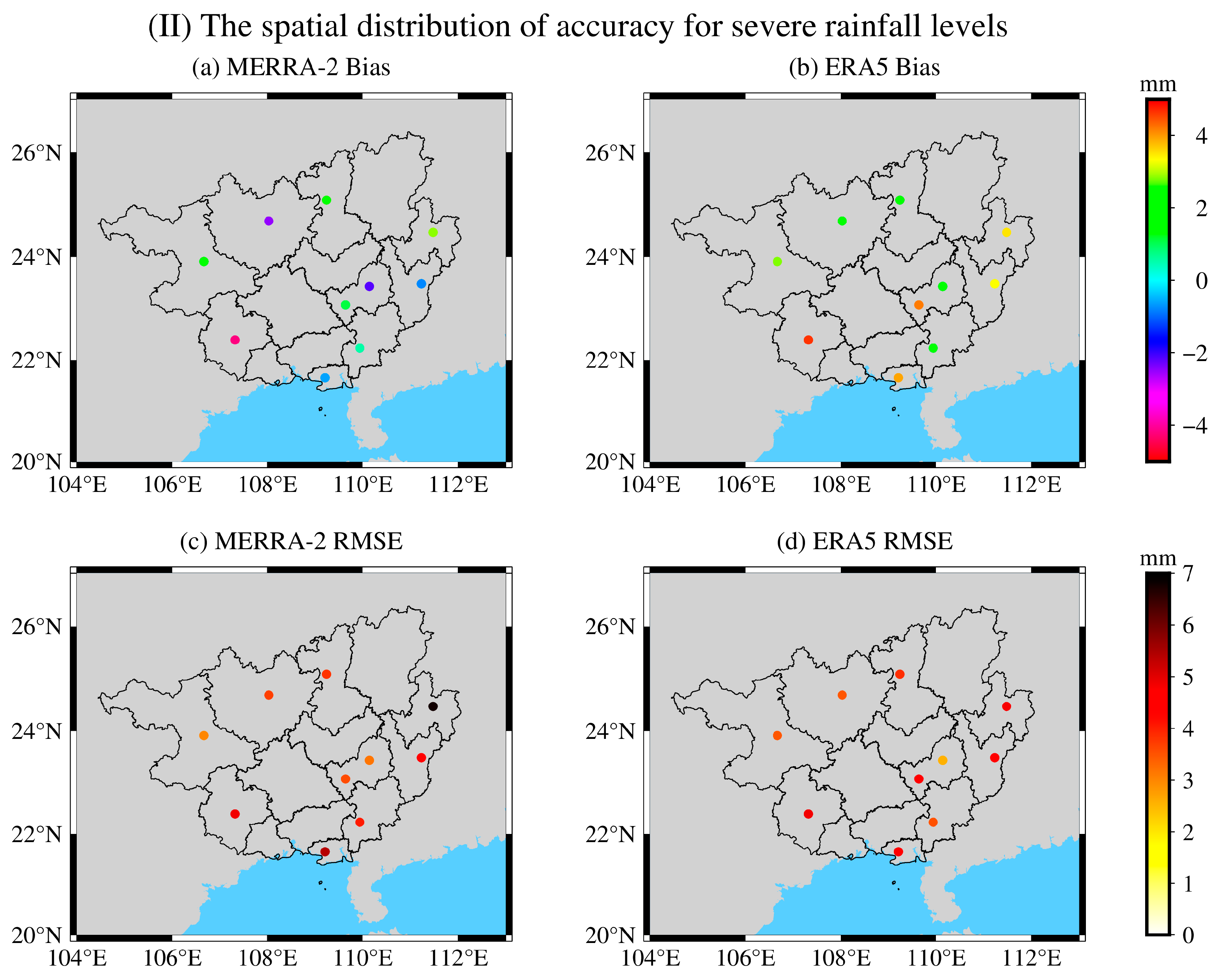
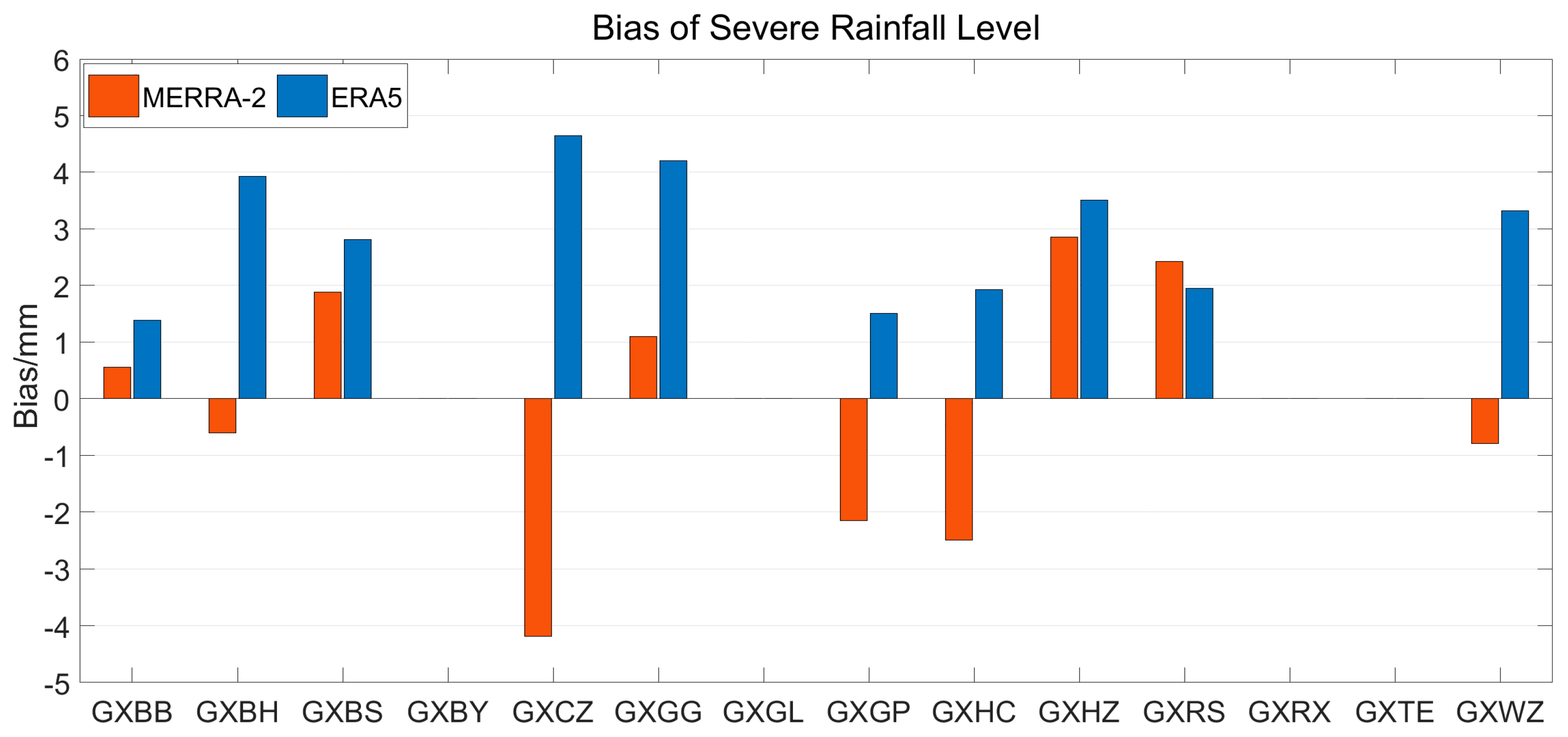
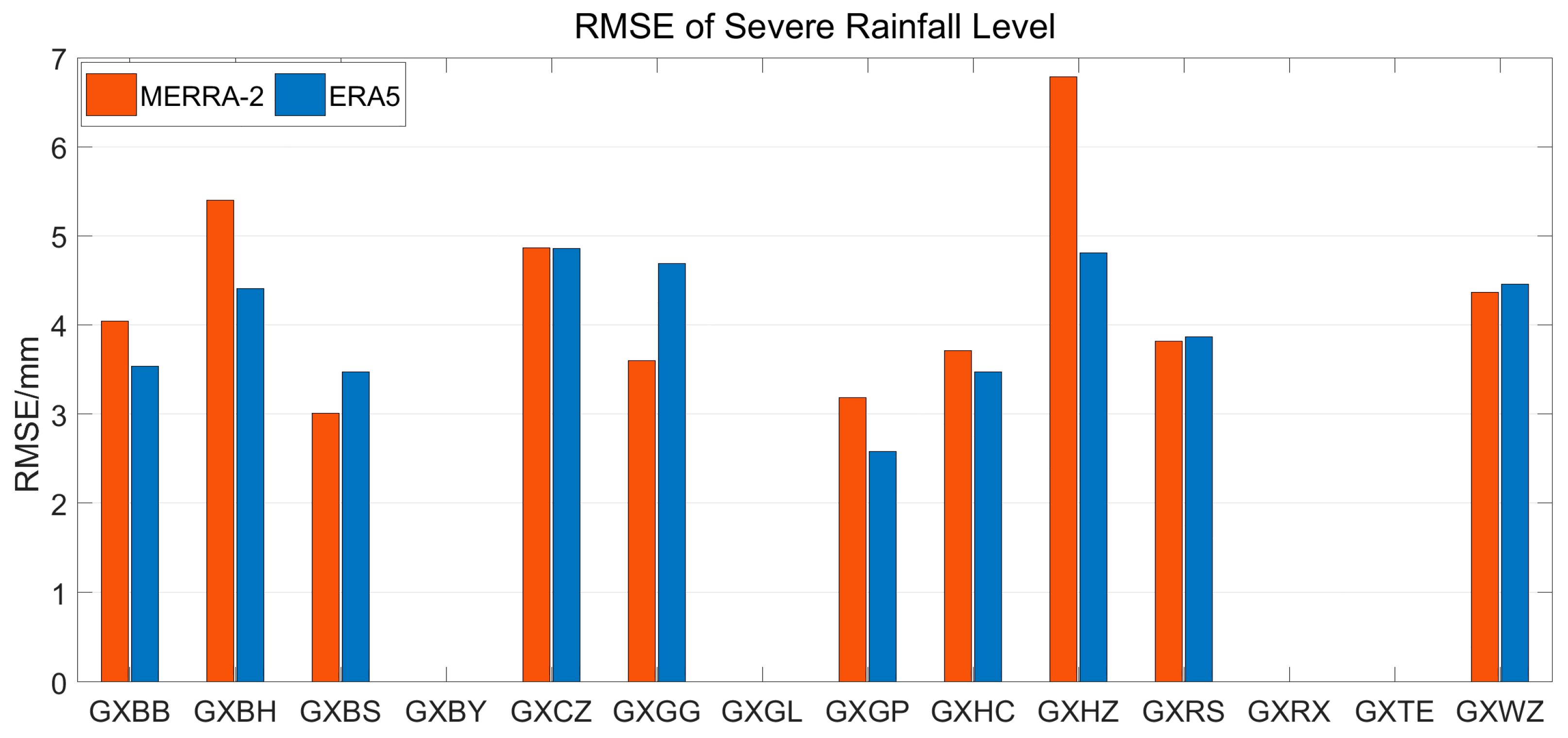
3.2. Accuracy Analysis of MERRA-2 and ERA5 PWV during Heavy and Severe Rainfall
3.3. Performance of MERRA-2 and ERA5 PWV during a Heavy Rainfall Event
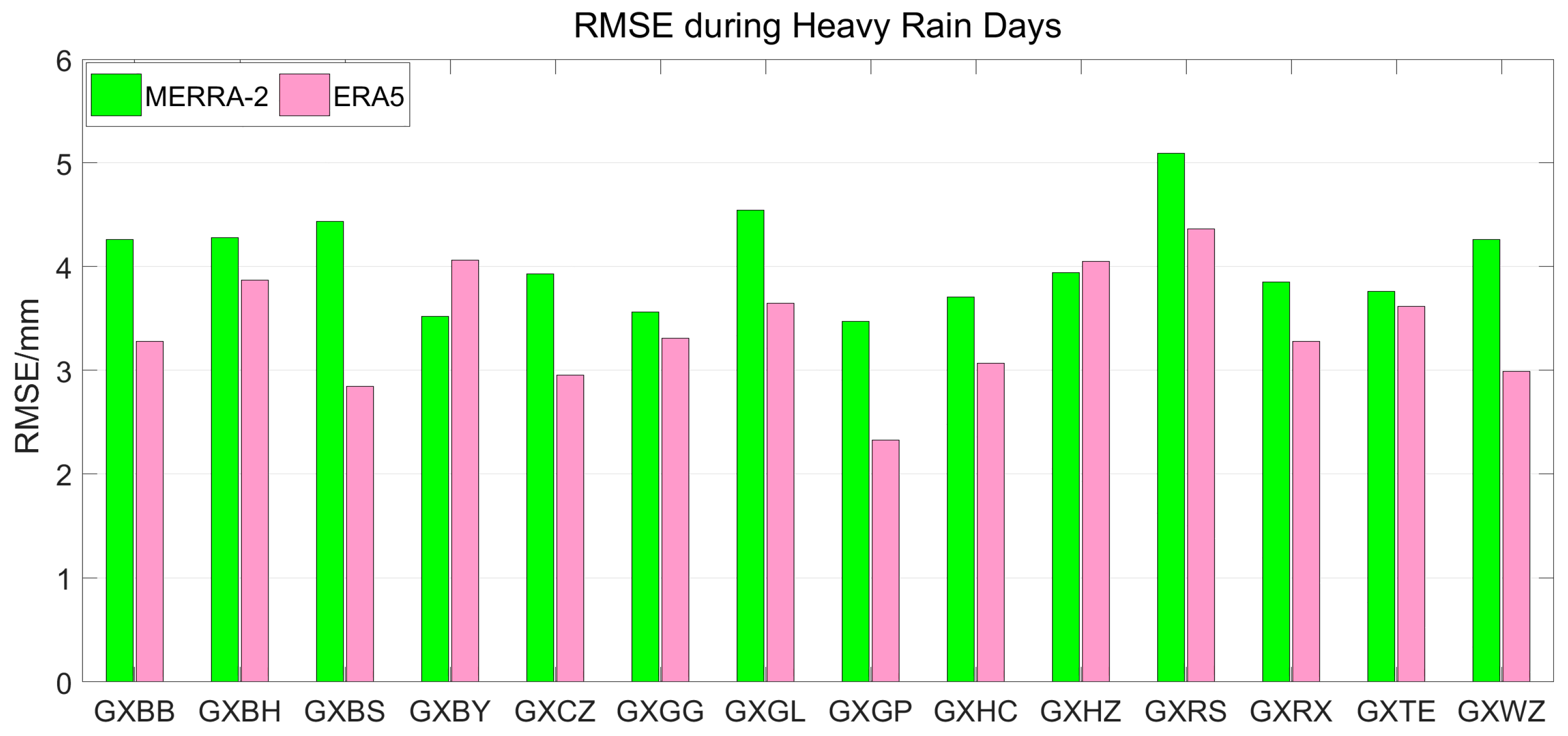
3.3.1. Analysis of the Daily Average Error during Heavy Rain Days
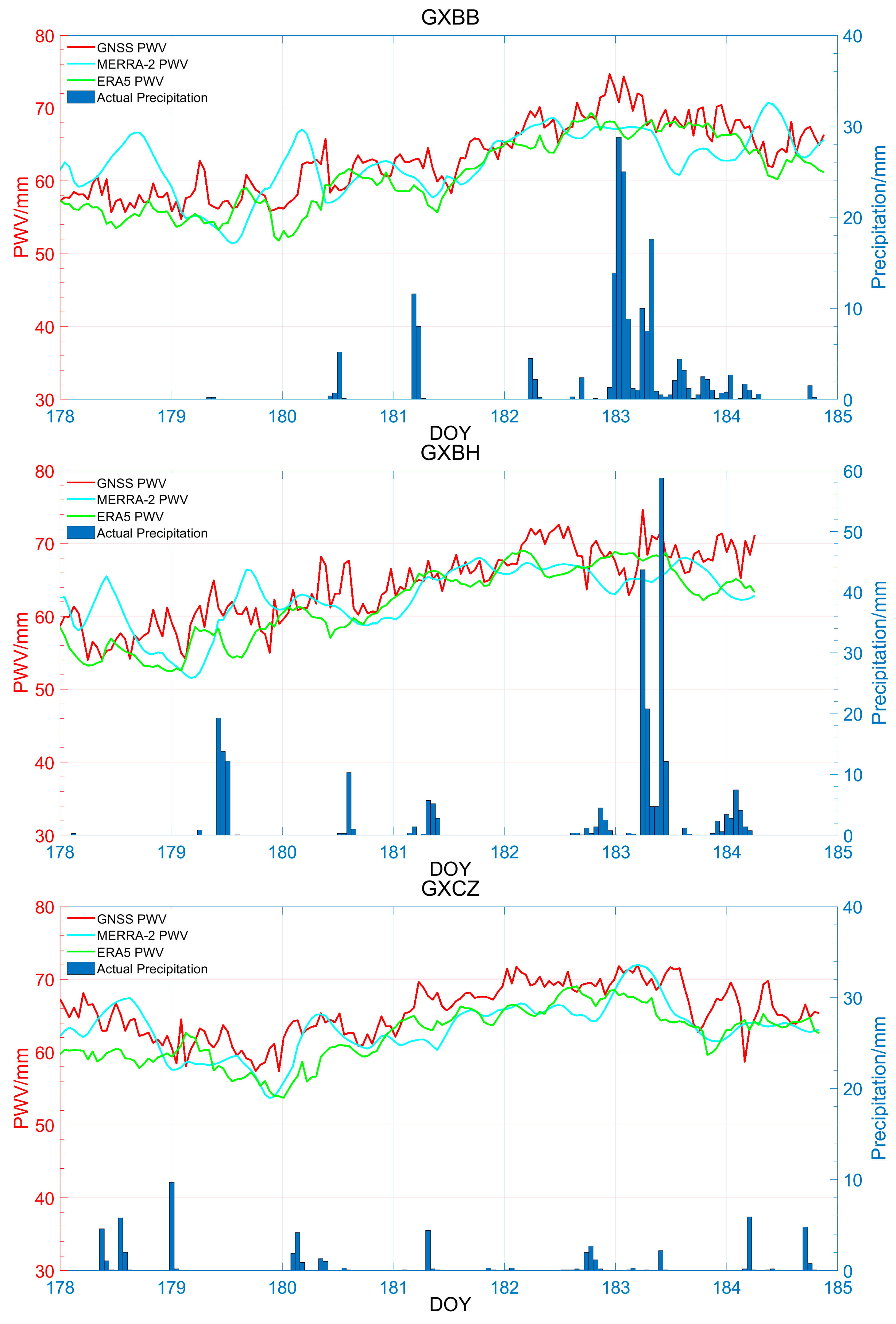
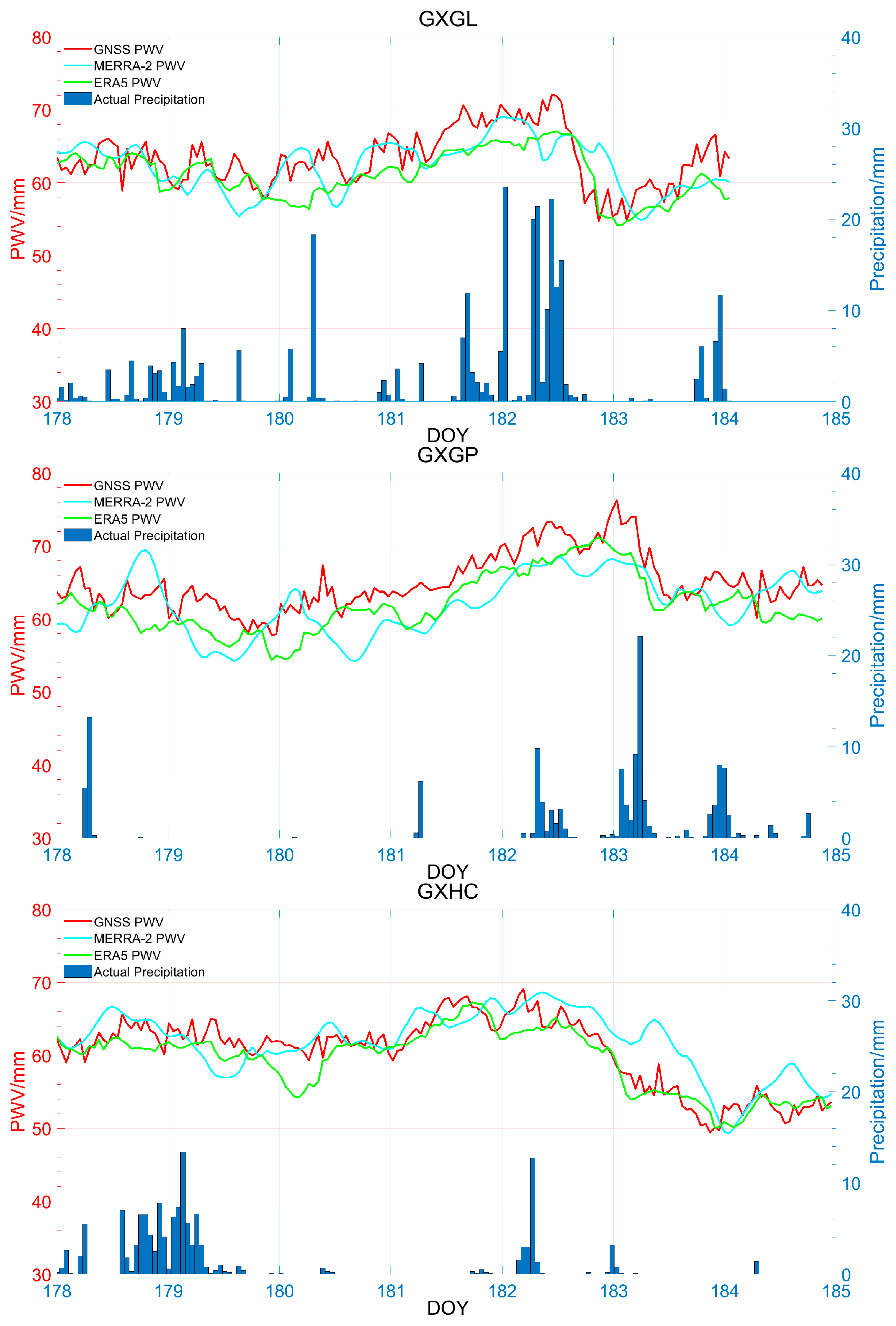
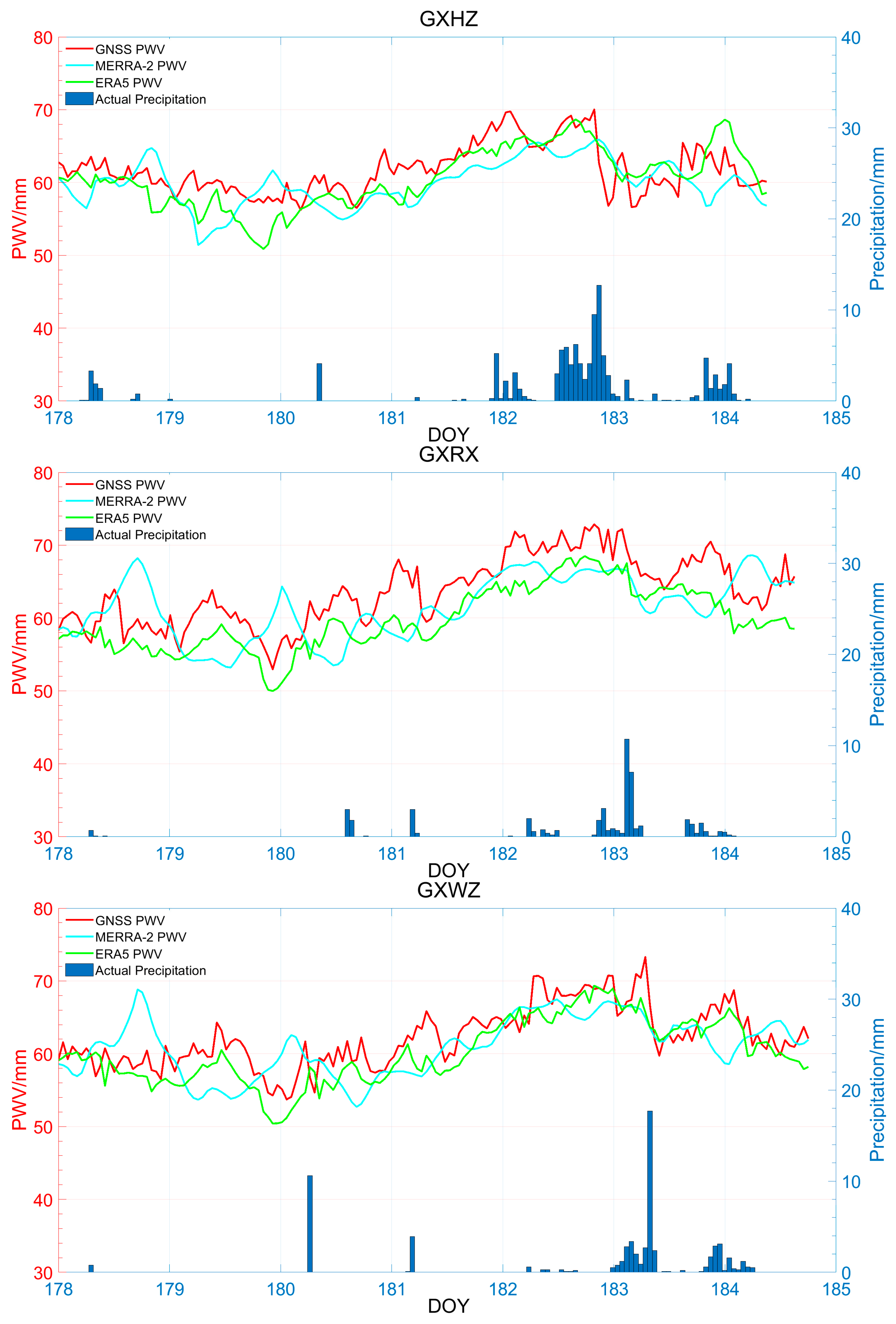
3.3.2. Temporal Variations of PWV and Hourly Precipitation during Heavy Rain Days
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barret, K.; et al. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report, Summary for Policymakers. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshawaf, F.; Balidakis, K.; Dick, G.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J. Estimating Trends in Atmospheric Water Vapor and Temperature Time Series over Germany. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadala, N.B.; Sridhar, M.; Dutta, G.; Yousuf, M.; Reddy, Y.K. Integrated Water Vapor during Active and Break Spells of Monsoon and Its Relationship with Temperature, Precipitation and Precipitation Efficiency over a Tropical Site. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y. Comprehensive Precipitable Water Vapor Retrieval and Application Platform Based on Various Water Vapor Detection Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, H.; Hu, H.; Liang, J.; Tu, M. Assimilation of GNSS PWV with NCAR-RTFDDA to Improve Prediction of a Landfall Typhoon. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Meng, Y.S.; Yuan, F.; Ong, J.T. GPS-Derived PWV for Rainfall Nowcasting in Tropical Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4835–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dick, G.; Ge, M.; Heise, S.; Wickert, J.; Bender, M. Real-time GPS Sensing of Atmospheric Water Vapor: Precise Point Positioning with Orbit, Clock, and Phase Delay Corrections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Cao, Y.; Wan, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, H. Meteorological Applications of Precipitable Water Vapor Measurements Retrieved by the National GNSS Network of China. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 6, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y. A Drought Monitoring Method Based on Precipitable Water Vapor and Precipitation. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10727–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.E.; Neelin, J.D. Temporal Relations of Column Water Vapor and Tropical Precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.E.; Neelin, J.D. Moisture Vertical Structure, Column Water Vapor, and Tropical Deep Convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1665–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, P. How Climate Change Affects Extreme Weather Events. Science 2016, 352, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, A. Global Estimates of Water-vapor-weighted Mean Temperature of the Atmosphere for GPS Applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 2005JD006215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Z. Global Water Vapor Variability and Trend from the Latest 36 Year (1979 to 2014) Data of ECMWF and NCEP Reanalyses, Radiosonde, GPS, and Microwave Satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 11,442–11,462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Liao, T.; Wang, H.; et al. Evaluation of Radiosonde, MODIS-NIR-Clear, and AERONET Precipitable Water Vapor Using IGS Ground-Based GPS Measurements over China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Van Malderen, R.; Yin, X.; Vogelmann, H.; Jiang, W.; Awange, J.; Heck, B.; Kutterer, H. Characterisations of Europe’s Integrated Water Vapour and Assessments of Atmospheric Reanalyses Using More than 2 Decades of Ground-Based GPS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 3517–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.K.; Fernandes, R.M.S.; Holub, K.L.; Gutman, S.I.; Barbosa, H.M.J.; Machado, L.A.T.; Calheiros, A.J.P.; Bennett, R.A.; Kursinski, E.R.; Sapucci, L.F.; et al. The Amazon Dense GNSS Meteorological Network: A New Approach for Examining Water Vapor and Deep Convection Interactions in the Tropics. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2151–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.K.; Fernandes, R.M.S.; Kursinski, E.R.; Maia, J.M.; Sapucci, L.F.; Machado, L.A.T.; Vitorello, I.; Monico, J.F.G.; Holub, K.L.; Gutman, S.I.; et al. A Dense GNSS Meteorological Network for Observing Deep Convection in the Amazon. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2011, 12, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Chiswell, S.; Herring, T.A.; Anthes, R.A.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H. GPS Meteorology: Mapping Zenith Wet Delays onto Precipitable Water. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1988–2005 1994, 33, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, Y.L.; Adams, D.K.; Minjarez-Sosa, C.; Moker, J.M.; Arellano, A.F.; Castro, C.L.; Quintanar, A.I.; Alatorre, L.; Granados, A.; Vazquez, G.E.; et al. The North American Monsoon GPS Transect Experiment 2013. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 2103–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, D.E.; Gutman, S.I. Developing an Operational, Surface-Based, GPS, Water Vapor Observing System for NOAA: Network Design and Results. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, S.I.; Sahm, S.R.; Benjamin, S.G.; Schwartz, B.E.; Holub, K.L.; Stewart, J.Q.; Smith, T.L. Rapid Retrieval and Assimilation of Ground Based GPS Precipitable Water Observations at the NOAA Forecast Systems Laboratory: Impact on Weather Forecasts. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2004, 82, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, S.I.; Benjamin, S.G. The Role of Ground-Based GPS Meteorological Observations in Numerical Weather Prediction. GPS Solut. 2001, 4, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Adams, D.K.; Leuthold, M. GPS Observations of Precipitable Water and Implications for the Predictability of Precipitation during the North American Monsoon. CLIVAR Exch. 2008, 45, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; de Rosnay, P.; Bell, B.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; Abdalla, S.; Alonso-Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bechtold, P.; et al. Operational Global Reanalysis: Progress, Future Directions and Synergies with NWP; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Suarez, M.; Bacmeister, J. Development of the GEOS-5 Atmospheric General Circulation Model: Evolution from MERRA to MERRA2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Yan, X. A Refined Regional Model for Estimating Pressure, Temperature, and Water Vapor Pressure for Geodetic Applications in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Nie, W.; Jiang, C.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of Precipitable Water Vapor from Five Reanalysis Products with Ground-Based GNSS Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Water Vapor Estimation Using Near-Surface Radar Refractivity during IHOP_2002; Library and Archives Canada = Bibliothèque et Archives Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2006; ISBN 978-0-494-06439-9. [Google Scholar]
- Puviarasan, N.; Giri, R.K.; Ranalkar, M. Precipitable Water Vapour Monitoring Using Ground Based GPS System. Mausam 2010, 61, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Navascues, B.; Ruffini, G.; Elósegui, P.; Rius, A.; Vilà, J. The Use of GPS to Validate NWP Systems: The HIRLAM Model. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Z.; Xie, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Kang, C.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of GNSS-Derived Precipitable Water Vapor during Heavy Rainfall Events in Guilin, China. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Z.; Wong, W.-K.; Woo, W.-C. Detecting Water Vapor Variability during Heavy Precipitation Events in Hong Kong Using the GPS Tomographic Technique. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y. Precision analysis of PWV calculated from ERA5/MERRA-2 data during a rainstorm process in Guilin. China Sci. 2023, 18, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, S.; Huang, L.; Xie, S.; Liu, L. Investigating the ERA5-Based PWV Products and Identifying the Monsoon Active and Break Spells with Dense GNSS Sites in Guangxi, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.X.; Wang, J.N.; Gao, L.; Hong, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Lu, Q.Q. Observed Trends of Different Rainfall Intensities and the Associated Spatiotemporal Variations during 1958–2016 in Guangxi, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, E2880–E2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, C.; Chen, B.; Dai, W. Consistency Evaluation of Precipitable Water Vapor Derived from ERA5, ERA-Interim, GNSS, and Radiosondes over China. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, W. A Global Assessment of Precipitable Water Vapor Derived From GNSS Zenith Tropospheric Delays With ERA5, NCEP FNL, and NCEP GFS Products. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Li, L. Evaluation and Calibration of MODIS Near-Infrared Precipitable Water Vapor over China Using GNSS Observations and ERA-5 Reanalysis Dataset. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Climate Applications of a Global, 2-Hourly Atmospheric Precipitable Water Dataset Derived from IGS Tropospheric Products. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, B.; Cao, N. GTm-III: A New Global Empirical Model for Mapping Zenith Wet Delays onto Precipitable Water Vapour. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 197, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, B. A Real-Time Precipitable Water Vapor Monitoring System Using the National GNSS Network of China: Method and Preliminary Results. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Song, S.; Heise, S.; Liou, Y.-A.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, J. Assessment of ZTD Derived from ECMWF/NCEP Data with GPS ZTD over China. GPS Solut. 2011, 15, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Fan, S.; Cheng, Y. Water Vapor-Weighted Mean Temperature and Its Impact on the Determination of Precipitable Water Vapor and Its Linear Trend. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 833–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the Theory of Atmospheric Refraction. Bull. Géod. 1946–1975 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askne, J.; Nordius, H. Estimation of Tropospheric Delay for Microwaves from Surface Weather Data. Radio Sci. 1987, 22, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Ye, S. A New Global Grid Model for the Determination of Atmospheric Weighted Mean Temperature in GPS Precipitable Water Vapor. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Z.; Liu, L.; Xie, S. An Empirical Model for the Vertical Correction of Precipitable Water Vapor Considering the Time-Varying Lapse Rate for Mainland China. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2021, 50, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model Coefficients | A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 72.367 | 0.732 | −0.001 | −0.145 | 0.452 | −0.235 | −0.060 | −0.263 |
| Model Coefficients | A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | −0.350 | −0.026 | −0.015 | 0.008 | 0.026 |
| Rainfall Intensity | Total Precipitation in 24 h (mm) |
|---|---|
| Light rain | 0.1–9.9 |
| Moderate rain | 10–24.9 |
| Heavy rain | 25–49.9 |
| Severe rain | 50–99.9 |
| Heavy torrential rain | 100–249.9 |
| Severe torrential rain | ≥250 |
| GNSS Station | Bias (mm) | RMSE (mm) | Correlation Coefficient (R) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GXWZ | −0.81 | 3.48 | 0.97 |
| GXGL | −0.88 | 4.12 | 0.97 |
| GXBS | −2.92 | 4.50 | 0.98 |
| Rainfall Level | MERRA-2 Bias/mm | ERA5 Bias/mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | |
| Heavy rain | 1.89 | −2.20 | −0.22 | 4.13 | 0.11 | 1.84 |
| Severe rain | 2.85 | −4.19 | −0.14 | 4.65 | 1.39 | 2.92 |
| Rainfall Level | MERRA-2 RMSE/mm | ERA5 RMSE/mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | |
| Heavy rain | 4.79 | 2.66 | 3.72 | 4.90 | 2.54 | 3.31 |
| Severe rain | 6.79 | 3.00 | 4.28 | 4.86 | 2.58 | 4.01 |
| GNSS Station | Bias/mm | RMSE/mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MERRA-2 | ERA5 | MERRA-2 | ERA5 | |
| GXBB | 0.61 | 2.37 | 4.26 | 3.28 |
| GXBH | 1.52 | 2.52 | 4.28 | 3.87 |
| GXBS | 0.47 | 2.09 | 4.43 | 2.84 |
| GXBY | 2.36 | 3.25 | 3.52 | 4.06 |
| GXCZ | 0.51 | 1.82 | 3.93 | 2.95 |
| GXGG | 1.03 | 2.21 | 3.56 | 3.31 |
| GXGL | 3.02 | 2.98 | 4.54 | 3.64 |
| GXGP | −1.32 | 1.21 | 3.47 | 2.33 |
| GXHC | 1.92 | 1.25 | 3.71 | 3.06 |
| GXHZ | −0.07 | 2.88 | 3.94 | 4.05 |
| GXRS | 2.22 | 3.89 | 5.09 | 4.36 |
| GXRX | −0.37 | 2.53 | 3.85 | 3.28 |
| GXTE | −0.28 | 2.83 | 3.76 | 3.61 |
| GXWZ | 1.28 | 2.00 | 4.26 | 2.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, N.; Fu, S.; Chen, B.; Huang, L.; Jin, W. Assessing the Performance of Water Vapor Products from ERA5 and MERRA-2 during Heavy Rainfall in the Guangxi Region of China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030306
Huang N, Fu S, Chen B, Huang L, Jin W. Assessing the Performance of Water Vapor Products from ERA5 and MERRA-2 during Heavy Rainfall in the Guangxi Region of China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(3):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030306
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ning, Shiyang Fu, Biyan Chen, Liangke Huang, and Wenping Jin. 2024. "Assessing the Performance of Water Vapor Products from ERA5 and MERRA-2 during Heavy Rainfall in the Guangxi Region of China" Atmosphere 15, no. 3: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030306
APA StyleHuang, N., Fu, S., Chen, B., Huang, L., & Jin, W. (2024). Assessing the Performance of Water Vapor Products from ERA5 and MERRA-2 during Heavy Rainfall in the Guangxi Region of China. Atmosphere, 15(3), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030306







