Evaluation and Wind Field Detection of Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar with Automatic Intelligent Processing in North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
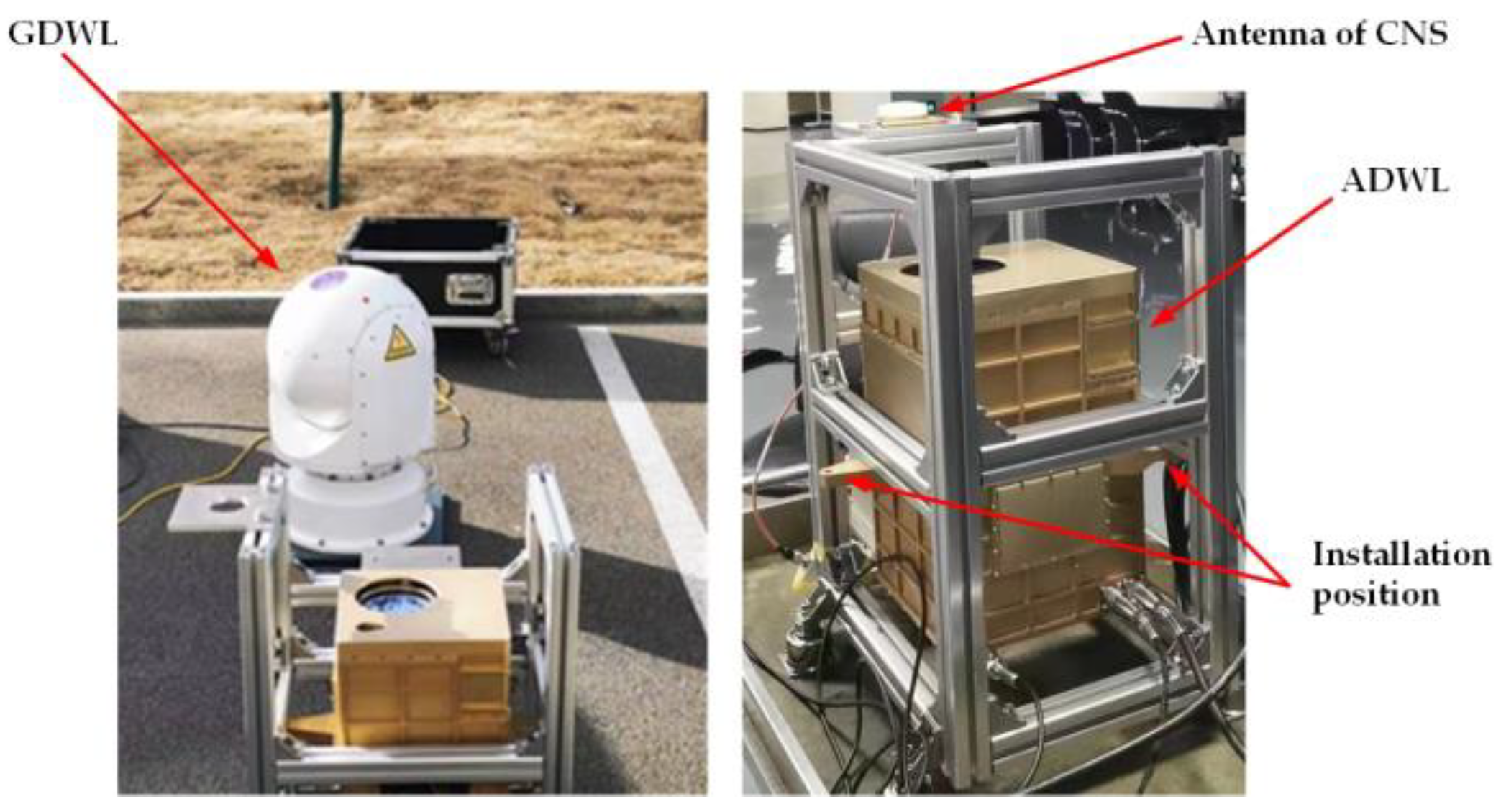
2.1. Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar System
2.2. Automatic Real-Time Processing Approach
2.2.1. Processing Flow of the Integrated Approach on the Core Board
2.2.2. Real-Time Wind Retrieval Method
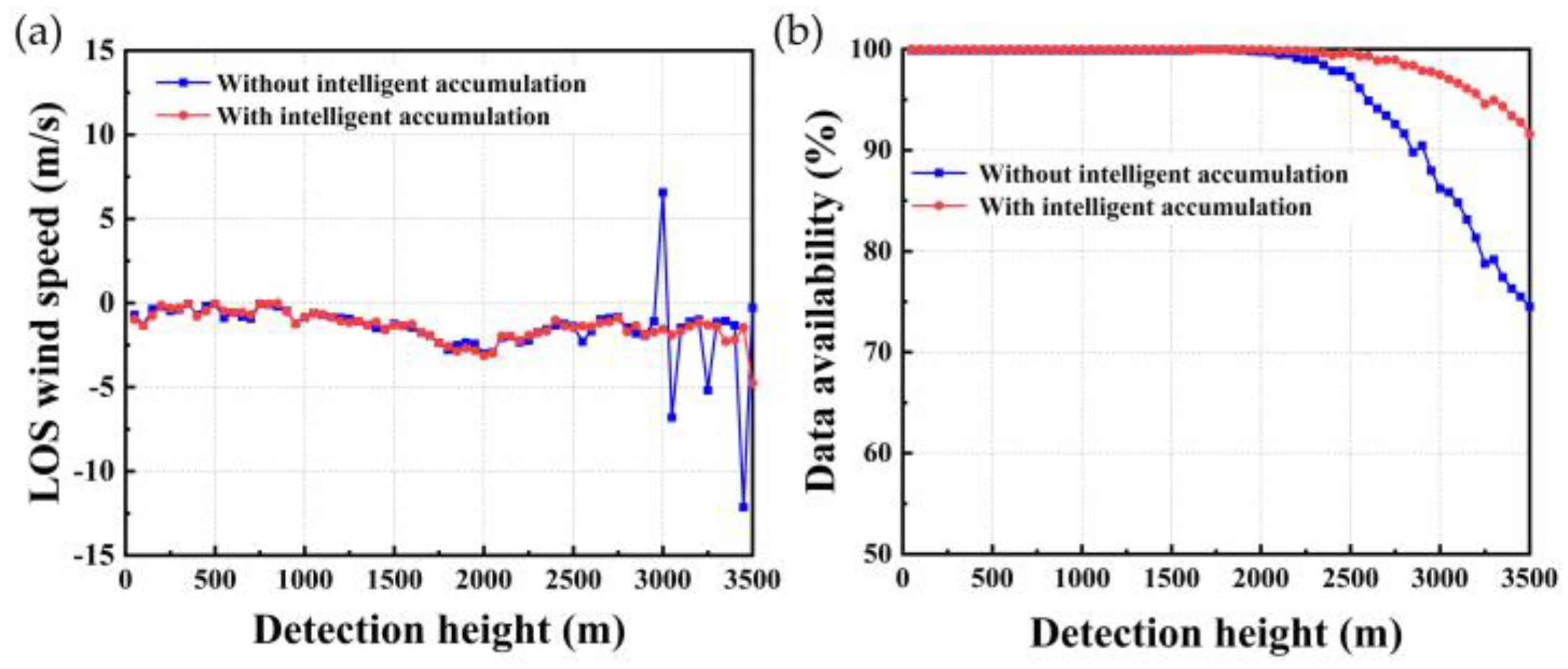
2.2.3. Intelligent Processing Method
3. Results
3.1. Ground-Based Verification Experiments
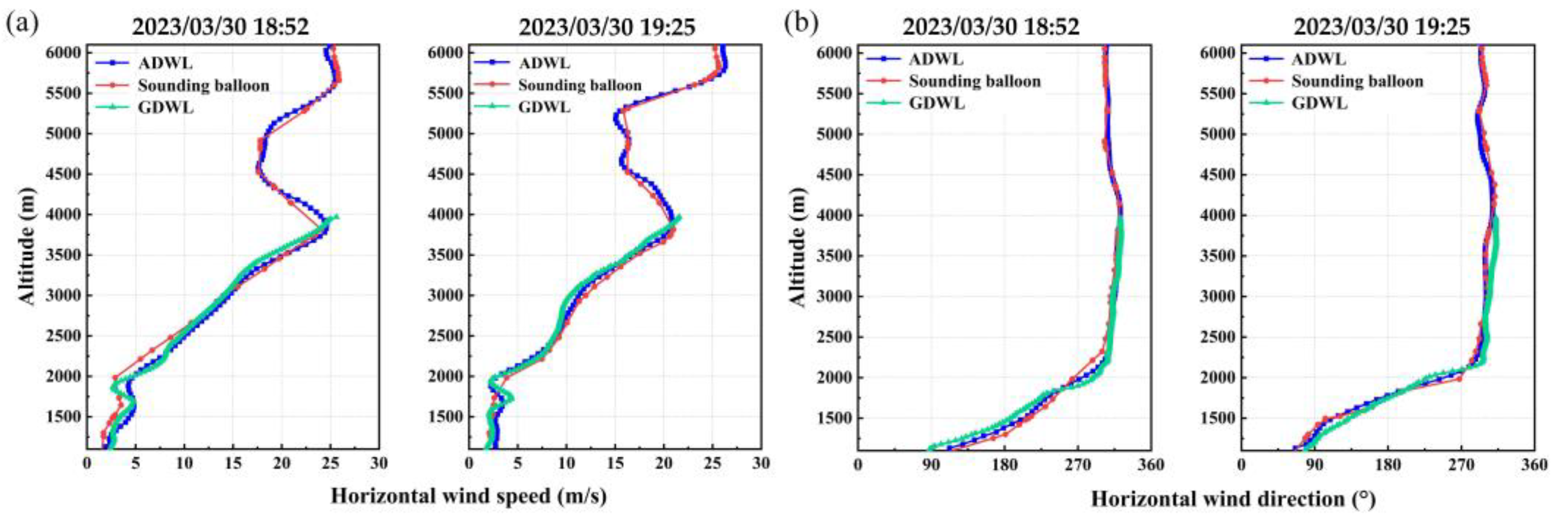
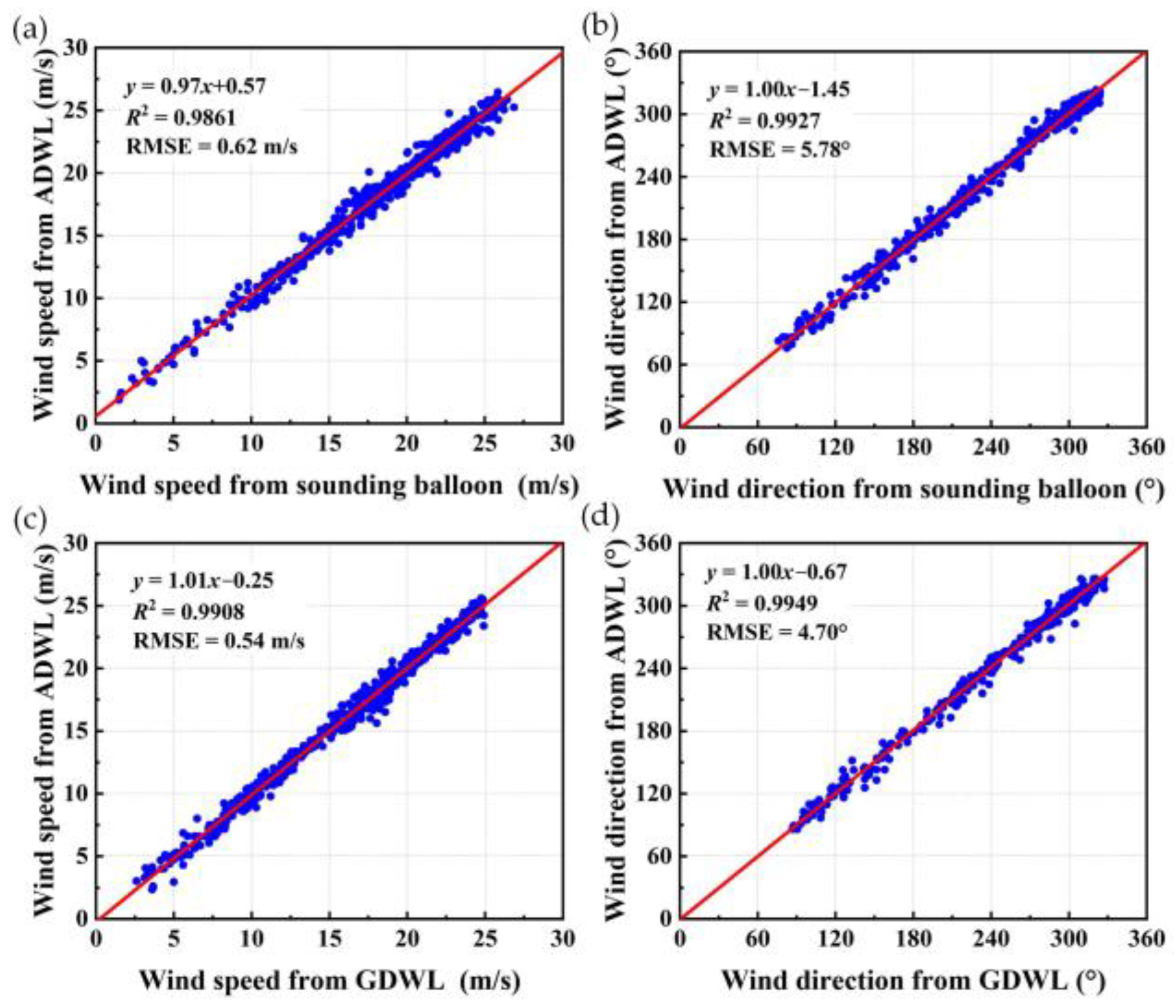
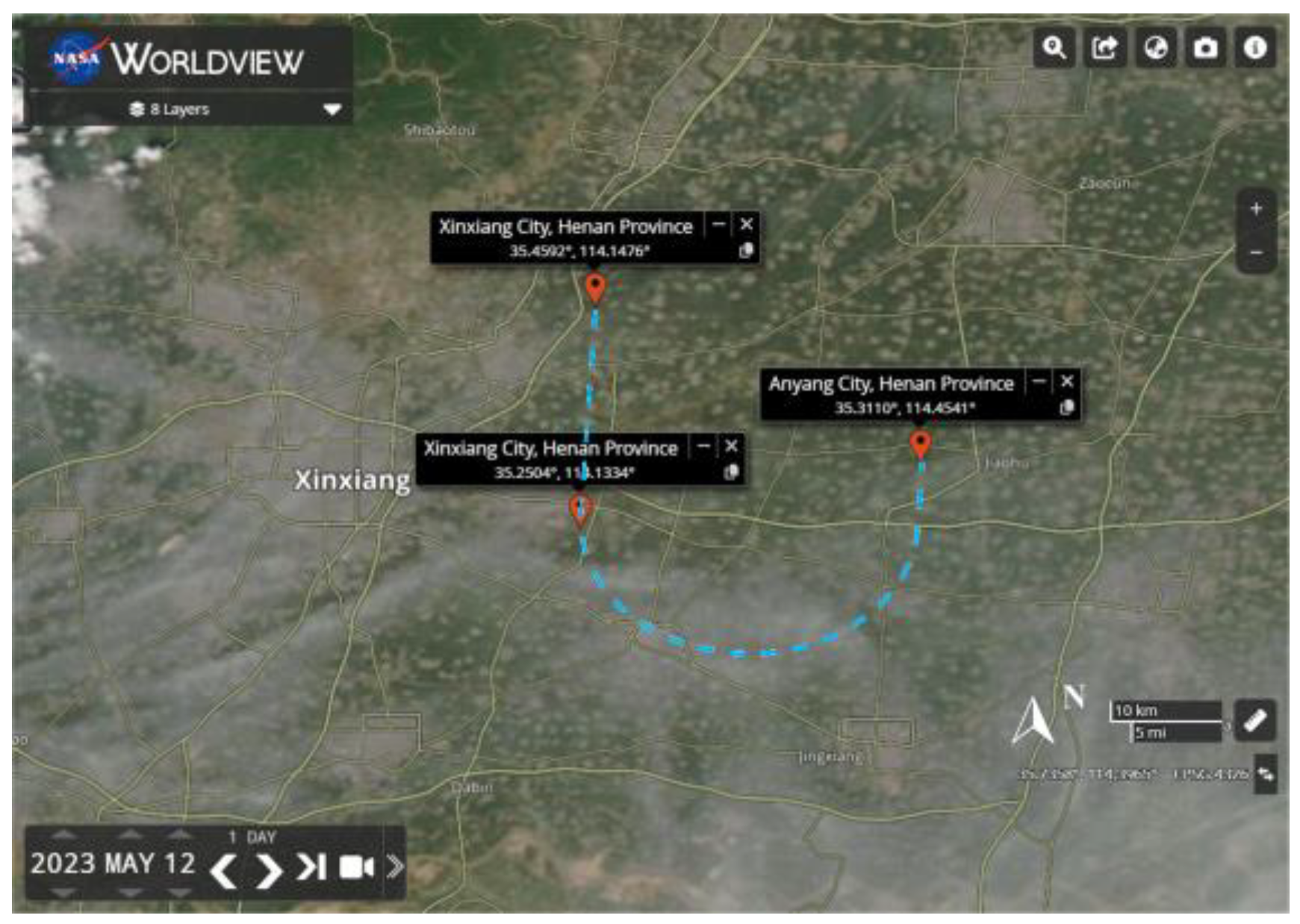
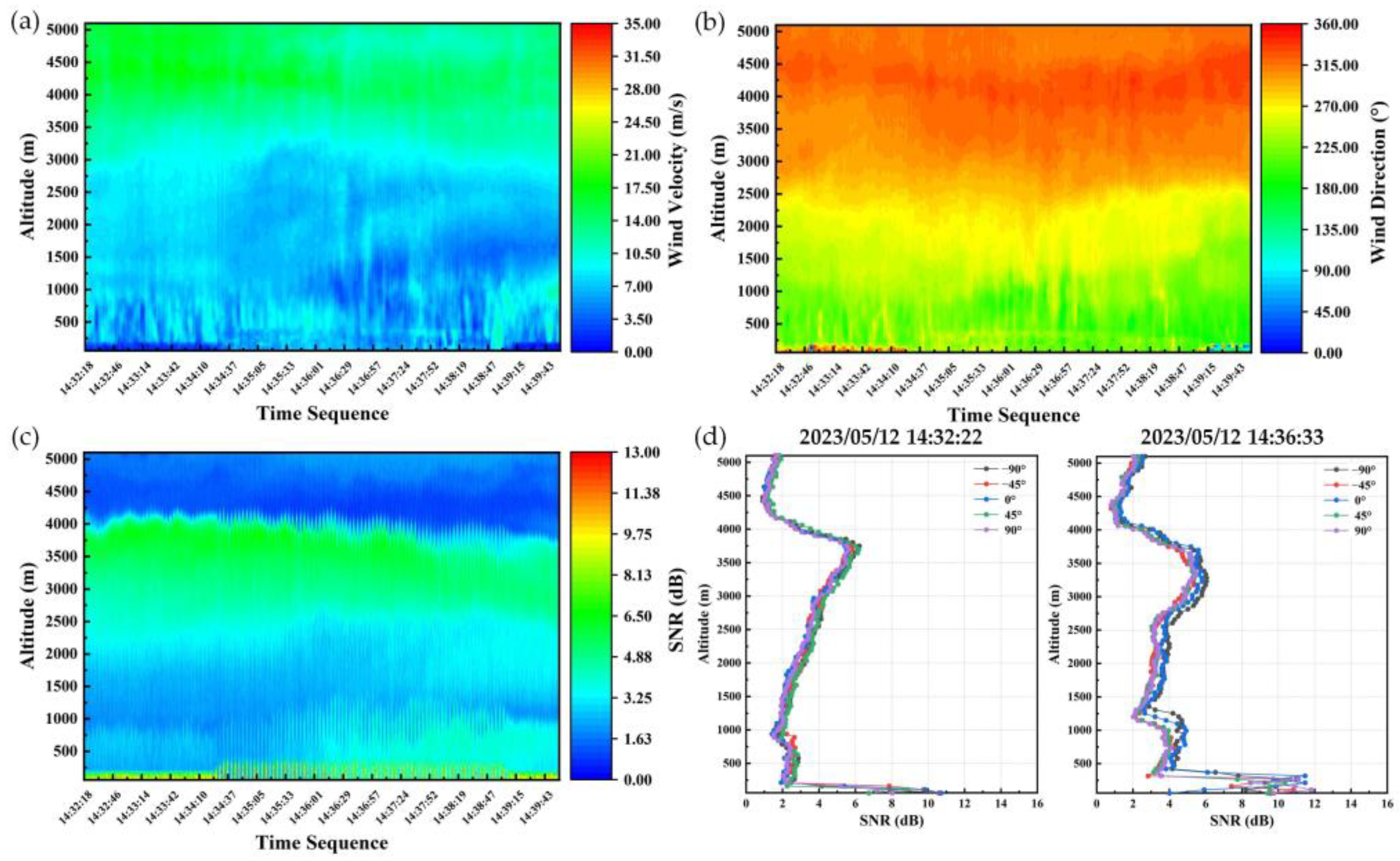
3.2. Airborne Verification Experiments
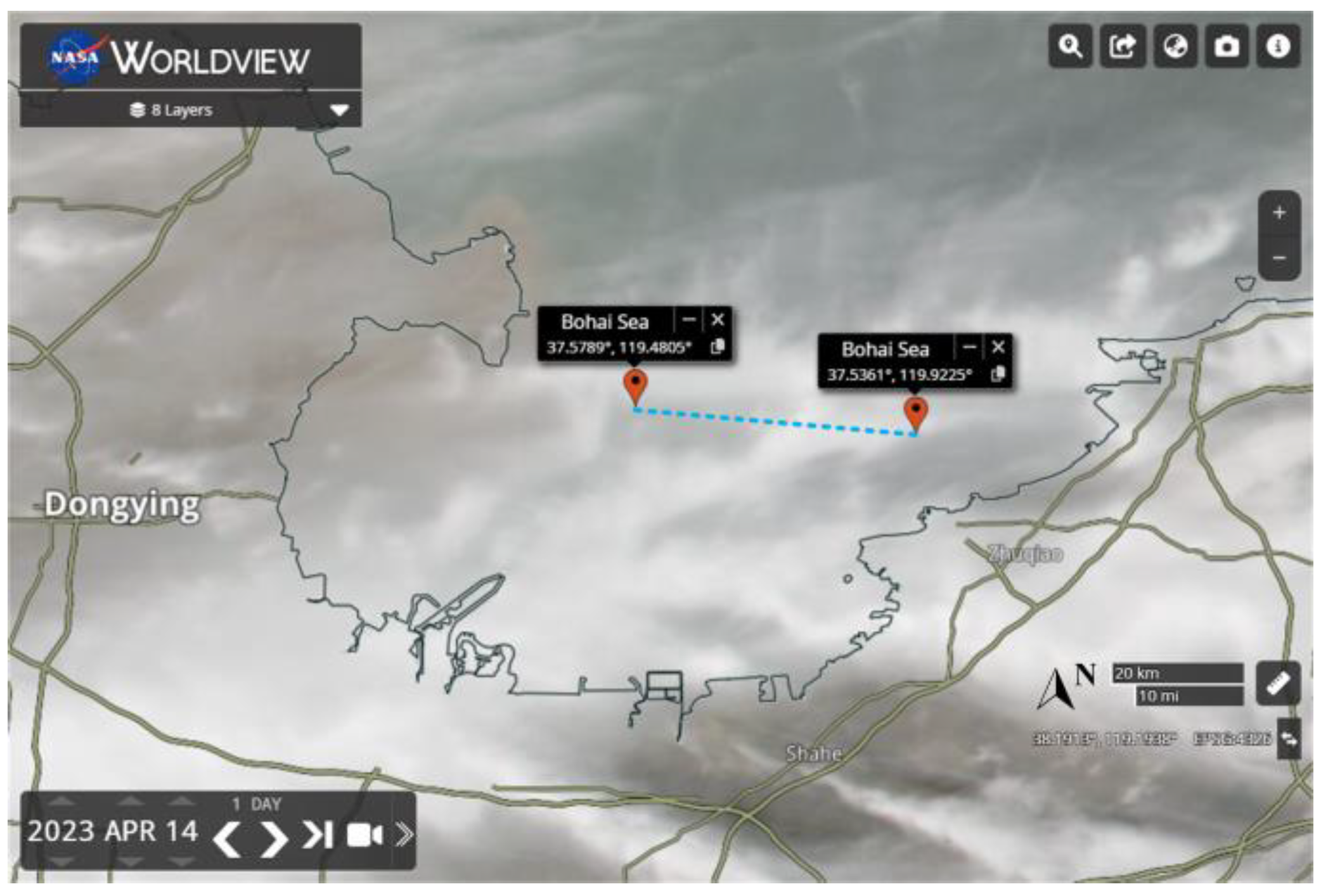
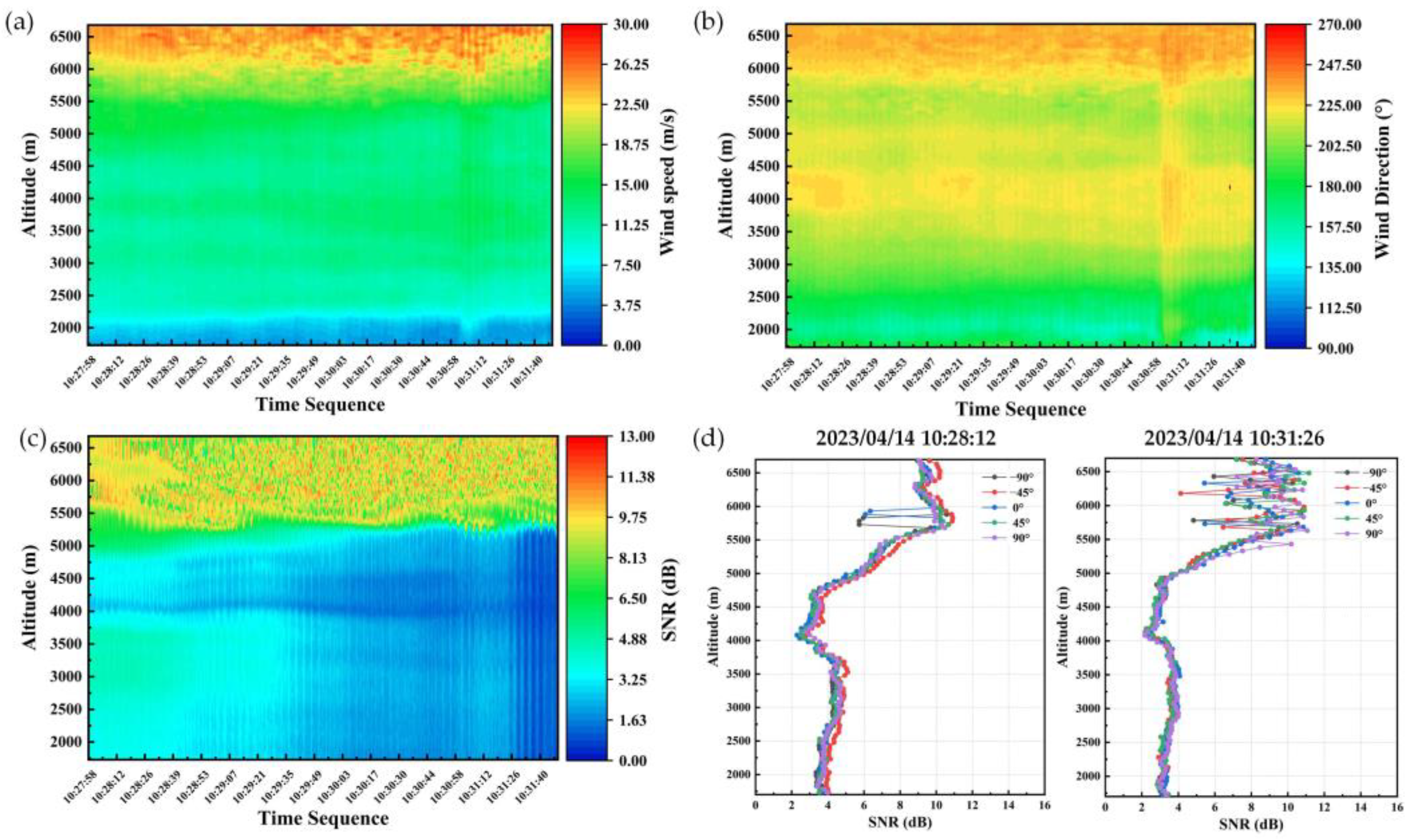
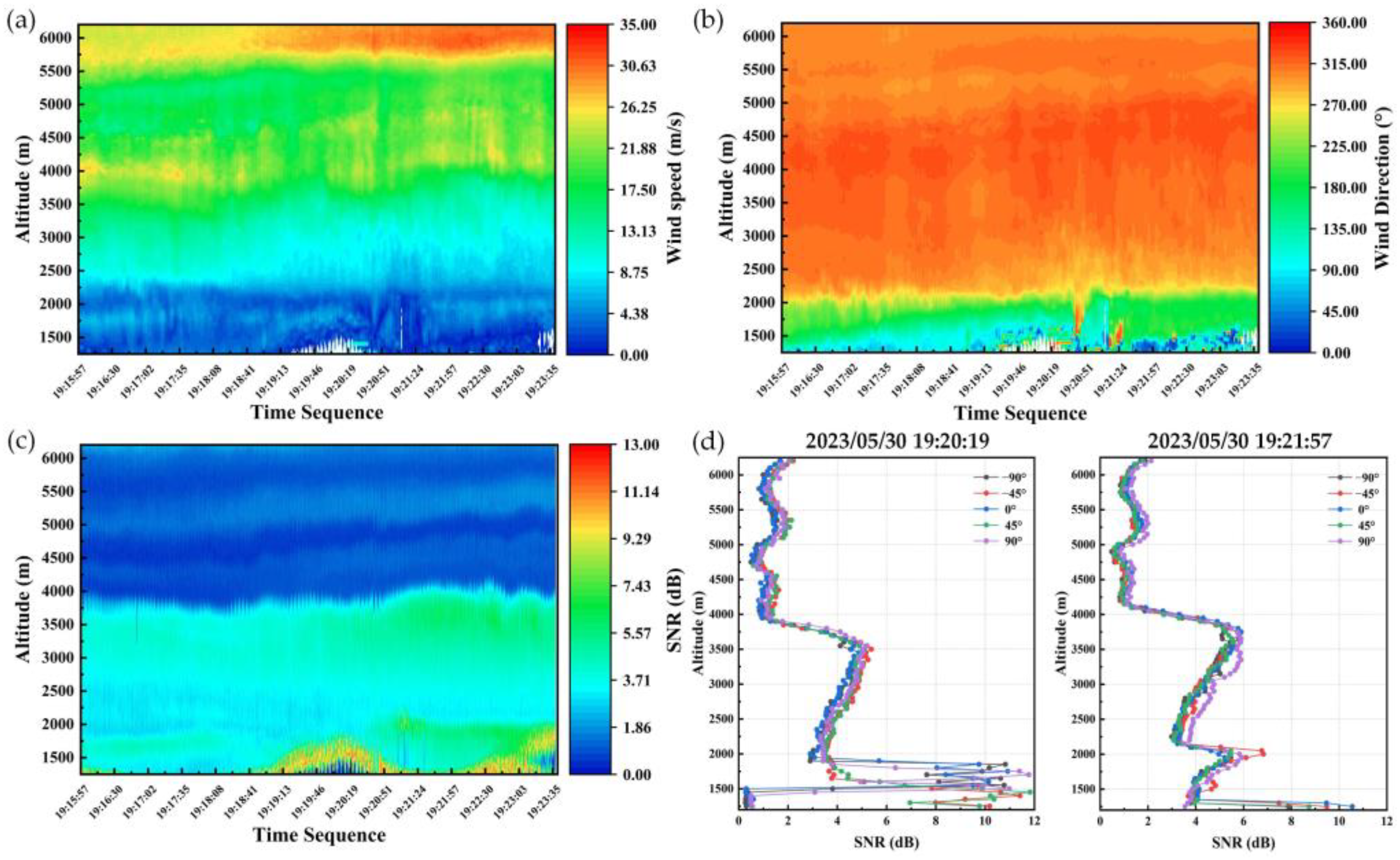
3.3. Airborne Wind Detection Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paskin, L.; Conan, B.; Perignon, Y.; Aubrun, S. Evidence of Ocean Waves Signature in the Space–Time Turbulent Spectra of the Lower Marine Atmosphere Measured by a Scanning LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.L.; Xia, H.Y.; Wei, T.W.; Wang, L.; Yue, B.; Wu, Y.B. Identifying cloud, precipitation, windshear, and turbulence by deep analysis of the power spectrum of coherent Doppler wind lidar. Opt. Express 2020, 12, 37406–37418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, L.R.; O’Handley, C.; Emmitt, G.D.; Zhang, J.A.; Ryan, K.; Atlas, R. Validation of an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar in Tropical Cyclones. Sensors 2018, 18, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, R.; Zhang, J.A.; Emmitt, G.D.; Bucci, L.R.; Ryan, K. Application of Doppler wind lidar observations to hurricane analysis and prediction. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring 2017, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Su, L.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhen, G.; Li, J. Microburst, Windshear, Gust Front, and Vortex Detection in Mega Airport Using a Single Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pîrloagă, R.; Adam, M.; Antonescu, B.; Andrei, S.; Ştefan, S. Ground-Based Measurements of Wind and Turbulence at Bucharest–Măgurele: First Results. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, D.; Han, F.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, R.; Xue, X.; Chen, T.; Zhen, F.; Lu, Y. Fine gust front structure observed by coherent Doppler lidar at Lanzhou Airport (103°49′ E, 36°03′ N). Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Canat, G.; Lombard, L.; Valla, M.; Durécu, A.; Besson, C. Long-range wind monitoring in real time with optimized coherent lidar. Opt. Eng. 2016, 56, 031217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakimura, T.; Hirosawa, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ando, T.; Kameyama, S.; Asaka, K.; Tanaka, H.; Furuta, M.; Hagio, M.; Hirano, Y.; et al. 1.55-μm high-peak, high-average-power laser amplifier using an Er,Yb:glass planar waveguide for wind sensing coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 24175–24187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.X.; Gao, C.Q.; Lin, Z.F.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.W.; Huang, S.; Chen, C.Y. 1645 nm coherent Doppler wind lidar with a single-frequency Er:YAG laser. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 14694–14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YIM, S.H.L. Development of a 3D Real-Time Atmospheric Monitoring System (3DREAMS) Using Doppler LiDARs and Applications for Long-Term Analysis and Hot-and-Polluted Episodes. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.L.; Wu, Y.B.; Shu, Z.F.; Su, L.; Tang, D.W.; Yang, Y.J.; Dong, J.J.; Yu, S.F.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, H.Y. Real-Time Synchronous 3-D Detection of Air Pollution and Wind Using a Solo Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Wang, X.; Gong, Z.; Liu, K.; Hua, D.; Wang, X. Retrieval of the planetary boundary layer height from lidar measurements by a deep-learning method based on the wavelet covariance transform. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 16297–16312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, X.; Weng, N.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J. Simultaneous Extraction of Planetary Boundary-Layer Height and Aerosol Optical Properties from Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar. Sensors 2022, 22, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witschas, B.; Rahm, S.; Dörnbrack, A.; Wagner, J.; Rapp, M. Airborne Wind Lidar Measurements of Vertical and Horizontal Winds for the Investigation of Orographically Induced Gravity Waves. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.A.; Smalikho, I.N. The Impact of Internal Gravity Waves on the Spectra of Turbulent Fluctuations of Vertical Wind Velocity in the Stable Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhao, Y. Field Verification of Vehicle-Mounted All-Fiber Coherent Wind Measurement Lidar Based on Four-Beam Vertical Azimuth Display Scanning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Bosch, A.; Farré-Guarné, J.; Araújo da Silva, M.P.; Rocadenbosch, F.A. Unified Formulation for the Computation of the Six-Degrees-of-Freedom-Motion-Induced Errors in Floating Doppler Wind LiDARs. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, J.; Xia, H.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y. Marine Mixed Layer Height Detection Using Ship-Borne Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar Based on Constant Turbulence Threshold. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasch, P.; Kasic, J.; Maas, O.; Wang, Z. Advancing airborne Doppler lidar wind profiling in turbulent boundary layer flow—An LES-based optimization of traditional scanning-beam versus novel fixed-beam measurement systems. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 5495–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakh, V.A.; Smalikho, I.N. Lidar observations of atmospheric internal waves in the boundary layer of the atmosphere on the coast of Lake Baikal. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5239–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Smoothed accumulated spectra based wDSWF method for real-time wind vector estimation of pulsed coherent Doppler lidar. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, A.; Wildmann, N.; Smalikho, I.N. Effectiveness of the MFAS Method for Determining the Wind Velocity Vector from Windcube 200s Lidar Measurements. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2019, 32, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, L.C.; Fan, C.H.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, J.Q.; Dai, B.; Xiao, W.G.; Zhu, X.L.; Chen, W.B. Wind retrieval for genetic algorithm-based coherent Doppler wind lidar employing airborne platform. Appl. Phys. B 2023, 129, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Li, L.; Wang, K.X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.Q. Coherent Doppler wind lidar signal denoising adopting variational mode decomposition based on honey badger algorithm. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 25774–25787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelberlau, F.; Neshaug, V.; Lønseth, L.; Bracchi, T.; Mann, J. Taking the Motion out of Floating Lidar: Turbulence Intensity Estimates with a Continuous-Wave Wind Lidar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake, N.; Sakamaki, H.; Imaki, M.; Miwa, Y.; Ando, T.; Yabugaki, Y.; Enjo, M.; Kameyama, S. Intelligent and compact coherent Doppler lidar with fiber-based configuration for robust wind sensing in various atmospheric and environmental conditions. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 20038–20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaya, M.; Beyon, J.; Koch, G.; Petros, M.; Petzar, P.; Singh, U.; Trieu, B.; Yu, J. The Doppler Aerosol Wind (DAWN) Airborne, Wind-Profiling Coherent-Detection Lidar System: Overview and Preliminary Flight Results. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 826–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Emmitt, G.D.; Garstang, M.; Kavaya, M. Doppler Aerosol WiNd (DAWN) Lidar during CPEX 2017: Instrument Performance and Data Utility. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Yin, B.; Zhai, X. Airport low-level wind shear lidar observation at Beijing Capital International Airport. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 96, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Xue, X.H.; Dou, X.K.; Chen, T.D. Meter-scale and sub-second-resolution coherent Doppler wind LIDAR and hyperfine wind observation. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 3179–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Barlow, J.F.; Chan, P.-W.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, Y.; Ren, C.; Mak, H.W.L.; Ng, E. A Review of Progress and Applications of Pulsed Doppler Wind LiDARs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklakova, V.; Han, Y.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Qin, Z.; Xue, X.H.; Chen, T.D.; Sun, D.S.; Zhao, Y.M.; Zheng, J. Field programmable gate array-based coherent lidar employing the ordinal statistics method for fast Doppler frequency determination. Opt. Eng. 2022, 61, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augere, B.; Valla, M.; Durécu, A.; Dolfi-Bouteyre, A.; Goular, D.; Gustave, F.; Planchat, C.; Fleury, D.; Huet, T.; Besson, C. Three-Dimensional Wind Measurements with the Fibered Airborne Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar LIVE. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.W.; Xia, H.Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Yuan, J.L.; Wang, C.; Dou, X. Inversion probability enhancement of all-fiber CDWL by noise modeling and robust fitting. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 29662–29675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, A.; Mann, J.; Angelou, N.; Jacobsen, A. A Motion-Correction Method for Turbulence Estimates from Floating Lidars. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, K.S.; De Wekker, S.F.J.; Emmitt, G.D. Retrieving Winds in the Surface Layer over Land Using an Airborne Doppler Lidar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
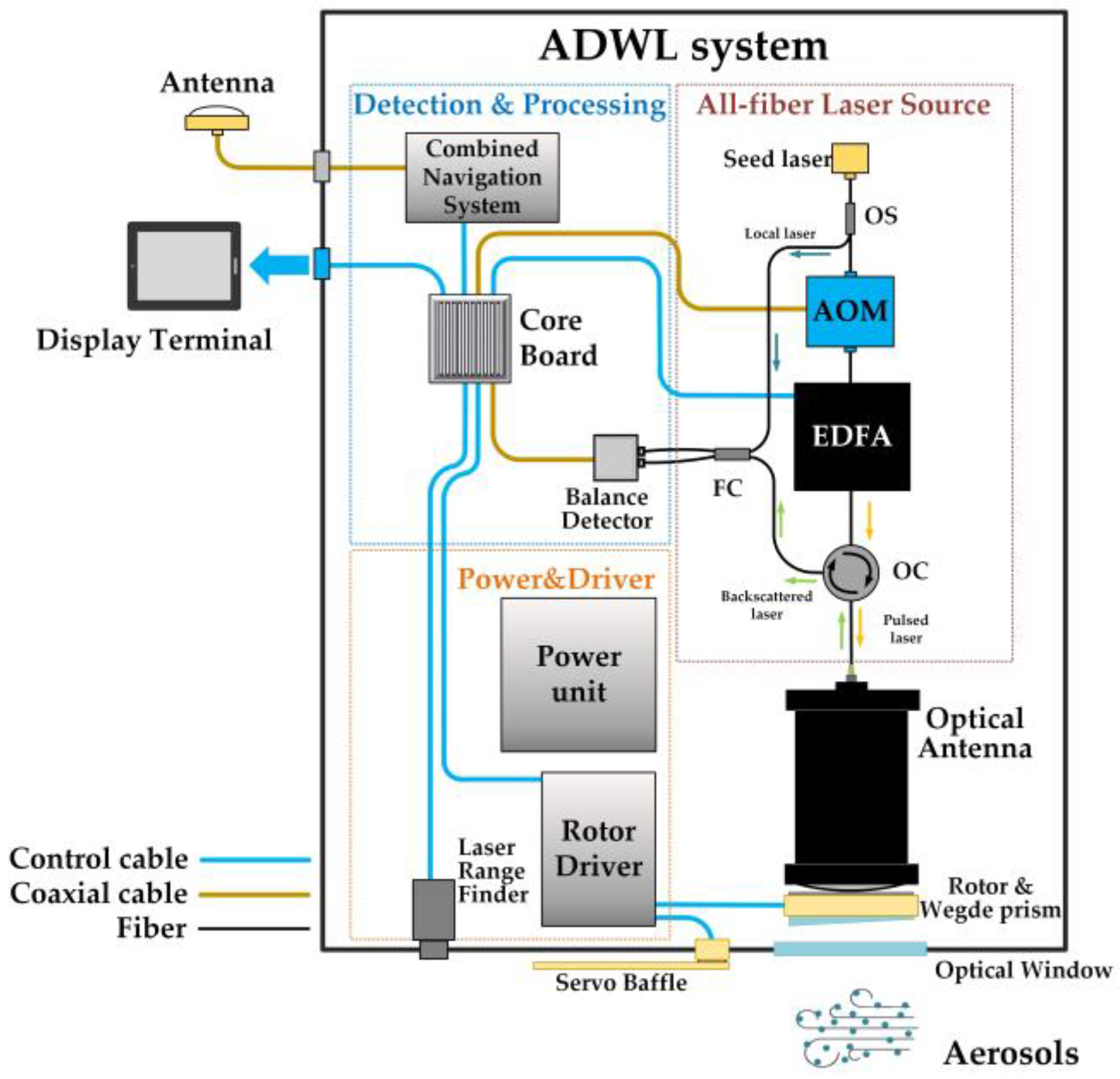
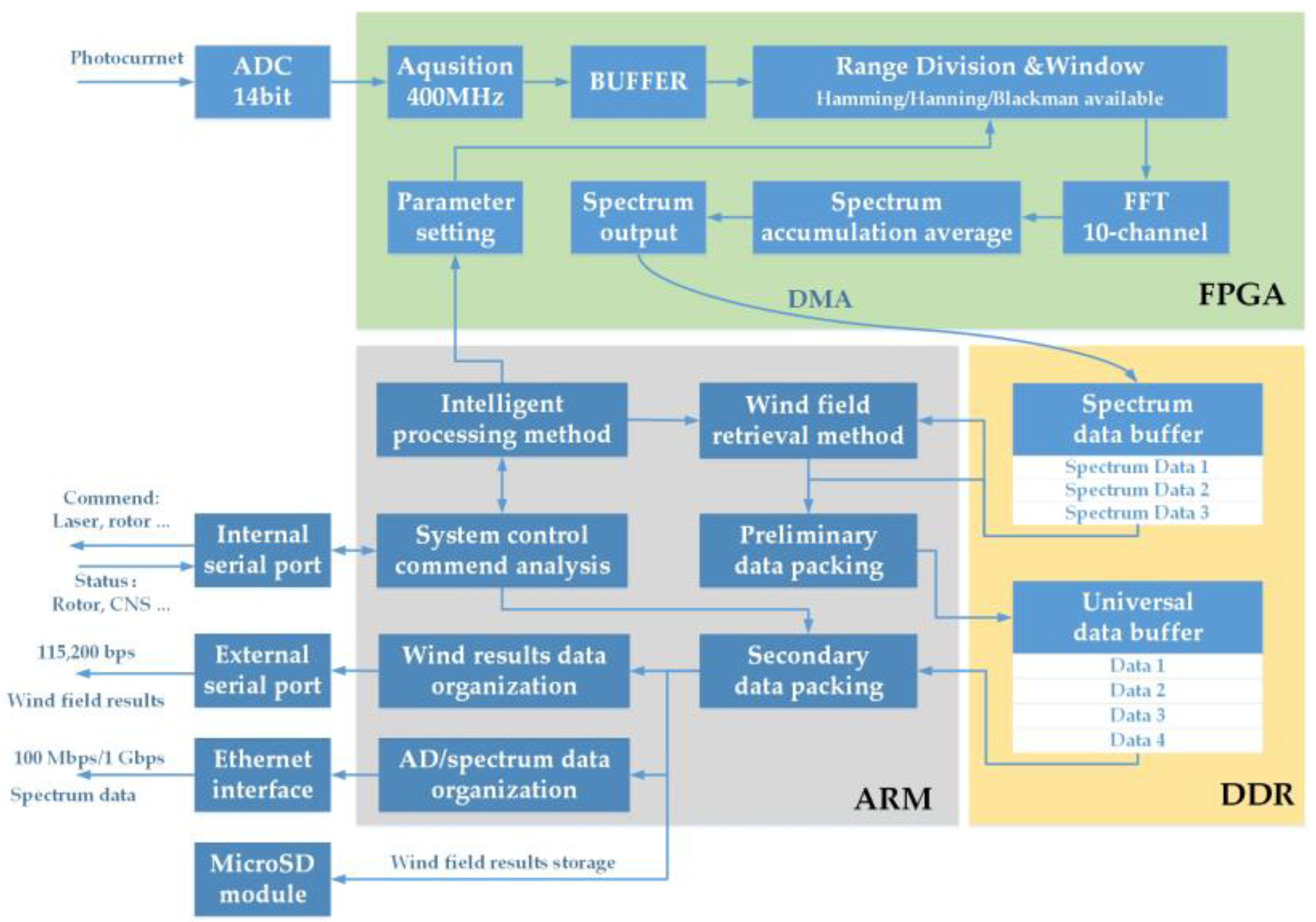
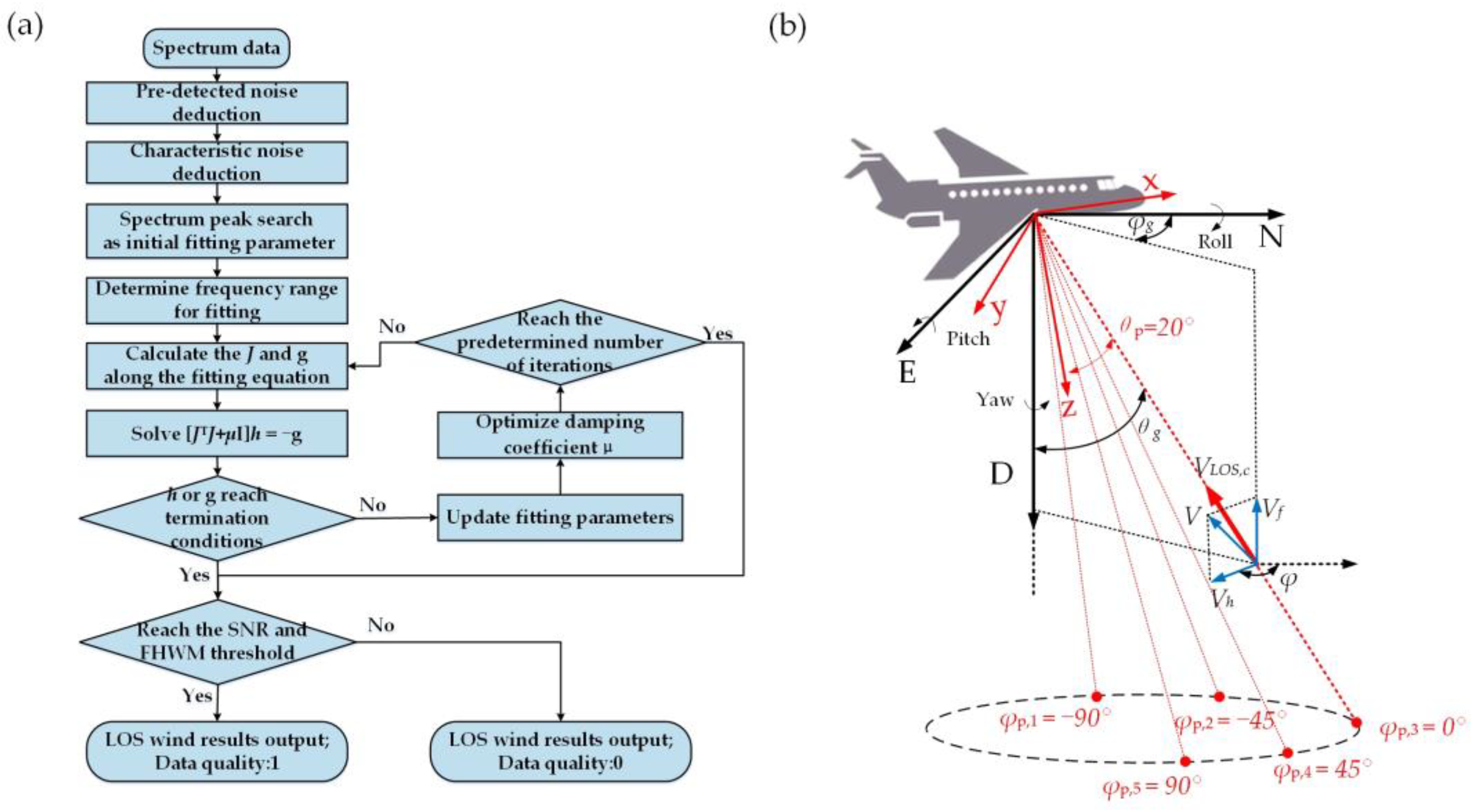
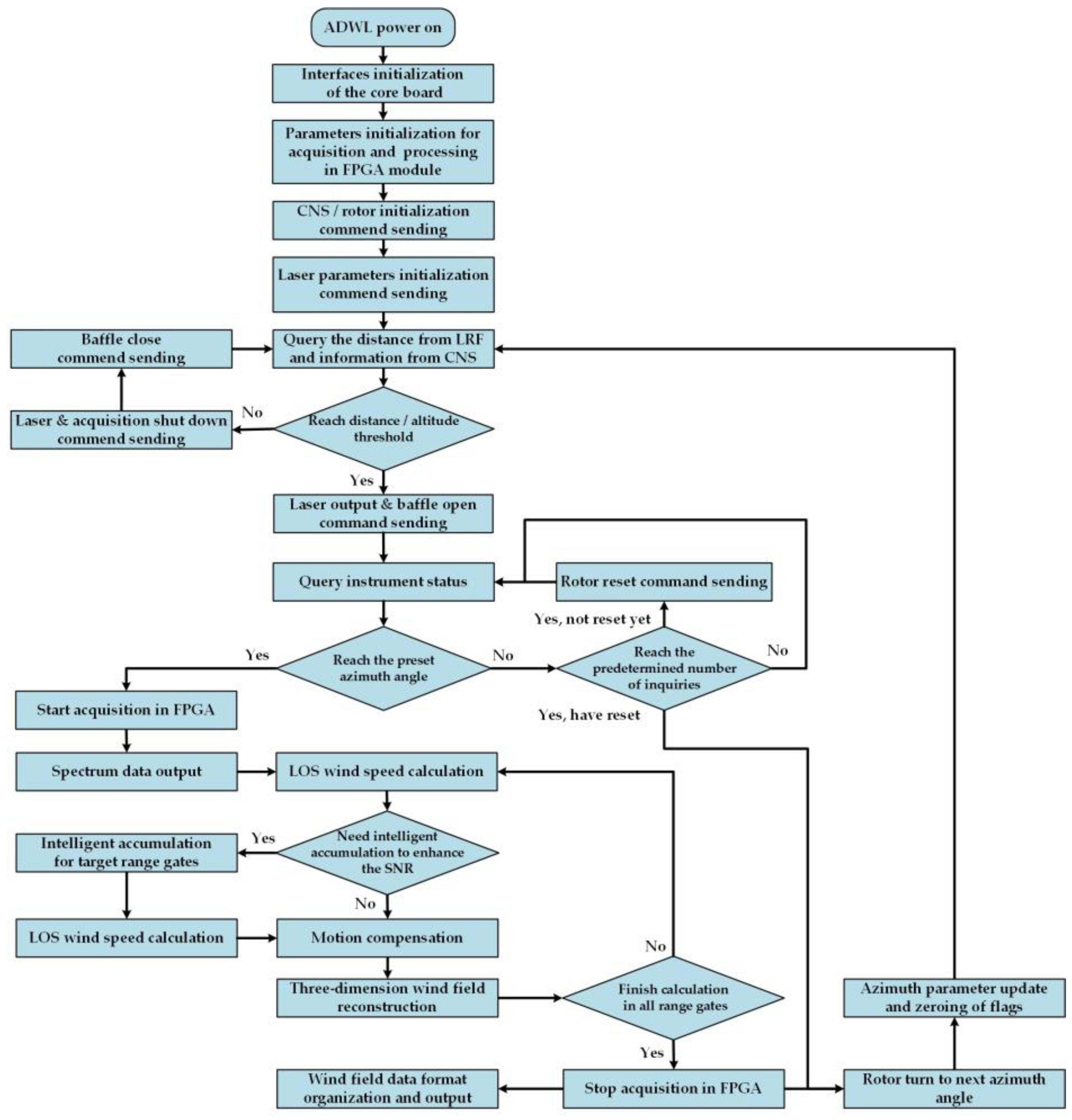



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser wavelength | 1550 nm |
| Maximum pulse energy | 300 μJ |
| Pulse width | 100~600 ns selectable |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 10 kHz |
| Optical antenna aperture | 100 mm |
| Vertical range resolution | 50 m |
| Nadir angle | 20° |
| Sampling frequency | 400 MHz |
| Data rate | 2 Hz |
| Weight | ~20 kg |
| Size | 250 mm × 250 mm × 400 mm |
| Consumption | ≤200 W |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Laser wavelength | 1550 nm |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 10 kHz |
| Measurement range | 80~5000 m (maximum) |
| Wind speed detection range | −55~55 m/s |
| Optical antenna aperture | 100 mm |
| Range resolution | 22.5 m |
| LOS wind measurement accuracy | ≤0.1 m/s |
| Wind direction accuracy | ≤3° |
| Nadir angle | 20° |
| Data rate | 1 Hz |
| Scanning mode | VAD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Lin, Z.; Gao, C.; Han, C.; Fan, L.; Zhao, X. Evaluation and Wind Field Detection of Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar with Automatic Intelligent Processing in North China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050536
Zhang X, Lin Z, Gao C, Han C, Fan L, Zhao X. Evaluation and Wind Field Detection of Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar with Automatic Intelligent Processing in North China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xu, Zhifeng Lin, Chunqing Gao, Chao Han, Lin Fan, and Xinxi Zhao. 2024. "Evaluation and Wind Field Detection of Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar with Automatic Intelligent Processing in North China" Atmosphere 15, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050536
APA StyleZhang, X., Lin, Z., Gao, C., Han, C., Fan, L., & Zhao, X. (2024). Evaluation and Wind Field Detection of Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar with Automatic Intelligent Processing in North China. Atmosphere, 15(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050536





