Spatiotemporal Variation Patterns of Drought in Liaoning Province, China, Based on Copula Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
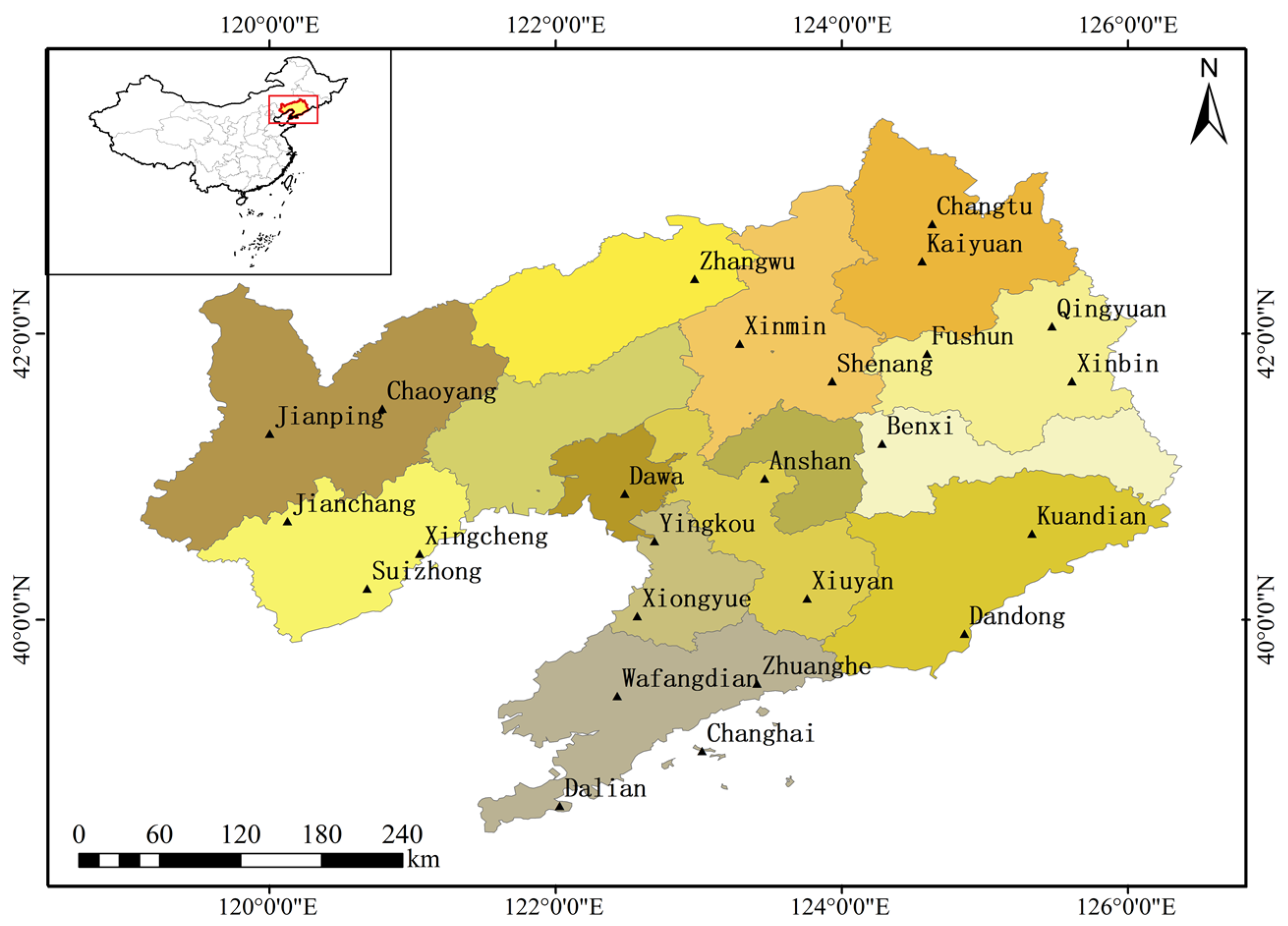
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Calculation of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration
2.3.2. Calculation of Drought Indices
- (1)
- Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
- (2)
- Evaporative Demand Drought Index (EDDI)
- (3)
- Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI)
- (4)
- Combined Joint Drought Index (CJDI)
2.3.3. Calculation of Drought Return Period
2.3.4. Data Analysis Methodology
3. Results
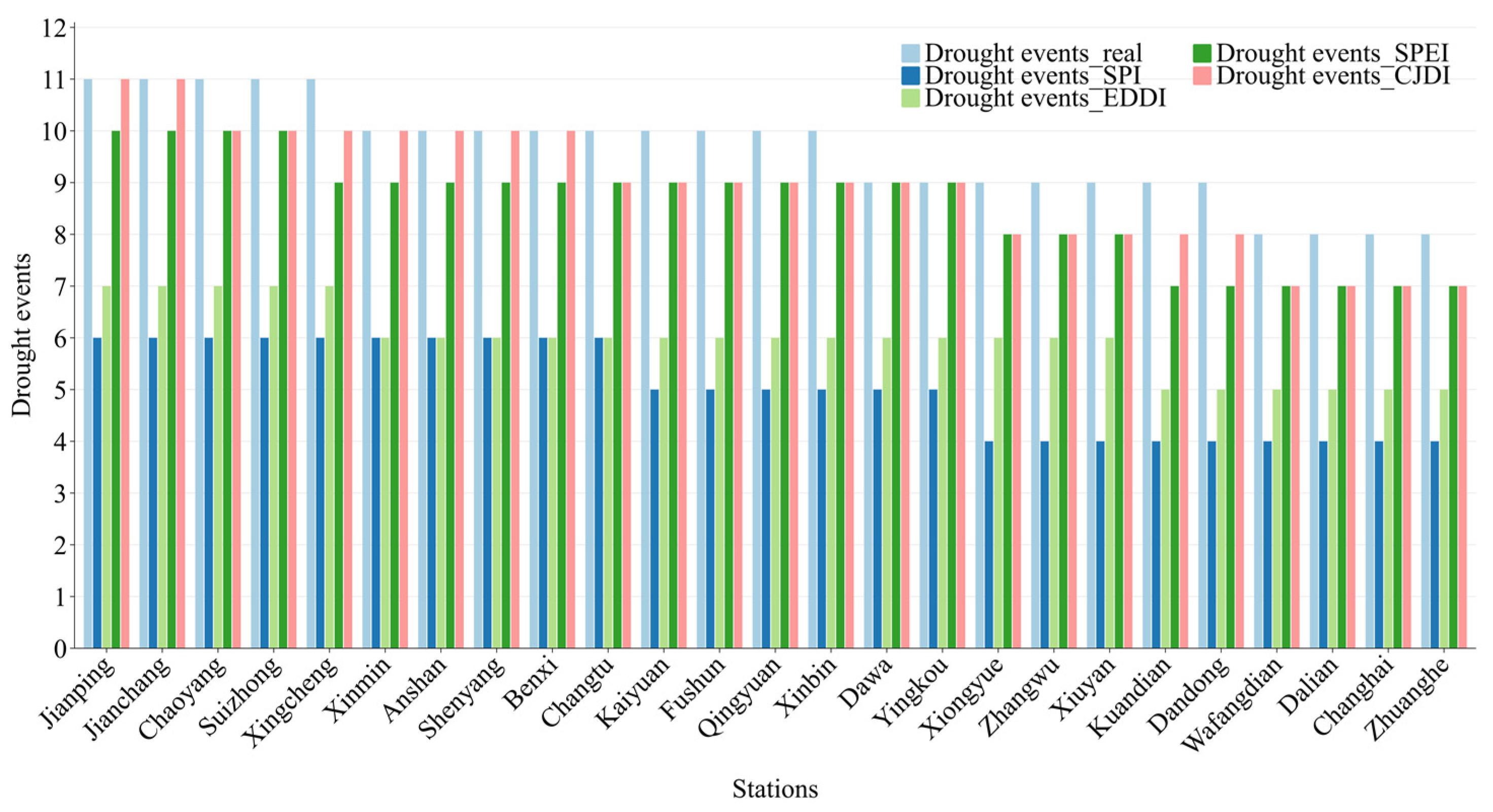
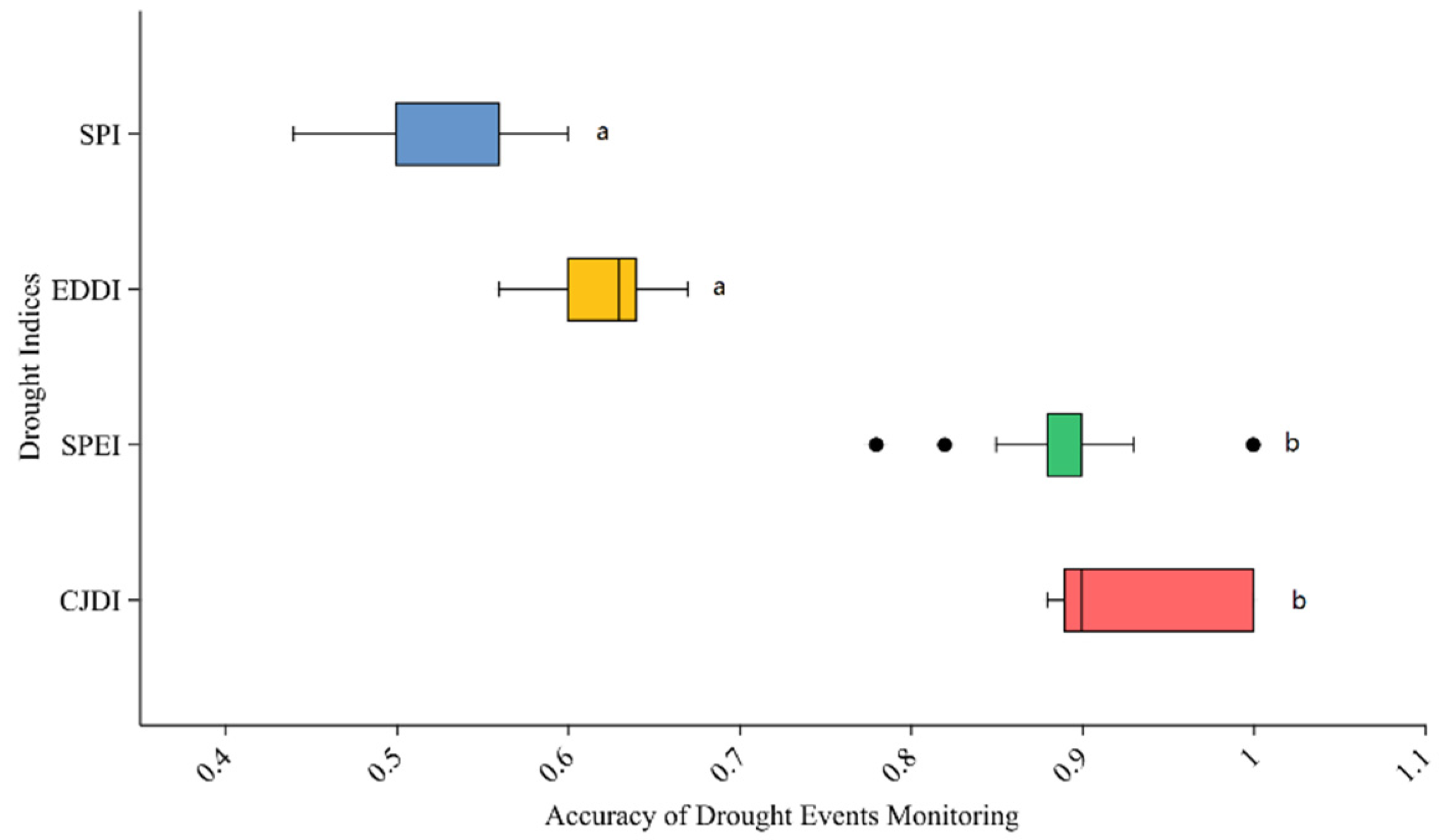
3.1. Comparison of Drought Indices in Monitoring Actual Drought Events
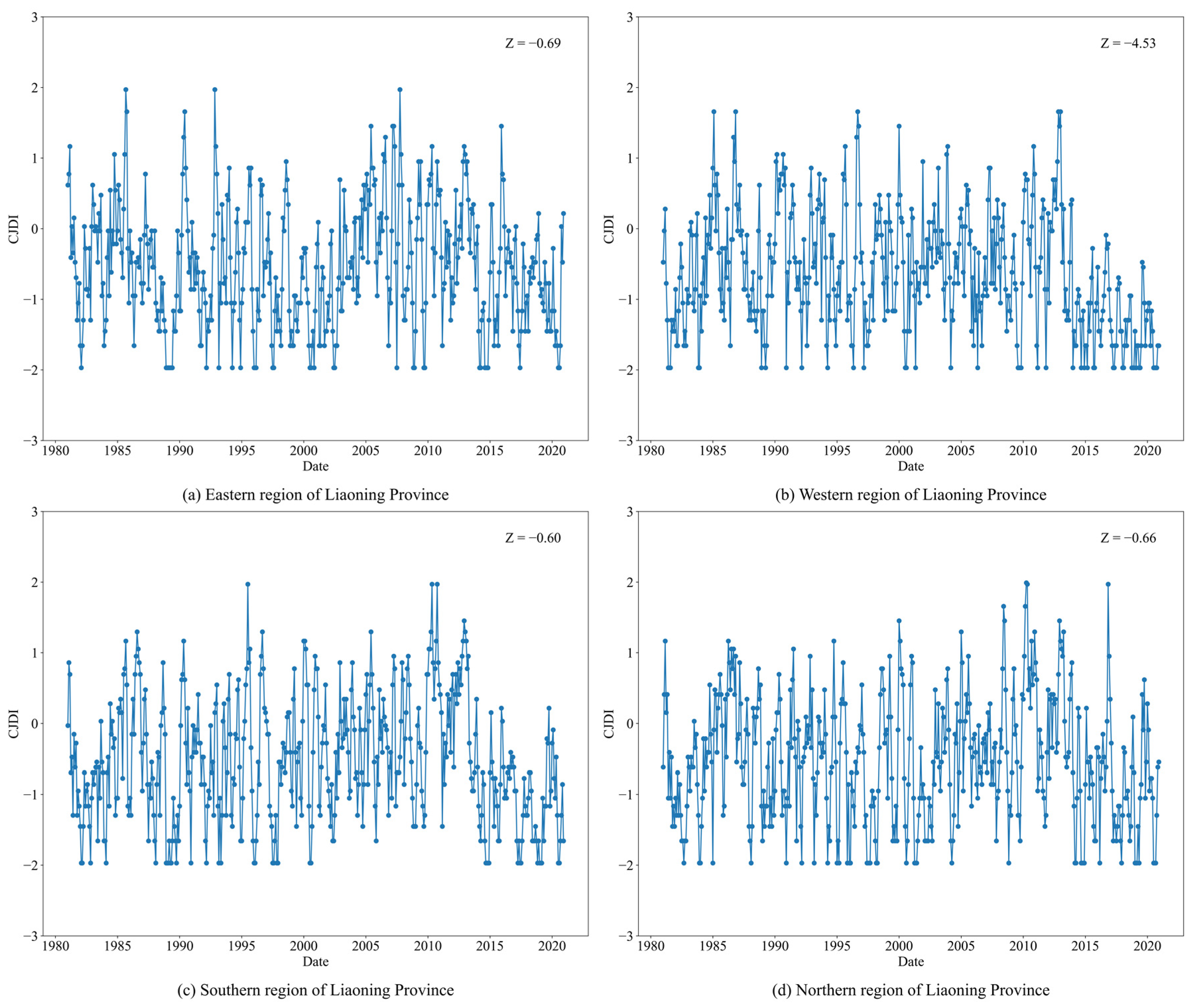
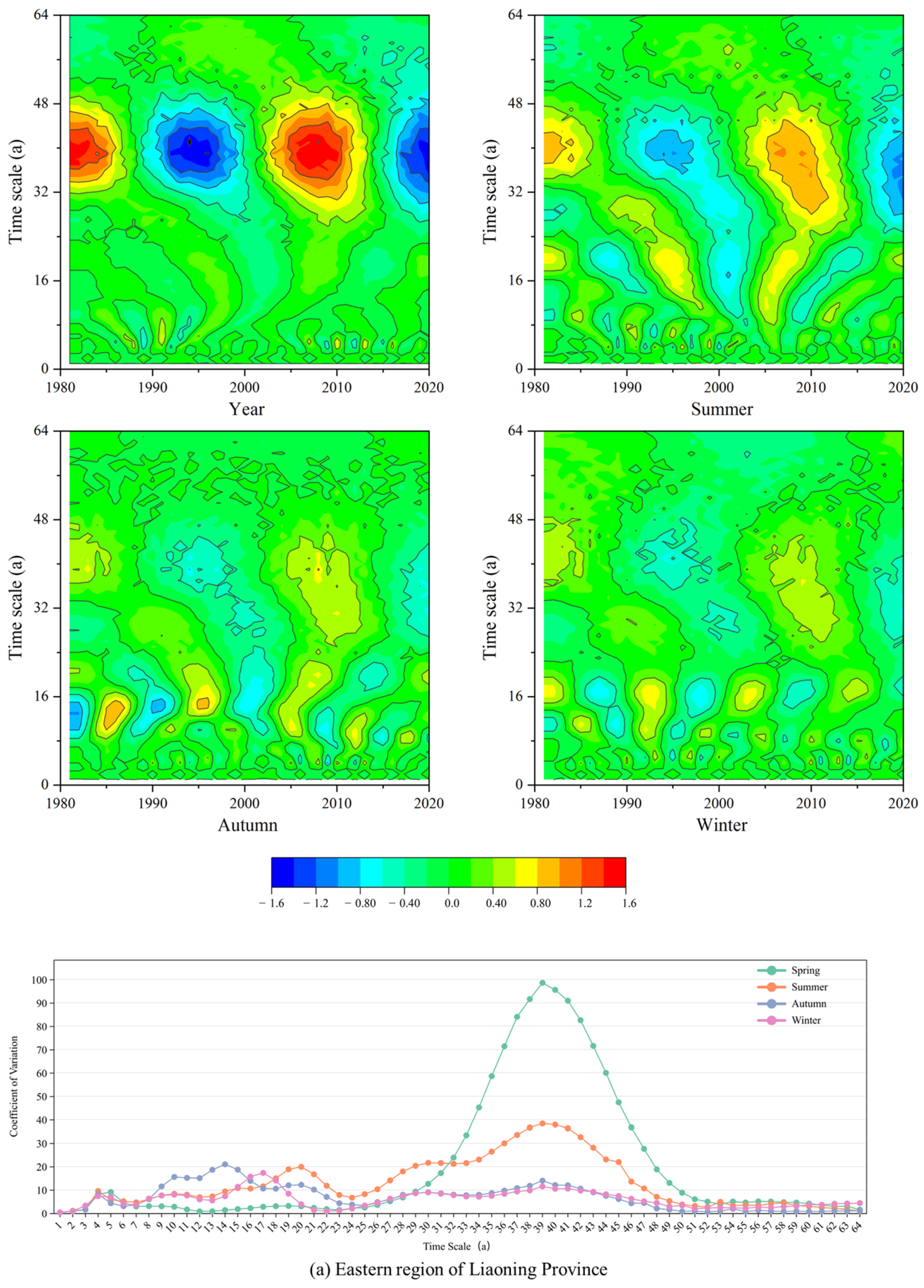
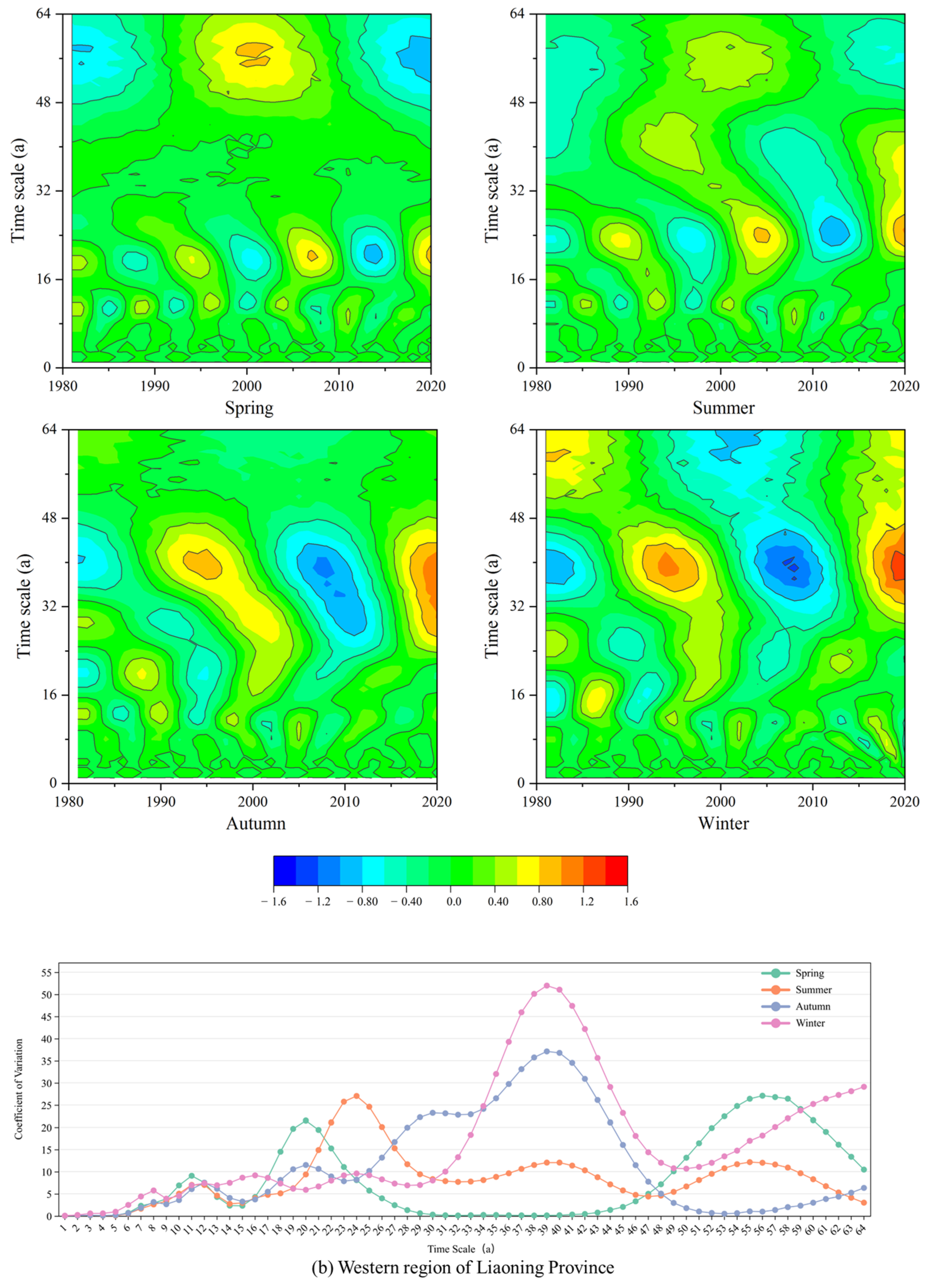
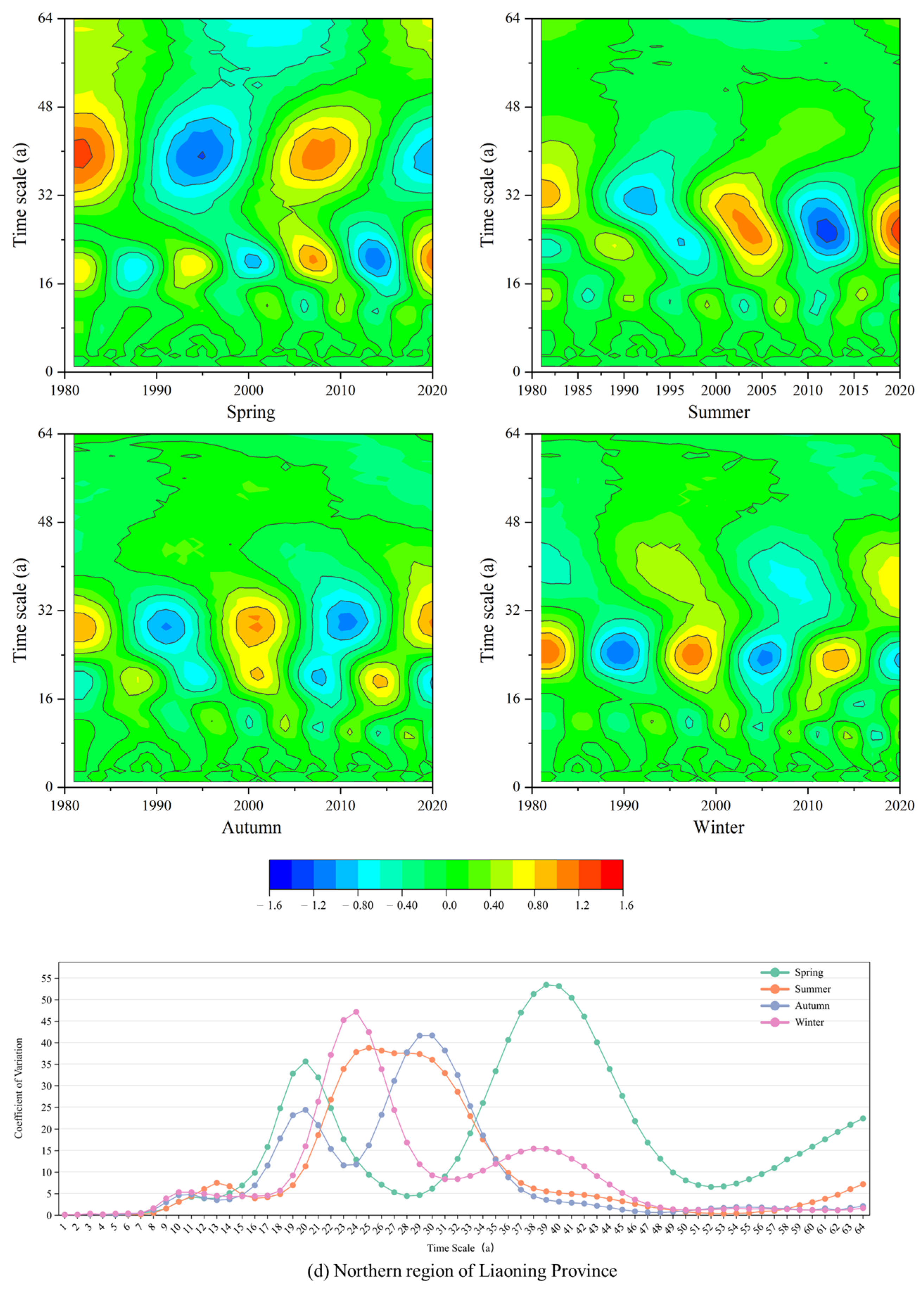
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation Patterns of Drought in Liaoning Province
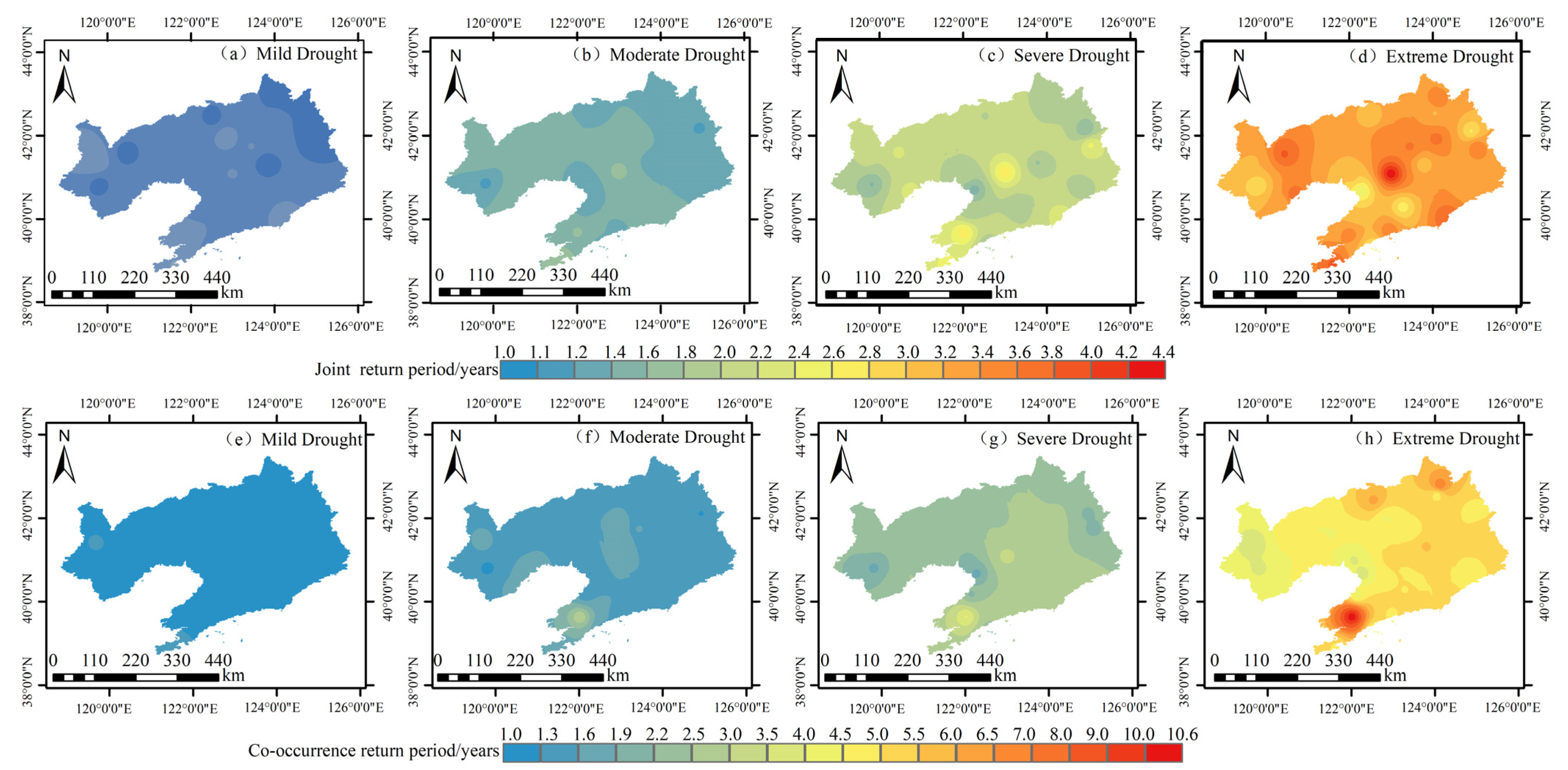
3.3. Analysis of Drought Recurrence Periods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, L.; Huang, Q.; Huang, S.; Liu, D.; Leng, G.; Wang, L.; Li, P. Propagation dynamics and causes of hydrological drought in response to meteorological drought at seasonal timescales. Hydrol. Res. 2022, 53, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahopelto, L.; Kallio, M.; Heino, M.; Kinnunen, P.; Fallon, A.; Kummu, M. Quantifying the co-occurrence of hydrological, meteorological, and agricultural droughts on a global scale. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2020, Online, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bake, B.; Zhang, J.; Rasulov, H. Spatio-temporal patterns of drought in North Xinjiang, China, 1961–2012 based on meteorological drought index. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Hannaford, J.; Su, Z.; Barker, L.; Qu, Y. Drought risk assessment of spring maize based on APSIM crop model in Liaoning province, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 45, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Gu, J.; Shi, W.; Zhao, H.; Sun, C.; You, S. Drought and Waterlogging Status and Dominant Meteorological Factors Affecting Maize (Zea mays L.) in Different Growth and Development Stages in Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Ji, R.; Wu, J.; Feng, R.; Mi, N.; Chen, N. Combined Effects of Heat and Drought Stress on the Growth Process and Yield of Maize (Zea mays L.) in Liaoning Province, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, Y.; Lei, T.; Peng, L. Drought evolution, severity and trends in mainland China over 1961–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G. A revised drought index based on precipitation and pan evaporation. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polong, F.; Chen, H.; Sun, S.; Ongoma, V. Temporal and spatial evolution of the standard precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI) in the Tana River Basin, Kenya. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 138, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziei, T. Revisiting the Rainfall Anomaly Index to serve as a Simplified Standardized Precipitation Index. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenang, G.; Kamga, F. Computation of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and Its Use to Assess Drought Occurrences in Cameroon over Recent Decades. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 2310–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; Volume 17, pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbins, M.; Wood, A.; McEvoy, D.; Huntington, J.; Morton, C.; Anderson, M.; Hain, C. The Evaporative Demand Drought Index. Part I: Linking Drought Evolution to Variations in Evaporative Demand. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1745–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Bei, X.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Jiang, B.; Shang, K.; Xu, J.; Chen, X. Assessing the Remotely Sensed Evaporative Drought Index for Drought Monitoring over Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, I.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Vicente-Serrano, S. Flash Drought Response to Precipitation and Atmospheric Evaporative Demand in Spain. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Assessment of the effect of PET calculation method on the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI). Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Sung, J.; Lee, B.; Kim, D. Evaluation on the Impact of Extreme Droughts in South Korea using the SPEI and RCP8.5 Climate Change Scenario. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2013, 13, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismallianto Isia, T.; Hadibarata, T.; Jusoh, M.N.H.; Bhattacharjya, R.; Shahedan, N.F.; Bouaissi, A.; Fitriyani, N.L.; Syafrudin, M. Drought analysis based on Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index and Standardized Precipitation Index in Sarawak, Malaysia. Sustainability 2022, 15, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayantobo, O.; Li, Y.; Song, S. Multivariate Drought Frequency Analysis using Four-Variate Symmetric and Asymmetric Archimedean Copula Functions. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, O.; Kim, S. Copula-based Joint Drought Index using SPI and EDDI and its application to climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, W.; Luo, X.; Guo, J.; Yuan, Z. The Spread of Multiple Droughts in Different Seasons and Its Dynamic Changes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yao, J. Comprehensive drought characteristics analysis based on a nonlinear multivariate drought index. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, L. Variation Characteristics of Heat Resources in Liaoning Province, China in Recent 60 Years and Their Impact on Meteorological Services. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2022, 10, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Pruitt, W.; Wright, J.; Howell, T.; Ventura, F.; Snyder, R.; Itenfisu, D.; Steduto, P.; Berengena, J.; Yrisarry, J.; et al. A recommendation on standardized surface resistance for hourly calculation of reference ET0 by the FAO56 Penman-Monteith method. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 81, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Cai, S.; Xu, Z.; Peng, D.; Kan, G.; Sun, W.; Pang, B.; Yang, H. Assessment of meteorological and agricultural droughts using in-situ observations and remote sensing data. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh Kumar, M.; Murthy, C.S.; Sesha Sai, M.V.R.; Roy, P.S. On the use of Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) for drought intensity assessment. Meteorol. Appl. 2009, 16, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P.; Guo, H.; Yu, F.X. Parameter estimation for 3-parameter log-logistic distribution (LLD3) by POME. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 1993, 7, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D. Multivariate ensemble Model Output Statistics using empirical copulas. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Babovic, V. A new scheme for multivariate, multisite weather generator with inter-variable, inter-site dependence and inter-annual variability based on empirical copula approach. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 2247–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevjevich, V. An Objective Approach to Definitions and Investigations of Continental Hydrologic Droughts; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1967; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Zheng, H.; Lei, Z. Applicability analysis of SPEI for drought research in Northeast China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 3787–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.X. A better way to define and describe Morlet wavelets for time-frequency analysis. NeuroImage 2019, 199, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, P.; Krishna, B.; Nafisa, S.; Sravani, T.; Madhuri, J.; Vanditha, C. Prediction of Droughts using SPEI. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 12th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), Bhopal, India, 8–9 April 2023; pp. 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyanto, D.; Aziz, A.; Komariah, K.; Sumani, S.; Abara, M. Comparing the accuracy of estimating soil moisture using the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and the Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI). Sains Tanah J. Soil Sci. Agroclimatol. 2020, 17, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serinaldi, F.; Bonaccorso, B.; Cancelliere, A.; Grimaldi, S. Probabilistic characterization of drought properties through copulas. Phys. Chem. Earth 2009, 34, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shen, S.; Wang, Q. Trend and Variability in Droughts in Northeast China Based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index. Water 2018, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xia, G.; Liu, T.; Chen, W.; Chi, D. Assessment of Drought Impact on Main Cereal Crops Using a Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index in Liaoning Province, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tan, M.; Hawcroft, M.; Catto, J.; Hodges, K.; Haywood, J. Monsoonal precipitation over Peninsular Malaysia in the CMIP6 HighResMIP experiments: The role of model resolution. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 2783–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Du, L.; Peng, C.; Yang, J.; Gao, W. The Composite Drought Index Incorporated Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence Enhances the Monitoring Capability of Short-Term Drought. J. Hydrol. 2024, 637, 131361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Yang, D.; Xu, X.; Lei, H. Copula based drought frequency analysis considering the spatio-temporal variability in Southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Regions | Included Meteorological Stations |
|---|---|
| Eastern | Fushun, Qingyuan, Xinbin, Benxi, Kuandian, Dandong |
| Western | Jianping, Jianchang, Chaoyang, Suizhong, Xingcheng, Zhangwu |
| Southern | Dalian, Changhai, Wafangdian, Xiongyue, Yingkou, Dawa, Anshan, Xiuyan |
| Northern | Changtu, Kaiyuan, Xinmin, Shenyang |
| Drought Events Levels | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Light Drought and above | Drought Duration > 1 Drought Intensity > 1 |
| Moderate Drought and above | Drought Duration > 3 Drought Intensity > 3 |
| Severe Drought and above | Drought Duration > 5 Drought Intensity > 5 |
| Extreme Drought and above | Drought Duration > 5 Drought Intensity > 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cai, H. Spatiotemporal Variation Patterns of Drought in Liaoning Province, China, Based on Copula Theory. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091063
Wu J, Li Y, Zhang X, Cai H. Spatiotemporal Variation Patterns of Drought in Liaoning Province, China, Based on Copula Theory. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(9):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiayu, Yao Li, Xudong Zhang, and Huanjie Cai. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Variation Patterns of Drought in Liaoning Province, China, Based on Copula Theory" Atmosphere 15, no. 9: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091063
APA StyleWu, J., Li, Y., Zhang, X., & Cai, H. (2024). Spatiotemporal Variation Patterns of Drought in Liaoning Province, China, Based on Copula Theory. Atmosphere, 15(9), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091063






