Driving Factors and Decoupling Effects of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture in Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methodology
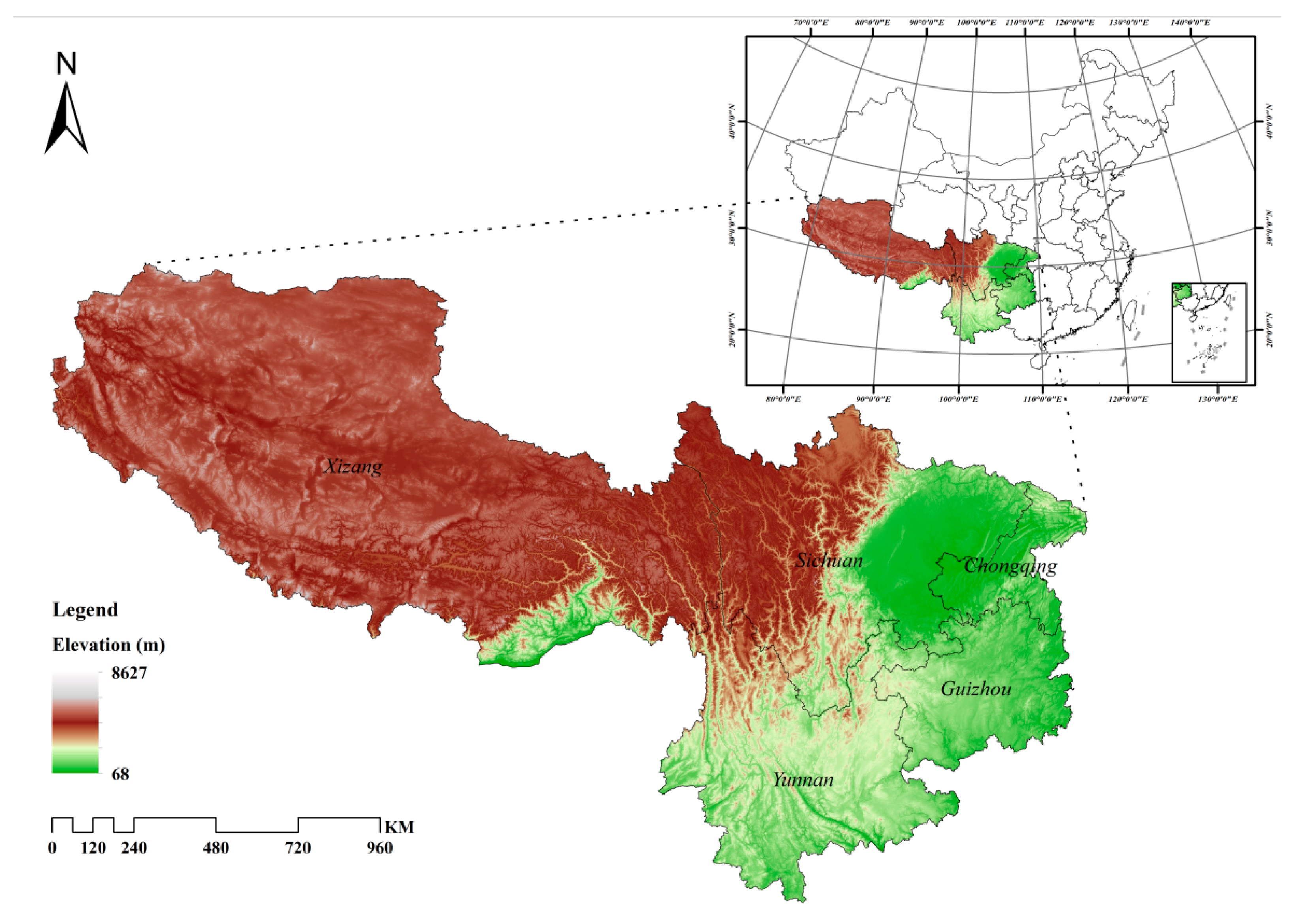
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Methodology
2.3. STIRPAT Model
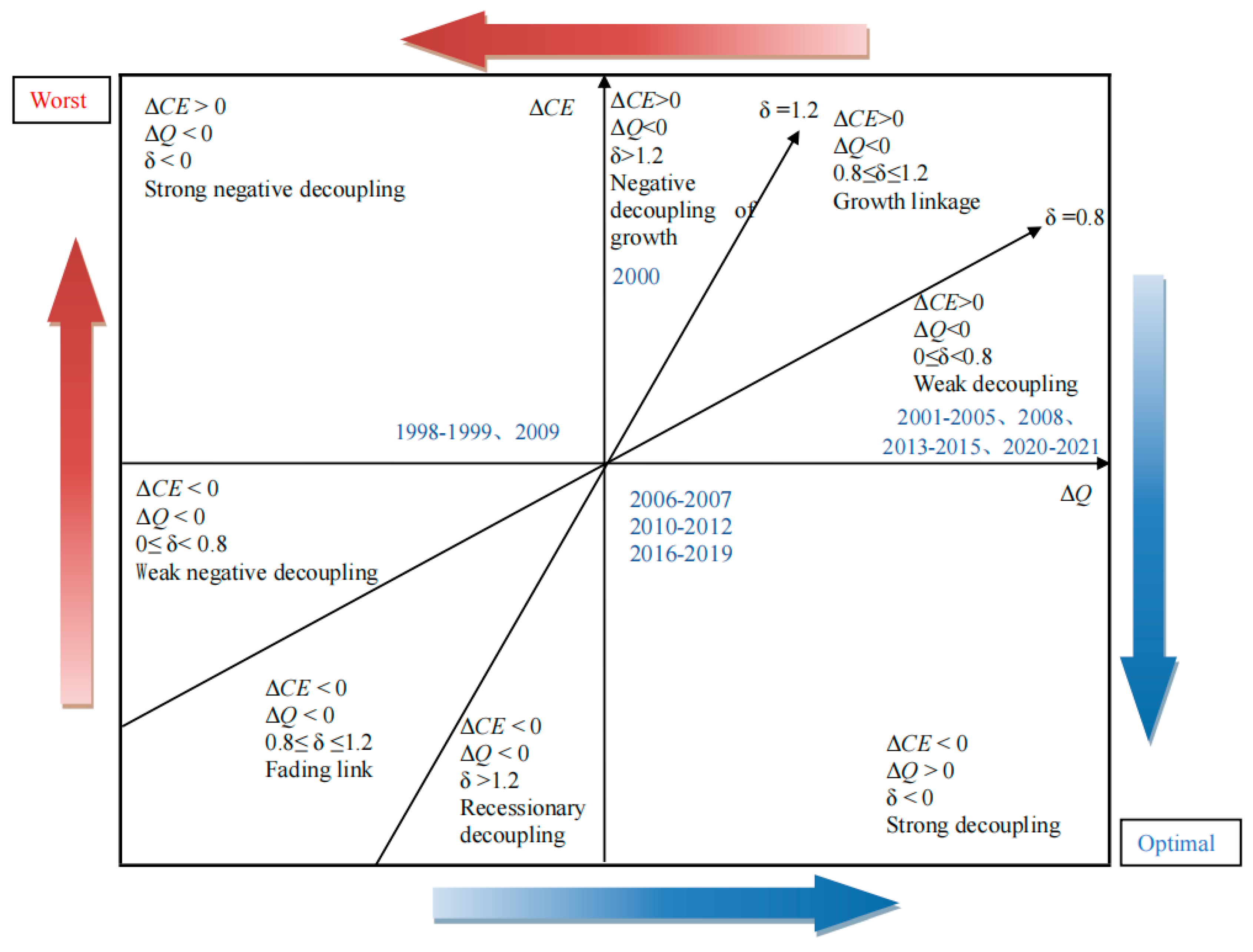
2.4. Tapio Decoupling Model
2.5. Data Resources
3. Results and Discussion
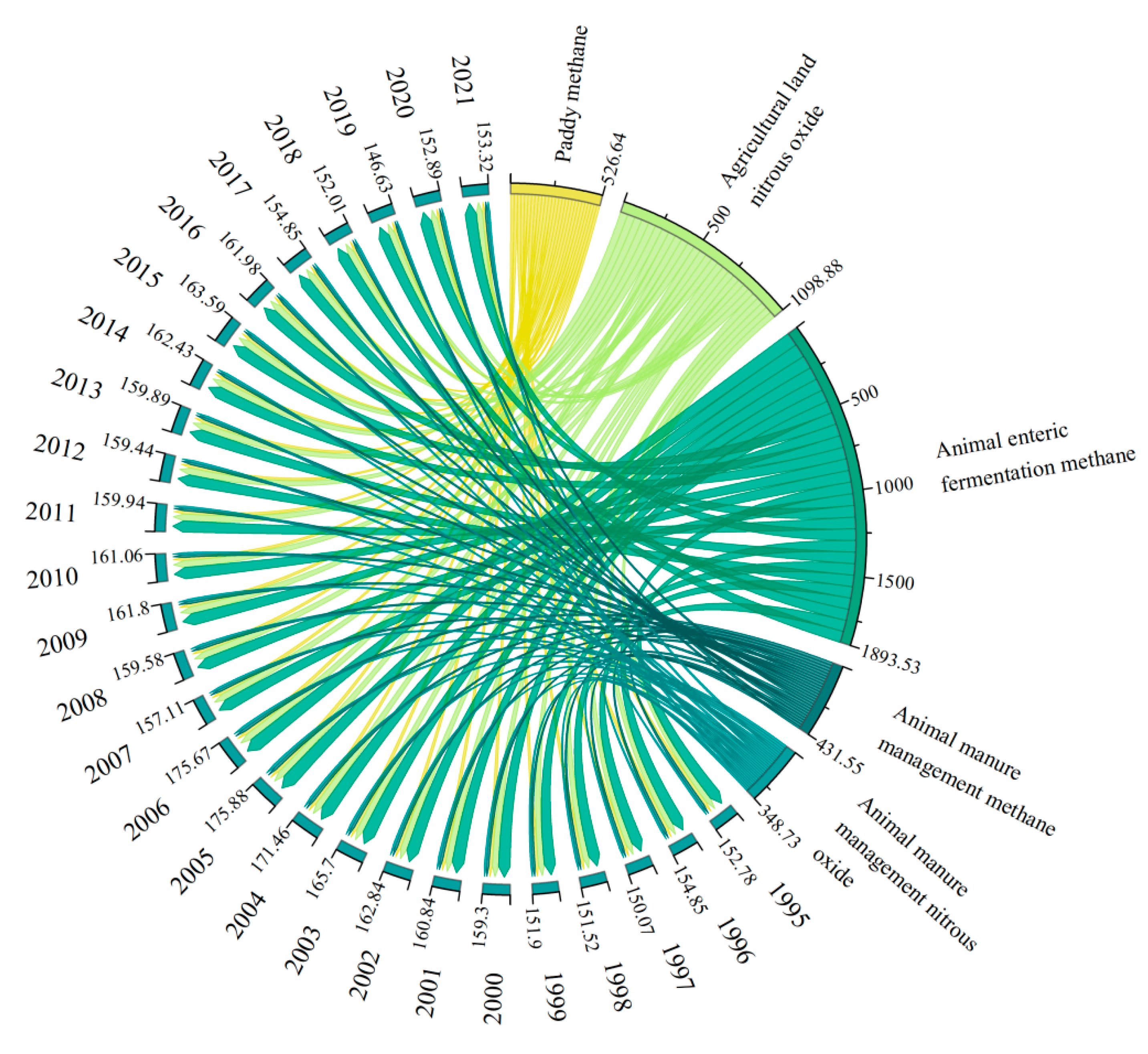
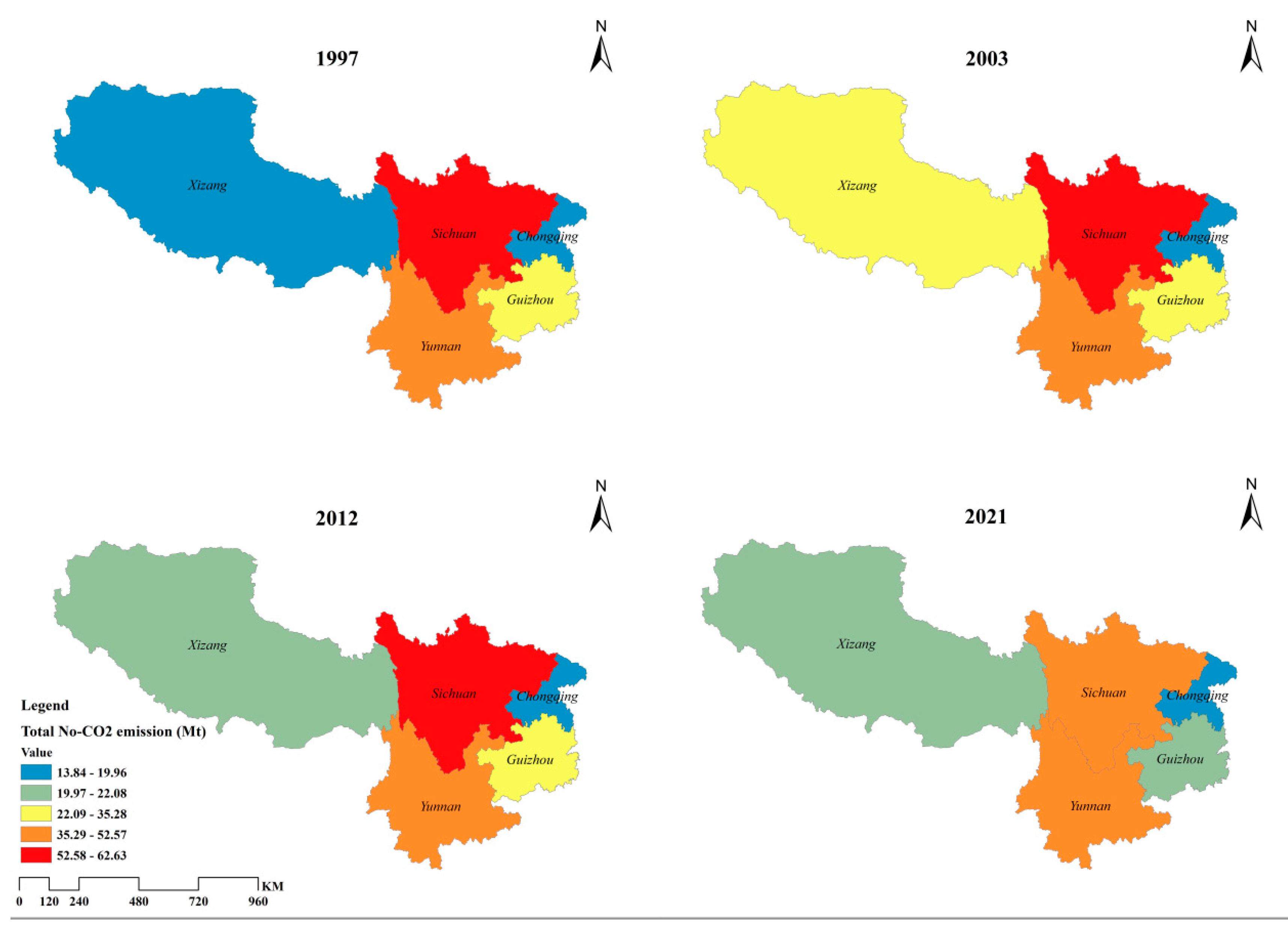
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Non-CO2 GHG Emissions in Southwest China
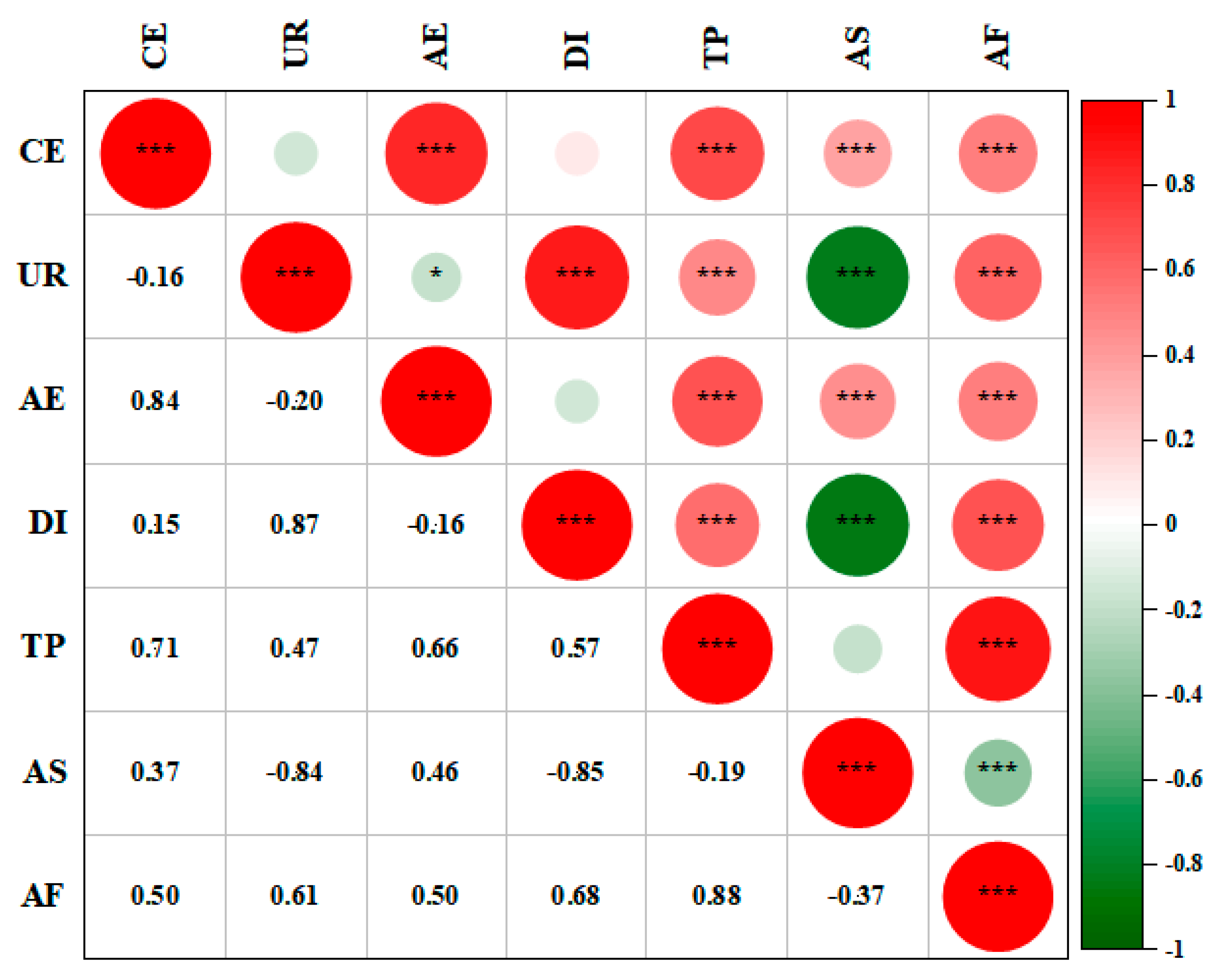
3.2. Drivers of Non-CO2 GHG Emissions from Agriculture in Southwest China
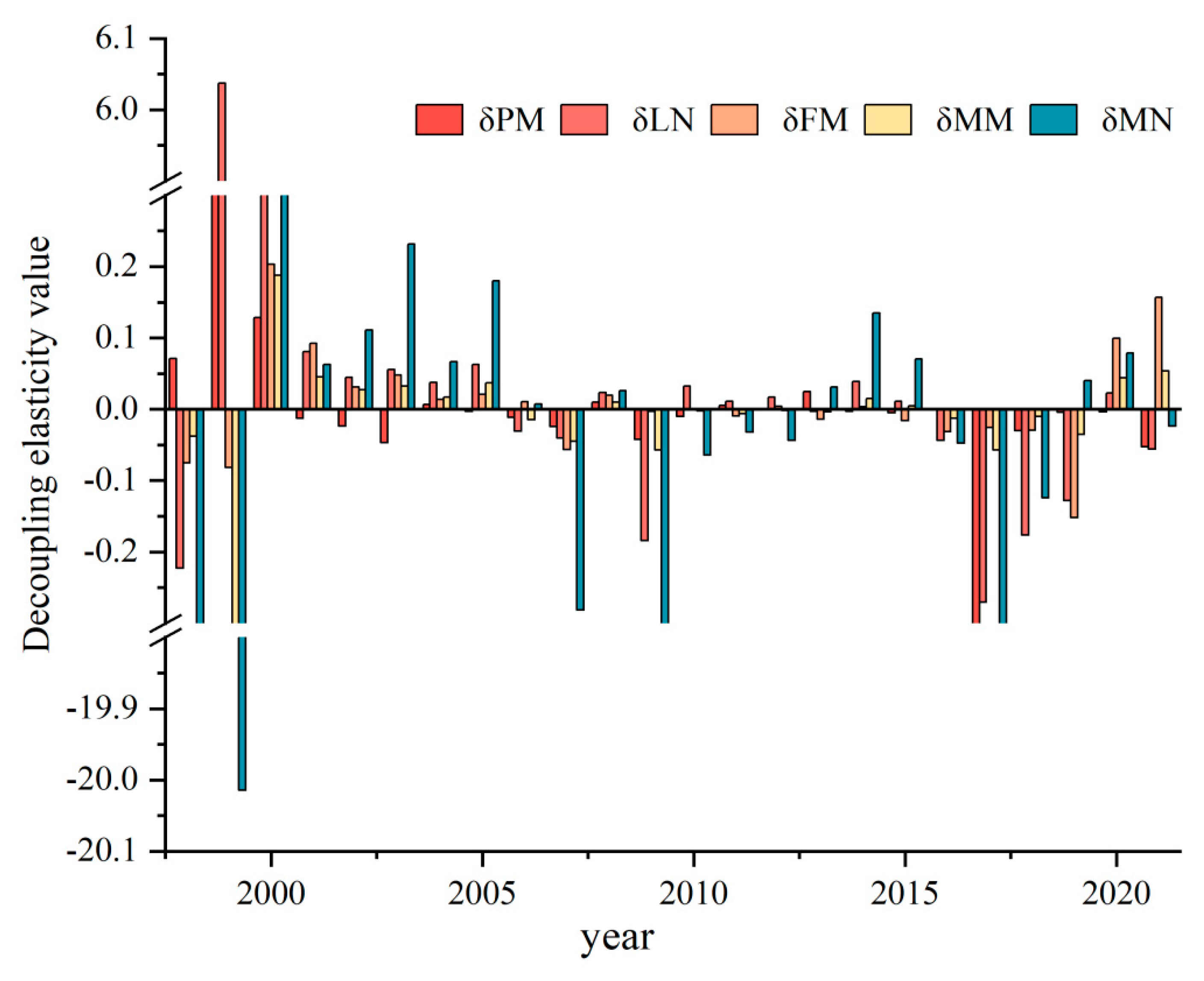
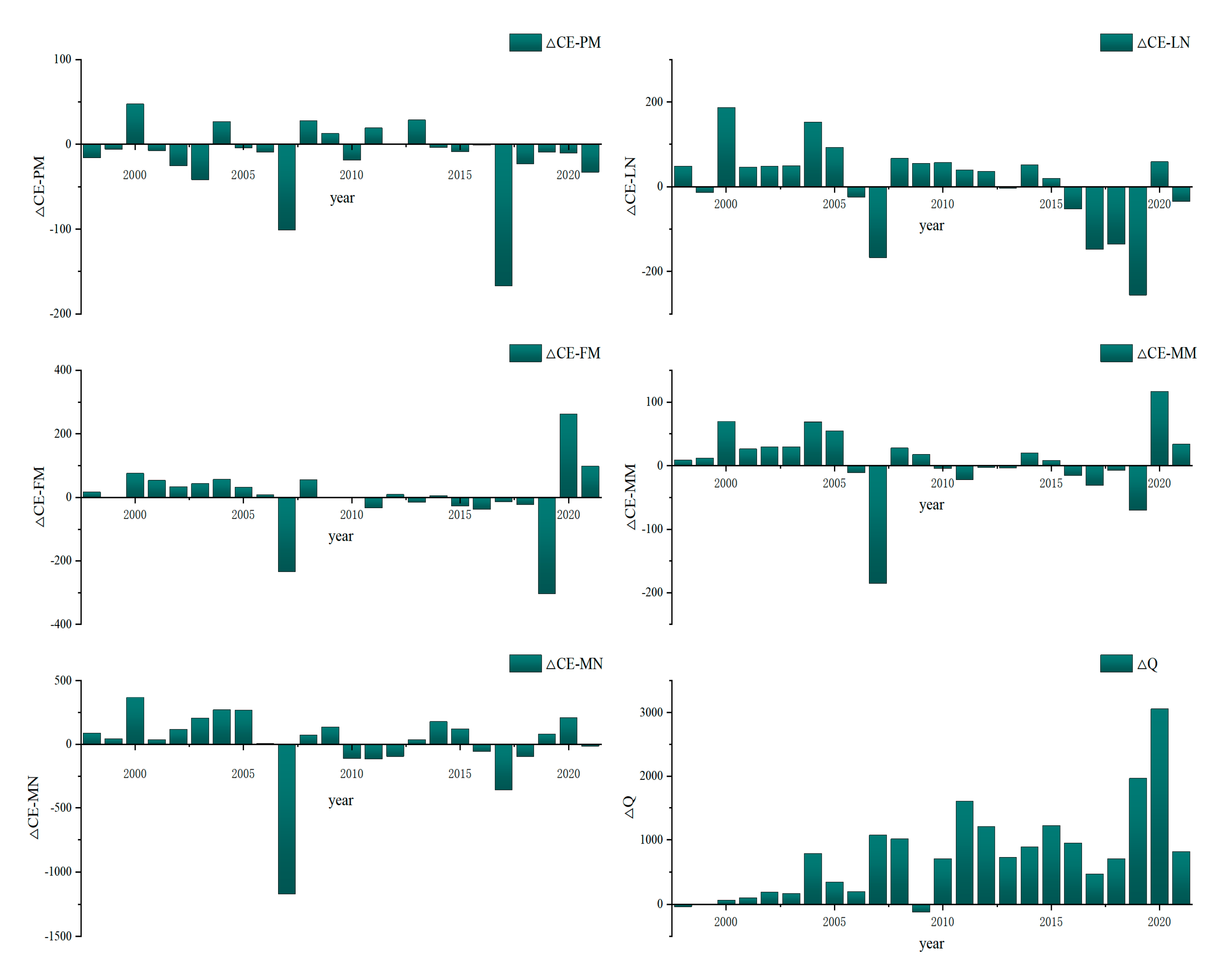
3.3. Analysis of the Decoupling Effect of Agricultural Non-CO2 GHG Emissions from Economic Development
4. Conclusions and Implications
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Fei, Y.; Wan, Z. The relationship between the development of global maritime fleets and GHG emission from shipping. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Cao, L.; Geng, Z.; Ping, W.; Zuo, X.; Fan, J.; Wan, J.; Lu, G. Novel economy and carbon emissions prediction model of different countries or regions in the world for energy optimization using improved residual neural network. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; You, C.; Yang, Z.; Yao, J. The impact of sustainable development policy for resource-based cities on green technology innovation: Firm-level evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 469, 143246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Yang, C.; Albitar, K. The Impact of Fintech on Corporate Carbon Emissions: Towards Green and Sustainable Development. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2024, 33, 5776–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, W.; Jiang, T.; Mao, Y.; Shi, W. Driving carbon emission reduction in China through green finance and green innovation: An endogenous growth perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 14318–14332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Havlík, P.; Stehfest, E.; van Meijl, H.; Witzke, P.; Pérez-Domínguez, I.; van Dijk, M.; Doelman, J.C.; Fellmann, T.; Koopman, J.F.L.; et al. Agricultural non-CO2 emission reduction potential in the context of the 1.5 °C target. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Global Anthropogenic Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions: 1990–2030; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Gao, C.; Mangi, E.; Ali, C. The potential for bioenergy generated on marginal land to offset agricultural greenhouse gas emissions in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, J.H.M.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Nayak, D.R.; Hof, A.F.; Höglund-Isaksson, L.; Lucas, P.L.; Nielsen, J.B.; Smith, P.; Stehfest, E. Long-term marginal abatement cost curves of non-CO2 greenhouse gases. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 99, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, L. Assessment of agricultural carbon emissions and their spatiotemporal changes in China, 1997–2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C. Spatio-temporal evolution of agricultural carbon emissions in China, 2000–2020. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Guo, Y.-C.; Tang, L.-J.; Zhong, C.-Y.; Zhang, J.-W.; Li, X.-L.; Qiao, D.-W. Spatial–temporal characteristics and driving factors’ contribution and evolution of agricultural non-CO2 greenhouse gas emissions in China: 1995–2021. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 19779–19794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Zheng, X.; Wu, R.; Liu, X.; Xiao, S.; Sun, L.; Hu, T.; Gao, Z.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; et al. Agriculture related methane emissions embodied in China’s interprovincial trade. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Y. Research on Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Driving Factor of Agricultural Carbon Emissions in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Yang, D.; Xia, F.; Huo, J. Changes in agricultural carbon emissions and factors that influence agricultural carbon emissions based on different stages in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Characteristics, influence factors, and prediction of agricultural carbon emissions in Shandong Province. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fan, B.; Pan, C. Study on mechanisms underlying changes in agricultural carbon emissions: A case in Jilin Province, China, 1998–2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Su, K.; Li, X. Spatial-temporal characteristics of the driving factors of agricultural carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from Fujian, China. Energies 2019, 12, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Fan, J.; Chen, J. Spatial and temporal characteristics and drivers of agricultural carbon emissions in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Yang, H.; Xiang, P.; Liu, D.; Li, L. Drivers of agricultural carbon emissions in Hunan Province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhan, P.; Zhu, J. Carbon emission drivers and decoupling effects of agricultural energy consumption in China. China Sci. Technol. Forum 2017, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Che, W. Measurement, spatial spillover and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions efficiency in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hu, S.; Frazier, A.E. Spatiotemporal variation and driving factors of carbon emissions in three industrial land spaces in China from 1997 to 2016. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 169, 120837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Chen, S.; Xu, L. Driving factors analysis of agricultural carbon emissions based on extended STIRPAT model of Jiangsu Province, China. Growth Chang. 2020, 51, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Decoupling and Decomposition Analysis of Agricultural Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Heilongjiang Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Hu, C.; Mei, Y.; Hu, W. Temporal and spatial characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emission in Hubei Province based on Kaya model. Green Technol. 2020, 4, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Liao, M.; Xie, X.; Guo, B.; Lu, X.; Qiu, H. Agricultural carbon emissions in Zhejiang Province, China (2001–2020): Changing trends, influencing factors, and has it achieved synergy with food security and economic development? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Qin, H.; Zhang, M. Driving factors and decoupling effects of agricultural carbon emissions in Jiangxi Province based on time-varying parameter C-D production function. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2023, 34, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokmenoglu, K.K.; Taspinar, N. Testing the agriculture-induced EKC hypothesis: The case of Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22829–22841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Bae, J. The impact of renewable energy and agriculture on carbon dioxide emissions: Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve in four selected ASEAN countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastola, A.; Viccaro, M.; Grippo, V.; Genovese, F.; Romano, S.; Cozzi, M. The Decoupling Effect in Italian Agricultural Waste: An Empirical Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Tan, Y.; Chen, H. Decoupling relationship between greenhouse gas emissions from cropland utilization and crop yield in China: Implications for green agricultural development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 97160–97177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Luo, P.; Li, L. Driving factors and decoupling trend analysis between agricultural CO2 emissions and economic development in China based on LMDI and Tapio decoupling. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 13093–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, S. Decoupling elasticity and driving factors of agricultural carbon emissions in Hunan Province–Based on Tapio decoupling model and LMDI analysis. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2023, 41, 952–960. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.B.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Guo, Y.; Xi, F.; Liu, S. Coupling and decoupling effects of agricultural carbon emissions in China and their driving factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25280–25293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, J. Study on the Measurement, Decoupling Characteristics and Driving Factors of Carbon Emissions from Cultivation in China. China Agric. Resour. Zoning 2022, 43, 1–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Liao, M.; Jiang, J. Research on Agricultural Carbon Emissions and Regional Carbon Emissions Reduction Strategies in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Xu, C.; Kong, F. Decoupling agriculture pollution and carbon reduction from economic growth in the Yangtze River Delta, China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Xue, W. Inter-provincial factors decomposition and decoupling analysis of generalized agricultural carbon emissions in China. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2024, 16, 015902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Yu, D.; He, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, D. Countermeasures and suggestions for developing climate-smart agriculture in southwest China. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Her. 2021, 23, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, P.R.; Holdren, J.P. Impact of Population Growth. Science 1971, 171, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, R.; Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: Analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 46, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, Y. Impacts of Urbanization and Technology on Carbon Dioxide Emissions of Yangtze River Economic Belt at Two Stages: Based on an Extended STIRPAT Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Hu, H.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, X. An empirical relationship between urbanization and carbon emissions in an ecological civilization demonstration area of China based on the STIRPAT model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 2465–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapio, P. Towards a theory of decoupling: Degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001. Transp. Policy 2005, 12, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehmas, J.; Kaivo-oja, J.; Luukkanen, J. Global Trends of Linking Environmental Stress and Economic Growth; Finland Futures Research Centre: Turku, Finland, 2003; pp. 6–9. ISBN 951-564-109-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vehmas, J.; Luukkanen, J.; Kaivo-oja, J. Linking analyses and environmental Kuznets curves for aggregated material flows in the EU. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Pei, X.D.; Yang, G.J.; Shi, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.H. Decoupling relationship and driving effect between livestock carbon emissions and economic efficiency in Qinghai Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development; National Bureau of Statistics: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, E.L.; D’Abrera, H.J.M. Nonparametrics: Statistical Methods Based on Ranks; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 292, 300+323. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Fan, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yao, J. Temporal-spatial characteristics of energy-based carbon dioxide emissions and driving factors during 2004–2019, China. Energy 2022, 261, 124965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, R.; Yu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Cao, Y. Temporal and spatial characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emission in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on STIRPAT model. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2020, 29, 32–37+132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X. Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions in Southwest China. Guangdong Seric. 2019, 53, 32–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, D.; Wang, R.; Gao, C.; Song, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, G. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Influence Factors of Carbon Emission from Livestock Industry in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, P.J.; Hristov, A.; Henderson, B.; Makkar, H.; Oh, J.; Lee, C.; Meinen, R.; Montes, F.; Ott, T.; Firkins, J.; et al. Technical options for the mitigation of direct methane and nitrous oxide emissions from livestock: A review. Animal 2013, 7, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Dong, H. Greenhouse gas emissions from livestock in China and mitigation options within the context of carbon neutrality. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Region | Methane Emission Factors in Rice Field (kg/ha) | Direct Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors from Agricultural Land | Indirect Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors from Agricultural Land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition | Nitrogen Leaching Runoff Loss | |||
| Sichuan, Chongqing | 156.2 | 0.0109 | 0.01 | 0.0075 |
| Yunnan, Guizhou | 156.2 | 0.0106 | 0.01 | 0.0075 |
| Xizang | 156.2 | 0.0056 | 0.01 | 0.0075 |
| Source | Intestinal Fermentation Methane Emission Factor (kg/head/year) | Fecal Management Methane Emission Factors (kg/head/year) | Fecal Management Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors (kg/head/year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pig | 1 | 4.18 | 0.159 |
| Cow | 88.1 | 6.51 | 1.884 |
| Buffalo | 70.5 | 1.53 | 1.197 |
| Non-buffalo | 52.9 | 3.21 | 0.691 |
| Goat | 8.9 | 0.53 | 0.064 |
| Horse | 18 | 1.64 | 0.330 |
| Donkey/mule | 10 | 0.90 | 0.188 |
| Poultry | / | 0.02 | 0.007 |
| ∆CE | ∆Q | δ | Decoupling State |
|---|---|---|---|
| <0 | >0 | (−∞, 0) | Strong decoupling |
| >0 | >0 | (0, 0.8) | Weak decoupling |
| <0 | <0 | (1.2, +∞) | Recessionary decoupling |
| >0 | >0 | (0.8, 1.2) | Growth linkage |
| <0 | <0 | (0.8, 1.2) | Fading link |
| <0 | <0 | (0, 0.8) | Weak negative decoupling |
| >0 | >0 | (1.2, +∞) | Negative decoupling of growth |
| >0 | <0 | (−∞, 0) | Strong negative decoupling |
| Data | |
|---|---|
| Basic data used to calculate non-CO2 GHG emissions from agriculture | China Rural Statistical Yearbook (1996–2022) (National Bureau of Statistics of China) Chinese Agricultural Yearbook (1996–2022) (Ministry of Agriculture of China) Provincial Statistical Yearbook (1996–2022) (Statistics Bureau of provinces in southwest China) |
| Socio-economic factors (e.g., disposable income of rural residents, funds for agricultural science and technology activities, industrial structure) | China Statistical Yearbook (1996–2022) Statistics Bureau of provinces in southwest China China Statistical Yearbook of Science and Technology (1996–2022) (Department of Social Science, Technology, and Cultural Industries Statistics and Department of Strategic Planning, Ministry of Science and Technology, National Bureau of Statistics, China) |
| Vector data of five provinces in southwest China | National Basic Geographic Information Database |
| Variables | Southwest China | Chongqing | Sichuan | Guizhou | Yunnan | Xizang |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnUR | −0.24 *** [0.000] | −0.135 *** [0.000] | −0.074 * [0.067] | −0.238 ** [0.039] | −0.094 [0.103] | 0.069 [0.666] |
| lnAE | −0.454 *** [0.000] | 1.196 *** [0.000] | 0.114 [0.244] | 0.449 ** [0.020] | −0.148 [0.445] | −0.014 [0.927] |
| lnDI | −0.214 *** [0.000] | 0.170 *** [0.006] | −0.362 *** [0.000] | −0.231 [0.143] | −0.021 [0.809] | −0.277 *** [0.000] |
| lnTP | 0.747 *** [0.000] | 0.277 [0.245] | 0.754 *** [0.000] | 0.143 [0.210] | 0.164 * [0.054] | 0.177 *** [0.001] |
| lnAS | 1.018 *** [0.000] | −0.317 ** [0.023] | 0.255 ** [0.027] | 0.237 ** [0.030] | 0.031 [0.755] | −0.217 ** [0.021] |
| lnAF | 0.132 *** [0.000] | 0.012 [0.811] | 0.078 [0.105] | 0.262 *** [0.001] | 0.040 [0.117] | 0.016 [0.370] |
| Ad R-s | 0.893 | 0.879 | 0.906 | 0.860 | 0.916 | 0.908 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, R.; Chu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Yao, J. Driving Factors and Decoupling Effects of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture in Southwest China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091084
Tang R, Chu Y, Liu X, Yang Z, Yao J. Driving Factors and Decoupling Effects of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture in Southwest China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(9):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091084
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Ruiyi, Yuanyue Chu, Xiaoqian Liu, Zhishan Yang, and Jian Yao. 2024. "Driving Factors and Decoupling Effects of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture in Southwest China" Atmosphere 15, no. 9: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091084
APA StyleTang, R., Chu, Y., Liu, X., Yang, Z., & Yao, J. (2024). Driving Factors and Decoupling Effects of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agriculture in Southwest China. Atmosphere, 15(9), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091084





