Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Study Domain and Monitoring Conditions
2.3. Quality Assurance and Data Processing
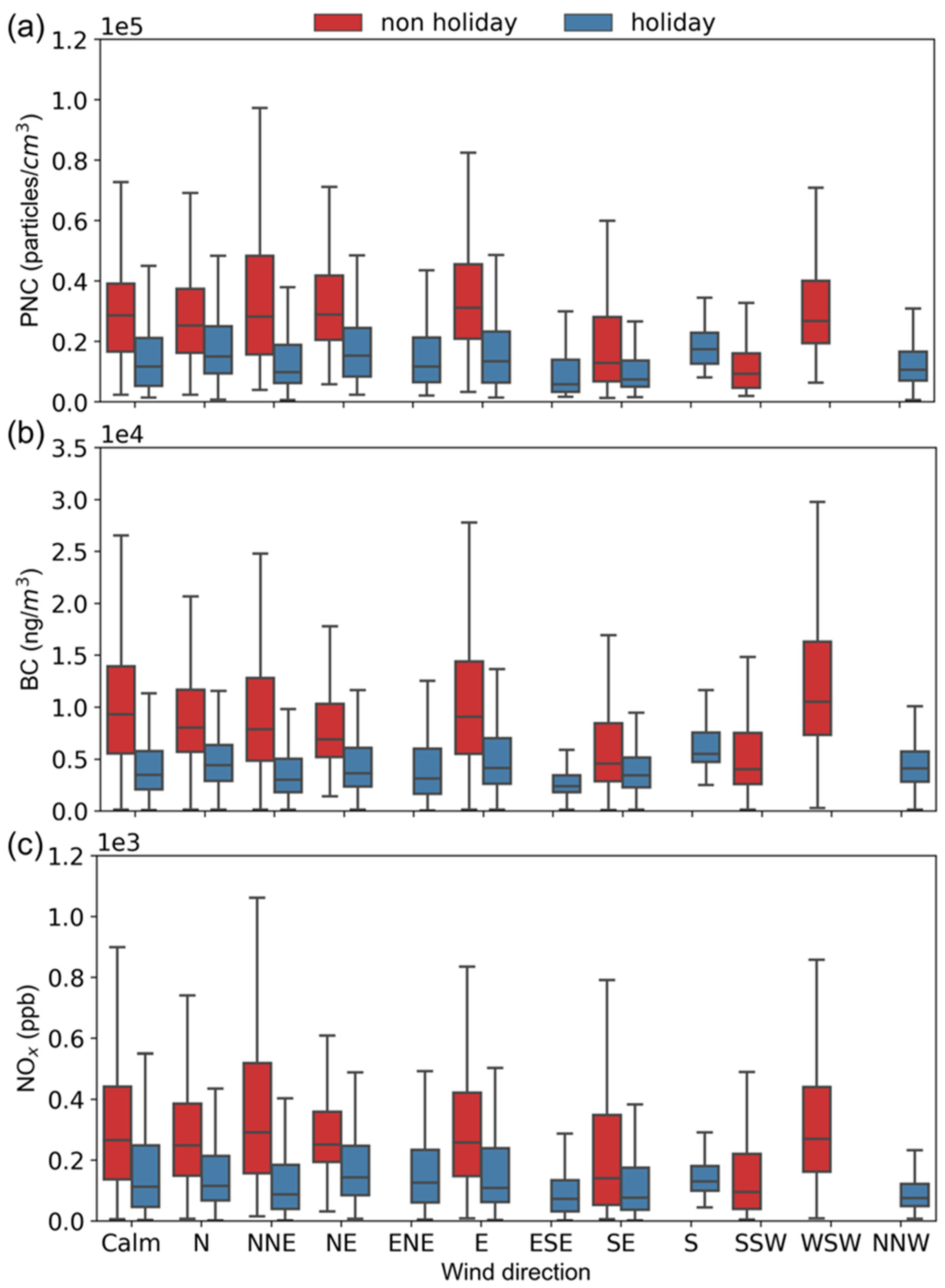
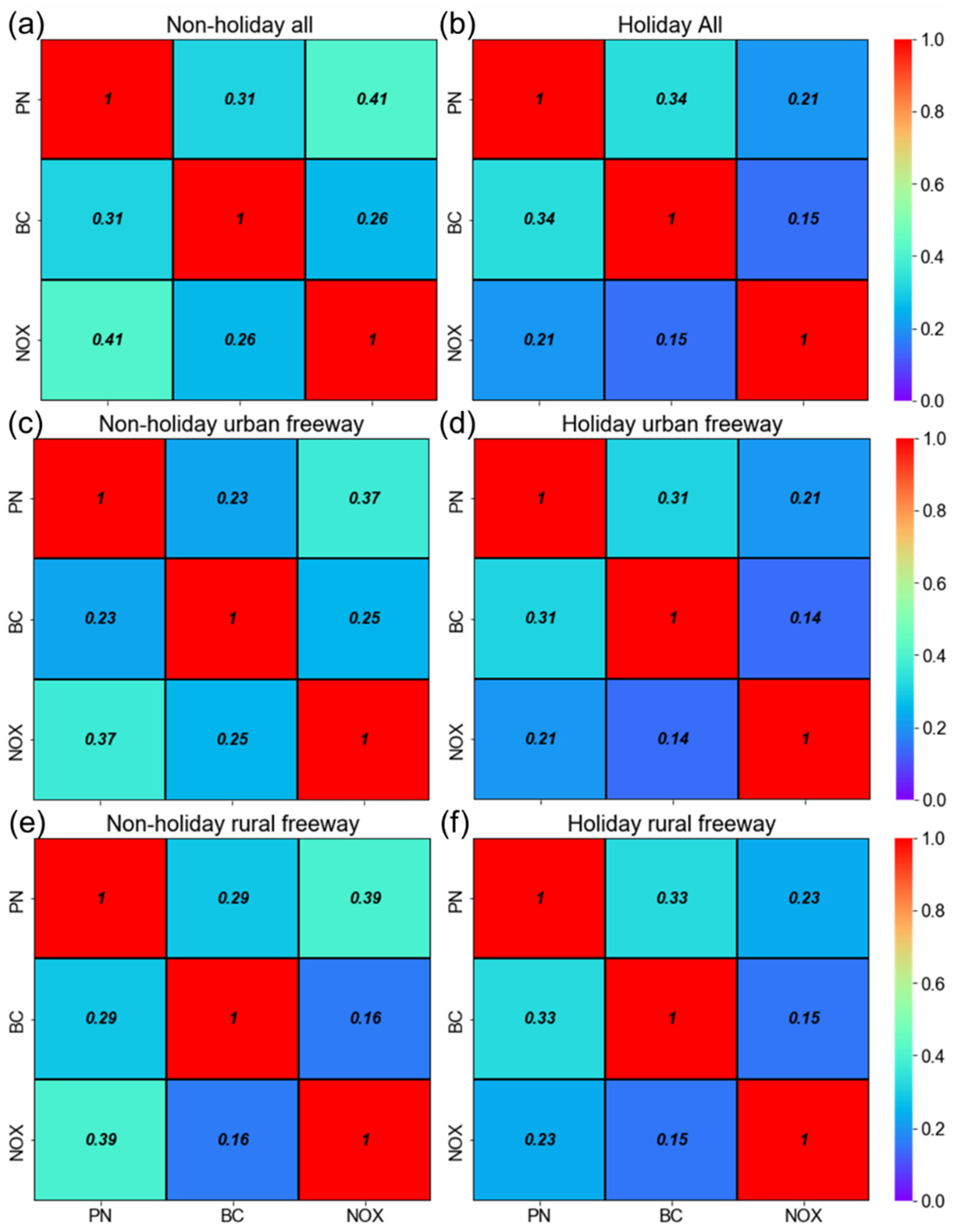
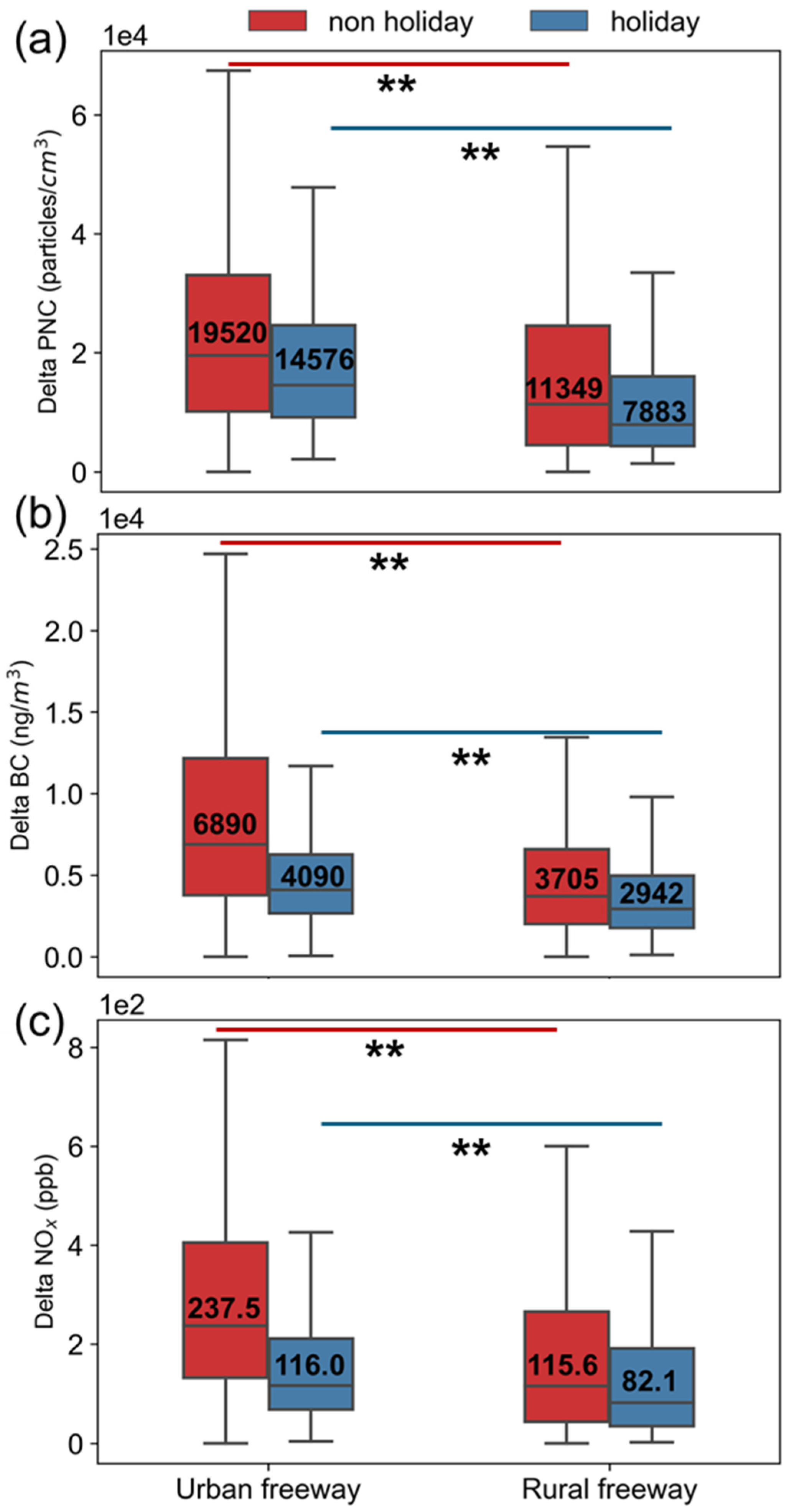
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Monitoring Conditions
3.2. Traffic-Related Air Pollutants’ Intercorrelation
3.3. Temporal-Spatial Variations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TRAPs | Traffic-related air pollutants |
| PNC | Particle number concentration |
| BC | Black carbon |
| NOx | Nitrogen oxides |
| HDDV | Heavy-duty diesel vehicle |
| UFPs | Ultrafine particles |
References
- Panel, H. On the health effects of long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution. In Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Selected Health Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C.; Kim, S.; Sioutas, C. Concentration and size distribution of ultrafine particles near a major highway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban-Weiss, G.A.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Harley, R.A.; Lunden, M.M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Kean, A.J.; Strawa, A.W.; Stevenson, E.D.; Kendall, G.R. Long-term changes in emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter from on-road gasoline and diesel vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Targino, A.C.; Landi, T.P.; Ketzel, M. Determination of black carbon, PM2.5, particle number and NOx emission factors from roadside measurements and their implications for emission inventory development. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 186, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Paul, K.C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Folle, A.D.; Wu, J.; Bronstein, J.M.; Ritz, B. Traffic-related air pollution and Parkinson’s disease in central California. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, N.A.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; Van Bree, L.; Ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B. Black carbon as an additional indicator of the adverse health effects of airborne particles compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, R.J. Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and exposure to air toxics: Linkages between occupational, indoor, and community air pollution research. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olstrup, H.; Flanagan, E.; Persson, J.-O.; Rittner, R.; Krage Carlsen, H.; Stockfelt, L.; Xu, Y.; Rylander, L.; Gustafsson, S.; Spanne, M. The Long-Term Mortality Effects Associated with Exposure to Particles and NOx in the Malmö Diet and Cancer Cohort. Toxics 2023, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Manchanda, C. High-resolution urban air pollution mapping. Science 2024, 385, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeulen, R.C.; Hamburg, S.P. High-resolution air pollution mapping with Google street view cars: Exploiting big data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yim, S.H.L.; He, X.; Xia, X.; Ho, K.-F.; Yu, J.Z. High spatial resolution estimates of major PM2.5 components and their associated health risks in Hong Kong using a coupled land use regression and health risk assessment approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Gu, P.; Ye, Q.; Zimmerman, N.; Robinson, E.S.; Subramanian, R.; Apte, J.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A. Spatially dense air pollutant sampling: Implications of spatial variability on the representativeness of stationary air pollutant monitors. Atmos. Environ. X 2019, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambliss, S.E.; Pinon, C.P.; Messier, K.P.; LaFranchi, B.; Upperman, C.R.; Lunden, M.M.; Robinson, A.L.; Marshall, J.D.; Apte, J.S. Local-and regional-scale racial and ethnic disparities in air pollution determined by long-term mobile monitoring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2109249118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.M.; Si, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y. Characterizing spatial variations of city-wide elevated PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations using taxi-based mobile monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, T.; You, Y.; Si, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Evaluation of City-Scale Disparities in PM2.5 Exposure Using Hyper-Localized Taxi-Based Mobile Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13584–13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velizarova, M.; Dimitrova, R.; Hristov, P.O.; Burov, A.; Brezov, D.; Hristova, E.; Gueorguiev, O. Evaluation of Emission Factors for Particulate Matter and NO2 from Road Transport in Sofia, Bulgaria. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Vranckx, S.; Van Laer, J.; Hofman, J.; Vandeninden, B.; Vanpoucke, C.; Lefebvre, W. Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ü.A.; Onat, B.; Akın, Ö.; Ayvaz, C.; Uzun, B.; Mangır, N.; Doğan, M.; Harrison, R.M. Temporal variations of atmospheric black carbon and its relation to other pollutants and meteorological factors at an urban traffic site in Istanbul. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, L.; Duan, Y.; Liang, L.; Li, Y. Identifying the O3 chemical regime inferred from the weekly pattern of atmospheric O3, CO, NOx, and PM10: Five-year observations at a center urban site in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.M.; Zheng, H.; Xing, J.; Wu, Y.; Hao, J. Four-month changes in air quality during and after the COVID-19 lockdown in six megacities in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Ghaffarpasand, O.; Pope, F.D. Assessing the Impact of Calendar Events upon Urban Vehicle Behaviour and Emissions Using Telematics Data. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 3071–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.-H.; Chou, C.; Liang, J.-Y.; Chou, C.C.-K.; Shiu, C.-J. Air pollution “holiday effect” resulting from the Chinese New Year. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, I. A national day with near zero emissions and its effect on primary and secondary pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Lai, Y. Effect of fireworks, Chinese new year and the COVID-19 lockdown on air pollution and public attitudes. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Brimblecombe, P. Changes in air pollutants from fireworks in chinese cities. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.P. Air Pollution Meteorology and Dispersion; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 310. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Noll, K.E. Evaluation of the Relationship between Momentum Wakes behind Moving Vehicles and Dispersion of Vehicle Emissions Using Near-Roadway Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10483–10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Brimblecombe, P.; Yu, Y.T.; Noll, K.E.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Hao, K. An Integrated Field Study of Turbulence and Dispersion Variations in Road Microenvironments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 20566–20576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, P.; Xiang, S.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Fu, Q. A Python toolkit for integrating geographic information system into regulatory dispersion models for refined pollution modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 183, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengdu Bureau of Statistics. Chengdu Statistical Yearbook; Chengdu Bureau of Statistics: Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB 3095-2012). 2012. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GB3095-2012 (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Y.T.; Li, Z.; Wallington, T.J.; Shen, W.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Q. Mobile Measurements of Carbonaceous Aerosol in Microenvironments to Discern Contributions from Traffic and Solid Fuel Burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.T.; Wallington, T.J.; Shen, W.; Kirchner, U.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, Z. Variability of NO2/NOx Ratios in Multiple Microenvironments from On-Road and Near-Roadway Measurements. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Y. Evaluating Ultrafine Particles and PM2.5 in Microenvironments with Health Perspectives: Variability in Concentrations and Pollutant Interrelationships. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 230046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, J.F.; Morawska, L.; Mengersen, K. Spatial variation in particle number size distributions in a large metropolitan area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Thomas, S.; Bofinger, N.; Wainwright, D.; Neale, D. Comprehensive characterization of aerosols in a subtropical urban atmosphere: Particle size distribution and correlation with gaseous pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2467–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prévôt, A.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Major Figures on 2020 Population Census of China. 2020. Available online: https://www.chinayearbooks.com/major-figures-on-2020-population-census-of-china.html (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Chengdu Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. Municipal Planning of Chengdu 2011–2020. Chengdu Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. 2021. Available online: https://mpnr.chengdu.gov.cn/ghhzrzyj/ztgh/2019-07/14/content_39be6057b8194c4d89afde1e26625a69.shtml (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Brimblecombe, P.; Townsend, T.; Lau, C.F.; Rakowska, A.; Chan, T.L.; Močnik, G.; Ning, Z. Through-tunnel estimates of vehicle fleet emission factors. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Characterization of Dispersion and Ultrafine-particle Emission Factors Based on Near-roadway Monitoring Part I: Light Duty Vehicles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Characterization of Dispersion and Ultrafine-particle Emission Factors Based on Near-roadway Monitoring Part II: Heavy Duty Vehicles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.F.; Rakowska, A.; Townsend, T.; Brimblecombe, P.; Chan, T.L.; Yam, Y.S.; Močnik, G.; Ning, Z. Evaluation of diesel fleet emissions and control policies from plume chasing measurements of on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wen, Y.; Wu, Y. Mitigation potential of black carbon emissions from on-road vehicles in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.P.; Perkins, J.; Zamore, W.; Levy, J.I.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. Spatial and temporal differences in traffic-related air pollution in three urban neighborhoods near an interstate highway. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.P.; Collins, C.; Naumova, E.N.; Zamore, W.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. An hourly regression model for ultrafine particles in a near-highway urban area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, D.L.; Goldberg, M.S.; Ross, N.A. A prediction-based approach to modelling temporal and spatial variability of traffic-related air pollution in Montreal, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5075–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, E.A.; Schaal, L.; Sasakura, M.; Crampton, R.; Gould, T.R.; Hartin, K.; Sheppard, L.; Larson, T.; Simpson, C.D.; Yost, M.G. Correlations between short-term mobile monitoring and long-term passive sampler measurements of traffic-related air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhai, W.; Wen, D.; Noll, K.E. Concentration of Ultrafine Particles near Roadways in an Urban Area in Chicago, Illinois. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ketzel, M.; Ellermann, T.; Wåhlin, P.; Jensen, S.; Fang, D.; Massling, A. Particle number, particle mass and NO x emission factors at a highway and an urban street in Copenhagen. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, N.; Wang, J.M.; Jeong, C.-H.; Healy, R.M.; Sofowote, U.; Debosz, J.; Su, Y.; Noble, M.; Munoz, A.; Doerksen, G. Traffic-related air pollution near roadways: Discerning local impacts from background. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5247–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Tian, M.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the Relationship between Meteorological Variables and NO x Emission Factors Based on Plume-Chasing Measurements. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, H.; Hagler, G.; Kimbrough, E.; Williams, R.; Mukerjee, S.; Neas, L. Mobile air monitoring data-processing strategies and effects on spatial air pollution trends. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2169–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wen, Y.; Xiang, S.; Yang, P.; Zheng, X.; You, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Cost-Effective Mapping of Hyperlocal Air Pollution Using Large-Scale Mobile Monitoring and Land-Use Machine Learning. ACS EST Air 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Hao, K.; Wu, Y. Significant NO2 Formation in Truck Exhaust Plumes and Its Association with Ambient O3: Evidence from Extensive Plume-Chasing Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


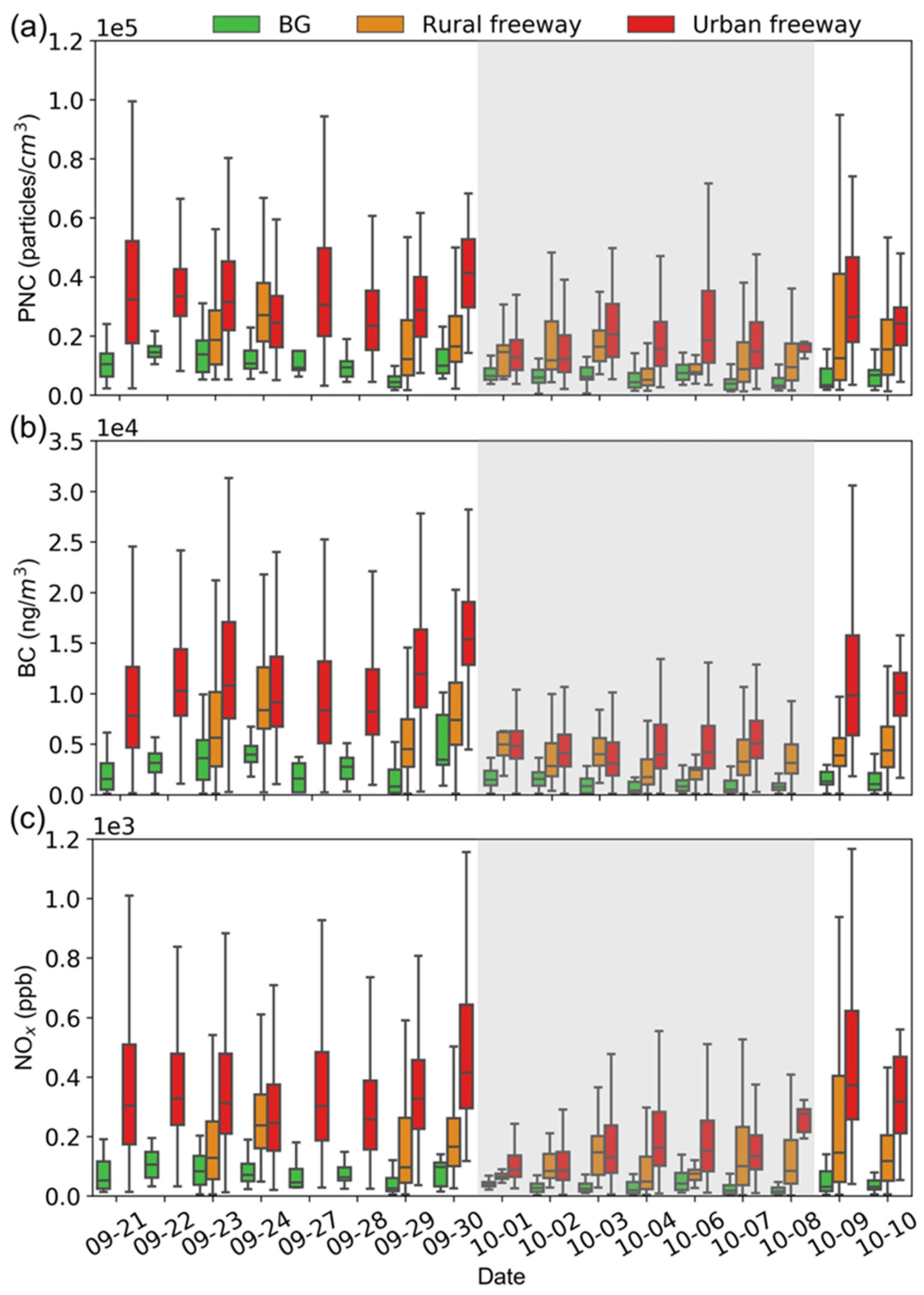
| Date(mm-dd) | Background | Urban Freeway | Rural Freeway | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNC * | BC # | NOx $ | PNC * | BC # | NOx $ | PNC * | BC # | NOx $ | ||
| Non-holiday | 9-21 | 10,517 | 1561 | 52.6 | 32,366 | 7808 | 303.7 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| 9-22 | 14,507 | 3152 | 104.9 | 33,507 | 10,256 | 328.6 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
| 9-23 | 13,863 | 3611 | 82.8 | 31,579 | 10,804 | 312.6 | 18,665 | 5627 | 127.6 | |
| 9-24 | 10,738 | 3969 | 71.2 | 24,467 | 9138.5 | 244.7 | 27,082 | 8348 | 237.8 | |
| 9-27 | 9353 | 1581 | 45.0 | 30,620 | 8330 | 302.5 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
| 9-28 | 9437 | 2778 | 62.2 | 23,531 | 8196 | 257.3 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
| 9-29 | 4405 | 820 | 24.7 | 28,861 | 11,929 | 326.3 | 12,199 | 4522 | 96.0 | |
| 9-30 | 10,022 | 3474 | 97.7 | 41,457 | 15,373 | 415.3 | 16,520 | 7407 | 164.9 | |
| 10-9 | 3440 | 1306 | 31.0 | 26,502 | 9847 | 372.3 | 12,525 | 3887 | 145.3 | |
| 10-10 | 6790 | 1066 | 30.1 | 24,300 | 10,059 | 316.7 | 15,492 | 4377 | 116.8 | |
| Holiday | 10-1 | 6552 | 1469 | 39.8 | 12,770 | 4826 | 87.6 | 14,611 | 4984 | 65.8 |
| 10-2 | 6020 | 1546 | 26.8 | 12,193 | 4104 | 85.8 | 11,841 | 2849 | 84.0 | |
| 10-3 | 6258 | 841 | 24.6 | 20,598 | 3063 | 129.4 | 16,391 | 3989 | 146.7 | |
| 10-4 | 4411 | 417 | 19.3 | 15,687 | 3975 | 162.3 | 5261 | 1742 | 47.4 | |
| 10-6 | 7524 | 813 | 40.8 | 18,615 | 4187 | 150.5 | 7780 | 2454 | 74.9 | |
| 10-7 | 3943 | 515 | 17.0 | 14,822 | 5091 | 133.0 | 8816 | 3274 | 99.7 | |
| 10-8 | 3272 | 791 | 14.9 | 17,182 | n.a. | 275.5 | 9543 | 3161 | 84.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, S.; Yu, J.; Yu, Y.T.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, T.; Yue, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171
Xiang S, Yu J, Yu YT, Zhao P, Zheng T, Yue J, Yang Y, Liu H. Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Sheng, Jiaojiao Yu, Yu Ting Yu, Pengbo Zhao, Tie Zheng, Jingsong Yue, Yuanyuan Yang, and Haobing Liu. 2025. "Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171
APA StyleXiang, S., Yu, J., Yu, Y. T., Zhao, P., Zheng, T., Yue, J., Yang, Y., & Liu, H. (2025). Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China. Atmosphere, 16(2), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171








