Abstract
During industrial production, a significant amount of oil mist is generated, posing health risks because it is a fine particulate matter that is easily inhaled by the human body. Electrostatic collection has been widely applied in machining workshops as an effective method for capturing oil mist. While existing research has made substantial progress in improving the collection efficiency of electrostatic methods, the challenge of achieving high-efficiency oil mist collection remains unresolved. The inherent physical properties of oil mist contribute to difficulties in its efficient collection. Additionally, the deposition characteristics of oil mist, as well as the structure and operational parameters of the electrostatic precipitator (ESP), directly affect collection efficiency. This paper reviews the literature from the past decade, introduces the mechanisms of oil mist generation, and presents oil mist monitoring technologies. Based on the deposition characteristics of oil mist, it explores high-efficiency collection technologies using electrostatic methods and summarizes studies on optimizing the performance of electrostatic precipitators. Finally, the paper provides an outlook on the development prospects of oil mist purification technologies.
1. Introduction
In machining workshops, the extensive use of metalworking fluids (MWF) during processes such as cutting, grinding, and rolling generates a substantial amount of oil mist particles through impact, atomization, and evaporation/condensation [1,2]. These inhalable oil mist particles, similar to particulate matter like PM2.5 in the atmosphere, can penetrate deep into the lungs and pose significant risks to human health. They not only significantly increase the incidence of respiratory diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis, allergic skin diseases, and even cancer [3,4,5], but also, like other harmful particulate matter in the air, can accumulate over time and cause severe damage to the human respiratory and cardiovascular systems, leading to a variety of serious diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to reduce the oil mist concentration in industrial buildings to safe levels to ensure the health of workers and the safety of production operations [6].
In recent years, various countries have established occupational exposure limits for indoor oil mist to protect indoor environments in industrial buildings and safeguard workers’ health. Significant differences exist in the exposure limits proposed by different organizations for various types of oil mist. Lower exposure limits benefit workers’ health but substantially increase the operational costs of industrial buildings. Currently, the occupational exposure limits for MWF set by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) are widely applied in the machining industry. However, many facilities still exceed the NIOSH limits [7,8,9]. Therefore, reducing oil mist concentrations below permissible limits has become critical. Oil mist purification technology is the most direct approach to ensuring that oil mist concentrations remain within allowable levels.
Currently, various effective control technologies have been developed for the collection of oil mist and particulate matter, such as filtration and separation techniques [10,11]. Among these, the electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is widely used due to its high collection efficiency, low energy consumption, minimal maintenance costs, and negligible pressure loss [12]. ESP purifies air by generating ions through corona discharge or other discharge methods to charge particles, which are then separated from the airflow under the influence of an electric field. Based on electrode arrangement, ESPs can be classified into single-stage and two-stage types [13]. Single-stage precipitators perform particle charging and collection within the same region, while two-stage precipitators divide these processes into two zones: the first zone focuses on particle charging, and the second zone is primarily responsible for capturing the charged particles. Compared to single-stage precipitators, two-stage precipitators achieve higher collection efficiency. As a result, two-stage precipitators are commonly employed in modern industrial oil mist purification [14].
In the field of numerical simulation for two-stage electrostatic purification, numerous studies have focused on improving purification efficiency. Gao et al. [15] used numerical simulation to investigate physical processes in two-stage ESPs, such as flow field distribution, particle charging, and motion, which are difficult to measure directly. Wang et al. [16] explored the impact of humidity on ESPs, including its effects on electric field and charge density distribution, through experiments and numerical simulations. Zhang et al. [17] applied CFD simulation techniques to model and optimize the entire dust collection process of wire-plate electrostatic precipitators, finding that dust collection efficiency was relatively lower under conditions of high voltage, low inlet velocity, and large particle sizes. H. Ait-Said et al. [18] conducted simulations and experimental studies on the positive and negative corona discharge behavior of wire-plate electrostatic precipitators, calculating current-voltage characteristics and charge carrier mobility using the Cooperman model. Li et al. [19] performed multi-physics coupling and experimental validation for electrostatic oil mist purification, optimizing the design of oil mist injectors; results showed that increasing the electrode plate voltage enhanced oil droplet removal efficiency. Hua et al. [13] developed electrostatic purification equipment suitable for high-concentration oil mist exhaust, using a corona section composed of serrated blades and ionizing wires, along with a small-spacing collection section, to improve purification efficiency and enhance adaptability to high-concentration oil mist. Yang et al. [20] studied the effects of corona electrode diameter, number, and wire-plate distance, analyzing the influence of key geometric parameters on purification performance based on experimental results.
Furthermore, oil mist generated by different processes exhibits significant differences in particle size distribution, concentration, and type [8,9,21]. Achieving effective purification of oil mist in industrial buildings requires a clear understanding of the characteristics of oil mist particles from the pollution source. Understanding the particle characteristics of oil mist from various processes and analyzing the factors contributing to their generation is critical for determining suitable purification methods for different scenarios. Therefore, to comprehensively analyze the collection efficiency of electrostatic precipitators, it is essential to consider the interrelation and interactions among corona discharge, internal flow field distribution, particle charging, transport processes, and the inherent properties of the particles.
Although some technologies and expertise currently exist for oil mist purification, the inherent physical properties of oil mist still pose challenges for further optimization of high-efficiency collection technologies based on electrostatic methods [22]. Therefore, this paper reviews the research progress in oil mist purification technologies over the past decade. Based on the generation mechanisms and characteristics of oil mist, the deposition properties of oil mist particles during the electrostatic precipitation process are discussed. Additionally, existing studies on optimizing the performance of the ESP are summarized. Finally, the limitations of current oil mist purification technologies are analyzed, and future development directions are proposed.
2. Oli Mist Generation Mechanism
The characteristics and generation mechanisms of oil mist particles are closely related to the selection of control technologies and purification effectiveness. These characteristics depend on the production process, with different processes resulting in variations in particle size, shape, distribution, and chemical composition [8,9,21]. To achieve efficient control of oil mist in industrial buildings, it is essential to clarify its generation mechanisms, understand the characteristics and influencing factors of oil mist particles under different processes, and develop appropriate control methods.
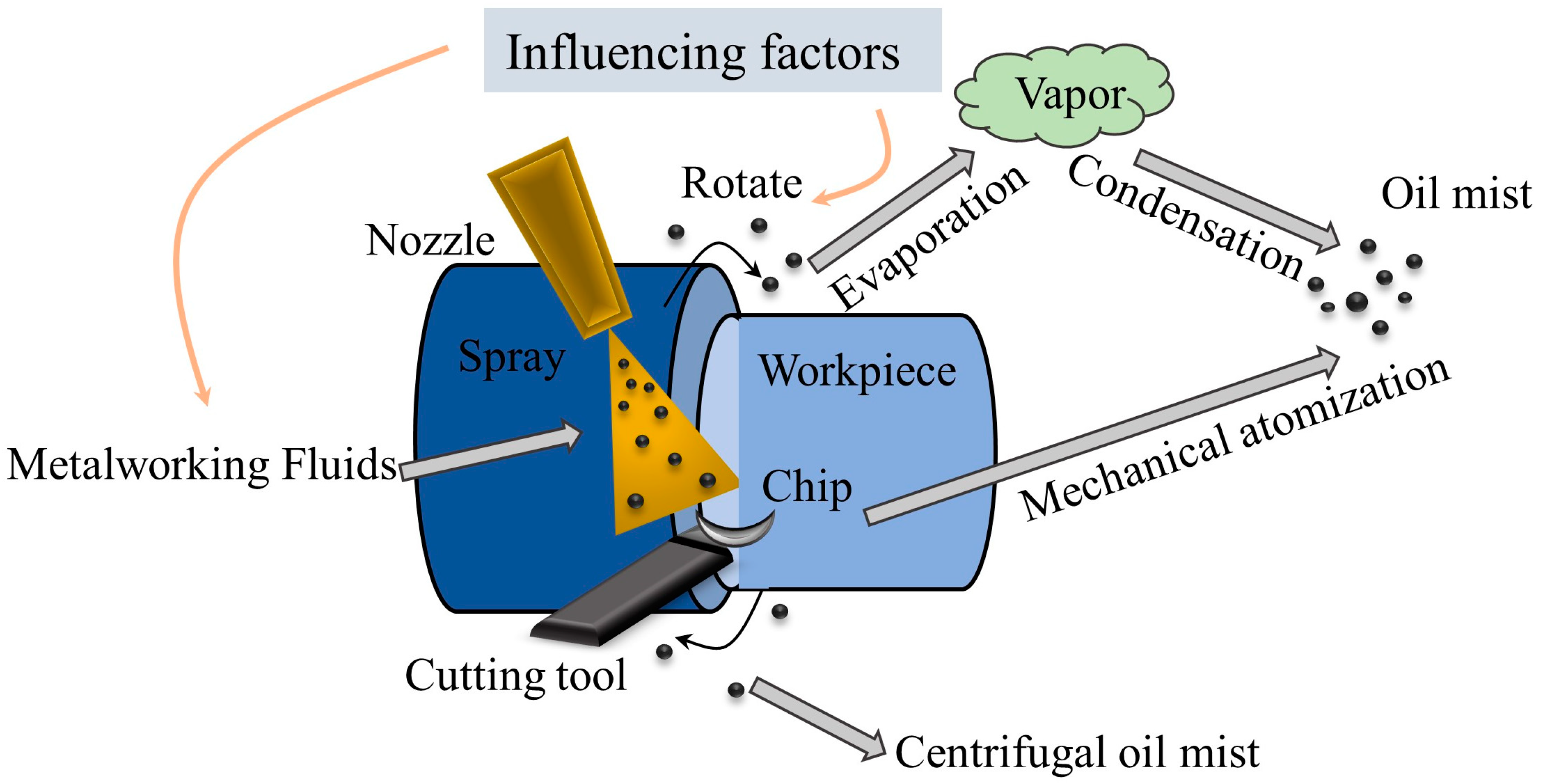
Industrial buildings often produce significant amounts of particulate matter, with pollution exceeding permissible limits being common due to varying processes across factories. In machining workshops, the particles are predominantly fine and harmful, with oil mist generation primarily attributed to evaporation/condensation, collision splashing, and centrifugal force [2,23], as shown in Figure 1. During machining processes, the oil undergoes partial evaporation due to exposure to heat sources such as frictional heat. This process causes oil molecules to transition into a gaseous state, forming oil vapor. As the oil vapor cools in the air, the initial stage of oil mist formation begins.
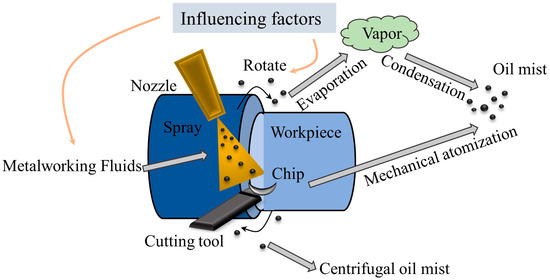
Figure 1.
The generation process of machining oil mist.
MWF are commonly used during machining to cool, clean, lubricate, and protect tools and workpieces [24]. These fluids come in a variety of types, primarily categorized into oil-based and water-based fluids. Water-based cutting fluids include emulsifiable cutting fluids, synthetic cutting fluids, and semi-synthetic cutting fluids, which require dilution with water during use, typically in a ratio ranging from 1% to 20%, with the most common ratio being 5% [25]. The relative high-speed motion between the tool and the workpiece generates frictional heat [26], causing the MWF to produce oil mist particles through collision, centrifugal force, and evaporation/condensation mechanisms. The higher the tool surface temperature, the higher the percentage of fine oil mist particles and the concentration of oil mist. Collision and centrifugal force result in mechanical atomization, breaking the cutting fluid into droplet-sized particles. These droplets form particulate matter through condensation, adsorption, and other processes. Suspended particles are predominantly formed through evaporation and condensation [27], wherein oil vapor condenses on the fine solid particles generated during machining, encapsulating them in oil-coated particulates [3].
When droplets in the oil mist remain suspended in the air, processes such as condensation and adsorption may occur, leading to the formation of particulate matter. The growth of these particles may be achieved through collision aggregation and the adsorption of other pollutants. The particles suspended in the air are primarily formed through evaporation and condensation. The condensation process involves the condensation of oil vapor onto solid particles, resulting in the formation of oil-coated particulate matter [28]. This process involves the volatilization of liquid substances at high temperatures, turning them into vapor that is released into the air. Meanwhile, small solid particles are also released into the air during the machining process. As the vapor cools, it condenses onto these fine solid particles, which act as condensation nuclei.
From the atomization process, it can be seen that the flow rate of the MWF adhered to the tool surface is directly related to the emission rate of oil mist particles during machining. Theoretically, the maximum atomization flow rate is given by Equation (1) [1]:
where represents the atomization flow density, m3/s; is the tool’s rotational speed, rad/s; is the tool’s radius, m; is the width of the liquid film layer, m. consists of two parts, and , where ’s maximum value is the distance from the point of metalworking fluid entry to the tool’s bottom. According to the law of energy conservation, can be calculated using Equation (2).
where is the incident velocity of the metalworking fluid, in m/s; is the gravitational acceleration, 9.8 m/s2; is the angle between the incident angle of the metalworking fluid and the horizontal direction.
The formation of oil mist particles in machining processes exhibits a certain degree of randomness and is often described using probability density functions or empirical formulas [29]. The Rosin–Rammler distribution function, due to its few mathematical parameters and clear physical significance, has been widely applied in the study of particle size distribution in industries such as environmental protection and chemical engineering [30]. The expression of the Rosin–Rammler distribution function is as follows:
where represents the particle diameter in micrometers, μm; is the probability distribution of particles with a diameter smaller than D; is the characteristic particle diameter in micrometers, μm; is the distribution coefficient, a parameter that characterizes the range of particle size distribution.
To address the oil mist pollution in industrial buildings, scholars have studied oil mist particles generated by different factories [9,31] and equipment [32]. However, there is a lack of systematic analysis of the factors affecting particle formation. Traditional liquid cooling methods utilize water pumps to spray cutting fluid, while the recently developed minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) method uses compressed air to inject and atomize the lubricant, which is then sprayed onto the workpiece and tool for cooling and lubrication. In the MQL mode, oil mist primarily originates from high-pressure atomization and the evaporation/condensation mechanism, and the lubrication system and process parameters influence its particle characteristics.
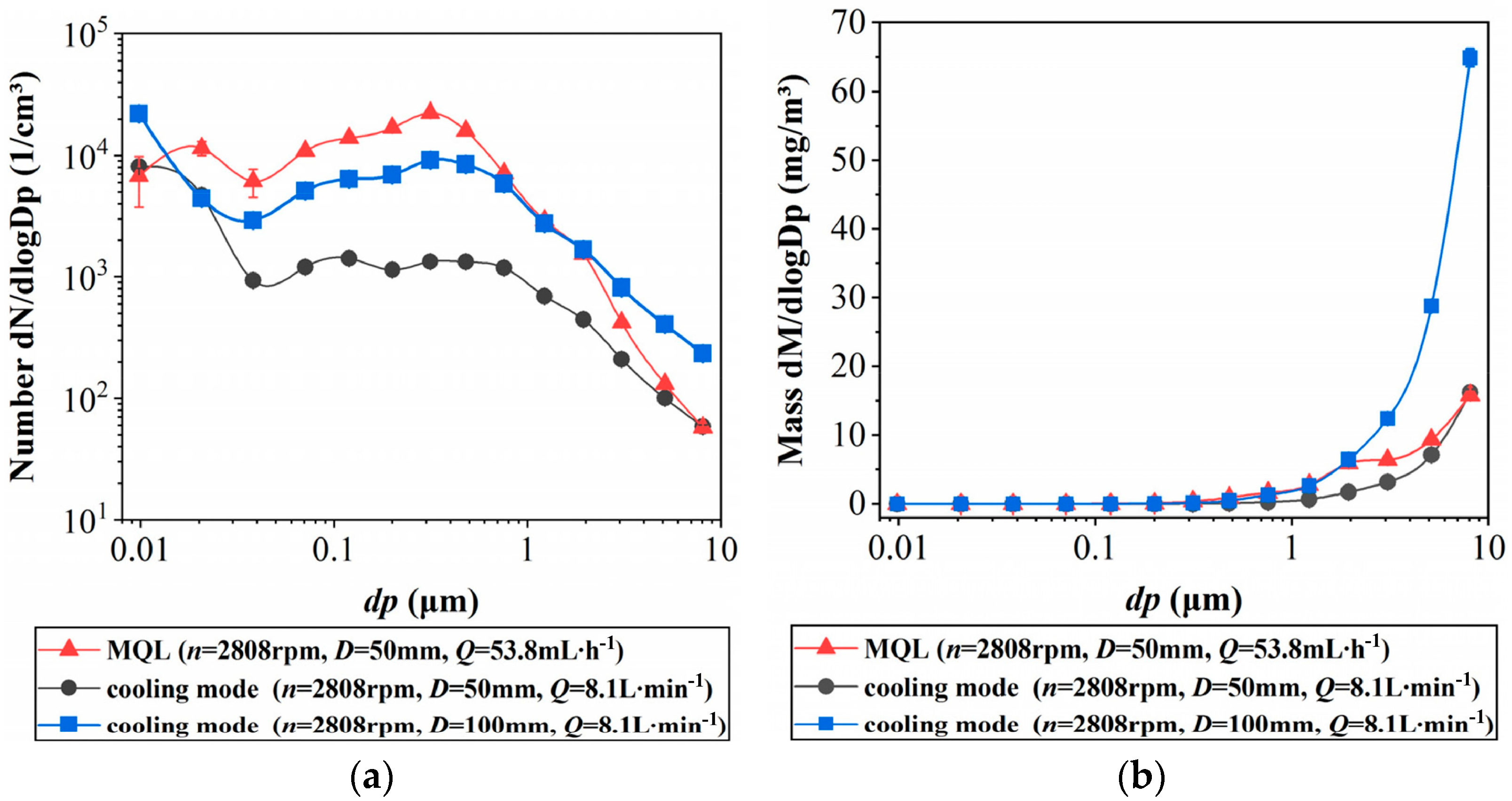
In the lubrication system, the flow rate of the MWF is the main factor influencing oil mist concentration and particle size distribution during high-pressure atomization [26,33,34]. Figure 2 compares the oil mist generated under minimal lubrication and spray cooling modes at the same rotational speed. The oil mist concentration generated under minimal lubrication cooling is on the same order of magnitude as that generated under spray cooling. Still, the particle size of the oil mist produced in the minimal lubrication mode is smaller. In the spray cooling mode, the oil mist mainly consists of thoracic deposition particles (<10 μm), while in the minimal lubrication mode, the oil mist primarily consists of respirable particles (<4 μm). This implies that, compared to the spray cooling mode, the minimal lubrication cooling mode generates more oil mist particles. Therefore, minimal lubrication cooling primarily reduces the consumption of cutting fluid but is more detrimental to air quality.
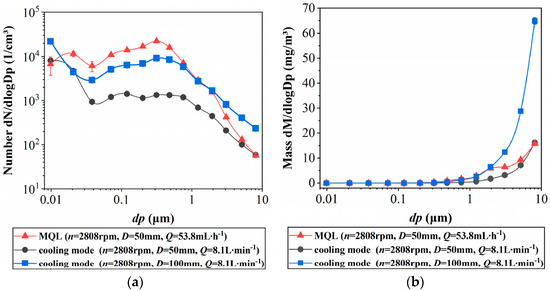
Figure 2.
Oil mist without the generation of evaporation/condensation aerosol in minimum quantity lubrication mode and flood cooling mode: (a) minimum quantity lubrication by number, (b) comparison of size distribution by mass [26].
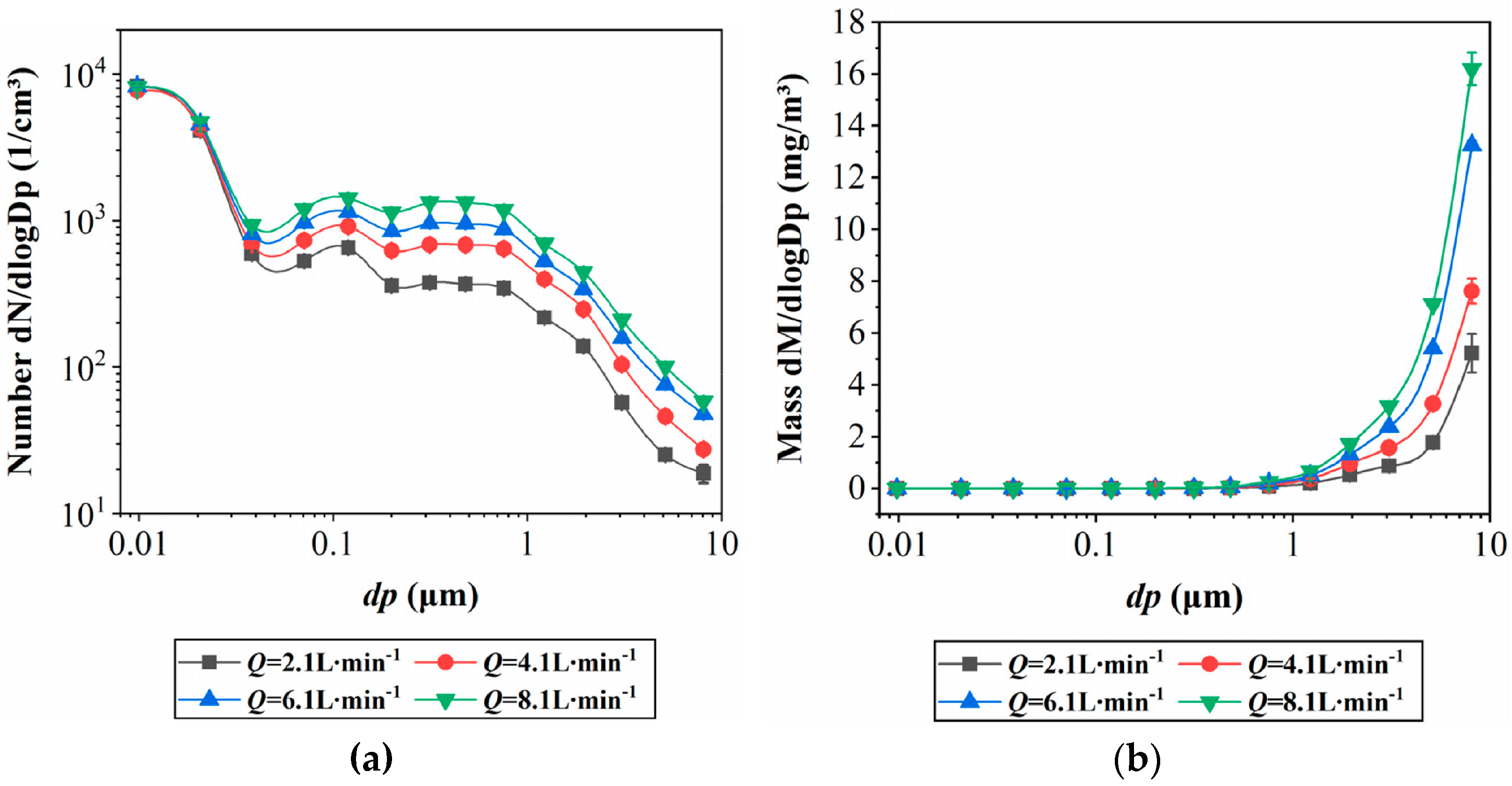
Figure 3 illustrates the impact on centrifugal aerosols when the flow rate of the metal cutting fluid is increased for a workpiece with a diameter of 5 cm. As the flow rate of the cutting fluid rises from 2.1 L/min to 8.1 L/min, the oil mist concentration steadily increases from 1.65 mg/m3 to 5.6 mg/m3. However, no changes are observed in the mass median diameter (MMD) and the Sauter mean diameter (SMD) of the particulate matter. Figure 3a visually demonstrates that the particle size distribution of the centrifugal aerosols remains nearly consistent across different flow rates, particularly within the range between 0.006 μm and 0.017 μm, where the particle count remains unchanged. The increase in oil mist mass concentration is primarily attributed to the elevation in the number of particles larger than 1 μm, as shown in Figure 3b. The cooling liquid flow rate is the most important parameter affecting the amount of oil mist dispersed, and the amount of oil mist dispersed is directly proportional to the flow rate of the cooling liquid.
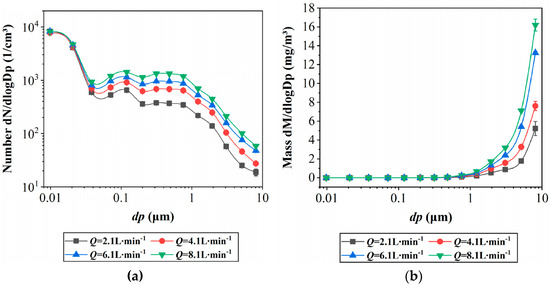
Figure 3.
Effect of cutting oil flow rate in MQL mode: (a) effect on particle size distribution by number, (b) effect on size distribution by mass [26].
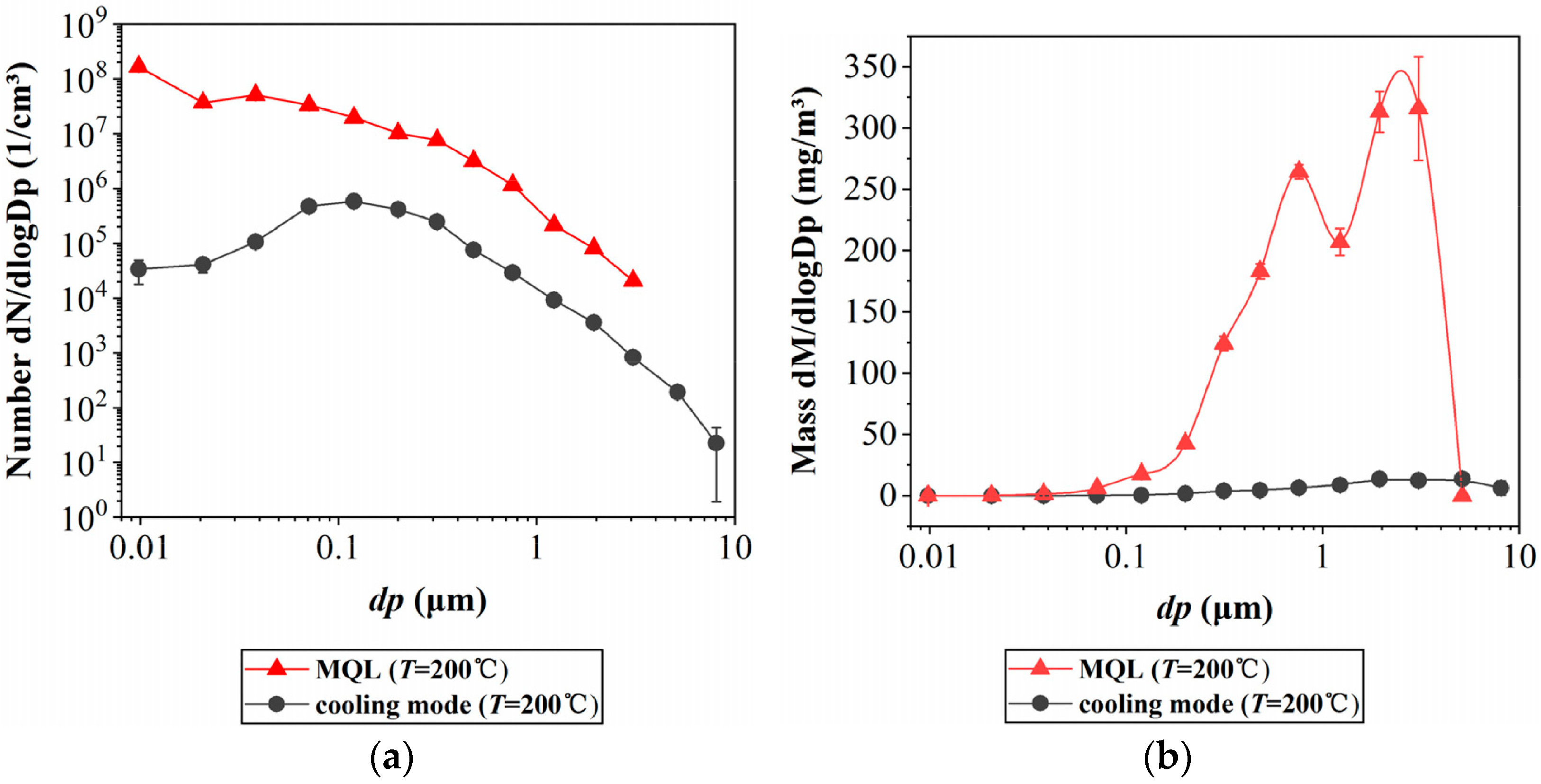
As for evaporation/condensation aerosol, both the number concentration and the mass concentration in the MQL mode were much higher than in the flood cooling mode, and this difference can be clearly seen in Figure 4. The oil mist particles generated under the cooling mode primarily consist of aerosols deposited in the thoracic region, with respirable particulate matter (RPM) accounting for 10% to 70% of the total oil mist mass. In contrast, RPM constitutes the primary component of the oil mist produced in MQL, comprising 40% to 100% of the total oil mist mass. Furthermore, the number concentration of submicron particles in the MQL mode exceeds 108 particles/cm3, which is significantly higher than that observed in the cooling mode.
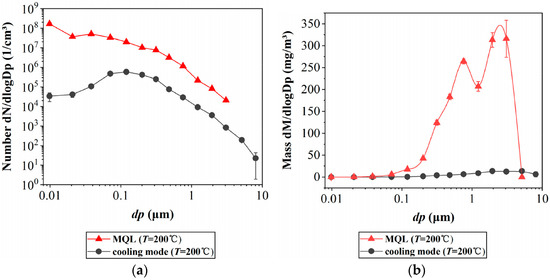
Figure 4.
Comparison of evaporating/condensing aerosols under MQL and cooling mode: (a) Comparison of particle size distribution by number, and (b) Comparison of size distribution by mass [26].
In terms of process parameters, tool rotational speed affects the tool surface temperature, which in turn makes the evaporation/condensation mechanism a key factor influencing particle characteristics [26,35]. The higher the tool surface temperature, the higher the percentage and concentration of small oil mist particles. Under cooling methods, oil mist is primarily influenced by centrifugal force, and its particle characteristics are related to the lubrication system, process parameters, and type of cutting fluid. When the MWF flow rate [3,26] or tool rotational speed increases, the oil mist concentration increases, but the particle size distribution remains relatively unchanged.
3. Oil Mist Occupational Exposure Limits
Long-term exposure to oil mist environments makes workers susceptible to respiratory diseases such as asthma and bronchitis, as well as occupational diseases like allergic dermatitis and malignant tumors [36,37]. During machining processes, oil mist particles can remain suspended in the air and, upon deposition in the lungs, enter the bloodstream, affecting the entire body [38,39]. The hazards of inhalation exposure are often difficult to detect, and protecting workers’ health is urgent. Furthermore, the concentration of oil mist that poses a risk to personnel safety needs to be clearly defined, underscoring the necessity for in-depth research on oil mist hazards and the establishment of relevant standards.
Various countries have established exposure limit standards for oil mist. For instance, Germany has set the limit for liquid oil mist aerosols and vapors at 10 mg/m3, while Japan, Finland, and other nations have set it at 3 mg/m3. France recommends a limit not exceeding 1 mg/m3. In 1993, the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) considered that pure oil mist concentrations below 5 mg/m3 are relatively safe, but oil mist from metalworking fluids containing carcinogenic substances may pose a risk at concentrations exceeding 0.2 mg/m3.
Internationally, exposure limit regulations for oil mist in industrial workshops are documented in Table 1, encompassing the historical changes in occupational exposure limits (OELs) for aerosols, particularly those related to mineral oil mist. The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) has repeatedly adjusted the occupational exposure limits for oil mist. In 1994, a new classification system was introduced, dividing oil mist into two categories: “poorly refined” and “highly refined.” In 2001, the concept of time-weighted average (TWA) was proposed, with varying carcinogenicity levels and limits based on the degree of mineral oil refinement. In 2019, the exposure limit for inhalable particulate mineral oil mist was reduced from 0.2 mg/m3 to a TLV-TWA of 0.1 mg/m3.
Before 1998, NIOSH recommended an oil mist exposure limit of 10 mg/m3. In 1998, the exposure limit for MWF aerosols was revised to 0.4 mg/m3 (thoracic particles with a diameter smaller than 10 μm) or 0.5 mg/m3 (total particulate matter, based on specific time-weighted average concentrations). In the same year, the Occupational Safety and Health Standards Board (OSHA) set the 8 h time-weighted average permissible exposure limit for oil mist particles to 0.5 mg/m3 (total particulate matter) [40]. In 1993, NIOSH investigated the carcinogenicity of MWF and proposed a total exposure limit of 0.5 mg/m3 and a thoracic particulate mass limit of 0.4 mg/m3. The UK Health and Safety Executive in 2002 recommended guideline values of 3 mg/m3 and 1 mg/m3 for oil-based and water-soluble fine particles, respectively (based on inhalable aerosol measurements).
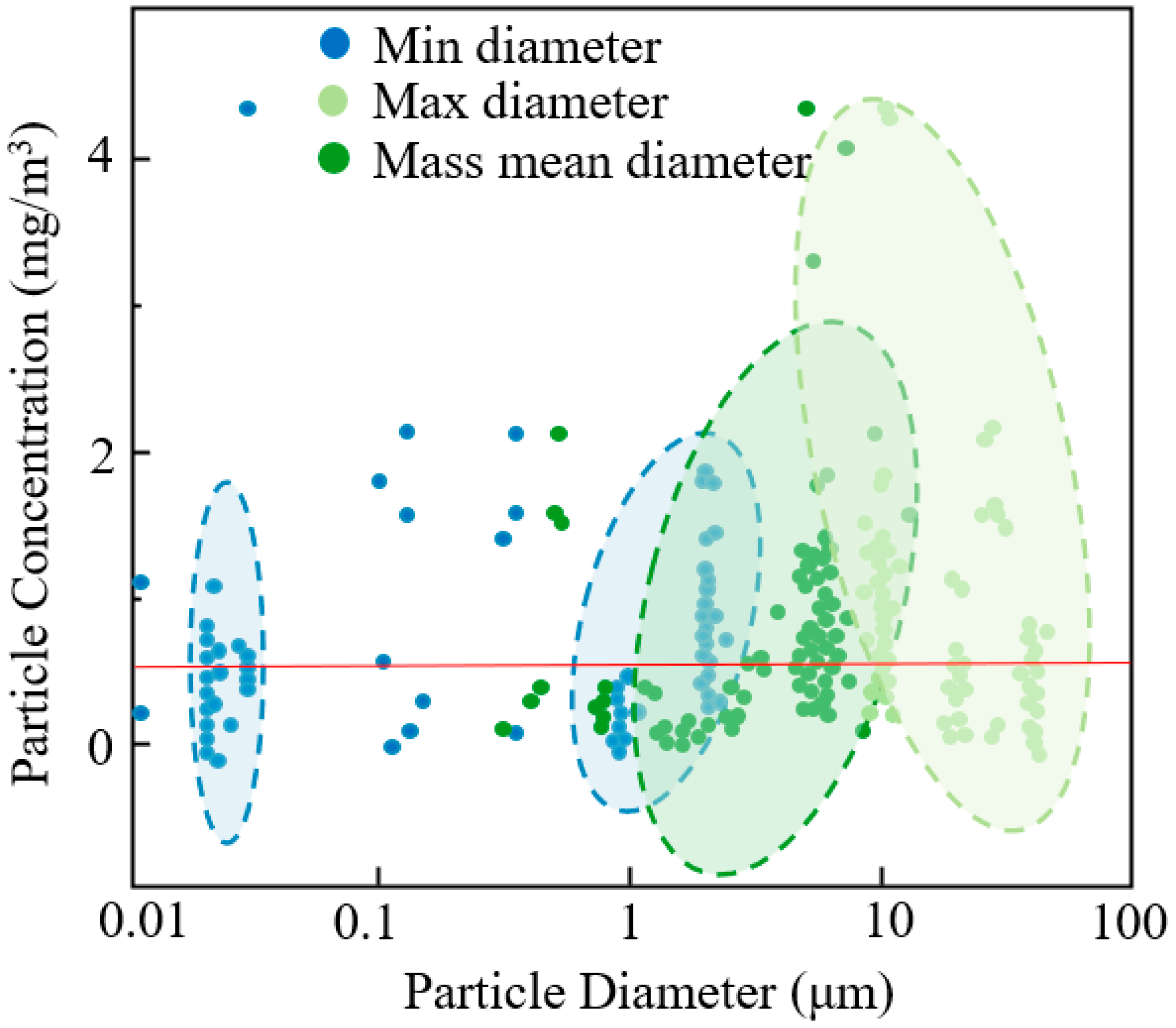
China’s latest indoor air quality standards require reducing indoor PM10 concentrations in residential and office buildings to 0.1 mg/m3. However, the actual oil mist concentrations in machining workshops often exceed relevant standards. In 2003, sampling revealed that over 60% of workshops exceeded 0.5 mg/m3, and a 2020 study found that during working hours, oil mist concentrations in machining workshops generally surpassed NIOSH’s 0.5 mg/m3 limit. Figure 5 summarizes the concentrations and particle sizes of oil mist in different factories [41]. Numerous studies indicate that oil mist concentrations in most factories far exceed NIOSH standards, with some reaching two to eight times the permissible limit. This underscores the importance of controlling and monitoring occupational exposure limits for oil mist, implementing protective measures, and researching the emission characteristics of oil mist. Such efforts are critical for safeguarding worker health and promoting sustainable industrial development.
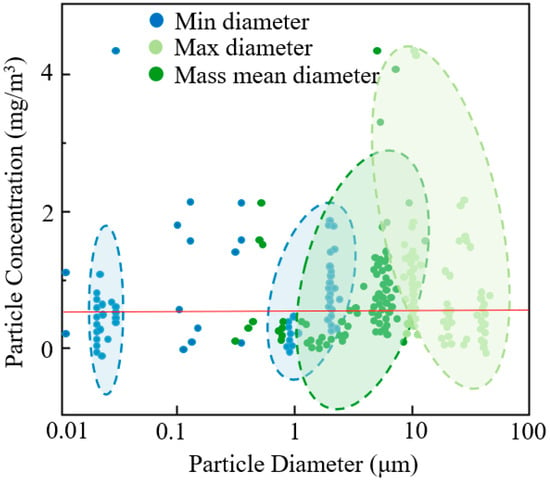
Figure 5.
Particle concentration and particle diameter in different factories.

Table 1.
Development of occupational exposure limits for oil mist.
Table 1.
Development of occupational exposure limits for oil mist.
| Organization | Years | Nation | Exposure Limit | Liquid Type | Particle Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACGIH [42] | 1964–2008 | USA | TWA 5 mg/m3 STEL 10 mg/m3 | Oil mist | All ranges |
| 2008–2009 | TWA 5 mg/m3, STEL 10 mg/m3 | Oil mist Withdrawal adopted | All ranges | ||
| 2001–2005 | TWA 0.2 mg/m3 (NIC) | Mineral oil | Inhalable | ||
| 2006–2008 | TWA 0.2 mg/m3 (NIC) | Mineral oils for metalworking | Inhalable | ||
| 2009–2010 | TWA 5 mg/m3 (NIC) | Refined mineral oil | Inhalable | ||
| 2010–2011 | TWA 5 mg/m3 | Mineral oils, excluding MWF | Inhalable | ||
| 2001–2008 | A2 (NIC) | Mineral oil used in metalworking–poorly and mildly refined mineral oil | NA | ||
| 2009 | A2 (NIC) | Mineral oil–poorly and mildly refined mineral oil | NA | ||
| 2010–2011 | A2 | Mineral oil, excluding MWF–poorly and mildly refined mineral oil | NA | ||
| OSHA [43] | 1964–2007 | USA | TWA 5 mg/m3 STEL 10 mg/m3 | Mineral oil | All ranges |
| 1998 | REL 0.5 mg/m3 | All types | All ranges | ||
| NIOSH [44] | <1998 | USA | TWA 5 mg/m3 STEL 10 mg/m3 | NI | All ranges |
| 1998 | REL 0.5 mg/m3 | All types | All ranges | ||
| REL 0. 4 mg/m3 | All types | Thoracic | |||
| Japan Occupational Health Association (JOSH) [45] | 1996 | Japan/Finland/Sweden | TLV-TWA 0.3 mg/m3 | Cutting fluid mist | All ranges |
| UK Health and Safety Executive(HSE) [46] | 1990–2007 | U.K. | TWA 5 mg/m3 STEL 10 mg/m3 | Oil mist | All ranges |
| 2002 | ACTS guidance values TWA 3 mg/m TWA 1 mg/m3 | Oil-based (neat oil) Water-soluble | Inhalable Inhalable |
Note: TWA: time-weighted average; STEL: short-term exposure limit; REL: recommended exposure limits; SAC: Standards Advisory Committee; ACTS: Toxic Substances Advisory Committee; NIC: notification of intended changes; NI: no information; NA: not applicable.
In 1997, the NIOSH set an 8 h time-weighted average exposure limit of 0.4 mg/m3 for chest-area oil mist exposure [47]. Subsequent research conducted by Kennedy et al. [48] revealed a key finding, the presence of statistically significant cross-shift reductions in Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second (FEV1) among workers exposed to oil mists characterized by an aerodynamic diameter of less than 9.8 μm, at exposure concentrations exceeding 0.20 mg/m3. This observation further emphasizes the importance of accurately measuring the particle size distribution of oil mist, which is critical for assessing the potential risk of oil mist exposure to different respiratory zones.
Numerous evaluations have been conducted on oil mist exposure among workers across various industries, encompassing multiple occupational groups, such as steelworkers [49], cable manufacturers [50], automobile manufacturing workers [51], ship engine maintenance workers [52,53], tunnel construction workers [54], and fastener manufacturing workers [55] (as detailed in Table 2). Among these industries, oil mist exposure levels were particularly prominent among automobile manufacturing workers, reaching the highest value of 2.6 mg/m3. These studies not only enrich our understanding of the occupational health risks of oil mist exposure, but they also emphasize the urgency of developing effective exposure control measures to protect workers’ respiratory health.

Table 2.
The average oil mist exposure levels for workers in different industries.
4. Oil Mist Monitor Technology
The high oil mist concentrations generated by MWF in industrial workshops pose a significant threat to worker health. Monitoring the spatial and temporal distribution of particulate matter concentrations plays a crucial role in the effective collection of these particles. Low-cost sensors have seen widespread application due to the traditional monitoring instruments’ bulkiness, high cost, and maintenance challenges. Some calibrated particulate matter (PM) sensors exhibit good linearity after regression, even in harsh environments [56]. However, variations in humidity, temperature, and airflow can cause these sensors to drift or become distorted.
Some researchers have simplified the impact of humidity using the k-Kohler theory and applied particle size distribution correction algorithms to account for the effects of relative humidity [57,58]. Experiments by Wang et al. demonstrated that, at the same mass concentration, the output of low-cost optical scattering particulate matter sensors first increased and then decreased as relative humidity rose from 20% to 90%. Although temperature affects particle characteristics, its influence on sensor output is significantly less compared to humidity [59]. However, researchers often overlook the effects of temperature and airflow, as these factors, especially the latter, have minimal impact on sensor output.
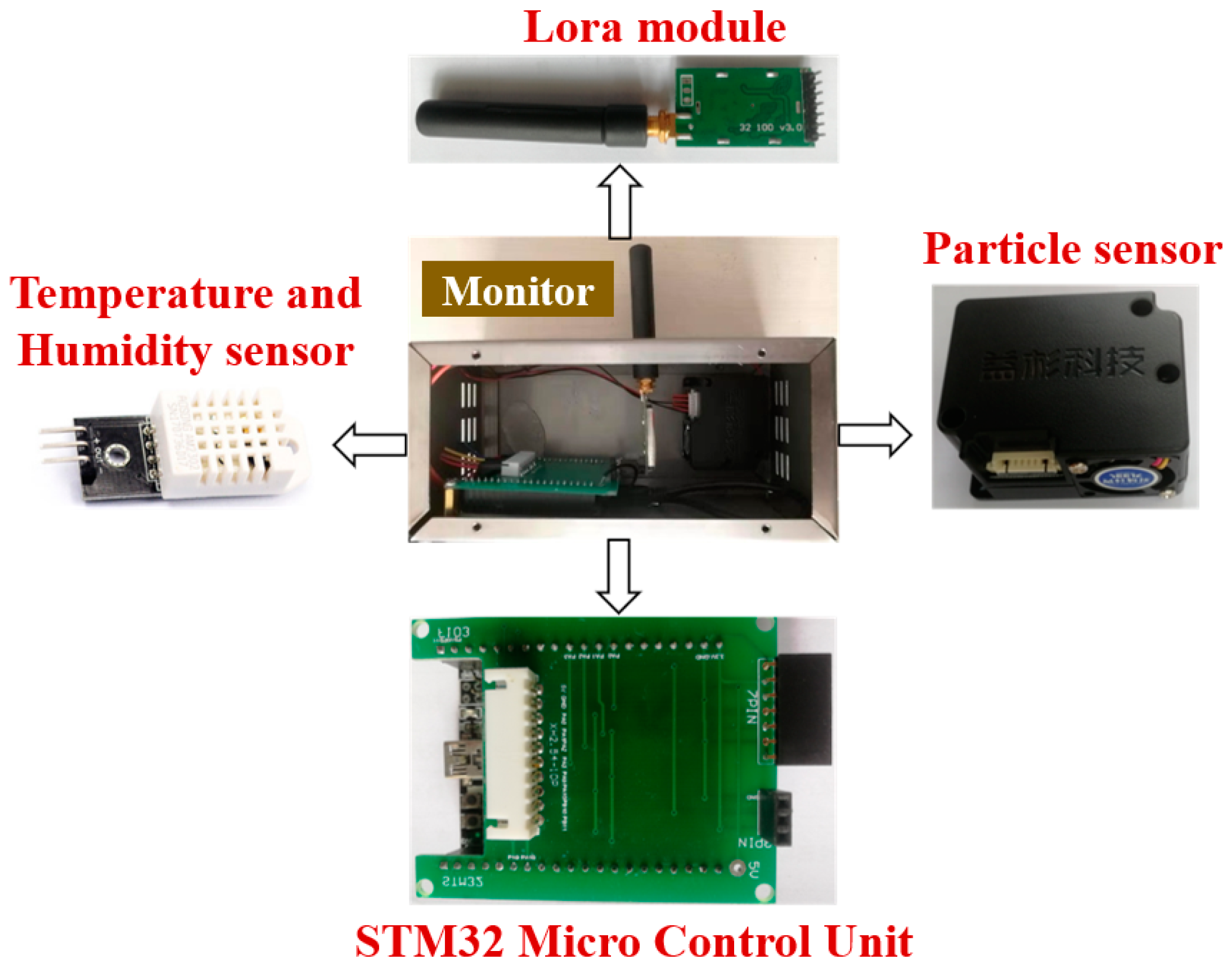
Integrating air quality data with airflow fields can better predict and track the propagation and diffusion of pollutants [60,61]. Sensors require on-site calibration to ensure monitoring accuracy [62], and placing monitors at a height of 2.5 m may lead to underestimations of pollutant concentrations [63]. Zhang [64] developed a real-time oil mist concentration monitoring system using a distributed network of low-cost sensors based on LoRa technology. Each monitor includes a temperature and humidity sensor, particulate matter sensor, LoRa wireless module, and a microcontroller (STM32F103C8T6), as shown in Figure 6. The microcontroller collects data from the sensors, which is transmitted from the sub-nodes to the main node via the LoRa module. After receiving the data, the LoRa module of the main node forwards it to the Sina Cloud platform for recording through a wireless transmission device.
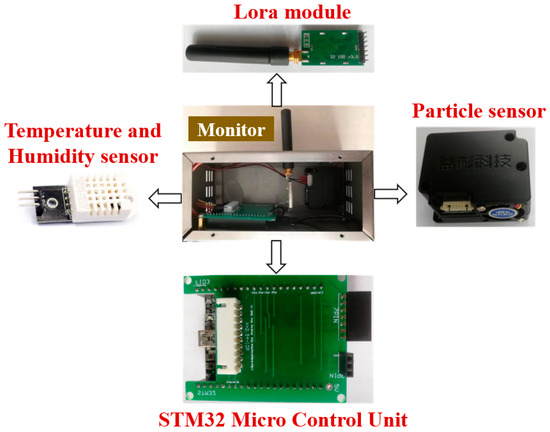
Figure 6.
Monitor structure diagram [64].
The IoT system built using LoRa technology enables flexible communication between nodes and significantly reduces investment costs. Furthermore, by analyzing the spatiotemporal distribution of oil mist concentrations based on workshop equipment layouts, it was found that oil mist concentration positively correlates with temperature and humidity. Particulate matter tends to absorb moisture in high-humidity environments, causing low-cost sensors to overestimate oil mist concentrations. Meanwhile, high temperatures accelerate oil mist generation, thereby increasing the actual oil mist concentration in workshops. These research findings provide critical theoretical support for controlling oil mist concentrations in workshops and confirm the feasibility and effectiveness of low-cost sensors for long-term oil mist monitoring.
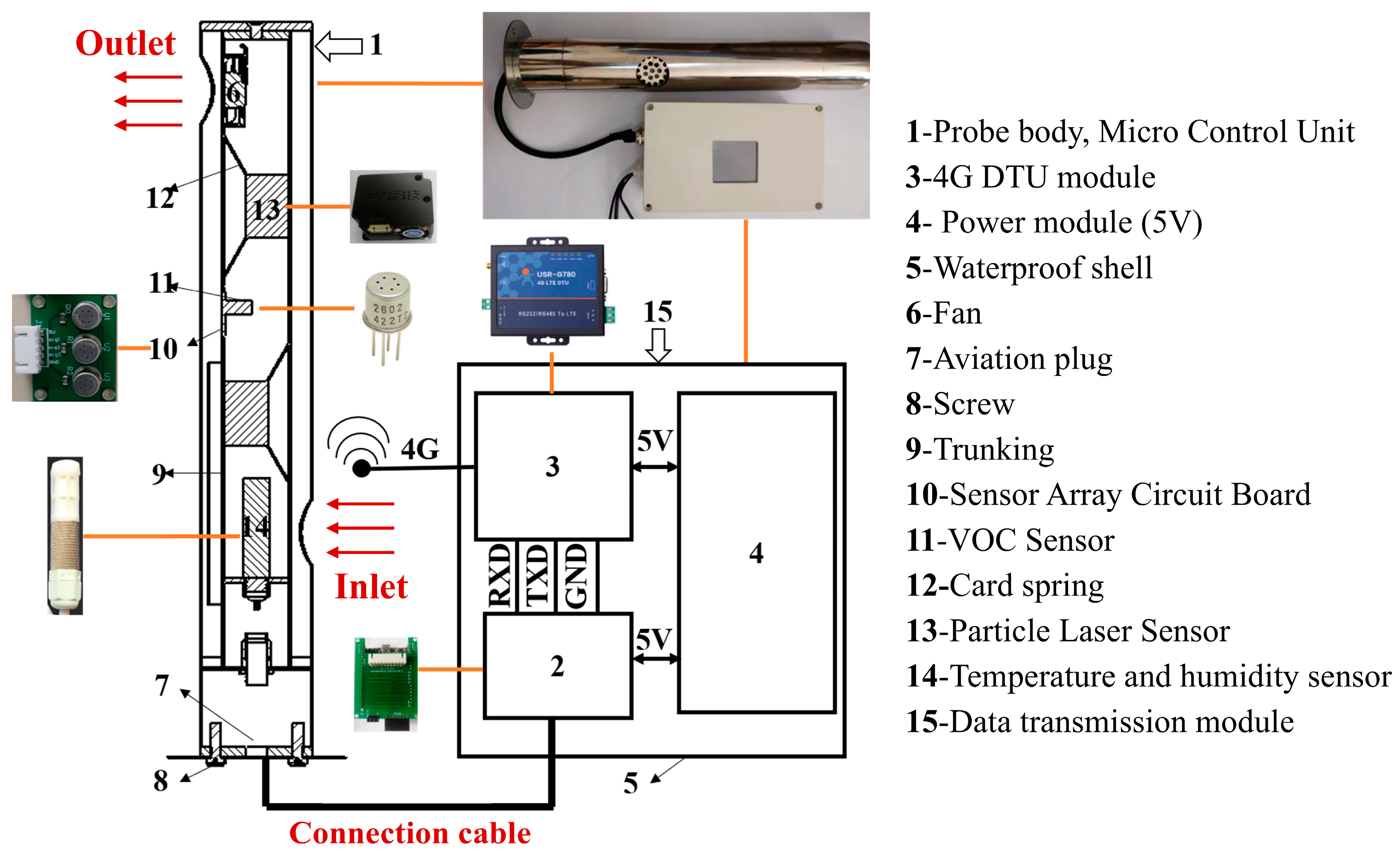
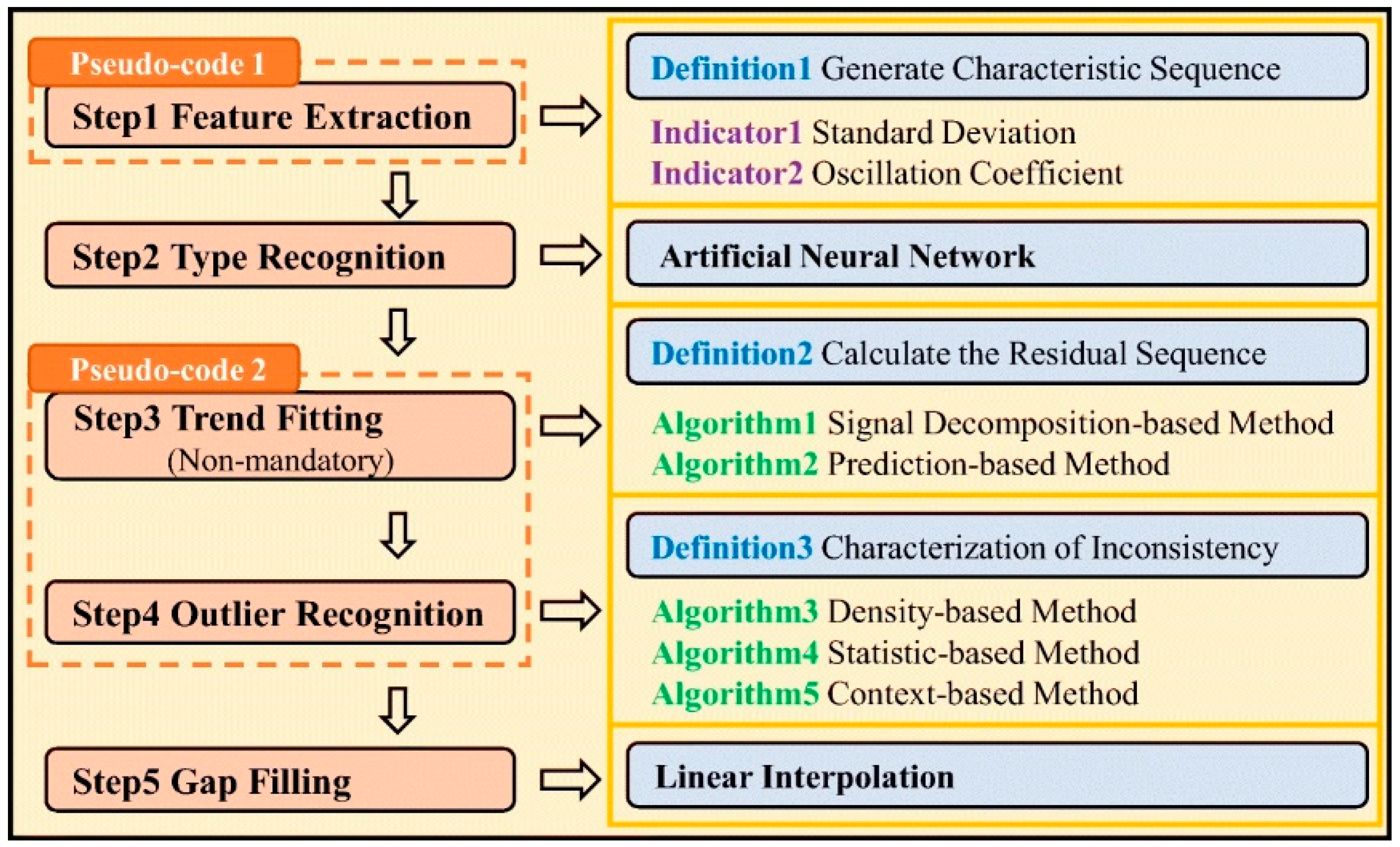
Zhang [65] designed a detachable low-cost oil mist probe with three parameters based on multi-sensor fusion technology. The probe mainly consists of the probe body and a data transmission module, as shown in Figure 7. The probe employs LoRa technology for data transmission. In practical applications, the probe demonstrates good stability during long-term monitoring, with outputs from multiple co-located sensors being consistent, effectively improving data quality. Additionally, Xu et al. [66] proposed an anomaly detection model framework for monitoring pollutants in industrial workshops, utilizing five independent core steps to address the fundamental task of outlier detection, as illustrated in Figure 8. The anomaly detection framework improves the accuracy of identifying anomalies in three typical data types to 70–90%, with anomaly detection and data quality enhancement outperforming other algorithmic combination strategies within the framework.
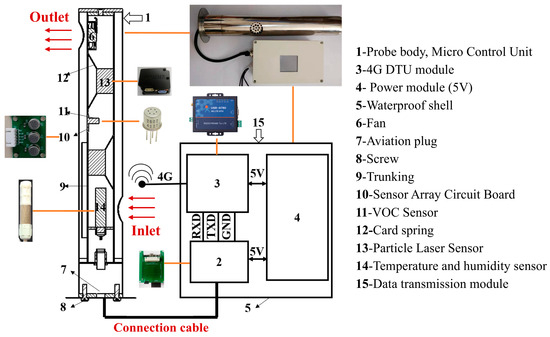
Figure 7.
Structural diagram of oil fume monitoring probe [65].
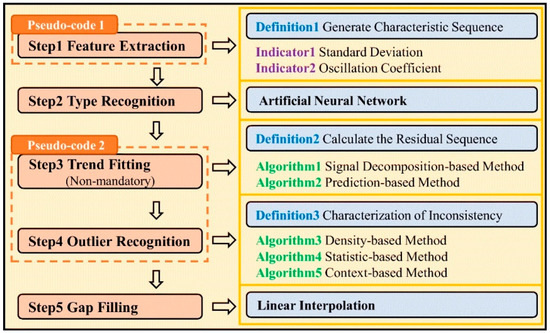
Figure 8.
An overview of the components in each of the core steps in the framework [66].
In addition, monitoring the smallest droplets is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics of oil mist. These tiny droplets not only have a significant impact on air quality, but they may also pose a potential threat to the health and safety of workers. Therefore, accurately monitoring the size and concentration of the smallest droplets is of great importance for assessing the effectiveness of oil mist control technologies.
There are various techniques for monitoring the smallest droplets in oil mist. Optical methods are one of the commonly used techniques for measuring droplet size and concentration. The light flicker method, based on the principle of light scattering, is an effective technique for detecting micro- and nano-sized oil mist droplets [67]. Using the particle system layer model and Lambert–Beer law, the transmittance of the measuring layer is treated as a Poisson distribution random variable. When light passes through a medium containing oil mist droplets, a flickering phenomenon occurs. By analyzing parameters such as flickering frequency, information about the oil mist droplet concentration can be determined, which in turn allows for the inference of the characteristics of the smallest droplets. Studies have shown that, under low-concentration oil mist conditions (0 to 50 mg/m3), the measurement accuracy of the light flicker method exceeds that of traditional light transmission methods. Furthermore, the light flicker method is unaffected by optical window contamination, features a simple structure, and is suitable for real-time online monitoring.
Electrostatic monitoring technology utilizes the ability of an electric field to capture and transport droplets, enabling high-precision monitoring of the smallest droplets [68]. For example, a novel bionic electrostatic system can efficiently manipulate micron-scale droplets by capturing and transporting them using electrostatic attraction. This technology is not only suitable for laboratory environments but also has the potential for application in industrial monitoring. Digital image processing technology collects oil mist field images using CCD cameras, and by applying grayscale processing and edge detection algorithms, it extracts droplet information and calculates relevant parameters [69]. This method offers high measurement accuracy, fast processing speeds, and the ability to handle large volumes of images, outputting droplet characteristics as parameter curves and contour maps. However, it requires specific image capture equipment and shooting conditions, and the image processing difficulty increases in complex backgrounds or under special concentrations.
5. Electrostatic Collection Technology for Oil Mist
5.1. Principle of Electrostatic Collection Technology
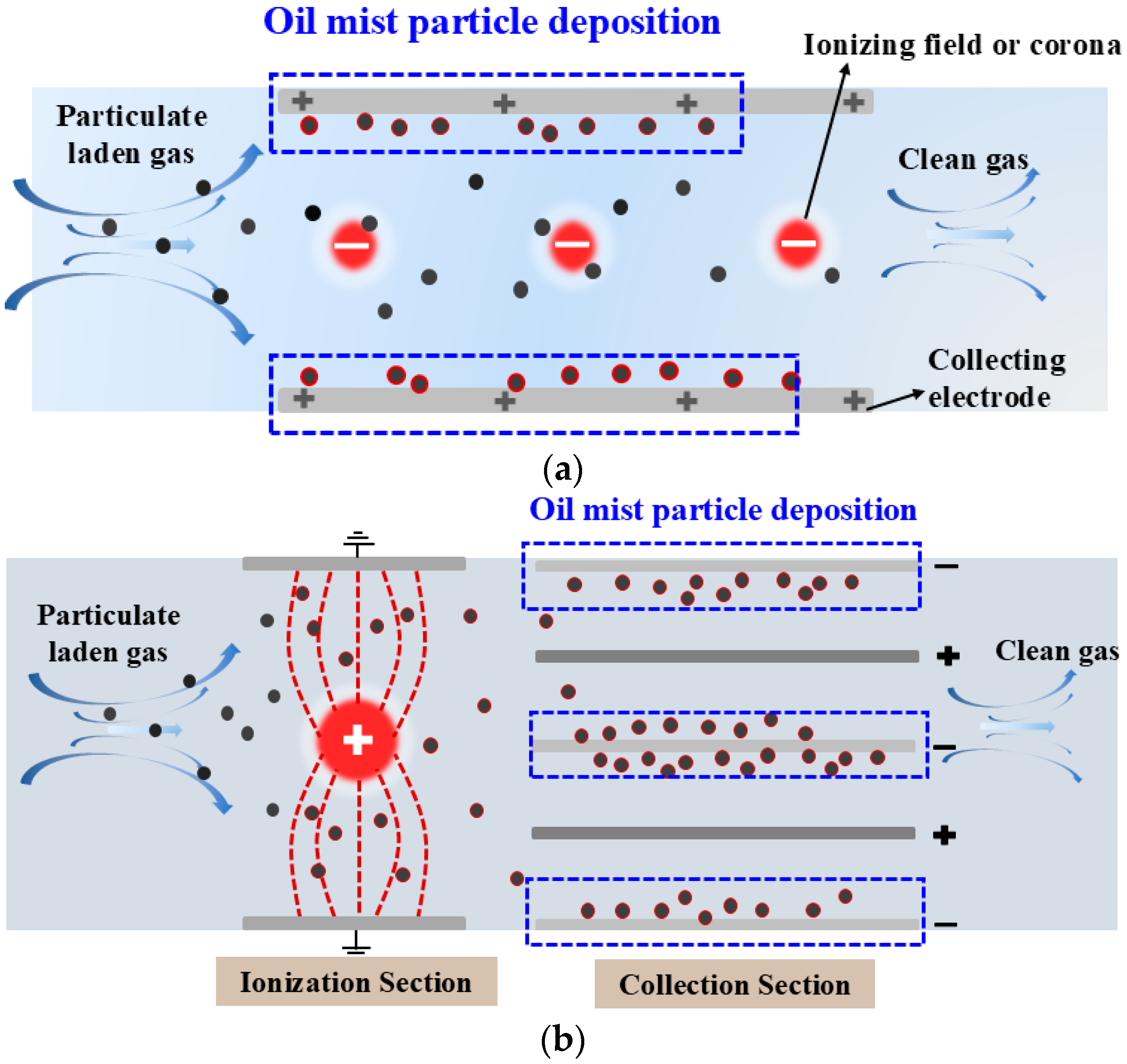
Electrostatic collection is an effective method for purifying oil mist. Its principle involves using electrode arrangements to generate corona discharge, distributing charged ions and electrons within the ESP [70]. When particles enter the ESP, they propagate under the combined influence of the flow field and electric field. During this process, the particles interact with surrounding ions and acquire charges. The charged particles are then driven by Coulomb force toward the collection plates, as illustrated in Figure 9a.
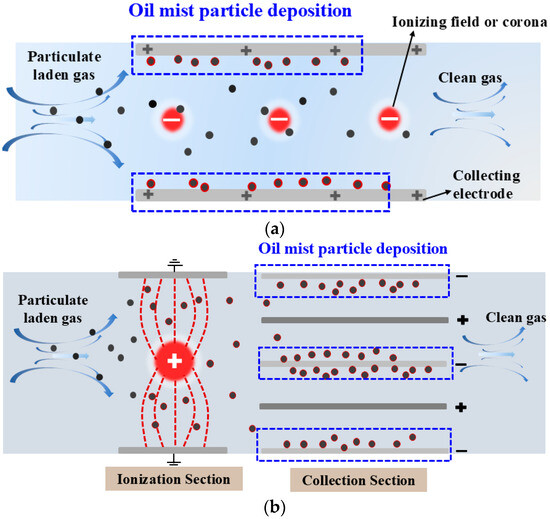
Figure 9.
Mechanism diagram of electrostatic precipitator: (a) single stage and (b) two stage.
Compared to other purification devices, ESPs have significant advantages, including high efficiency in purifying oil mist and dust, low ventilation resistance, reduced energy consumption, and minimal operating costs [71]. They also exhibit high collection efficiency for submicron particles. Experiments have demonstrated that the electrostatic collection method achieves the highest efficiency in collecting biomass pyrolysis bio-oil [72], making it widely applicable in industrial oil mist and kitchen fume purification.
The charged stage and dust collection stage of a two-stage ESP are arranged separately. The dust collection stage can use a smaller electrode gap to achieve a larger collection area and has a higher upper voltage limit, thereby achieving higher collection efficiency. As a result, two-stage ESPs have gradually become the mainstream equipment for oil mist purification in workshops [15]. Their working principle involves the charging of particles in the charging stage and the collection of particles in the dust collection stage. In the charging stage, free electrons and positive ions are generated through processes such as corona discharge. Free electrons outside the corona zone form negative ions, which collide with the oil mist particles, imparting charge to them. Subsequently, in the collection stage, the electric field force generated by the strong electric field drives the charged oil mist particles toward the collection electrodes, where they are adsorbed, thereby separating the oil mist particles from the airflow and achieving air purification. Figure 9b illustrates the particle movement process in the two-stage ESP.
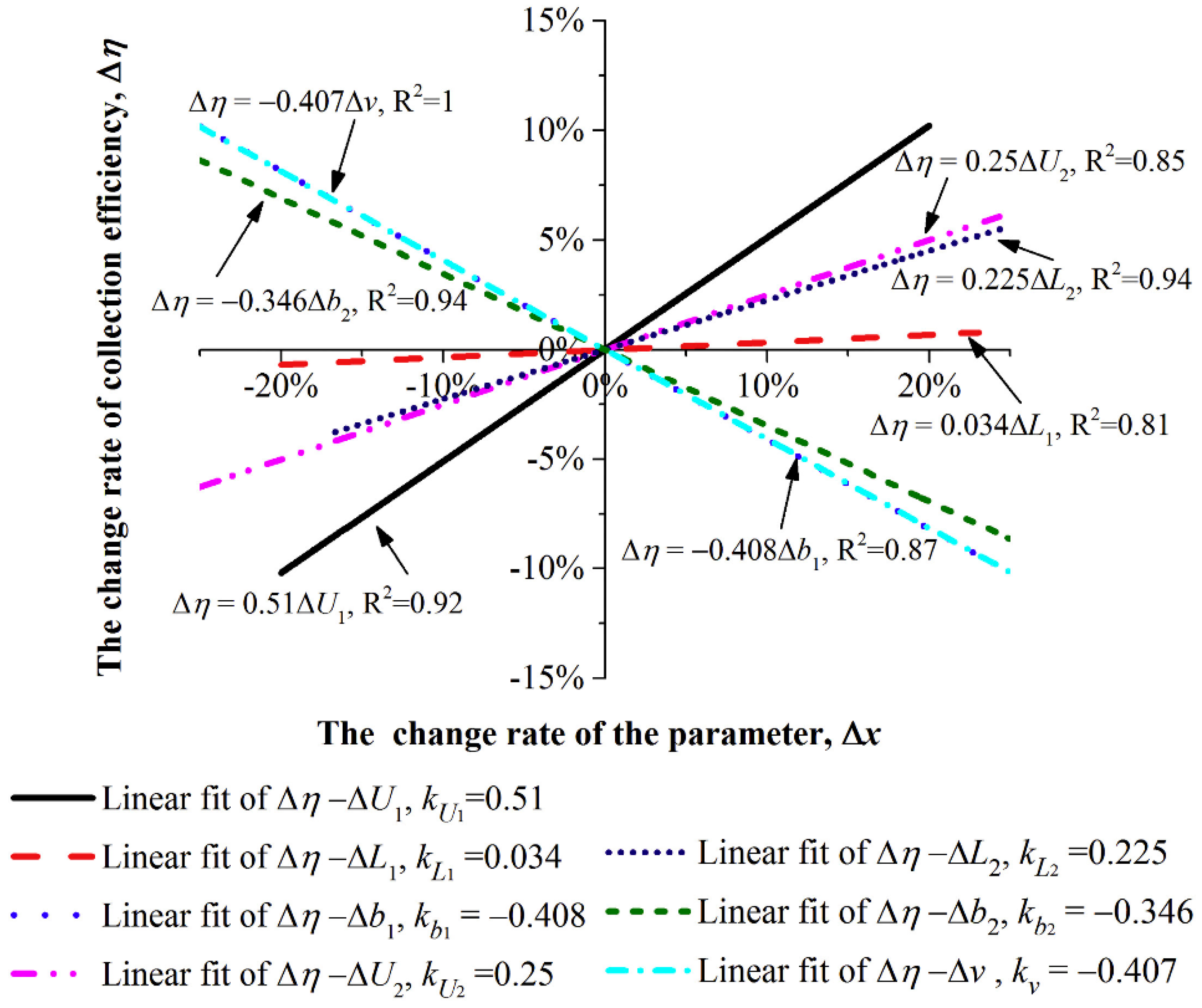
Due to the characteristics of electrostatic collection, the factors affecting its collection efficiency include the electrode configuration, charging stage voltage, length of the grounding plate in the charging stage, distance between opposite electrodes in the charging stage, voltage and electrode length in the dust collection stage, distance between opposite electrodes in the dust collection stage, and airflow velocity. Li et al. [73] analyzed the sensitivity of the collection efficiency to these factors and performed comparisons, as shown in Figure 10. “” and “” represent the change rate of this parameter and the corresponding efficiency, respectively. Based on the absolute values of the slopes of the fitted lines, the order of sensitivity is |kU1| > |kb1| > |kv| > |kb2| > |kU2|> |kL2| > |kL1|. Therefore, the factors affecting the collection efficiency, in descending order of importance, are: charging stage voltage (U1), distance between opposite electrodes in the charging stage (b1), airflow velocity (v), distance between opposite electrodes in the dust collection stage (b2), dust collection stage voltage (U2), electrode length in the dust collection stage (L2), and length of the grounding plate in the charging stage (L1). Consequently, in the design process of a two-stage ESP, the parameters should be considered in this order, but due to the presence of breakdown voltage in the charging stage, the voltage cannot be increased indefinitely.
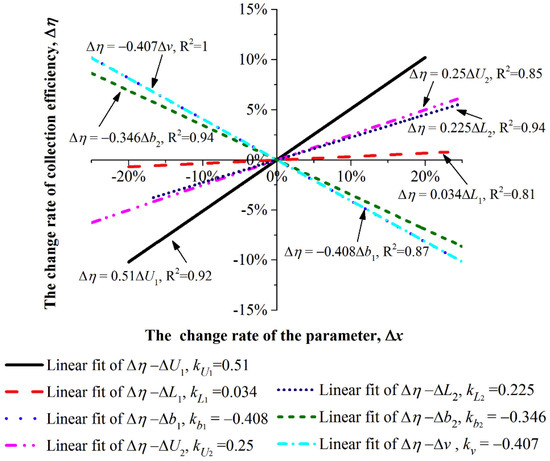
Figure 10.
Sensitivity analysis diagram of efficiency for parameters based on experimental data [73].
5.2. Oil Mist Deposition Characteristics
The deposition characteristics of particulate matter directly influence the collection efficiency of an ESP [74,75]. Particle deposition can lead to an increase in the dust layer thickness, which in turn triggers back corona discharge and further reduces the collection efficiency. However, oil mist particles, being liquid in nature, have physical properties that are distinctly different from dust and other particulate matter. Understanding the deposition characteristics of oil mist in the ESP is beneficial for optimizing the efficient collection of oil mist in electrostatic precipitator systems.
Particle deposition typically includes dense deposition and dendritic deposition, and the structure of the dust layer significantly affects the current density [76]. However, oil mist particles have unique characteristics. As fluid-like particles, oil mist particles are prone to deformation, phase transition, fragmentation, and melting. During the purification or filtration process, oil mist particles can break and collide, leading to deposition and coalescence, resulting in flow phenomena on purification equipment or materials. Additionally, oil mist particles possess high viscosity, which causes them to adhere to the surfaces of purification equipment or media during the separation process, hindering airflow movement and the particle separation process. When deposited on vertical collection plates, the particles are influenced by the combined effects of gravity, surface tension, and wall adhesion forces, forming an oil film [77], which weakens the current density of the ESP and reduces the collection efficiency [78].
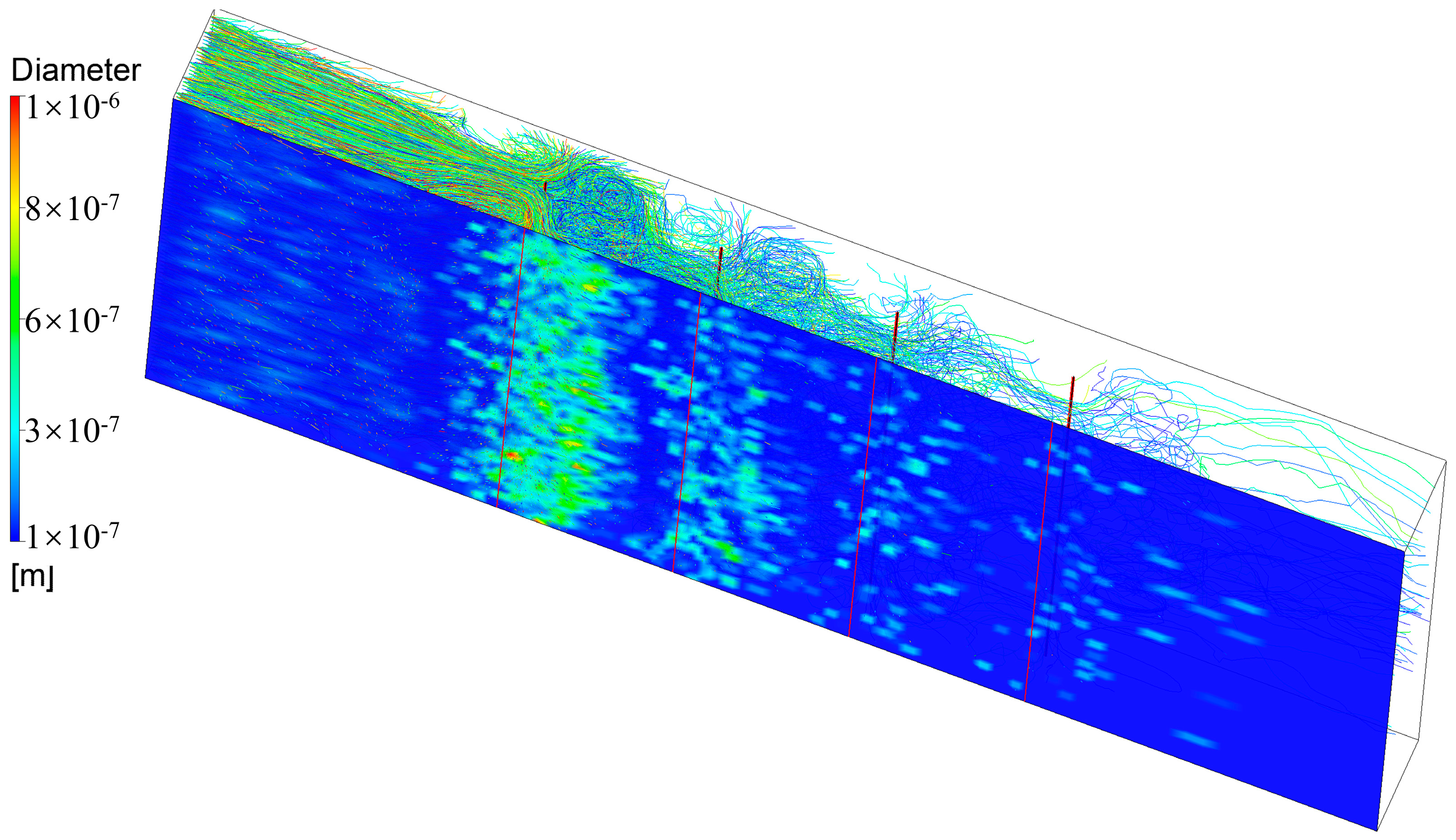
After oil mist particles enter the ESP, particles at the edges of the flow path first deposit on the inlet electrode plates. Most particles, however, will move along the flow lines under the combined effects of electric field force, gravity, and aerodynamic drag. When the airflow reaches the vicinity of the first corona line, secondary vortices will accelerate the airflow, changing its direction and bringing it closer to the dust collection electrode plate, as shown in Figure 11. During this process, some particles will directly deposit on the electrode plate aligned with the corona line, while a small number of particles will be drawn upstream by the vortex before depositing. The majority of particles will continue to move forward along the electrode plate, depositing when impacted by the skewed airflow. When approaching the second corona line, the secondary vortex effect will again alter the particle flow direction.
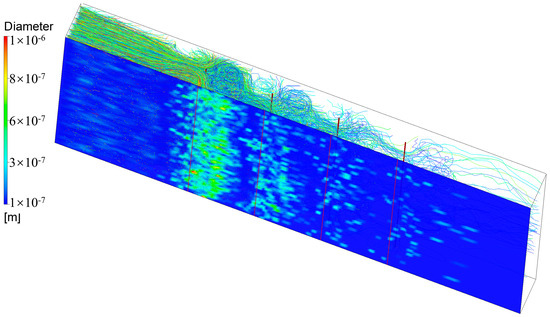
Figure 11.
0.1–1 μm oil mist particle trajectory [77].
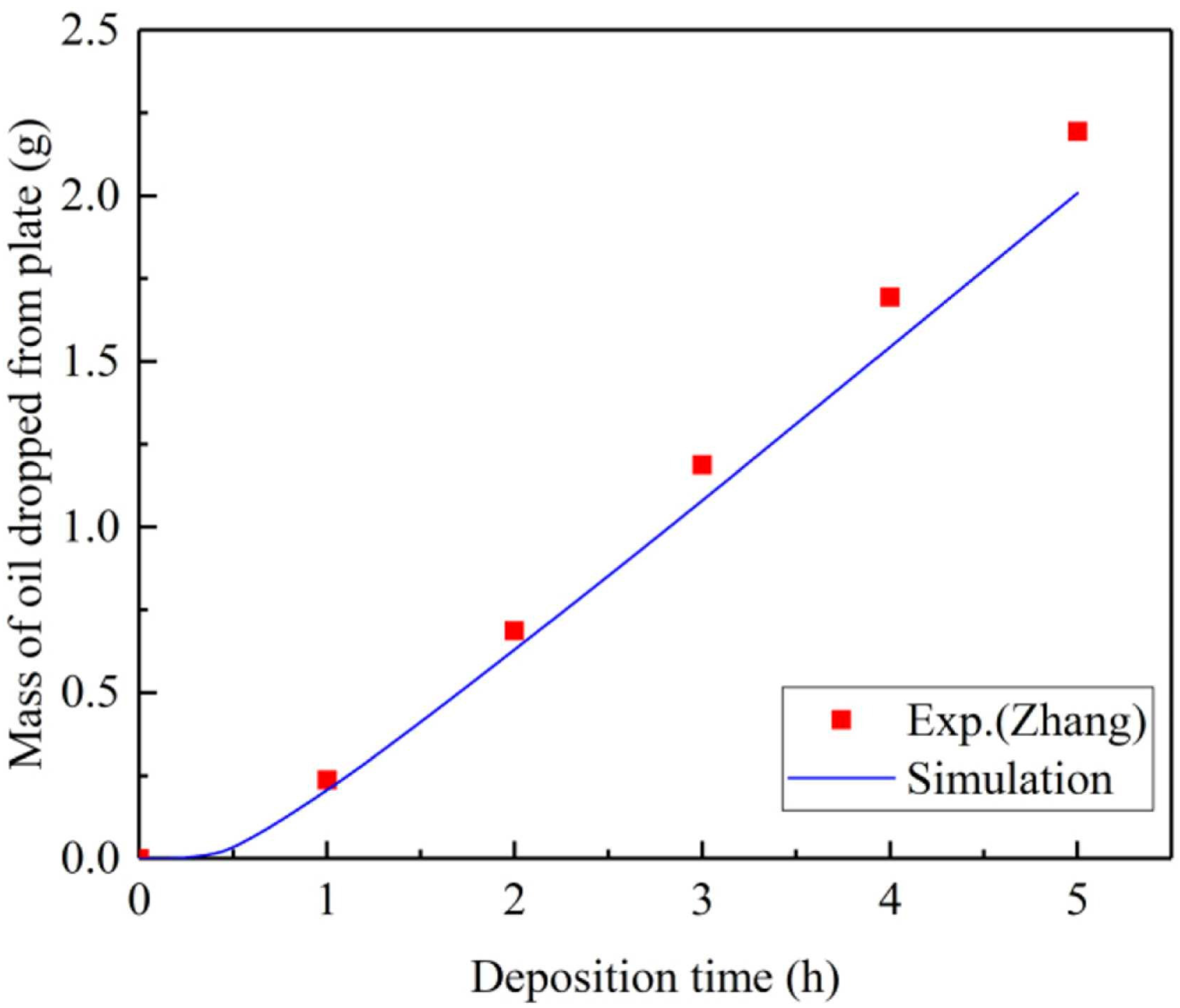
The oil-to-water ratio of oily particles is a key factor that affects the dielectric constant and specific resistivity, thereby influencing the charge acquisition of oily particles and the filtration efficiency of the ESP [79]. Furthermore, the formation and thickness variation of the oil film on the electrode plate are closely related to the oil-to-water ratio of the oily particles. Generally, the thicker the oil film, the lower the collection efficiency of the ESP [77,78]. Zhang et al. [78] conducted experiments to investigate the deposition characteristics of oil mist on the dust collection electrode plate. They found that after the ESP had been operating, the mass of oil droplets dripping from the collection electrode plate increased linearly with deposition time. Gao et al. [77] obtained the same conclusion through numerical simulations and compared it in detail with Zhang’s research, as shown in Figure 12. Precise data calculations show that the mass of oil mist particles removed per unit of time is equal to the mass of oil droplets in the collection container, as shown in Equation (4). This result fully demonstrates that the dust collection electrode plate can reach a saturated state when collecting oil mist particles, at which point the oil film thickness remains relatively stable. However, the saturation level is not fixed; it changes with variations in factors such as concentration and humidity. This is because these parameters indirectly affect the adhesive forces between the oil mist particles and between the particles and the electrode plate.
where (m2) is the outlet cross-sectional area, (m/s) is the air velocity, C1 is the inlet oil mist concentration, C2 is the outlet oil mist concentration, t (s) is the operating time of the ESP, and (g) is the mass difference of two consecutive weighings of the oil box.
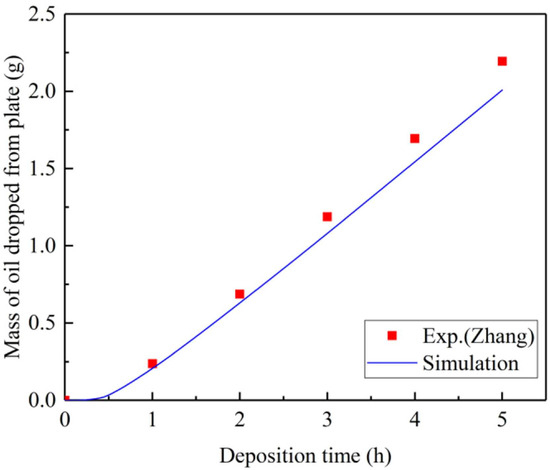
Figure 12.
Comparison of the mass of oil dropped from plate [77].
Oil mist deposits on the electrode plate form an oil film, and the distribution of this oil film is a core factor affecting the collection efficiency of the ESP [78]. This is because a dense oil film generates minimal back corona phenomena. The deposition of particles in the airflow direction exhibits uneven characteristics, and when deposition reaches a certain level, a saturated state is formed, meaning that the amount of oil mist deposited on the collection plate reaches equilibrium with the amount of oil mist flowing out due to film drainage. At this point, the oil film thickness no longer changes with time. In the electrostatic field, the oil film is relatively thin in areas with high electric field strength [77] and thicker at the collection electrode plates corresponding to the inlet and the positions between adjacent corona lines. The peak oil film thickness appears at the electrode plate corresponding to the middle of the first two electrode lines. When the inlet air velocity increases or the discharge electrode voltage is applied, the average oil film thickness increases, and the oil film distribution becomes more uniform.
In conclusion, the deposition characteristics of oil mist are complex and diverse, influenced not only by its physical properties such as fluidity, viscosity, and oil-water ratio, but also by environmental factors such as the electric field force, airflow movement, and secondary flow vortices within the ESP. Future research aimed at improving oil mist collection efficiency should comprehensively consider factors such as inlet airflow characteristics, applied voltage, and air environment. By precisely controlling these factors, it is possible to effectively reduce the accumulation thickness of the oil film during the operation of the ESP, thereby achieving a significant improvement in oil mist collection efficiency.
5.3. Two-Stage Electrostatic Collection
Research on two-stage ESPs both domestically and internationally can be classified into three main categories: material development, structural design, and parameter optimization. In terms of material development, Kim et al. [80] used carbon brush electrodes to reduce ozone generation, but due to the high viscosity of oil mist, these electrodes are prone to failure and require frequent replacement, making them unsuitable for removing high-concentration oil mist in industrial settings. Regarding structural design, Takashima et al. [81] studied a two-stage ESP consisting of an inductively charged region and a parallel plate collection region. Particles in the air can be charged by induction without generating corona discharge, thus reducing ozone production. Although energy efficient, this design is only suitable for low-velocity conditions and exhibits low efficiency under high air volume conditions in factories. Currently, there is substantial research on optimizing the performance of the ESP, with optimization parameters and content for these precipitators outlined in Table 3.

Table 3.
Research summary.
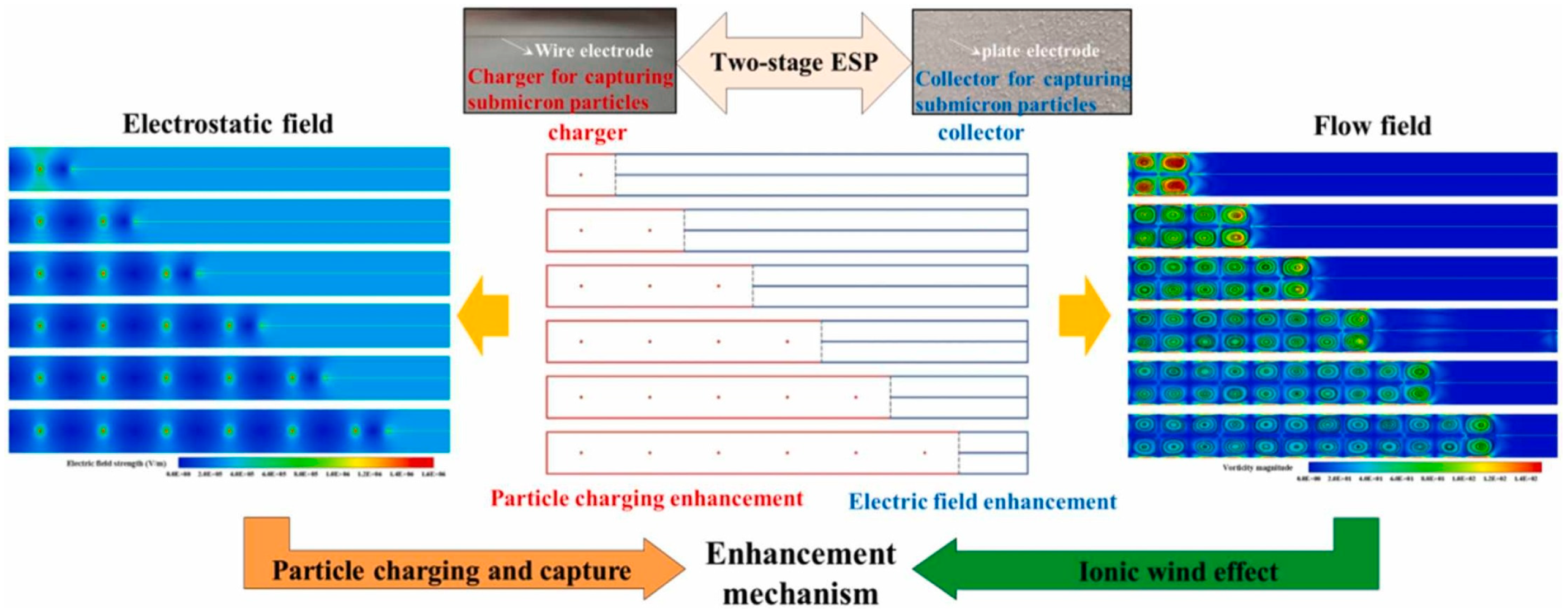
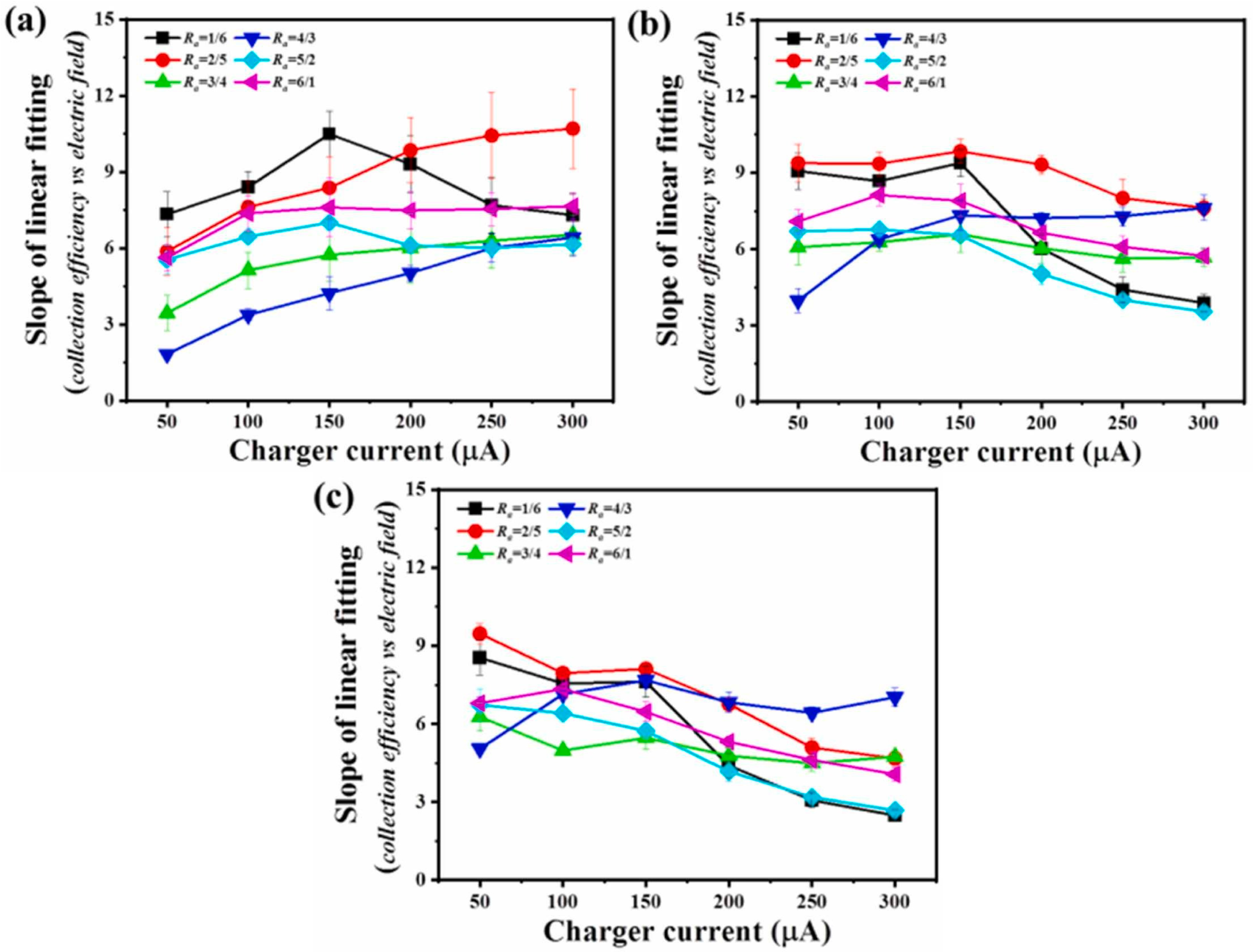
The structural parameters (corona wire diameter, spacing, and number) and operational parameters (applied voltage, airflow velocity) of a two-stage ESP have a significant impact on its purification performance [91]. Recent research on two-stage ESP has mainly focused on structural optimization and mechanism studies [92]. In terms of structural optimization, experimental results by Wen et al. [93] indicate that, compared to other electrode types, cylindrical corona electrodes generate a stronger electric field, thereby improving collection efficiency. Additionally, using serrated needle electrodes and increasing the length of the collection plates can also enhance the dust removal efficiency of two-stage ESPs [73]. Feng et al. [94] proposed a novel electrostatic-enhanced air filtration system with a needle-type filter medium and grounded conductive plate structure, which improves the collection efficiency of fine particles without increasing pressure drop. Wen et al. [95] designed a new ESP with porous foam covering the collection plates to reduce particle carryover, thereby improving collection efficiency. Zhu et al. [96] used numerical simulation methods to study the impact of the length ratio between the charged region and the dust removal region on dust removal efficiency, proposing optimization design principles. Zhu et al. [97] designed six two-stage ESPs with different ratios of charged region to collection region, aiming to explore the enhanced capture mechanisms of submicron particles, as shown in Figure 13. The study found that the two-stage ESP with a ratio of 1:6, while benefiting from electrostatic field characteristics that enhance collection efficiency, exhibited poor stability. Considering the ion wind effect and ozone emission, and due to advantages such as sufficient particle charging and ample collection space, the two-stage ESP with a ratio of 2:5 is prioritized. Meanwhile, Zhu et al. [97] compared the linear fitting slopes of collection efficiency for 0.25 µm, 0.35 µm, and 0.45 µm particles with the electric field strength of the collector, as shown in Figure 14. When the linear fitting slope is used as an indicator of electric field enhancement, the two-stage ESP with a 2:5 ratio proves to be the most advantageous in improving collection efficiency through electric field enhancement. It also demonstrates strong potential in both particle charge enhancement and electric field enhancement. This is because the two charger units in the two-stage ESP ensure complete charging of the submicron particles, while the long collector provides sufficient time for the charged particles to migrate and settle onto the collection plate.
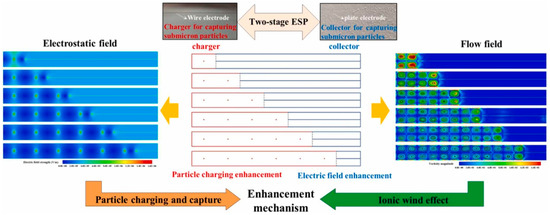
Figure 13.
Two-stage ESP with different ratios of charging stage and dust collection stage units [97].
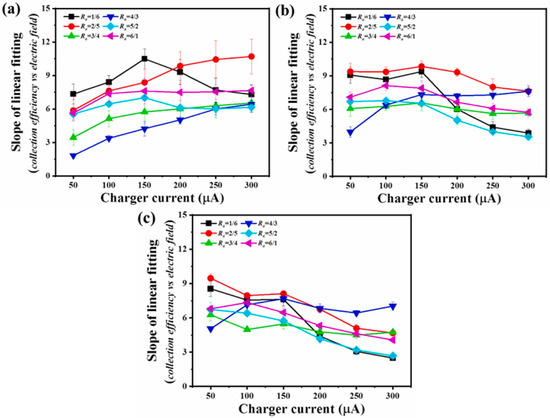
Figure 14.
Under the different ratios of the charger and collector, the slope of linear fitting of (a) 0.25 µm, (b) 0.35 µm, (c) 0.45 µm particles between collection efficiency and electric field strength of collector varies with charger current [97].
In mechanism studies, understanding the impact of temperature on particle charging and the collection efficiency of the ESP is crucial. An increase in temperature leads to a decrease in operating voltage, which in turn reduces collection efficiency [98,99]. Guo et al. used numerical simulations to analyze the effect of temperature in a line-plate electrostatic precipitator, finding that as the temperature rises, the collection efficiency for particles decreases. They attributed this result to the increased gas dynamic viscosity [100]. Many studies have aimed to improve the collection efficiency of ESPs by altering internal voltage or increasing the number of channels. Generally, when voltage increases, the current strength also increases, causing the capture rate for larger particles to be lower than that for smaller particles. Li et al. [101] explored the particle collection efficiency of an acupuncture pole two-stage electrostatic oil mist ESP and found that increasing the voltage effectively improves the purification efficiency for both large and fine particles. However, the purification efficiency for particles in the medium size range is low and difficult to improve, with the lowest purification efficiency observed for fine particles in the 0.3 μm size range. The average current density between the electrodes is higher, and the charging current distribution is more uniform, which facilitates effective particle charging. During the collection stage in the two-stage ESP, Xu et al. [102] and Kiatsiriroat et al. [103] employed pulsed excitation. During the pre-charging phase, short pulses are preferred as they generate electron densities and energy levels much higher than continuous DC, which can only charge particles to lower levels [104]. During the pulse duty cycle, the electric field is temporarily enhanced, increasing the average particle migration speed and cohesion within the dust layer. Short pulses also help avoid spark or back corona discharge. However, pulsed excitation reduces the penetrability of particles through the pre-charger by half, which is a drawback of this excitation mode [105].
Additionally, the relative humidity in the charged stage affects the characteristics of corona discharge, particle deposition, purification efficiency, ozone concentration distribution, and the concentration distribution of oil vapor in the collection stage. An increase in humidity reduces the corona current while increasing the space charge density, and these two factors exhibit a secondary relationship [106]. Gao et al. [107] developed a numerical model to describe the physical processes in a two-stage ESP, thereby studying its dust removal performance and influencing factors. Both the charged phase parameters (the product of ion concentration and charging time) and the collection phase parameters (electrostatic intensity, length, and width) significantly impact the collection efficiency [108]. Kawada et al. [88] used the finite element method to calculate the electric field and space charge distribution in the pre-charger for different grounding electrode lengths, finding that there is an optimal length for the grounding electrode in the pre-charging particle charger.
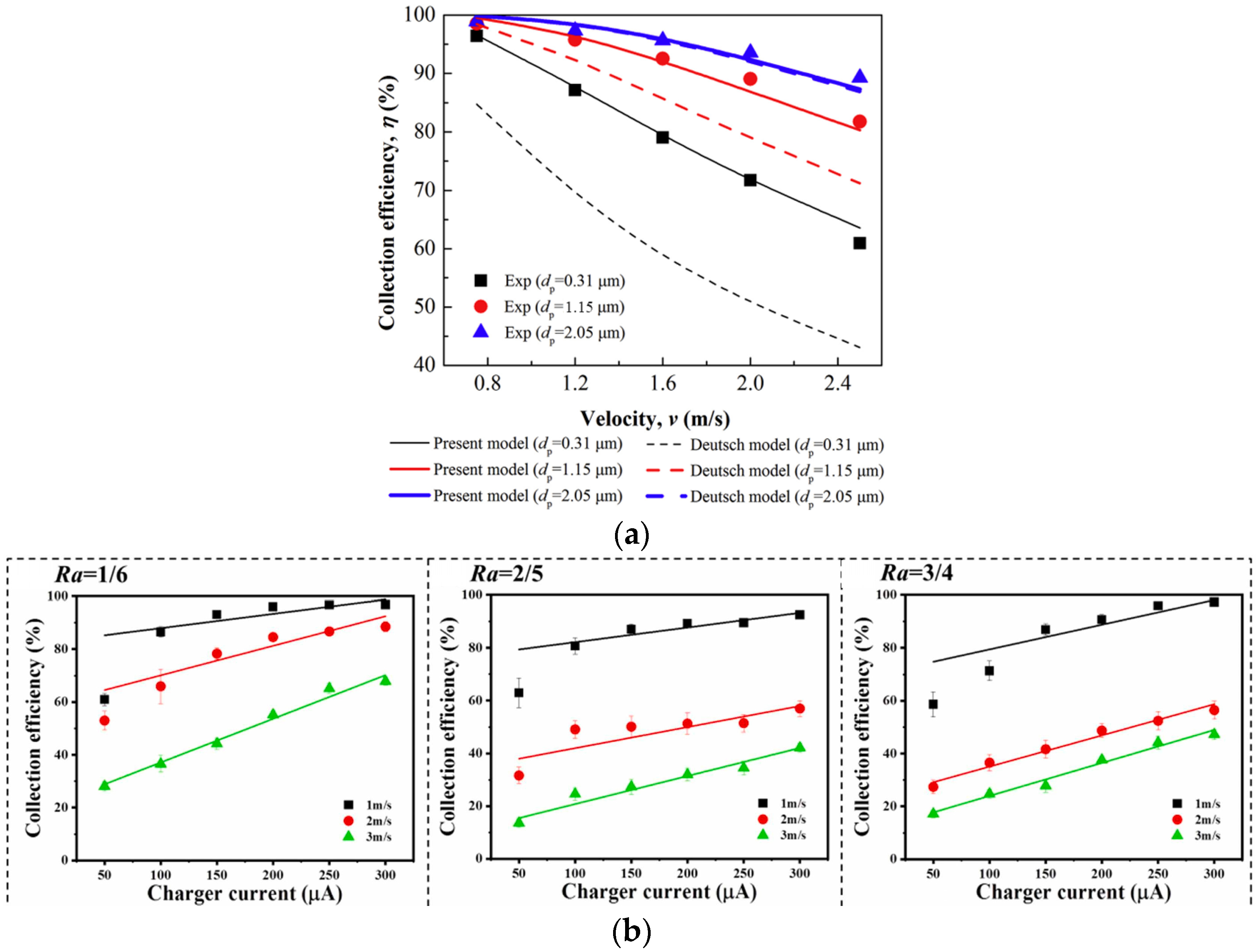
The core of electrostatic deposition technology lies in utilizing electric field forces to direct the movement and adsorption of oil mist particles. Its purification effectiveness is influenced by the electric field intensity, particle charge, and airflow velocity [109,110]. High electric field intensity helps particles move quickly toward the electrodes, but excessively high electric fields may trigger corona discharge, reducing the stability of the equipment. Larger charge amounts result in stronger forces, making particles more easily adsorbed. Meanwhile, airflow velocity affects the residence time of oil mist particles in the electric field [111]; an optimal airflow velocity ensures sufficient interaction between the particles and the electric field, while too high a velocity causes particles to escape. Li et al. [73] compared the numerical results and simulation results for different airflow velocities and particle sizes. The study found that as the airflow velocity increased from 0.75 m/s to 2.5 m/s, the collection efficiency of 0.31 μm, 1.15 μm, and 2.05 μm particles decreased by 35%, 17%, and 10%, respectively, as shown in Figure 15a. Zhu et al. [97] investigated the collection efficiency at different charge region-to-collection region ratios, demonstrating that the collection efficiency decreases with an increase in airflow velocity, as shown in Figure 15b. For a specific dual-zone electrostatic module, while reducing the airflow velocity in the electric field can improve oil mist collection efficiency, it also reduces the air handling capacity, weakening the overall purification ability of the dual-zone electrostatic precipitator. To maintain the air volume while reducing the airflow velocity, the electrostatic module size would need to be increased, which not only raises equipment costs but also causes operational inconvenience. Therefore, the airflow velocity within the electrostatic module must be carefully optimized. Researchers need to optimize the structural design and parameters, such as improving electrode shape and layout, exploring voltage ranges, and investigating electrode material and surface treatments, to enhance the collection efficiency of oil mist particles and reduce secondary escape.
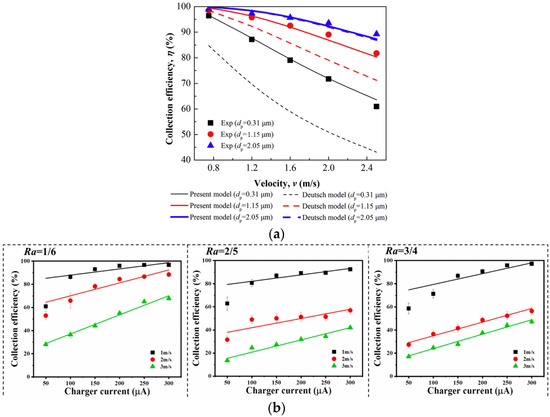
Figure 15.
Comparison of collection efficiency under different airflow velocities: (a) different particle sizes [73], and (b) ratio Ra between different charge regions and collection regions [97].
With the development of artificial intelligence (AI), its integration with oil mist control technology has become a growing trend. AI algorithms have great potential in the field of oil mist control. By optimizing control parameters, AI can analyze oil mist data, build predictive models through machine learning, and dynamically adjust equipment parameters such as fan speed, filter medium replacement cycles, and electrostatic adsorption voltage to improve purification efficiency. In fault diagnosis, deep learning algorithms can predict failures based on parameters such as equipment vibration and temperature, thereby reducing losses [112]. In complex industrial environments, AI can also sense changes in real-time and optimize control strategies. When combined with the Internet of Things (IoT), it enables equipment collaboration and data sharing. From a sustainability perspective, the promotion of the ESP requires an analysis of their environmental and operational costs. The ESP offers high oil mist capture efficiency, reduces air pollution, complies with regulations, and minimizes environmental impact. Some systems can even recover oil mist, facilitating resource recycling, reducing the demand for new oil, and minimizing waste. In terms of operational costs, although initial investment is high, long-term energy consumption is low. Intelligent control avoids energy waste, simplifies maintenance, reduces consumable costs, and minimizes safety risks, offering a long-term cost advantage.
5.4. The Practical Application Significance of the ESP
In actual industrial production, ESPs play a crucial role in oil mist control across various industries, including machining, electronics manufacturing, chemical production, food processing, and printing.
In the machining industry, workshops involved in automotive and aerospace component manufacturing generate large amounts of oil mist due to the use of metalworking fluids, which pose health risks to workers and affect machining accuracy. ESPs, with their high collection efficiency and low energy consumption, are key equipment for this purpose. For example, in automotive engine manufacturing workshops, the installation of a two-stage ESP reduces oil mist concentration, ensures worker health, extends equipment lifespan, and improves production efficiency.
The electronics manufacturing industry requires high environmental cleanliness, as even small oil mist particles can affect the performance of electronic products. ESPs installed in workshop ventilation systems can efficiently remove oil mist. In semiconductor chip manufacturing workshops, ESPs precisely capture submicron oil mist, improving chip yield rates and reducing costs.
In chemical production, exhaust gases contain pollutants such as oil mist and chemical particulates. ESPs can adjust their parameters according to the characteristics of the exhaust gases and effectively remove these pollutants. In petroleum refining, ESPs not only remove oil mist but also help eliminate other pollutants, reducing atmospheric pollution, recovering oil mist resources, and lowering operational costs for enterprises.
During food processing, oil fumes and oil mist generated by frying and baking affect the production environment and food quality. Large food processing plants can install ESPs to purify exhaust gases, reduce oil mist deposition, lower fire risks, and ensure food safety.
In the printing process, ink and fountain solutions generate oil mist and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). ESPs, working in conjunction with other equipment, remove oil mist and partially adsorb VOCs. For example, in large printing factories, the installation of ESPs can reduce harmful substance concentrations in the workshop, improve the working environment, and reduce pollution in surrounding areas.
6. Conclusions
- In actual processing workshops, continuous production by equipment leads to severe oil mist pollution, and many factories still exceed the NIOSH limit of 0.5 mg/m3. In these processing workshops, efficient electrostatic oil mist collection methods and collaborative purification strategies therefore require further research.
- During cutting and milling, the coolant flow rate is the primary parameter affecting the amount of oil mist emitted. Compared to spray lubrication, the minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) mode generates a larger number of oil mist particles. Thus, while MQL largely reduces coolant consumption, it can be more detrimental to air quality. When selecting purification control technologies, both the characteristics of the oil mist and the process requirements should be considered.
- Electrostatic deposition is an effective method for oil mist purification, and the two-stage ESP has become the mainstream equipment for oil mist purification in workshops due to its dust collection area, which can be expanded by using smaller plate spacing. However, the impact of particle size distribution on deposition characteristics requires further investigation. Additionally, most current studies on the particle deposition characteristics of ESPs are conducted in single-stage systems, and the deposition characteristics of particles in two-stage ESPs need further exploration.
- The oil mist collection efficiency of the electrostatic collection method is influenced by the combined effects of multiple physical fields. Studying the coupling effects of factors such as inlet airflow characteristics, applied voltage, and air environment, and optimizing the electrostatic precipitator’s collection efficiency based on these factors, may lead to better optimization results.
- Optimizing the structural design and parameters of the two-stage ESP (such as electrode plate distance, voltage, electrode plate, and material) can improve the oil mist particle collection efficiency and reduce secondary escape. This is an effective strategy for enhancing efficiency, and the impact of relevant parameters still requires further systematic study.
- The oil mist deposition characteristics are complex and directly impact collection efficiency. Future research aimed at improving oil mist collection efficiency must consider factors such as inlet airflow characteristics, applied voltage, and the air environment. Precise regulation is required to reduce the oil film thickness during ESP operation and enhance collection efficiency. Moreover, AI algorithms have enormous potential in the field of oil mist control. They can analyze oil mist data, dynamically adjust equipment parameters to improve purification efficiency, predict equipment failures based on operational parameters, and, when integrated with the IoT, enable equipment collaboration and data sharing. This provides a smarter and more efficient solution for oil mist control.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Z.L. and T.Y.; investigation, Y.L., L.L. and L.Z.; resources, Z.L. and T.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L., Y.L., Z.L. and W.L.; writing—review and editing, L.L. and Y.L.; funding acquisition, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51878442) and the National Key Research and Development Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2022YFB4100702).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Wenjun Leng is employee of Wuhan Second Ship Design and Research Institute. Lei Zhang is employee of The Sixth Design and Research Institute of North China Municipal Engineering Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd. The paper reflects the views of the scientists, and not the company.
References
- Yue, Y.; Sun, J.; Gunter, K.; Michalek, D.; Sutherland, J. Character and behavior of mist generated by application of cutting fluid to a rotating cylindrical workpiece, part 1: Model development. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2004, 126, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.-N.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Quan, M. Distribution of oil mist particles and air quality improvement in the working area of the cutting workshop. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Y. Exposure levels of oil mist particles under different ventilation strategies in industrial workshops. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Lung, S.-C.C.; Chen, K.-F.; Wang, W.-C.V.; Chou, C.-T.; Lai, C.-H. Environmental concentration of spray paint particulate matters causes pulmonary dysfunction in human normal bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cell. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Long, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, Q. Strategy for Studying Ventilation Performance in Factories. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotrecchiano, N.; Montano, L.; Bonapace, I.M.; Giancarlo, T.; Trucillo, P.; Sofia, D. Comparison Process of Blood Heavy Metals Absorption Linked to Measured Air Quality Data in Areas with High and Low Environmental Impact. Processes 2022, 10, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhou, W.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, H. The actuality and development of metalworking fluids (MWFS) mist control. Lubr. Oil 2003, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; Long, Z. Physicochemical characterization of oily particles emitted from different machining processes. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 96, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, B.; Shao, M. Field measurement of oil mist particle concentration distribution in machining workshops. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2022, 49, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, B.; Zhan, R.; Lin, H.; Huang, Z. Review of the state-of-the-art of exhaust particulate filter technology in internal combustion engines. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeesh, P.; Sen, A.K. Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: A review. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 17, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Li, S. Numerical study on fine-particle charging and transport behaviour in electrostatic precipitators. Powder Technol. 2018, 330, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Cui, P.; Liu, J. Research on Electrostatic Purification Equipment Suitable for High-concentration Oil Mist Exhaust Gas. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2022, 49, 115–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Tian, A. Numerical Simulation of Dual-Zone Electrostatic Oil Mist Purifier. SSRN 2014, 4715148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Shangguan, W. Numerical simulation study of two-stage electrostatic precipitator. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 3698–3703. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; You, C. Effect of humidity on negative corona discharge of electrostatic precipitators. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2013, 20, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.P. Numerical analysis of charged particle collection in wire-plate ESP. J. Electrost. 2015, 74, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Said, H.A.; Aissou, M.; Nouri, H.; Zebboudj, Y. Analysis of the Current-Voltage Characteristic during the Corona Discharge in Wires-To-Planes Electrostatic Precipitator under Variable Air Humidity. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2019, 135, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, S. Numerical Simulation and Structure Optimization of Electrostatic Precipitator. CFHI Technol. 2019, 50–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhong, K. Performances of Double-Stage Electrostatic Air Cleaners. Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2005, 25, 149–152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Long, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X. Monitoring and purification of oil mist particles in a machining workshop. Heat. Vent. Air Cond. 2019, 49, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, Q.; Qiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.-N.; Yang, C.; Pan, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, F. Purification technology of oil mist in industrial buildings: A review. Build. Environ. 2023, 235, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yin, Y. Hazards of pollutants and ventilation control strategy in industrial workshops: Current state and future trend. Build. Environ. 2024, 251, 111229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, P.C.; Kim, S.W.; Bhattacharya, M. Mist generation from metalworking fluids formulated using vegetable oils. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 49, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, P.; Oberwalleney, S. Life-cycle planning of cutting fluids—A review. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 1997, 119, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Murga, A.; Long, Z.; Yoo, S.; Ito, K. Experimental study of oil mist characteristics generated from minimum quantity lubrication and flood cooling. Energy Built Environ. 2021, 2, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, D.J.; Hii, W.W.-S.; Sun, J.; Gunter, K.L.; Sutherland, J.W. Experimental and analytical efforts to characterize cutting fluid mist formation and behavior in machining. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2003, 18, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zong, S.; Jing, H.; Gao, N.; Ye, H.; Chen, J. The influence of ventilation modes on oil mist particles diffusion in a machining workshop. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, A.H.; McDonell, V.G. Atomization and Sprays; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Macıas-Garcıa, A.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Dıaz-Dıez, M. Application of the Rosin–Rammler and Gates–Gaudin–Schuhmann models to the particle size distribution analysis of agglomerated cork. Mater. Charact. 2004, 52, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’arcy, J.; Dasch, J.; Gundrum, A.; Rivera, J.; Johnson, J.; Carlson, D.; Sutherland, J. Characterization of process air emissions in automotive production plants. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2016, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Cao, C.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Z. Volume-based size distribution of accumulation and coarse particles (PM0.1–10) from cooking fume during oil heating. Build. Environ. 2013, 59, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khettabi, R.; Nouioua, M.; Djebara, A.; Songmene, V. Effect of MQL and dry processes on the particle emission and part quality during milling of aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Feldshtein, E.; Pusavec, F.; Szydlowski, M.; Legutko, S.; Sobczak-Kupiec, A. A study on droplets sizes, their distribution and heat exchange for minimum quantity cooling lubrication (MQCL). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, A.R.; Roe, M.W.; Evans, J.N.; Davis, G.S. Deposition and translocation of inhaled silica in rats. Quantification of particle distribution, macrophage participation, and function. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods 1982, 47, 533. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Lin, Y.-X.; Lee, T.-H.; Lin, C.-H. Adverse pulmonary impacts of environmental concentrations of oil mist particulate matter in normal human bronchial epithelial cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hao, W.; Liu, W.; Long, Z. Simulation study of the purification system for indoor oil mist control in machining factories. Build. Simul. 2023, 16, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Lai, W.; Liu, X.; Xi, Z.; Lin, B. Combined multi-omics analysis reveals oil mist particulate matter-induced lung injury in rats: Pathological damage, proteomics, metabolic disturbances, and lung dysbiosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Yoo, S.-J.; Long, Z.; Ito, K. Error analysis of human inhalation exposure simulation in industrial workshop. Build. Environ. 2022, 224, 109573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Stear, M.; Groves, J.; Piney, M.; Bradley, S.; Stagg, S.; Crook, B. Occupational exposure to metalworking fluid mist and sump fluid contaminants. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2003, 47, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R. Experimental study of oil particle emission rate and size distribution during milling. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists. Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices; American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Rosner, D.; Markowitz, G. A short history of occupational safety and health in the United States. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirer, F.E. New evidence on the health hazards and control of metalworking fluids since completion of the OSHA advisory committee report. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2010, 53, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockery, D.W. Health effects of particulate air pollution. Ann. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stear, M.A. Controlling health risks from workplace exposure to metalworking fluids in the United Kingdom engineering industry. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2003, 18, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Occupational Exposure Banding; The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH): Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Kennedy, S.M.; Greaves, L.A.; Kriebel, D.; Eisen, E.A.; Smith, T.J.; Woskie, S.R. Acute pulmonary responses among automobile workers exposed to aerosols of machining fluids. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1989, 15, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monarca, S.; Pasquini, R.; Sforzolini, G.S.; Savino, A.; Viola, V. Mutagenic/carcinogenic hazards in a cold-rolling steel plant exposed to mineral oils: Environmental monitoring phase. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1984, 54, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønneberg, A.; Skyberg, K. Mortality and incidence of cancer among oil exposed workers in a Norwegian cable manufacturing company. Part I. Exposure conditions 1920-79. Occup. Environ. Med. 1988, 45, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameille, J.; Wild, P.; Choudat, D.; Ohl, G.; Vaucouleur, J.F.; Chanut, J.C.; Brochard, P. Respiratory symptoms, ventilatory impairment, and bronchial reactivity in oil mist-exposed automobile workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1995, 27, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, K.; Hilt, B. Exposure to mineral oil mist and respiratory symptoms in marine engineers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1997, 32, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, K. Measurements of mineral oil mist, hydrocarbon vapor, and noise in engine rooms of ships. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 1999, 14, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, B.; Stewart, P.; Ulvestad, B.; Eduard, W. Dust and gas exposure in tunnel construction work. AIHAJ-Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. 2001, 62, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-R.; Tsai, P.-J.; Chang, C.-C.; Shih, T.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Liao, P.-C. Particle size distributions of oil mists in workplace atmospheres and their exposure concentrations to workers in a fastener manufacturing industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayahi, T.; Butterfield, A.; Kelly, K. Long-term field evaluation of the Plantower PMS low-cost particulate matter sensors. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Antonio, A.; Popoola, O.A.; Ouyang, B.; Saffell, J.; Jones, R.L. Developing a relative humidity correction for low-cost sensors measuring ambient particulate matter. Sensors 2018, 18, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crilley, L.R.; Shaw, M.; Pound, R.; Kramer, L.J.; Price, R.; Young, S.; Lewis, A.C.; Pope, F.D. Evaluation of a low-cost optical particle counter (Alphasense OPC-N2) for ambient air monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Jing, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Biswas, P. Laboratory evaluation and calibration of three low-cost particle sensors for particulate matter measurement. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-T.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Chue, J.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-J.; Cheng, C.-W.; Wu, C.-M.; Huang, C.-M. Calibration of low-cost particle sensors by using machine-learning method. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Chengdu, China, 26–30 October 2018; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bulot, F.M.; Johnston, S.J.; Basford, P.J.; Easton, N.H.; Apetroaie-Cristea, M.; Foster, G.L.; Morris, A.K.; Cox, S.J.; Loxham, M. Long-term field comparison of multiple low-cost particulate matter sensors in an outdoor urban environment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelo-Ordinas, J.M.; Doudou, M.; Garcia-Vidal, J.; Badache, N. Self-calibration methods for uncontrolled environments in sensor networks: A reference survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 88, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.W.; Sousan, S.; Tatum, M.; Liu, X.; Zuidema, C.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Koehler, K.A.; Peters, T.M. Low-cost, distributed environmental monitors for factory worker health. Sensors 2018, 18, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Pan, W.; Long, Z. Low-cost sensor system for monitoring the oil mist concentration in a workshop. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 14943–14956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Research on Oily Particulate Online Monitoring Device and Sampling System; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Long, Z.; Pan, W.; Wang, Y. Low-Cost Sensor Outlier Detection Framework For on-Line Monitoring of Particle Pollutants in Multiple Scenarios. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52963–52980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Hu, F.; Ji, Z.; Liu, Z. Oil Mist Concentration On-line Measurement by Optical Scintillation Method. Acta Photonica Sin. 2024, 53, 0112001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Yang, P.; Bai, Z.; Shen, T.; Liu, Z.; Qin, S.; Hu, J.; Yu, C.; Dong, Z.; Chen, X. Bioinspired Electrostatic Capture-and-Release System for Precise Microdroplet Manipulation. Adv. Mater. 2025, 2418711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Li, P.; Wang, S. A Rapid Measurement Method for Liquid Mist Characteristics Based on Digital Image Processing Technology. Chinese Patent CN104020086B, 2 March 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Long, Z.; Yao, Q.; Song, Q.; Li, S. A second-order accurate finite volume method for the computation of electrical conditions inside a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator on unstructured meshes. J. Electrost. 2009, 67, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Long, Z.; Chen, Q. Voltage–current characteristics of needle-plate system with different media on the collection plate. J. Electrost. 2014, 72, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Toba, M.; Yoshimura, Y. Effect of electrostatic precipitator on collection efficiency of bio-oil in fast pyrolysis of biomass. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2013, 56, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.; Pan, W.; Long, Z.; Yu, T. Experimental and theoretical study of the collection efficiency of the two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Powder Technol.Technol. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Wet Dry Part. Syst. 2019, 356, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Zheng, C.; Guo, J.; Gao, X.; Yu, A. A numerical investigation of the effect of dust layer on particle migration in an electrostatic precipitator. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zheng, H.; Sun, D.; Gao, X. Effect of dust layer in electrostatic precipitators on discharge characteristics and particle removal. Fuel 2020, 278, 118335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D.; Atten, P.; Dumitran, L.M. Correlation between current density and layer structure for fine particle deposition in a laboratory electrostatic precipitator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Long, Z.; Feng, Z.; Lin, B.; Yu, T. Numerical simulation of the characteristics of oil mist particles deposition in electrostatic precipitator. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pan, W.; Zhang, H.; Long, Z.; Yu, T. High-efficient removal of airborne oil mist in a wire-plate electrostatic precipitator. J. Electrost. 2020, 108, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, K. Numerical models in simulating wire-plate electrostatic precipitators: A review. J. Electrost. 2013, 71, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Han, B.; Kim, Y.-J.; Hwang, K.-D.; Oh, W.-S.; Yoo, S.-Y.; Oda, T. Fine particle removal performance of a two-stage wet electrostatic precipitator using a nonmetallic pre-charger. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, K.; Kohno, H.; Katatani, A.; Kurita, H.; Mizuno, A. Two-stage electrostatic precipitator using induction charging. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 174002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukeran, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Ehara, Y.; Matsuyama, M.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, T.; Kawakami, H.; Takamatsu, T. Two-stage-type electrostatic precipitator re-entrainment phenomena under diesel flue gases. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1999, 35, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitran, L.; Blanchard, D.; Atten, P.; Notingher, P. Estimate of effective migration velocity of fine particles from fractional efficiency measurements in an electrostatic precipitator. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Fifth IAS Annual Meeting and World Conference on Industrial Applications of Electrical Energy (Cat. No. 00CH37129), Roma, Italy, 8–12 October 2000; pp. 559–562. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-H.; Chen, C.-C. Ultrafine aerosol penetration through electrostatic precipitators. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4625–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shujairi, S. Comparing Electrostatic Precipitator Performance of Two-Stage with Single-Stage to Remove Dust from Air Stream. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, W. Experimental Investigation of Double-Stage Electrostatic Air Cleans’ Performances. Contam. Control Air-Cond. Technol. 2014, 3, 33–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Hong, Y.; Li, S.; Li, J. Influence factors and theoretical equation study for dust removal efficiency of two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Environ. Pollut. Control 2017, 39, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kawada, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Zukeran, A. Considerations of suitable grounded electrode length of pre-charger in two-stage-type electrostatic precipitator. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, U.; Beroual, A.; Alotaibi, F.; Khan, Y.; Al-Arainy, A. Experimental and analytical study on the performance of novel design of efficient two-stage electrostatic precipitator. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2018, 12, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Dixit, A.; Srivastava, A.K. Design and optimization of the shape of electrostatic precipitator system. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3871–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-L.; Bai, H. Effects of Some Geometric Parameters on the Electrostatic Precipitator Efficiency at Different Operation Indexes. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z. Enhanced size-dependent efficiency of removal of ultrafine particles:New solution of two-stage electrostatic precipitator with thermophoresis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.Y.; Su, J.L. Corona discharge characteristics of cylindrical electrodes in a two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Long, Z.; Mo, J. Experimental and theoretical study of a novel electrostatic enhanced air filter (EEAF) for fine particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 102, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, H.; Krichtafovitch, I.; Mamishev, A. Novel electrodes of an electrostatic precipitator for air filtration. J. Electrost. 2015, 73, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Shi, J.; Shangguan, W. Enhancement of air purification by unique W-plate structure in two-stage electrostatic precipitator: A novel design for efficient capture of fine particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tao, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Shangguan, W. Experimental research of capture enhancement mechanism of submicron particles by designing two-stage electrostatic precipitators with various ratios of charger and collector units. Chem. Eng. Res. 2023, 189, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Yan, P.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Particle migration and collection in a high-temperature electrostatic precipitator. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 143, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zheng, C.; Xiao, G.; Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Characteristics of negative DC corona discharge in a wire–plate configuration at high temperatures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 139, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.Y.; Yu, A.B.; Guo, J. Numerical modeling of electrostatic precipitation: Effect of Gas temperature. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 77, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, M.; Li, H. Analysis on the performance of interactive cascade ventilation for space heating based on non-uniform indoor environment demand. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Zhongyang, L.; Bo, W.; Lina, W.; Xiang, G.; Mengxiang, F.; Kefa, C. Electrostatic Capture of PM 2.5 Emitted from Coal-fired Power Plant by Pulsed Corona Discharge Combined with DC Agglomeration. In Proceedings of the Electrostatic Precipitation: 11th International Conference on Electrostatic Precipitation, Hangzhou, China, 15 October 2008; pp. 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Thonglek, V.; Kiatsiriroat, T. Agglomeration of sub-micron particles by a non-thermal plasma electrostatic precipitator. J. Electrost. 2014, 72, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukeran, A.; Looy, P.C.; Chakrabarti, A.; Berezin, A.A.; Jayaram, S.; Cross, J.D.; Ito, T.; Chang, J.-S. Collection efficiency of ultrafine particles by an electrostatic precipitator under DC and pulse operating modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1999, 35, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykov, A.; Kolchin, K.; Bochkov, V.; Gnedin, I.; Amirov, R.; Samoilov, I.; Sergeev, A.; Balykin, A. Investigations of pulse energization and agentless conditioning at pilot electrostatic precipitator of 300 MW coal fired boiler. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Electrostatic Precipitation, Kyongju, Republic of Korea, 20–25 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Gao, H.; Long, Z. Study of the multi-physics field-coupled model of the two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Build. Simul. 2024, 17, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, X.; Shi, J.; Shangguan, W. Dust removal performance of two-stage electrostatic precipitators and its influencing factors. Powder Technol. 2019, 348, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Christofides, P.D. Collection efficiency of nanosize particles in a two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8484–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Yao, Q.; Song, Q.; Li, S. Three-dimensional simulation of electric field and space charge in the advanced hybrid particulate collector. J. Electrost. 2009, 67, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Yao, Q. Numerical simulation of the flow and the collection mechanism inside a scale hybrid particulate collector. Powder Technol. 2012, 215, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Yao, Q. Evaluation of various particle charging models for simulating particle dynamics in electrostatic precipitators. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saufi, S.R.; Ahmad, Z.A.B.; Leong, M.S.; Lim, M.H. Challenges and opportunities of deep learning models for machinery fault detection and diagnosis: A review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 122644–122662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).