Simultaneous Determination of Six Common Microplastics by a Domestic Py-GC/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Atmospheric Sampling
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Microplastics
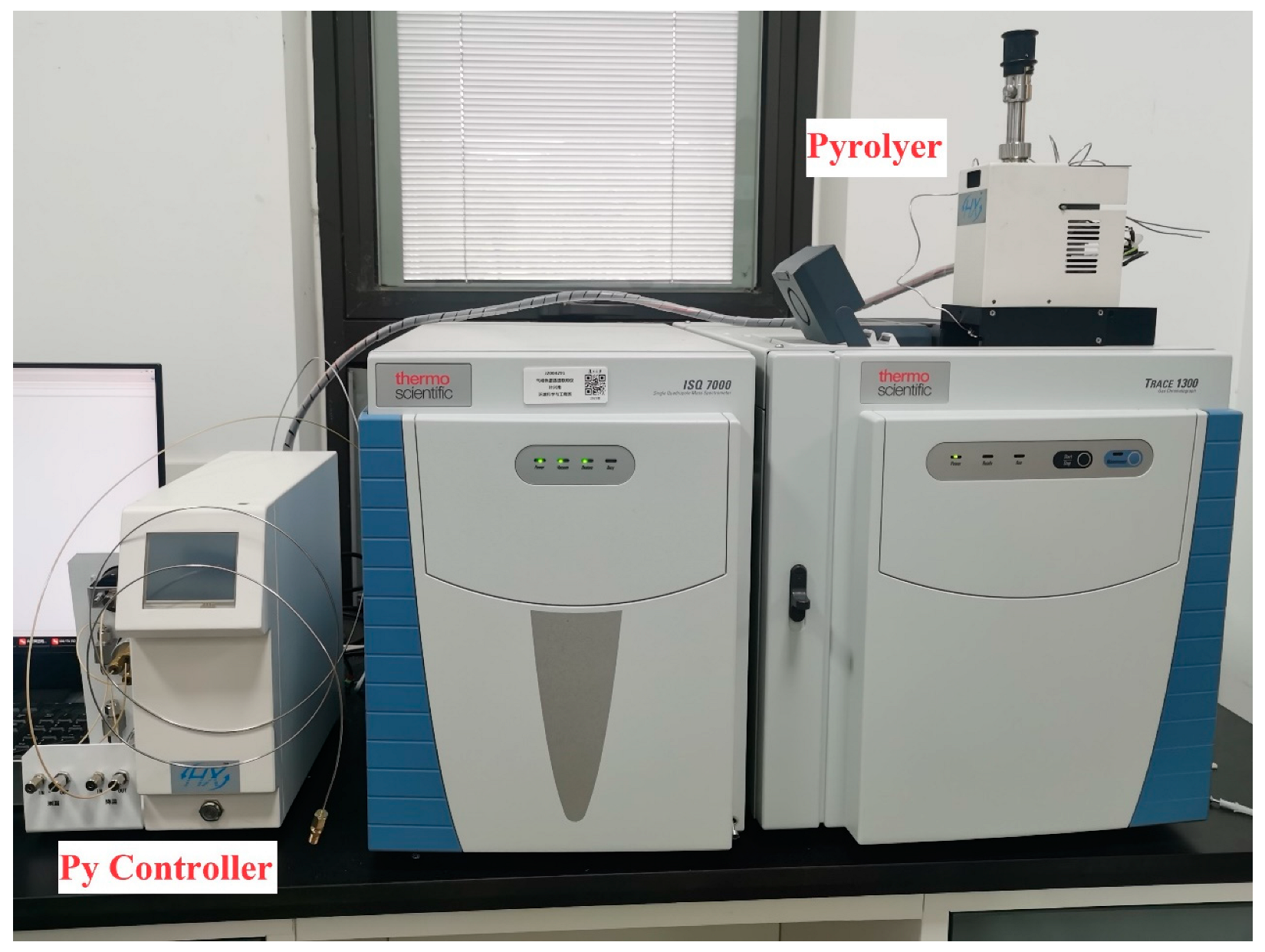
2.4. Py-GC/MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
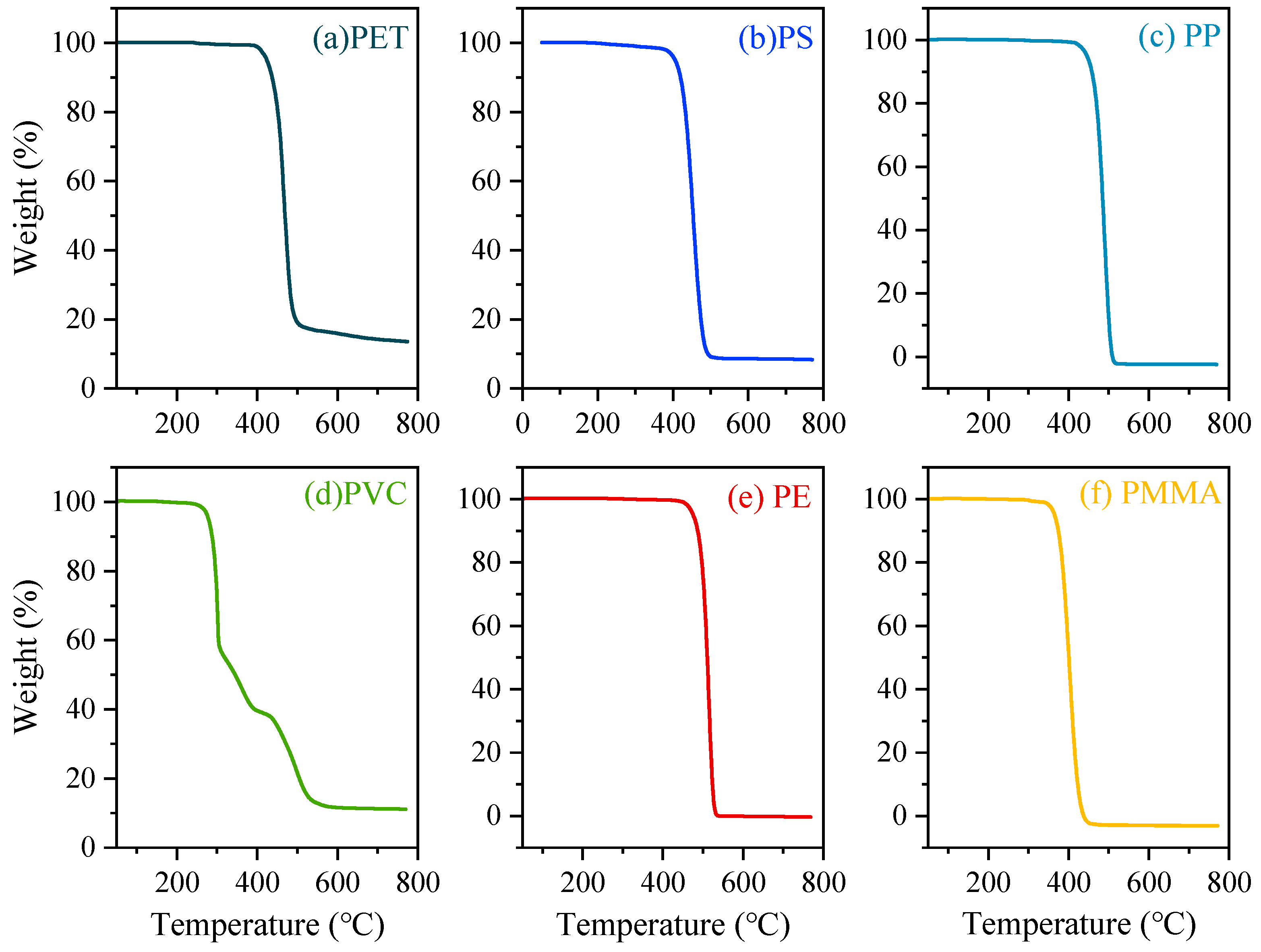
3.1. TGA Curves of Typical Microplastics
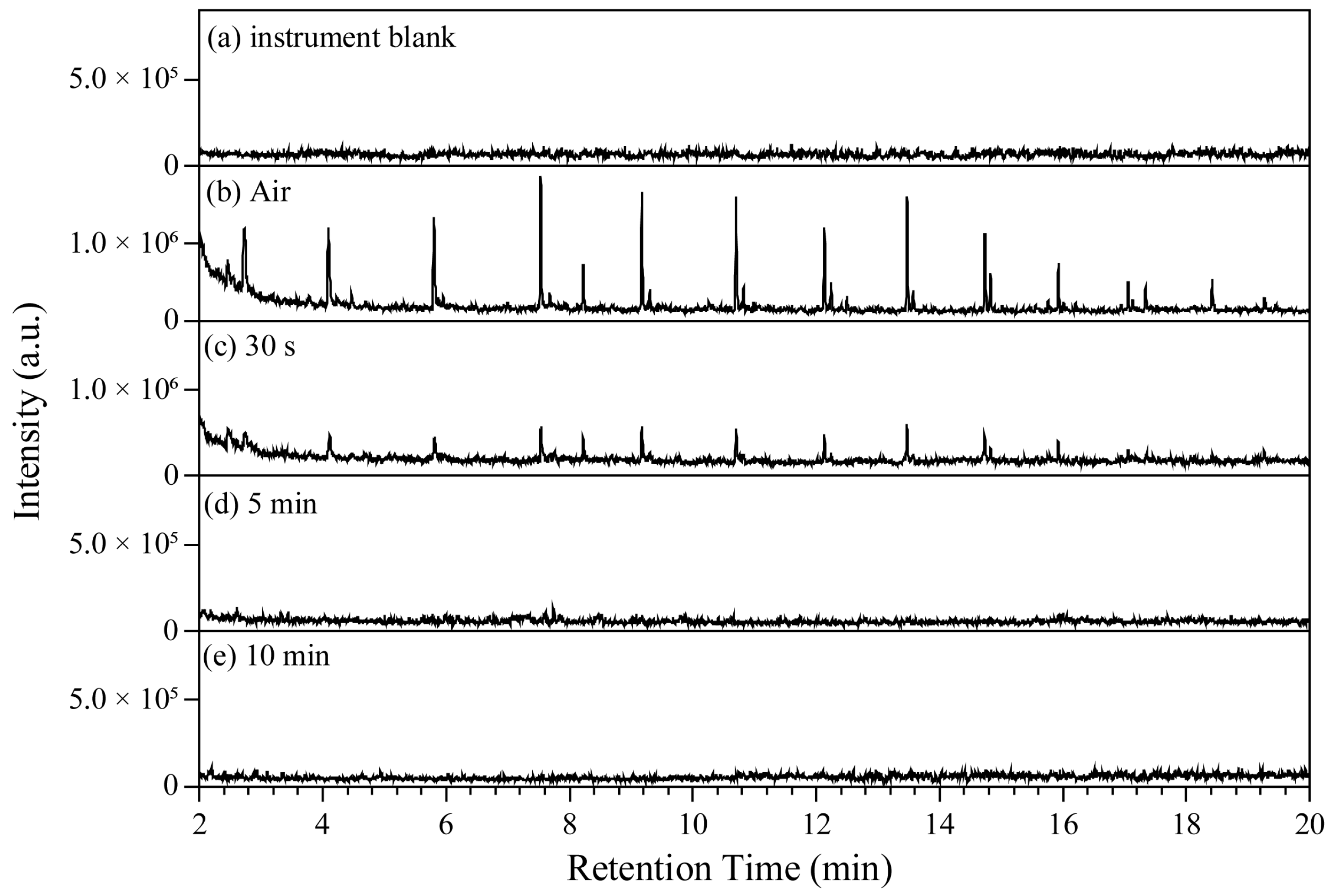
3.2. Interference from Injection Air
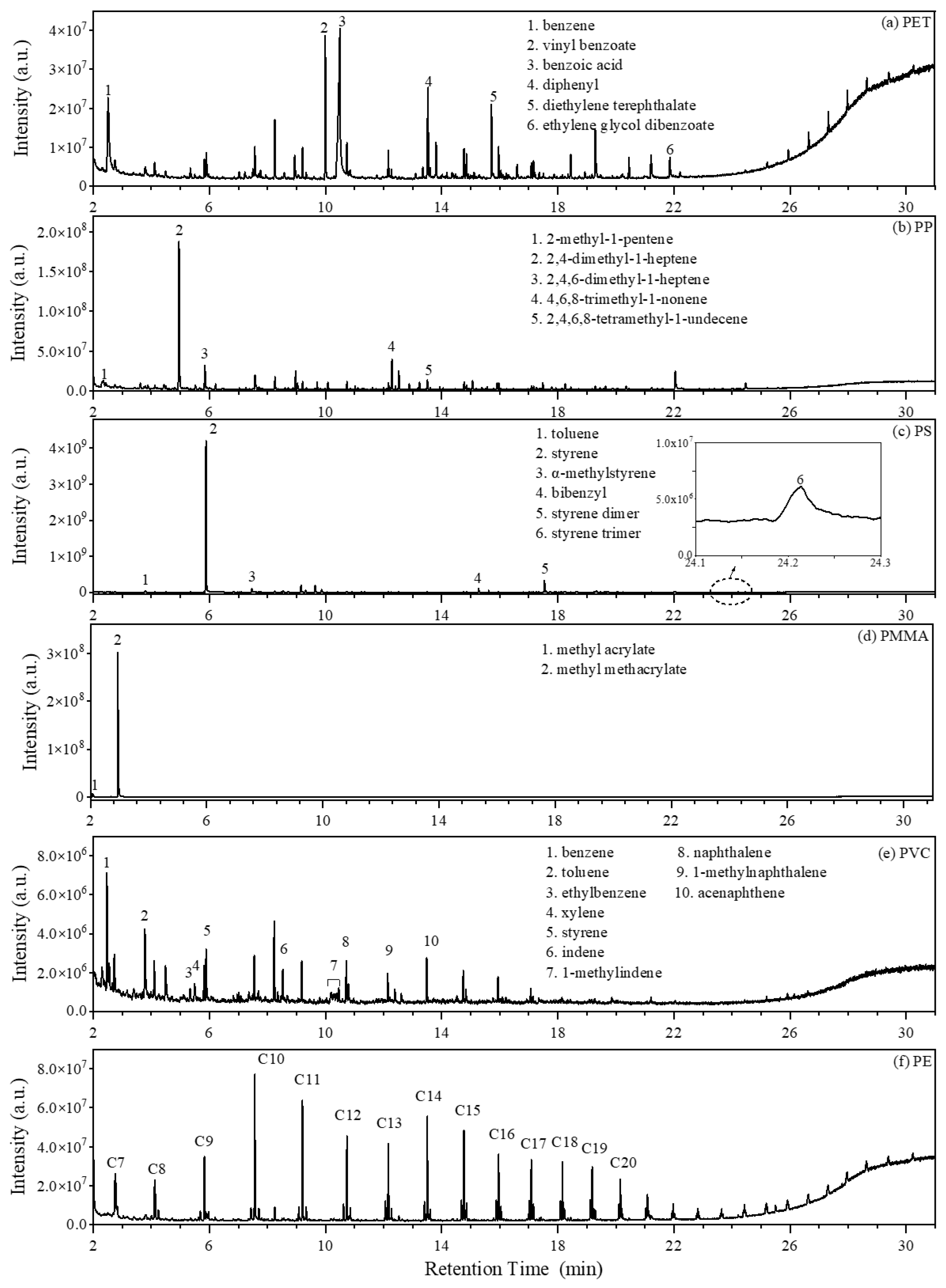
3.3. Py-GC/MS Chromatograms of Microplastic Standards
3.4. Identification of Quantitative References
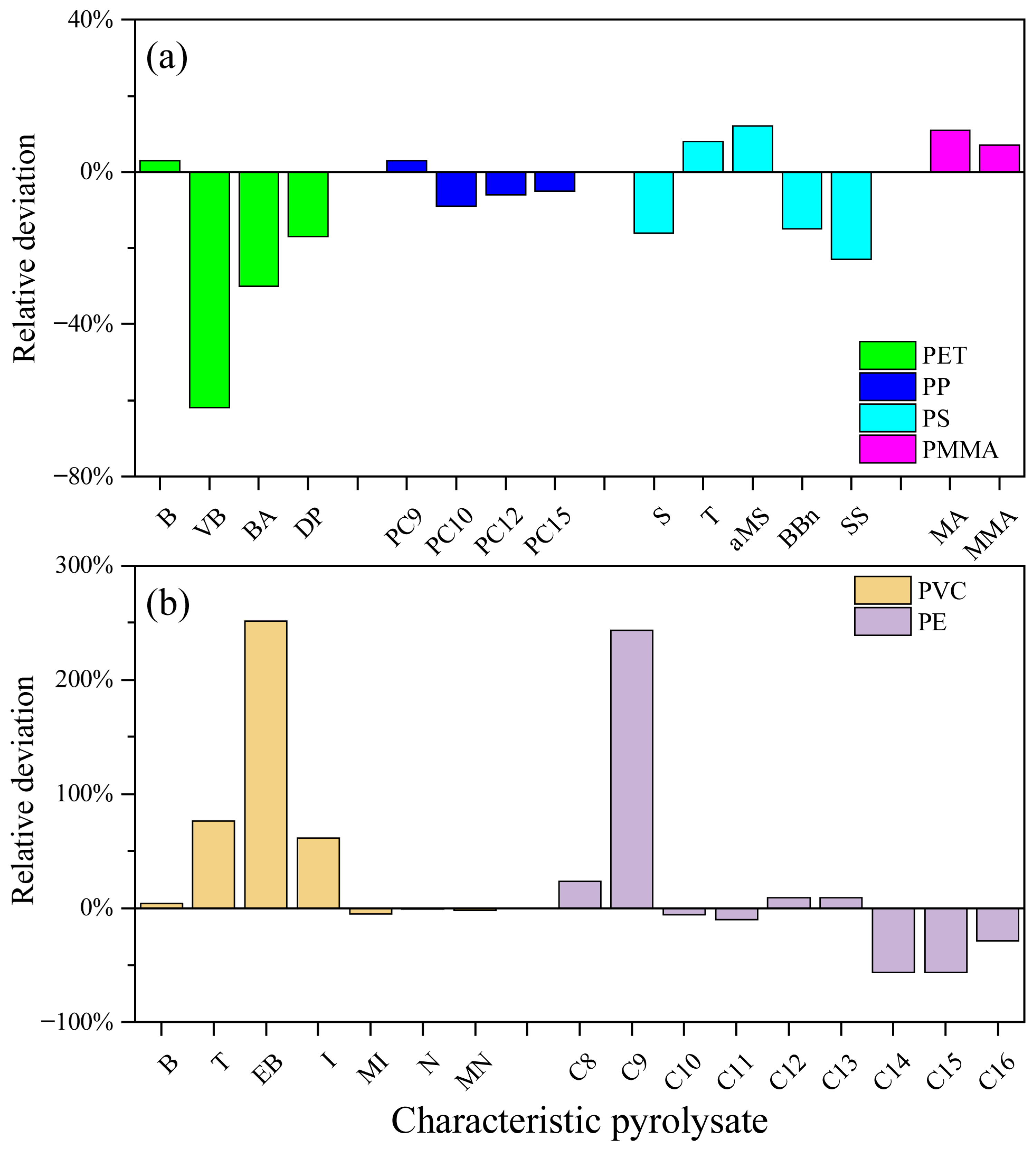
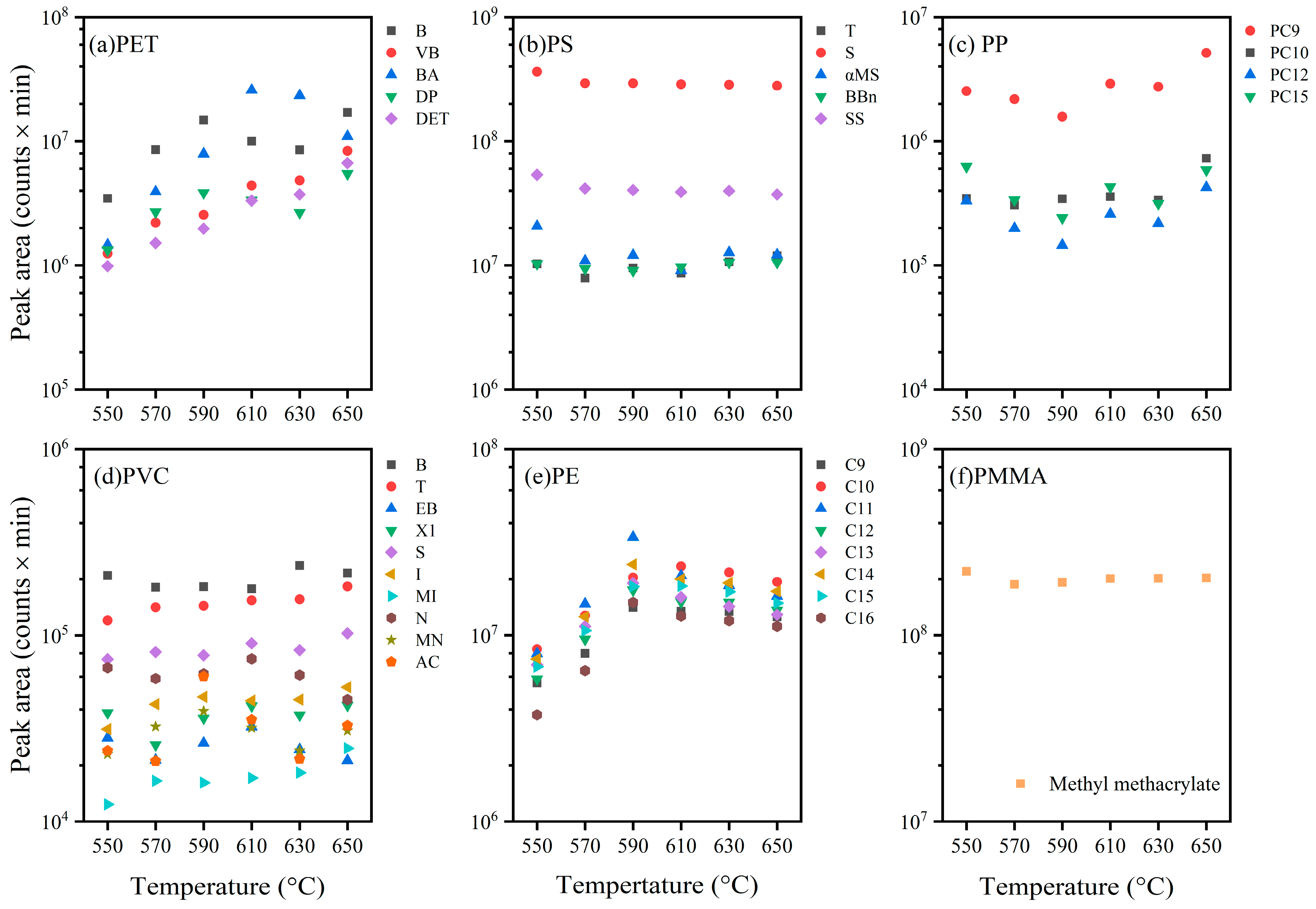
3.5. Response Intensities Depending on Pyrolysis Temperature
3.6. Optimizations of Py-GC/MS Procedure
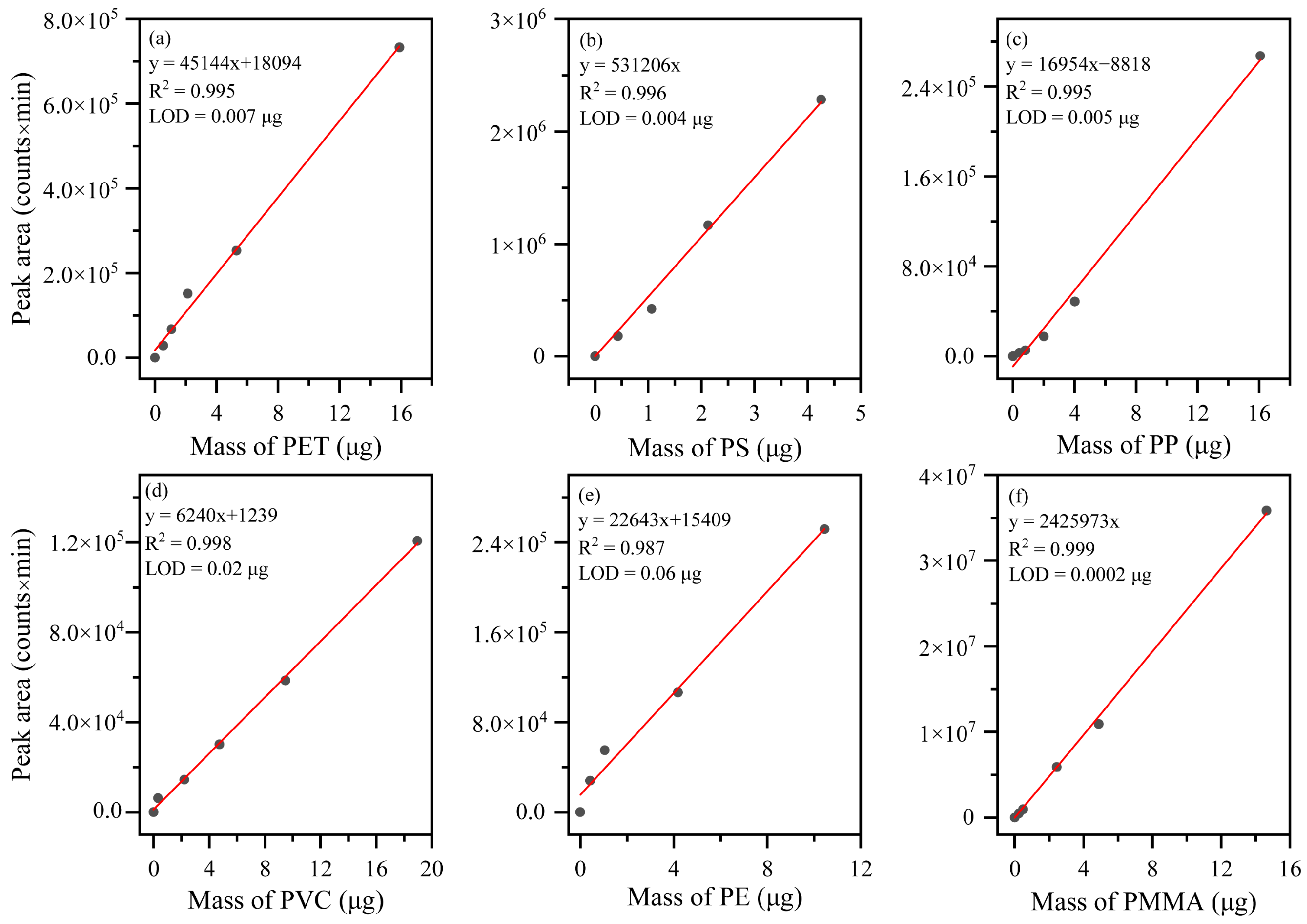
3.6.1. Calibration Curves
3.6.2. Method Repeatability
3.6.3. Validations of the Domestic Py-GC/MS Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lebreton, L.; Andrady, A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal. Palgrave Commun. 2019, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Jiménez, P.D.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, E.; Minor, E.C.; Schreiner, K. Microplastic Abundance and Composition in Western Lake Superior As Determined via Microscopy, Pyr-GC/MS, and FTIR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.F.; Jiang, F.H.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Sun, C.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fu, L.; Ding, N.X.; He, C.F. Microplastics in the Coral Reef Systems from Xisha Islands of South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8036–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Salmond, J.A.; Dirks, K.N.; Cabedo Sanz, P.; Miskelly, G.M.; Rindelaub, J.D. Evidence and Mass Quantification of Atmospheric Microplastics in a Coastal New Zealand City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17556–17568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, T.; Xu, P.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Jing, S.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Song, Z.; Xie, L.F.; Shang, X.A.; Fu, H.B.; Yang, X.D.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, M.H.; et al. Quantification and Characterization of Fine Plastic Particles as Considerable Components in Atmospheric Fine Particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4691–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments and organisms of the Western Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botterell, Z.L.R.; Bergmann, M.; Hildebrandt, N.; Krumpen, T.; Steinke, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Lindeque, P.K. Microplastic ingestion in zooplankton from the Fram Strait in the Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Correction to Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Xia, J.F.; Li, S.J.; Lv, J.W.; Zhuge, A.X.; Tang, R.Q.; Wang, S.T.; Wang, K.C.; Chang, K.V.; Li, L.J. Airborne polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics induce nasal and lung microbial dysbiosis in mice. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.W.; Huang, D.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Jiang, G.Y.; Gao, A. Inhaled polystyrene microplastics impaired lung function through pulmonary flora/TLR4-mediated iron homeostasis imbalance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.H.; Zhang, W.B.; Tang, H.J.; Wang, P.J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Qiu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, R.; et al. Microplastics exposure causes the senescence of human lung epithelial cells and mouse lungs by inducing ROS signaling. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Ma, Y.; Lv, B.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dahlgren, R.; et al. Airborne microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments of a coastal city in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Fang, M.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Mu, Q.; Shi, C.; Lu, C.; Deng, H.; et al. Airborne Microplastic Concentrations in Five Megacities of Northern and Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12871–12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Ribeiro, G.; Galvao, L.D.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Okochi, H.; Tani, Y.; Niida, Y.; Tachibana, T.; Saigawa, K.; Katayama, K.; Moriguchi, S.; Kato, T.; Hayama, S. Airborne microplastics detected in the lungs of wild birds in Japan. Chemosphere 2023, 321, 138032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Bai, M.; He, Q.; Peng, Z.; Wang, L.; Dong, C.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z. A Novel Strategy to Directly Quantify Polyethylene Microplastics in PM2.5 Based on Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 3556–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainic, M.; Flores, J.M.; Pinkas, I.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Lombard, F.; Bourdin, G.; Gorsky, G.; Boss, E.; Rudich, Y.; Vardi, A.; et al. Airborne microplastic particles detected in the remote marine atmosphere. Commun. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gibson, C.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M.; Fang, C. Identification and visualisation of microplastics/nanoplastics by Raman imaging (i): Down to 100 nm. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, Y.; Barceló, D. Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in environmental analysis: Focus on organic matter and microplastics. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albignac, M.; Ghiglione, J.F.; Labrune, C.; ter Halle, A. Determination of the microplastic content in Mediterranean benthic macrofauna by pyrolysis-gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, A.; Oysæd, K.B.; Agustsson, T.; van Hoytema, N.; van Thiel, T.; Grati, F. First record of characterization, concentration and distribution of microplastics in coastal sediments of an urban fjord in south west Norway using a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Hensel, F.; Gomiero, A.; Iordachescu, L.; Vianello, A.; Wittgren, H.B.; Vollertsen, J. Drinking plastics?—Quantification and qualification of microplastics in drinking water distribution systems by μFTIR and Py-GCMS. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.Y.; Lai, Y.J.; Yu, S.J.; Li, Q.C.; Zhou, Q.X.; Liu, J.F. Quantitation of Atmospheric Suspended Polystyrene Nanoplastics by Active Sampling Prior to Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10754–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, M.E.; Lynch, J.M. Previous successes and untapped potential of pyrolysis-GC/MS for the analysis of plastic pollution. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 2873–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Insa, S.; Arxé, M.; Buttiglieri, G.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D. Analysis of microplastics in the environment: Identification and quantification of trace levels of common types of plastic polymers using pyrolysis-GC/MS. Methodsx 2023, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, H.; Takeda, H.; Kinoshita, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Takayanagi, T.; Teramae, N.; Pipkin, W.; Matsui, K.; Watanabe, A.; Watanabe, C. Direct analysis of airborne microplastics collected on quartz filters by pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 171, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goßmann, I.; Herzke, D.; Held, A.; Schulz, J.; Nikiforov, V.; Georgi, C.; Evangeliou, N.; Eckhardt, S.; Gerdts, G.; Wurl, O.; et al. Occurrence and backtracking of microplastic mass loads including tire wear particles in northern Atlantic air. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.H.; Ou, Q.; Jiao, M.; Liu, G.; van der Hoek, J.P. Identification and Quantification of Nanoplastics in Surface Waterand Groundwater by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-MassSpectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4988–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Wang, X.; Wright, S.L.; Samanipour, S.; Rauert, C.; Toapanta, T.Y.A.; Albarracin, R.; et al. Airborne emissions of microplastic fibres from domestic laundry dryers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasager, F.; Björgvinsdóttir, Þ.N.; Vinther, S.F.; Christofili, A.; Kjærgaard, E.R.; Petters, S.S.; Bilde, M.; Glasius, M. Development and validation of an analytical pyrolysis method for detection of airborne polystyrene nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1717, 464622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoris, E.; Gallo, G.; Rosso, B.; Piazza, R.; Corami, F.; Gambaro, A. Microplastics analysis: Can we carry out a polymeric characterisation of atmospheric aerosol using direct inlet Py-GC/MS? J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 170, 105903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, S.; Ohtani, H.; Watanabe, C. Pyrolysis-GC/MS Data Book of Synthetic Polymers: Pyrograms, Thermograms and MS of Pyrolyzates, 1st ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dibke, C.; Fischer, M.; Scholz-Böttcher, B.M. Microplastic Mass Concentrations and Distribution in German Bight Waters by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry/Thermochemolysis Reveal Potential Impact of Marine Coatings: Do Ships Leave Skid Marks? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, T.; Luo, X.; Han, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. TG/FTIR analysis on co-pyrolysis behavior of PE, PVC and PS. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoffo, E.D.; Ribeiro, F.; O’Brien, J.W.; O’Brien, S.; Tscharke, B.J.; Gallen, M.; Samanipour, S.; Mueller, J.F.; Thomas, K.V. Identification and quantification of selected plastics in biosolids by pressurized liquid extraction combined with double-shot pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, F.; Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Song, J.; Wang, W.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yan, J. Influence of interaction on accuracy of quantification of mixed microplastics using Py-GC/MS. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Ruj, B.; Sadhukhan, A.K.; Gupta, P. A TG-FTIR investigation on the co-pyrolysis of the waste HDPE, PP, PS and PET under high heating conditions. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.C.; Lai, Y.J.; Yu, S.J.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.X.; Dong, L.J.; Liu, X.; Yao, Z.W.; Liu, J.F. Sequential Isolation of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Environmental Waters by Membrane Filtration, Followed by Cloud-Point Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.X.; He, S.; Gao, Y.; Chi, H.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Li, Z.C.; Yan, B. Quantitative Analysis of Polystyrene and Poly(methyl methacrylate) Nanoplastics in Tissues of Aquatic Animals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Rauert, C.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Burrows, S.D.; Toapanta, T.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Quantification of selected microplastics in Australian urban road dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Boricaud, B.; Kazour, M.; Amara, R.; Cassone, A.-L.; Laurentie, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Soudant, P.; Dehaut, A.J.A. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6663–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, J. Thermal desorption single particle mass spectrometry of ambient aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Apparatus | Parameters | Settings |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolyzer | Pyrolysis temperature | 650 °C |
| Interface temperature | 320 °C | |
| Pyrolysis time | 5 s | |
| Gas Chromatograph | Carrier gas | Helium |
| Injection mode | Split | |
| Split ratio | 50:1 | |
| Injection temperature | 300 °C | |
| Column | TG-5SILMS (30 m, 0.25 mm I.D., 0.25 μm film thickness) | |
| Column flow | 1 mL min−1 | |
| Temperature program | ||
| Transfer line temperature | 280 °C | |
| Mass Spectrometer | Ionization energy | 70 eV |
| Ion source temperature | 280 °C | |
| Scan rate | 0.2 s | |
| Scan range | 39 to 650 m/z |
| Plastic | Characteristic Compound | Abbreviation | Indicator Ion (m/z) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | benzene | B | 30, 52, 74, 78, | 2.44 |
| vinyl benzoate | VB | 51, 77, 105, 148 | 9.99 | |
| benzoic acid | BA | 77, 105, 122 | 10.51 | |
| diphenyl | DP | 76, 131, 154 | 13.53 | |
| diethylene terephthalate | DET | 163, 194 | 15.71 | |
| ethylene glycol dibenzoate | EGD | 77, 105, 227 | 21.86 | |
| PP | 2-methyl-1-pentene | PC6 | 56, 69, 84 | 2.01 |
| 2,4-dimethyl-1-heptene | PC9 | 70, 83, 126 | 4.95 | |
| 2,4,6-trimethyl-1-heptene | PC10 | 70, 83, 111, 126 | 5.84 | |
| 4,6,8-trimethyl-1-nonene | PC12 | 97, 112, 125 | 12.29 | |
| 2, 4, 6, 8-tetramethyl-1-undecene | PC15 | 83, 111, 125 | 13.51 | |
| PS | toluene | T | 51, 65, 89, 91 | 3.76 |
| styrene | S | 98, 104 | 5.88 | |
| α-methylstyrene | αMS | 78, 103, 118 | 7.46 | |
| bibenzyl | BBz | 65, 91, 182 | 15.27 | |
| styrene dimer | SS | 91, 130, 193, 208 | 17.54 | |
| Styrene trimer | SSS | 91, 117, 194, 207, 312 | 24.21 | |
| PMMA | methyl acrylate | MA | 55, 85 | 2.06 |
| methyl methacrylate | MMA | 69, 89, 100 | 2.93 | |
| PVC | benzene | B | 39, 52, 74, 78 | 2.44 |
| toluene | T | 51, 65, 89, 91 | 3.76 | |
| ethylbenzene | EB | 77, 91, 106 | 5.34 | |
| xylene | X1 | 77, 91, 106 | 5.60 | |
| styrene | S | 78, 104 | 5.88 | |
| indene | I | 116, 119 | 8.54 | |
| 1-methylindene | MI | 51, 64, 77, 91, 115, 130, 132 | 10.23 | |
| naphthalene | N | 77, 102, 116, 128, 146 | 10.81 | |
| 1-methylnaphthalene | MN | 91, 115, 129, 142, 158 | 12.63 | |
| acenaphthene | AC | 76, 102, 128, 143, 154 | 13.96 | |
| PE | 1-heptene | C7 | 70, 83, 98 | 2.76 |
| 1-octene | C8 | 70, 83, 112 | 4.12 | |
| 1-nonene | C9 | 83, 97, 111 | 5.83 | |
| 1-decene | C10 | 83, 97, 111, 140 | 7.56 | |
| 1-undecene | C11 | 83, 97, 111, 126, 152 | 9.22 | |
| 1-dodecene | C12 | 83, 97, 111, 125 | 10.74 | |
| 1-tridecene | C13 | 83, 97, 111, 125 | 12.16 | |
| 1-tetradecene | C14 | 83, 97, 55, 69, 111, 125, 140 | 13.51 | |
| 1-pentadecene | C15 | 55, 69, 83, 97, 111 | 14.76 | |
| 1-cetene | C16 | 55, 69, 83 | 15.96 | |
| 1-heptadecene | C17 | 55, 69, 83 | 17.09 | |
| 1-octadecene | C18 | 83, 97, 111, 246 | 18.15 | |
| 1-nonadecene | C19 | 83, 97, 111, 246 | 19.18 | |
| 1-eicosene | C20 | 83, 97, 111, 207 | 20.13 |
| Date | MS Peak Area (Counts × min) | TIC Peak Area (Counts × min) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 1,395,200 | 7,406,631 |
| 3rd | 1,267,058 | 6,744,248 |
| 4th | 1,093,711 | 5,886,701 |
| 7th | 1,117,202 | 6,028,831 |
| 8th | 1,112,876 | 5,994,636 |
| 15th | 1,704,181 | 9,236,345 |
| RSD (%) (8 Days) | 9.76 | 9.08 |
| RSD (%) (15 Days) | 18.55 | 18.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Fu, B.; Che, J.; Ye, X. Simultaneous Determination of Six Common Microplastics by a Domestic Py-GC/MS. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040476
Zhou Y, Fu B, Che J, Ye X. Simultaneous Determination of Six Common Microplastics by a Domestic Py-GC/MS. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040476
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuanqiao, Bingyue Fu, Jinshui Che, and Xingnan Ye. 2025. "Simultaneous Determination of Six Common Microplastics by a Domestic Py-GC/MS" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040476
APA StyleZhou, Y., Fu, B., Che, J., & Ye, X. (2025). Simultaneous Determination of Six Common Microplastics by a Domestic Py-GC/MS. Atmosphere, 16(4), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040476






