An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review Articles about Measuring Particulate Matter
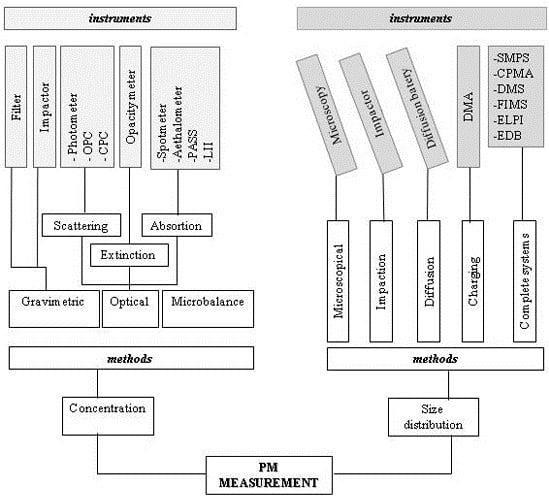
3. Instruments for Measuring Particulate Matter
3.1. Concentration Measurement Methods

3.1.1. Gravimetric Method
3.1.2. Optical Methods
3.1.3. Microbalance Methods
3.2. Size Distribution Measurement Methods
3.2.1. Microscopy
3.2.2. Impactor
3.2.3. Diffusion Battery (EDB)
3.2.4. Mobility Analyzer
3.2.5. Centrifugal Measurement of Particle Mass
3.2.6. Differential Mobility Spectrometers (DMS)
3.2.7. Fast Integrated Mobility Spectrometer (FIMS)
3.2.8. Electrical Low Pressure Impactor (ELPI)
3.2.9. Aerodynamic Sizers
4. Discussion
| Instrument | Real Time | Dilution Required | Detection Limit | Size Range (nm) | A (%) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filter | No | Yes | 10 μg/m3 | D | 5 | Simple; reliable; chemical analysis | Lots of work |
| Scattering | Yes | No (hot) | 10 μg/m3 | >50 | 30 | - | Measuring large PM |
| Spotmeter | No | No (hot) | 25 μg/m3 | All | 15 | Measuring BC | High response time |
| PASS; LII | Yes | Yes, No | 5 μg/m3 | >10 | 10 | Measuring BC | Necessitate calibration |
| Opacity | Yes | No (hot) | 0.1% opacity | >50 | 20 | - | Depends of several factors |
| TEOM | Yes | Depends sampling site | - | D | - | Agrees well with filter samples | If concentration is high, filter has to be changed |
| DLPI | No | No | - | 30–10,000 | - | Large size ranges | Not suitable for smaller particles |
| SMPS | No | Yes | 100 /cm3 | 3–700 | 15 | Very small particles | Not suitable for larger particles |
| FMPS | Yes | Yes | 1000 /cm3 | 5–700 | 25 | Fast; Indicates changes in process well | More inaccurate than SMPS |
| ELPI | Yes | Yes | 1000 /cm3 | 10–10,000 | 25 | Robust and large size range | Wide channels plates may affect the result |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demirbas, A. Combustion characteristics of different biomass fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2004, 30, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Jones, J.M.; Ma, L.; Pourkashanian, M. Pollutants from the combustion of solid biomass fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Pandithurai, G.; Attri, S.D.; Srivastava, A.K.; Soni, V.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Anil Kumar, V.; Srivastava, M.K. Aerosol optical properties and their relationship with meteorological parameters during wintertime in Delhi, India. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipal, A.S.; Gursumeeran Satsangi, P. Study of carbonaceous species, morphology and sources of fine (PM2.5) and coarse (PM10) particles along with their climatic nature in India. Atmos. Res. 2015, 154, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Z. An Investigation of Aerosol Scattering and Absorption Properties in Wuhan, Central China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Tao, R. Variations in PM10, PM2.5 and PM1.0 in an Urban Area of the Sichuan Basin and Their Relation to Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Evolving from Studies of Ultrafine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Brugha, R.E.; Jacobs, L.; Grigg, J.; Nawrot, T.S.; Nemery, B. Carbon loading in airway macrophages as a biomarker for individual exposure to particulate matter air pollution—A critical review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74C, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafael, S.; Tarelho, L.; Monteiro, A.; Sá, E.; Miranda, A.I.; Borrego, C.; Lopes, M. Impact of forest biomass residues to the energy supply chain on regional air quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Dockery, D.W.; Muller, J.E.; Mittleman, M.A. Increased particulate air pollution and the triggering of myocardial infarction. Circulation 2001, 103, 2810–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A.; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M. A.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, B.A.; Brook, R.; Pope, C.A., III. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2015, 40, 207–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utell, M.J.; Frampton, M.W. Acute health effects of ambient air pollution: the ultrafine particle hypothesis. J. Aerosol Med. 2000, 13, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissari, J.; Lyyränen, J.; Hytönen, K.; Sippula, O.; Tapper, U.; Frey, A.; Saarnio, K.; Pennanen, A.S.; Hillamo, R.; Salonen, R.O.; et al. Fine particle and gaseous emissions from normal and smouldering wood combustion in a conventional masonry heater. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7862–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasny, F.; Madl, P.; Hofmann, W. Correlation of air quality data to ultrafine particles (UFP) concentration and size distribution in ambient air. Atmosphere 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Li, Q.; Cocker, D.; Weise, D.; Miller, A.; Shrivastava, M.; Miller, J.W.; Mahalingam, S.; Princevac, M.; Jung, H. Particle size distributions from laboratory-scale biomass fires using fast response instruments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8065–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.A.M.; Carvalho, J.A.; Neto, T.G.S.; Anselmo, E.; Lima, B.A.; Kura, L.T.U.; Santos, J.C. Real-time sampling of particulate matter smaller than 2.5 μm from Amazon forest biomass combustion. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, D.D.A.; Longo, K.M.; Neto, T.G.S.; Santos, J.C.; Freitas, S.R.; Rudorff, B.F.T.; Cortez, E.V.; Anselmo, E.; Carvalho, J.A. Pre-Harvest Sugarcane Burning: Determination of Emission Factors through Laboratory Measurements. Atmosphere 2012, 3, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Sano, I.; Mukai, S.; Holben, B. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Atmospheric Aerosol in Osaka. Atmosphere 2013, 4, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskinen, J.; Tissari, J.; Uski, O.; Virén, A.; Torvela, T.; Kaivosoja, T.; Lamberg, H.; Nuutinen, I.; Kettunen, T.; Joutsensaari, J.; et al. Fine particle emissions in three different combustion conditions of a wood chip-fired appliance—Particulate physico-chemical properties and induced cell death. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumer, T.; Czasch, C.; Klippel, N.; Johansson, L.; Tullin, C. Particulate emissions from biomass combustion in IEA countries. In Proceeding of the 16th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Zurich, Switzerland, 2–6 June 2008; p. 40.
- Obaidullah, M.; Bram, S.; Verma, V.; de Ruyck, J. A review on particle emissions from small scale biomass combustion. Int. J. Renew. Eergy Res. 2012, 2, 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, W.E.; Chow, J.C.; Claiborn, C.; Fusheng, W.; Engelbrecht, J.; Watson, J.G. Monitoring of particulate matter outdoors. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 1009–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Maricq, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dardiotis, C.; Wang, X.; Axmann, H.; Bergmann, A.; Schindler, W. Review of motor vehicle particulate emissions sampling and measurement: From smoke and filter mass to particle number. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 67, 48–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wark, K.; Warner, C.F.; Davis, W.T. Air Pollution: Its Origin and Control, 3rd ed.; Addison-Wesley-Longman: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J.H. Aerosol Sampling: Science, Standards, Instrumentation and Applications; JohnWiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.; Colbeck, I. Physical and chemical properties of atmospheric aerosols. In Environmental Chemistry of Aerosols, 3rd ed.; Colbeck, I., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, P.; Baron, P.A.; Willeke, K. Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications, 3rd ed.; JohnWiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, Z.; Campanella, L.; Gray, C.; Al Masud, A.; Marter-Kenyon, J.; Pennise, D.; Charron, D.; Zuzhang, X. Measurement and modeling of indoor air pollution in rural households with multiple stove interventions in Yunnan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, G.F.; Zanetta, D.M.T.; Arbex, M.A.; Braga, A.L.; Pereira, L.A.A.; de Marchi, M.R.R.; de Melo Loureiro, A.P.; Marcourakis, T.; Sugauara, L.E.; Gattás, G.J.F.; et al. Burnt sugarcane harvesting: particulate matter exposure and the effects on lung function, oxidative stress, and urinary 1-hydroxypyrene. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Bell, M.L. A Comparison of Particulate Matter from Biomass-Burning Rural and Non-Biomass-Burning Urban Households in Northeastern China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torvela, T.; Tissari, J.; Sippula, O.; Kaivosoja, T.; Leskinen, J.; Virén, A.; Lähde, A.; Jokiniemi, J. Effect of wood combustion conditions on the morphology of freshly emitted fine particles. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Lovejoy, E.R.; Baynard, T.; Pettersson, A.; Ravishankara, A.R. Aerosol Absorption Measurement Using Photoacoustic Spectroscopy: Sensitivity, Calibration, and Uncertainty Developments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Ström, J.; Johansson, C. Carbon content of atmospheric aerosols in a residential area during the wood combustion season in Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6974–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, R.; Shaddix, C. Laser-induced incandescence. In Applied Combustion Diagnostics; Kohse-Höinghaus, K., Jeffries, J., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 252–286. [Google Scholar]
- Mellon, D.; King, S.J.; Kim, J.; Reid, J.P.; Orr-Ewing, A.J. Measurements of extinction by aerosol particles in the near-infrared using continuous wave cavity ring-down spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 115, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, A.; Lovejoy, E.R.; Brock, C.A.; Brown, S.S.; Ravishankara, A.R. Measurement of aerosol optical extinction at with pulsed cavity ring down spectroscopy. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, E. Performance, emissions, combustion and injection characteristics of a diesel engine fuelled with canola oil–hazelnut soapstock biodiesel mixture. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsasser, M.; Crippa, M.; Orasche, J.; Decarlo, P.F.; Oster, M.; Pitz, M.; Cyrys, J.; Gustafson, T.L.; Pettersson, J.B.C.; Zimmermann, R. Organic molecular markers and signature from wood combustion particles in winter ambient aerosols : Aerosol mass spectrometer (AMS) and high time-resolved GC-MS measurements in Augsburg, Germany. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 6113–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wentzel, M.; Gorzawski, H.; Naumann, K.-H.; Saathoff, H.; Weinbruch, S. Transmission electron microscopical and aerosol dynamical characterization of soot aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1347–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, C.; Rao, G.U.M. Emission Factors of Carbon Monoxide and Size-Resolved Aerosols from Biofuel Combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierz, M.; Houle, C.; Steigmeier, P.; Burtscher, H. Design, Calibration, and Field Performance of a Miniature Diffusion Size Classifier. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.M.M.; Park, S.; Kim, J.S.; Park, K. Volatility and mixing states of ultrafine particles from biomass burning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Symonds, J.P.R.; Olfert, J.S. Mass–Mobility Measurements Using a Centrifugal Particle Mass Analyzer and Differential Mobility Spectrometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilli, K.A.; Poulain, L.; Held, A.; Nowak, A.; Birmili, W.; Wiedensohler, A. Hygroscopic properties of the Paris urban aerosol in relation to its chemical composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfert, J.S.; Kulkarni, P.; Wang, J. Measuring aerosol size distributions with the fast integrated mobility spectrometer. J. Aerosol Sci. 2008, 39, 940–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudray, N.; Dieterlen, A.; Roth, E.; Trouvé, G. Density measurement of fine aerosol fractions from wood combustion sources using ELPI distributions and image processing techniques. Fuel 2009, 88, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, J.T.; Leard, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Davidovits, P.; Smith, K.A.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R. Development of an Aerosol Mass Spectrometer for Size and Composition Analysis of Submicron Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.S.; de Carvalho, J.A.; Costa, M.A.M.; Neto, T.G.S.; Dellani, R.; Leite, L.H.S. Comparative study for hardwood and softwood forest biomass: chemical characterization, combustion phases and gas and particulate matter emissions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, S.S.; De Carvalho, J.A., Jr.; Costa, M.A.M.; Pinheiro, C. An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1327-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6091327
Amaral SS, De Carvalho JA Jr., Costa MAM, Pinheiro C. An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(9):1327-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6091327
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Simone Simões, João Andrade De Carvalho, Jr., Maria Angélica Martins Costa, and Cleverson Pinheiro. 2015. "An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments" Atmosphere 6, no. 9: 1327-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6091327
APA StyleAmaral, S. S., De Carvalho, J. A., Jr., Costa, M. A. M., & Pinheiro, C. (2015). An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments. Atmosphere, 6(9), 1327-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6091327