Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive methodology to model and determine the annual sediment balance of a complex system of interconnected reservoirs, based on the detailed interpretation of a multi-decadal data series of reservoir management and modelling of sediment fluxes. This methodology is applied to the reservoirs of Oberaar, Grimsel, Räterichsboden, and Trift, which are located in the Swiss Alps. Additionally, the effects of climate warming on the annual sediment yield are investigated. Modelling results show that at present, the hydropower cascade formed by Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden retains about 92% of the annual sediment yield, of which only the finest fraction leaves the system and enters the river network. Very fine sediments (d < 10 μm) account for 28% of the total sedimentation rate and in the case of Oberaar, it can reach up to 46% of the total sedimentation rate. Under a climate warming scenario, both sediment yield and runoff are expected to increase in terms of the annual average throughout the XXIst century, which will likely lead to greater annual inputs of sediments to the reservoirs. This, in turn, will lead to a higher sedimentation rate and suspended sediment concentration in the reservoirs, unless active management of the sediment fluxes is implemented.
1. Introduction
Reservoir sedimentation is at present a major concern in the operational management of dams, as the volume of sediments deposited annually in water reservoirs reduces their storage capacity and may even threaten the operability of dams and their sustainability [1]. At a global scale, the annual loss of capacity was quantified as being between 0.5% to 1% of the total worldwide storage capacity [2,3]. Namely, in Asia, 80% of the available capacity for hydropower production will be lost by 2035 [4]. Moreover, the impoundment of sediments by dams often modifies the sediment balance of the river catchment [5,6,7,8,9], which may result in negative impacts on the riverine environment and coastal areas.
In Alpine rivers where the catchments are partially covered by glaciers, the sediment load supplied by small creeks to the rivers is characterized by a high concentration of suspended sediments [7,10,11,12,13], mainly in the spring and summer time. When these fine sediments enter a reservoir, they plunge beneath the clear water surface owing to their higher density, thereby forming a turbidity current that progresses downstream to the dam [1,14,15]. The presence of fine sediments in the vicinity of the dam may result in partial or total blockages of the water release structures, and in turbine abrasion if they are absorbed by the power intakes [16]. In the case of reservoirs of pumped-storage schemes, fine sediment can move back and forth from one reservoir to the other during the different operation cycles [7,11,17]. The first step to deal with the negative effects related to sediment settling in reservoirs is to characterize the sediment balance of the catchment associated with each reservoir. However, the follow-up of sedimentation processes in reservoirs is a long-haul activity that requires several decades of follow-up, data acquisition, and storage, before funded conclusions can be drawn. To document event-based processes like turbidity currents, the timely mobilization of monitoring resources is paramount, leading to high stand-by costs over several seasons. Therefore, the monitoring of sediment deposits is still done intermittently and is geographically scattered. The present paper aims to provide a methodology for long-term assessment of the sediment balance in Alpine reservoirs by characterizing the in- and out-fluxes of sediments to each reservoir of the system analyzed. The method is developed and tested in a cascade of three hydropower reservoirs in the Swiss Alps, taking advantage of the availability and quality of long-term data records shared by the operator. Beyond previous studies on Alpine reservoirs, such as those of Bonalumi et al. (2011) and Anselmetti et al. (2007) and [7,11], the methodology proposed in this study allows the characterization of all sediment in- and out-fluxes for each reservoir considering all sediment fractions. The validation of the methodology using data from past decades allows us to estimate what may happen in the future considering climate change. Available data of future precipitation and glacier coverage, based on global climate change scenarios scaled down to the specific river basin, are used to anticipate changes in sediment yield and then in sediment budget. Replication of the procedure for analogous cases, with variable degrees of data availability and quality, is a collective challenge for the decades to come, as well as continuous refinement of the approach with further insights into the governing physical processes. Therefore, the objectives of the present paper are to:
- Characterize the present sediment balance of a complex hydropower cascade, by quantifying and modelling the annual sediment inputs and outputs and determining the sedimentation rate of each reservoir.
- Estimate the effects of climate warming on the sediment dynamics of the catchments and assess the future evolution of sediment trapping in the reservoirs by means of the previously established model.
2. Case Study
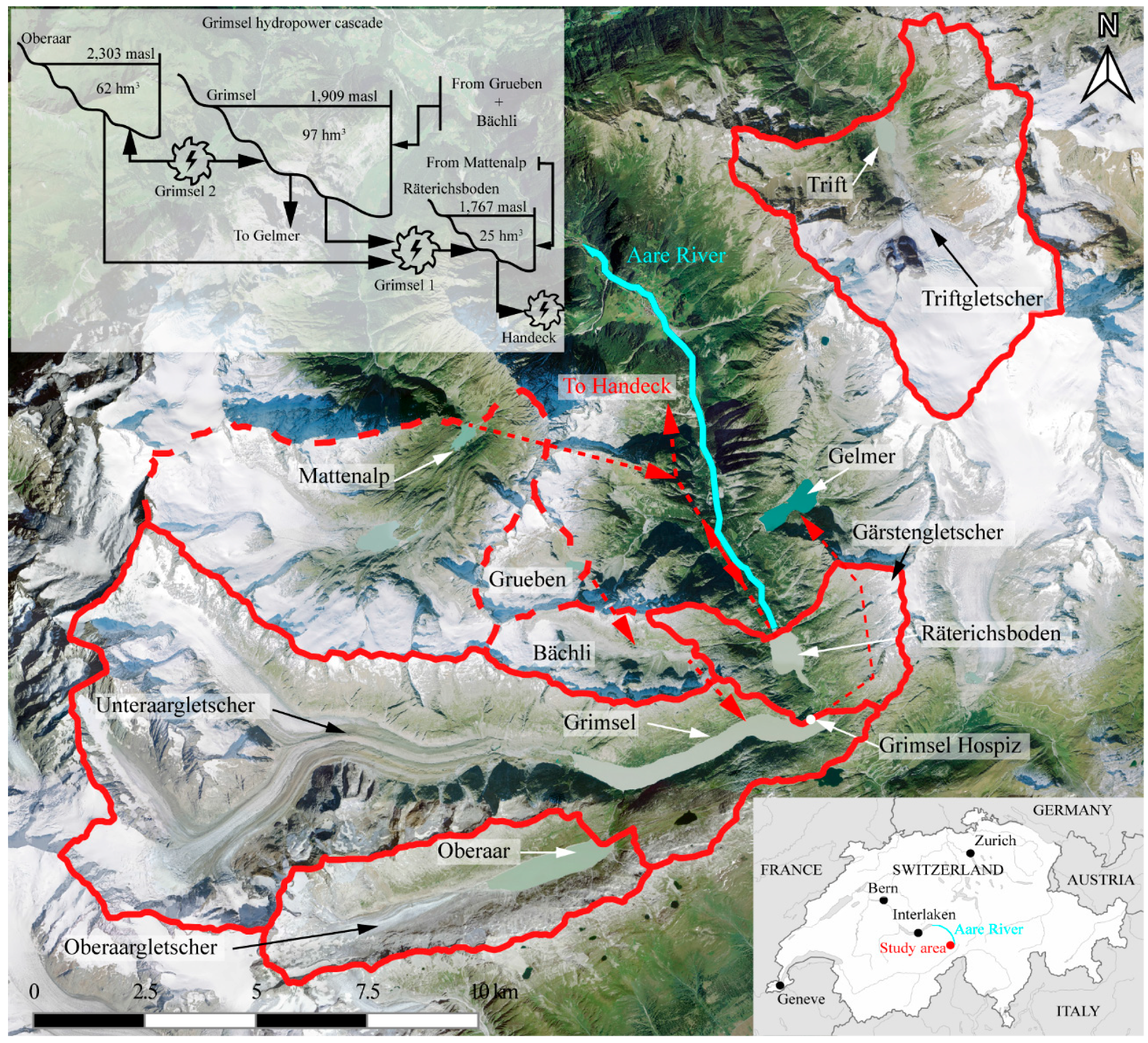
The present study focuses on a hydropower system formed by three hydropower reservoirs in cascade (Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden), the so-called Grimsel hydropower cascade. In addition, the sediment balance of Lake Trift is analyzed. This lake is a periglacial reservoir planned to be built in the upcoming years for hydropower purposes. These reservoirs are located in the Swiss Alps, in the south-eastern part of the Canton of Bern. Figure 1 depicts the analyzed reservoirs with their respective catchments, together with an operating diagram of the Grimsel hydropower cascade. Table 1 contains the values of the main dimensions of the catchments and reservoirs analyzed in this study. The catchments of Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden reservoirs are part of the Aare River’s catchment, upstream of the Lake Brienz (Figure 1). The Trift reservoir is planned to be located on the catchment of the Gadmerwasser River (not shown), which is a tributary of the Aare River. The catchment of the Grimsel hydropower cascade has a surface of 108.31 km2, of which 19.24 km2 correspond to the catchment of the Oberaar dam, 77.56 km2 correspond to the catchment of the Grimsel dam, and 11.51 km2 correspond to the catchment of the Räterichsboden dam (Table 1). Adjacent to the catchments of the Grimsel and Räterichsboden dams, there are three catchments diverting flow to the reservoirs of Grimsel and Räterichsboden, by means of diversion intakes and tunnels (Figure 1). These catchments are those of Mattenalp, with a surface of 36.0 km2; Bächli, with a surface of 7.73 km2; and Grueben, with a surface of 4.39 km2 (Figure 1). In the catchments of the Grimsel hydropower cascade (Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden), the altitude varies from 1650 m a.s.l. to 4262 m a.s.l., with a mean altitude of 2729 m a.s.l. for Oberaar, 2669 m a.s.l. for Grimsel, and 2426 m a.s.l. for Räterichsboden (Table 1). The catchment of Trift has a surface of 33.52 km2 and the altitude ranges between 1652 m a.s.l. and 3486 m a.s.l., resulting in a mean altitude of 2667 m a.s.l. (Table 1). The catchments analyzed, apart from that of Räterichsboden, are partially covered by glaciers (the main ones being Oberaargletscher, Unteraargletscher, and Triftgletscher in Figure 1). The percentage of glaciated area in 2012 was approximately 29% for Oberaar, 35% for Grimsel, and 46% for Trift (Table 1). In the case of Räterichsboden, the influence of the glacier was neglected as the area covered by the glacier Gärstengletscher (Figure 1) in 2000 accounted for less than 5% of the catchment area [18]. For the adjacent catchments, the glaciated area was 52% for Mattenalp, 57% for Grueben, and 35% for Bächli [18]. Regarding the reservoirs, Oberaar has a capacity of 62 hm3 and a surface of 1.60 km2 at its maximum supply level (msl) (2303 m a.s.l.), Grimsel has a capacity of 97 hm3 and a surface of 2.82 km2 at 1909 m a.s.l., Räterichsboden has a capacity of 25 hm3 and a surface of 0.65 km2 at 1767 m a.s.l., and Trift is planned to store 85 hm3 and to cover a surface of 1.10 km2 at 1767 m a.s.l. (Table 1). Precipitation records at the Grimsel Hospiz gauging station, located at an altitude of 1979 m a.s.l. (Figure 1), reveal an annual average precipitation of 2000 mm/year, of which 70% is snow and the rest (30%) is observed as rain from June to September.
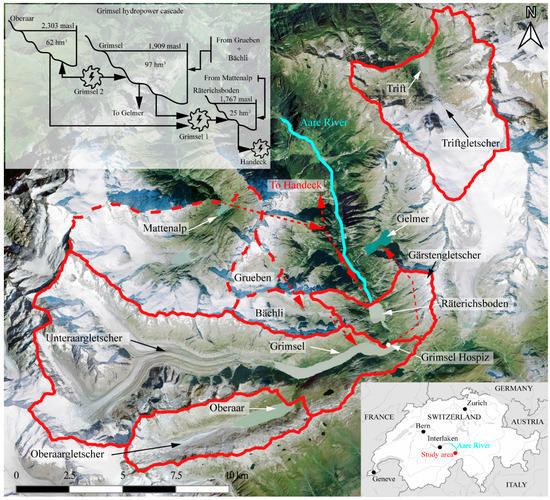
Figure 1.
Aerial view of the catchments analyzed and operating diagram of the Grimsel hydropower cascade. (Background image: www.swisstopo.ch).

Table 1.
Topographic data and main dimensions of the catchments and reservoirs analyzed in this study.
The Grimsel hydropower cascade is part of a complex hydropower system operated by Kraftwerke Oberhasli AG (KWO). In this system, Oberaar and Grimsel reservoirs are connected by the pumped-storage plant Grimsel 2, allowing the transfer of water between these two reservoirs (Figure 1). Oberaar and Grimsel supply water to the Räterichsboden reservoir by means of the hydropower plant Grimsel 1 (Figure 1). The Räterichsboden reservoir supplies water to the hydropower plant Handeck, and receives water diverted from the catchment of Mattenalp (Figure 1). In addition, Grimsel provides water to Gelmer and receives water diverted from the Bächli catchment, which in turn receives water from the Grueben catchment (Figure 1). The dams existing in these catchments retain most of the sediments originating from the Mattenalp, Bächli, and Grueben. Hence, the contribution of these catchments to the sediment balance of the Grimsel hydropower cascade is limited to the fine sediments transferred through the power waterways as suspended load.
3. Methodology
3.1. Sediment Yield
For each catchment, the annual sediment yield (SY) was estimated by means of the formula proposed by Beyer Portner (1998) [19]. This formula reads:
where VA (m3·km−2·year−1) is the annual sediment yield per unit area, Hsummer (mm) is the precipitation registered between June and September, SE (%) is the surface of erodible soil (not including the glacier), SV (%) is the surface without vegetation (including the glacier), and ΔLG (%) is the annual decrease of the glacier length. This formula was purposely calibrated to estimate the sediment yield for Alpine catchments. In fact, the results obtained for these catchments by other methods, such as the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) [20] and that proposed by Gavrilovic (1988) [21], differed significantly from field measurements [19]. The Beyer Portner’s (1998) [19] formula was validated by comparing the results obtained with the formula to the measurements performed in 19 Alpine catchments. In these catchments, Hsummer ranges from 247 mm to 938 mm, SE from 26% to 92%, SV from 2% to 91%, and ΔLG from 0% to −3%. The values obtained in this study for each of these parameters are included within these ranges, which makes the formula proposed by Beyer Portner (1998) [19] suitable to estimate the annual sediment yield for each of the catchments analyzed herein. In this study, the parameters of the formula are characterized annually from 1990 to 2099, and they are grouped in three time periods:
- Period I, from 1990 to 2012, for which the parameters are characterized by field measurements.
- Period II, from 2013 to 2065, and Period III, from 2066 to 2099, for which the parameters are characterized by the predictions based on the A1B climate change scenario [22].
The difference between Periods II and III results from the different trends of the predicted data for Hsummer.
The annual value of Hsummer corresponds to the sum of the daily values of precipitation from 1st of June to 30th of September for each year. For Period I, the daily values of precipitation were obtained from the data measured at the Grimsel Hospiz gauging station, assumed as representative for all catchments analyzed (Figure 1). For Periods II and III, the daily values of precipitation were obtained from the estimations corresponding to the Grimsel Hospiz station, based on the A1B climate change scenario. This scenario is one of the three scenarios considered by the CH2011 project to assess the impact of climate change over the XXIst century in Switzerland [22]. The CH2011 project considers two non-intervention green-house-emission scenarios (A2 and A1B) that predict an increase in emissions, and one climate stabilization scenario (RCP3PD) that supposes that emissions are reduced by about 50% by 2050. These scenarios are based on statistical analyses of global and regional climate model simulations (GCM and RCM, respectively). The present study considers the A1B scenario for which data for local and daily precipitation at the Grimsel Hospiz station and for glacier recession are available. The A1B emission scenario is characterized by a balance across fossil-intensive and non-fossil energy sources. It envisages a rapid economic growth, a global population that reaches a maximum at the mid-century and decreases thereafter, and the rapid introduction of new and more efficient technologies in terms of GHG emissions [22]. The data set obtained from the A1B climate change scenario consists of bias-corrected daily climate scenarios for 28 temperatures and 27 precipitation stations in Switzerland, among which only those corresponding to the Grimsel Hospiz station were considered. The scenarios are based on the quantile mapping methodology, they are available for 15 GCM-RCM model chains of the ENSEMBLES project [23], and they provide transient time series for the entire period of 1980–2099 [24,25].
The values of SE and SV were derived from the land use data obtained from the Swiss Federal Office for Topography (www.swisstopo.admin.ch). SE varied according to the glacier surface, whereas SV was assumed to be constant for the three periods.
For Period I, the glacier surface and the annual variation of the glacier length (ΔLG) were derived from the data provided by the Swiss Glacier Monitoring Network (www.swiss-glaciers.glaciology.ethz.ch). For Periods II and III, the annual glacier surface was obtained from the simulations performed by Farinotti et al. (2012) and Huss et al. (2008) [26,27], based on the A1B climate change scenario within the framework of the ENSEMBLES project [23]. For these last two periods, the annual variation of the glacier length was assumed to be identical to the annual variation of the glacier surface, thereby assuming a constant glacier width. In the case of Räterichsboden, the term ΔLG was considered equal to 1, since the glacier coverage in the direct sub-catchment is negligible.
3.2. Sedimentation Rate
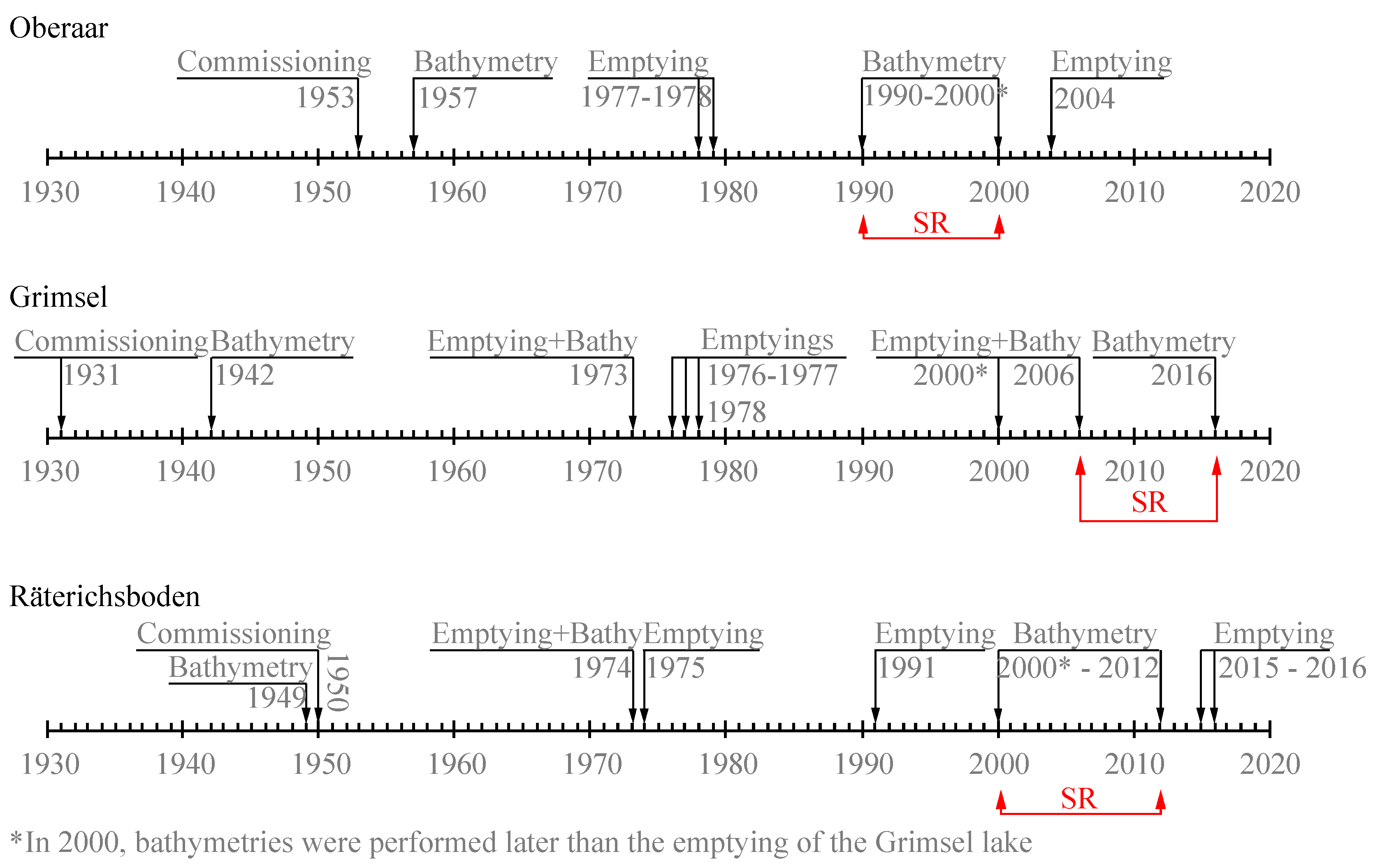
For Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden, the sedimentation rate (SR) was estimated from the difference in storage curves derived from bathymetric surveys. Thus, SR was calculated as the difference in volume between two consecutive bathymetries divided by the time elapsed between them. The pairs of consecutive bathymetries were chosen by considering those time intervals during which the lakes were not emptied. These intervals are: from 1990 to 2000 for Oberaar, from 2006 to 2016 for Grimsel, and from 2000 to 2012 for Räterichsboden. They are shown in Figure 2, which visualizes the chronology of emptying events and bathymetries carried out in Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden reservoirs since their commissioning. It is important to notice that in 2000, the bathymetric surveys conducted in Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden were performed after the emptying of Lake Grimsel.
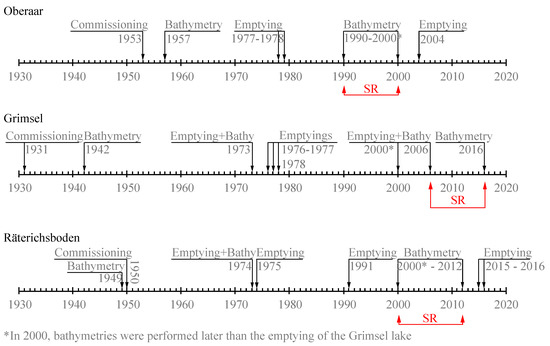
Figure 2.
Chronology of the emptying events and bathymetric surveys conducted in the lakes of Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden since their commissioning.
The sedimentation rates thus obtained were then compared to those reported by Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11], who quantified the volume of sediment deposits for each reservoir since their commissioning by means of seismic surveys of the reservoirs’ bottoms conducted in 2001 and 2002, correlated with core samples. In the case of Trift, the sedimentation rate was assumed to be equal to the sediment yield since no sediment management strategies are planned for this reservoir yet.
3.3. Sedimentation Rate for Fine Sediments
The volume of fine sediments (d < 10 μm) deposited annually in each reservoir (SRF) was estimated according to Bonalumi et al. (2011), who proposed the following expression:
where SRF (m3) is the volume of fine sediments deposited annually in each reservoir, ρb (kg/m³) stands for the bulk density, ws (m/s) is the settling velocity, SSC (t) (kg/m3) is the evolution of the suspended sediment concentration of the reservoir during a year, and A(t) (m2) is the evolution of the surface area of the lake during a year (variable according to the reservoir’s filling ratio). The settling velocity was computed according to the expression proposed by van Rijn (1984) [28] for stagnant water:
where ρs and ρw (kg/m3) stand for the density of sediment and water, respectively; g (m/s2) is the gravitational acceleration; d50 (m) is the median grain size diameter of the sediment mixture; and ν = 1.5 × 10−6 m2/s is the kinematic viscosity of water at a temperature of 5 °C. For Oberaar and Grimsel, the characteristics of the suspended sediments, as well as the annual evolution of the suspended sediment concentration (SSC (t)), were obtained from Bonalumi et al. (2011) [7], who characterized the spatial and temporal distribution of sediment concentration for these two lakes. In this study, only the measurements performed in deep water and close to the dams were considered. In the case of Räterichsboden and Trift, the sediment characteristics were assumed to be the same as those for the other two lakes, and the SSC(t) was assumed as the average of those of Oberaar and Grimsel. According to Anselmetti et al.’s (2007) [11] data, the grain density of the sediment mixture is ρs = 2600 kg/m3, and the bulk density ρb = 1700 kg/m3, considering a porosity of 35%. The median grain diameter considered in this study is d50 = 3.1 μm, which was obtained as the average of the median diameter of the samples collected by Bonalumi (2012) [29]. The settling velocity was characterized with a constant value of approximately 0.5 m/day, by assuming that the sediment characteristics remain constant in time. The evolution of the surface of the reservoir (A(t)) was obtained from the data provided by KWO, which consisted of: (i) daily values of water level and hydropower operations for Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden (from 1980 to 2014); and (ii) inundated area curves for each reservoir. In the case of Trift, A(t) is defined considering an annual filling ratio curve equal to the daily averaged value of the other three reservoirs.
3.4. Sedimentation Exchange through Power Waterways
The annual volume of sediments exchanged by hydropower operations (SPW) was estimated as follows:
where SPW (m3) is the volume of sediment annually exchanged through the power waterways, C(t) [kg/m3] is the concentration of suspended sediments of the exchanged volume of water, and Q(t) [m3/s] is the discharge of hydropower operations. For the water exchanges originating in Oberaar and Grimsel (those exchanged through Grimsel 1 and 2), C(t) was characterized by means of the turbidity measurements performed by Müller et al. (2014) [17]. These measurements were conducted from October 2010 to June 2011 in the pressure shaft of the pumped-storage plant of Grimsel 2. For the discharges transferred from Bächli to Grimsel, from Mattenalp to Räterichsboden, and from Räterichsboden to Handeck, C(t) was characterized by means of an average value of 50 mg/L resulting from the turbidity measurements performed in 2016 at Handeck, immediately downstream of Räterichsboden, by KWO (not published). Q(t) was characterized by means of the daily data of hydropower operations (from 1980 to 2014) provided by KWO. These data were daily averaged over the whole data series to obtain daily average values of Q(t), representative of an average year. As no daily data was available for the discharge transferred from Bächli to Grimsel, the mean annual volume reported by Kraftwerke Oberhasli AG (2018) [30] was considered.
4. Results
4.1. Sediment Yield
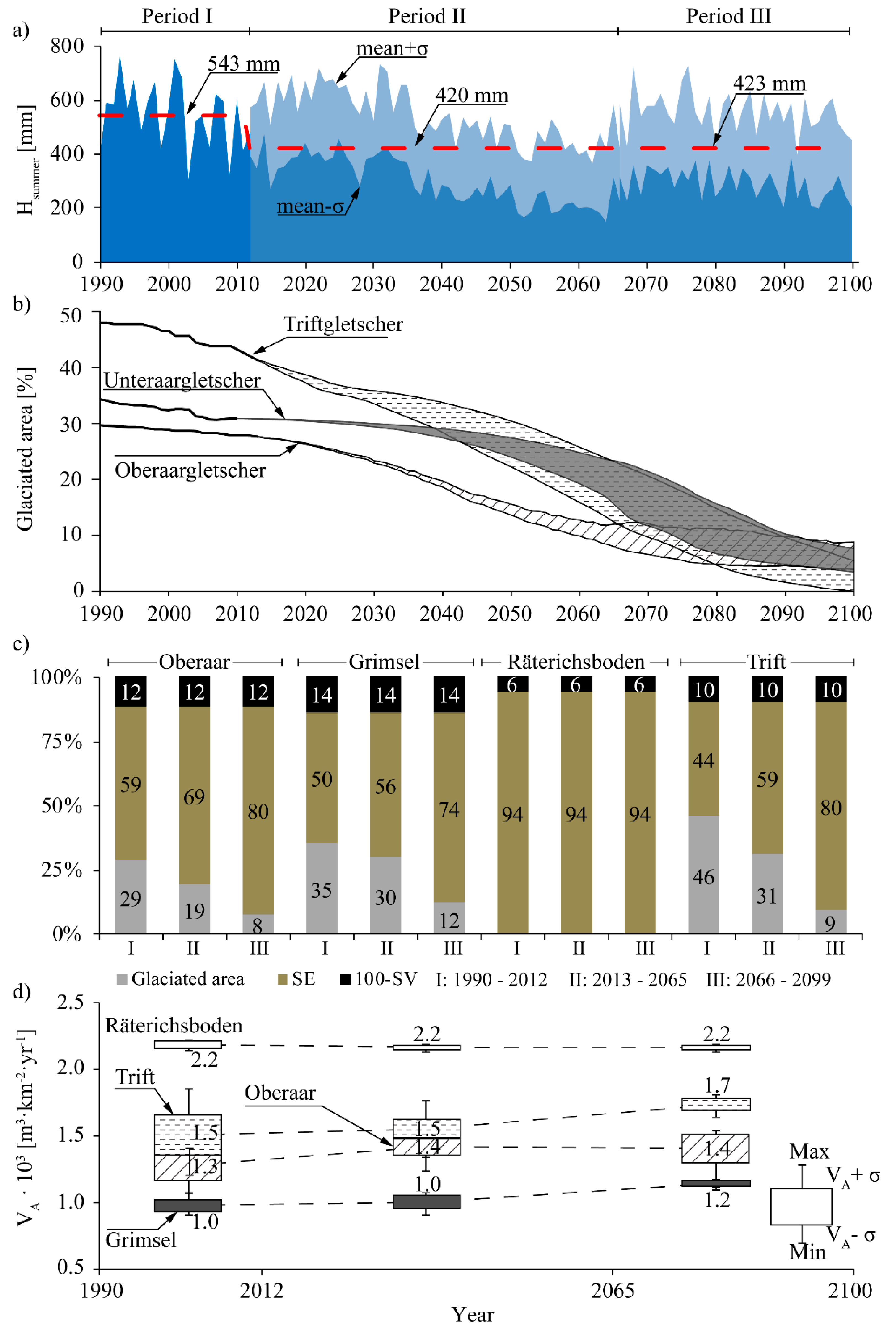
The evolution of Hsummer and the percentage of glaciated area from 1990 to 2099 are illustrated in Figure 3a,b. Measurements and estimations show a decrease of Hsummer from 1990 to 2099. This decrease is roughly constant for Periods I and II and becomes attenuated for Period III. Thus, the mean value of Hsummer is 543 mm for Period I, 420 mm for Period II, and 423 mm for Period III, and the decreasing rate is approximately 5.5 mm/year for Period I, 4.6 mm/year for Period II, and 2.1 mm/year for Period III (Figure 3a). The glaciated area decreases continuously from 1990 to 2099 for the three glaciers analyzed (Figure 3b). Thus, during Period III, the percentage of glaciated area reduces from 30% to 10% for Oberaar, from 35% to 10% for Grimsel, and from nearly 50% to approximately 10% for Trift (Figure 3b). As the glaciated area diminishes, the erodible surface (SE) increases. This increase is illustrated in Figure 3c, which shows the percentage, averaged for each period, of glaciated area; erodible surface; and vegetated surface for each catchment. Among the main glaciated catchments (Oberaar, Grimsel, and Trift), the greatest increase of erodible surface is expected for Trift, which would pass from 44% in Period I to 80% in Period III. For Oberaar and Grimsel, SE would increase from 59% to 80% and from 50% to 74%, respectively, as well as from Period I to Period III. In the case of Räterichsboden, no changes are expected in the percentage of erodible surface as the glaciated area is negligible in this catchment. Figure 3d shows the average value of the annual sediment yield per unit area (VA) for the three periods analyzed and for each catchment. Furthermore, Figure 3d shows the standard deviation and the maximum and minimum values of VA for each period and each catchment. The values of VA and those of the absolute sediment yield (SY = VA·Surface) are shown in Table 2 for each catchment and period. For Oberaar, Grimsel, and Trift, the annual sediment yield per unit area (VA) increases over the three periods analyzed. This increase is attributed to the increase of SE reported for these catchments (Figure 3c). In the case of Räterichsboden, VA remains roughly constant for the three periods because no changes are expected in the erodible surface (Figure 3c,d). Among the four catchments analyzed, Räterichsboden has the highest value of VA, followed by Trift, Oberaar, and Grimsel (Figure 3d and Table 2). This ranking can be justified by the fact that, comparatively, Räterichsboden has the highest percentage of erodible surface and the lowest of vegetated surface (100-SV in Figure 3c), Trift has lower values of 100-SV than Oberaar, and Grimsel has the lowest values of SE and the highest of 100-SV (Figure 3c).
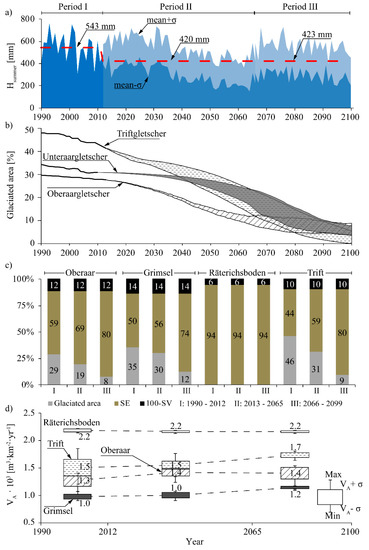
Figure 3.
(a) Annual values of Hsummer from 1990 to 2099. From 1990 to 2012, the values correspond to those measured at the Grimsel-Hospiz gauging station. From 2013 to 2099, the figure shows the range of values (mean ± σ) estimated according to the A1B-climate change scenario. The dashed line corresponds to the mean value of Hsummer for each period. (b) Evolution of the glaciated area for the three glaciers analyzed. From 1990 to 2012, the values were derived from field measurements. From 2013 to 2099, the figure shows the range of values (mean ± σ) estimated according to A1B climate change scenarios. (c) Percentage of the glaciated area, erodible soil (SE), and vegetated surface (100-SV), averaged for the three periods analyzed (I, II, and III), for each catchment. (d) Annual sediment yield per unit area of each catchment. The values correspond to VA averaged for each period.

Table 2.
Values of the sediment yield per unit area and of the absolute sediment yield (VA and SY, respectively) in [m3/year] for each catchment and for each period.
4.2. Sedimentation Rate
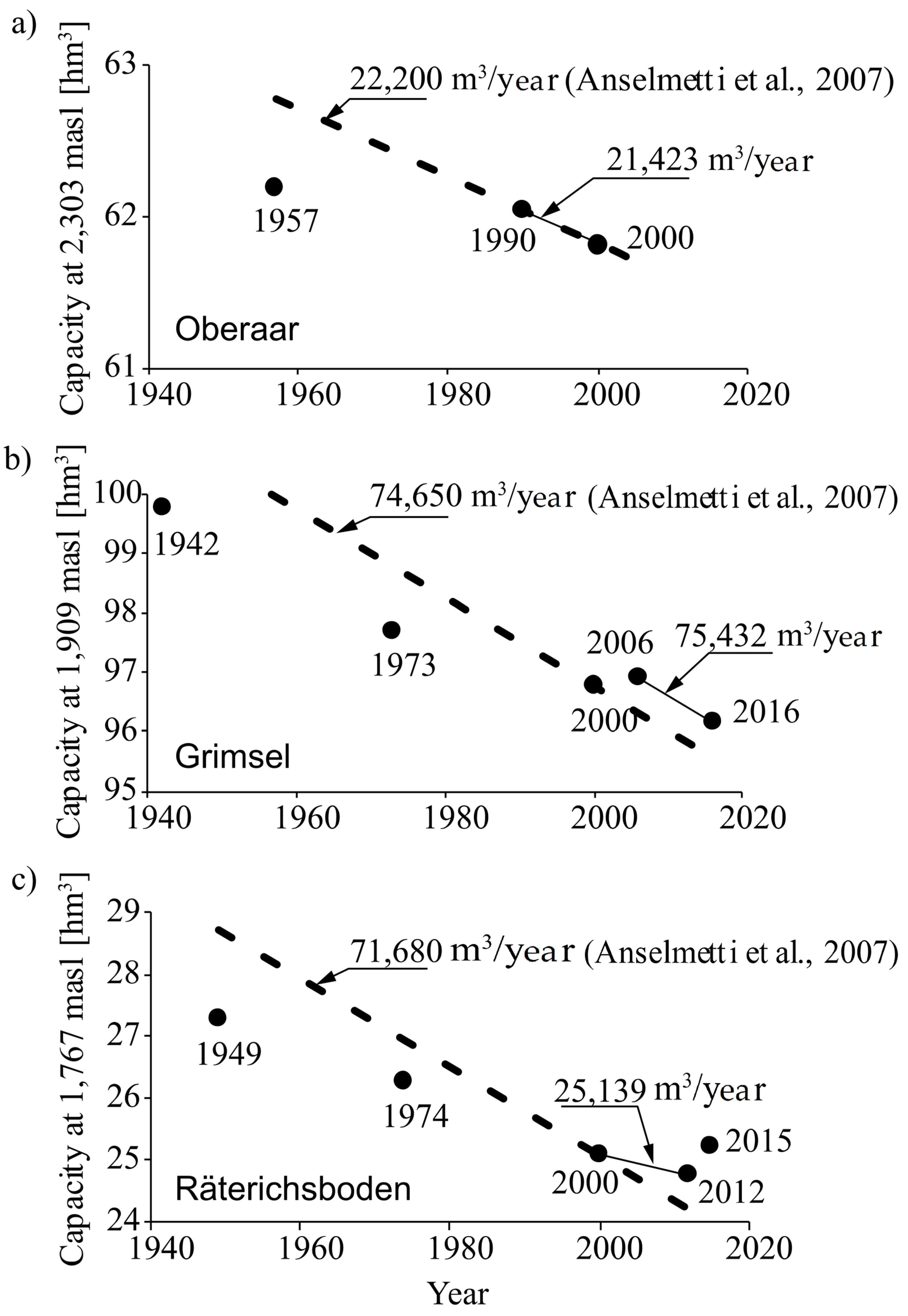
Figure 4 illustrates the evolution of the storage capacity of Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden reservoirs, at their respective maximum supply level since their commissioning. It also shows the sedimentation rates estimated for the three reservoirs in 2001 by Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11]. In the case of Oberaar and Grimsel, the sedimentation rates derived from bathymetries between 1990 and 2000 and between 2000 and 2012, respectively, show a very good agreement with those reported by Anselmetti et al. (2007) (Figure 4a,b). In contrast, in the case of Räterichsboden, the sedimentation rate by Anselmetti et al. (2007) differs significantly from that derived from bathymetries (Figure 4c). This discrepancy is probably related to the fact that in 2000, Grimsel was emptied completely (Figure 2) and a large amount of sediment was delivered into Räterichsboden. This volume of sediments may have altered the measurements performed in Räterichsboden in 2001 by Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11]. In this study, the annual sedimentation rate of Räterichsboden was characterized by means of those bathymetries performed in 2000 and 2012. The sedimentation rate thus obtained is not altered by the emptying of Grimsel in 2000, as the bathymetric survey in Räterichsboden was performed later than the emptying of Grimsel. In summary, the annual sedimentation rates (SR) considered in this study correspond to those reported by Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11] for Oberaar and Grimsel (22,200 m3/year and 74,650 m3/year, respectively), and that obtained from bathymetries for Räterichsboden (25,139 m3/year).
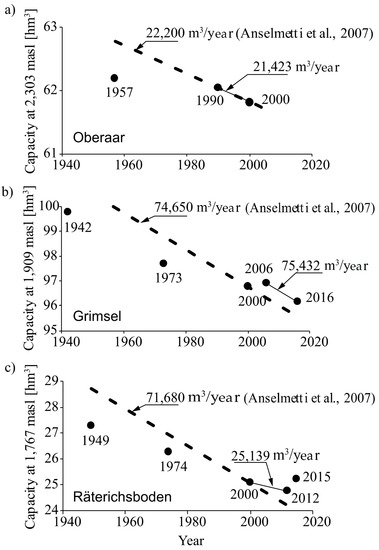
Figure 4.
Sedimentation rates estimated from bathymetric surveys and those reported by Anselmetti et al. (2007) for: (a) Oberaar; (b) Grimsel; and (c) Räterichsboden.
4.3. Sedimentation Rate of Fine Sediments
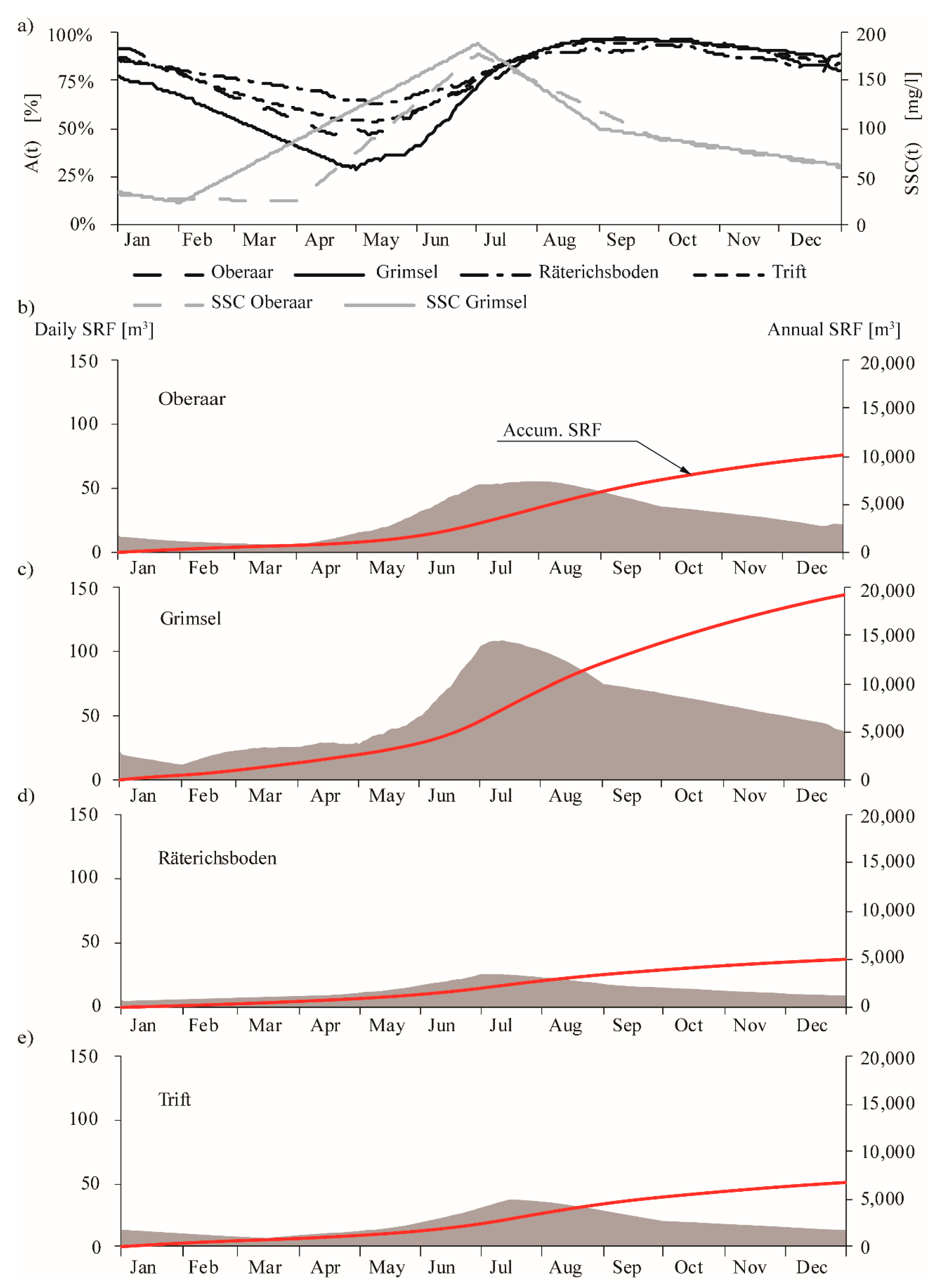
For Oberaar and Grimsel, the evolution of suspended sediment concentration during a year (SSC(t)) was observed to increase from spring to summer and to decrease from autumn to winter by Bonalumi et al. (2011) (Figure 5a). The increase of concentration coincides with the period of snow melting followed by a period of glacier melting, during which the so-called “glacier milk” provides high concentrated flows into the reservoirs. On the contrary, the decrease of concentration is related to the decrease in ambient temperatures in autumn, the absence of sediment-laden inflows, and the sediment settling in the reservoirs. Additionally, this decrease can be attenuated eventually by runoffs originating from rainstorms in autumn [7,11,17]. According to the hydropower operations, the evolution of the reservoirs’ water surface during a year (A(t)) is characterized by a minimum between April and May and a maximum between August and September (Figure 5a). The annual evolution of the SSC(t) is replicated by the daily sedimentation rate of fine sediments, i.e., it increases from early spring to summer, reaching a maximum in July, and it decreases until the next spring, reaching a minimum in March. In absolute terms, Grimsel has the highest SRF among the four reservoirs (19,220 m3/year), whereas for Oberaar, Räterichsboden, and Trift, SRF is 10,139 m3/year, 4996 m3/year, and 6767 m3/year, respectively (Figure 5b–e). In relative terms, the ratio between SRF and the annual sedimentation rate is 46% for Oberaar, 25% for Grimsel, 20% for Räterichsboden, and 13% for Trift.
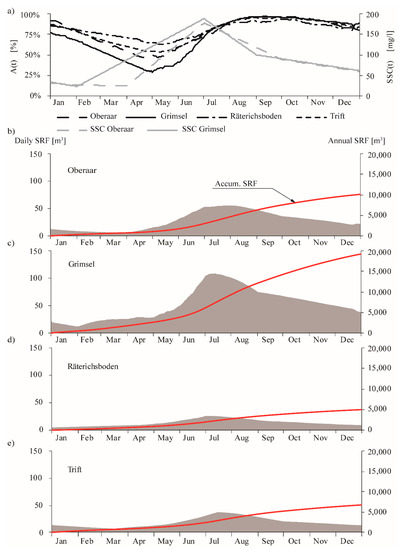
Figure 5.
(a) Daily evolution of SSC in an average year for Oberaar and Grimsel, and daily evolution of A(t) for Oberaar, Grimsel, Räterichsboden, and Trift. (b–e) Daily evolution of SRF and accumulated values of SRF in an average year for Oberaar, Grimsel, Räterichsboden, and Trift, respectively.
4.4. Sediment Fluxes through the Power Waterways
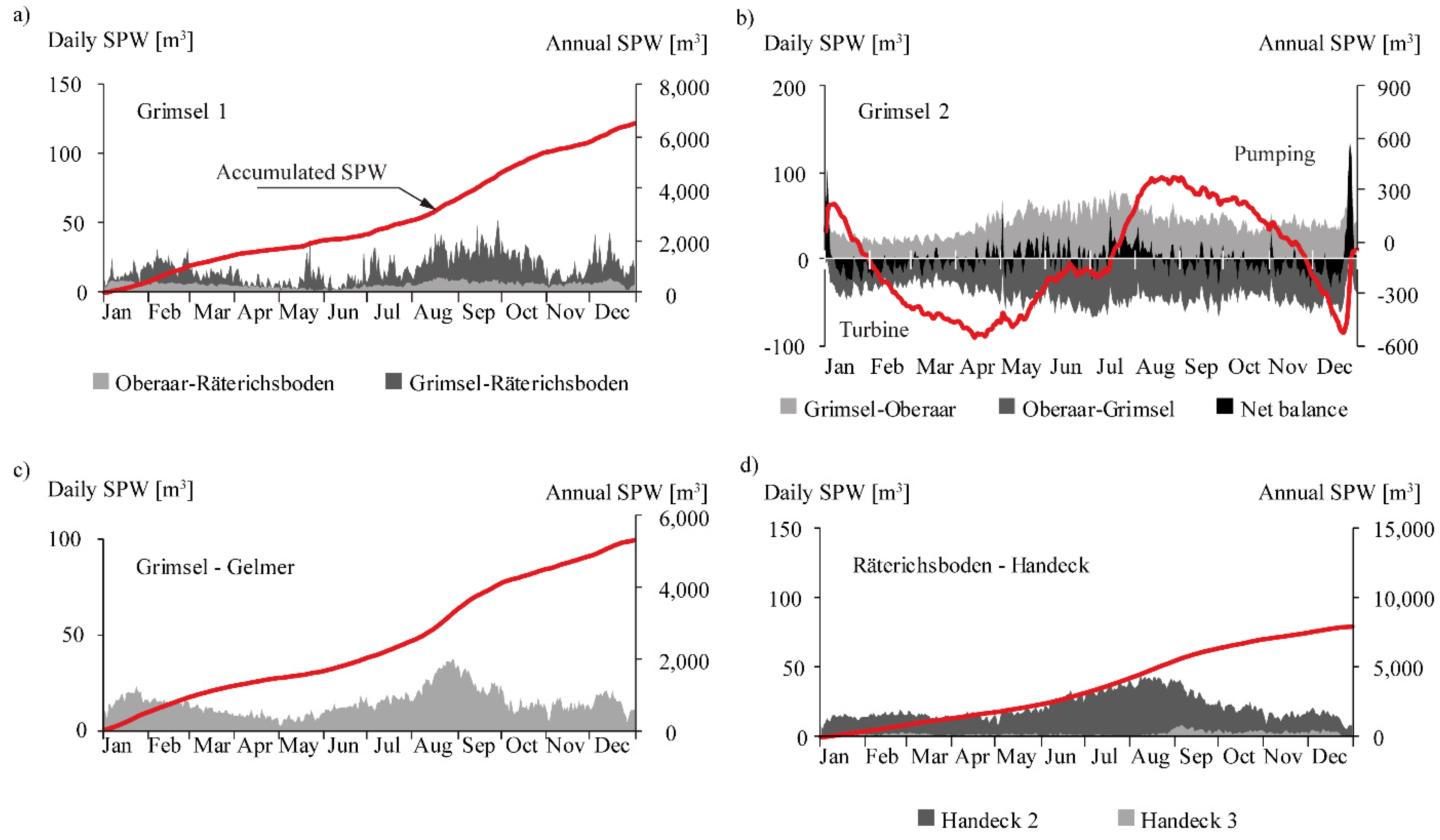
Figure 6 visualizes the daily volumes of sediments exchanged through the power waterways of the Grimsel hydropower cascade. Annually, 6000 m3 of fine sediments are transferred from Oberaar (2000 m3) and Grimsel (4000 m3) to Räterichsboden (Figure 6a) through Grimsel 1. The results show that the annual balance of sediments exchanged between Oberaar and Grimsel through Grimsel 2 is nearly nil (Figure 6b) as the sediment volumes transferred from Oberaar to Grimsel in turbine mode are equivalent to those sediment volumes transferred from Grimsel to Oberaar in pumping mode (Figure 6b). From Grimsel, 5300 m3 of fine sediments are transferred annually to Gelmer (Figure 6c). From Räterichsboden, approximately 8000 m3 of fine sediments per year are transferred to Handeck (Figure 6d). The volume of sediments transferred from Bächli to Grimsel was estimated in approximately 1000 m3, which results from the product of the mean annual volume of water, approximately 29 hm3 [30], the average concentration measured at Handeck (50 mg/L), and the bulk density ρb = 1700 kg/m3. Similarly, the volume of sediment transferred from Mattenalp to Räterichsboden was estimated to be approximately 300 m3 by considering a mean annual volume of water of 10.55 hm3 [30].
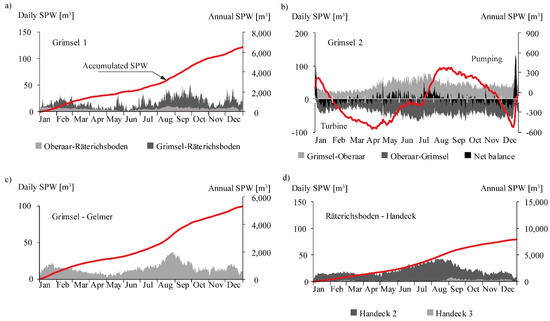
Figure 6.
Daily values of SPW and accumulated values of SPW during an average year for: (a) Grimsel 1; (b) Grimsel 2; (c) Grimsel to Gelmer; and (d) Räterichsboden to Handeck.
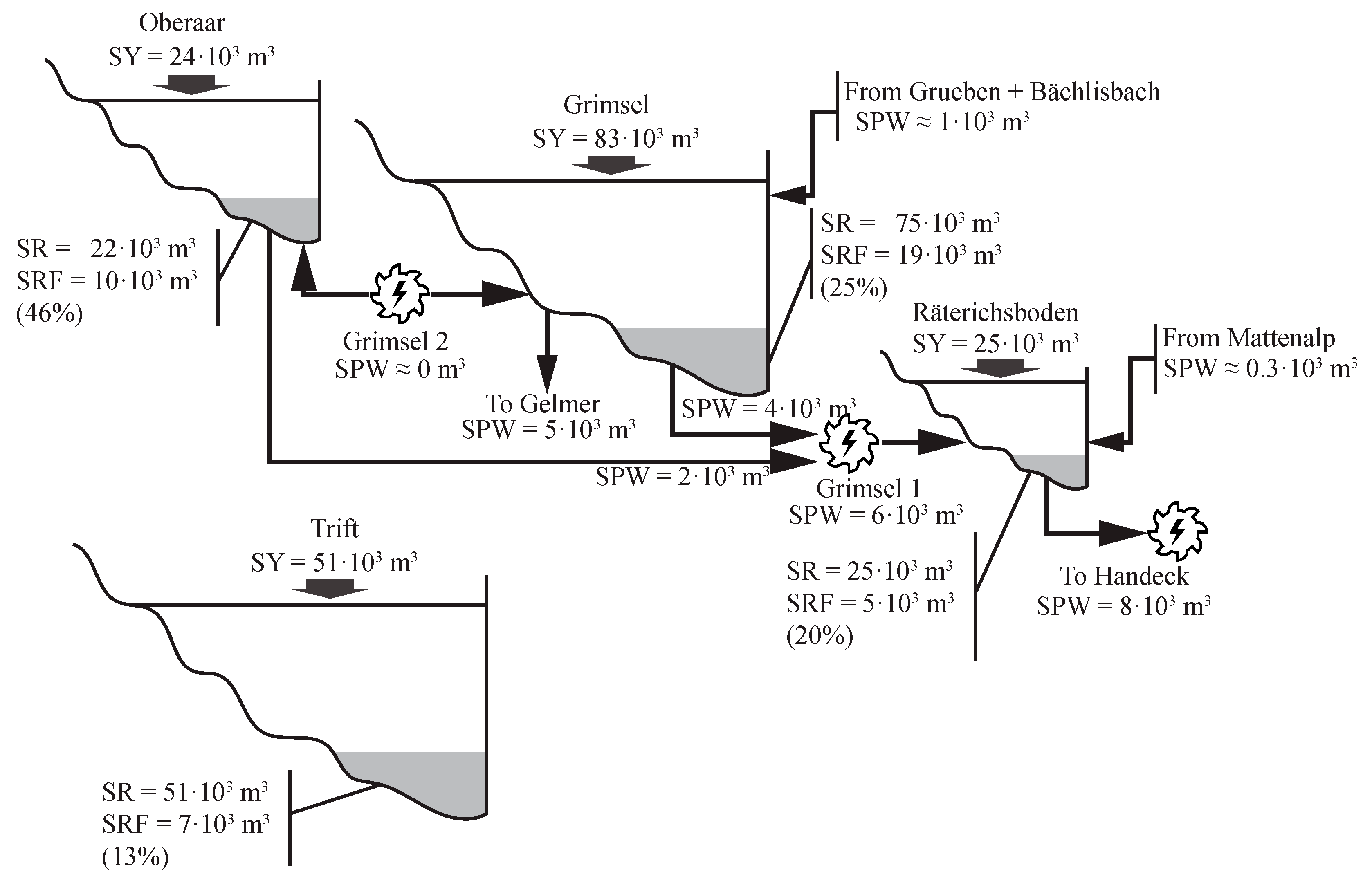
4.5. Sediment Balance at Present
The annual sediment balance of the four catchments analyzed is illustrated in Figure 7. This balance is based on the field measurements recorded during Period I. The results show that for Oberaar, the sedimentation rate is approximately 92% of the sediment yield and the volume of fine sediments deposited can reach up to 46% of the total sedimentation rate. In Grimsel, 89% of the annual sediment yield is deposited and the percentage of fine sediments can reach up to 25% of the total sedimentation rate. For Räterichsboden, the whole sediment yield is deposited and the volume of fine sediments can reach up to 20% of the total sedimentation rate. In Räterichsboden, the method yields an imbalance of approximately 1700 m3 (7% with respect to SY and SR), which can be related to the accuracy of the method. In the case of Trift, it was assumed that the annual sediment yield is fully deposited and the percentage of fine sediments was estimated to be up to 13% of the total deposits.
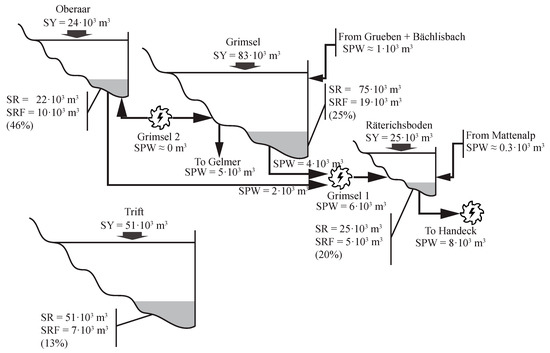
Figure 7.
Annual sediment balance for the hydropower cascade formed by the reservoirs Oberaar, Grimsel, and Räterichsboden, and for Trift.
5. Discussion
5.1. Present Situation
The Grimsel hydropower cascade receives 132,510 m3 of sediments annually from its catchment, of which 122,771 m3 (92%) are deposited in the reservoirs (Figure 7). These values are lower than those reported by Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11] for the same catchment, i.e., approximately 160,000 m3/year (271 kt/year) as the annual sediment yield, and approximately 138,000 m3/year (232 kt/year) as the annual sedimentation rate for the three reservoirs. On the one hand, the difference in the annual sediment yield is attributed to the fact that Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11] computed this value by adding the annual volume of suspended sediments transported by the Aare River in Innerkirtchen (23,000 m3, 39 kt) to the annual sedimentation rate. Thus, Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11] considered the sediment supplies from Räterichsboden to Innerkirtchen, which were not considered in this study. On the other hand, the difference in the annual sedimentation rate is justified by the fact that the measurements performed by Anselmetti et al. (2007) [11] in Räterichsboden might be biased by the volume of sediments released during the flushing of Grimsel in 2000, which yielded an annual sedimentation rate about three times higher (approximately three times) than that estimated in this study (Figure 4c).
The denudation rates resulting from the computed values of sediment yield per unit area (VA) for the whole catchment of the Grimsel hydropower cascade and for Trift are 1.2 mm/year and 1.5 mm/year, respectively. These values are within the range of those reported by Schlatter et al. (2005) [31] (between 1 mm/year and 1.6 mm/year) for the central Swiss Alps, but they are higher than the general values reported for Alpine catchments (between 0.1 to 0.65 mm/year) by Einsele and Hinderer (1997, 1998), Hinderer (2001), and Hinderer et al. (2013) [13,32,33,34]. This discrepancy can be attributed to the high degree of glaciation (>30%) of the catchments analyzed herein, as the denudation rate of highly glaciated catchments was observed to be higher than for catchments with little or no glaciated area [11,13,35]. By comparing the four catchments analyzed in this study, one observes that the sediment yield per unit area (VA) decreases as the catchment area increases (Figure 3) [13,36,37]. Moreover, VA increases with the glaciated area when comparing the catchment of Trift to the whole catchment of the Grimsel hydropower cascade [13].
The volume of fine sediments deposited annually in the reservoirs of the Grimsel hydropower cascade was estimated to be 34,335 m3 (58 kt), accounting for 28% of the total sedimentation rate (Figure 7). Additionally, 20,600 m3 (34 kt) of fine sediments are transported annually through the power waterways, of which 13,300 m3 (22 kt) leave the system to Gelmer and Handeck (5300 m3 and 8000 m3, respectively, Figure 7). Therefore, the annual input of fine sediments (d < 10 µm) to the Grimsel hydropower cascade is SRF + SPW = 54,935 × 103 m3 (93 kt), which accounts for approximately 41% of the total annual input.
5.2. Perspectives Based on Climate Warming
Owing to the high degree of glaciation and the seasonality of rainfall, glacier, and hillslope erosion, together with landslides, are identified as the main sediment sources of the catchments analyzed in this study, among the four sediment sources cataloged by Costa et al. (2017) [12] for Alpine environments. Glacier erosion is associated with bedrock fracturing and abrasion at the base of the glacier, which provide large amounts of sediments. Discharges originating from glacier melt are characterized by high suspended sediment concentrations [7,10,12]. Intense rainfall events in summer, when the snow cover is minimum, result in the erosion of large amounts of sediments that are conveyed downstream to the lakes. Moreover, these summer rainfalls may trigger landslides or debris flows that supply large amounts of sediments to the lakes. These mechanisms of erosion are strongly influenced by climate changes [12,35,38,39,40].
The climate change scenario considered in this study predicts a temperature increase from 2020 to 2100 that ranges from 2.7 °C to 4.1 °C and a decrease of summer mean precipitation that ranges from 21% to 28% (Figure 3a), with respect to the values registered from 1980 to 2009 [22,25]. The rise of temperature would reduce the glaciated area by up to 10% of the area of the catchments analyzed in this study (Figure 3b). These estimations are based on the numerical simulations performed by Farinotti et al. (2012) and Huss et al. (2008) [26,27]. The reduction of the glaciated area would make large amounts of sediments, formerly accumulated beneath the glacier, available for erosion, thereby increasing the sediment yield [35]. However, temporally, glacier recession may lead to an increase of the annual water yield and consequently, to an increase of the sediment transport capacity [35,41]. Another effect of the temperature increase, not investigated in this study, consists of the reduction of snowfall days in favor of rainfall days [42]. This was observed to increase the rainfall erosivity, which in turn contributes to increasing the suspended sediment concentration [12,42]. The decrease of summer mean precipitation may result in a decrease of the annual sediment yield owing to the reduced runoff generation during summer [39,43]. Both trends (glacier recession and summer precipitation) are combined in this study by means of the formula proposed by Beyer Portner (1998) [19], to estimate the sediment yield per unit area (VA) of each catchment. The results obtained for Periods II and III show an increase of VA in all catchments except for Räterichsboden (Figure 3d), with respect to the values obtained for Period I. In the case of Räterichsboden, the negligible glaciated area leads to similar values of VA for the three time periods analyzed, with a negligible influence of the trend of the summer precipitation. The increase of VA predicted for Periods II and III with respect to Period I is similar for Grimsel and Trift, i.e., 3% and 18%, respectively, for Grimsel; and 2% and 14%, respectively, for Trift (Figure 3d). In contrast, the increase of VA for Oberaar is of about 13% for Period II and about 11% for Period III, both with respect to Period I (Figure 3d). The different patterns observed for VA when comparing the results obtained for Oberaar to those obtained for Grimsel can be explained by the different patterns of the evolution of the glaciated surface obtained for these two glaciers (Figure 3b). Whilst the glaciated surface of Oberaargletscher decreases rapidly during Period II and becomes nearly constant during Period III, the glaciated surface of Grimsel decreases weakly during Period II and experiences a rapid decrease during Period III (Figure 3b). The distinct patterns of VA observed between Oberaar and Trift can be attributed to the higher percentage of glaciated area of Trift with respect to Oberaar, and to the lower elevation of the Trift lake. This, together with the empirical expression of Beyer Portner (1998) [19], gives more weight to the changes in SE than to the changes in ΔLG. Thus, though the glaciated area decreases about 33% during Period II in both catchments (Figure 3b,c), the erodible surface (SE) increases 16% for Oberaar and 33% for Trift during the same period (Figure 3b,c). The predicted increase of sediment yield is in agreement with the general trend reported by Costa et al. (2017), Lane et al. (2017), and Micheletti and Lane (2016) [12,35,38], who also expect a rise of the sediment yield associated with the glacier recession. However, these results contrast with the results by Raymond Pralong et al. (2015) [39], as they predicted a decrease of the sediment yield due to the reduced runoff generation during summer. This discrepancy can be attributed to the different methodologies undertaken to estimate the sediment yield. Apparently, the model used by Raymond Pralong et al. (2015) [39] gives more weight to the transport capacity associated with summer precipitation, whereas, in this study, the formula proposed by Beyer Portner (1998) gives more weight to the effect of glacier recession on the sediment yield.
Based on the predictions made for Alpine catchments characterized by glacier recession by Costa et al. (2017), Farinotti et al. (2012), Lane et al. (2017), and Micheletti and Lane, (2016) [12,27,35,38], the annual runoff and its suspended sediment concentration are expected to increase in the upcoming decades, until the glacier disappears. The increased sediment yield along with the increased runoff and suspended sediment concentration will result in greater annual sediment inputs to the reservoirs, thereby increasing their suspended sediment concentration and their annual sedimentation rate, unless a sediment management plan is undertaken. This, in turn, will lead to the deterioration of the water quality owing to higher turbidity, to the higher risk of blockage of the outlet structures, and to the higher risk of turbine abrasion in hydropower schemes [16]. Measures such as an increase of the turbulence level of the reservoirs by means of hydropower operations may mitigate the negative effects of fine sediments settling, by keeping them in suspension until being evacuated to the river network through the power waterways [6,7,17,44,45,46,47].
6. Conclusions
The paper proposes a comprehensive model of the sediment in- and out-fluxes of a complex cascade of interconnected reservoirs. The model established at the annual scale includes detailed sub-models of monthly and daily sediment exchanges.
The first application of the model concerns a well-documented hydropower cascade in Switzerland. In this case study, calibration is possible and relies on an extensive dataset of reservoir bathymetries and operational data of both hydropower and dam maneuvers across more than seven decades. These data series allowed quantifying the sediment in- and out-fluxes and the sedimentation rate of each reservoir. Subsequent replication of the model in new locations, for instance, for new reservoirs (e.g., the Trift project, also in Switzerland), can benefit from the long experience acquired in similar infrastructure in neighboring catchments.
Nowadays, the Grimsel hydropower cascade retains about 92% of the annual sediment yield produced within its catchment. Only a small amount of these sediments, corresponding to the finest fraction, is transferred downstream to the fluvial network, mainly through the power waterways. The fine sediments account for about 28% of the total sedimentation rate, which can even reach values of up to 46% in the case of Oberaar. In the case of Trift, the annual sedimentation rate of fine sediments may reach up to 13% of the total sedimentation rate.
The developed model is also helpful in the assessment of the future impacts of climate warming on reservoir sedimentation a ceteris paribus. In fact, in a scenario of climate warming in which the glaciated area is expected to decrease, a rise of the annual sediment yield is foreseen, despite the predicted decrease of mean summer precipitation. The rise of available sediments, combined with a presumably increased annual runoff and higher suspended sediment concentration, will lead to larger annual inputs of sediments to the reservoirs, thereby increasing the annual sedimentation rate and the suspended sediment concentration of the reservoirs, if reservoir operations remain identical to current practice.
The methodology developed in this paper reproduces the most important sediment fluxes in a complex cascade of reservoirs with several powerplants. Its makes extensive use of valuable monitoring data collected and archived across several decades and is suitable for replication in other hydropower cascades providing sound data.
Author Contributions
All authors made a significant contribution to the research. S.G.L. performed the formal analysis of data and developed the methodology under the guidance and supervision of A.J.S. and P.A.M. Results were thoroughly discussed by the three authors. S.G.L. prepared an original draft of the paper that was revised and improved by P.A.M. and A.J.S.
Funding
This study is part of the interdisciplinary research project FLEXSTOR of the Swiss Competence Centre for Energy Research—Supply of Electricity (SCCER-SoE, Phase II), with co-funding by the Swiss Commission for Technology and Innovation (grant CTI—17902.3 PFIW-IW) and by Kraftwerke Oberhasli AG (KWO).
Acknowledgments
The authors deeply thank KWO project counterparts Andreas Fankhauser, Benno Schwegler, and Jan Stamm for their precise indications and profound knowledge of such a complex hydropower system and territory, paramount for the preparation of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Morris, G.L.; Fan, J. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and Management of Dams, Reservoirs, and Watersheds for Sustainable Use; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Basson, G.R. Management of siltation in existing and new reservoirs. General Report Q. 89. In Proceedings of the 23rd Congress of the International Commission on Large Dams CIGB-ICOLD, Brasilia, Brazil, 25–29 May 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, V.; Kastens, J.; De Noyelles, F.; Jakubauskas, M.; Martinko, E.; Huggins, D.; Gnau, C.; Liechti, P.; Campbell, S.; Callihan, R.; et al. Examining Storage Capacity Loss and Sedimentation Rate of Large Reservoirs in the Central U.S. Great Plains. Water 2018, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J.; Juez, C.; De Cesare, G. Reservoir sedimentation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Rubin, Z.K.; Minear, J.T. Dams on the Mekong: Cumulative sediment starvation. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, D.; Schmid, M.; Wüest, A. Effects of upstream hydropower operation on riverine particle transport and turbidity in downstream lakes. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonalumi, M.; Anselmetti, F.S.; Kaegi, R.; Wüest, A. Particle dynamics in high-Alpine proglacial reservoirs modified by pumped-storage operation. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Walling, D.E.; He, Y. Review: The International Sediment Initiative case studies of sediment problems in river basins and their management. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2018, 33, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.S.A.; Crosato, A.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Abdalla, S.H.; Wright, N.G. Sediment balances in the Blue Nile River Basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2014, 29, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, E.; Bogen, J. Colors of glacier water. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmetti, F.S.; Bühler, R.; Finger, D.; Girardclos, S.; Lancini, A.; Rellstab, C.; Sturm, M. Effects of Alpine hydropower dams on particle transport and lacustrine sedimentation. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Molnar, P.; Stutenbecker, L.; Bakker, M.; Silva, T.A.; Schlunegger, F.; Lane, S.N.; Loizeau, J.-L.; Girardclos, S. Temperature signal in suspended sediment export from an Alpine catchment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, M.; Kastowski, M.; Kamelger, A.; Bartolini, C.; Schlunegger, F. River loads and modern denudation of the Alps—A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 118, 11–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, S.; De Cesare, G.; Schleiss, A.J. Venting turbidity currents for the sustainable use of reservoirs. Int. J. Hydropower Dams 2016, 23, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Alavian, V.; Jirka, G.H.; Denton, R.A.; Johnson, M.C.; Stefan, H.G. Density Currents Entering Lakes and Reservoirs. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1992, 118, 1464–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, R.; Auel, C.; Hagmann, M.; Albayrak, I. Sediment bypass tunnels to mitigate reservoir sedimentation and restore sediment continuity. In Reservoir Sedimentation; Schleiss, A.J., De Cesare, G., Franca, M.J., Pfister, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 221–228. ISBN 9781138026759. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.; De Cesare, G.; Schleiss, A.J. Continuous Long-Term Observation of Suspended Sediment Transport between Two Pumped-Storage Reservoirs. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 05014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberli, W.; Bütler, M.; Huggel, C.; Müller, H.; Schleiss, A. Formation des nouveaux lacs suite au recul des glaciers en haute montagne – chances et risques. Forschungsbericht des Nationalen Forschungsprogramms 2013, 61, 159–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer Portner, N. Erosion des Bassins Versants Alpins par Ruissellement de Surface, Communication 6; École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne EPFL: Lausanne, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Gavrilovic, Z. Use of an Empirical Method (Erosion Potential Method) for Calculating Sediment Production and Transportation in Unstudied or Torrential Streams. In Proceedings of the International Conference on River Regime, Wallingford, UK, 18–20 May 1988; Hydraulic Research Limited: Wallingford, UK, 1988; pp. 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Appenzeller, C.; Bey, I.; Croci Maspoli, M.; Fuhrer, J.; Knutti, R.; Kull, C.; Schär, C. Swiss Climate Change Scenarios CH2011; C2SM, Meteo Swiss, ETH, NCCR Climate, OcCC: Zürich, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 9783033030657. [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden, P.; Mitchell, J.F.B. ENSEMBLES: Climate Change and Its Impacts—Summary of Research and Results from the ENSEMBLES Project; Met Office Hadley Centre: Exeter, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, M.A.; Kotlarski, S. Assessing distribution-based climate model bias correction methods over an alpine domain: Added value and limitations. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2633–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarski, S.; Ivanov, M.; Schär, C. Bias-Corrected Transient Scenarios at the Local Scale and at Daily Resolution; CH2011 Extension series; OcCC: Zürich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huss, M.; Farinotti, D.; Bauder, A.; Funk, M. Modelling runoff from highly glacierized alpine drainage basins in a changing climate. Hydrol. Processes 2008, 22, 3888–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinotti, D.; Usselmann, S.; Huss, M.; Bauder, A.; Funk, M. Runoff evolution in the Swiss Alps: Projections for selected high-alpine catchments based on ENSEMBLES scenarios. Hydrol. Processes 2012, 26, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Sediment Transport, Part II: Suspended Load Transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1613–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonalumi, M. Effect of Pumped-Storage Operations on Temperature, Turbidity and Sedimentation in Reservoirs and possible Mitigation Measures. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kraftwerke Oberhasli AG; (Wasserhaushalt der KWO 1997–2015). Internal communication, Unpublished work. 2018.
- Schlatter, A.; Schneider, D.; Geiger, A.; Kahle, H.-G. Recent vertical movements from precise levelling in the vicinity of the city of Basel, Switzerland. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2005, 94, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, G.; Hinderer, M. Terrestrial sediment yield and the lifetimes of reservoirs, lakes, and larger basins. Geol. Rundsch. 1997, 86, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsele, G.; Hinderer, M. Quantifying denudation and sediment-accumulation systems (open and closed lakes): Basic concepts and first results. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1998, 140, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, M. Late Quaternary denudation of the Alps, valley and lake fillings and modern river loads. Geodin. Acta 2001, 14, 231–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N.; Bakker, M.; Gabbud, C.; Micheletti, N.; Saugy, J.-N. Sediment export, transient landscape response and catchment-scale connectivity following rapid climate warming and Alpine glacier recession. Geomorphology 2017, 277, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, W.W. Detrital sediment fluxes from continents to oceans. Chem. Geol. 1998, 145, 287–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Geomorphic/Tectonic Control of Sediment Discharge to the Ocean: The Importance of Small Mountainous Rivers. J. Geol. 1992, 100, 525–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, N.; Lane, S.N. Water yield and sediment export in small, partially glaciated Alpine watersheds in a warming climate. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 4924–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond Pralong, M.; Turowski, J.M.; Rickenmann, D.; Zappa, M. Climate change impacts on bedload transport in alpine drainage basins with hydropower exploitation. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2015, 40, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H. Climate Change Impacts on Flow and Suspended Sediment Yield in Headwaters of High-Latitude Regions—A Case Study in China’s Far Northeast. Water 2017, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefli, B.; Manso, P.; Fischer, M.; Huss, M.; Farinotti, D. The role of glacier retreat for Swiss hydropower production. Renew. Energy 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serquet, G.; Marty, C.; Dulex, J.-P.; Rebetez, M. Seasonal trends and temperature dependence of the snowfall/precipitation-day ratio in Switzerland. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, Y. Runoff and Sediment Yield Variations in Response to Precipitation Changes: A Case Study of Xichuan Watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2015, 7, 5638–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; De Cesare, G.; Schleiss, A.J. Experiments on the effect of inflow and outflow sequences on suspended sediment exchange rates. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenzer Althaus, J.M.I.; De Cesare, G.; Schleiss, A.J. Sediment Evacuation from Reservoirs through Intakes by Jet-Induced Flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Manso, P.A.; Venuleo, S.; Lindsay, N.; Leupi, C.; Schleiss, A.J. Computational hydraulic modelling of fine sediment stirring and evacuation through the power waterways at the Trift reservoir. In Shaping the Future of Hydropower; Aqua Media International Ltd.: Seville, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guillén-Ludeña, S.; Manso, P.A.; Schleiss, A.J. Fine sediment routing in a cascade of alpine reservoirs: Influence of the inlet angle on settling of fine sediments. In Shaping the Future of Hydropower; Aqua Media International Ltd.: Seville, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).