Impact of Eastern Redcedar Proliferation on Water Resources in the Great Plains USA—Current State of Knowledge
Abstract
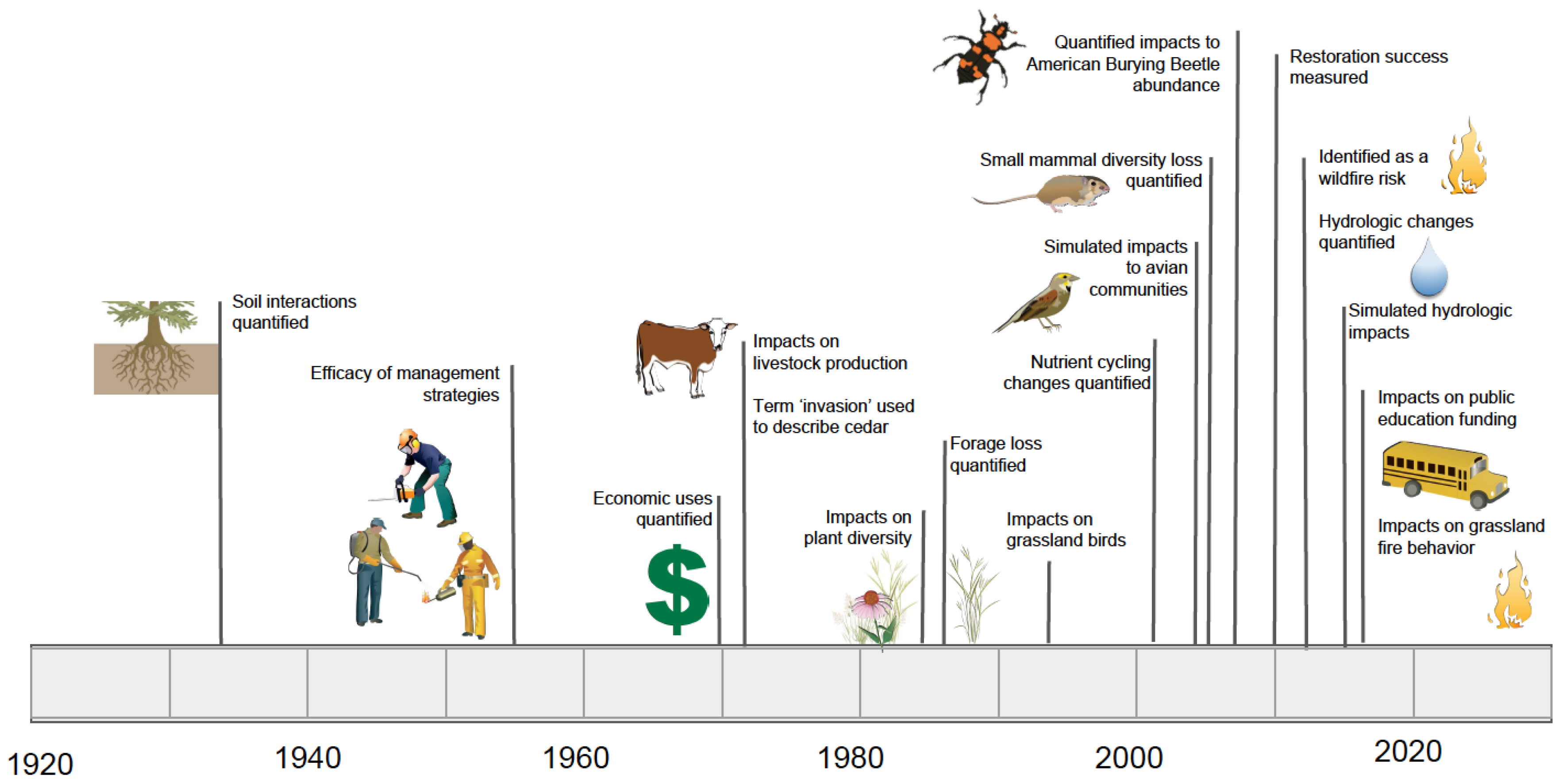
1. Introduction
2. Redcedar and Its Proliferation
2.1. Distribution and Dynamics
2.2. Morphological and Physiological Traits of Redcedar
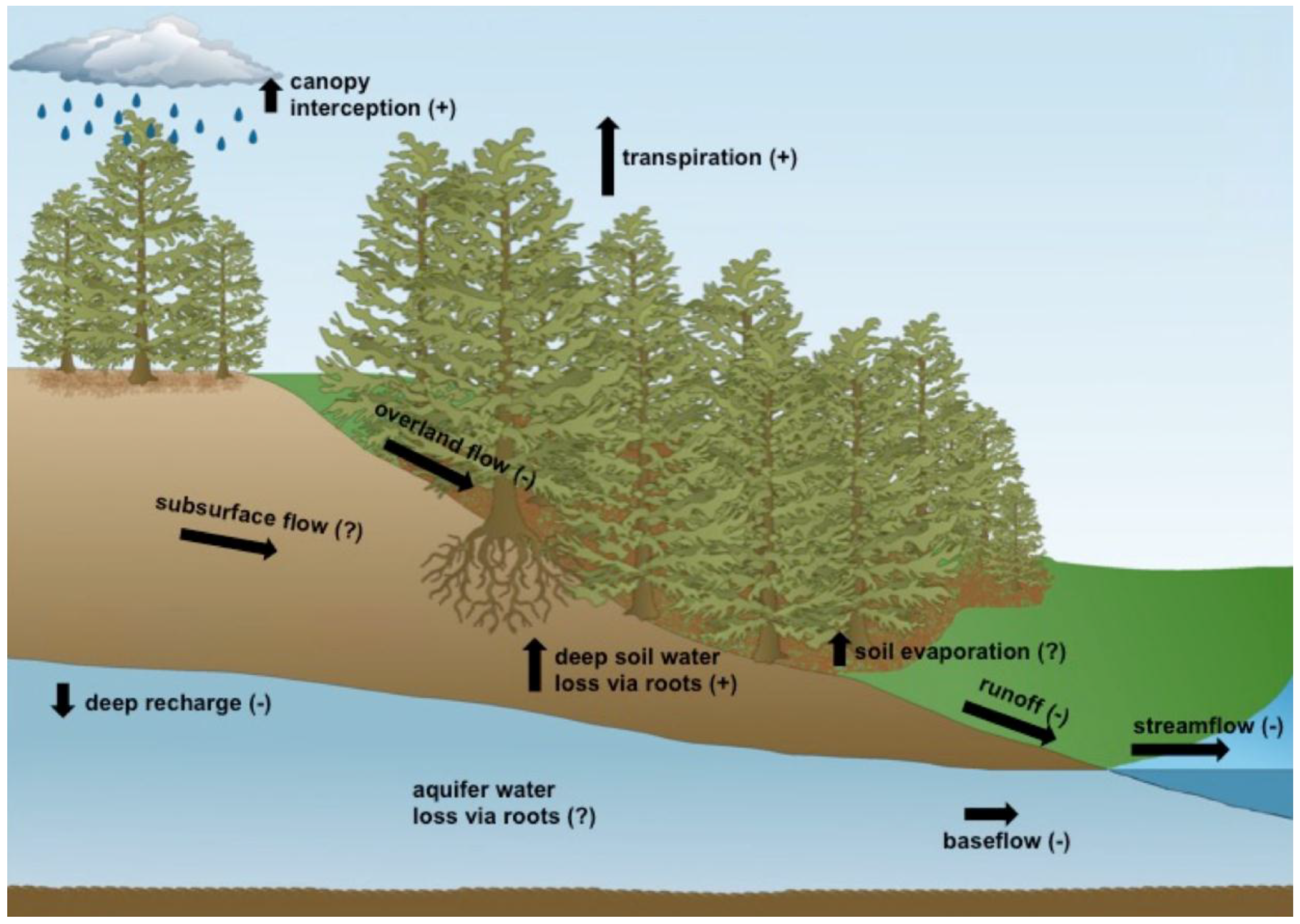
3. Alteration and Rebalance of Water Budget after Redcedar Encroachment
3.1. Evapotranspiration
3.1.1. Transpiration
3.1.2. Evaporation from Vegetation (Ec and El)
3.1.3. Evaporation from Soil
3.2. Soil Water
3.3. Impact on Water Resources Available for Non-Ecosystem Use
3.3.1. Surface Runoff
3.3.2. Subsurface Flow and Groundwater Recharge
4. Redcedar Control and Recuperation of Water
5. Challenges and Potential Opportunities
5.1. Water Security in a Warmer World
5.2. Water Quality
5.3. Precipitation Loss to Grass Canopy Interception
5.4. Soil Type, Substrates, and Infiltration
5.5. Land Surface and Climate Interaction
5.6. Redcedar Encroachment into Deciduous Forest
5.7. Cross-Scale Hydrological Modeling and Forecasting
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scanlon, B.R.; Keese, K.E.; Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E.; Gaye, C.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Simmers, I. Global synthesis of groundwater recharge in semiarid and arid regions. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 3335–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Dowhower, S.L.; Teague, W.R.; Thurow, T.L. Long-term water balance in a semiarid shrubland. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 59, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.M.; Hoch, G.A.; Johnson, L.C. Assessing the rate, mechanisms, and consequences of the conversion of tallgrass prairie to Juniperus virginiana forest. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, D.L.; Will, R.E.; Zou, C.B.; Lillie, N.D. Encroachment dynamics of juniperus virginiana l. And mesic hardwood species into cross timbers forests of north-central oklahoma, USA. Forests 2018, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, D.M.; Coppedge, B.R.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. From the dust bowl to the green glacier: Human activity and environmental change in great plains grasslands. In Western North American Juniperus Communities; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Coppedge, B.R.; Engle, D.M.; Masters, R.E.; Gregory, M.S. Avian response to landscape change in fragmented southern great plains grasslands. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Els, P.; Will, R.E.; Palmer, M.W.; Hickman, K.R. Changes in forest understory associated with juniperus encroachment in oklahoma, USA. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2010, 13, 356–368. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, D.J.; Engle, D.M.; McCollum, E.T. An economic assessment of risk and returns from prescribed burning on tallgrass prairie. J. Range Manag. 1988, 41, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, E.R. Juniperus virginiana L. Eastern redcedar. Silv. N. Am. 1990, 1, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- McKinley, D.C.; Norris, M.D.; Blair, J.M.; Johnson, L.C. Altered ecosystem processes as a consequence of Juniperus virginiana L. Encroachment into north american tallgrass prairie. In Western North American Juniperus Communities; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 170–187. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Geissler, G.; Zhang, G.; Cejda, N.; Alikhani, B.; Doughty, R.B. Mapping the dynamics of eastern redcedar encroachment into grasslands during 1984–2010 through palsar and time series landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Dong, J.; Zou, Z. Characterizing the encroachment of juniper forests into sub-humid and semi-arid prairies from 1984 to 2010 using palsar and landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguzzo, D.M.; Liknes, G.C. Status and trends of eastern redcedar (Juniperus virginiana) in the central united states: Analyses and observations based on forest inventory and analysis data. J. For. 2015, 113, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, V.M.; Burnett, J.L.; Bielski, C.H.; Birgé, H.E.; Bevans, R.; Twidwell, D.; Allen, C.R. Social–ecological landscape patterns predict woody encroachment from native tree plantings in a temperate grassland. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogarty, D.T.; Twidwell, D.; Allen, C.R. Incipient tree invasions signal heightened vulnerability of an “uninvadable” grassland region. 2018; under review. [Google Scholar]
- Twidwell, D.; Rogers, W.E.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Wonkka, C.L.; Engle, D.M.; Weir, J.R.; Kreuter, U.P.; Taylor, C.A., Jr. The rising great plains fire campaign: Citizens’ response to woody plant encroachment. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, e64–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, R.D.; Hallgren, S.W.; Stahle, D.W. Drought and fire suppression lead to rapid forest composition change in a forest-prairie ecotone. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 261, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, N.N.; Archer, S.R.; Campbell, J.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Morton, J.A.; Knapp, A.K. Woody plant proliferation in north american drylands: A synthesis of impacts on ecosystem carbon balance. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas Forests Resource Bulletin NRS-26. Available online: https://www.nrs.fs.fed.us/pubs/rb/rb_nrs26.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Ormsbee, P.; Bazzaz, F.A.; Boggess, W.R. Physiological ecology of Juniperus virginiana in oldfields. Oecologia 1976, 23, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassoie, J.P.; Dougherty, P.M.; Reich, P.B.; Hinckley, T.M.; Metcalf, C.M.; Dina, S.J. Ecophysiological investigations of understory eastern redcedar in central missouri. Ecology 1983, 64, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, D.L.; Will, R.E.; Zou, C.B.; Weir, J.R.; Gregory, M.S.; Lillie, N.D. Estimating increased fuel loading within the cross timbers forest matrix of oklahoma, USA due to an encroaching conifer, juniperus virginiana, using leaf-off satellite imagery. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 409, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Turton, D.J.; Wilson, D.S.; Zou, C.B. Water use of Juniperus virginiana trees encroached into mesic prairies in oklahoma, USA. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Wine, M.; Hendrickx, J. Biohydrologic effects of eastern redcedar encroachment into grassland, Oklahoma, USA. Biologia 2013, 68, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Qiao, L.; Wilcox, B.P. Woodland expansion in central oklahoma will significantly reduce streamflows—A modelling analysis. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wine, M.L.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Cadol, D.; Zou, C.B.; Ochsner, T.E. Deep drainage sensitivity to climate, edaphic factors, and woody encroachment, Oklahoma, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3779–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, P.J.; Venuto, B.C.; Dugas, W.A.; Kiniry, J. Measurements of canopy interception and transpiration of openly-grown eastern redcedar in central Okalhoma. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2014, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Wu, X.; Bajgain, R.; Du, L. Enhanced gross primary production and evapotranspiration in juniper encroached grasslands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5655–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.B.; Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E.; Turton, D. Canopy interception for a tallgrass prairie under juniper encroachment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, D.M.; Stritzke, J.F.; Claypool, P.L. Herbage standing crop around eastern redcedar trees. J. Range Manag. 1987, 40, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wine, M.L.; Ochsner, T.E.; Sutradhar, A.; Pepin, R. Effects of eastern redcedar encroachment on soil hydraulic properties along oklahoma’s grassland-forest ecotone. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Halihan, T.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.E. Vegetation controls on the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of deep moisture in the unsaturated zone: A hydrogeophysical evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Turton, D.J.; Will, R.E.; Engle, D.M.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Alteration of hydrological processes and streamflow with juniper (Juniperus virginiana) encroachment in a mesic grassland catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 6173–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Stebler, E.; Will, R.E. Woody plant encroachment reduces annual runoff and shifts runoff mechanisms in the tallgrass prairie, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 4838–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E. Calibration of swat model for woody plant encroachment using paired experimental watershed data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, P.J.; Moriasi, D.N. Impact of eastern redcedar encroachment on stream discharge in the north canadian river basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 72, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Hao, Y.; Ochsner, T.E.; Zou, C.B. Woody plant encroachment alters soil hydrological properties and reduces downward flux of water in tallgrass prairie. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisenbee, W.A.; Fox, G.; Zou, C.; Storm, D.; Penn, C.; Stebler, E.; Mittelstet, A. Predicted influence of eastern redcedar removal on water quantity and quality using the water erosion prediction project (WEPP). In Proceedings of the 2015 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 7–10 July 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Awada, T.; El-Hage, R.; Geha, M.; Wedin, D.A.; Huddle, J.A.; Zhou, X.; Msanne, J.; Sudmeyer, R.A.; Martin, D.L.; Brandle, J.R. Intra-annual variability and environmental controls over transpiration in a 58-year-old even-aged stand of invasive woody Juniperus virginiana L. In the Nebraska Sandhills, USA. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.D.; Stubbendieck, J. Production of tall-grass prairie herbs below eastern redcedar. Prairie Nat. 1990, 22, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.L.; Johnson, L. Vegetation-mediated changes in microclimate reduce soil respiration as woodlands expand into grasslands. Ecology 2004, 85, 3348–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adane, Z.A.; Gates, J.B. Determining the impacts of experimental forest plantation on groundwater recharge in the Nebraska Sand Hills (USA) using chloride and sulfate. Hydrogeol. J. 2015, 23, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.M.; Reich, P.B. The effects of eastern red cedar (Juniperus virginiana) invasion and removal on a dry bluff prairie ecosystem. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggemeyer, K.D.; Awada, T.; Harvey, F.E.; Wedin, D.A.; Zhou, X.; Zanner, C.W. Seasonal changes in depth of water uptake for encroaching trees Juniperus virginiana and pinus ponderosa and two dominant C4 grasses in a semiarid grassland. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adane, Z.; Nasta, P.; Gates, J.B. Links between soil hydrophobicity and groundwater recharge under plantations in a sandy grassland setting, Nebraska Sand Hills, USA. For. Sci. 2017, 63, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurc, S.A.; Small, E.E. Dynamics of evapotranspiration in semiarid grassland and shrubland ecosystems during the summer monsoon season, central New Mexico. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesterhaus, J.L. A Micrometeorology Study of Stock Watering Ponds, Rangelands, and Woodlands in the Flint Hills of Kansas. Ph.D. Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wagle, P.; Xiao, X.; Scott, R.L.; Kolb, T.E.; Cook, D.R.; Brunsell, N.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Basara, J.; Matamala, R.; Zhou, Y. Biophysical controls on carbon and water vapor fluxes across a grassland climatic gradient in the United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zou, C.B.; Wilcox, B.; Stebler, E. Effect of vegetation on the energy balance and evapotranspiration in tallgrass prairie: A paired study using the eddy-covariance method. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.; Oren, R. Intra-and inter-annual variation in transpiration of a pine forest. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wullschleger, S.D.; Meinzer, F.C.; Vertessy, R.A. A review of whole-plant water use studies in tree. Tree Physiol. 1998, 18, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, E.S.; Crouse, R.P. Rainfall Interception by Annual Grass and Chaparral… Losses Compared. Available online: https://www.fs.fed.us/psw/publications/documents/psw_rp048/psw_rp048.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Thurow, T.L.; Blackburn, W.H.; Warren, S.D.; Taylor, C.A., Jr. Rainfall interception by midgrass, shortgrass, and live oak mottes. J. Range Manag. 1987, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seastedt, T.R. Canopy interception of nitrogen in bulk precipitation by annually burned and unburned tallgrass prairie. Oecologia 1985, 66, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliam, F.S.; Seastedt, T.R.; Knapp, A.K. Canopy rainfall interception and throughfall in burned and unburned tallgrass prairie. Southwest. Nat. 1987, 32, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, F.A.; Chang, M. Throughfall in planted stands of four southern pine species in east texas 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1981, 17, 880–885. [Google Scholar]
- Link, T.E.; Unsworth, M.; Marks, D. The dynamics of rainfall interception by a seasonal temperate rainforest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 124, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Stebler, E.; Zou, C.B. Monitoring litter interception of rainfall using leaf wetness sensor under controlled and field conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxman, T.E.; Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Scott, R.L.; Snyder, K.A.; Small, E.E.; Hultine, K.; Pockman, W.T.; Jackson, R.B. Ecohydrological implications of woody plant encroachment. Ecology 2005, 86, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hao, Y.; Stebler, E.; Tanaka, N.; Zou, C.B. Impact of plant functional types on coherence between precipitation and soil moisture: A wavelet analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Gaitán, C.F.; Hong, Y.; McPherson, R.A. Analysis of precipitation projections over the climate gradient of the arkansas red river basin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.D.; Trimble, S.W. Environmental Hydrology. CRC Press, 2015. Available online: https://www.crcpress.com/Environmental-Hydrology-Third-Edition/Ward-Trimble-Burckhard-Lyon/p/book/9781466589414 (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Wilcox, B.P.; Huang, Y.U.N.; Walker, J.W. Long-term trends in streamflow from semiarid rangelands: Uncovering drivers of change. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Sejna, M. The hydrus-1d software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. Univ. Calif. Riverside Res. Rep. 2005, 3, 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bargués Tobella, A.; Reese, H.; Almaw, A.; Bayala, J.; Malmer, A.; Laudon, H.; Ilstedt, U. The effect of trees on preferential flow and soil infiltrability in an agroforestry parkland in semiarid Burkina Faso. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3342–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, B.; Kharel, G.; Zou, C.; Wilcox, B.; Halihan, T. Woody plant encroachment impacts on groundwater recharge: A review. Water 2018, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P. Shrub control and streamflow on rangelands: A process based viewpoint. J. Range Manag. 2002, 55, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Huang, Y. Woody plant encroachment paradox: Rivers rebound as degraded grasslands convert to woodlands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Barre, D.A.; Owens, M.K. Does shrub removal increase groundwater recharge in southwestern texas semiarid rangelands? Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Owens, M.K.; Dugas, W.A.; Ueckert, D.N.; Hart, C.R. Shrubs, streamflow, and the paradox of scale. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 3245–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twidwell, D.; Allred, B.W.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. National-scale assessment of ecological content in the world’s largest land management framework. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.R.; Angeler, D.G.; Cumming, G.S.; Folke, C.; Twidwell, D.; Uden, D.R. Quantifying spatial resilience. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.; Kakani, G.; Stebler, E. Runoff responses to conversion of encroached juniper woodland to native prairie and panicum virgatum biofuel feedstock production. In Proceedings of the Ecological Society of American Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–10 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B.B.; Thompson, C.; Giri, A.; Van NewKirk, S. Nebraska Irrigation Fact Sheet. Available online: https://agecon.unl.edu/a9fcd902-4da9-4c3f-9e04-c8b56a9b22c7.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- National Water Information System Data. Water Data for the Nation. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/water-data-nation-national-water-information-system (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Mittelstet, A.R.; Gilmore, T.E.; Rudnick, D.R. Development of Multiple Regression Models to Predict Nitrate Concentrations in Nebraska Surface Waters. In Proceedings of the 2017 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 16–19 July 2017; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- West, A.L.; Zou, C.B.; Stebler, E.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Allred, B. Pyric-herbivory and hydrological responses in tallgrass prairie. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 69, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.D.; Blair, J.M.; Johnson, L.C.; McKane, R.B. Assessing changes in biomass, productivity, and C and N stores following Juniperus virginiana forest expansion into tallgrass prairie. Can. J. For. Res. 2001, 31, 1940–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.D.; Blair, J.M.; Johnson, L.C. Land cover change in eastern kansas: Litter dynamics of closed-canopy eastern redcedar forests in tallgrass prairie. Can. J. Bot. 2001, 79, 214–222. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Zou, C. Impacts of woody plant encroachment on regional climate in the southern great plains of the united states. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9093–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volder, A.; Briske, D.D.; Tjoelker, M.G. Climate warming and precipitation redistribution modify tree–grass interactions and tree species establishment in a warm-temperate savanna. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.F.; Bates, J.D.; Svejcar, T.J.; Pierson, F.B.; Eddleman, L.E. Biology, Ecology, and Management of Western Juniper (Juniperus occidentalis); Technicak Bulletin 152; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pierson, F.B.; Bates, J.D.; Svejcar, T.J.; Hardegree, S.P. Runoff and erosion after cutting western juniper. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 60, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonkka, C.L.; Twidwell, D.; Bielski, C.H.; Allen, C.R.; Stambaugh, M.C. Regeneration and invasion of cottonwood riparian forest following wildfire. Restor. Ecol. 2018, 26, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, C.B.; Twidwell, D.; Bielski, C.H.; Fogarty, D.T.; Mittelstet, A.R.; Starks, P.J.; Will, R.E.; Zhong, Y.; Acharya, B.S. Impact of Eastern Redcedar Proliferation on Water Resources in the Great Plains USA—Current State of Knowledge. Water 2018, 10, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121768
Zou CB, Twidwell D, Bielski CH, Fogarty DT, Mittelstet AR, Starks PJ, Will RE, Zhong Y, Acharya BS. Impact of Eastern Redcedar Proliferation on Water Resources in the Great Plains USA—Current State of Knowledge. Water. 2018; 10(12):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121768
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Chris B., Dirac Twidwell, Christine H. Bielski, Dillon T. Fogarty, Aaron R. Mittelstet, Patrick J. Starks, Rodney E. Will, Yu Zhong, and Bharat Sharma Acharya. 2018. "Impact of Eastern Redcedar Proliferation on Water Resources in the Great Plains USA—Current State of Knowledge" Water 10, no. 12: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121768
APA StyleZou, C. B., Twidwell, D., Bielski, C. H., Fogarty, D. T., Mittelstet, A. R., Starks, P. J., Will, R. E., Zhong, Y., & Acharya, B. S. (2018). Impact of Eastern Redcedar Proliferation on Water Resources in the Great Plains USA—Current State of Knowledge. Water, 10(12), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121768







