Rehabilitation Planning of Water Distribution Network through a Reliability—Based Risk Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Reliability Theory Applied to Water Distribution System
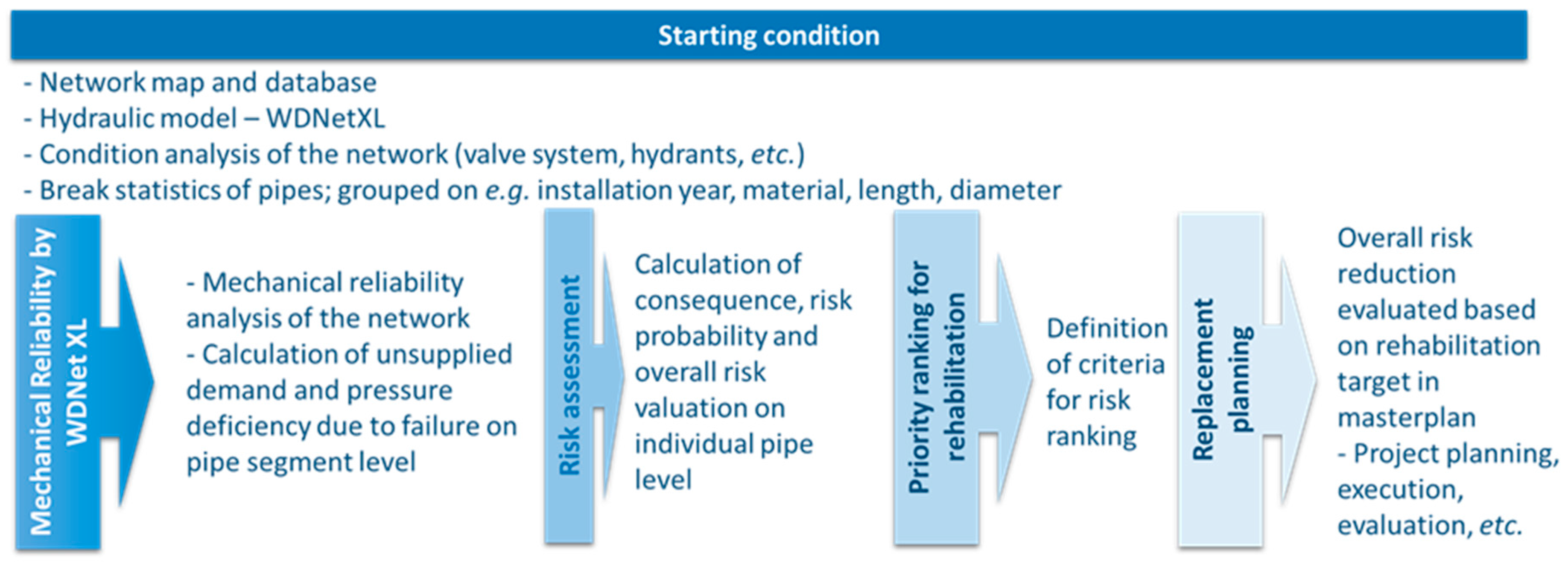
2. Methodology
2.1. The Reliability Indicators Implemented in WDNetXL
- i, e and t are subscripts indicating respectively the i-th node, the e-th failure event and the time t of the EPS during time interval T; e = 0 represents for normal condition;
- dact and pact are the actual customer demand computed in pressure driven analysis (PDA) using the Wagner’s model [29] and actual nodal pressure evaluated in PDA or demand driven analysis (DDA).
- drequ is the required customer demand varying over time;
- pnormal is the nodal pressure in normal conditions computed varying over time;
- nn and ne are the number of nodes and events, respectively.
2.2. Risk Assessment Approach
- λ represents the frequency of break in a year;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- p subscript indicating the p-th pipe.
2.3. Replacement Planning
- p depicts the p-th pipe
- is the direct cost of the p-th pipe
- is the cumulative sum of the direct costs of pipes until pipe p − 1
- is the risk associated to the p-th pipe
- is the cumulative sum of the risks of pipes until pipe p − 1
3. Case Study—Laives
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Innovation and Research for Water Infrastructure for the 21st Century—Research Plan; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development—National Risk Management Research Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2007.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Rehabilitation of Wastewater Collection and Water Distribution Systems—State of Technology Review Report; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development—National Risk Management Research Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2009.
- European Commission. EU Reference document Good Practices on Leakage Management WFD CIS WG PoM—Main Report; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- Billinton, R.; Li, W. Basic Concepts of Power System Reliability Evaluation. In Reliability Assessment of Electric Power Systems Using Monte Carlo Methods; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bazovsky, I. Reliability Theory and Practice; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Billinton, R.; Allan, R.N. Reliability Evaluation of Engineering Systems: Concepts and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Walski, M.; Chase, D.; Savic, D.; Grayman, W.; Beckwith, S.; Koelle, E. Advanced Water Distribution Modelling and Management; Haestad: Waterbury, CT, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, L.W.; Tung, Y.K. Hydrosystems Engineering and Management; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Walski, T.M. Practical aspects of providing reliability in water distribution systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1993, 42, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tolikas, D. Assessing the Performance Level of a water system. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2004, 4, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V. Vulnerability based management of water resources systems. Hydroinformatics 2004, 6, 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Gargano, R.; Pianese, D. Reliability as Tool for Hydraulic Network Planning. J. Hydraul. Eng.-ASCE 2000, 126, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khomsi, D.; Walters, G.A.; Thorley, A.R.D.; Ouazar, D. Reliability tester for water distribution networks. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 1996, 10, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Savic, D.A.; Berardi, L.; Laucelli, D. An Excel-based solution to bring water distribution network analysis closer to users. In Proceedings of the Computer and Control in Water Industry (CCWI), Exeter, UK, 5–7 September 2011; Savic, D.A., Kapelan, Z., Butler, D., Eds.; Volume 3, pp. 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Berardi, L.; Laucelli, D.; Giustolisi, O. InnoWatING: Water Distribution Network Modelling of the Oppegård Municipality in Oslo; Research at Politecnico di Bari: General Report 2014, 1st Workshop on the State of Art and Challenges of Research Efforts at POLIBA 3–5 December 2014; University in Bari: Bari, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Giustolisi, O.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.A. Extended period simulation analysis considering valve shutdowns. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustolisi, O.; Savic, D.A. Identification of segments and optimal isolation valve system design in water distribution networks. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, L.; Ugarelli, R.; Røstum, J.; Giustolisi, O. Assessing mechanical vulnerability in water distribution networks under multiple failures. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2586–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengström, T.R. Comparative Analysis of Pipe Break Rates: A Literature Review. Publication 2:93; Department of Sanitary Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Samaras, P.; Zouboulis, A.; Demetriou, G. Developing appropriate Performance Indicators for urban water supply systems evaluation across the Mediterranean. Water Util. J. 2011, 1, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Samaras, P.; Zouboulis, A.; Banovec, P. A new set of water losses related Performance Indicators focused on areas facing water scarcity conditions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 2994–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Zouboulis, A. WATERLOSS project: Developing from theory to practice an integrated approach towards NRW reduction in urban water systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Cerk, M.; Banovec, P.; Samaras, P.; Zouboulis, A. Basic principles of a DSS tool developed to prioritize NRW reduction measures in water pipe networks. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2015, 7, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragalli, C.; Giansanti, F.; Zingali, L.; Montanari, A. Multi criteria decision analysis to set the priority of interventions in water distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Hydroinformatics—HIC2018, Palerm, Italy, 1–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Bhave, P.R. Reliability analysis of water distribution systems. J. Environ. Eng. 1994, 120, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanymboh, T.T.; Tabesh, M.; Burrow, R. Appraisal of source head methods for calculating reliability of water distribution networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2001, 127, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liserra, T.; Maglionico, M.; Ciriello, V.; Di Federico, V. Evaluation of reliability indicators for WDSs with demand-driven and pressure-driven models. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1201–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, L.; Laucelli, D.B.; Simone, A.; Raspati, G.; Ugarelli, R.M.; Giustolisi, O. Mechanical reliability analysis of a real network to support the design of Isolation Valve System. In Proceedings of the Computing and Control for the Water Industry (CCWI2017), Sheffield, UK, 5–7 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.M.; Shamir, U.; Marks, D.H. Water distribution reliability: Simulation methods. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 1988, 114, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 31000:2009 Risk Management. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:31000:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 28 September 2017).
- ISO Guide 73:2009 Risk Management—Vocabulary. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:guide:73:ed-1:v1:en:term:3.7.1 (accessed on 28 September 2017).
- Delibera Della Giunta Provinciale. Decreto del Presidente Della Provincia del 20/03/2006 n.12. Available online: http://lexbrowser.provinz.bz.it (accessed on 8 June 2017).










| UN | PRser | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Failure Event | Number of Affected Nodes | Failure Event | Number of Affected Nodes |
| 1 | 48 | 34 | 306 | 54 |
| 2 | 59 | 29 | 321 | 54 |
| 3 | 321 | 29 | 59 | 45 |
| 4 | 306 | 28 | 101 | 42 |
| 5 | 101 | 20 | 85 | 40 |
| 6 | 347 | 16 | 87 | 37 |
| 7 | 348 | 16 | 90 | 37 |
| 8 | 335 | 14 | 88 | 35 |
| 9 | 26 | 13 | 93 | 35 |
| 10 | 310 | 13 | 48 | 34 |
| Failure Event | Pipe ID | Length | UN | PRser | λ | Break | Break Norm | CpUNdem | CpPRser | C_tot | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 87 | 32 | 41.62 | 4 | 37 | 0.601 | 0.025 | 0.028 | 0.112 | 1.035 | 0.116 | 0.070 |
| 88 | 33 | 53.37 | 2 | 35 | 0.601 | 0.032 | 0.036 | 0.072 | 1.255 | 0.090 | 0.054 |
| 90 | 34 | 19.36 | 4 | 37 | 0.601 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.052 | 0.482 | 0.025 | 0.015 |
| 93 | 35 | 28.63 | 2 | 35 | 0.601 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.038 | 0.674 | 0.026 | 0.016 |
| Rank | Failure Event | Pipe ID | λ | Ctot | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 312 | 129 | 1.164698 | 42.71896815 | 49.75472 |
| 2 | 328 | 159 | 1.164698 | 29.4251172 | 34.27139 |
| 3 | 27 | 70 | 0.921421 | 21.52369527 | 19.83238 |
| 4 | 59 | 405 | 0.601952 | 31.91113549 | 19.20899 |
| 5 | 59 | 404 | 0.601952 | 31.12305147 | 18.7346 |
| 6 | 48 | 390 | 0.728958 | 19.76419825 | 14.40727 |
| 7 | 52 | 136 | 1.164698 | 8.184900227 | 9.532941 |
| 8 | 135 | 364 | 1.164698 | 7.065763846 | 8.229484 |
| 9 | 305 | 131 | 0.728958 | 9.332392247 | 6.802922 |
| 10 | 52 | 137 | 1.496754 | 4.497545577 | 6.731719 |
| 11 | 42 | 99 | 1.164698 | 5.14500632 | 5.992381 |
| 12 | 42 | 100 | 1.164698 | 4.966474288 | 5.784445 |
| 13 | 247 | 217 | 0.921421 | 6.021586638 | 5.548415 |
| 14 | 27 | 69 | 0.921421 | 5.53121004 | 5.096572 |
| 15 | 304 | 130 | 1.164698 | 4.058647449 | 4.7271 |
| 16 | 313 | 138 | 0.921421 | 4.96502344 | 4.574876 |
| 17 | 48 | 408 | 0.728958 | 5.395299548 | 3.932946 |
| 18 | 27 | 163 | 1.164698 | 3.258599588 | 3.795286 |
| 19 | 321 | 121 | 0.728958 | 5.067614029 | 3.694078 |
| 20 | 315 | 133 | 1.164698 | 2.94751094 | 3.432961 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Ercole, M.; Righetti, M.; Raspati, G.S.; Bertola, P.; Maria Ugarelli, R. Rehabilitation Planning of Water Distribution Network through a Reliability—Based Risk Assessment. Water 2018, 10, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030277
D’Ercole M, Righetti M, Raspati GS, Bertola P, Maria Ugarelli R. Rehabilitation Planning of Water Distribution Network through a Reliability—Based Risk Assessment. Water. 2018; 10(3):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030277
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Ercole, Marianna, Maurizio Righetti, Gema Sakti Raspati, Paolo Bertola, and Rita Maria Ugarelli. 2018. "Rehabilitation Planning of Water Distribution Network through a Reliability—Based Risk Assessment" Water 10, no. 3: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030277
APA StyleD’Ercole, M., Righetti, M., Raspati, G. S., Bertola, P., & Maria Ugarelli, R. (2018). Rehabilitation Planning of Water Distribution Network through a Reliability—Based Risk Assessment. Water, 10(3), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030277





