Freshwater Ecosystem Services in Mining Regions: Modelling Options for Policy Development Support
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Freshwater Ecosystem Services in Mining Regions
1.2. Justification of This Review
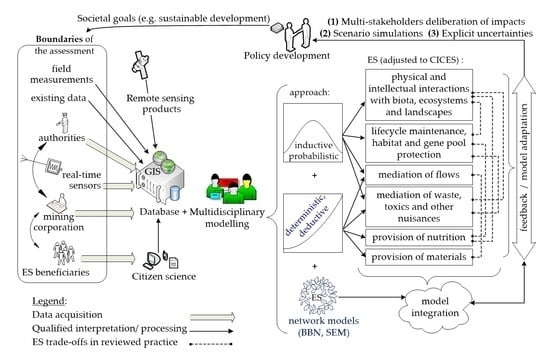
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Methodological Choices for ESA in Mining Contexts
3.1.1. Focus on Mining and Its Impacts
3.1.2. Data for ES Valuation in Mining Contexts
3.1.3. Indicators of Water Biophysical State
3.1.4. Complexity, Human–Ecosystem Integration and Ecological Functionality in ES Models
3.2. Policy-Oriented Efforts in Reviewed Assessments
3.2.1. Scenario Simulation, Trade-Offs and Uncertainties
3.2.2. Stakeholders Involvement and ESA Outcome
3.3. Fitting the Practice in an Environmental Management Scheme
4. Main Discussion
4.1. Data Science, Acquisition and Transformation
4.2. Process-Oriented Modelling
4.3. Monitoring Freshwater ES in Mining Contexts
4.4. Implications for Institutional Stakeholders
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Author (Year) | Water ES Model Foundation. | Final Output 1 | Public Participation | Simulation | Expert Knowledge | Trade-Off Assessment | Explicit Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Zhang et al. (2010) | LULC-based provision. | V | |||||
| 2. Bai et al. (2011) | Water productivity from statistics. | V+R | X | ||||
| 3. Li et al. (2011) | Water loss cost analysis. | V | |||||
| 4. Hogan et al. (2012) | LULC-based water quality. Validated models. | V | X | X | |||
| 5. Haase et al. (2012) | LULC-based cultural value regulation. | V | X | ||||
| 6. Larondelle et al. (2012) | Groundwater recharge model. | V | X | ||||
| 7. Boissiere et al. (2013) | Not directly assessed. Only rainfall. | K | X | ||||
| 8. Breffle et al. (2013) | Cultural water ES from rainfall. | K | X | X | |||
| 9. Evans et al. (2013) | Not directly assessed. | K | X | ||||
| 10. Bian and Lu (2013) | LULC-based. | V | |||||
| 11.Zhang et al. (2013) | LULC-based. | V | X | ||||
| 12. Woziwoda et al. (2014) | Not directly assessed. | R | X | ||||
| 13. Fu et al. (2015) | Water yield modelling. | V | X | ||||
| 14. Pandit et al. (2015) | Market price in a river stretch. | V | X | ||||
| 15. Fan and Ding (2015) | LULC-based. | V | X | X | |||
| 16. Mazzotta et al. (2015) | Fish habitat. Recreational fishing. | V+R | X | X | |||
| 17. Zhang et al. (2016) | LULC-based. Use of rainfall. | V+R | X | X | |||
| 18. Pullanikkatil et al. (2016) | LULC-based cultural value. | R | X | ||||
| 19. Blaen et al. (2016) | Not directly assessed. | V | X | X | |||
| 20. Fan et al. (2016) | LULC-based. Use of rainfall. | V | X | ||||
| 21. Molina et al. (2016) | Cultural value of photographs. | V | X | X | X | ||
| 22. Preece et al. (2016) | LULC-based. | V | X | X | |||
| 23. Duarte et al. (2016) | Not directly assessed. | V | X | X | X | ||
| 24. Wilker et al. (2016) | Not directly assessed, only scoped. | V | X | X | |||
| 25. Burges et al. (2016) | Proxies from field experiments. | V | X | ||||
| 26. Rosa et al. (2016) | Not directly assessed, only scoped. | R | X |
| Criteria | Class | Amount | Ratio | Criteria | Class | Amount | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mining focus | primary | 20  | 77% | Ecological functionality | null | 6  | 19% |
| secondary | 6  | 23% | low | 12  | 46% | ||
| Basis for ES valuation | LULC | 16  | 62% | mid | 6  | 19% | |
| cultural | 10  | 39% | high | 2  | 8% | ||
| ƒ(eco) # | 11  | 42% | Human–ecosystem integration | low | 2  | 8% | |
| +proxies * | 24  | 92% | mid | 16  | 62% | ||
| Main data sources | GIS | 16  | 62% | high | 8  | 30% | |
| Interviews | 13  | 50% | Model complexity | low | 7  | 27% | |
| field | 9  | 35% | mid | 10  | 39% | ||
| experiment | 2  | 8% | high | 9  | 35% | ||
| secondary data | 18  | 70% | ESA Output | value | 20  | 77% | |
| Indicator of water ES | area | 14  | 54% | response | 6  | 23% | |
| flow | 7  | 27% | only knowledge | 3  | 12% | ||
| quality | 3  | 12% | Scenario simulation | 7  | 27% | ||
| soil moisture | 2  | 8% | Trade-offs | 3  | 12% | ||
| Expert knowledge | 6  | 23% | Uncertainties | 6  | 23% | ||
References
- MEA. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Goethals, P.; Volk, M. Implementing sustainability in water management: Are we still dancing in the dark? Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackbart, V.C.S.; de Lima, G.T.N.P.; dos Santos, R.F. Theory and practice of water ecosystem services valuation: Where are we going? Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 23, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Bernhardt, E.S.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Eshleman, K.N.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Hendryx, M.S.; Lemly, A.D.; Likens, G.E.; Loucks, O.L.; Power, M.E.; et al. Mountaintop Mining Consequences. Science 2010, 327, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ELAW. Guidebook for Evaluating Mining Project EIAs; Environmental Law Alliance Worldwide: Eugene, OR, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Murrill, M.; Das, R.; Patil, S.G.; Sarkar, A.; Dadapeer, H.J.; Yendigeri, S.; Ahmed, R.; Das, K.K. Environmental arsenic contamination and its health effects in a historic gold mining area of the Mangalur greenstone belt of Northeastern Karnataka, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, H.; O’Leary, K.G. Mercury Exposure and Health Impacts among Individuals in the Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining Community: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela-Almeida, D.; Kuijk, F.; Wyseure, G.; Kosoy, N. Lessons from Yanacocha: Assessing mining impacts on hydrological systems and water distribution in the Cajamarca region, Peru. Water Int. 2016, 41, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, G.M.; Seanego, E.S.; Nkwonta, O.I. Impacts of mining on water resources in South Africa: A review. Sci. Res. Essays 2010, 5, 3351–3357. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, P.; Wood, P.J.; Reid, I. The Impairment of River Systems by Metal Mine Contamination: A Review Including Remediation Options. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 2017–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedieu, N.; Rhone, M.; Vigouroux, R.; Cereghino, R. Assessing the impact of gold mining in headwater streams of Eastern Amazonia using Ephemeroptera assemblages and biological traits. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graedel, T.E.; Allwood, J.; Birat, J.P.; Buchert, M.; Hageluken, C.; Reck, B.K.; Sibley, S.F.; Sonnemann, G. What Do We Know About Metal Recycling Rates? J. Ind. Ecol. 2011, 15, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Recycling Rates of Metals—A Status Report; International Resource Panel, Working Group on the Global Metal Flows, Ed.; UNEP: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP-WEF-CCSI-SDSN. Mapping Mining to the Sustainable Development Goals: An Atlas; United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), World Economic Forum (WEF), Columbia Center on Sustainable Investment (CCSI) and Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN): New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Environmental Impact Assessment Training Resource Manual; Sadler, B., McCabe, M., Eds.; UNEP: Paris, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, A.; McAllister, M.L.; Fitzpatrick, P. Sustainability reporting among mining corporations: A constructive critique of the GRI approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Stoen, M.; Hirsch, C. Environmental Impact Assessments, local power and self-determination: The case of mining and hydropower development in Guatemala. Extr. Ind. Soc. Int. J. 2015, 2, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandham, L.A.; Hoffmann, A.R.; Retief, E.P. Reflections on the quality of mining EIA reports in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2008, 108, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Jeronimo, R.P.; Rap, E.; Vos, J. The politics of Land Use Planning: Gold mining in Cajamarca, Peru. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azapagic, A. Developing a framework for sustainable development indicators for the mining and minerals industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2004, 12, 639–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; dArge, R.; deGroot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; ONeill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, R.S.; Wilson, M.A.; Boumans, R.M.J. A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C.; Matson, P.A. Ecosystem services: From theory to implementation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9455–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geneletti, D. Ecosystem services in environmental impact assessment and strategic environmental assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 40, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honrado, J.P.; Vieira, C.; Soares, C.; Monteiro, M.B.; Marcos, B.; Pereira, H.M.; Partidário, M.R. Can we infer about ecosystem services from EIA and SEA practice? A framework for analysis and examples from Portugal. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 40, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, J.C.S.; Sanchez, L.E. Advances and challenges of incorporating ecosystem services into impact assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rega, C.; Spaziante, A. Linking ecosystem services to agri-environmental schemes through SEA: A case study from Northern Italy. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 40, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Sheate, W.R.; Phillips, P.; Eales, R. Ecosystem services in environmental assessment—Help or hindrance? Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 40, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, T.P.; Marttunen, M.; Sarkki, S.; Rytkonen, A.M. Integrating ecosystem services into environmental impact assessment: An analytic-deliberative approach. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 40, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.M.; Hermoso, V.; Pantus, F.; Olley, J.; Linke, S.; Poff, N.L. A proposed framework to systematically design and objectively evaluate non-dominated restoration tradeoffs for watershed planning and management. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 127, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Llorens, P.; Latron, J.; Cid, N.; Rieradevall, M.; Prat, N. Validating alternative methodologies to estimate the regime of temporary rivers when flow data are unavailable. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buytaert, W.; Dewulf, A.; De Bievre, B.; Clark, J.; Hannah, D.M. Citizen Science for Water Resources Management: Toward Polycentric Monitoring and Governance? J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauman, K.A.; Daily, G.C.; Duarte, T.K.; Mooney, H.A. The Nature and Value of Ecosystem Services: An Overview Highlighting Hydrologic Services. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2007, 32, 67–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallouin, T.; Bruen, M.; Christie, M.; Bullock, C.; Kelly-Quinn, M. Challenges in Using Hydrology and Water Quality Models for Assessing Freshwater Ecosystem Services: A Review. Geosciences 2018, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.T.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Paglia, A.P. Ecosystem Services Modeling as a Tool for Defining Priority Areas for Conservation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Fu, M.C.; Zeng, H.; Geng, Y.H.; Hassani, F.P. Variations in Ecosystem Service Values and Local Economy in Response to Land Use: A Case Study of Wu’an, China. L. Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, B.; Jin, J.; Hu, D. Evaluating and modeling ecosystem service loss of coal mining: A case study of Mentougou district of Beijing, China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, L.D.; van Oosterzee, P.; Dungey, K.; Standley, P.M.; Preece, N.D. Ecosystem service valuation reinforces world class value of Cape York Peninsula’s ecosystems but environment and indigenous people lose out. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 18, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woziwoda, B.; Kopec, D. Afforestation or natural succession? Looking for the best way to manage abandoned cut-over peatlands for biodiversity conservation. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 63, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Zipper, C.E.; Burger, J.A.; Strahm, B.D.; Villamagna, A.M. Reforestation practice for enhancement of ecosystem services on a compacted surface mine: Path toward ecosystem recovery. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipper, C.E.; Burger, J.A.; Skousen, J.G.; Angel, P.N.; Barton, C.D.; Davis, V.; Franklin, J.A. Restoring Forests and Associated Ecosystem Services on Appalachian Coal Surface Mines. Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.T.; Mitchell, K.; O’Connell, D.W.; Verhoeven, J.; Van Cappellen, P. The legacy of surface mining: Remediation, restoration, reclamation and rehabilitation. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 66, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, P.; Quétier, F.; Lavorel, S. The diversity of the ecosystem services concept and its implications for their assessment and management. C. R. Biol. 2011, 334, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, M. Modelling ecosystem services–Challenges and promising future directions. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2013, 1–2, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorstius, A.C.; Spray, C.J. A comparison of ecosystem services mapping tools for their potential to support planning and decision-making on a local scale. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerema, A.; Rebelo, A.J.; Bodi, M.B.; Esler, K.J.; Meire, P. Are ecosystem services adequately quantified? J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterbroek, B.; de Kraker, J.; Huynen, M.M.T.E.; Martens, P. Assessing ecosystem impacts on health: A tool review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; DeFries, R.S.; Diaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Oteng-Yeboah, A.; Pereira, H.M.; et al. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP-WCMC. Developing Ecosystem Service Indicators: Experiences and Lessons Learned from Sub-Global Assessments and Other Initiatives; Technical Series No. 58; Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Landuyt, D.; Broekx, S.; Engelen, G.; Uljee, I.; Van der Meulen, M.; Goethals, P.L.M. The importance of uncertainties in scenario analyses—A study on future ecosystem service delivery in Flanders. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, P.; Bryant, B.P. Uncertainty assessment in ecosystem services analyses: Common challenges and practical responses. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 24, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.; Schulp, C.J.E.; Verburg, P.H. Mapping ecosystem services demand: A review of current research and future perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 55, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, N.; Dong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ya, X.; Zhao, Y. Integrating supply and social demand in ecosystem services assessment: A review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 25, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, W.; Srinivasan, R.; Perez-Minana, E.; Willcock, S.P.; Quintero, M. Using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to model ecosystem services: A systematic review. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelble, C.R.; Loomis, D.K.; Lovelace, S.; Nuttle, W.K.; Ortner, P.B.; Fletcher, P.; Cook, G.S.; Lorenz, J.J.; Boyer, J.N. The EBM-DPSER Conceptual Model: Integrating Ecosystem Services into the DPSIR Framework. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EEA Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services (CICES). Available online: www.cices.eu (accessed on 4 October 2017).
- Voinov, A.; Kolagani, N.; McCall, M.K.; Glynn, P.D.; Kragt, M.E.; Ostermann, F.O.; Pierce, S.A.; Ramu, P. Modelling with stakeholders—Next generation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 77, 196–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lautenbach, S. A quantitative review of relationships between ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; McIntyre, N.; Witt, K.; Raymond, C.M.; Arnold, S.; Scott, M.; Rifkin, W. Challenges of integrated modelling in mining regions to address social, environmental and economic impacts. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 93, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, A.; Epelde, L.; Benito, G.; Artetxe, U.; Becerril, J.M.; Garbisu, C. Enhancement of ecosystem services during endophyte-assisted aided phytostabilization of metal contaminated mine soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.D.; Ding, S.Y. Response of ecosystem services to land use change in county scale of Fengqiu, Henan Province, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 9015–9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Ding, S. Landscape pattern changes at a county scale: A case study in Fengqiu, Henan Province, China from 1990 to 2013. Catena 2016, 137, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, A.; Ekka, A.; Sharma, A.P.; Bhattacharjya, B.K.; Katiha, P.K.; Biswas, D.K. Economic valuation of natural ecosystems—An empirical study in a stretch of Bramhaputra River in Assam, North-East India. Indian J. Fish. 2015, 62, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Boissiere, M.; Locatelli, B.; Sheil, D.; Padmanaba, M.; Sadjudin, E. Local Perceptions of Climate Variability and Change in Tropical Forests of Papua, Indonesia. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, B.; Yang, L.L.; Wu, Z.L.; Zhang, X.S. Ecosystem Services Evaluation and Its Spatial Characteristics in Central Asia’s Arid Regions: A Case Study in Altay Prefecture, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8335–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudka, S.; Domy C, A. Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietron, J.; Chalov, S.R.; Chalova, A.S.; Alekseenko, A.V.; Jarsjö, J. Extreme spatial variability in riverine sediment load inputs due to soil loss in surface mining areas of the Lake Baikal basin. Catena 2017, 152, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedieu, N.; Allard, L.; Vigouroux, R.; Brosse, S.; Céréghino, R. Physical habitat and water chemistry changes induced by logging and gold mining in French Guiana streams. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaee, M.; Obiri, S.; Green, A.; Long, R.; Cobbina, S.J.; Nartey, V.; Buck, D.; Antwi, E.; Basu, N. Integrated Assessment of Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Ghana-Part 2: Natural Sciences Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8971–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, J.A.P.; Ali, S.H. Gemstone mining as a development cluster: A study of Brazil’ s emerald mines. Resour. Policy 2011, 36, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Liu, L.; Yu, Q.; Liu, S. Tunneling in abandoned coal mine areas: Problems, impacts and protection measures. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. Inc. Trenchless Technol. Res. 2013, 38, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEA. Mining and Biodiversity Guideline: Mainstreaming Biodiversity into the Mining Sector; Typo Colour Specialists cc: Pretoria, South Africa, 2013; ISBN 9780621417470. [Google Scholar]
- Vela-Almeida, D.; Brooks, G.; Kosoy, N. Setting the limits to extraction: A biophysical approach to mining activities. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, M.; Tao, J.; Huang, Y.; Hassani, F.P.; Bai, Z. Response of ecological storage and conservation to land use transformation: A case study of a mining town in China. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larondelle, N.; Haase, D. Valuing post-mining landscapes using an ecosystem services approach—An example from Germany. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, M.; Wainger, L.; Sifleet, S.; Petty, J.T.; Rashleigh, B. Benefit transfer with limited data: An application to recreational fishing losses from surface mining. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.L.; Wang, R.S.; Jin, J.S. Water eco-service assessment and compensation in a coal mining region—A case study in the Mentougou District in Beijing. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, D.M.; Labiosa, W.; Pearlstine, L.; Hallac, D.; Strong, D.; Hearn, P.; Bernknopf, R. Estimating the Cumulative Ecological Effect of Local Scale Landscape Changes in South Florida. Environ. Manag. 2012, 49, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilker, J.; Rusche, K.; Benning, A.; MacDonald, M.A.; Blaen, P. Applying ecosystem benefit valuation to inform quarry restoration planning. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 20, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrod, F.; Armsworth, P.R.; Anderson, B.J.; Heinemeyer, A.; Gillings, S.; Roy, D.B.; Thomas, C.D.; Gaston, K.J. The impact of proxy-based methods on mapping the distribution of ecosystem services. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 47, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.; De Jonge, V.N.; Marques, J.C. Linking biodiversity indicators, ecosystem functioning, provision of services and human well-being in estuarine systems: Application of a conceptual framework. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.; Vaissiere, A.-C.; Bas, A.; Calvet, C. Investigating the inclusion of ecosystem services in biodiversity offsetting. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.; Schwarz, N.; Strohbach, M.; Kroll, F.; Seppelt, R. Synergies, trade-offs, and losses of ecosystem services in urban regions: An integrated multiscale framework applied to the leipzig-halle region, Germany. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; y Silva, F.R.; Herrera, M.Á. Integrating economic landscape valuation into Mediterranean territorial planning. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 56, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaen, P.; MacDonald, M.; Bradbury, R. Ecosystem services provided by a former gravel extraction site in the uk under two contrasting restoration states. Conserv. Soc. 2016, 14, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullanikkatil, D.; Palamuleni, L.G.; Ruhiiga, T.M. Land use/land cover change and implications for ecosystems services in the Likangala River Catchment, Malawi. Phys. Chem. Earth 2016, 93, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breffle, W.S.; Muralidharan, D.; Donovan, R.P.; Liu, F.; Mukherjee, A.; Jin, Y. Socioeconomic evaluation of the impact of natural resource stressors on human-use services in the Great Lakes environment: A Lake Michigan case study. Resour. Policy 2012, 38, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, C.C.D.; Atkinson, P.M.; Dearing, J.A. Remote sensing of ecosystem services: A systematic review. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulp, C.J.; Burkhard, B.; Maes, J.; Van Vliet, J.; Verburg, P.H. Uncertainties in ecosystem service maps: A comparison on the European scale. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nelson, E.J.; Daily, G.C. Modelling ecosystem services in terrestrial systems. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2010, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, A.D.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 489, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, R.A.; Pearson, S.M.; Turner, M.G. Species richness alone does not predict cultural ecosystem service value. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 201701370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangenberg, J.H.; Settele, J. Precisely incorrect? Monetising the value of ecosystem services. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfatsion, L.; Rehmann, C.R.; Cardoso, D.S.; Jie, Y.; Gutowski, W.J. An agent-based platform for the study of watersheds as coupled natural and human systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 89, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.H.; Pedersen, L.C.; Vilsgaard, K.D.; Elbæk Nielsen, I.; Hansen, S.F. Environmental and Ethical Aspects of Sustainable Mining in Greenland. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2013, 3, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Buytaert, W.; Zulkafli, Z.; Grainger, S.; Acosta, L.; Alemie, T.C.; Bastiaensen, J.; De Bièvre, B.; Bhusal, J.; Clark, J.; Dewulf, A.; et al. Citizen science in hydrology and water resources: Opportunities for knowledge generation, ecosystem service management, and sustainable development. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Lu, Q. Ecological effects analysis of land use change in coal mining area based on ecosystem service valuing: A case study in Jiawang. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Lanzanova, D.; Liquete, C.; Reynaud, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Assessing water ecosystem services for water resource management. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 61, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.; Burkhard, B. The indicator side of ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarras-Wahlberg, N.H.; Flachier, A.; Lane, S.N.; Sangfors, O. Environmental impacts and metal exposure of aquatic ecosystems in rivers contaminated by small scale gold mining: The Puyango River basin, southern Ecuador. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 278, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohan, D.A.; Landuyt, D.; Ma, A.; Macfadyen, S.; Martinet, V.; Massol, F.; McInerny, G.; Montoya, J.M.; Mulder, C.; Pascual, U.; et al. Networking Our Way to Better Ecosystem Service Provision. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boumans, R.; Costanza, R.; Farley, J.; Wilson, M.A.; Portela, R.; Rotmans, J.; Villa, F.; Grasso, M. Modeling the dynamics of the integrated earth system and the value of global ecosystem services using the GUMBO model. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 529–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, S.; Mao, F.; Buytaert, W. Environmental data visualisation for non-scientific contexts: Literature review and design framework. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 85, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Cao, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H. Exploring an ecologically sustainable scheme for landscape restoration of abandoned mine land: Scenario-based simulation integrated linear programming and CLUE-S model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slocombe, D. Lessons from experience with ecosystem-based management. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Villarreal, M.L.; Niraula, R.; Meixner, T.; Frisvold, G.; Labiosa, W. Framing scenarios of binational water policy with a tool to visualize, quantify and valuate changes in ecosystem services. Water 2013, 5, 852–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, S.; Volk, M.; Gruber, B.; Dormann, C.F.; Strauch, M.; Seppelt, R. Quantifying Ecosystem Service Trade-offs. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software Modelling for Environment’s Sake, Fifth Biennial Meeting, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 5–8 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Carpentier, S.; Filotas, E.; Handa, I.T.; Messier, C. Trade-offs between timber production, carbon stocking and habitat quality when managing woodlots for multiple ecosystem services. Environ. Conserv. 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peh, K.S.H.; Balmford, A.; Bradbury, R.B.; Brown, C.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Hughes, F.M.R.; Stattersfield, A.; Thomas, D.H.L.; Walpole, M.; Bayliss, J.; et al. TESSA: A toolkit for rapid assessment of ecosystem services at sites of biodiversity conservation importance. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, E51–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, I.E.; Evangelinos, K.I. A SWOT analysis of environmental management practices in Greek Mining and Mineral Industry. Resour. Policy 2010, 35, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.L.; Renne, E.; Roncoli, C.; Agyei-Baffour, P.; Tenkorang, E.Y. Integrated Assessment of Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining in Ghana—Part 3: Social Sciences and Economics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8133–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voinov, A.; Seppelt, R.; Reis, S.; Nabel, J.E.M.S.; Shokravi, S. Values in socio-environmental modelling: Persuasion for action or excuse for inaction. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 53, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borja, A.; Galparsoro, I.; Solaun, O.; Muxika, I.; Tello, E.M.; Uriarte, A.; Valencia, V. The European Water Framework Directive and the DPSIR, a methodological approach to assess the risk of failing to achieve good ecological status. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Frostell, B. The DPSIR Framework and a Pressure-Oriented Water Quality Monitoring Approach to Ecological River Restoration. Water 2012, 4, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gari, S.R.; Newton, A.; Icely, J.D. A review of the application and evolution of the DPSIR framework with an emphasis on coastal social-ecological systems. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 103, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swenson, J.J.; Carter, C.E.; Domec, J.C.; Delgado, C.I. Gold Mining in the Peruvian Amazon: Global Prices, Deforestation, and Mercury Imports. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmons, J.A.; Currie, W.S.; Eshleman, K.N.; Kuers, K.; Monteleone, S.; Negley, T.L.; Pohlad, B.R.; Thomas, C.L. Forest to reclaimed mine land use change leads to altered ecosystem structure and function. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garris, H.W.; Baldwin, S.A.; Van Hamme, J.D.; Gardner, W.C.; Fraser, L.H. Genomics to assist mine reclamation: A review. Restor. Ecol. 2016, 24, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem Esmail, B.; Geneletti, D. Design and impact assessment of watershed investments: An approach based on ecosystem services and boundary work. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hobaib, A.S.; Al-Jaseem, K.Q.; Baioumy, H.M.; Ahmed, A.H. Environmental impact assessment inside and around Mahd Adh Dhahab gold mine, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2012, 5, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneberg, P. Burrowing bird’s decline driven by EIA over-use. Resour. Policy 2013, 38, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, S.M.; McKenzie, E.; Ricketts, T.H. Policy impacts of ecosystem services knowledge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, L.; Loomis, J.; Kroeger, T.; Casey, F. The role of bene fi t transfer in ecosystem service valuation. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 115, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, G.; Claverie, A.; Pasco, X.; Darnis, J.; De Maupeou, B.; Lafaye, M.; Morel, E. Acta Astronautica Towards disruptions in Earth observation? New Earth Observation systems and markets evolution: Possible scenarios and impacts ☆ ground Sampling Distance. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 137, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Martin-Lopez, B.; Lavorel, S.; Berraquero-Diaz, L.; Escalera-Reyes, J.; Comin, F.A. Ecosystem Services Flows: Why Stakeholders’ Power Relationships Matter. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landuyt, D.; Broekx, S.; D’hondt, R.; Engelen, G.; Aertsens, J.; Goethals, P.L.M. A review of Bayesian belief networks in ecosystem service modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 46, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Shirkey, G.; John, R.; Wu, S.R.; Park, H.; Shao, C. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: An updated review. Ecol. Process. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeyn, S.; Volk, M.; Dominguez-granda, L.; Goethals, P.L.M. Environmental Modelling & Software Input variable selection with a simple genetic algorithm for conceptual species distribution models: A case study of river pollution in Ecuador. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 92, 269–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Lautenbach, S.; Van Delden, H.; Newham, L.T.H.; Seppelt, R. How can we make progress with decision support systems in landscape and river basin management? lessons learned from a comparative analysis of four different decision support systems. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, J.L.; Chenu, C.; Lorenz, K. Ecosystem services provided by soils of urban, industrial, traffic, mining, and military areas (SUITMAs). J. Soils Sediments 2014, 15, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanni, M.; Raffaet, A. Deductive and inductive reasoning on spatio-temporal data. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2005, 3392, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landuyt, D.; Perring, M.P.; Seidl, R.; Taubert, F.; Verbeeck, H.; Verheyen, K. Modelling understorey dynamics in temperate forests under global change–Challenges and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 31, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumans, R.; Roman, J.; Altman, I.; Kaufman, L. The multiscale integrated model of ecosystem services (MIMES): Simulating the interactions of coupled human and natural systems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Semmens, D.J.; Waage, S.; Winthrop, R. A comparative assessment of decision-support tools for ecosystem services quantification and valuation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, E27–E39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, J.; Budds, J. The hydrosocial cycle: Defining and mobilizing a relational-dialectical approach to water. Geoforum 2014, 57, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppelt, R.; Dormann, C.F.; Eppink, F.V.; Lautenbach, S.; Schmidt, S. A quantitative review of ecosystem service studies: Approaches, shortcomings and the road ahead. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Mahoney, M.; Sprenger, M. Science of the Total Environment A comparison of the ef fi cacy and ecosystem impact of residual-based and topsoil-based amendments for restoring historic mine tailings in the Tri-State mining district. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jax, K. Function and “functioning” in ecology: What does it mean? Oikos 2005, 111, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Liquete, C.; Teller, A.; Erhard, M.; Luisa, M.; Barredo, J.I.; Grizzetti, B.; Cardoso, A.; Somma, F.; Petersen, J.; et al. An indicator framework for assessing ecosystem services in support of the EU Biodiversity Strategy to 2020. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 17, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Breuer, L. Water resources in South America: Sources and supply, pollutants and perspectives. Underst. Freshw. Qual. Probl. Chang. World 2013, 361, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, I.A.; Ryan, M.M. Impact of mining and industrial pollution on stream macroinvertebrates: Importance of taxonomic resolution, water geochemistry and EPT indices for impact detection. Hydrobiologia 2016, 772, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muradian, R.; Arsel, M.; Pellegrini, L.; Adaman, F.; Aguilar, B.; Agarwal, B.; Corbera, E.; De Blas, D.E.; Leroy, P.; May, P.; et al. Payments for ecosystem services and the fatal attraction of win-win solutions. Conserv. Lett. 2013, 6, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Klein, A.M.; Kruess, A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Thies, C. Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity—Ecosystem service management. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Criteria |
|
| Mining focus |
|
| Basis for ES valuation |
|
| Data sources |
|
| Indicator of water biophysical state |
|
| Ecological functionality 1 |
|
| Human–ecosystem integration |
|
| Model complexity |
|
| ESA output |
|
| Policy-oriented aspects in models: (1) scenario simulation; (2) trade-offs analysis; (3) uncertainty assessment; and (4) stakeholder participation. | |
| Ecological Functionality | High Complexity | Medium Complexity | Low Complexity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High ecological functionality |  | Burges et al. (2013) | Larondelle et al. (2012) | |
| Medium ecological functionality |  | Li et al. (2011) Hogan et al. (2012) Evans et al. (2013) | Haase et al. (2012) Bai et al. (2011) | Wilker et al. (2016) |
| Low ecological functionality |  | Zhang et al. (2010) Duarte et al. (2016) Zhang et al. (2016) Mazzotta et al. (2015) Fu et al. (2015) | Molina et al. (2016) Blaen et al. (2016) Bian et al. (2013) | Pullanikkatil et al. (2016) Pandit et al. (2015) Boissiere et al. (2013) Woziwoda et al. (2014) |
| Null ecological functionality |  | Rosa et al. (2016) Preece et al. (2016) Fan et al. (2016) Zhang et al. (2013) | Fan et al. (2015) Breffle et al. (2013) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercado-Garcia, D.; Wyseure, G.; Goethals, P. Freshwater Ecosystem Services in Mining Regions: Modelling Options for Policy Development Support. Water 2018, 10, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040531
Mercado-Garcia D, Wyseure G, Goethals P. Freshwater Ecosystem Services in Mining Regions: Modelling Options for Policy Development Support. Water. 2018; 10(4):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040531
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercado-Garcia, Daniel, Guido Wyseure, and Peter Goethals. 2018. "Freshwater Ecosystem Services in Mining Regions: Modelling Options for Policy Development Support" Water 10, no. 4: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040531
APA StyleMercado-Garcia, D., Wyseure, G., & Goethals, P. (2018). Freshwater Ecosystem Services in Mining Regions: Modelling Options for Policy Development Support. Water, 10(4), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040531