Abstract
The current study was performed with an aim to investigate the performance of ecological revetments implemented on the bank of the Cuatien River in Vinh city, Vietnam. Based on the ecological, topographical, and hydrological conditions of the Cuatien River, the gabion and riprap models were introduced to investigate the effect of ecological revetment on the slope stability and ecological restoration characteristics. The effect of prevailing climatic indicators, such as temperature, precipitation, sunlight hours, and humidity were investigated to ascertain the characteristics of weather conditions on the subtropical area. On the surface soil layer of the gabion and riprap, the nutrient indicators of soil organic matter (SOM) and available nitrogen (AN) increased in the spring, summer, and winter, but decreased in autumn, and available phosphorus (AP) did not show an obvious change in the four seasons. The biomass growth rate of Vetiver grass on the gabion and riprap revetments was found to be the highest during the summer, at 15.11 and 17.32 g/month, respectively. The root system of Vetiver and other native plants could increase the cohesion of soil. After 6 and 12 months, the shear strength of the soil behind the gabion revetment increased by 59.6% and 162.9%, while the shear strength of the soil under the riprap also increased by 115.6% and 239.1%, respectively. The results also indicated that the gabion and riprap revetments could improve the river water purification effect and increase the ecological diversity in the region. In the current study, 26 floral and 9 faunal species were detected in the riprap revetment, whereas 14 floral and 5 faunal species were detected in the gabion revetment, respectively. Through high sequencing technology, the number of bacterial species in the present study was found to be 198, 332, and 351 in the water, gabion, and riprap samples, respectively.
1. Introduction
Since the 1990s, the economy of Vietnam has experienced a very rapid development. As a result, existing construction technologies in the country have not been able to keep up with the demand of a more modern urban infrastructure [1]. Urban river ecosystems and their quality in Vietnam has been severely affected due to industrial activities, rapid urbanization, which has led to several negative effects on human health and the environment [1,2]. Ecological revetment is one of the effective, cost-efficient, sustainable eco-technologies that can be used to restore urban ecological systems. Vinh city is among the rapidly-developing cities in Vietnam [2], where effective urban development planning and more efficient construction technologies are required for flood control and environmental protection.
Conventionally, concrete and rock materials have been widely used in river bank revetment to control flooding and erosion. The strong revetment with stable construction is essential to ensure the safety of people and their property. However, an appropriately designed, hard revetment can negatively affect the ecosystem, including aquatic and amphibian habitats, river water quality, and aesthetic value [3]. In addition, after heavy rainfall events, storm water runoff scours the road surface, which results in riverbed erosion and water pollution related problems [4]. In order to construct a secure bank revetment with fewer negative effects on the river ecosystem, the ecological impact of revetment must be considered. With the consideration of topographical, hydrological, and ecological conditions of the river, ecological revetment must be combined with civil engineering technologies and ecological science to ensure good stability of the bank slope and ecological restoration effects [5]. Ecological revetment (which integrates plants and a more porous structure) can have a positive effect on the ecosystem as it can facilitate ground and river water circulation, and river bank ecological restoration. This is an indispensable part of the concept of ‘’sponge city’’ [5,6,7]. Ecological revetment can also be constructed using locally-available limestone materials [6,7,8]. Ecological revetment with a porous structure can provide a habitat for microbial and plant reproduction, which plays an important role in removing water pollutants. Plant and microbial growth and their diversity can also improve the river water quality.
There have been some recent examples of revetment design with systematic ecological consideration. In 2001, the Soil and Water Conservation Department of Taiwan worked on the development and integration of ecological engineering, and presented some examples of existing ecological engineering methods using stone revetment, boxed gabion revetment, and arc-shape stone streambed sill for bank protection, respectively [6]. In another study, Chen et al. [7] evaluated the ecological restoration capability of the revetment, and proposed hexagonal precast blocks, bamboo, and complex natural material to construct ecological revetment works for the Liudaxian channel bank in China. Gabriel et al. [8] demonstrated that a well designed riprap can have positive effects in increasing the ecological diversity and the amount of fauna, flora, and microbial communities present in the region, and enhancing pollutant removal.
Plant roots and the stones present in the ecological revetment provides a good habitat for microbial reproduction, which can improve the water quality, as well as the stability of river slopes [7,8]. Ramli et al. [9] studied the ability of gabion to collectively deform under aggravated loads, under the influence of soil-hydrostatic pressures, and evaluated the stability of the gabion wall for earth retaining structure in flood-prone areas. Helal et al. [10] showed that plant roots provide the ideal habitat for microbial growth and reproduction that can improve the effect of naturally occurring biodegradation and the adsorption of pollutants from soil and water. Previous studies have proved that Vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) has a high ability to increase the stability of the soil slope. Ali et al. [11] showed that Vetiver grass, due to its unique root characteristics, could increase the shear strength of the soil and improve the stability of the bank slope. Many existing ecological engineering works have proved the feasibility, ecological restoration, and bank slope stable effectiveness of the ecological revetment and Vetiver grass.
Being low-cost and easy to construct, gabion and riprap revetments are ideal for fast growing countries, like Vietnam. Therefore, in this study, riprap and gabion revetments were combined with Vetiver grass to increase the slope stability and the ecological restoration effect. The gabion and riprap models were designed and applied to investigate the ecological revetment structure and performance, by considering the prevailing ecological, topographical, and hydrological conditions of the Cuatien River. The objectives of this study can be stated as follows:
- Investigate the effect of climatic factors, such as temperature, precipitation, sunlight hours, and humidity, which directly affect the growth of Vetiver grass on the ecological revetments.
- Determine the soil organic matter, available nitrogen, and phosphorus contents in order to understand the soil nutrient effects on the growth of Vetiver grass.
- Investigate the soil strength to envisage the effect of plant root system on the soil shear strength values.
- Evaluate the ecological revetments with regard to the faunal, floral, and the microbial diversity and their impact on their overall performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
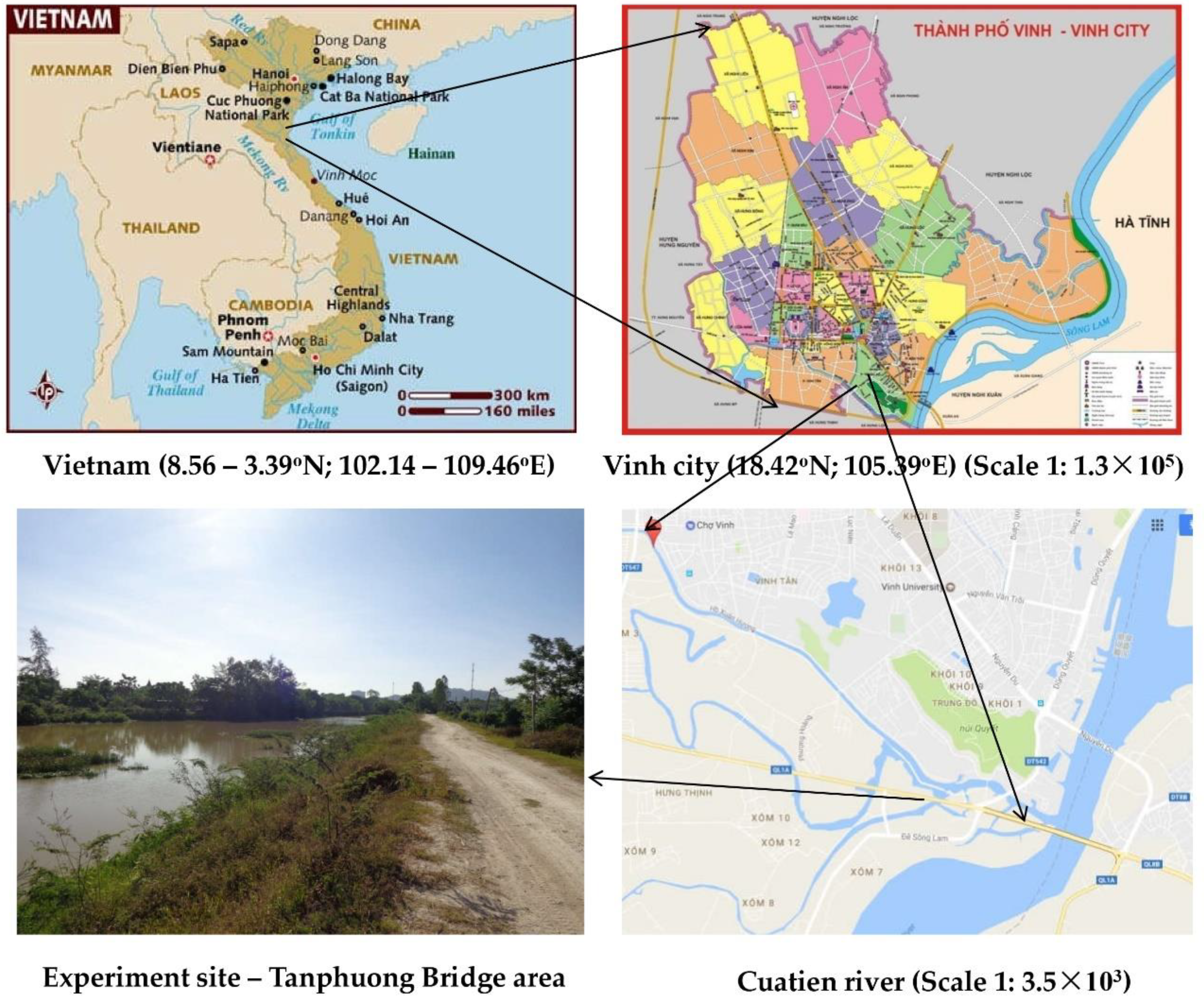
Vinh City is located in the Nghe An province, Vietnam and it has subtropical monsoon [2,12]. The current study sites were located near the Tanphuong bridge area (18°42′ latitude and 105°39′ longitude) of the Cuatien River. These sites were located within a straight reach. The width of the riprap and gabion revetments were 8 and 3 m, respectively, along the river bank. The distance between the two experimental plots was approximately 500 m, to ensure that the environmental and hydrological regimes and their influences were nearly similar in the two experimental plots. The experimental plots were constructed at a location on the Cuatien River bank which were eroded by the rapid fluctuations in river water level and flow. Cuatien River has a length of 25 km, a width of 18 to 60 m, and a depth of 0.86 to 2.45 m. It starts from Namdan county and flows through the delta of Hungnguyen county and merges with the Lam River in Vinh city (Figure 1). It is not only an important source of freshwater for the region, but it also plays an important role in the water ecological system of Vinh city. There are residential areas, farm lands, and animal farms on both sides of the Cuatien River catchments, which produce large amounts of domestic sewage and garbage. The lack of proper garbage collection and sewage treatment systems are the key factors that contribute to the deterioration of river water quality.
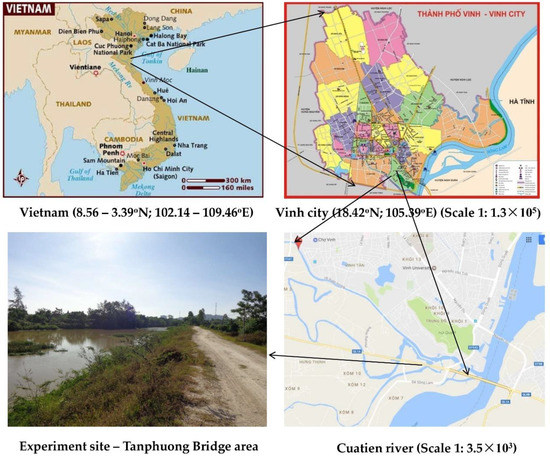
Figure 1.
Location of the experimental site at Cuatien River.
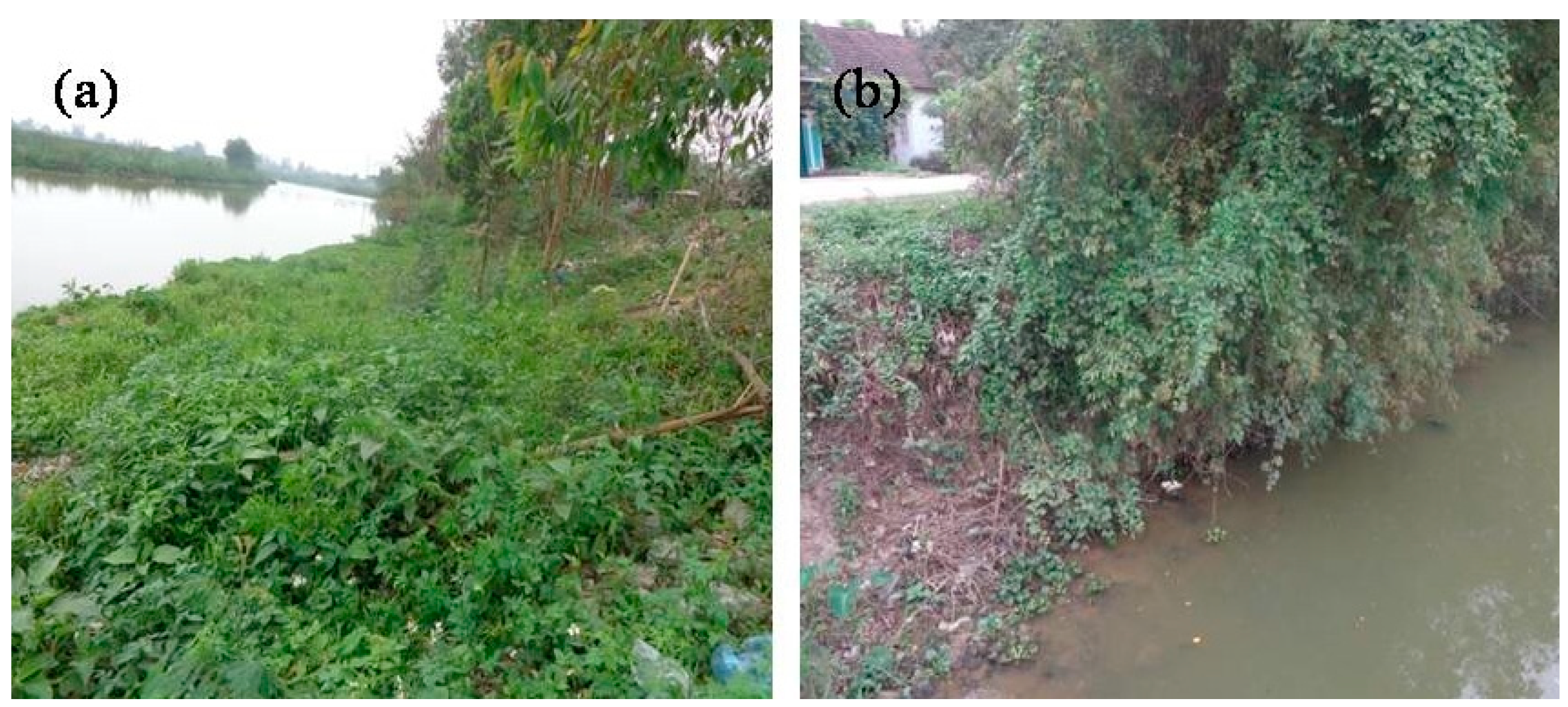
A water flow meter, fitted with a flow probe (Xiuyan Precision Instrument Factory, Anshan Liaoning, China) was used to determine the velocity of the river flow. The flow meter was fixed to the boat to determine the flow velocity along the river. The velocity of the river flow ranged from 0.05–0.09 m/s during the dry season and 0.31–0.53 m/s during the rainy season. Although the flow velocity is not high in Cuatien River, the hydrological behavior is significantly affected by the exchange of tide regime at the mouth of the Lam River. Therefore, the water level changes frequently, which is the main cause of erosion in the river banks (Figure 2). Hence, the prevailing river hydrological conditions were considered to design and construct the ecological revetments. In addition, on both sides of the river, the soil levee work was constructed to prevent flood that is too easy to convert and construct the ecological revetment work. Sandy clay soil with the following characteristics: cohesion C = 6.8 (kPa), internal friction angle Ф = 23°, and proportion ɣ = 1.8 (t/m3), was used as the main construction material to build the levee structures. Since the slope along the river bank is different from the topography, which has a slope rate of 18–63°, a proper design of the ecological revetment to transform the bank structure is extremely important. Riprap is relatively easy to install, is flexible and can be easily repaired, requires low maintenance, and has a natural appearance. Side slopes from 1:3 (18°) to 1:2 (26°) are recommended for riprap stability [13]. The riprap revetment structure was applied in the low slope banks where the slope is lower than 26° (steepness m = 0.5), whereas the gabion revetment structure was applied on a high slope bank where the slope is higher than 26° (steepness m = 0.5) [14].

Figure 2.
Experimental site at Cuatien River bank: (a) low slope bank; and (b) high slope bank (photos were taken on 9 November 2015).
2.2. Construction Materials
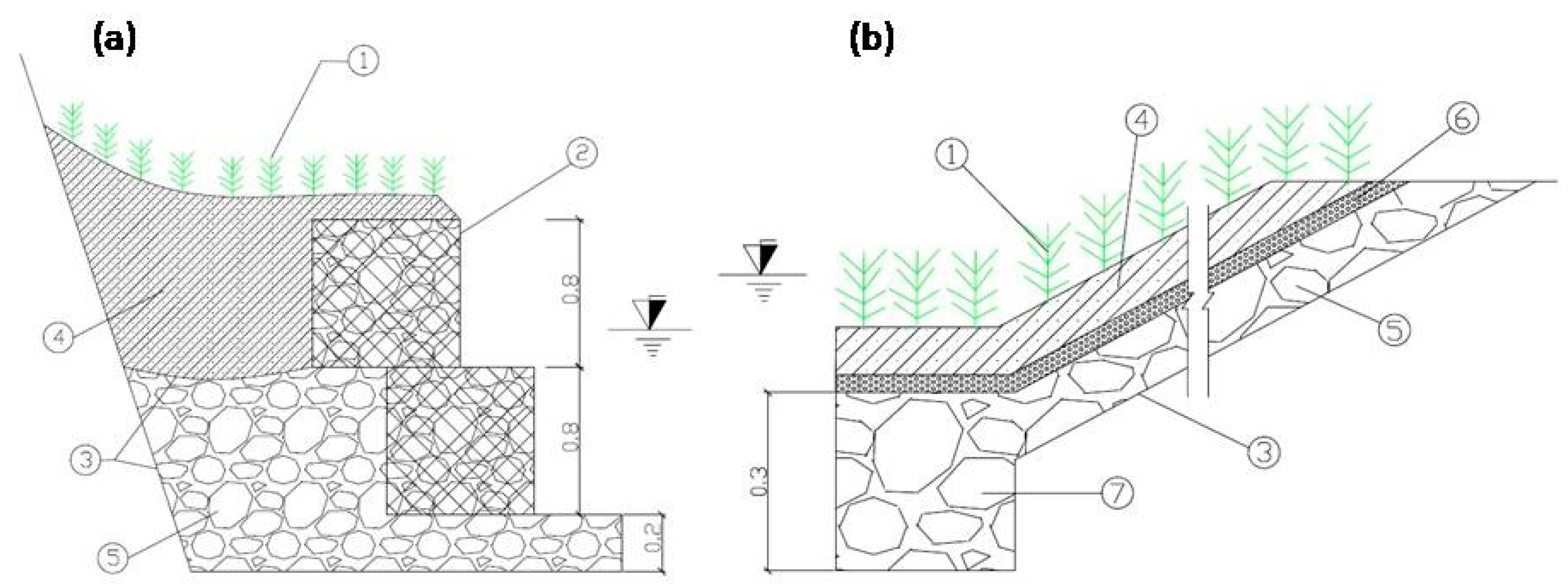
Two ecological revetment models (experimental setup) were constructed using natural materials, such as limestone, soil, and Vetiver grass, in conjunction with artificial materials (steel frames, polyethylene nets, geotextile, mesh wire 5 × 5 cm). The construction of riprap and gabion revetments were done in accordance with the design presented in Figure 3.
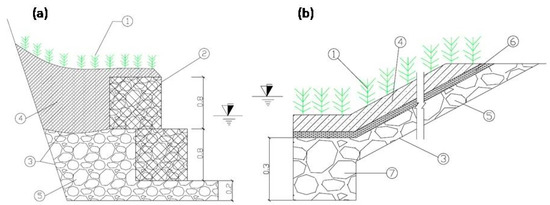
Figure 3.
Schematic design of: (a) gabion revetment structure; and (b) riprap revetment structure (1. Vetiver plants; 2. gabion; 3. geotextile; 4. fill soil; 5. limestone; 6. gravel; and 7. base structure).
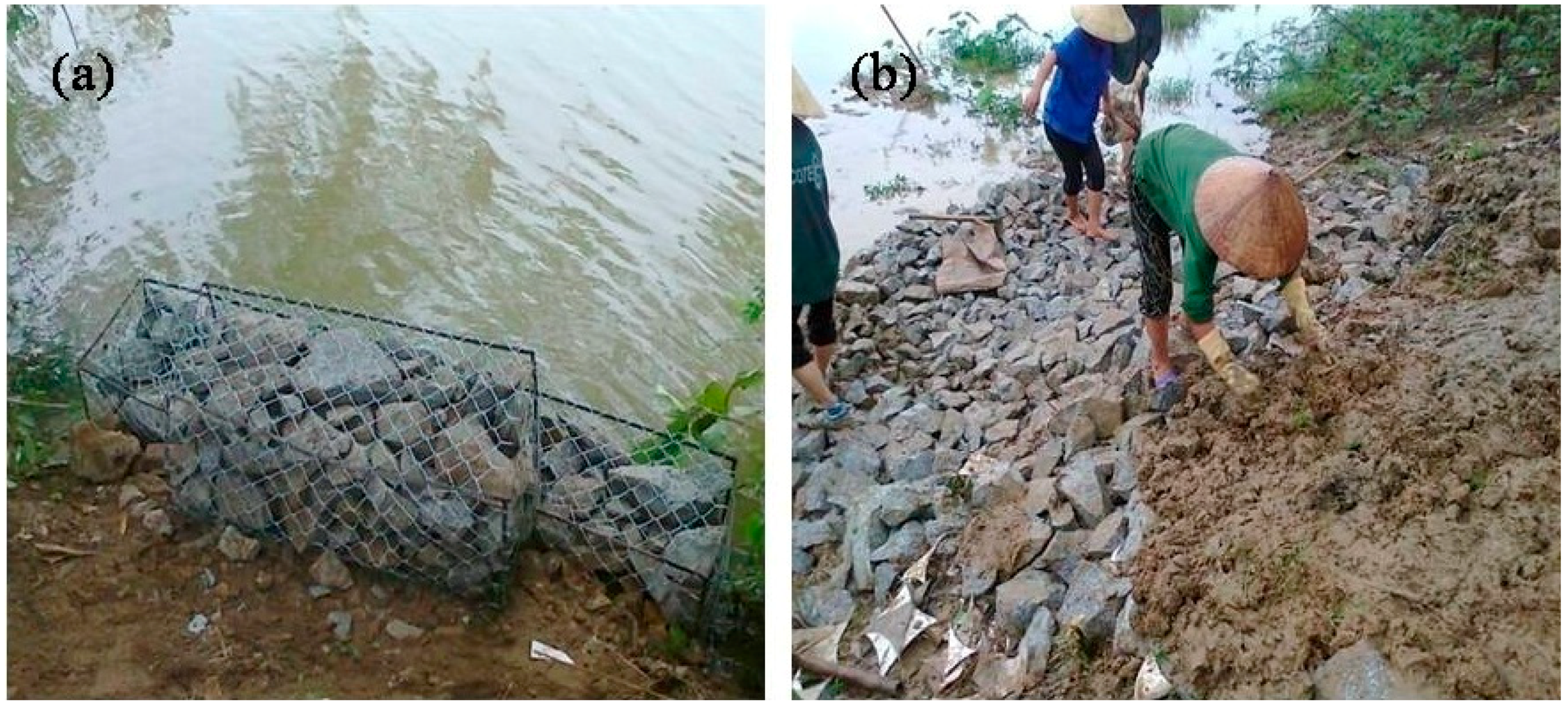
The river bank was selected to construct the gabion at a slope of approximate 57° (steepness m = 1.54). The gabion revetment was constructed as shown in Figure 4a. Firstly, the surface soil layer was excavated at a depth of 0.15 m, and then the geo-textiles were covered on the pit, and the stones were used as filling material to form the stable base. Three gabion structures with the following dimension: 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.8 m of length, height, and width were installed to form the gabion revetment. In order to ensure sufficient porosity and stability of the gabion revetment, which is beneficial for the development of plants on the gabion, the diameter of the stones was selected in the range of 8–12 cm (>5 cm) to fill the steel-framed structure [15]. These structures were installed at a stable position and then filled with limestone. In the next step, the soil was used to cover the top of the gabion structure.

Figure 4.
Experimental site: (a) gabion; and (b) riprap revetments (photos were taken on 19 November 2015).
The riprap revetment structure was installed in an area of 4 × 8 m. The sloping bank was selected to construct the riprap revetment, with a slope of approximately 22° (steepness m = 0.42). The riprap revetment was constructed as shown in Figure 4b. In the first step, the surface soil layer was excavated up to a depth of 0.1 m. Then, geo-textiles were used to separate the soil and the limestone layer. In order to ensure proper porosity and stability of the revetment, the limestone diameter was selected in the range of 0.15–0.2 m, as a heap, for covering the ground surface. Thereafter, the polyethylene net was covered on the surface of the limestone layer to prevent erosion caused due to the water flow [16]. In the bottom of the riprap, the soil layer was excavated to a depth of 0.3 m and filled with stones to increase the stability of the revetment structure [17].
After construction of the revetment structures, Vetiver grass was planted on the top soil layers. The weight of five random Vetiver plants at the time of plantation was 2.31 ± 0.28 g. In order to ensure proper growth of Vetiver grass, the distance between the plants was maintained at 22–25 cm, resulting in a plant density of 25 plants/m2.
2.3. Climate Data Collection
The data pertaining to temperature, precipitation, sunlight hours, and humidity in Vinh city were collected on a daily basis. The average values of climatic data in different seasons, such as spring, summer, autumn, and winter were calculated.
2.4. Soil Nutrient Test
The mid-point of the soil surface layer of riprap and gabion were selected for the collection of soil samples. A shear soil ring with 80 mm diameter and 20 mm height was used to collect the soil samples from the revetment surface. Soil samples were collected during the initial stages of the experimental work (18 December 2015), at the end of the spring (22 April 2016), the summer (16 July 2016), the autumn (20 October 2016), and the winter (20 January 2016) seasons, respectively. Experiments pertaining to the measurement of soil nutrient tests of the soil samples were performed at the Chemical Laboratory, Vinh University (Vietnam). The available nitrogen (AN) content was determined using the micro-diffusion technique after alkaline hydrolysis of the samples [18]. The available phosphorus (AP) was determined according to the Olsen method [18], and the soil organic matter (SOM) was determined using the K2CrO7-H2SO4 oxidation method [19], respectively.
2.5. Plant Growth Determination
The growth of Vetiver grass was determined once a month, and five Vetiver plant samples were selected from the center point and at sites adjacent to the four sides of the gabion and riprap surface, respectively. The plant weight was determined by an ES-S electronic balance (Leqi, Tianjin, China). The average weight of five samples values was used to determine the growth rate of the Vetiver grass. In order to determine the differences in weight of the five plants, the standard deviation (SD) was calculated. Accordingly, small values of SD means that the values in the data are close to the averaged mean, and a large SD means that the values in the data are farther from the average.
2.6. Soil Shear Strength Test
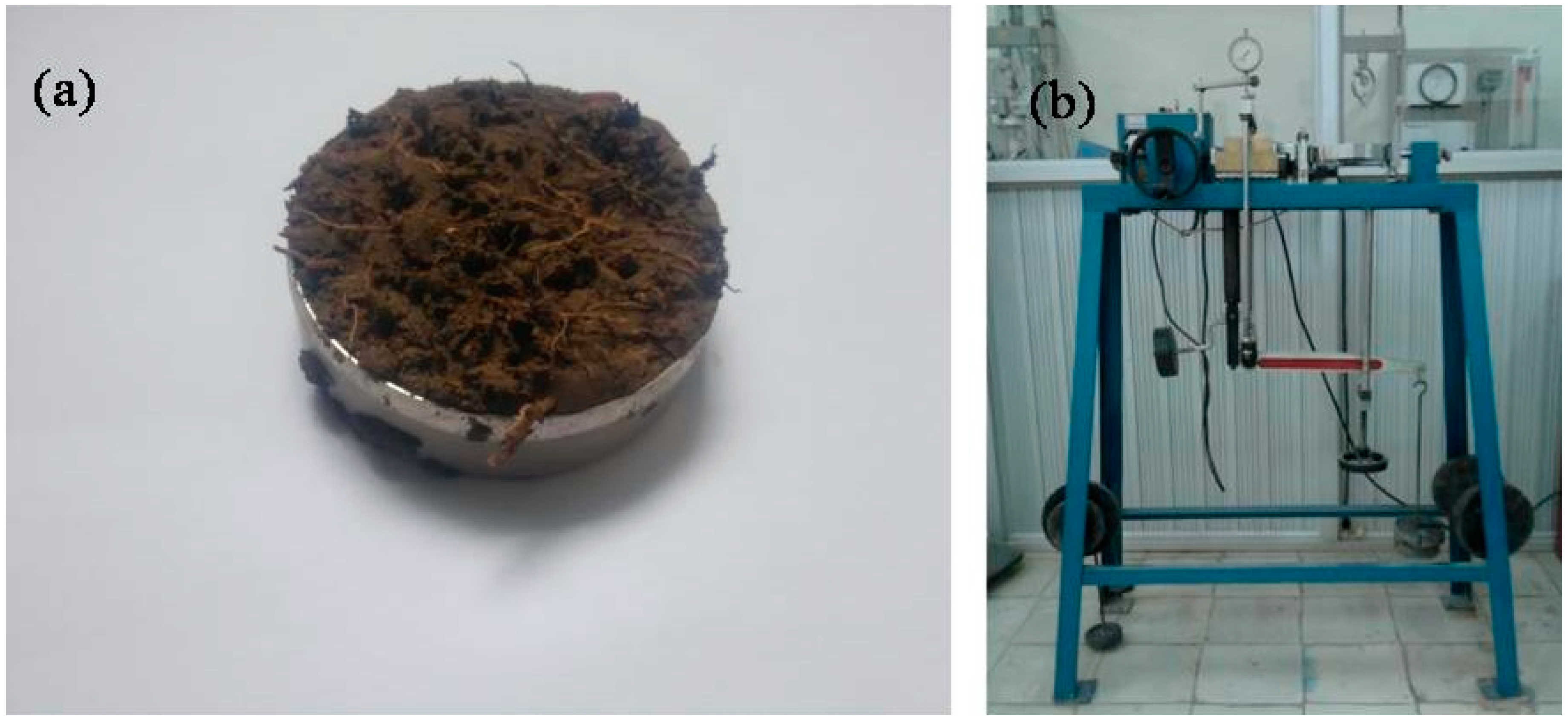
The center riprap surface point beneath the riprap rock layer and sites behind the gabion wall were selected as sites to collect the soil samples. Soil layer with a depth of 10 cm was dug out to make the space for experimental sampling. Shear soil ring with 80 mm diameter and 20 mm height was used to collect the soil samples. The soil samples were collected at the initial stage of the experimental work, i.e., after six months and after 12 months, respectively. The soil direct shear strength experiment was performed at the soil mechanics laboratory of Vinh University (Figure 5). The shear strength (τ) of the soil samples was determined by a direct shear strength experimental device EDJ-2 (Yueke Instrument Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China) with normal stress (δ) values of 10, 20, 50, and 100 kPa, respectively. The tests were performed according to the ASTM D3080 standards with a shear rate of 1.5 mm/min. The cohesion C and internal friction angle Ф were determined according to the Coulomb formula shown in Equation (1) [20]:
where τ is the shear strength (kPa); C is the cohesion (kPa); δ is the normal stress (kPa); and Ф is the internal friction angle.
τ = C + δtgФ

Figure 5.
Experimental setup for determining the direct shear strength of the soil: (a) soil sample; and (b) experimental device for measuring the direct shear strength (photos were taken on 26 May 2016).
2.7. Determination of Floral and Faunal Diversity
Floral and faunal diversity were investigated in the current work. The studied area was as follows: surface of natural slope (4 × 8 m), gabion (4 × 3 m), and riprap (4 × 8 m). Samples were collected three times per week to investigate the growth of floral and faunal species, as well as for the frequency of the occurrence of the species in the experimental area. This experimental work was carried out for a period of one year.
2.8. Determination of Microbial Diversity
Water and mud samples were collected to determine the characteristics of microorganisms. Samples included: #1 river water near the shore, #2 gabion near the water mud interface, and #3 riprap near the water mud interface. High-throughput deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing technology was adopted to explore the influence of spray microbial liquid to improve the microorganism community in river water and sediments [21]. The Miseq high-throughput sequencing process was performed as follows: (1) The extracted genomic DNA was detected with the help of 1% agarose gel electrophoresis; (2) Specific primers with “5” Barcode “3” were synthesized according to the designated sequencing region; (3) All samples were tested according to the standard protocol, wherein each sample measurement was repeated thrice and the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product of the same samples were purified, mixed, and detected with 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; (4) The PCR products were quantified by Qubit according to the preliminary quantitative result of electrophoresis; and (5) Miseq sequencing on the machine. Adequate data analysis was performed on the experimental data in the form of valid sequence statistics, optimization of sequence statistics, diversity index, and species classification [21].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Climate Conditions
The average daily temperature is 24.5 °C, the temperature reached the highest value during the summer period (29.4 °C), and reached the lowest value during the winter period (19.9 °C). The average yearly precipitation is 155 mm, with a lowest average precipitation of 54.2 mm during the spring period. The climate of Vinh city can be divided into the dry and the rainy seasons. The dry season (winter and spring) starts from November to April, where the average rainfall is 54.2 mm (spring) and 111.8 mm (winter). During this season, a longer duration of rainfall prevails; however, with a low rainfall intensity (3.3 mm/h). The rainy season starts from May to October, and the average rainfall is 131.2 mm (spring) and 322.6 mm (autumn), respectively. The duration of rainfall is short, but with a high rainfall intensity of 87.3 mm/h. This often causes severe flooding in the region. The average monthly sunshine hours for the year is 142.5 h/month. The monthly sunshine hour value is high during the summer (224.7 h) and the autumn (171.5 h) period, but it is low during the spring (85.3 h) and the winter (88.5 h) seasons. Additionally, the humidity is always high in Vinh city, wherein the values vary between 81.3% and 87.7%. Olsen et al. [12] carried out a similar study in Nghe An province (Vietnam) and reported that the average temperature was 24.2 °C, annual precipitation was 1610 mm and the average humidity was 84%, respectively. The average values of daily temperature, humidity, and monthly sunshine hours during the four seasons are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the prevailing climatic conditions of Vinh city, Vietnam.
3.2. Soil Nutrient Test
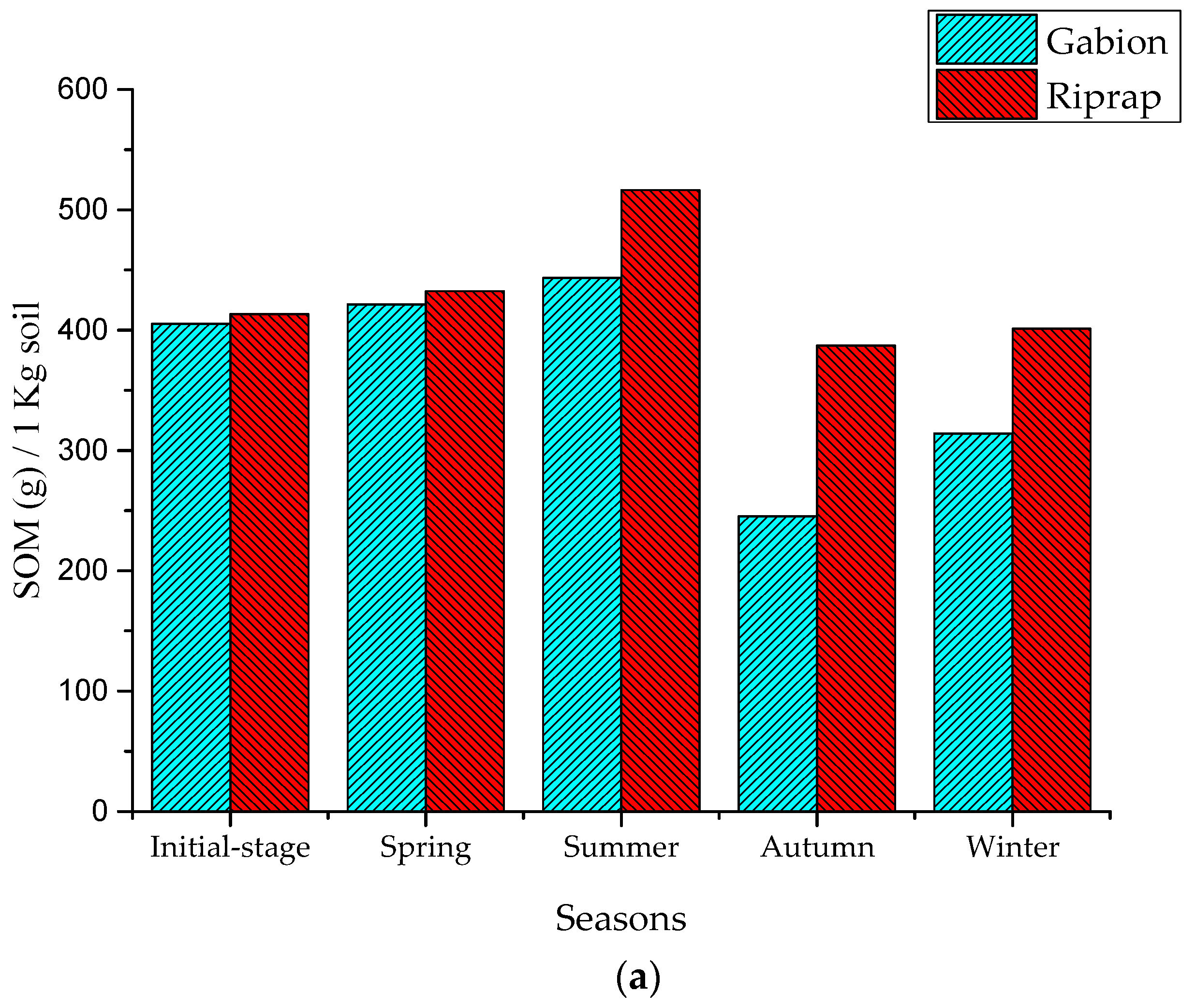
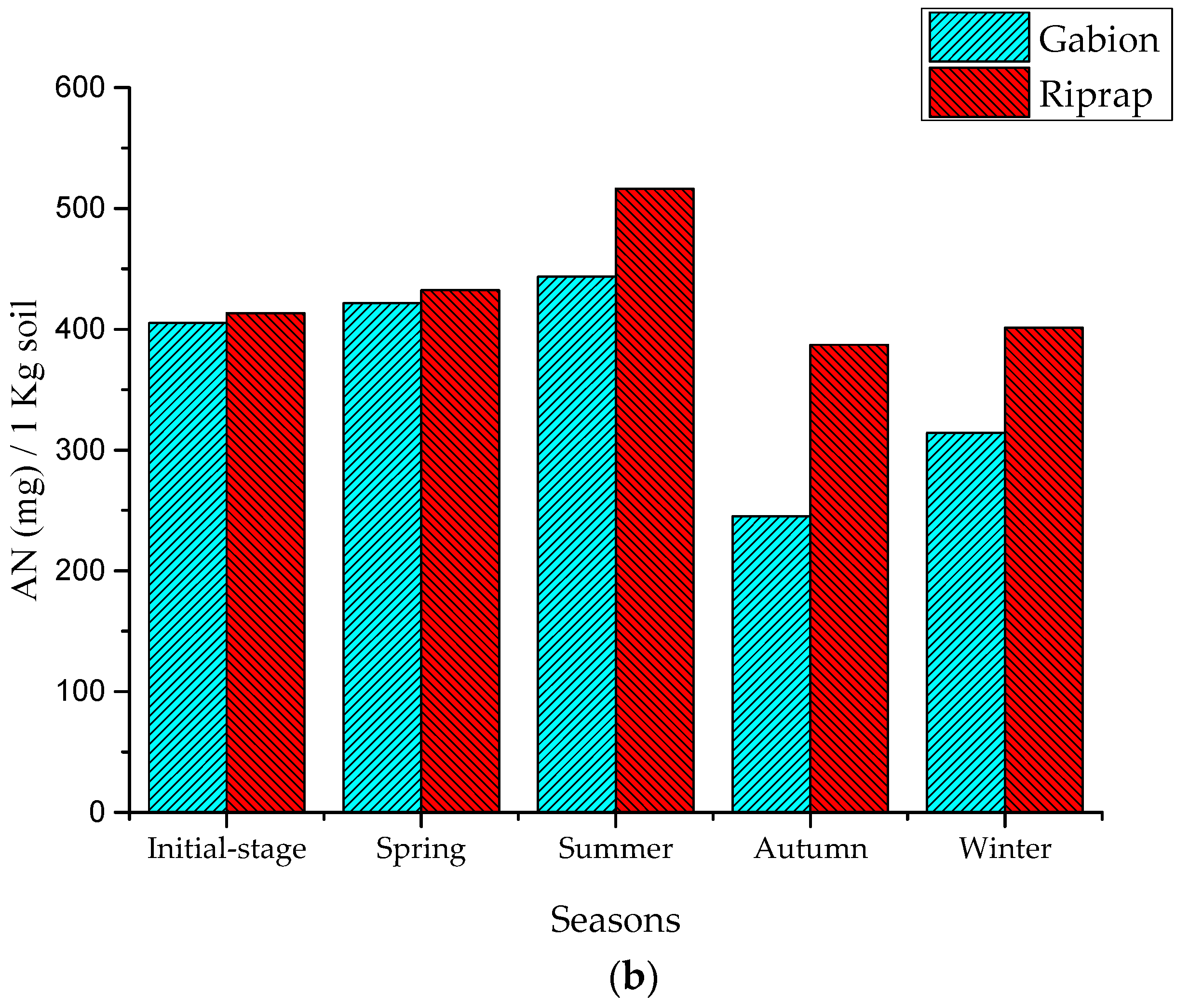
The results show that the SOM and AN levels were increasing in the seasons of spring and summer. In the three months of spring, the riprap’s SOM and AN indicator values of the surface soil layer increased to 3.74 g/kg and 19.02 mg/kg, while the gabion’s SOM and AN indicator values increased to 2.75 g/kg and 19.02 mg/kg, respectively (Figure 6). During the three months of summer, the riprap’s SOM and AN indicator values increased to 7.06 g/kg and 84.08 mg/kg, while the gabion’s SOM and AN indicator values increased to 3.86 g/kg and 21.95 mg/kg, respectively.
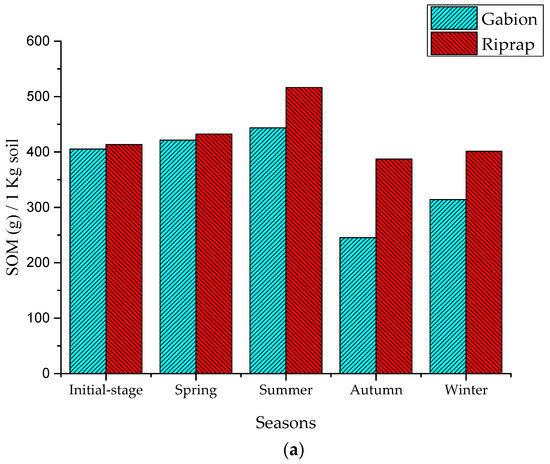
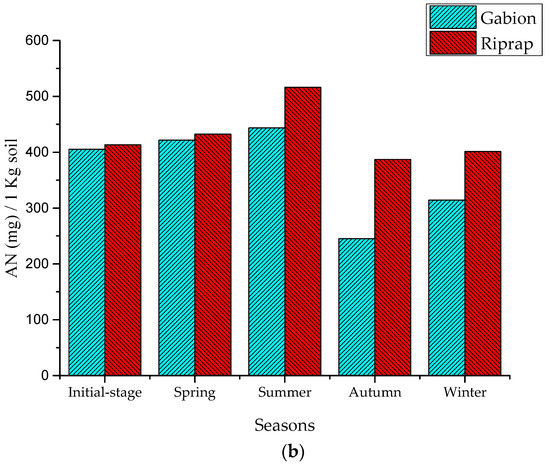
Figure 6.
Nutrient indicators in the slope soil layer: (a) SOM indicators; and (b) AN indicators.
This increase is presumably because, during the spring and summer periods of small and medium rainfall, the pollutants present in the road surface were scoured and transferred to the revetment surface by storm runoff, and the pollutants accumulated in the revetment surface soil layer [4]. The amount of SOM and AN accumulated in the riprap revetment surface soil layer was higher than the gabion revetment. The riprap has a gentle slope and, therefore, the water runoff velocity was slow on the surface soil layer. Hence, the sediments and the pollutants were easily captured by the plant system [22].
During the period of three months in autumn, the SOM and AN indicator values in the riprap revetment decreased to 9.69 g/kg and 129.21 mg/kg, respectively, while the gabion’s SOM and AN indicator values decreased to 13.75 g/kg and 198.19 mg/kg, respectively. The autumn season, with the continuous occurrence of heavy storms, caused extreme runoff periods which had diluted the scoured sediments and nutrients on the surface soil layer of the revetment [22,23]. This eventually led to a decrease in the nutrient concentration, subsequently leading to a decrease in the SOM and AN indicator values. Khan et al. [23] reported nutrient losses of 8.46 kg mineral nitrogen (N), 19 kg phosphorus (P), and 220 kg organic matter ha–1 due to water erosion from maize crops in the upland sloping soil. The amount of SOM and AN lost in the gabion revetment was higher than the riprap revetment. With its vertical form and porous structure, the nutrients and organic maters easily permeated through the voids of the gabion, and this structural configuration caused the soil layer to easily lose its nutrients. Concerning the riprap, it has a gentle slope that was covered with high floral diversity and distribution. This feature caused the riprap soil to improve its nutrient accumulation capacity, and avoided the nutrient scouring effect from stormwater [22]. Nevertheless, during the winter season, with the decrease in rainfall intensity, the SOM and AN indicator values showed a steep increase. It is noteworthy to mention that, during all the four seasons, AP indicator values were not significant because the P index in the soil was high (85.24–87.63 mg/kg), and the P content in storm water did not show any effect on the AP of the soil. These results clearly prove that the storm runoff has a significant effect on the slope soil nutrient concentration. This was also reflected on the good growth of Vetiver grass on the riprap surface. The SOM and AN indicator values significantly increased during the spring, summer, and winter periods; however, they decreased during the autumn season.
3.3. Plant Growth Conditions
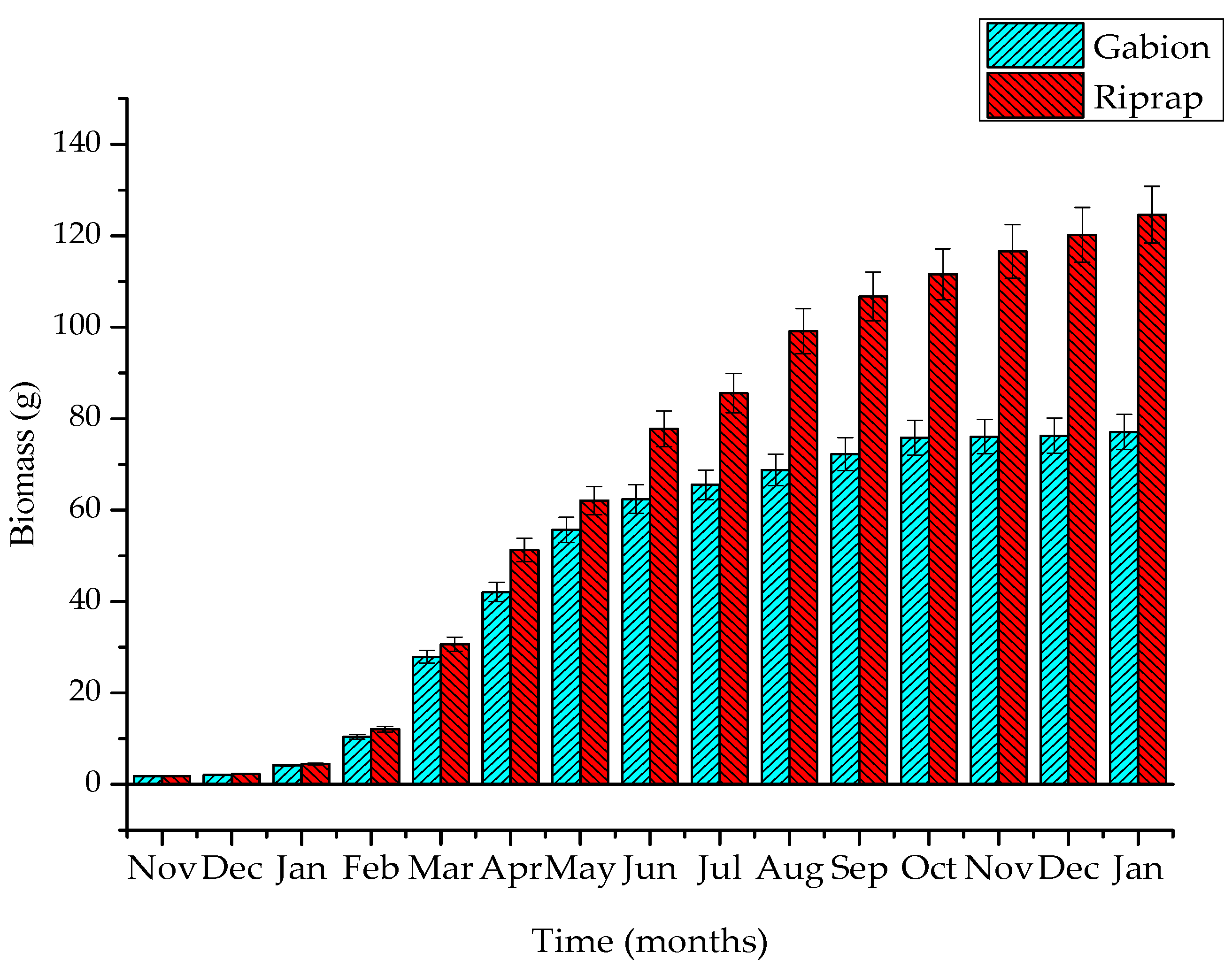
The experimental data obtained for the five samples (S1–S5), the average and SD values for Vetiver biomass grown on the gabion and the riprap revetments are shown in Table 2 and Table 3, and Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively.

Table 2.
Vetiver biomass grown on the gabion revetment.

Table 3.
Vetiver biomass grown on the riprap revetment.
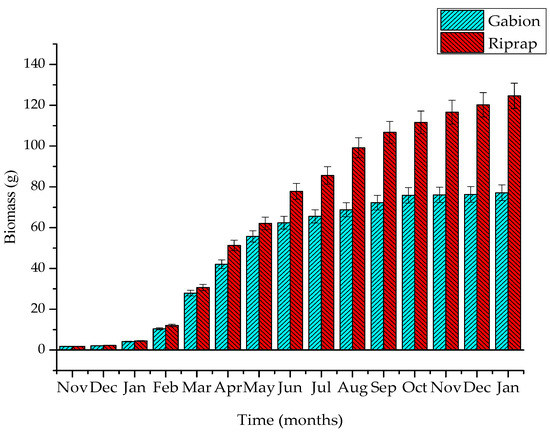
Figure 7.
Growth of Vetiver grass on two types of ecological revetments (the error bars represent the standard deviation for the weight of Vetiver grass).

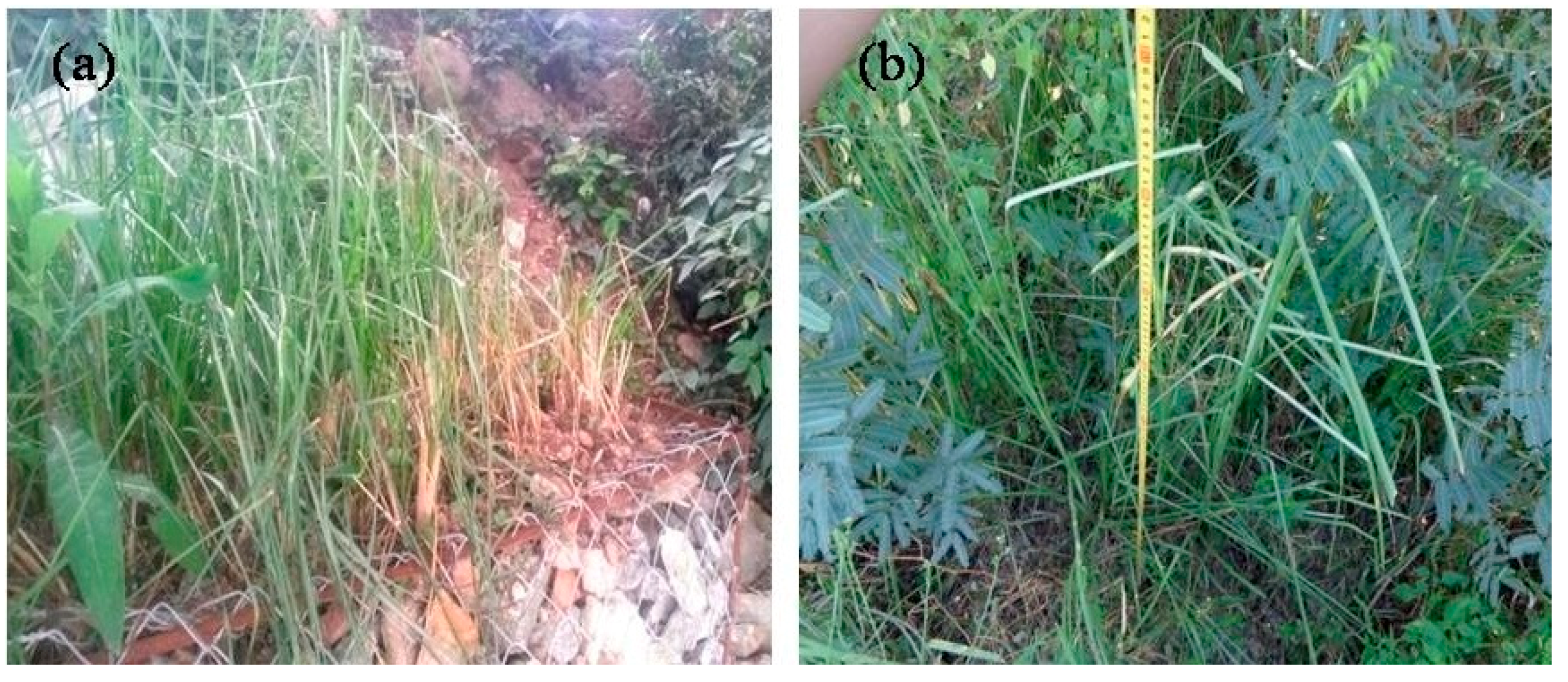
Figure 8.
Vetiver growth on: (a) gabion; and (b) riprap revetments (photos were taken on 23 October 2016).
At the beginning of the plantation time, on the gabion and riprap revetments, the average weight of Vetiver grass was 2.31 ± 0.28 g. During the spring season (from February to April), with a mild warm climate (21.3 °C), high humidity (89.3%), the Vetiver grass began to develop, and its biomass weight on the gabion and riprap revetments was 10.41 ± 0.52 and 12.13 ± 0.61 g, respectively. The rate of Vetiver biomass growth on the gabion and riprap revetments was 2.70 and 3.27 g/month, respectively. In summer (from May to July), under high rainfall (131.2 mm/month), relatively warm temperature (29.4 °C), and sunshine hour (224.7 h/month) conditions, the tropical flora showed the best growth conditions. In addition, the soil nutrients in terms of SOM and AN reached the highest value during this period. Therefore, the Vetiver grass could strongly grow on the riprap and gabion revetment surfaces and yield higher biomass. The Vetiver grass biomass weighed 55.74 ± 2.79 and 64.1 ± 3.11 g, respectively, in the gabion and riprap revetments. The results from this study shows that the rate of Vetiver biomass growth on the gabion and riprap revetments were 15.11 and 17.32 g/month, respectively. The storm runoff scours containing high nutrient concentrations and pollutants from the road surface caused the amount of SOM and AN to reach its highest values in the gabion and riprap soil layers [4].
During the autumn season (from August to October), the growth of Vetiver grass on the gabion and riprap revetments were 68.79 ± 3.43 and 99.14 ± 4.96 g, respectively. The Vetiver biomass growth rate in the gabion and riprap revetments was 4.35 and 11.68 g/month, respectively. During the autumn season, the continuous heavy storms (332.6 mm/month) caused a reduction in the soil nutrient concentrations, leading to low values of SOM and AN. This adversely affected the Vetiver grass biomass on the gabion and riprap revetments. With a vertical form and porous structure, the gabion soil layer lost nutrient and soil particles significantly, causing dissatisfaction of Vetiver grass nutrition. However, after a planting period of eight months, the riprap’s Vetiver grass root pierced through the stone layer and directly absorbed nutrients from beneath the riprap stone layer. Therefore, Vetiver did not primarily depend on the nutrient source from the riprap surface soil layer. Under such conditions, the biomass weight of the gabion’s Vetiver grass was significantly lower than the riprap’s. During the winter season (from November to January), with lower temperatures (19.9 °C), rainfall (111.8 mm/month), and low sunshine hours (88.5 h/month), Vetiver plant biomass growth in the gabion and riprap revetments significantly declined. The biomass of Vetiver grass on the gabion and riprap revetments were 77.12 ± 3.94 and 124.61 ± 6.23 g, respectively. The Vetiver plant biomass growth rate in gabion and riprap revetments were 2.78 and 8.49 g/month, respectively. Riprap’s Vetiver grass showed rapid growth in spring, summer, autumn, and slow growth in winter. On the other hand, the gabion’s Vetiver grass showed rapid growth in spring, summer, and slow growth in autumn and winter. Mickovski et al. [24] showed that the dry shoots of 22 Vetiver plants could reach a weight of 70.05 ± 8.04 g with in a period of one year (2012–2013) when grown on different types of ecological revetments. The experimental results from this study revealed that Vetiver grass has good ability for growth and reproduction on the ecological revetments. The results indicated that high values of temperature and humidity, long sunshine hours. And soil nutrient content during the spring and the summer season, will facilitate the rapid development of the Vetiver biomass. However, the Vetiver biomass began to decrease with rainfall, due to the decline of the nutrient content during the autumn season.
3.4. Slope Stability Effect
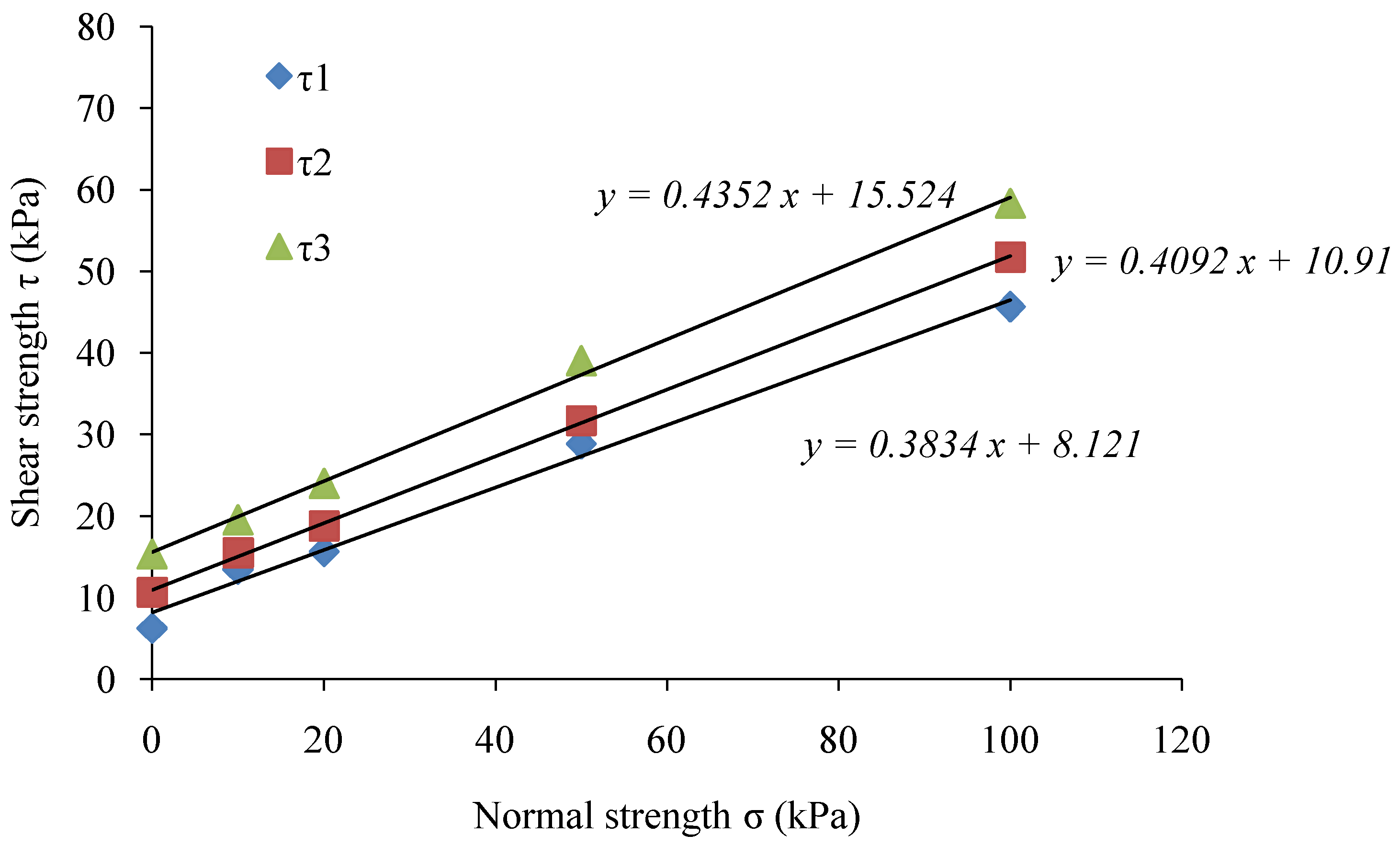
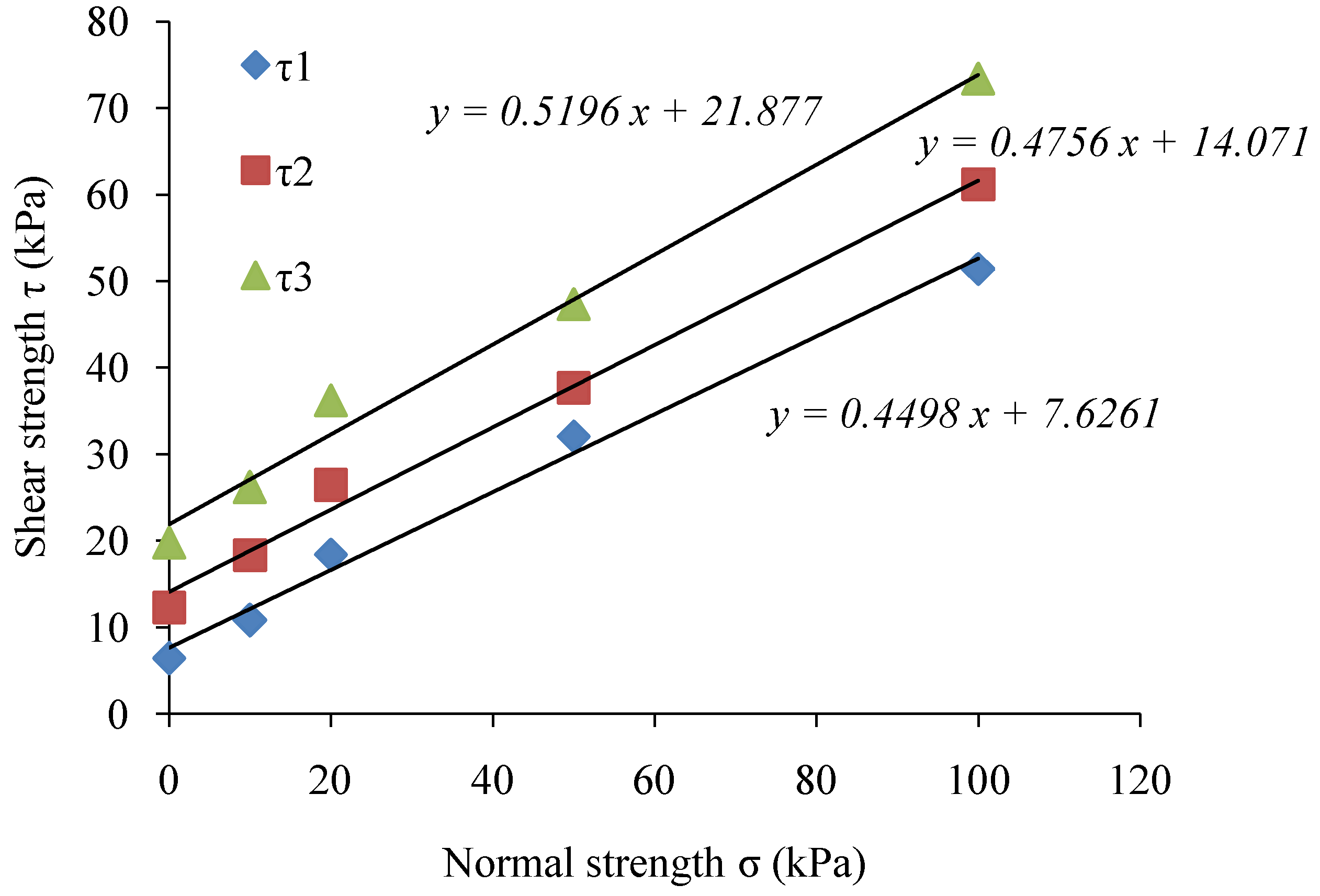
To investigate the effect of shear strengths (τ1, τ2, and τ3) of the soil samples during 0, 6, and 12 months, the soil samples were subjected to direct shear test under normal strength as σ1 = 10 kPa, σ2 = 20 kPa, σ3 = 50 kPa, and σ4 = 100 kPa. The results of the shear strength experiments are shown in Figure 9. The cohesion C, and internal friction angle Ф, calculated through the Coulomb formula (Equation (1)) are presented in Table 4.
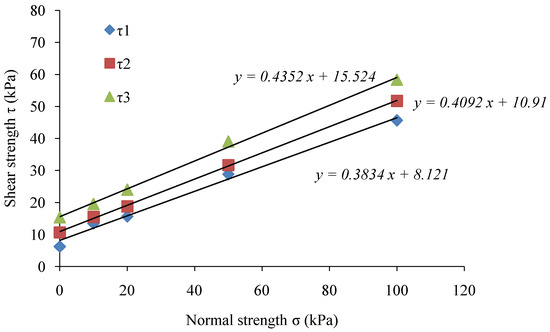
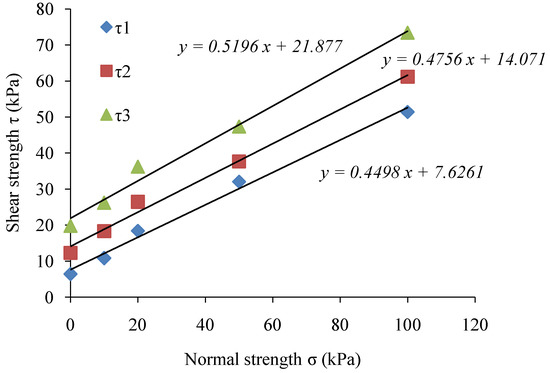
Figure 9.
Normal strength and shear strength values for: (a) gabion; and (b) riprap revetments.

Table 4.
Soil shear strength parameters for gabion and riprap revetments.
The results of direct shear strength tests revealed that the cohesion of soil increased, but the internal friction angle showed a rather slow increase by only 1–3°. After a period of 6 and 12 months, the cohesion of soil samples collected from the gabion revetment increased by 59.6% and 162.9%, respectively. The cohesion in soil samples collected from the riprap revetment after 6 and 12 months increased by 115.6% and 239.1%, respectively. Therefore, the shear strength results proved that the root system of Vetiver grass and native plants could increase the cohesion and internal friction angle of soil, and enhance the bank slope stability.
Ali et al. [11] studied the shear strength of soil containing vegetable roots and noticed that after 6 months, under soil suction-free condition, the root of Leucaena leucocephala could increase the cohesion of soil by 116 (0.1 m), 225.0 (0.3 m) and 413.4% (0.5 m), which increases the shear strength of the soil to improve the stability of the bank. In addition, the Vetiver grass root system has high tensile and shear strength, and this unique property would increase the soil shear strength. Noorasiyikin et al. [25] also carried out a tensile strength test of the Vetiver grass root system and showed a significant relationship between the soil shear strength and plant root diameter. Hawke et al. [26] reported that the high moisture condition in the soil can reduce the soil metric tension, and decrease the soil cohesion, leading to a severe instability of the bank slope. As examples, the following two literatures have clearly shown that the Vetiver grass can grow to deeper depths and that their roots are strong enough to provide good reinforcement in the lands where they grow: Truong [27] showed that the Vetiver grass was able to penetrate to a depth of 3–4 m in the soil within a period of one year. In another study, Islam et al. [28] also indicated that Vetiver root grew up to 0.9 m in pure sand soil within three months. This tendency of root growth increased the soil cohesion, but it also absorbed the soil moisture, nutrients, and other pollutants present in the soil layer [24,29]. Current results proved that the roots of the Vetiver grass penetrated up to a depth of 3–4 m in the soil and increased the soil cohesion, enhancing the stability of the river bank.
During periods of storm runoff scouring, the increase of soil cohesion characteristics by the plant root system significantly reduces the soil layer erosion in slopes. Cuellar et al. [30] simulated the transient erosion caused by a vertical fluid jet impinging on the surface of a granular assembly and indicated that the relative eroded mass decreased when the cohesive bond increased from 0–2.5 N, and the relative eroded mass was zero when the cohesion C = 2.5 N. In another study, Niu et al. [31] ascertained the role of Cleistogenes songorica for the sustainable development and protection of the soil ecosystem and indicated that Cleistogenes songorica roots has a major role in increasing the soil aggregates and enhances the resistance to soil erosion under storm-runoff incidents. In conclusion, the current results revealed that the Vetiver grass with a developed root system could increase the soil cohesion, which significantly reduced the loss of the soil layer by storm runoff.
3.5. Improving the Diversity of Flora and Fauna on the Revetments
3.5.1. Floral Diversity
In addition to Vetiver grass, 24, 14, and 26 native plant species were detected on the natural slope, gabion, and riprap revetments, respectively (Table 5). The plant species are as follows: Ageratum conyzoides, Lantana camara, Mimosa pudica L., Bindens pilosa, Trianthema portulacastrum L., Eclipta alba, Euphorbia thymifolia Burm, Fimbristylis miliacea, Cyperusiria, Cypirus digitatus, Taraxacum mongolicum Hand-Mazz, Sonchus arvensis Linn, Portulaca oleracea L., Sorghum halepense, Alligator Alternanthera Herb, Conyza canadensis, Ageratum conyzoides, Asplenium antiquum, Oxalis corymbosa DC, Centella asiatica, Cyperus tegetiformis, Fimbristylis miliacea, Echinochloa crus-galli, Leptochloa chinensis, Choromolaena odorata, and Cenchrus echinatus L. The gabion’s plant species number is lower than that of the natural slope and riprap revetment because of low surface area and lesser amount of soil nutrients. Additionally, the natural plant’s species number was lower than the riprap. This might be due to the nature of soil used to fill the riprap revetment. Strayer et al. [32] studied the vegetation of the riprap revetments along the Hudson River (USA) and showed that 11 plant species were detected within a range of 25 m from the shore. The result from this study confirms the fact that the gabion and riprap revetments, with their highly porous structures, could provide an ideal habitat for plant growth and reproduction.

Table 5.
The floral and faunal diversity in different revetment types.
3.5.2. Faunal Diversity
In the present study nine, five, and nine faunal species were detected on the natural slope, gabion, and riprap revetment, respectively (Table 5). The insects identified on the revetments were as follows: Acrida chinensis, Gryllidae, Rhopalocera, Mantodea, Pheidole megacephala, Cryllustestaceus walker, and Catharsius molossus L. The results also revealed that the phylum Nemathelminthes and centipede insect species were present in the plant root system. The gabion’s faunal species number were found to be lower than the natural slope and riprap, because the gabion surface area and the development of flora were lower than the natural slope and riprap revetment, causing a lack of ideal habitat space for faunal living and reproduction. Gabriel et al. [8] compared the plant and animal species in five adjacent pairs of riprap and natural shorelines and reported that the proportional coverage by aquatic macrophytes at the armored shoreline was obviously higher than the natural site. Additionally, the amount of fish captured by the fyke net in the armored riprap shoreline was lower than that of the natural shoreline. These results clearly reveal that the riprap revetments with a porous structure could provide a good living habitat to aquatic flora and fauna and the fish can take refuge in the riprap porous structure to avoid capture by the fyke net.
3.6. Microbial Community Diversity
In the present study, water and mud samples were collected and analyzed through Miseq high-throughput sequencing [21] to determine the microbial population diversity attached on the surface of gabion and riprap revetments. The sequence information and the diversity index of the three samples are shown in Table 6. The ACE index is also used to estimate the number of OTUs (operational taxonomic units). The total number of species was high based on the Chao and ACE index [21,33,34]. It can be seen from Table 6 that the total number of species in samples determined by Chao index and ACE index is #3 > #2 > # 1, from high to low. The Shannon index and Simpson index were used to estimate the microbial community diversity in the samples. According to Shannon index and Simpson index values, the diversity of microbial community in the samples were ranked as #3 > #2 > #1 from high to low [35,36].

Table 6.
Sequence information and the diversity index.
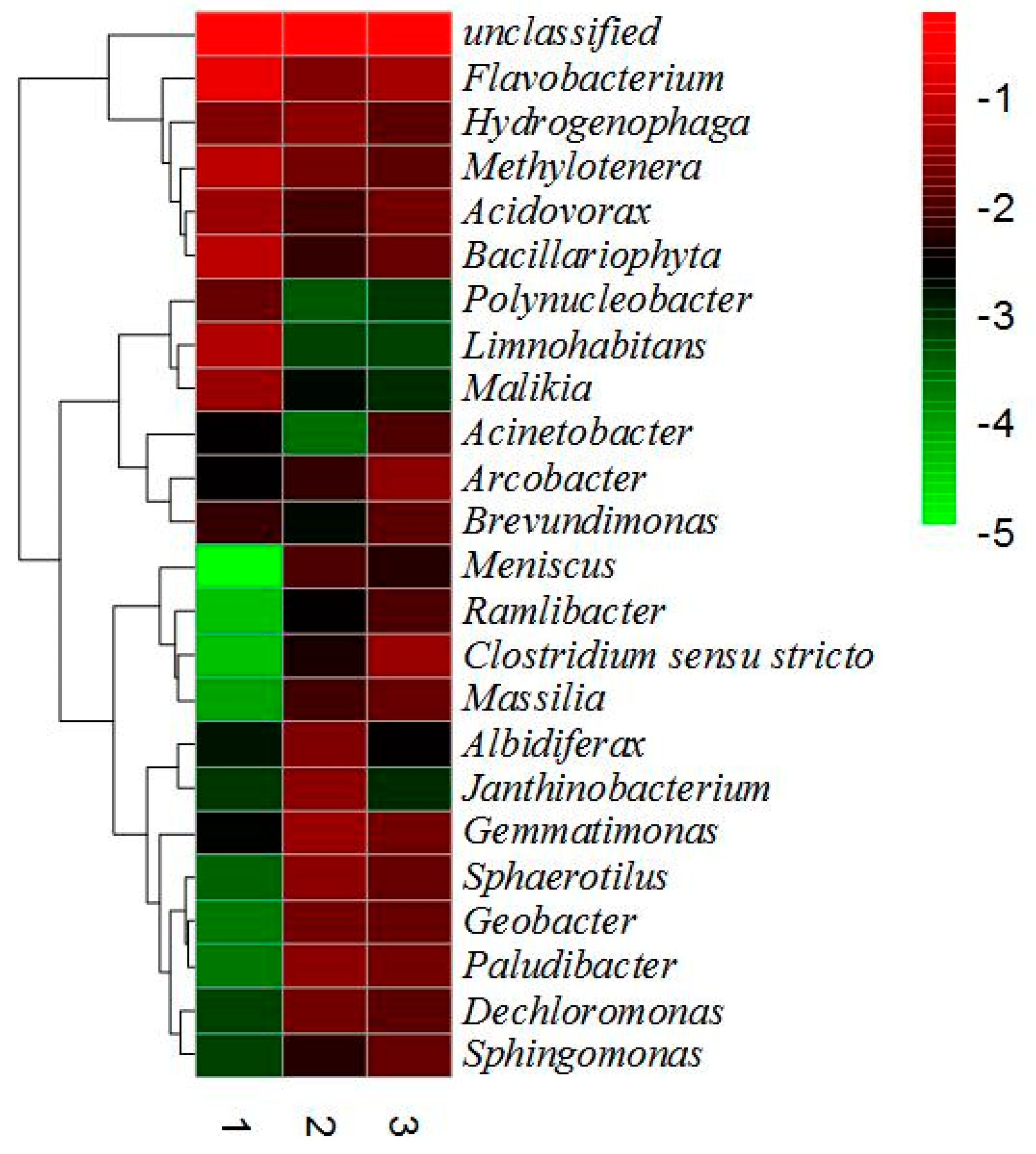
The results showed that the total number and diversity of microorganisms attached on the gabion and riprap revetments were much higher than that of the suspended microorganisms in the water. The results revealed that the total number of microbial communities and their diversity in the riprap revetment was highest, because the riprap revetment is suitable for the growth of plants, it has a rather strong root systems, and the gap between the stones also provide adequate conditions for the growth of microorganisms. It is one of the main reasons for rich microbial diversity in the riprap revetment [33]. Through high sequencing technology, the number of bacteria was estimated at 198, 332, and 351 in water #1, gabion #2 and riprap #3 samples, respectively. The results of species composition, based on its detection and classification at the genus level, is shown in Figure 10.
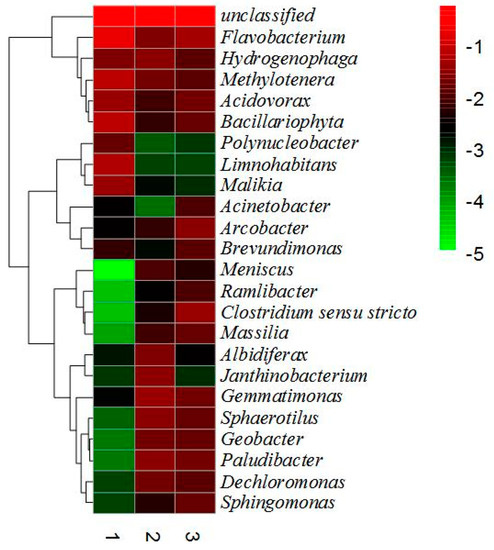
Figure 10.
The classification at the genus level.
It can be seen from Figure 10 that the total amount of microbes and the relative content of dominant microorganisms on the two kinds of ecological bank revetments are obviously higher than those in the water body. This clearly indicates that the gaps and plant roots can provide good habitat for microbial attachment and growth.
Microorganisms in the river will gradually attach, reproduce and develop to form the biofilm on the surface of rock and plants root. It plays an important role in transformation and reduction of the pollutants in river water. The amount and diversity of microorganisms attached to the ecological revetments are significantly higher than the water-suspended microbes. Among them, Polynuclebacter, Menicius, Mssila, Geobacter, Gemmatimonas, Albidiferax, Ramlibacter, Janthino bacterium, Sphaerotilus, Clostridium sensu stricto, pauludibacter, Dechoromonas, Sphingomonas, and Dechloromonas were significantly higher. Previous studies have shown that Polynuclebacter, Geobacter, Gemmatimonas, Ramlibacter, Clostridium sensu strict, pauludibacter, Dechoromonas, and Sphingomonas have a strong ability to reduce pollutant levels in river water [36]. Its main role is to uptake nutrient in river water to form a biofilm. Earlier studies have classified Ramlibacter, Gemmatimonas, and Sphingomonas as aerobic denitrifying bacteria [37], and Pauludibacter and Geobacteras anaerobic denitrifying bacteria [38]. Gabion and riprap revetments, with their highly porous structure, could provide a good habitat for the growth and reproduction of a large number of microorganisms which also enhances the natural purification process of the river.
4. Conclusions
The study area, Vinh city, Vietnam, is located in a subtropical monsoon area. The average daily temperature, monthly precipitation, monthly sunshine hours, and humidity were 24.5 °C, 155 mm/month, 142.5 h/month, and 85.4%, respectively. The soil nutrient levels on the revetments increased during the spring, autumn, and winter seasons, but it decreased during the autumn season due to high rainfall. However, during the summer season, with high temperature and soil nutrient concentrations, the Vetiver grass biomass of riprap and gabion revetments reached its highest growth rate as 15.11 and 17.32 g/month, respectively. With the decrease in temperature and nutrient concentration during the autumn and winter season, the growth rate of Vetiver grass biomass decreased. The Vetiver grass biomass on the riprap was higher than the gabion, which proved that the riprap structure with a gentle slope was not affected severely by the storm runoff erosion. The results revealed that the root system of Vetiver grass and native plants increase the soil cohesion, i.e., it increased by 162.9% in the gabion and 239.1% in the riprap revetment, respectively, after a period of one year and the internal friction angle from 2.6° to 3.2°, leading to an increase in the soil shear strength and good stability of the bank slope. The floral and faunal species detected on the gabion and riprap revetments were similar to the species found on the natural slope. In addition, the rich microbial diversity was also observed in the gabion and riprap revetments. These observations proved the fact that the gabion and riprap revetments provided a good habitat for floral, faunal, and microbial growth, which enhances the ecological restoration capacity of the river bank.
Author Contributions
D.F. and V.T.T. conceived and designed the experiments; V.T.T., T.N.B., and T.T.T.S. performed the experiments at the site in Vietnam; R.P.S. and V.T.T. contributed to the procurement of reagents, materials, monitoring, and data analysis; and R.P.S., V.T.T., and E.R.R. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
This study was co-funded by the National Key Technologies R and D Program, China (no. 2015BAL02B05) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51650410657).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bolay, J.C.; Cartoux, S.; Cunha, A.; Du, T.T.N.; Bass, M. Sustainable development and urban growth: Precarious habitat and water management in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Habitat. Int. 1997, 21, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Letter. Available online: http://vinhcity.gov.vn/?detail=2/open-letter (accessed on 10 March 2008).
- Böhm, H.R.; Schramm, S.; Bieker, S.; Zeig, C.; Anh, T.H.; Thanh, N.C. The semi-centralized approach to integrated water supply and treatment of solid waste and wastewater—A flexible infrastructure strategy for rapidly growing urban regions: The case of Hanoi/Vietnam. Clean. Technol. Environ. 2011, 13, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chang, N.; Fen, C.; Chen, C. Assessing the storm-runoff impact to an urban river ecosystem using estuarine water quality simulation model. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2010, 21, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Yue, H.; Li, L. Analysis on current situation and development trend of ecological revetment works in middle and lower reaches of Yangtze river. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.L.; Feng, Z.Y. Ecological engineering methods for soil and water conservation in Taiwan. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, S.; Jin, Y. Evaluation on ecological restoration capability of revetment in land restricted channel. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 20, 2548–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGabriel, O.; Bodensteiner, L.R. Impacts of riprap on wetland shorelines, upper Winnebago pool lakes, Wisconsin. Wetlands 2012, 32, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, M.; Karasu, T.J.R.; Dawood, E.T. The stability of gabion walls for earth retaining structures. Alexandria Eng. J. 2013, 52, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, H.M.; Beck, D.S. Effect of plant roots on carbon metabolism of soil microbial biomass. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 1986, 149, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.H. Shear strength of a soil containing vegetation roots. Soils Found. 2008, 48, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.; Thuan, L.K.; Murrell, K.D.; Dalsgaard, A.; Johansen, M.V.; De, N.V. Cross-sectional parasitological survey for helminth infections among fish farmers in Nghe An province, Vietnam. Acta Trop. 2006, 100, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.L.; Liu, Z.Z.; Xu, G.L.; Huang, X.J. Protection technology and application of gabion. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Structural & Geotechnical Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 8–10 September 2009; pp. 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Pagliara, S.; Chiavaccini, P. Urban Stream Restoration Structures; Springer Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 43, pp. 239–252. [Google Scholar]
- Beikircher, B.; Florineth, F.; Mayr, S. Restoration of rocky slopes based on planted gabions and use of drought-preconditioned woody species. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salivcop, V.G. Protection of banks and roadbeds from erosion on river “Nip”. Power Technol. Eng. 1986, 20, 575–580. [Google Scholar]
- Crusoe, G.E., Jr.; Cai, Q.; Shu, J.; Han, L.; Barvor, Y.J. Effects of weak layer angle and thickness on the stability of rock slopes. Int. J. Min. Geo-Eng. 2016, 50, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, A. Soil Physical—Chemical Analysis; Institute of Soil Science: Nanjing, China; Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E.; Sparks, D.L.; Page, A.L.; Helmke, P.A.; Loeppert, R.H.; Soltanpour, P.N.; Tabatabai, M.A.; Johnston, C.T.; Sumner, M.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3—Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Book Series; Crop Science Society of America (CSSA): Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, K.; Rogers, J.D.; Ahmed, M.F. Effect of densification on the shear strength of landslide material: A case study from salt range, Pakistan. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2008, 48, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, W.; Liu, J.; Singh, R.P.; Fu, D. Effect of alternate dry-wet patterns on the performance of bioretention units for nitrogen removal. Desal. Water Treat. 2016, 59, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, S.J. Effects of land use, land cover and rainfall regimes on the surface runoff and soil loss on karst slopes in southwest China. Catena 2012, 90, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Bhatti, A.U.; Khattak, R.A. Soil and nutrient losses through sediment and surface runoff under maize monocropping and maize-legumes intercropping from upland sloping field. Pak. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 19, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mickovski, S.B.; Beek, L.P.H.V.; Salin, F. Uprooting of vetiver uprooting resistance of vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides). Plant Soil 2005, 278, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorasyikin, M.N.; Zainap, M. A tensile strength of Bermuda grass and Vetiver grass in terms of root reinforcement ability toward soil slope stabilization. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 136, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawke, R.; McConchie, J. In situ measurement of soil moisture and pore-water pressures in an ‘incipient’ landslide: Lake Tutira, New Zealand. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, P.; Van, T.T.; Pinners, E. Vetiver System Applications Technical Reference Manual; The Vetiver Network International (TVNI): San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008; pp. 1–126. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Arif, M.Z.U.; Badhon, F.F.; Mallick, S.; Islam, T. Investigation of vetiver root growth in sandy soil. In Proceedings of the BUET-ANWAR ISPAT 1st Bangladesh Civil Engineering SUMMIT 2016, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 23–26 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, M.; Rosary, S.C.; Sebastian, M.; Cherian, S.M. Effectiveness of Vetiver for treatment of wastewater from institutional kichen. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, P.; Philippe, P.; Bonelli, S.; Benahmed, N.; Brunier-Coulin, F.; Ngoma, J.; Delenne, J.; Radjaï, F. Micromechanical analysis of the surface erosion of a cohesive soil by means of a coupled LBM-DEM model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Particles, Barcelona, Spain, 28–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.; Nan, Z. Roots of Cleistogenes songorica improved soil aggregate cohesion and enhance soil water erosion resistance in rainfall simulation experiments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Kiviat, E.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Slowik, N. Vegetation of rip rapped revetments along the freshwater tidal Hudson River, New York. Aquatic Sci. 2016, 78, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Xiao, C.; Ding, L.; Xu, K.; Geng, J.; Ren, H. Evaluation of the treatment performance and microbial communities of a combined constructed wetland used to treat industrial park wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 10990–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Xue, C.; Xun, W.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q. Pyrosequencing reveals contrasting soil bacterial diversity and community structure of two main winter wheat cropping systems in China. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennifer, B.H.; Jessica, J.H.; Taylor, H.R.; Brendan, J.M.B. Counting the uncountable: Statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4399–4406. [Google Scholar]
- Telias, A.; White, J.R.; Pahl, D.M.; Ottesen, A.R.; Walsh, C.S. Bacterial community diversity and variation in spray water sources and the tomato fruit surface. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoki, T.; Catalan-Sakairi, M.A.B.; Yasushi, S.; Isao, K.; Zhou, Z.; Shoun, H. Aerobic denitrifying bacteria that produce low levels of nitrous oxide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3152–3157. [Google Scholar]
- Jalil, J.; Alireza, M.; Ramin, N.; Mohammad, H.; Hossein, K.; Amir, H.M. Influence of upflow velocity on performance and biofilm characteristics of anaerobic fluidized bed reactor (AFBR) in treating high-strength wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2014, 12, 139. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).