Nutrient Control to Prevent the Occurrence of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Lake in Southern Sweden, Used for Drinking Water Supply
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutrient Condition at Lake Vombsjön
3.2. Seasonal Pattern of Cyanobacteria
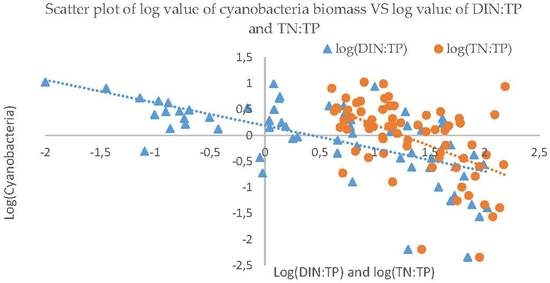
3.3. Nutrients Influence on Cyanobacteria
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; ISBN 0419239308. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Hao, H.; He, Z. Mechanisms and assessment of water eutrophication. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ekholm, P. N:P Ratios in Estimating Nutrient Limitation in Aquatic Systems; Finnish Environment Institute: Helsingfors, Finland, 2008; pp. 11–14.
- Jeppesen, E.; Kronvang, B.; Meerhoff, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Hansen, K.M.; Andersen, H.E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liboriussen, L.; Beklioglu, M.; Özen, A.; et al. Climate Change Effects on Runoff, Catchment Phosphorus Loading and Lake Ecological State, and Potential Adaptations. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Ekvall, M.K.; Hansson, L.A. Local food web management increases resilience and buffers against global change effects on freshwaters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.A.; Gustafsson, S.; Rengefors, K.; Bomark, L. Cyanobacterial chemical warfare affects zooplankton community composition. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Small Systems with a Big Problem: Harmful Algal Blooms. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sciencematters/small-systems-big-problem-harmful-algal-blooms (accessed on 23 April 2018).
- Westrick, J.A.; Szlag, D.C.; Southwell, B.J.; Sinclair, J. A review of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins removal/inactivation in drinking water treatment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestana, C.J.; Reeve, P.J.; Sawade, E.; Voldoire, C.F.; Newton, K.; Praptiwi, R.; Collingnon, L.; Dreyfus, J.; Hobson, P.; Gaget, V.; et al. Fate of cyanobacteria in drinking water treatment plant lagoon supernatant and sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, A.; Brock, T.D. Effect of temperature on blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria) in Lake Mendota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 36, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitton, B.A. (Ed.) Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-94-007-3855-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, E.S.; Hilt, S. Impact of water-level fluctuations on cyanobacterial blooms: Options for management. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.B.; Lou, W.J.; Ke, W.T.; Song, W.Y.; Price, N.M.; Qiu, B.S. New insights into iron acquisition by cyanobacteria: An essential role for ExbB-ExbD complex in inorganic iron uptake. ISME J. 2015, 9, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining critical nutrient thresholds needed to control harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.L.; Pollard, A.I. Deriving nutrient targets to prevent excessive cyanobacterial densities in U.S. lakes and reservoirs. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmful, C.; Blooms, A. Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 619, ISBN 9780387758640. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Canada. ARCHIVED-Environment and Climate Change Canada-Water-Phosphorus and Excess Algal Growth. Available online: http://www.ec.gc.ca/grandslacs-greatlakes/default.asp?lang=en&n=6201fd24-1 (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Huang, L.; Fang, H.; He, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, C. Effects of internal loading on phosphorus distribution in the Taihu Lake driven by wind waves and lake currents. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Parkefelt, L.; Persson, K.M.; Pekar, H. Improving cyanobacteria and cyanotoxin monitoring in surface waters for drinking water supply. J. Water Secur. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.; Muro-Pastor, A.M.; Flores, E. Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, A.A.-S.; Abd-Alla, M.H.; Ohyama, T. Nitrogen Fixing Cyanobacteria: Future Prospect. In Advances in Biology and Ecology of Nitrogen Fixation; InTechOpen: London, England, 2014; pp. 23–48. ISBN 978-953-51-1216-7. [Google Scholar]
- Beversdorf, L.J.; Miller, T.R.; McMahon, K.D. The Role of Nitrogen Fixation in Cyanobacterial Bloom Toxicity in a Temperate, Eutrophic Lake. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, G.P.; Sarnelle, O.; White, J.D.; Hamilton, S.K.; Kaul, R.R.B.; Bressie, J.D. Nitrogen availability increases the toxin quota of a harmful cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res. 2014, 54, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution of Phosphorus Limitation in Lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havens, K.E.; James, R.T.; East, T.L.; Smith, V.H. N:P ratios, light limitation, and cyanobacterial dominance in a subtropical lake impacted by non-point source nutrient pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Low Nitrogen to Phosphorus Ratios Favor Dominance by Blue-Green Algae in Lake Phytoplankton. Science 1983, 221, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudnell, H.K.; Dortch, Q.; Zenick, H. Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: Chapter 1: An Overview of the Interagency, International Symposium on Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms (ISOC-HAB): Advancing the Scientific Understanding of Freshwater Harmful Algal Blooms. In U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Papers; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 39. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M.; Conley, D.J.; Carstensen, J.; Sánchez-Camacho, M. Return to Neverland: Shifting Baselines Affect Eutrophication Restoration Targets. Estuar. Coasts 2009, 32, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsell, A.S.; Scharfenberger, U.; Özkundakci, D.; Walters, A.; Hansson, L.-A.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Nõges, P.; Reid, P.C.; Schindler, D.E.; Van Donk, E.; et al. Evaluating early-warning indicators of critical transitions in natural aquatic ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8089–E8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rigosi, A.; Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Brookes, J.D. The interaction between climate warming and eutrophication to promote cyanobacteria is dependent on trophic state and varies among taxa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SMHI. Svenskt Vattenarkiv. Available online: https://www.smhi.se/klimatdata/hydrologi/svenskt-vattenarkiv (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- SMHI Vattenwebb-Älvar, Floder, Åar, Bäckar, Sjöar, S-HYPE, Vattenmyndigheten. Available online: http://vattenweb.smhi.se/ (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Vattenanknuten Recipientkontroll. Regeringsuppdrag-Havs-Och Vattenmyndigheten. 2014. Available online: https://www.havochvatten.se/hav/uppdrag--kontakt/vart-uppdrag/regeringsuppdrag/regeringsuppdrag/vattenanknuten-recipientkontroll-2014.html (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Provtagnings-Och Analysprogram. Kävlingeåns Vattenvårdsförbund. Available online: http://kavlingeans-vvf.com/undersokningar/provtagnings-och-analysprogram/ (accessed on 23 April 2018).
- Olsson, A.; Svärd, C.; Madeleine, S. Kävlingeån 2016 Kävlingeåns Vattenråd; Kävlingeåns vattenråd: Lund, Sweden, 2017; Available online: http://www.kavlingeans-vvf.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Kavlingean_arsrapport_2016.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2018).
- Lund, J.W.G.; Kipling, C.; Le Cren, E.D. The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis of estimations by counting. Hydrobiologia 1958, 11, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemot, P.; Li, J.; Parkefelt, L.; Persson, T.; Feuillade, G.; Sydvatten, Lund, Sweden. 2016; Unpublished Work.
- Lehman, A.; O’Rourke, N.; Hatcher, L.; Stepanski, E.J. JMP® for Basic Univariate and Multivariate Statistics Methods for Researchers and Social Scientists Second Edition; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Poutot, F. Investigation of the Phosphorus Balance in the Vomb Lake; Sydvatten: Lund, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sundahl, A.-C.; Wennberg, C.; Tilly, L.; Wettemark, F.; Magnusson, P.; Schuster, J. Vombsjön–ett Ramdirektivprojekt Vombsjön—A Water Framework Directive Project; Föreningen Vatten: Stockholm, Sweden, 2008; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Lindegarth, M.; Carstensen, J.; Drakare, S.; Johnson, R.K.; Nyström Sandman, A.; Söderpalm, A.W.S.A. Ecological Assessment of Swedish Water Bodies; Swedish Institute for the Marine Environment: Göteborg, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I. Current Approaches to Cyanotoxin Risk Assessment, Risk Management and Regulations in Different Countries. 2012. Available online: http://www.uba.de/uba-info-medien-e/4390.html (accessed on 23 May 2018).
- WHO. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystin-LR in Drinking-Water Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, M.M.; Belisle, B.S.; Watson, S.B.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Status, causes and controls of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.P.; Lewis, W.M. Phytoplankton nutrient limitation in Colorado mountain lakes. Freshw. Biol. 1988, 20, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolman, A.M.; Wiedner, C. Predicting phytoplankton biomass and estimating critical N:P ratios with piecewise models that conform to Liebig’s law of the minimum. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolzau, S.; Wiedner, C.; Rücker, J.; Köhler, J.; Köhler, A.; Dolman, A.M. Seasonal patterns of Nitrogen and Phosphorus limitation in four German Lakes and the predictability of limitation status from ambient nutrient concentrations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GNF-Success Lake Constance II. Available online: http://www.globalnature.org/19081/Success-Lake-Constance-I/Success-Lake-Constance-II/02_vorlage.asp (accessed on 23 May 2018).
- Lake Erie Action Plan to Reduce Phosphorus Loads by 40%. Available online: https://www.watercanada.net/lake-erie-action-plan-to-reduce-phosphorus-loads-by-40/ (accessed on 23 May 2018).







| Item | TN | DIN | TP | DP | TN:TP | DIN:TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient | −0.56 | −0.65 | 0.62 | 0.31 | −0.63 | −0.66 |
| p-Values | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Hansson, L.-A.; Persson, K.M. Nutrient Control to Prevent the Occurrence of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Lake in Southern Sweden, Used for Drinking Water Supply. Water 2018, 10, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070919
Li J, Hansson L-A, Persson KM. Nutrient Control to Prevent the Occurrence of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Lake in Southern Sweden, Used for Drinking Water Supply. Water. 2018; 10(7):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070919
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jing, Lars-Anders Hansson, and Kenneth M. Persson. 2018. "Nutrient Control to Prevent the Occurrence of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Lake in Southern Sweden, Used for Drinking Water Supply" Water 10, no. 7: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070919
APA StyleLi, J., Hansson, L. -A., & Persson, K. M. (2018). Nutrient Control to Prevent the Occurrence of Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Eutrophic Lake in Southern Sweden, Used for Drinking Water Supply. Water, 10(7), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070919