Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Global Trends of Soil Salinization in Croplands
1.2. Impact of Soil Salinization on Plants
1.3. Impact of Soil Salinization on Soil Physical and Hydraulic Properties
2. Soil Salinization Processes and Associated Hydrological Processes
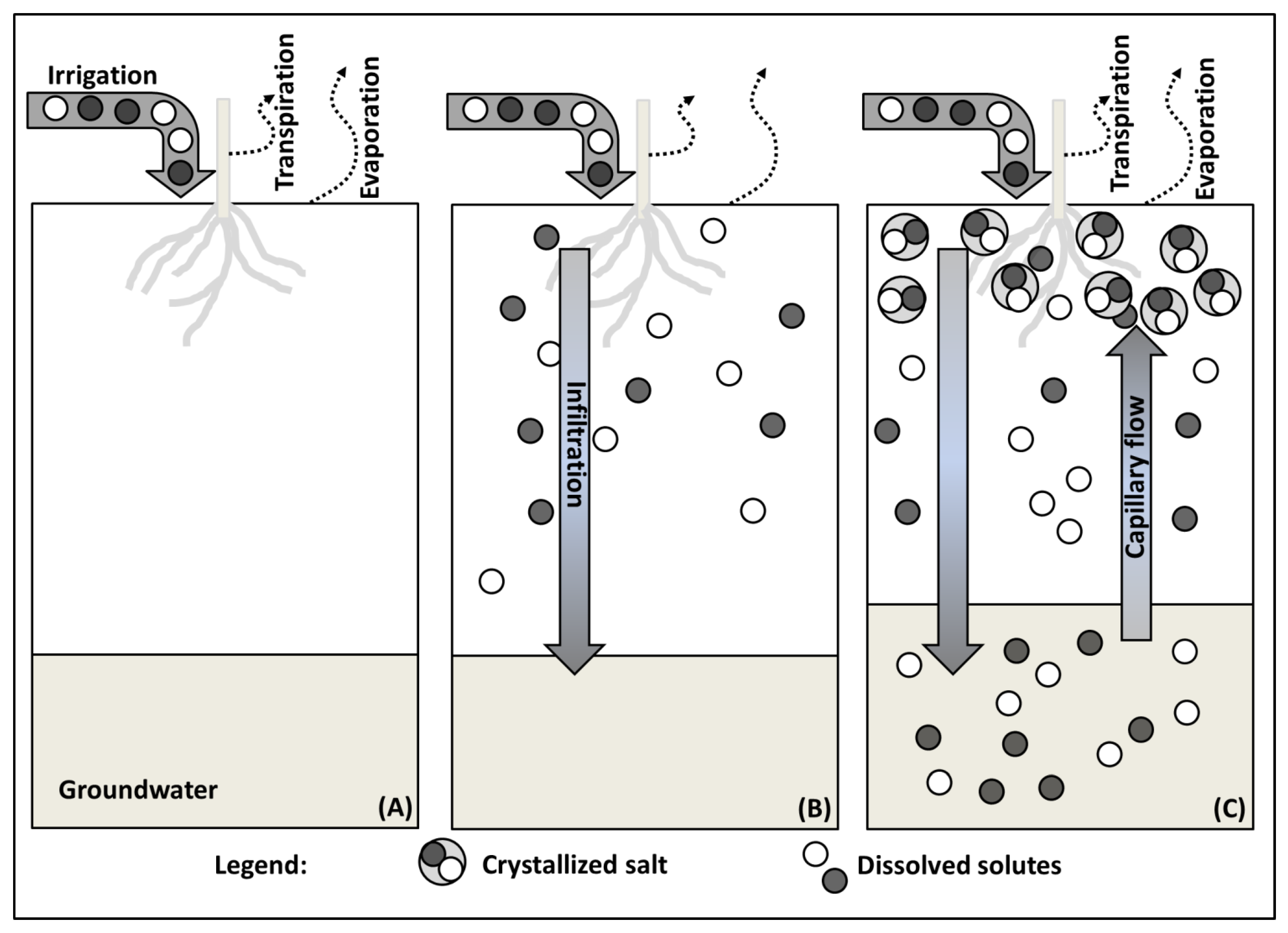
2.1. Salt Transport
2.2. Salt Originating from Parent Geological Material
2.3. Salt Originating from Shallow and Salt Rich Groundwater
2.4. Soil Salinization by Irrigation Water
3. Key Factors in Soil Salinization
3.1. Climatic Conditions
3.2. Soil Properties
3.3. Groundwater Levels
4. Coping with Soil Salinization in Agricultural Regions
4.1. Leaching
4.2. Drainage
4.3. Biological Solutions
4.4. Water Desalination and Blending
4.5. Cultivation Practices
5. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrick, J.E. Soil quality: An indicator of sustainable land management? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J. The business case for soil. Nature 2017, 543, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McBratney, A.; Field, D.J.; Koch, A. The dimensions of soil security. Geoderma 2014, 213, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Defries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, A.; Mcbratney, A.; Adams, M.; Field, D.; Hill, R.; Crawford, J.; Minasny, B.; Lal, R.; Abbott, L.; O’Donnell, A.; et al. Soil Security: Solving the Global Soil Crisis. Glob. Policy 2013, 4, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farifteh, J.; Farshad, A.; George, R.J. Assessing salt-affected soils using remote sensing, solute modelling, and geophysics. Geoderma 2006, 130, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisch, L.; Eberle, U.; Lorek, S. Sustainable food consumption: An overview of contemporary issues and policies. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2013, 9, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, A. Soils, Land and Food: Managing the Land during the Twenty-First Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization and waterlogging: A threat to environment and agricultural sustainability. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Alam, M.; Bhowmik, P.C.; Hossain, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Narasimha, M.; Prasad, V.; Ozturk, M.; Fujita, M. Potential Use of Halophytes to Remediate Saline Soils. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 589341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Hanjra, M.A.; Dheeravath, V.; Gumma, M. A holistic view of global croplands and their water use for ensuring global food security in the 21st century through advanced remote sensing and non-remote sensing approaches. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 211–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kendall, W.H.; Pimentel, D. Constraints on the expansion of the global food supply. Ambio 1994, 1, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S. Global croplands and their importance for water and food security in the twenty-first century: Towards an ever green revolution that combines a second green revolution with a blue revolution. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Rajesh, K. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, A.J. Salinization of Non-Irrigated Soils and Associated Streams: A Review. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1978, 16, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, A.; Riaz, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Gene expression profiling of plants under salt stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Lin, Z.; Liu, L.; Zimmermann, D. Assessing secondary soil salinization risk based on the PSR sustainability framework. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenkabail, P.; Lyon, G.J.; Turral, H.; Biradar, C.M. Remote Sensing of Global Croplands for Food Security; CRC Press-Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Biradar, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Dheeravath, V.; Li, Y.J.; Velpuri, M.; Gumma, M.; Reddy, G.P.O.; Turral, H.; Cai, X.L.; et al. Global irrigated area map (GIAM), derived from remote sensing, for the end of the last millennium. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3679–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Management of Irrigation-Induced Saltaffected Soils; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Harris, P.J.C. Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Schmidhalter, U. Drought and salinity: A comparison of their effects on mineral nutrition of plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L. Effects of salinity and sodicity on plant growth. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1975, 13, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of Salinity Tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.E. Kind, position and toxicity of alkali salts in certain Alberta irrigated soils. Sci. Agric. 1937, 18, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Magistad, O.C.; Ayers, A.D.; Wadleigh, C.H.; Gauch, H.G. Effect of salt concentration, kind of salt, and climate on plant growth in sand cultures. Plant Physiol. 1943, 18, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppuhn, H.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Grieve, C.M. Root-zone salinity: I. Selecting a product-yield index and response function for crop tolerance. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibull, W. A statistical distribution function of wide application. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Steppuhn, H.; Wang, H.; Gan, Y. Evaluating Russian wild ryegrass emergence from saline seedbeds using the Gompertz function. Can. Agric. Eng. 1998, 40, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V.; Hoffman, G.J. Crop salt tolerance–current assessment. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1977, 103, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. Analyzing Crop Salt Tolerance Data: Model Description and User’s Manual; USSL: Washington, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Hoffman, G.J. Analysis of crop production. In Soil Salinity under Irrigation; Shainberg, I., Shalhevet, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 258–271. [Google Scholar]
- Kaner, A.; Tripler, E.; Hadas, E.; Ben-Gal, A. Feasibility of desalination as an alternative to irrigation with water high in salts. Desalination 2017, 416, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Gupta, S.K. A reassessment of the crop response function. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1993, 41, 730–737. [Google Scholar]
- Shani, U.; Ben-Gal, A.; Tripler, E.; Dudley, L.M. Plant response to the soil environment: An analytical model integrating yield, water, soil type, and salinity. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, A.; Aragüés, R. Salinity-yield response functions of barley genotypes assessed with a triple line source sprinkler system. Plant Soil 1999, 209, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, R.M.; Franke, L.; Deckelmann, G. Phase changes of salts in porous materials: Crystallization, hydration and deliquescence. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U.; Weisbrod, N.; Dragila, M.I.; Grader, A. Combined evaporation and salt precipitation in homogeneous and heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U.; Weisbrod, N. Beyond the Salt Crust: On Combined Evaporation and Subflorescent Salt Precipitation in Porous Media. Transp. Porous Media 2015, 110, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Doehne, E. Salt weathering: Influence of evaporation rate, supersaturation and crystallization pattern. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chu, J. Cementation of sand due to salt precipitation in drying process. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2017, 35, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljauwad, S.N.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B. Geotechnical behaviour of saline sabkha soils. Géotechnique 1995, 45, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, R.; Gerson, R.; Yaalon, D.H. Stages and rate of the gravel shattering process by salts in desert Reg soils. Geoderma 1993, 57, 295–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U. Seepage weathering impacts on erosivity of arid stream banks: A new conceptual model. Geomorphology 2016, 261, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, H.; Shimano, T.; Inoue, M.; Nakane, K. Effect of a Salt Crust on Evaporation from a Bare Saline Soil. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, M.; Carrera, J.; Olivella, S.; Saaltink, M.W. Modeling evaporation processes in a saline soil from saturation to oven dry conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ling, L.; Lockington, D. Numerical study of evaporation-induced salt accumulation and precipitation in bare saline soils: Mechanism and feedback. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8084–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brady, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soils; Macmillan Publishing Company Incorporated: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, H.; Alexander, R.; Teeuw, R.; Zukowskyj, P. Variations in soil dispersivity across a gully head displaying shallow sub-surface pipes, and the role of shallow pipes in rill initiation. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2004, 29, 1143–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shainberg, I.; Letey, J. Response of soils to sodic and saline condtions. Hilgardia 1984, 52, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, R.W.; Boucher, S.C.; Naidu, R.; Fritsch, E. Environmental consequences of soil sodicity. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1994, 32, 1069–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Lei, T.; Yu, J.; Shainberg, I.; Mamedov, A.I.; Ben-Hur, M.; Levy, G.J. Runoff and Interrill Erosion in Sodic Soils Treated with Dry PAM and Phosphogypsum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, N. Pore-scale dynamics of salt transport and distribution in drying porous media. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 012106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treguier, A.M.; Deshayes, J.; Le Sommer, J.; Lique, C.; Madec, G.; Penduff, T.; Molines, J.M.; Barnier, B.; Bourdalle-Badie, R.; Talandier, C. Meridional transport of salt in the global ocean from an eddy-resolving model. Ocean Sci. 2014, 10, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, T.; Cai, X. Prediction of salt transport in different soil textures under drip irrigation in an arid zone using the SWAGMAN Destiny model. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoua, K.; Pandit, A.; Heck, H. Stochastic Nature of Salt Mass Transport in Porous Media under Unstable Conditions. Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2017, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Gabchenko, M.V.; Junrong, X. Eolian transport of salts—A case study in the area of Lake Ebinur (Xinjiang, Northwest China). J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics, 1st ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; ISBN 9780123485250. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0849304792. [Google Scholar]
- Leij, F.J.; Genuchten, M.T. van Solute Transport. In Soil Physics Companion; Warrick, A.W., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 189–248. [Google Scholar]
- Awada, L.; Lindwall, C.W.; Sonntag, B. The development and adoption of conservation tillage systems on the Canadian Prairies. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennock, D.; Bedard-Haughn, A.; Kiss, J.; van der Kamp, G. Application of hydropedology to predictive mapping of wetland soils in the Canadian Prairie Pothole Region. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; van der Kamp, G.; Rosenberry, D.O. Hydrology of Prairie Wetlands: Understanding the Integrated Surface-Water and Groundwater Processes. Wetlands 2016, 36, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U.; Ireson, A.; van der Kamp, G.; Davies, S.R.; Wheater, H. Impacts of climate variability on wetland salinization in the North American prairies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachshon, U.; Ireson, A.; van der Kamp, G.; Wheater, H. Sulfate salt dynamics in the glaciated plains of North America. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinremi, O.O.; McGinn, S.M.; Cutforth, H.W. Precipitation trends on the Canadian Prairies. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2996–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kamp, G.; Hayashi, M.; Gallén, D. Comparing the hydrology of grassed and cultivated catchments in the semi-arid Canadian prairies. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stempvoort, D.R.; Hendry, M.J.; Schoenau, J.J.; Krouse, H.R. Sources and dynamics of sulphur in weathered till, western glaciated plains of North America. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kamp, G.; Hayashi, M. Groundwater–wetland ecosystem interaction in the semiarid glaciated plains of North America. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.K.; van der Kamp, G.; Cherry, J.A. Hydrogeochemistry of a clayey till: 1. Spatial variability. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 27, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; van Der Kamp, G.; Rudolph, D.L. Mass transfer processes between a prairie pothole and adjacent uplands, 2: Chloride cycle. J. Hydrol. 1998, 207, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitch, J.W.; Hernandez, M.E. Landscape and climate change threats to wetlands of North and Central America. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 75, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, K.R.; Pomeroy, J.W. Memory effects of depressional storage in Northern Prairie hydrology. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3890–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadell, J.; Jackson, R.B.; Ehleringer, J.B.; Mooney, H.A.; Sala, O.E.; Schulze, E.D. Maximum rooting depth of vegetation types at the global scale. Oecologia 1996, 108, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finstad, K.; Pfeiffer, M.; McNicol, G.; Barnes, J.; Demergasso, C.; Chong, G.; Amundson, R. Rates and geochemical processes of soil and salt crust formation in Salars of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Geoderma 2016, 284, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutt, D.F.; Hynek, S.A.; Munk, L.A.; Corenthal, L.G. Rapid recharge of fresh water to the halite-hosted brine aquifer of Salar de Atacama, Chile. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4720–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, S.W.; Munoz, J.F.; Wood, W.W. The response of playa and sabkha hydraulics and mineralogy to climate forcing. Groundwater 2006, 44, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vengosh, A.; Rosenthal, E. Saline groundwater in Israel: Its bearing on the water crisis in the country. J. Hydrol. 1994, 156, 389–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengosh, A.; Spivack, A.J.; Artzi, Y.; Ayalon, A. Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1877–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvirtzman, H.; Shalev, E.; Dahan, O.; Hatzor, Y.H. Large-scale infiltration experiments into unsaturated stratified loess sediments: Monitoring and modeling. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.K. The 25-m DTM (Digital Terrain Model) of Israel. Israel J. Earth Sci. 2008, 57, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.; Tubiello, F.N.; Van Velthuizen, H.; Wiberg, D.A. Climate change impacts on irrigation water requirements: Effects of mitigation, 1990–2080. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2007, 74, 1083–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doll, P.; Siebert, S. Global modeling of irrigation water requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.M. Irrigation with saline water: Benefits and environmental impact. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Tal, A.; Fine, P.; Yermiyahu, U.; Ben-Gal, A.; Hass, A. Practices that simultaneously optimize water and nutrient use efficiency: Israeli experiences in fertigation and irrigation with treated wastewater. In Managing Water and Fertilizer for Sustainable Agricultural Intensification; Drechsel, P., Heffer, P., Magen, H., Mikkelsen, R., Wichelns, D., Eds.; International Fertilizer Industry Association: Paris, France, 2015; pp. 209–241. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, T.; Atallah, T.; El Moujabber, M.; Khatib, N. Salinity evolution and crop response to secondary soil salinity in two agro-climatic zones in Lebanon. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Xiu, L.; Wu, L. Effects of salinity and fertigation practice on cotton yield and 15N recovery. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira Barradas, J.M.; Abdelfattah, A.; Matula, S.; Dolezal, F. Effect of fertigation on soil salinization and aggregate stability. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2014, 141, 5014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, L.M.; Ben-Gal, A.; Lazarovitch, N. Drainage water reuse: Biological, physical, and technological considerations for system management. J. Environ. 2008, 37, S25–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, S.R.; Westcot, W.D. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Rhoades, J.D.; Šimůnek, J. Leaching requirement for soil salinity control: Steady-state versus transient models. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, E.V. Crop salt tolerance. In Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management; Tanji, K.K., Ed.; ASCE Manuals and Reports on Engineering, No. 71; ASCE: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 262–304. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.L.; Gilley, J.R. Irrigation Water Requirements. In National Engineering Handbook; Part 623; USDA, Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; p. 284. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Vincent, B.; Yang, J.; Bouarfa, S.; Vidal, A. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Changes in Soil Salinity: A Case Study in Inner Mongolia, China. Sensors 2008, 8, 7035–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Qu, Z.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the groundwater dynamics and impacts of water saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, C. Analysis of salinization dynamics by remote sensing in Hetao Irrigation District of North China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Xu, X.; Hao, Y.; Huang, G. Modeling and assessing field irrigation water use in a canal system of Hetao, upper Yellow River basin: Application to maize, sunflower and watermelon. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.G.; Mao, Z.; Fang, S.X.; Liu, H.S. The Yellow River basin and case areas. In Water Saving in China, the Yellow River Basin: Issues and Decision Support Tools in Irrigation; Pereira, L.S., Cai, L.G., Musy, A., Minhas, P.S., Eds.; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Meybeck, M.; He, D.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Spatial and temporal analysis of water chemistry records (1958–2000) in the Huanghe (Yellow River) basin. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Z.; Wang, X.K.; Feng, Z.W. Soil N and salinity leaching after the autumn irrigation and its impact on groundwater in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 71, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiuling, F.S.C. Rationally utilizing water resources to control soil salinity in irrigation districts. In Proceedings of the Sustaining the Global Farm, Selected Papers from the 10th International Soil Conservation Organization Meeting, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 24–29 May 1999; pp. 1134–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Jordán, M.M.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; García-Sánchez, E.; Mateu, J.; Juan, P. Spatial dynamics of soil salinity under arid and semi-arid conditions: Geological and environmental implications. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Salinity Management for Sustainable Irrigation: Integrating Science, Environment, and Economics; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, R.B.; Otto, C.J.; Fitzpatrick, R.W. Contributions of groundwater conditions to soil and water salinization. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, A.; Ityel, E.; Dudley, L.; Cohen, S.; Yermiyahu, U.; Presnov, E.; Zigmond, L.; Shani, U. Effect of irrigation water salinity on transpiration and on leaching requirements: A case study for bell peppers. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, J. Field-Scale Water Flow and Solute Transport: SWAP Model Concepts, Parameter Estimation, and Case Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Šimůnek, J.; Šejna, M.; van Genuchten, M.T. The HYDRUS-2D Software Package for Simulating Two-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media; Version 2.0.; US Salinity Lab.: Riverside, CA, USA, 1999.
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. Recent developments and applications of the HYDRUS computer software packages. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezniak, A.; Ben-Gal, A.; Mishael, Y.; Nachshon, U. Manipulation of Soil Texture to Remove Salts from a Drip-Irrigated Root Zone. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarovitch, N.J.; Vanderborght, Y.J.; van Genuchten, M.T. The Root Zone: Soil Physics and Beyond. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pessarakli, M. Formation of Saline and Sodic Soils and Their Reclamation. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. Toxicol. 1991, 26, 1303–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M. Drainage, waterlogging, and salinity. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, C.; Lu, P.; Bakour, A. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of summer maize (Zea mays L.) in subsurface drainage system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M. A Comparison between Horizontal and Vertical Drainage Systems (Include Pipe Drainage, Open Ditch Drainage, and Pumped Wells) in Anisotropic Soils. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2012, 4, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyamini, Y.; Mirlas, V.; Marish, S.; Gottesman, M.; Fizik, E.; Agassi, M. A survey of soil salinity and groundwater level control systems in irrigated fields in the Jezre’el Valley, Israel. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedema, L.K.; Abdel-dayem, S.; Ochs, W.J. Drainage and agricultural development. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2000, 14, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, T.H.S.; Watanabe, T.; Ogino, Y.; Tanji, K.K. Soil salinization in the Nile Delta and related policy issues in Egypt. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M.; Šimůnek, J. Leaching and reclamation of a biochar and compost amended saline-sodic soil with moderate SAR reclaimed water. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P.; Olsson, K. Sodicity and soil structure. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1991, 29, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinck, E.; Frost, C. Evaluation of amendments used to prevent sodificationof irrigated fields. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Qureshi, R.; Ahmad, N. Amelioration of calcareous saline–sodicsoils through phytoremediation and chemical strategies. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, A.; Gill, M.; Hassan, A.; Murtaza, G.; Qadir, M. Gypsum: Aneconomical amendment for amelioration of saline–sodic waters and soils, andfor improving crop yields. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2001, 3, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Oster, J.D.; Shainberg, I.; Abrol, I.P. Reclamation of salt-affected soil. Agric. Drain. Agron. Monogr. 1999, 38, 315–346. [Google Scholar]
- Amezketa, E.; Aragues, R.; Gazol, R. Efficiency of sulfuric acid, mined gypsum, and two gypsum by-products in soil crusting prevention and sodic soilreclamation. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.; Hassan, G.; Mehdi, S.; Hussain, N.; Jamil, M. Amelioration ofsaline–sodic soils with tillage implements and sulfuric acid application. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Oster, J.; Schubert, S.; Noble, A.; Sahrawat, K. Phytoremediation ofsodic and saline–sodic soils. Adv. Agron. 2007, 96, 197–247. [Google Scholar]
- Rozema, J.; Flowers, T. Crops for a Salinized World. Science 2008, 322, 1478–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Jagendorf, A.; Zhu, J.K. Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, D.A.; Ismail, S.; Butt, K.U.R.B.; Jed Brown, J. Evaluating the growth performance of eleven Salicornia bigelovii populations under full strength seawater irrigation using multivariate analyses. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2016, 10, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, Y.; Moreno, M.; Troyo, E. Growth promotion of the seawater-irrigated oilseed halophyte Salicornia bigelovii inoculated with mangrove rhizosphere bacteria and halotolerant Azospirillum spp. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 32, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, K.C.; Venkatesan, K.; Balakrishnan, V.; Chellappan, K.P.; Balasubramanian, T. Restoration of saline land by halophytes for Indian soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.F.; Cara, B.; Pérez-Martín, F.; Pineda, B.; Egea, I.; Flores, F.B.; Fernandez-Garcia, N.; Capel, J.; Moreno, V.; Angosto, T.; et al. The tomato mutant ars1 (altered response to salt stress 1) identifies an R1-type MYB transcription factor involved in stomatal closure under salt acclimation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelle, M.A.; Alspach, B.; Gilron, J.; Russell, C.; Davis, T.A. Enhancing Water Recovery Sustainably. Opflow 2015, 41, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welle, P.D.; Medellín-Azuara, J.; Viers, J.H.; Mauter, M.S. Economic and policy drivers of agricultural water desalination in California’s central valley. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebhun, M. Desalination of reclaimed wastewater to prevent salinization of soils and groundwater. Desalination 2004, 160, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, A.; Israeli, Y.; Elingold, I.; Levi, M.; Levkovitch, I.; Russo, D.; Assouline, S. Irrigation with desalinated water: A step toward increasing water saving and crop yields. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oster, J.D. Irrigation with poor quality water. Agric. Water Manag. 1994, 25, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jae-Kwon, S.; Won-Tae, S.; Su-Hwan, L.; Jin-Hee, R.; Jae-Young, C. Reclamation of a coastal reclaimed tidal land soil by gypsum and rice straw. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 761–770. [Google Scholar]
- Mlih, R.; Bol, R.; Amelung, W.; Brahim, N. Soil organic matter amendments in date palm groves of the Middle Eastern and North African region: A mini-review. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Limited effect of organic matter on soil available water capacity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Martius, C.; Lamers, J.P.A.; Devkota, K.P.; Sayre, K.D.; Vlek, P.L.G. Soil salinity management on raised beds with different furrow irrigation modes in salt-affected lands. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 152, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, H. Factors of Soil Formation: A System of Quantitative Pedology; McGRAW-HILL Book Company: New-York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]







© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nachshon, U. Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081030
Nachshon U. Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples. Water. 2018; 10(8):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081030
Chicago/Turabian StyleNachshon, Uri. 2018. "Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples" Water 10, no. 8: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081030
APA StyleNachshon, U. (2018). Cropland Soil Salinization and Associated Hydrology: Trends, Processes and Examples. Water, 10(8), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081030




