Drivers of Ecosystem Metabolism in Two Managed Shallow Lakes with Different Salinity and Trophic Conditions: The Sauce Grande and La Salada Lakes (Argentina)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
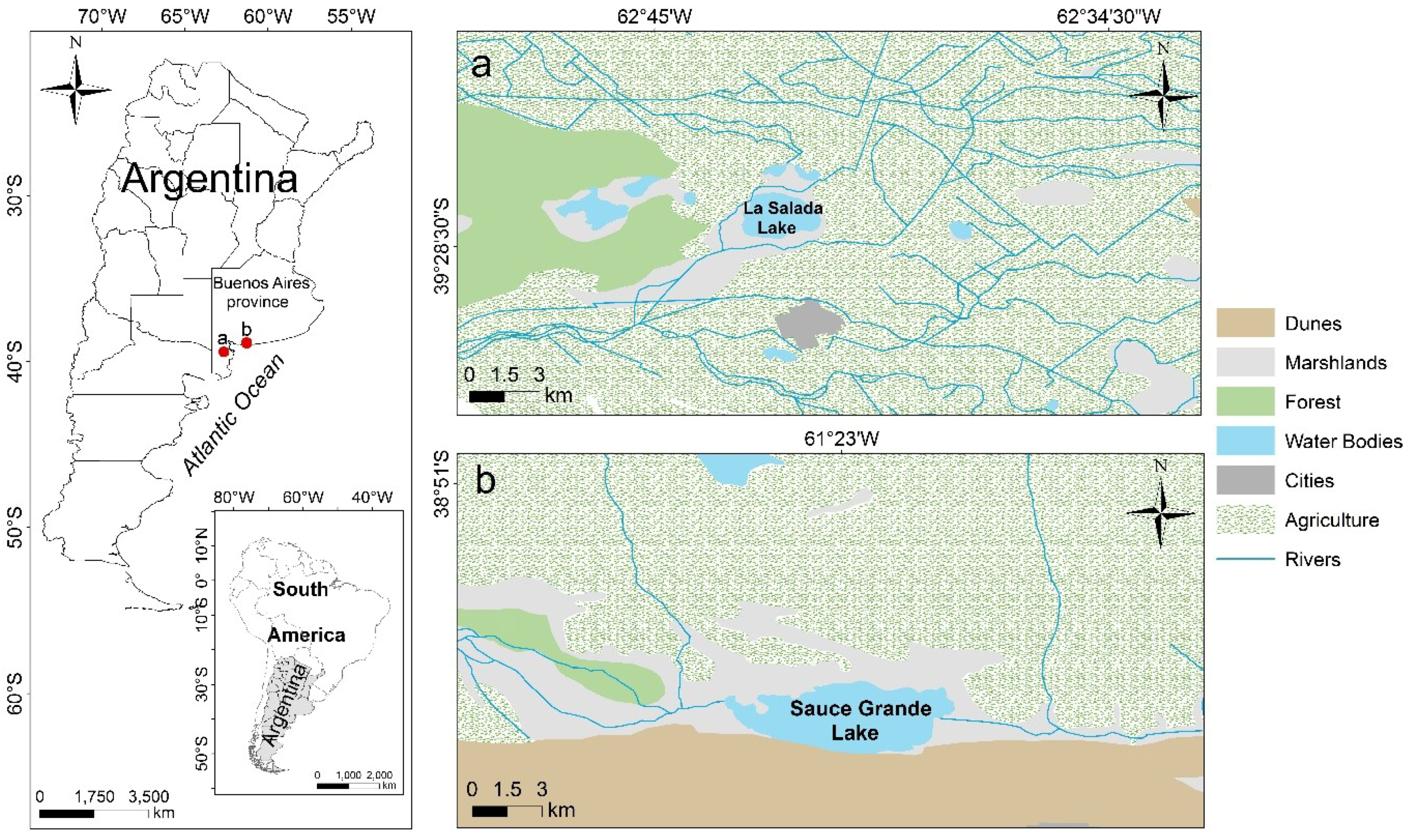
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Environmental Variables, Land Use, and Hydrological Conditions
2.3. Bathymetry
2.4. Estimation of Metabolism
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables, Land Use, and Hydrological Conditions
3.2. Lake Metabolism
3.3. Regulation of Lake Metabolism
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staehr, P.A.; Bade, D.; Van de Bogert, M.C.; Koch, G.R.; Williamson, C.; Hanson, P.; Kratz, T. Lake metabolism and the diel oxygen technique: State of the science. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods. 2010, 8, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, J.J.; Pace, M.L.; Carpenter, S.R.; Kitchell, J.F. Persistence of net heterotrophy in lakes during nutrient addition and food web manipulation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1718–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauster, G.H.; Hanson, P.C.; Kratz, T.K. Gross primary production and respiration differences among a littoral and pelagic habitats in northern Wisconsin lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand-Jensen, K.; Staher, P.A. Scaling of pelagic metabolism to size, trophy and forest cover in small Danish lakes. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr, P.A.; Baastrup-Spohr, L.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Stedmon, C. Lake metabolism scales with lake morphometry and catchment conditions. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laas, A.; Nõges, P.; Kõiv, T.; Nõges, T. High-frequency metabolism study in a large and shallow temperate lake reveals seasonal switching between net autotrophy and net heterotrophy. Hydrobiologia 2012, 694, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, M.B.; Vitale, A.J.; Menéndez, M.C.; Perillo, V.L.; Piccolo, M.C.; Perillo, G.M.E. Estimation of ecosystem metabolism from diel oxygen technique in a saline shallow lake: La Salada (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 2015, 752, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetta, D.; Staehr, P.A.; Schmitt, R.; Petrucio, M.M. Physical conditions driving the spatial and temporal variability in aquatic metabolism of a subtropical coastal lake. Limnologica 2016, 58, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.C.; Carey, C.C.; Bruesewitz, D.A.; Weathers, K.C. Intra-and inter-annual variability in metabolism in an oligotrophic lake. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, P.C.; Bade, D.L.; Carpenter, S.R. Lake metabolism: Relationships with dissolved organic carbon and phosphorus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heathwaite, A.L. Multiple stressors on water availability at global to catchment scales: Understanding human impact on nutrient cycles to protect water quality and water availability in the long term. Freshwater Biol. 2010, 55, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, M.B.; Zunino, J.; Piccolo, M.C. Impact of water input on plankton temporal dynamics from a managed shallow saline lake. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim. 2017, 53, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr, P.A.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Raun, A.L.; Nielsson, B.; Kidmose, J. Drivers of metabolism and net heterotrophy in contrasting lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Berggren, M.; Ask, J.; Byström, P.; Jonsson, A.; Laudon, H.; Jansson, M. Terrestrial organic matter support of lake food webs: Evidence from lake metabolism and stable hydrogen isotopes of consumers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, C.T.; Bruesewitz, D.A.; Richardson, D.C.; Rose, K.C.; Van de Bogert, M.C.; Hanson, P.C.; Kratz, T.K.; Larget, B.; Adrian, R.; Leroux, B.; et al. Ecosystem respiration: Drivers of daily variability and background respiration in lakes around the globe. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downing, J.A.; Prairie, Y.T.; Cole, J.J.; Duarte, C.M.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; McDowell, W.H.; Kortelainen, P.; Caraco, N.F.; Melack, J.M.; et al. The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serruya, C. Overview: An appraisal of concepts. In Large Lakes: Ecological Structure and Function Large; Tilzer, M., Serruya, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990; pp. 663–673. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsch, W.J.; Gosselink, J.G. The value of wetlands: Importance of scale and landscape setting. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 351, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diovisalvi, N.; Bohn, V.Y.; Piccolo, M.C.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Baigún, C.; Zagarese, H.E. Shallow-lakes from the Central Plains of Argentina: An overview and worldwide comparative analysis of their basic limnological features. Hydrobiologia 2014, 752, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirós, R.; Rennella, A.M.; Boveri, M.; Rosso, J.J.; Sosnovsky, A. Factores que afectan la estructura y el funcionamiento de las lagunas pampeanas. South. Ecol. 2002, 12, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Echaniz, S.A.; Vignatti, A.M.; De Paggi, S.J.; Paggi, J.C.; Pilati, A. Zooplankton seasonal abundance of south American saline shallow lakes. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2006, 91, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignatti, A.M.; Paggi, J.C.; Cabrera, G.C.; Echaniz, S.A. Zooplankton diversity and its relationship with environmental changes after the filling of a temporary saline lake in the semi-arid region of La Pampa, Argentina. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 40, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignatti, A.; Cabrera, G.; Echaniz, S. Changes in the zooplankton and limnological variables of a temporary hypo-mesosaline wetland of the central region of Argentina during its drying. Pan. Am. J. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 7, 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, B.D.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. The effects of salinity on plankton and benthic communities in the Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA: A microcosm experiment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet Balmaña, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Noges, T.; Bucak, T. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Kanstrup, E.; Petersen, B.; Henriksen, R.B.; Hammershøj, M.; Mortensen, E.; Jensen, J.P.; Have, A. Does the impact of nutrients on the biological structure and function of brackish and freshwater lakes differ? Hydrobiologia 1994, 275, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, T.; Hatton, K.; O’Connor, M.; Connor, L.; Moss, B. Effects of nitrate load on submerged plant biomass and species richness: Results of a mesocosm experiment. Fund. Appl. Limnol. 2008, 173, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.A.; Belovsky, G.E. Salinity and nutrients influence species richness and evenness of phytoplankton communities in microcosm experiments from Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenger-Kovács, C.; Lengyel, E.; Buczkó, K.; Tóth, M.F.; Crossetti, O.L. Vanishing world: Alkaline, saline lakes in Central Europe and their diatom assemblages. Inland Waters 2014, 4, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheffer, M.; Hosper, S.H.; Meijer, M.L.; Moss, B.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 8, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, I.; Allende, L.; Escaray, R.; Bustingorry, J.; Pérez, G.; Tell, G. Comparison of morpho-functional phytoplankton classifications in human-impacted shallow lakes with different stable states. Hydrobiologia 2012, 698, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilio, M.I.; Alfonso, M.B.; Ferrelli, F.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Piccolo, M.C. Ecosystem services provision, tourism and climate variability in shallow lakes: The case of La Salada, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Tourism Manag. 2017, 62, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornerón, C.F.; Piccolo, M.C.; Carbone, M.E. Análisis morfométrico de la laguna Sauce Grande (Argentina). Huellas 2010, 14, 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, C.; Salerno, C.M.; Paoloni, J.D.; Laurent, G.C. Water quality in a lagoon in the southeast pampa region of Argentina. Revista Argentina de Microbiología 2007, 39, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cony, N.L.; Ferrer, N.C.; Cáceres, E.J. Evolución del estado trófico y estructura del fitoplancton de un lago somero de la Región Pampeana: Laguna Sauce Grande (provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Biología Acuática 2014, 30, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Baleani, C.A.; Menéndez, M.C.; Alfonso, M.B.; Fornerón, C.F.; Piccolo, M.C. Composición y abundancia del mesozooplancton en una laguna Pampeana (Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Anales de Biología 2017, 39, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, M.B. Estructura y dinámica del zooplankton en una laguna con manejo antrópico: Laguna La Salada (Pedro Luro, Pcia. de Buenos Aires). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca, Argentina, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bersain, G.E. Laguna La Salada de Pedro Luro, Partido de Villarino. Campaña de relevamientos limnológicos e ictiológicos; Informe Técnico N°136; Estación Hidrobiológica de Chascomús: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bohn, V.Y.; Delgado, A.L.; Piccolo, M.C.; Perillo, G.M. Assessment of climate variability and land use effect on shallow lakes in temperate plains of Argentina. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, A.; Hannah, D.M.; Peiry, J.L.; Campo, A.M. Influence of dam-induced hydrological regulation on summer water temperature: Sauce Grande River, Argentina. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes Lenicov, M.; Colautti, D. Laguna Sauce Grande, Partido de Monte Hermoso. Campaña de Relevamientos Limnológicos e Ictiológicos; Informe técnico N°75; Dirección de Desarrollo Pesquero, Subsecretaría de Actividades Pesqueras, Ministerio de Asuntos Agrarios: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2003.
- Aliaga, V.S.; Ferrelli, F.; Piccolo, M.C. Regionalization of climate over the Argentine Pampas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clesceri, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; p. 1220. [Google Scholar]
- Marker, A.F.; Crowther, C.A.; Gunn, R.J.M. Methanol and acetone as solvents for estimating chlorophyll a and phaeopigments by spectrophotometry. Arch Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 1980, 14, 52–69. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Red de Información Agropecuaria Nacional. Available online: http://rian.inta.gov.ar/ (accessed on 19 June 2017).
- Du, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P. Analysis of dry/wet conditions using the standardized precipitation index and its potential usefulness for drought/flood monitoring in Hunan Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mission Planner Home. Available online: http://ardupilot.org/planner/ (accessed on 6 March 2017).
- EMAC. Available online: http://emac.iado-conicet.gob.ar/ (accessed on 19 June 2018).
- Ho, D.T.; Law, C.S.; Smith, M.J.; Schlosser, P.; Harvey, M.; Hill, P. Measurements of air-sea gas exchange at high wind speeds in the Southern Ocean: Implications for global parameterizations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L16611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Jeppesen, E. Alternative stable states. In The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes, 1st ed.; Jeppesen, E., Sondergaard, M., Sondergaard, M., Christofferson, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; Volume 131, pp. 397–406. ISBN 978-0-387-98284-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninkhof, R. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7373–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Caraco, N.F. Atmospheric exchange of carbon dioxide in a low-wind oligotrophic lake measured by the addition of SF6. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Strohmaier, F.E.; Oremland, R.S. Isolation of anaerobic oxalate-degrading bacteria from freshwater lake sediments. Arch. Microbiol. 1985, 141, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bendat, J.S.; Piersol, A.G. Random data: Analysis and Measurements Procedures, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Reati, G.J.; Florín, M.; Fernández, G.J.; Montes, C. The Laguna de Mar Chiquita (Córdoba, Argentina): A little known, secularly fluctuating, saline lake. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1997, 5, 187–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florín, M.; Montes, C. Which are the relevant scales to assess primary production of Mediterranean semiarid salt lakes? Int. J. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 1998, 24, 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, R.W.; Hoyer, M.V.; Canfield, D.E. Internal heterotrophy following the switch from macrophytes to algae in Lake Apopka, Florida. Hydrobiologia 2000, 418, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Archilla, A.I.; Molla, S.; Coleto, M.C.; Guerrero, M.C.; Montes, C. Ecosystem metabolism in a Mediterranean shallow lake (Laguna de Santa Olalla, Donana National Park, SW Spain). Wetlands 2004, 24, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.D.; Smit, B. A framework for assessing the vulnerability of communities in the Canadian Arctic to risks associated with climate change. Arctic 2004, 57, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, J.L.; Richardson, D.C.; Ewing, H.A.; Hargreaves, B.R.; Samal, N.R.; Vachon, D.; Pierson, D.C.; Lindsey, A.M.; O’Donnell, D.M.; Effler, S.W.; et al. Ecosystem effects of a tropical cyclone on a network of lakes in Northeastern North America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11693–11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachon, D.; Del Giorgio, P.A. Whole-lake CO2 dynamics in response to storm events in two morphologically different lakes. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, P.; Echeverría, H.; Sainz Rozas, H. Nitratos en el suelo a la siembra o al macollaje como diagnóstico de la nutrición nitrogenada en trigo en el sudeste bonaerense. Cienc. Suelo 2009, 27, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gasith, A.; Hosier, A.D. Airborne litterfall as a source of organic matter in lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1976, 21, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cony, N.L.; Ferrer, N.C.; Martínez, A.; Cáceres, E.J. Productividad, estado trófico y dinámica fitoplanctónica en la laguna Sauce Grande y su afluente homónimo (pcia. de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Biología Acuática 2016, 31, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Coloso, J.J.; Cole, J.J.; Pace, M.L. Short-term variation in thermal stratification complicates estimation of lake metabolism. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, S.M.; Hilt, S.; Attermeyer, K.; Grossart, H.P.; Kosten, S.; Lischke, B.; Köhler, J. A regime shift from macrophyte to phytoplankton dominance enhances carbon burial in a shallow, eutrophic lake. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Meerhoff, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Jensen, J.P. Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction—Some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezirci, G.; Akkas, S.B.; Rinke, K.; Yildirim, F.; Kalaylioglu, Z.; Severcan, F.; Beklioglu, M. Impacts of salinity and fish-exuded kairomone on the survival and macromolecular profile of Daphnia pulex. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Variable | Equation |
|---|---|
| Hourly NEP | |
| Diffusive oxygen exchange | |
| Coefficient of oxygen exchange | |
| Schmidt number for LS | |
| Schmidt number for SG | |
| Gas piston velocity | |
| Wind speed at 10 m | |
| Correction factor | |
| NEP during daytime | |
| R during daytime | |
| R | |
| NEP | |
| GPP |
| Variables | Sauce Grande | La Salada | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | |
| Temp (°C) | 17.1 | 6.5 | 12.1 | 24.5 | 16.0 | 5.7 | 7.5 | 25.2 |
| Cond (mS cm−1) | 2.5 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 49.9 | 4.7 | 41.6 | 58.0 |
| Level (m) | 1.7 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 3.20 |
| Caudal (m3 s−1) | 2.8 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 7.0 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.64 |
| Wind (m s−1) | 3.3 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 13.2 | 6.6 | 4.3 | 0.0 | 27.6 |
| Prec (mm) | 33.8 | 12.0 | 18.9 | 49.2 | 52.2 | 29.5 | 8.0 | 92.5 |
| Vol (km3) | 0.013 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.028 |
| pH | 10.0 | 0.4 | 9.7 | 10.4 | 8.1 | 0.4 | 7.1 | 8.6 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 5.9 | 1.3 | 4.9 | 7.4 | 9.8 | 2.0 | 6.5 | 12.2 |
| Chl a (µg L−1) | 59.6 | 36.6 | 20.9 | 93.7 | 9.0 | 5.0 | 3.1 | 15.6 |
| SPM (mg L−1) | 64.8 | 14.6 | 50.8 | 80.0 | 40.9 | 25.2 | 6.4 | 100.4 |
| POM (mg L−1) | 33.4 | 16.9 | 20.0 | 52.5 | 12.3 | 21.5 | 2.4 | 76.9 |
| Secchi disk (m) | 0.28 | 0.7 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| TP (mg L−1) | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| TNorg (mg L−1) | 12.8 | 4.7 | 9.4 | 18.2 | 3.5 | 0.2 | 3.3 | 3.8 |
| Lake | Dependent Variable | Parameter | R2 | Standarized Regression Coefficient | t | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La Salada | GPP | Temp | 0.392 | 0.51 | 1.32 | <0.0001 |
| Wind | 0.50 | −0.12 | <0.0001 | |||
| Vol | −1.50 | −294.61 | <0.0001 | |||
| R | Temp | 0.299 | 0.50 | 1.09 | <0.0001 | |
| Wind | 0.49 | −0.19 | <0.0001 | |||
| Vol | −1.50 | −507.73 | <0.0001 | |||
| NEP | Temp | 0.362 | 0.50 | 2.42 | <0.0001 | |
| Wind | 0.50 | −0.29 | <0.0001 | |||
| Vol | −1.50 | −831.22 | <0.0001 | |||
| Sauce Grande | GPP | Temp | 0.255 | 0.4 | 0.91 | <0.0001 |
| Wind | −0.09 | −0.68 | <0.0001 | |||
| Vol | −1.34 | −4.80 | <0.0001 | |||
| R | Temp | 0.302 | 1.1 | 1.29 | <0.0001 | |
| Wind | −0.72 | −0.57 | <0.0001 | |||
| Vol | 0.57 | 0.74 | <0.0001 | |||
| NEP | Temp | 0.314 | −0.35 | 2.30 | <0.0001 | |
| Wind | −0.57 | −1.14 | <0.0001 | |||
| Vol | 1.49 | 31.14 | <0.0001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfonso, M.B.; Brendel, A.S.; Vitale, A.J.; Seitz, C.; Piccolo, M.C.; Perillo, G.M.E. Drivers of Ecosystem Metabolism in Two Managed Shallow Lakes with Different Salinity and Trophic Conditions: The Sauce Grande and La Salada Lakes (Argentina). Water 2018, 10, 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091136
Alfonso MB, Brendel AS, Vitale AJ, Seitz C, Piccolo MC, Perillo GME. Drivers of Ecosystem Metabolism in Two Managed Shallow Lakes with Different Salinity and Trophic Conditions: The Sauce Grande and La Salada Lakes (Argentina). Water. 2018; 10(9):1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfonso, María Belén, Andrea Soledad Brendel, Alejandro José Vitale, Carina Seitz, María Cintia Piccolo, and Gerardo Miguel Eduardo Perillo. 2018. "Drivers of Ecosystem Metabolism in Two Managed Shallow Lakes with Different Salinity and Trophic Conditions: The Sauce Grande and La Salada Lakes (Argentina)" Water 10, no. 9: 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091136
APA StyleAlfonso, M. B., Brendel, A. S., Vitale, A. J., Seitz, C., Piccolo, M. C., & Perillo, G. M. E. (2018). Drivers of Ecosystem Metabolism in Two Managed Shallow Lakes with Different Salinity and Trophic Conditions: The Sauce Grande and La Salada Lakes (Argentina). Water, 10(9), 1136. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091136





