The Role of Attenuation and Land Management in Small Catchments to Remove Sediment and Phosphorus: A Modelling Study of Mitigation Options and Impacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
- Calibrate the CRAFT to the existing runoff, nutrient, and sediment data collected in October 2011–September 2012 and establish a baseline scenario [28].
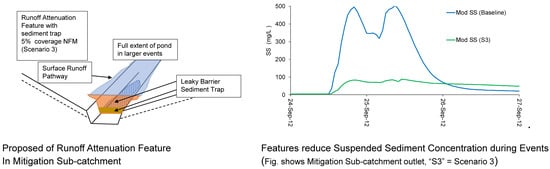
- Evaluate the performance of a series of demonstration RAFs in the Mitigation sub-catchment of the NBC (mass of sediment and P trapped) [24] and use the information to inform the future scenarios.
- Run simulations of the NBC using CRAFT with additional attenuation to represent three scenarios of land management.
- Interpret the results of these scenarios in terms of (i) local and catchment scale impacts on runoff, TP, and SS; and (ii) compare the modelled changes in TP and SS yield with the measured reductions from step 3.
2.1. Description of the CRAFT
2.2. Description of Case Study
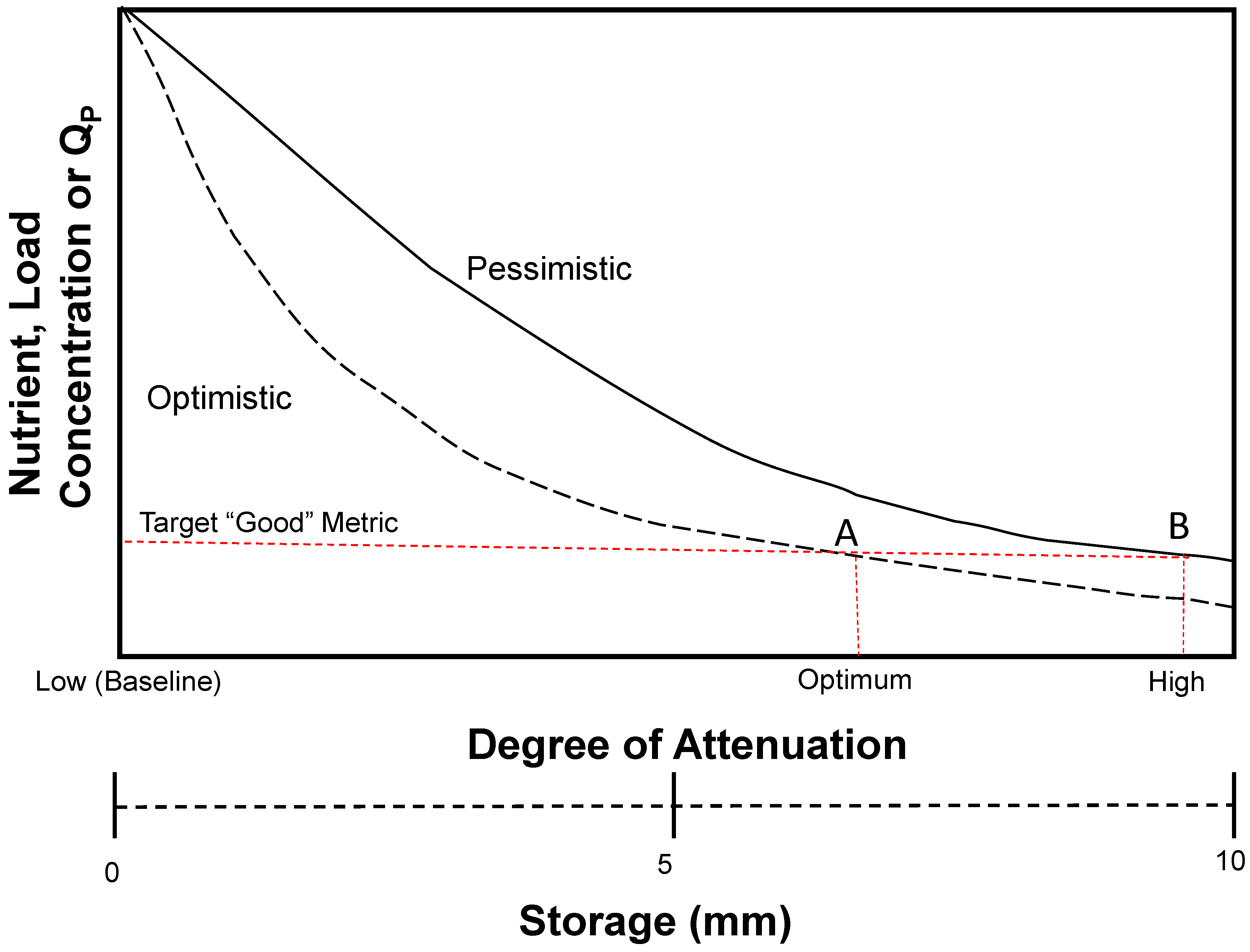
2.3. Mitigation Modelling Approach
CRAFT Mitigation Modelling
- KLAG = 0.75 h−1 (representing natural attenuation, from the “lagged” simulation [28].
- KRE = 0 (for the baseline with no trapping).
3. Results
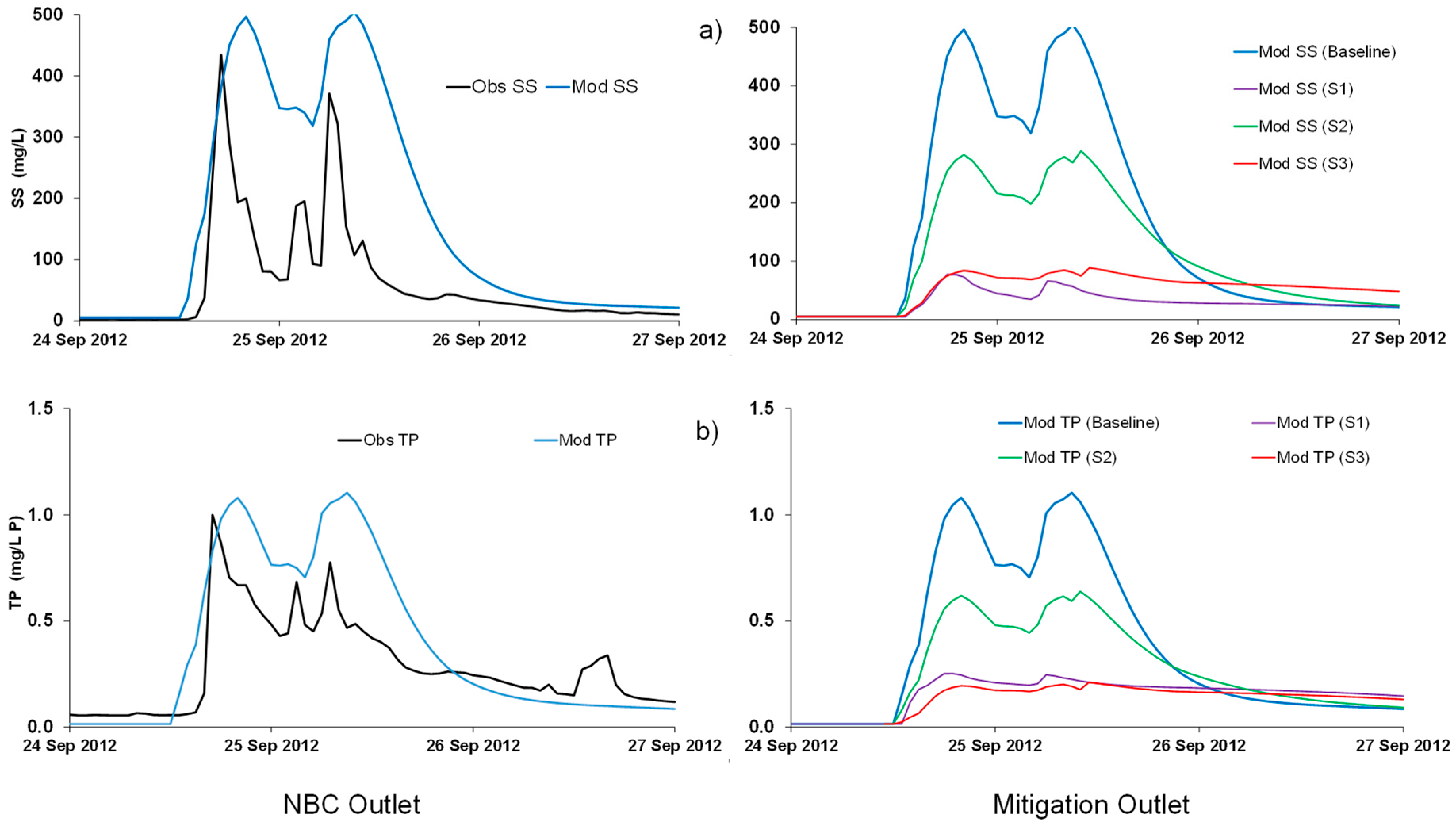
3.1. Results from the 2012 Events (Baseline Simulation)
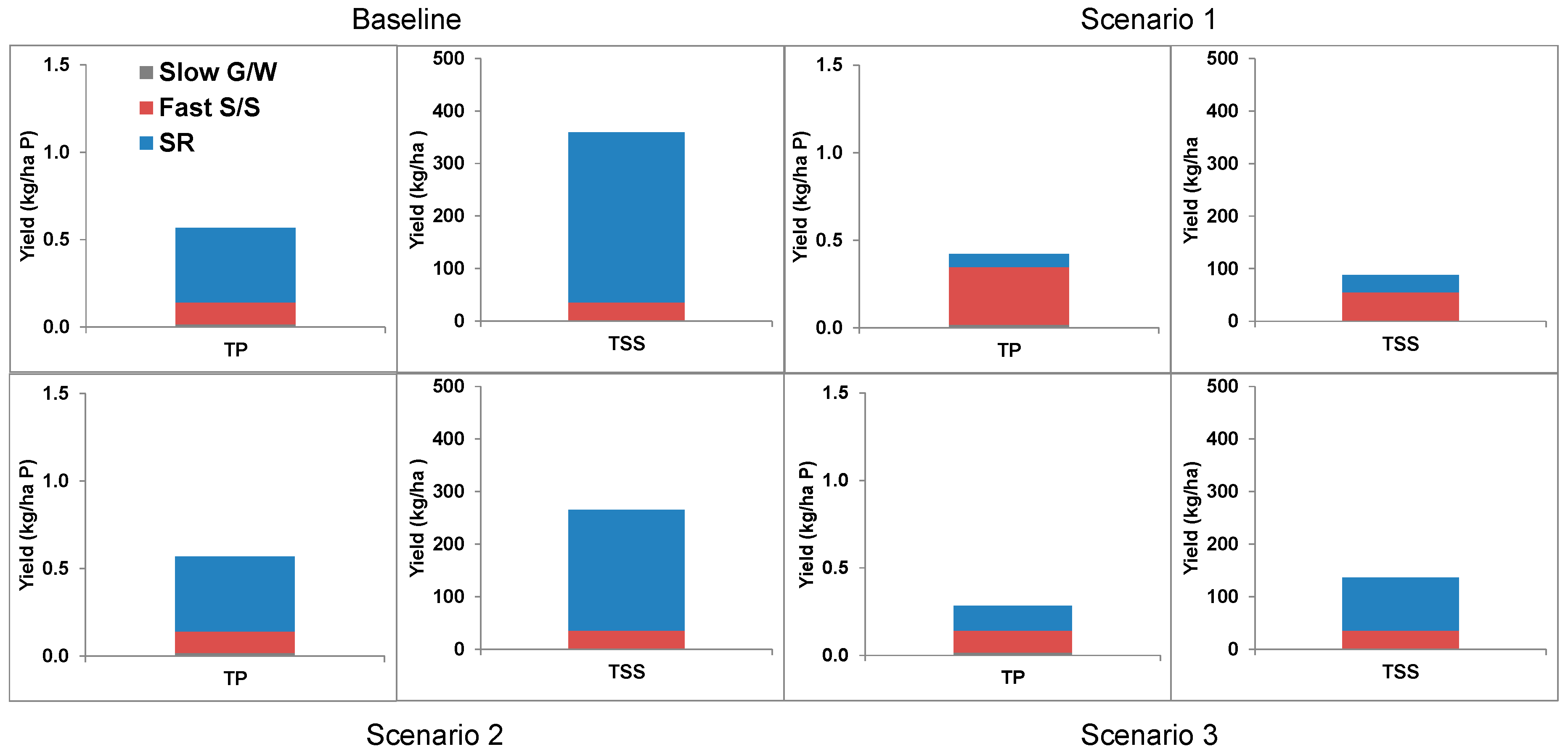
3.2. Results from Scenarios 1–3
3.3. Comparison of Recent Sampling Campaign and Model Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NWRM—Natural Water Retention Measures. European Union. Available online: www.nwrm.eu (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- Environment Agency Working with Natural Processes to Reduce Flood Risk. Available online: www.gov.uk/government/publications/working-with-natural-processes-to-reduce-flood-risk Published 31/10/2017 (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- O’Connell, P.E.; Ewen, J.; O’Donnell, G.; Quinn, P. Is there a link between agricultural land-use management and flooding? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, T.R.; Marrington, S.; Thomas, H.; Broadmeadow, S.B.; Valatin, G. Slowing the Flow at Pickering. Final Report for the Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs; Project RMP5455; DEFRA: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, P.; O’Donnell, G.; Nicholson, A.; Wilkinson, M.; Owen, G.; Jonczyk, J.; Barber, N.; Hardwick, M.; Davies, G. Potential Use of Runoff Attenuation Features in Small Rural Catchments for Flood Mitigation; Newcastle University, Environment Agency, Royal Haskoning DHV: Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth, S.M.; Booth, C.A. Sustainable Surface Water Management: A Handbook for SUDS; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- SEPA. Natural Flood Management Handbook, 2nd ed.; Scottish Environment Protection Agency: Stirling, UK, 2015; Available online: https://www.sepa.org.uk/media/163560/sepa-natural-flood-management-handbook1.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2018).
- Duffy, A.; Moir, S.; Berwick, N.; Shabashow, J.; D’Arcy, B.; Wade, R. Rural Sustainable Drainage Systems: A Practical Design and Build. Guide for Scotland’s Farmers and Landowner; CREW: Scotland, UK, 2015; Available online: http://crew.ac.uk/publications (accessed on 6 June 2018).
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Quinn, P.F.; Welton, P. Runoff management during the September 2008 floods in the Belford catchment, Northumberland. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2010, 3, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, T.R.; Thomas, H. Restoring Floodplain Woodland for Flood Alleviation. Final Report for the Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs; Project SLD2316; DEFRA: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, N. Sediment, Nutrient and Runoff Management and Mitigation in Rural Catchments. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, N.J.; Quinn, P.F. Mitigating diffuse water pollution from agriculture using soft engineered runoff attenuation features. Area 2012, 44, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deasy, C.; Quinton, J.N.; Silgram, M.; Bailey, A.P.; Jackson, B.; Stevens, C.J. Contributing understanding of mitigation options for phosphorus and sediment to a review of the efficacy of contemporary agricultural stewardship measures. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doody, D.G.; Archbold, M.; Foy, R.H.; Flynn, R. Approaches to the implementation of the Water Framework Directive: Targeting mitigation measures at critical source areas of diffuse phosphorus in Irish catchments. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcock, R.J.; Müller, K.; van Assema, G.B.; Bellingham, M.A.; Ovenden, R. Attenuation of nitrogen, phosphorus and E. coli inputs from pasture runoff to surface waters by a farm wetland: The importance of wetland shape and residence time. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, L.M. Rural Sustainable Drainage Systems (RSuDS); Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Blöschl, G. Scaling in hydrology. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; Stoate, C.; Williams, P.; Brown, C.; Casey, A.; Davies, S.; Diego, I.G.; Hawczak, A.; Kizuka, T.; McGoff, E.; et al. Water Friendly Farming Autumn 2016 Update; Freshwater Habitats Trust: Oxford, UK; Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust: Fordingbridge, UK, 2016; Available online: https://freshwaterhabitats.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Water-Friendly-Farming-update-2016.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2018).
- Fealy, R.M.; Buckley, C.; Mechan, S.; Melland, A.; Mellander, P.E.; Shortle, G.; Wall, D.; Jordan, P. The Irish Agricultural Catchments Programme: Catchment selection using spatial multi-criteria decision analysis. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 26, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, G.J.; Perks, M.T.; Benskin, C.M.H.; Wilkinson, M.E.; Jonczyk, J.; Quinn, P.F. Monitoring agricultural diffuse pollution through a dense monitoring network in the River Eden Demonstration Test Catchment, Cumbria, UK. Area 2012, 44, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, D.F.; Burke, S.P.; Collins, A.L.; Gartner, R.; Haft, M.R.; Harris, R.C.; Haygarth, P.M.; Hedges, M.C.; Hiscock, K.M.; Lovett, A.A. Developing demonstration test catchments as a platform for transdisciplinary land management research in England and Wales. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, P.; Beven, K.; Hankin, B.; Lamb, R. A modelling framework for evaluation of the hydrological impacts of nature-based approaches to flood risk management, with application to in-channel interventions across a 29 km2 scale catchment in the United Kingdom. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 1734–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, M.; Deelstra, J.; Stålnacke, P.; Eggestad, H.O.; Øygarden, L.; Pengerud, A. Monitoring catchment scale agricultural pollution in Norway: Policy instruments, implementation of mitigation methods and trends in nutrient and sediment losses. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.J.; Reaney, S.N.; Barker, P.A.; Benskin, C.; Burke, S.; Cleasby, W.; Haygarth, P.; Jonczyk, J.C.; Owen, G.J.; Snell, M.A.; et al. The treatment train approach to reducing nonpoint source pollution from agriculture. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, P.; Edwards, A.C.; Foulger, M. A review of the efficacy of contemporary agricultural stewardship measures for ameliorating water pollution problems of key concern to the UK water industry. Agric. Syst. 2009, 99, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ensign, S.H.; McMillan, S.K.; Thompson, S.P.; Piehler, M.F. Nitrogen and phosphorus attenuation within the stream network of a coastal, agricultural watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.; Quinn, P.F.; Bowes, M.J. The Catchment Runoff Attenuation Flux Tool, A minimum information requirement nutrient pollution model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1641–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Quinn, P.F.; Perks, M.; Barber, N.J.; Jonczyk, J.; Owen, G.J. Simulating high frequency water quality monitoring data using a catchment runoff attenuation flux tool (CRAFT). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heathwaite, A.L.; Quinn, P.F.; Hewett, C.J.M. Modelling and managing critical source areas of diffuse pollution from agricultural land using flow connectivity simulation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Is Hydrology kinematic? Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 667–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perks, M.T.; Owen, G.J.; Benskin, C.M.H.; Jonczyk, J.; Deasy, C.; Burke, S.; Haygarth, P.M. Dominant mechanisms for the delivery of fine sediment and phosphorus to fluvial networks draining grassland dominated headwater catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 523, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ockenden, M.C.; Deasy, C.E.; Benskin, C.M.; Beven, K.J.; Burke, S.; Collins, A.L.; Evans, R.; Falloon, P.D.; Forber, K.J.; Hiscock, K.M.; et al. Potential effects of changing climate on catchment processes and nutrient transfers: Evidence from high temporal concentration-flow dynamics in headwater catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ockenden, M.C.; Tych, W.; Beven, K.; Collins, A.; Evans, R.; Falloon, P.; Forber, K.; Hiscock, K.; Hollaway, M.; Kahana, R.; et al. Prediction of storm transfers and annual loads with data-based mechanistic models using high-frequency data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 18, 6425–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.F.; Bathurst, J.C. Spatial variability of suspended sediment yield in a gravel-bed river across four orders of magnitude of catchment area. Catena 2015, 133, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2000/60/EC: Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. (The Water Framework Directive); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Greene, S.; Johnes, P.J.; Bloomfield, J.P.; Reaney, S.M.; Lawley, R.; Elkhatib, Y.; Freer, J.; Odoni, N.; Macleod, C.J.; Percy, B. A geospatial framework to support integrated biogeochemical modelling in the United Kingdom. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 68, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hewett, C.J.; Quinn, P.F.; Heathwaite, A.L.; Doyle, A.; Burke, S.; Whitehead, P.G.; Lerner, D.N. A multi-scale framework for strategic management of diffuse pollution. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N.; Reaney, S.M.; Heathwaite, A.L. Representation of landscape hydrological connectivity using a topographically driven surface flow index. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reaney, S.M.; Lane, S.N.; Heathwaite, A.L.; Dugdale, L.J. Risk-based modelling of diffuse land use impacts from rural landscapes upon salmonid fry abundance. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WFD-UKTAG. UKTAG River Assessment Method—Phosphorus: River Phosphorus Standards; Water Framework Directive-United Kingdom Technical Advisory Group (WFD-UKTAG): Stirling, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, A.; Honti, M.; Zessner, M.; Eder, A.; Clement, A.; Blöschl, G. Identification of phosphorus emission hotspots in agricultural catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoumans, O.F.; Chardon, W.J.; Bechmann, M.E.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Hofman, G.; Kronvang, B.; Dorioz, J.M. Mitigation options to reduce phosphorus losses from the agricultural sector and improve surface water quality: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beven, K. On the generalized kinematic routing method. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.F.; Sivapalan, M.; Beven, K.; Band, L. Effects of spatial variability and scale with implications to hydrologic modeling. J. Hydrol. 1988, 102, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Quinn, P.F.; Barber, N.J.; Jonczyk, J. A framework for managing runoff and pollution in the rural landscape using a Catchment Systems Engineering approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Observation | Value |
|---|---|
| Catchment Area (km2) | 12.5 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 686 |
| Runoff (mm) | 303 |
| TP Yield (kg·ha−1) | 0.73 |
| SS Yield (t·km−2) | 18.1 |
| TP Load (kg) | 908 |
| SS Load (t) | 229 |
| TP mean Concentration (mg P·L−1) | 0.077 |
| SS mean Concentration (mg·L−1) | 4.3 |
| Scenario | KLAG (h−1) | S (Total) (mm) | S (Total) (m3) | S (Added) (m3) | KRE (-) | Other Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0.75 | 4.86 | 6075 | 0 | 0 | No changes |
| 1 | 0.75 | 4.86 | 6075 | 0 | 0 | Increased Infiltration Capacity |
| 2 | 0.83 | 6.46 | 8075 | 2000 | 0.4 | No changes |
| 3 | 0.93 | 11.3 | 14,075 | 8000 | 0.8 | No changes |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adams, R.; Quinn, P.; Barber, N.; Reaney, S. The Role of Attenuation and Land Management in Small Catchments to Remove Sediment and Phosphorus: A Modelling Study of Mitigation Options and Impacts. Water 2018, 10, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091227
Adams R, Quinn P, Barber N, Reaney S. The Role of Attenuation and Land Management in Small Catchments to Remove Sediment and Phosphorus: A Modelling Study of Mitigation Options and Impacts. Water. 2018; 10(9):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091227
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdams, Russell, Paul Quinn, Nick Barber, and Sim Reaney. 2018. "The Role of Attenuation and Land Management in Small Catchments to Remove Sediment and Phosphorus: A Modelling Study of Mitigation Options and Impacts" Water 10, no. 9: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091227
APA StyleAdams, R., Quinn, P., Barber, N., & Reaney, S. (2018). The Role of Attenuation and Land Management in Small Catchments to Remove Sediment and Phosphorus: A Modelling Study of Mitigation Options and Impacts. Water, 10(9), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091227