Sedimentation of Raw Sewage: Investigations For a Pumping Station in Northern Germany under Energy-Efficient Pump Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Investigation of the settling behavior of typical raw sewage at the inflow side of an urban influenced PS;
- Evaluation of the modification of the settling behavior by wet weather inflow (road runoff);
- Calculation of the sediment formation inside the connected pressure pipe in (i) two-point control and (ii) energy-efficient control; and
- Verification by determining the deposit’s height inside the pressure pipe by a daily observation of the pipe curve.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pumping Station, Control Modes, and Monitoring
2.1.1. Pumping Station
2.1.2. Two-Point Control
2.1.3. Rule-Based Control
2.1.4. Monitoring
2.2. Sampling and Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Sampling
2.2.2. Experimental Design and Procedure
- Filling tank and columns: Storage tank is filled with the sewage sample from the PS (30 L). 7 settling columns (each volume Vc = 2.415 L, height Hc = 380 mm) are filled subsequently via separate tubes by gravity from tank till overflow. Settling starts immediately.
- Settling: Parallel settling in all 7 columns until the specific settling duration t reached.
- Sampling and TSS analysis: After the specific settling duration t, a sample (volume = 0.345 L) is extracted from the bottom of the respective column i and analysed for TSS. The samples were extracted using a central vacuum pump, connected to a 10 mm glass tube, ending 10 mm above columns bottom.
2.3. Calculation of Sediment Formation and Deposit’s Height in the Pressure Pipe
2.3.1. Sediment Formation
2.3.2. Deposit’s Height
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Monitoring the Control Modes
3.2. Settling Properties of Dry and Wet Weather Samples
3.3. Sediment Formation
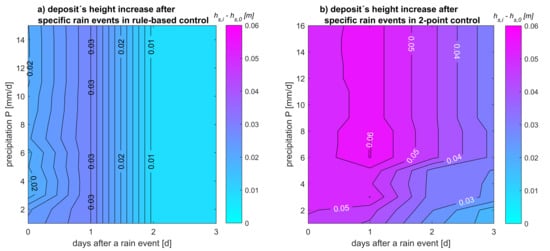
3.4. Verification by Calculated Deposit’s Height
4. Conclusions
- The adapted experimental setup (VICAS/VICPOL-protocol) is robust and provides reproducible results;
- Settling behavior from dry to combined inflow changes significantly in medium speed classes;
- Pump pauses decrease/pump sequences increase from conventional two-point control to rule-based control;
- Rule-based mode allows higher threshold values of settling velocity, especially for combined inflow, followed by a significant reduction of the sediment formation;
- Pipe curve observation leads to reliable findings about the deposit’s height;
- Daily variations in deposit’s height were registered, but no significant increase in sedimentation risk.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knubbe, A.; Fricke, A.; Ecktädt, H.; Neymeyr, K.; Schwarz, M.; Traenckner, J. Energieeffizienter Betrieb von Abwasserfördersystemen. Energy-efficient strategies for wastewater pumping systems. gwf-Wasser|Abwasser 2014, 155, 640–646. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. (DIN). Entwässerungssysteme außerhalb von Gebäuden, Pumpsysteme-Teil 2: Druckentwässerungssysteme; Deutsche Fassung EN 16932-2:2018. In Drain and Sewer Systems Outside Buildings-Pumping Systems-Part 2: Positive Pressure Systems; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Benoist, A.P.; Lijklema, L. Distribution of sedimentation rates of suspended solids and heavy metals in combined sewer overflows. Water Sci. Technol. 1990, 22, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelbach, S.; Woehrle, C. Settleable solids in a combined sewer system—Measurement, quantity, characteristics. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyack, J.N.; Hedges, P.D.; Smisson, R.P.M. The relationship between settling velocity grading and the characteristics of the contributing catchment. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, P.D.; Becker, F.A.; Smisson, R.P.M. The application of settling velocity as a parameter for characterising wastewater solids. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 37, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebbo, G.; Gromaire, M.-C.; Lucas, E. Protocole VICAS: Mesure de la vitesse de chute des MES dans les effluents urbains. TSM. Techn. Sci. Methodes Génie Urbain Génie Rural 2003, A98, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gromaire, M.C.; Kafi-Benyahia, M.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Moilleron, R.; Chebbo, G. Settling velocity of particulate pollutants from combined sewer wet weather discharges. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, M. Field and Laboratory Experiments on Settling Process in Stormwater Storage Tanks. Diploma Thesis, INSA de Lyon, Villeurbanne, France, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria, 15 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kang, J.-H.; Lau, S.-L.; Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Optimization of Settling Tank Design to Remove Particles and Metals. J. Environ. Eng. 2008, 134, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Slaa, S.; van Maren, D.S.; He, Q.; Winterwerp, J.C. Hindered Settling of Silt. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141, 4015020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, R.K.; Kaur, J. Noninvasive Measurement of Particle-Settling Velocity and Comparison with Stokes’ Law. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 140, 4013008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikora, V.; Aberle, J.; Green, M. Sediment Flocs: Settling Velocity, Flocculation Factor, and Optical Backscatter. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Maa, J.P.-Y. In Situ Measurements of Settling Velocity near Baimao Shoal in Changjiang Estuary. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, K.; Burns, A.D.; Ingham, D.B.; McCaffrey, W.D. Influence of Lift Force on the Settling Velocities of Rotating Particles in Two-Dimensional Shear Flow. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.-S. Effect of Concentration on Settling Velocity of Sediment Particles. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, S.S.Y. Formulas for Sediment Porosity and Settling Velocity. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenen, B. Simple and General Formula for the Settling Velocity of Particles. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebbo, G. Solides des Rejets Pluviaux Urbains: Caractérisation et Traitabilité. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, Paris, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chancelier, J.P.; Chebbo, G.; Lucas-Aiguier, E. Estimation of settling velocities. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3461–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L. Détermination des Vitesses de Chute des Polluants en Phase Particulaire des Rejets Urbains par Ajustement Numérique de la Courbe M(t) Pour le Protocole VICTOR; INSA de Lyon-Laboratoire URGC Hydrologie Urbaine: Villeurbanne, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. (DIN). Deutsche Einheitsverfahren zur Wasser-, Abwasser-und Schlammuntersuchung; Summarische Wirkungs-und Stoffkenngrößen (Gruppe H); Bestimmung des Gesamttrockenrückstandes, des Filtrattrockenrückstandes und des Glührückstandes (H 1) [German Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Waste Water and Sludge; General Measures of Effects and Substances (Group H); Determination of the Total Solids Residue, the Filtrate Solids Residue and the Residue on Ignition (H 1)]; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chebbo, G.; Gromaire, M.-C. VICAS—An Operating Protocol to Measure the Distributions of Suspended Solid Settling Velocities within Urban Drainage Samples. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnappan, B.G.; Exall, K.; Marsalek, J.; Rochfort, Q.; Kydd, S.; Baker, M.; Stephens, R.P. Variability of Settling Characteristics of Solids in Dry and Wet Weather Flows in Combined Sewers: Implications for CSO Treatment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinas, M.; Traenckner, J.; Koegst, T. Erosion characteristics of raw sewage: Investigations for a pumping station in northern Germany under energy-efficient pump control. Water Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro-Picallo, M.; Naves, J.; Anta, J.; Suárez, J.; Puertas, J. Monitoring accumulation sediment characteristics in full scale sewer physical model with urban wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lepot, M.; Pouzol, T.; Aldea Borruel, X.; Suner, D.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L. Measurement of sewer sediments with acoustic technology: From laboratory to field experiments. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Control Strategy | On-Level | Off-Level | Operation at Frequency | Soft Start Duration | Duty Point | Control Rules | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | H | ||||||
| (m) | (m) | (Hz) | (s) | (l/s) | (m) | ||
| Two-Point Control | 0.8 | 0.4 | 43–45 | 60 | 130 | 17.8 | transport-rules |
| Rule-Based Control | 0.8 | 0.4 | 41 (energy optimum) | 60 | 110 | 17.45 | energy- & transport-rules |
| Sample | Sampling Time | Sampling Volume (L) | TSSref (mg/L) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dry | 10:00 | 30 | 390.2 | Dry weather inflow |
| wet | 13:00 | 30 | 544.8 | Wet weather inflow: Precipitation height = 10.1 mm/d |
| Column | i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Settling Duration t | (s) | 15 | 45 | 180 | 420 | 1800 | 14,400 | 86,400 |
| Settling Velocity vs (Hc/t) | (mm/s) | 25.3 | 8.4 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.026 | 0.004 |
| vs range | F(vs)wet − F(vs)dry |
|---|---|
| (mm/s) | (%) |
| vs ≥ 40 | +1.19 |
| 13.3 ≤ vs ≤ 40 | +1.55 |
| 3.3 ≤ vs < 13.3 | +3.72 |
| 1.43 ≤ vs < 3.3 | +4.49 |
| 0.33 ≤ vs < 1.43 | +17.19 |
| 0.04 ≤ vs < 0.33 | +22.98 |
| 0.007 ≤ vs < 0.04 | +14.33 |
| vs < 0.007 | −65.43 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rinas, M.; Tränckner, J.; Koegst, T. Sedimentation of Raw Sewage: Investigations For a Pumping Station in Northern Germany under Energy-Efficient Pump Control. Water 2019, 11, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010040
Rinas M, Tränckner J, Koegst T. Sedimentation of Raw Sewage: Investigations For a Pumping Station in Northern Germany under Energy-Efficient Pump Control. Water. 2019; 11(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleRinas, Martin, Jens Tränckner, and Thilo Koegst. 2019. "Sedimentation of Raw Sewage: Investigations For a Pumping Station in Northern Germany under Energy-Efficient Pump Control" Water 11, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010040
APA StyleRinas, M., Tränckner, J., & Koegst, T. (2019). Sedimentation of Raw Sewage: Investigations For a Pumping Station in Northern Germany under Energy-Efficient Pump Control. Water, 11(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010040