Application of Numerical Tools to Investigate a Leaky Aquitard beneath Urban Well Fields
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
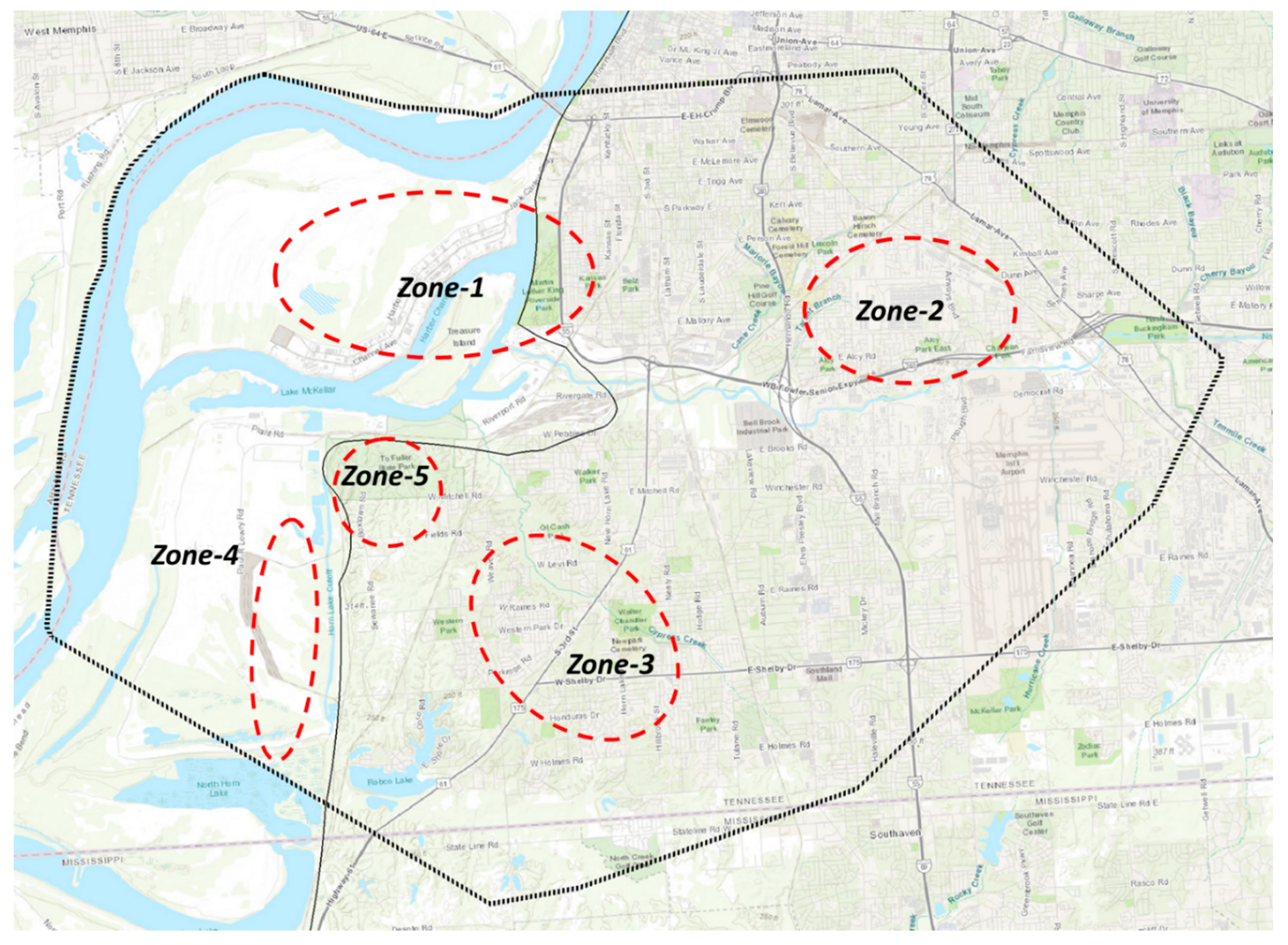
2.1. Extent of the Study Area
2.2. Conceptual Model
2.3. Groundwater model
2.4. Initial Conditions and Boundary Conditions
2.5. Internal Forcing Conditions
3. Numerical Analysis Results
3.1. Pilot Point Calibration Analyses (PPC)
3.2. Validation of PPC Results
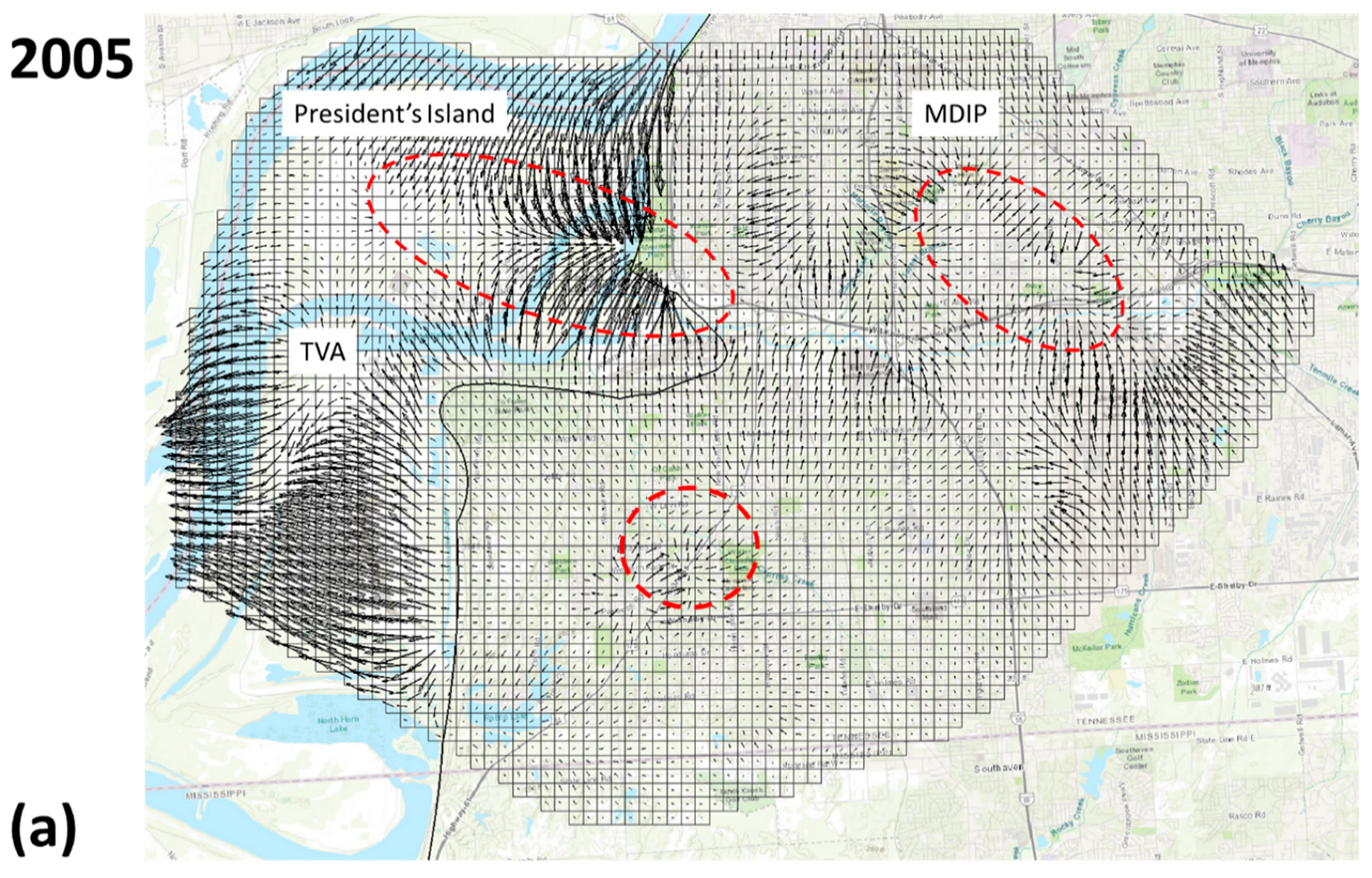
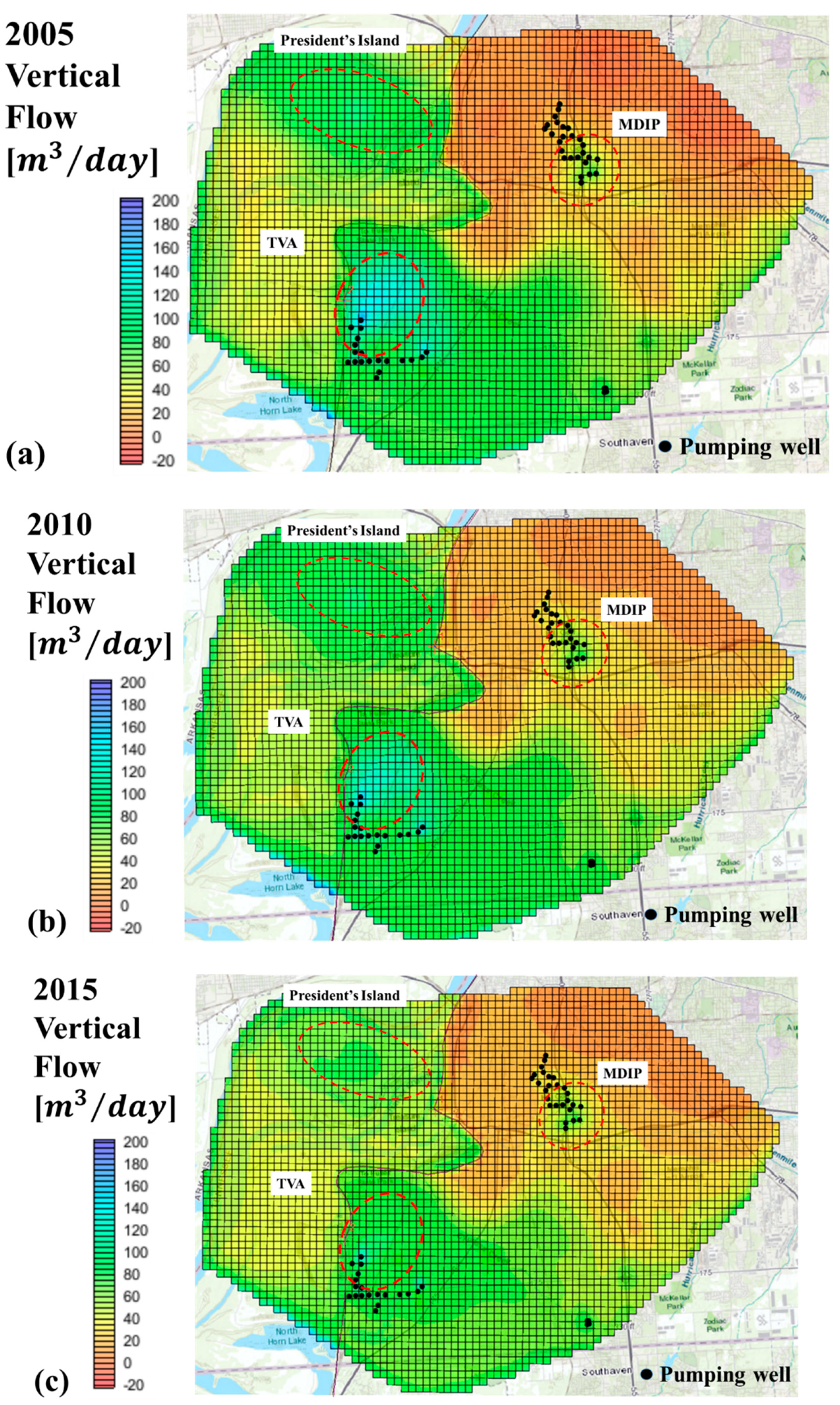
3.3. Velocity and Flow Budget Analyses (VFB)
3.4. Validation of VFB Results
3.5. Particle Tracking Analyses (PT)
3.6. Validation of PT Results
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

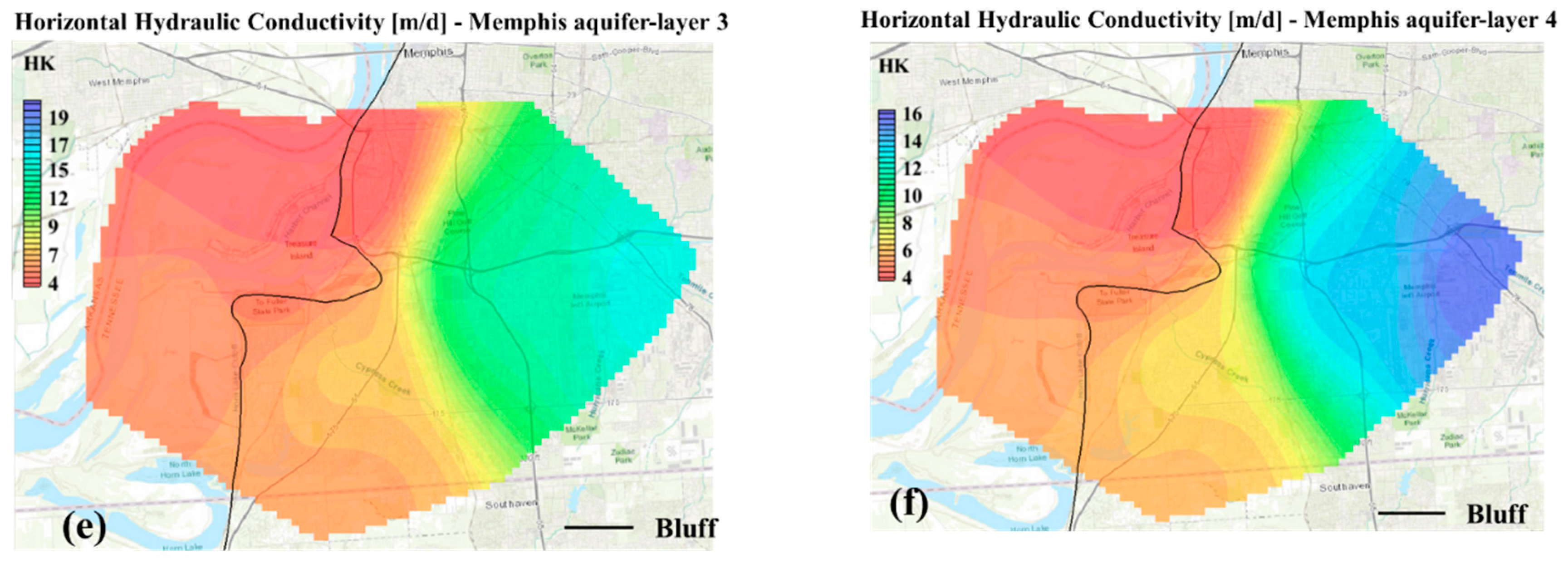
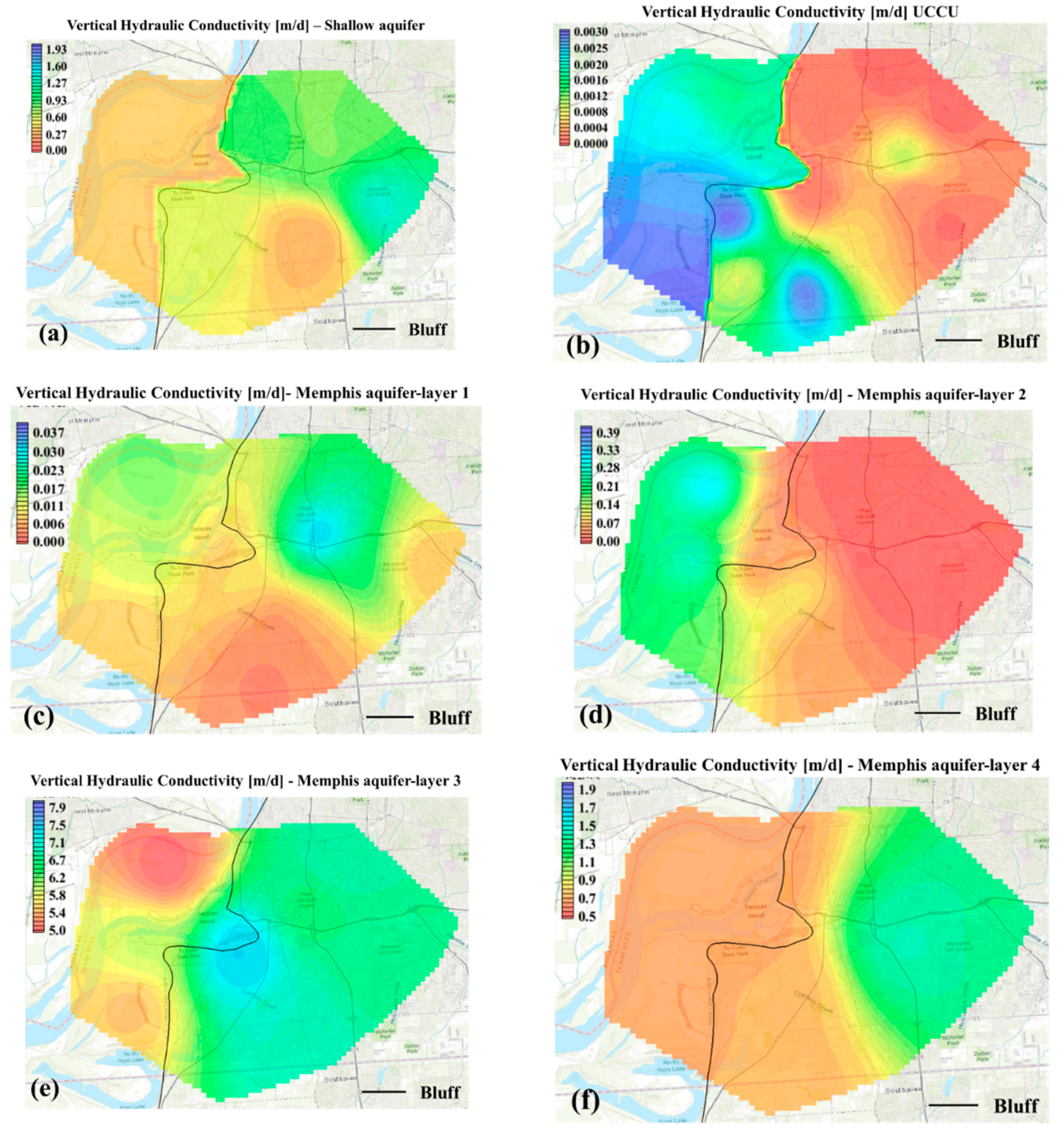
Appendix B

Appendix C

References
- Dieter, C.A.; Maupin, M.A.; Caldwell, R.R.; Harris, M.A.; Ivahnenko, T.I.; Lovelace, J.K.; Barber, N.L.; Linsey, K.S. Estimated Use of Water in the United States in 2015; US Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2018.
- Sparks, J.W. Industry Focus: Water Resources—Greater Memphis, 100 Trillion Gallons. Available online: https://businessfacilities.com/2015/06/industry-focus-water-resources-greater-memphis-100-trillion-gallons/ (accessed on 21 August 2018).
- Brahana, J.V.; Broshears, R.E. Hydrogeology and Ground-Water Flow in the Memphis and Fort Pillow Aquifers in the Memphis Area, Tennessee. 2001. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/wri894131/pdf/text_wri89-4131_1.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Clark, B.R.; Hart, R.M. The Mississippi Embayment Regional Aquifer Study (MERAS): Documentation of a Groundwater-Flow Model Constructed to Assess Water Availability in the Mississippi Embayment; US Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2009.
- Parks, W.S. Hydrogeology and Preliminary Assessment of the Potential for Contamination of the Memphis Aquifer in the Memphis Area, Tennessee; US Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1990.
- Kingsbury, J.A.; Parks, W.S. Hydrogeology of the Principal Aquifers and Relation of Faults to Interaquifer Leakage in the Memphis Area, Tennessee; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1993.
- Neretnieks, I. Age dating of groundwater in fissured rock: Influence of water volume in micropores. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busenberg, E.; Weeks, E.P.; Plummer, L.N.; Bartholomay, R.C. Age dating ground water by use of chlorofluorocarbons (CCl3F and CCl2F2), and distribution of chlorofluorocarbons in the unsaturated zone, Snake River plain aquifer, Idaho National Engineering Laboratory, Idaho. In USGS Water Resources Investigations Report; US Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, D.; Gentry, R.W.; Solomon, D.K. The geochemistry and mixing of leakage in a semi-confined aquifer at a municipal well field, Memphis, Tennessee, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1043–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.; Morat, J.; Waldron, B.; Ivey, S.; Anderson, J. Stream Loss Contributions to a Municipal Water Supply Aquifer in Memphis, Tennessee. Environ. Eng. Geosci. 2013, 19, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.; Waldron, B.; Schoefernacker, S.; Gallo, H.; Koban, J.; Bradshaw, E. Application of Environmental Tracers in the Memphis Aquifer and Implication for Sustainability of Groundwater Resources in the Memphis Metropolitan Area, Tennessee. J. Contemp. Water Res. Educ. 2016, 159, 78–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivey, S.S.; Gentry, R.W.; Larsen, D.; Anderson, J. Inverse Application of Age-Distribution Modeling Using Environmental Tracers H 3/ He 3. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidzadeh, H.; Uzun, H.; Ruecker, A.; Miller, D.; Vernon, J.; Zhang, H.; Bao, S.; Tsui, M.T.; Karanfil, T.; Chow, A.T. Extreme flooding mobilized dissolved organic matter from coastal forested wetlands. Biogeochemistry 2017, 136, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, A.; Cousin, I.; Samouëlian, A.; Boizard, H.; Richard, G. Structural heterogeneity of the soil tilled layer as characterized by 2D electrical resistivity surveying. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, B.A.; Harris, J.B.; Larsen, D.; Pell, A. Mapping an aquitard breach using shear-wave seismic reflection. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoefernacker, S. Evaluation and Evolution of a Groundwater Contaminant Plume at the Former Shelby County Landfill, Memphis, Tennessee. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Memphis, Memphis, TN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.P.; Woessner, W.W.; Hunt, R.J. Applied Groundwater Modeling: Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pollock, D.W. User’s Guide for MODPATH/MODPATH-PLOT, Version 3: A Particle Tracking Post-Processing Package for MODFLOW, the US: Geological Survey Finite-Difference Ground-Water Flow Model. 1994. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1994/0464/report.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Owen, S.J.; Jones, N.L.; Holland, J.P. A comprehensive modeling environment for the simulation of groundwater flow and transport. Eng. Comput. 1996, 12, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, D.A.; de Marsily, G.; Gotway, C.A.; Marietta, M.G.; Axness, C.L.; Beauheim, R.L.; Bras, R.L.; Carrera, J.; Dagan, G.; Davies, P.B. A comparison of seven geostatistically based inverse approaches to estimate transmissivities for modeling advective transport by groundwater flow. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 1373–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dam, J.C.; Feddes, R.A. Numerical simulation of infiltration, evaporation and shallow groundwater levels with the Richards equation. J. Hydrol. 2000, 233, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, H. A stochastic modeling approach to address hydrogeologic uncertainties in modeling wellhead protection boundaries in karst aquifers. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.J.; Jazaei, F.; Clement, T.P. How long does it take for aquifer recharge or aquifer discharge processes to reach steady state? J. Hydrol. 2013, 501, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazaei, F.; Simpson, M.J.; Clement, T.P. An analytical framework for quantifying aquifer response time scales associated with transient boundary conditions. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazaei, F.; Simpson, M.J.; Clement, T.P. Spatial analysis of aquifer response times for radial flow processes: Nondimensional analysis and laboratory-scale tests. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jazaei, F.; Simpson, M.J.; Clement, T.P. Understanding time scales of diffusive fluxes and the implication for steady state and steady shape conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upon Request: TDEC Dataviewers. Available online: https://www.tn.gov/environment/about-tdec/tdec-dataviewers.html (accessed on 21 August 2018).
- USGS Water Data for the Nation. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis? (accessed on 22 August 2018).
- Kingsbury, J.A. Altitude of the Potentiometric Surface, 2000–15, and Historical Water-Level Changes in the Memphis Aquifer in the Memphis Area, Tennessee (USGS Numbered Series No. 3415), Scientific Investigations Map; US Geological Survey: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2018.
- Bear, J. Hydraulics of Groundwater; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Niswonger, R.G.; Panday, S.; Ibaraki, M. MODFLOW-NWT, a Newton formulation for MODFLOW-2005. US Geol. Surv. Tech. Methods 2011, 6, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Narsimha, V.K. Altitudes of Ground Water Levels for 2005 and Historic Water Level Change in Surficial and Memphis Aquifers, Shelby County, Tennessee. Master’s Thesis, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rivergages.com: Providing River Gage Data for Rivers, Streams and Tributaries. Available online: http://rivergages.mvr.usace.army.mil/WaterControl/new/layout.cfm (accessed on 21 June 2018).
- U.S. Climate Data. Available online: https://www.usclimatedata.com/climate/memphis/tennessee/united-states/ustn0325 (accessed on 21 August 2018).
- Doherty, J. Ground water model calibration using pilot points and regularization. Groundwater 2003, 41, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, J. Manual for PEST: Model-Independent Parameter Estimation Manual, 5th ed.; Watermark Numerical Computing: Brisbane, Australia, 2002.
- Moore, C.; Doherty, J. The cost of uniqueness in groundwater model calibration. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, J.; Hunt, R.J. Two statistics for evaluating parameter identifiability and error reduction. J. Hydrol. 2009, 366, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.D.; Parks, W.S. Potential for Leakage among Principal Aquifers in the Memphis Area, Tennessee (Vol. 85, No. 4295); US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Moore, G.K. Geology and Hydrology of the Claiborne Group in Western Tennessee. US Government Printing Office, 1965. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wsp/1809f/report.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Parks, W.S.; Carmichael, J.K. Geology and Ground-Water Resources of the Cockfield Formation in Western Tennessee (Vol. 88, No. 4181); US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Parks, W.S.; Carmichael, J.K. Geology and Ground-Water Resources of the Fort Pillow Sand in Western Tennessee; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Carmichael, J.K.; Parks, W.S.; Kingsbury, J.A.; Ladd, D.E. Hydrogeology and Ground-Water Quality at Naval Support Activity Memphis, Millington, Tennessee; US Geological Survey Water Resources Investigation; 1997. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/1997/4158/report.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2018).
- Robinson, J.L.; Carmichael, J.K.; Halford, K.J.; Ladd, D.E. Hydrogeologic framework and simulation of ground-water flow and travel time in the shallow aquifer system in the area of Naval Support Activity Memphis, Millington, Tennessee. In US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report; US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, R.W.; Ku, T.L.; Luo, S.; Todd, V.; Larsen, D.; McCarthy, J. Resolving aquifer behavior near a focused recharge feature based upon synoptic wellfield hydrogeochemical tracer results. J. Hydrol. 2006, 323, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Ha, K.; Koo, M.-H. A distributed water balance approach to groundwater recharge estimation for Jeju volcanic island, Korea. Geosci. J. 2014, 18, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Mariethoz, G.; Brauchler, R.; Bayer, P. Smart pilot points using reversible-jump Markov-chain Monte Carlo. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3966–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, B.; Larsen, D.; Hannigan, R.; Csontos, R.; Anderson, J.; Dowling, C.; Bouldin, J. Mississippi embayment regional ground water study. In United States Environmental Protection Agency Publication 600/R-10/130; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Villalpando-Vizcaino, R. Development of a Numerical Multi-Layered Groundwater Model to Simulate Inter-Aquifer Water Exchange in Shelby County, Tennessee. Master’s Thesis, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Glantz, S.A.; Slinker, B.K.; Neilands, T.B. Primer of Applied Regression and Analysis of Variance; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ebina, T.; Minja, R.J.; Nagase, T.; Onodera, Y.; Chatterjee, A. Correlation of hydraulic conductivity of clay–sand compacted specimens with clay properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 26, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakayleh, Z.; Clement, T.P.; Fang, X. Understanding the Changes in Hydraulic Conductivity Values of Coarse-and Fine-Grained Porous Media Mixtures. Water 2018, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, E.A. Assessment of Ground-Water Leakage through the Upper Claiborne Confining Unit to the Memphis Aquifer in the Allen Well Field, Memphis, Tennessee. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, J.K.; Kingsbury, J.A.; Larsen, D.; Schoefernacker, S. Preliminary Evaluation of the Hydrogeology and Groundwater Quality of the Mississippi River Valley Alluvial Aquifer and Memphis Aquifer at the Tennessee Valley Authority Allen Power Plants, Memphis, Shelby County, Tennessee; US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.















| Minimum | Maximum | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | Vertical hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | Storage coefficients (1/m) | Specific yield (-) | Horizontal hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | Vertical hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | Storage coefficients (1/m) | Specific yield (-) | |
| Shallow aquifer - East of the bluff | 1 | 2.60 × 10−5 | - | 0.22 | 46 | 7.00 × 10−1 | - | 0.48 |
| Shallow aquifer - West of the bluff | 36 | - | - | 0.28 * | 119 | - | - | 0.28 * |
| UCCU | 6.10 × 10−6 | 1.50 × 10−6 | 9.84 × 10−4 * | - | 9.14 × 10−1 | 6.10 × 10−3 | 9.84 × 10−4 * | - |
| Memphis aquifer | 8 | - | 3.28 × 10−4 | - | 48 | - | 9.84 × 10−3 | - |
| Type of Analysis | Is it Consistent with Previous Investigations? | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPC | VFB | PT | ||
| Zone-1 | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | Yes |
| Zone-2 | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | Yes |
| Zone-3 | ☑ | ☑ | ☑ | N/A (no previous study) |
| Zone-4 | ☑ | □ | ☑ | Yes |
| Zone-5 | ☑ | □ | ☑ | N/A (no previous study) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jazaei, F.; Waldron, B.; Schoefernacker, S.; Larsen, D. Application of Numerical Tools to Investigate a Leaky Aquitard beneath Urban Well Fields. Water 2019, 11, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010005
Jazaei F, Waldron B, Schoefernacker S, Larsen D. Application of Numerical Tools to Investigate a Leaky Aquitard beneath Urban Well Fields. Water. 2019; 11(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleJazaei, Farhad, Brian Waldron, Scott Schoefernacker, and Daniel Larsen. 2019. "Application of Numerical Tools to Investigate a Leaky Aquitard beneath Urban Well Fields" Water 11, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010005
APA StyleJazaei, F., Waldron, B., Schoefernacker, S., & Larsen, D. (2019). Application of Numerical Tools to Investigate a Leaky Aquitard beneath Urban Well Fields. Water, 11(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010005




