Research Trends of Hydrological Drought: A Systematic Review
Abstract
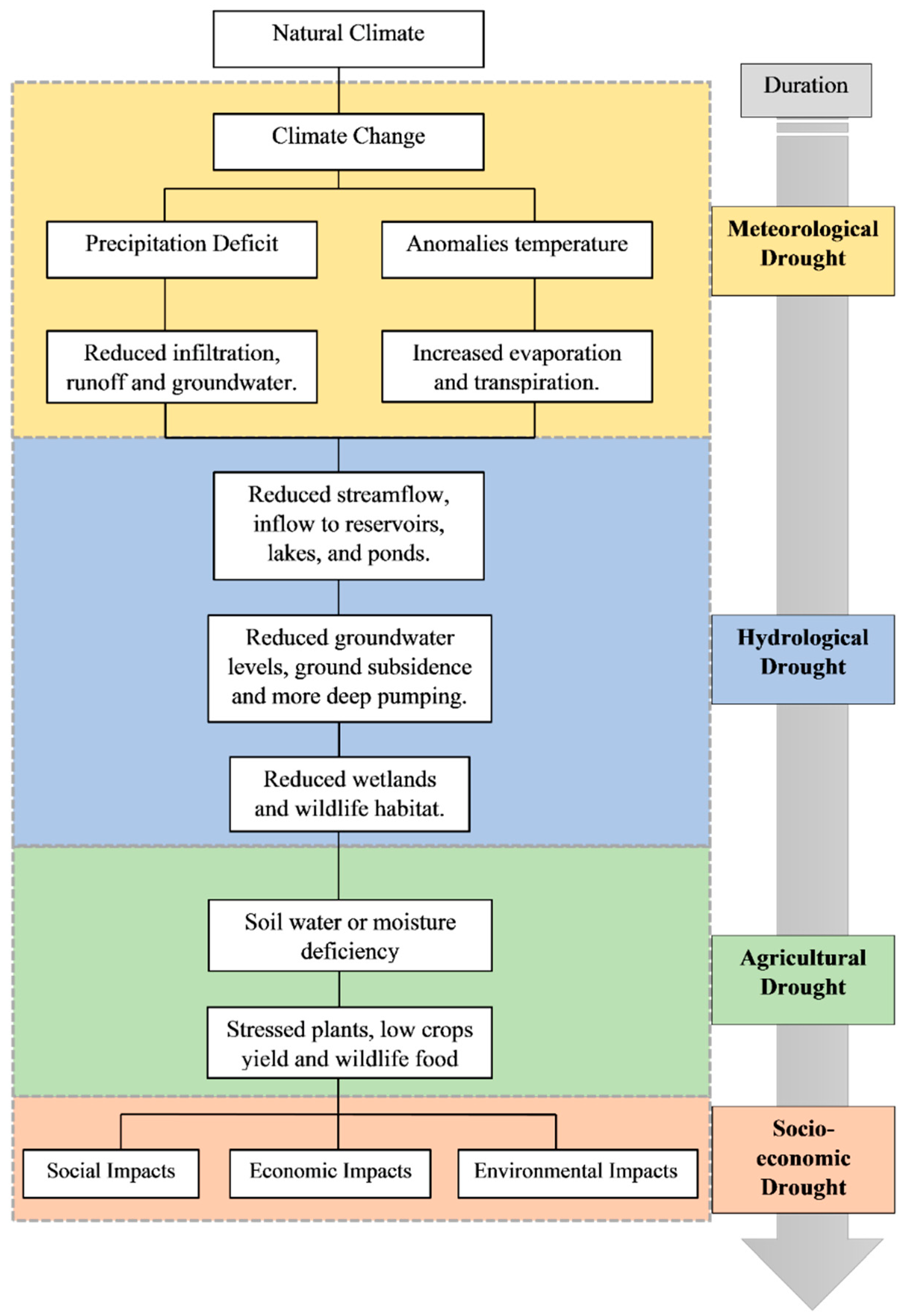
:1. Introduction
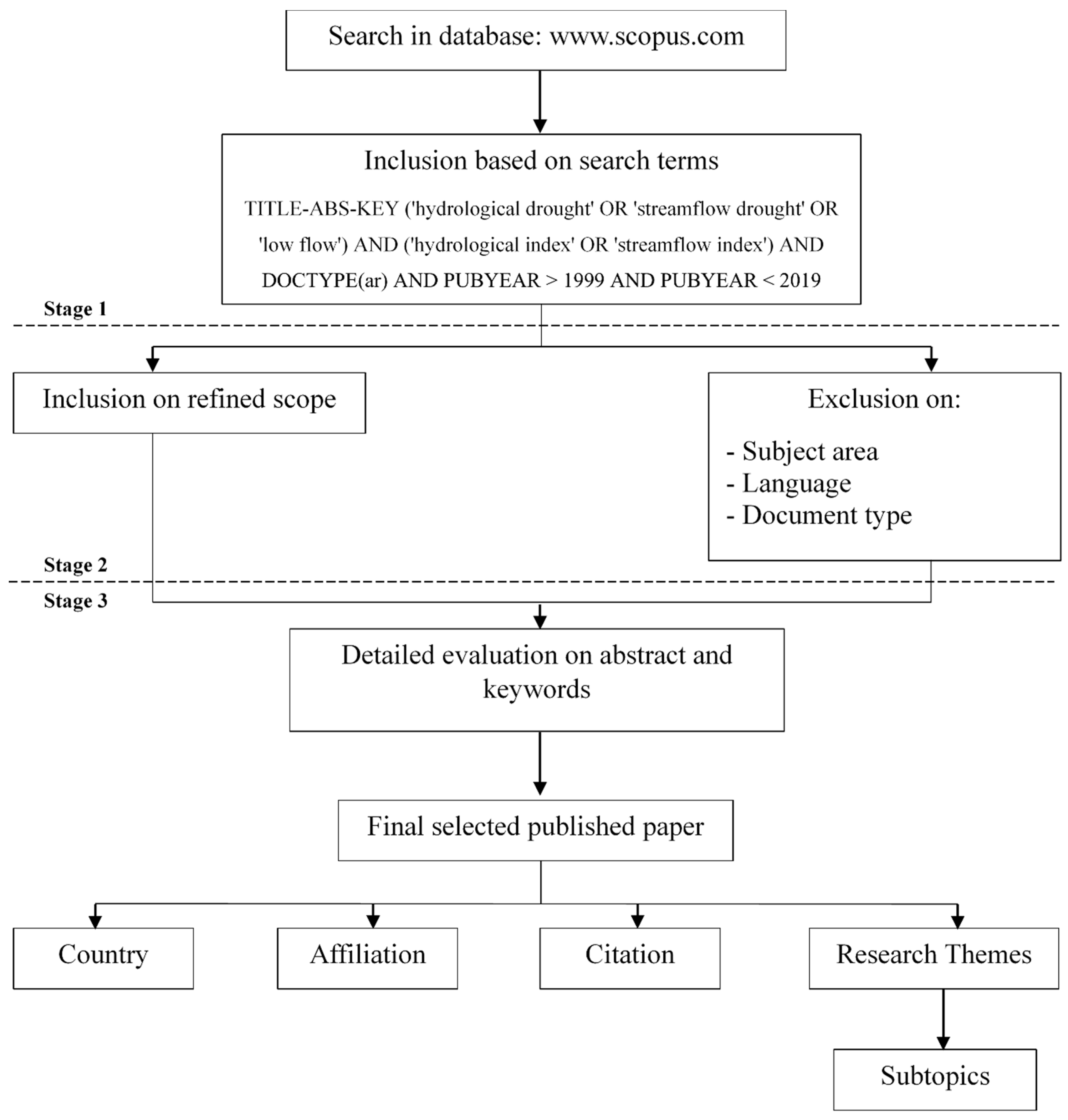
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening Stage
2.2. Examining Target Papers
- n = the total number of authors in the article,
- i = the order of the specific author.
3. Results
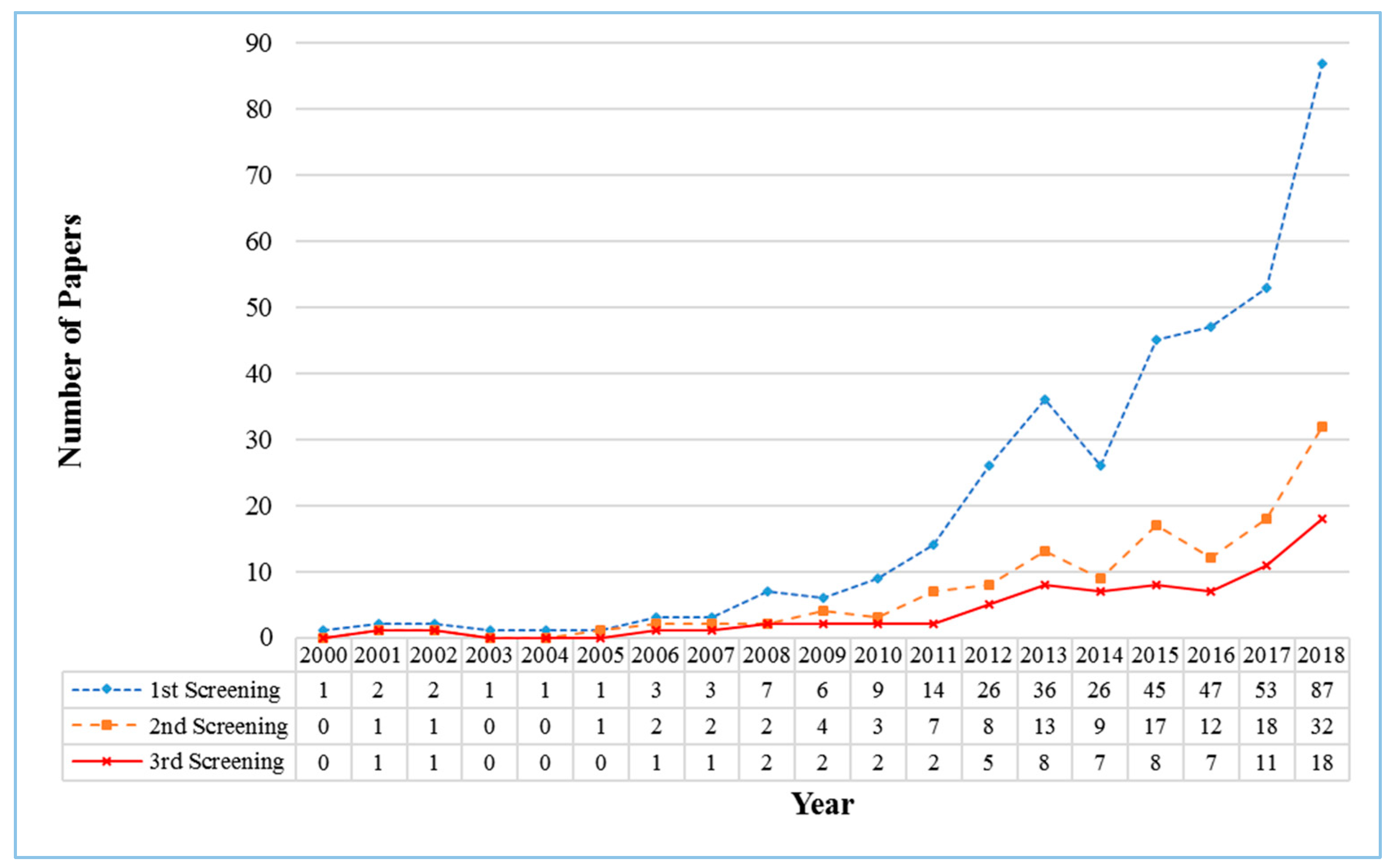
3.1. Annual Publications on Hydrological Drought from 2000 to 2018
3.2. CiteScore and Number of Papers Published
3.3. Authors’ Origin and Active Authors’ Contributors
3.4. Average of Total Citations Per Year of The Targeted Published Paper
3.5. Research Themes in Assessment of Hydrological Drought
4. Discussion
4.1. Drought Vulnerability
4.2. Drought Severity
4.3. Drought Forecast
4.4. Recommendation for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babatunde, K.A.; Begum, R.A.; Said, F.F. Application of computable general equilibrium (CGE) to climate change mitigation policy: A systematic review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, G.H.R. Impacts of Climate Change on Flow Regimes in Central Norway. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.M.H.; Muhammad, N.S.; El-Shafie, A. Wavelet-ANN versus ANN-based model for hydrometeorological drought forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleig, A.K.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Hisdal, H.; Demuth, S. A global evaluation of streamflow drought characteristics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasiliades, L.; Sarailidis, G.; Loukas, A. Hydrological modelling of low flows for operational water resources management. Eur. Water 2017, 57, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Botai, C.M.; Botai, J.O.; de Wit, J.P.; Ncongwane, K.P.; Adeola, A.M. Drought characteristics over the Western Cape Province, South Africa. Water 2017, 9, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allah, A.A.D.; Hashim, N.M.D.; Awang, A. Discovering Trends of Agricultural Drought in Tihama Plain, Yemen: A Preliminary Assessment. Indones. J. Geogr. 2017, 49, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.M.H.; Muhammad, N.S.; El-Shafie, A. A review of fundamental drought concepts, impacts and analyses of indices in Asian continent. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2018, 12, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Hisdal, H.; Tallaksen, L.M.; van Lanen, H.A.J.; Hannaford, J.; Sauquet, E. Trends in Low Flows and Streamflow Droughts across Europe; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhite, D.A. Chapter1 Drought as a Natural Hazard. In Drought: A Global Assessment; Routledge Publishers: London, UK, 2000; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Ren, L.; Singh, V.P.; Yuan, F.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Hydrologic model-based Palmer indices for drought characterization in the Yellow River basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1401–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F. Hydrological drought explained. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2015, 2, 359–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Wada, Y.; Van Lanen, H.A.J. Global hydrological droughts in the 21st century under a changing hydrological regime. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Wanders, N.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Van Loon, A.F. Hydrological drought across the world: Impact of climate and physical catchment structure. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1715–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbantis, I.; Tsakiris, G. Assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 881–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Behrawan, H. Drought risk assessment in the western part of Bangladesh. Nat. Hazards 2008, 46, 391–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntjens, P.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Grin, J. Climate change adaptation in European river basins. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2010, 10, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, S.E. Climate and climatic variability of rainfall over eastern Africa. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 590–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, J.F.; Portela, M.M.; Pulido-Calvo, I. Regionalization of droughts in Portugal. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 146, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Singh, V.P.; Li, J. Regionalization and spatial changing properties of droughts across the Pearl River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Wada, Y. Human and climate impacts on the 21st century hydrological drought. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarafshani, K.; Sharafi, L.; Azadi, H.; Van Passel, S. Vulnerability assessment models to drought: Toward a conceptual framework. Sustainability 2016, 8, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Xia, J.; Ning, L.; She, D.; Zhan, C. Identification of hydrological drought in Eastern China using a time-dependent drought index. Water 2018, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyen, L.; Dankers, R. Impact of global warming on streamflow drought in Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallaksen, L.M.; Van Lanen, H.A.J. Hydrological Drought: Processes and Estimation Methods for Streamflow and Groundwater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 0444516883. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Rahman, N.; Muhammad, N.S.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M. Evolution of research on water leakage control strategies: Where are we now? Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.S.; Cole, D.A.; Maxwell, S.E. Research productivity in psychology based on publication in the journals of the American Psychological Association. Am. Psychol. 1987, 42, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakke, N.; Ithnin, H.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Hussain, T.P.R.S. Kemarau hidrologi dan kelestarian sumber air di Malaysia: Kajian analisis sifat Lembangan Langat, Selangor (Hydrological drought and the sustainability of water resources in Malaysia: An analysis of the properties of the Langat Basin, Selangor). Geogr. Malaysian J. Soc. Sp. 2017, 12, 133–146. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Wang, S.; Chan, A.P.; Cheung, E. Research trend of public-private partnership in Construction Journals. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2009, 135, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Laaha, G. Hydrological drought severity explained by climate and catchment characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzieri, G.; Feyen, L.; Rojas, R.; Flörke, M.; Wimmer, F.; Bianchi, A. Ensemble projections of future streamflow droughts in Europe. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stahl, K.; Hisdal, H.; Hannaford, J.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Sauquet, E.; Demuth, S.; Fendekova, M.; Jordar, J. Streamflow trends in Europe: Evidence from a dataset of near-natural catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2367–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Van Beek, L.P.H.; Wanders, N.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Human water consumption intensifies hydrological drought worldwide. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 034036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panu, U.S.; Sharma, T.C. Challenges in drought research: Some perspectives and future directions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 47, S19–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Van Lanen, H.A.J. Making the distinction between water scarcity and drought using an observation-modeling framework. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1483–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisdal, H.; Stahl, K.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Demuth, S. Have streamflow droughts in Europe become more severe or frequent? Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.P.; Martin, E.; Franchistéguy, L.; Habets, F.; Soubeyroux, J.M.; Blanchard, M.; Baillon, M. Multilevel and multiscale drought reanalysis over France with the Safran-Isba-Modcou hydrometeorological suite. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majone, B.; Bovolo, C.I.; Bellin, A.; Blenkinsop, S.; Fowler, H.J. Modeling the impacts of future climate change on water resources for the Gllego river basin (Spain). Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Portela, M.M.; Almeida, A.B. Dam effects on droughts magnitude and duration in a transboundary basin: The lower river tagus, pain and Portugal. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Wagener, T.; Van Werkhoven, K.; Mann, M.E.; Crane, R. A trading-space-for-time approach to probabilistic continuous streamflow predictions in a changing climate-accounting for changing watershed behavior. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 3591–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.J.M.; Van Den Hurk, B.; Warmerdam, P.M.M.; Torfs, P.J.J.F.; Roulin, E.; Van Deursen, W.P.A. Impact of climate change on low-flows in the river Meuse. Clim. Chang. 2007, 82, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Moŕan-Tejeda, E.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Ĺopez-Moreno, J.I. Streamflow droughts in the Iberian Peninsula between 1945 and 2005: Spatial and temporal patterns. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadis, K.M.; Clark, E.A.; Wood, A.W.; Hamlet, A.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Twentieth-century drought in the Conterminous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 6, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurkmans, R.T.W.L.; De Moel, H.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Troch, P.A. Water balance versus land surface model in the simulation of Rhine river discharges. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, R.; Singh, V.P.; Song, C. Low flow regimes of the Tarim River Basin, China: Probabilistic behavior, causes and implications. Water 2018, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, A.; Castellarin, A.; Brath, A. Geostatistical prediction of flow-duration curves in an index-flow framework. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3801–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.H.; Chung, E.S. Development of streamflow drought severity-duration-frequency curves using the threshold level method. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G. Drought risk assessment and management. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 3083–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaford, J.; Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Keef, C.; Parry, S.; Prudhomme, C. Examining the large-scale spatial coherence of European drought using regional indicators of precipitation and streamflow deficit. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1146–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskula, J.; Wielgosz, I. Drought risk assessment in the Kopel river basin. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huijgevoort, M.H.J.; Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Teuling, A.J.; Uijlenhoet, R. Identification of changes in hydrological drought characteristics from a multi-GCM driven ensemble constrained by observed discharge. J. Hydrol. 2014, 512, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benninga, H.J.F.; Booij, M.J.; Romanowicz, R.J.; Rientjes, T.H.M. Performance of ensemble streamflow forecasts under varied hydrometeorological conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5273–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caillouet, L.; Vidal, J.P.; Sauquet, E.; Devers, A.; Graff, B. Ensemble reconstruction of spatio-temporal extreme low-flow events in France since 1871. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2923–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.; Chen, J.; Jiang, H.; Dong, L. Threshold behavior in a fissured granitic catchment in southern China: 2. Modeling and uncertainty analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2536–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussá, F.E.F.; Zhou, Y.; Maskey, S.; Masih, I.; Uhlenbrook, S. Groundwater as an emergency source for drought mitigation in the Crocodile River catchment, South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, T.C.; Panu, U.S. Analytical procedures for weekly hydrological droughts: A case of Canadian rivers. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.A.; Penalba, O.C.; Villalba, R.; Araneo, D.C. Spatio-temporal patterns of the 2010–2015 extreme hydrological drought across the Central Andes, Argentina. Water 2017, 9, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, V.; Lemann, T.; Zeleke, G.; Subhatu, A.T.; Nigussie, T.K.; Hurni, H. Effects of climate change on water resources in the upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saraiva Okello, A.M.L.; Masih, I.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Jewitt, G.P.W.; Van Der Zaag, P.; Riddell, E. Drivers of spatial and temporal variability of streamflow in the Incomati river basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshukov, A.; Douglas-Mankin, K. Hydrologic alterations predicted by seasonally-consistent subset ensembles of General Circulation Models. Climate 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Pangalou, D.; Vangelis, H. Regional drought assessment based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI). Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaha, G. Low flows and streamflow droughts-processes, indicators and requirements. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop of the Water Platform of the Alpine Convention on Drought Risk Management in the Alps, Vienna, Austria, 23 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hisdal, H.; Holmqvist, E.; Jónsdóttir, J.F.; Jónsson, P.; Järvet, A.; Lindström, G.; Kolcova, T.; Kriauciuniene, J.; Kuusisto, E.; Lizuma, L.; et al. Climate change signals in streamflow data in the Nordic and Baltic region. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Climate and Water, Helsinki, Finland, 3–6 September 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Engeland, K.; Hisdal, H.; Beldring, S. Predicting low flows in ungauged catchments. Clim. Var. Chang. 2006, 308, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Laaha, G.; Gauster, T.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Vidal, J.P.; Stahl, K.; Prudhomme, C.; Heudorfer, B. The European 2015 drought from a groundwater perspective. EGU Gen. Conf. Assem. Abstr. 2017, 19, 12781. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.X.; Xiong, L.; Gottschalk, L. Derivation of low flow distribution functions using copulas. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L.J.; Hannaford, J.; Chiverton, A.; Svensson, C. From meteorological to hydrological drought using standardised indicators. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 2483–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Sridhar, V. Combined statistical and spatially distributed hydrological model for evaluating future drought indices in Virginia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 12, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.C.; Panu, U.S. Prediction of hydrological drought durations based on Markov chains: Case of the Canadian prairies. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 705–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Post, D. How good are hydrological models for gap-filling streamflow data? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4593–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gain, A.K.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Sperna Weiland, F.C.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Impact of climate change on the stream flow of the lower Brahmaputra: Trends in high and low flows based on discharge-weighted ensemble modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Delgado, F.; Roupsard, O.; Le Maire, G.; Taugourdeau, S.; Pérez, A.; Van Oijen, M.; Vaast, P.; Rapidel, B.; Harmand, J.M.; Voltz, M.; et al. Modelling the hydrological behaviour of a coffee agroforestry basin in Costa Rica. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Vis, M.J.P.; Van Tiel, M.; Teuling, A.J.; Stahl, K.; Wanders, N. The role of glacier changes and threshold definition in the characterisation of future streamflow droughts in glacierised catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mundo, I.A.; Masiokas, M.H.; Villalba, R.; Morales, M.S.; Neukom, R.; Le Quesne, C.; Urrutia, R.B.; Lara, A. Multi-century tree-ring based reconstruction of the Neuquén River streamflow, northern Patagonia, Argentina. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troin, M.; Arsenault, R.; Brissette, F. Performance and Uncertainty Evaluation of Snow Models on Snowmelt Flow Simulations over a Nordic Catchment (Mistassibi, Canada). Hydrology 2015, 2, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolle, P.; Pushpalatha, R.; Perrin, C.; François, D.; Thiéry, D.; Mathevet, T.; Le Lay, M.; Besson, F.; Soubeyroux, J.M.; Viel, C.; et al. Benchmarking hydrological models for low-flow simulation and forecasting on French catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2829–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tijdeman, E.; Barker, L.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Stahl, K. Natural and Human Influences on the Link Between Meteorological and Hydrological Drought Indices for a Large Set of Catchments in the Contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6005–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotis, M.; Papadopoulos, C.; Angelidis, P.; Papadopoulos, B. Hybrid Fuzzy—Probabilistic Analysis and Classification of the Hydrological Drought. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2018, 2, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, A.I.; Veldkamp, T.I.E.; Ward, P.J. The effect of climate type on timescales of drought propagation in an ensemble of global hydrological models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4649–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Q.; Fok, H.S.; Chen, Q.; Chun, K.P. Water level reconstruction and prediction based on space-borne sensors: A case study in the Mekong and Yangtze river basins. Sensors 2018, 18, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjim, H.; Djedid, A. Drought and water mobilization in semi-arid zone: The example of Hammam Boughrara dam (North-West of Algeria). J. Water Land Dev. 2018, 37, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eris, E.; Aksoy, H.; Onoz, B.; Cetin, M.; Yuce, M.I.; Selek, B.; Aksu, H.; Burgan, H.I.; Esit, M.; Yildirim, I.; et al. Frequency analysis of low flows in intermittent and non-intermittent rivers from hydrological basins in Turkey. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2019, 19, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Lee, K.S. Regional low flow frequency analysis using Bayesian regression and prediction at ungauged catchment in Korea. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 14, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.H.; Muhammad, N.S.; El-Shafie, A. Drought characterisation in Peninsular Malaysia using DrinC software. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Trambauer, P.; Werner, M.; Winsemius, H.C.; Maskey, S.; Dutra, E.; Uhlenbrook, S. Hydrological drought forecasting and skill assessment for the Limpopo River basin, southern Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1695–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fundel, F.; Jörg-Hess, S.; Zappa, M. Monthly hydrometeorological ensemble prediction of streamflow droughts and corresponding drought indices. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jörg-Hess, S.; Kempf, S.B.; Fundel, F.; Zappa, M. The benefit of climatological and calibrated reforecast data for simulating hydrological droughts in Switzerland. Meteorol. Appl. 2015, 22, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.F.; Wang, J.; Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H. SDI and Markov chains for regional drought characteristics. Sustainability 2015, 7, 10789–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochola, W.O.; Kerkides, P. A Markov chain simulation model for predicting critical wet and dry spells in Kenya: Analysing rainfall events in the kano plains. Irrig. Drain. 2003, 52, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Saghafian, B.; Nasiri Saleh, F.; Farokhnia, A.; Noori, R. Uncertainty analysis of streamflow drought forecast using artificial neural networks and Monte-Carlo simulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L.; Flores, F.; Moneo, M. Challenges to manage the risk of water scarcity and climate change in the Mediterranean. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasa, I.W.; Bisri, M.; Sholichin, M.; Andawayanti, U. Hydrological drought index based on reservoir capacity- Case study of Batujai dam in Lombok Island, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. J. Water Land Dev. 2018, 38, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No of Authors | Order of Authors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| 1 | 1.000 | ||||||
| 2 | 0.600 | 0.400 | |||||
| 3 | 0.470 | 0.320 | 0.210 | ||||
| 4 | 0.420 | 0.280 | 0.180 | 0.120 | |||
| 5 | 0.380 | 0.260 | 0.170 | 0.110 | 0.080 | ||
| 6 | 0.370 | 0.240 | 0.160 | 0.110 | 0.070 | 0.050 | |
| 7 | 0.354 | 0.236 | 0.157 | 0.105 | 0.070 | 0.047 | 0.031 |
| Source Title | Number of Papers | CiteScore 2017 a |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrology and Earth System Sciences | 28 | 4.10 |
| Water Resources Research | 9 | 4.39 |
| Water (Switzerland) | 8 | 2.32 |
| Journal of Hydrology Regional Studies | 3 | 3.21 |
| Environmental Research Letters | 2 | 4.83 |
| Geophysical Research Letters | 2 | 4.51 |
| Hydrological Sciences Journal | 2 | 2.01 |
| International Journal of Climatology | 2 | 3.7 |
| Journal of Hydrology | 2 | 4.06 |
| Sustainability (Switzerland) | 2 | 2.37 |
| Country Origin | Number of Research Institutions | Number of Researchers | Study Area | Number of Papers | Cumulative Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 29 | 51 | United States | 12 | 15.28 |
| Ethiopia | 1 | ||||
| Netherlands | 12 | 44 | Netherlands | 11 | 12.26 |
| South Africa | 1 | ||||
| United Kingdom | 11 | 36 | United Kingdom | 4 | 7.40 |
| South Africa | 1 | ||||
| United States | 1 | ||||
| China | 12 | 25 | China | 6 | 5.89 |
| Canada | 2 | 6 | Canada | 3 | 3.42 |
| Germany | 6 | 18 | Germany | 2 | 3.34 |
| United Kingdom | 1 | ||||
| United States | 1 | ||||
| Italy | 6 | 13 | Italy | 4 | 3.27 |
| Spain | 1 | ||||
| France | 14 | 34 | France | 3 | 3.17 |
| Spain | 9 | 26 | Spain | 2 | 3.01 |
| Portugal | 1 | ||||
| South Korea | 7 | 8 | South Korea | 2 | 2.65 |
| United States | 1 | ||||
| Norway | 3 | 12 | Norway | 3 | 2.48 |
| Australia | 4 | 13 | Australia | 2 | 2.00 |
| Austria | 3 | 6 | Austria | 1 | 1.66 |
| South Africa | 4 | 8 | South Africa | 2 | 1.56 |
| Switzerland | 3 | 5 | Switzerland | 2 | 1.53 |
| Brazil | 2 | 5 | Brazil | 1 | 1.34 |
| Argentina | 4 | 4 | Argentina | 1 | 1.00 |
| Denmark | 3 | 5 | Denmark | 1 | 1.00 |
| Iran | 4 | 5 | Iran | 1 | 1.00 |
| Poland | 2 | 4 | Poland | 1 | 1.00 |
| Uganda | 1 | 1 | Uganda | 1 | 1.00 |
| Lithuania | 1 | 3 | Lithuania | 1 | 0.79 |
| Taiwan | 1 | 3 | Taiwan | 1 | 0.72 |
| Author Name | Affiliation | Country | No of Paper | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sharma, T.C. | Lakehead University | Canada | 3 | 1.60 |
| Panu, U.S. | Lakehead University | Canada | 3 | 1.40 |
| Van Loon, A.F. | Wageningen University | Netherlands | 5 | 1.37 |
| Sung, J.H. | Han River Flood Control Office | South Korea | 2 | 1.20 |
| Van Lanen, H.A.J. | Wageningen University | Netherlands | 5 | 1.18 |
| Stahl, K. | University of Oslo | Norway | 6 | 1.09 |
| Tallaksen, L.M. | University of Oslo | Norway | 5 | 0.89 |
| Tijdeman, E. | University of Freiburg | Germany | 2 | 0.89 |
| Feyen, L. | Joint Research Centre | Italy | 2 | 0.84 |
| Parry, S. | Loughborough University | United Kingdom | 2 | 0.84 |
| Hisdal, H. | Norwegian Water Resources and Energy | Norway | 3 | 0.83 |
| Vicente-Serrano, S.M. | Pyrenean Institute of Ecology | Spain | 3 | 0.75 |
| Hannaford, J. | Centre for Ecology and Hydrology | United Kingdom | 4 | 0.75 |
| Laaha, G. | University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences | Austria | 2 | 0.73 |
| Vidal, J.P. | Hydrology-Hydraulics Research Unit | France | 3 | 0.71 |
| Zhang, Y. | CSIRO Land and Water | Australia | 2 | 0.70 |
| Barker, L.J. | Centre for Ecology and Hydrology | United Kingdom | 2 | 0.70 |
| Wanders, N. | University Utrecht | Netherlands | 4 | 0.69 |
| Prudhomme, C. | Loughborough University | United Kingdom | 4 | 0.57 |
| Werner, M. | Department of Water Science and Engineering | Netherlands | 2 | 0.56 |
| López-Moreno, J.I. | Pyrenean Institute of Ecology | Spain | 3 | 0.49 |
| Teuling, A.J. | Wageningen University | Netherlands | 2 | 0.42 |
| Caillouet, L. | Hydrology-Hydraulics Research Unit | France | 2 | 0.38 |
| Singh, V.P. | Texas University | United States | 3 | 0.30 |
| Demuth, S. | University of Freiburg | Germany | 3 | 0.27 |
| Bierkens, M.F.P. | Utrecht University | Netherlands | 2 | 0.24 |
| Sauquet, E. | Hydrology-Hydraulics Research Unit | France | 3 | 0.22 |
| Uhlenbrook, S. | Delft University of Technology | Netherlands | 2 | 0.21 |
| Soubeyroux, J.M. | Météo-France | France | 2 | 0.08 |
| Fendekova, M. | Comenius University | Slovakia | 2 | 0.02 |
| Author | Paper Title | Average of Total Citations/Year |
|---|---|---|
| Van Loon and Laaha [31] | Hydrological drought severity explained by climate and catchment characteristics | 55.0 |
| Shukla and Wood [32] | Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought | 33.9 |
| Forzieri et al. [33] | Ensemble projections of future streamflow droughts in Europe | 30.0 |
| Stahl et al. [34] | Streamflow trends in Europe: Evidence from a dataset of near-natural catchments | 27.3 |
| Wada et al. [35] | Human water consumption intensifies hydrological drought worldwide | 24.5 |
| Van Lanen et al. [15] | Hydrological drought across the world: Impact of climate and physical catchment structure | 19.0 |
| Panu and Sharma [36] | Challenges in drought research: Some perspectives and future directions | 16.7 |
| Van Loon and Van Lanen [37] | Making the distinction between water scarcity and drought using an observation-modelling framework | 16.3 |
| Hisdal et al. [38] | Have streamflow droughts in Europe become more severe or frequent? | 14.4 |
| Vidal et al. [39] | Multilevel and multiscale drought reanalysis over France with the Safran-Isba-Modcou hydrometeorological suite | 14.0 |
| Feyen and Dankers [25] | Impact of global warming on streamflow drought in Europe | 13.3 |
| Fleig et al. [5] | A global evaluation of streamflow drought characteristics | 13.0 |
| Majone et al. [40] | Modelling the impacts of future climate change on water resources for the Gallego river basin (Spain) | 10.0 |
| López-Moreno et al. [41] | Dam effects on droughts magnitude and duration in a transboundary basin: The lower river Tagus, Spain and Portugal | 9.9 |
| Singh et al. [42] | A trading-space-for-time approach to probabilistic continuous streamflow predictions in a changing climate-accounting for changing watershed behaviour | 8.7 |
| De Wit et al. [43] | Impact of climate change on low flows in the river Meuse | 6.9 |
| Major Themes | Subtopics | Year | Total | Percentage (%) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 2002 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | ||||
| Drought vulnerability | Anomaly Analysis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.30 |
| Bivariate correlations | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.30 | |
| Copulas Method | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2.60 | |
| Drought duration and deficit | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 6.49 | |
| Spatial and temporal | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 14.29 | |
| Total | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 20 | 25.97 | |
| Drought Severity | Hydrological Indices | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 13 | 16.88 |
| Hydrological Trends | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 7.79 | |
| Low Flow analysis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 13 | 16.88 | |
| Threshold Level Method | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 12.99 | |
| Total | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 14 | 42 | 54.55 | |
| Drought Forecast | Artificial Neural Network | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2.60 |
| Markov-chain Model | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3.90 | |
| Monte-Carlo Simulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.30 | |
| Regional hydrological | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 6.49 | |
| Regression Analysis | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5.19 | |
| Total | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 15 | 19.48 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, H.H.; Mohd Razali, S.F.; Muhammad, N.S.; Ahmad, A. Research Trends of Hydrological Drought: A Systematic Review. Water 2019, 11, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112252
Hasan HH, Mohd Razali SF, Muhammad NS, Ahmad A. Research Trends of Hydrological Drought: A Systematic Review. Water. 2019; 11(11):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Hasrul Hazman, Siti Fatin Mohd Razali, Nur Shazwani Muhammad, and Asmadi Ahmad. 2019. "Research Trends of Hydrological Drought: A Systematic Review" Water 11, no. 11: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112252
APA StyleHasan, H. H., Mohd Razali, S. F., Muhammad, N. S., & Ahmad, A. (2019). Research Trends of Hydrological Drought: A Systematic Review. Water, 11(11), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112252







