Fine Characterization of the Effects of Aquifer Heterogeneity on Solute Transport: A Numerical Sandbox Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Numerical Sandbox Construction
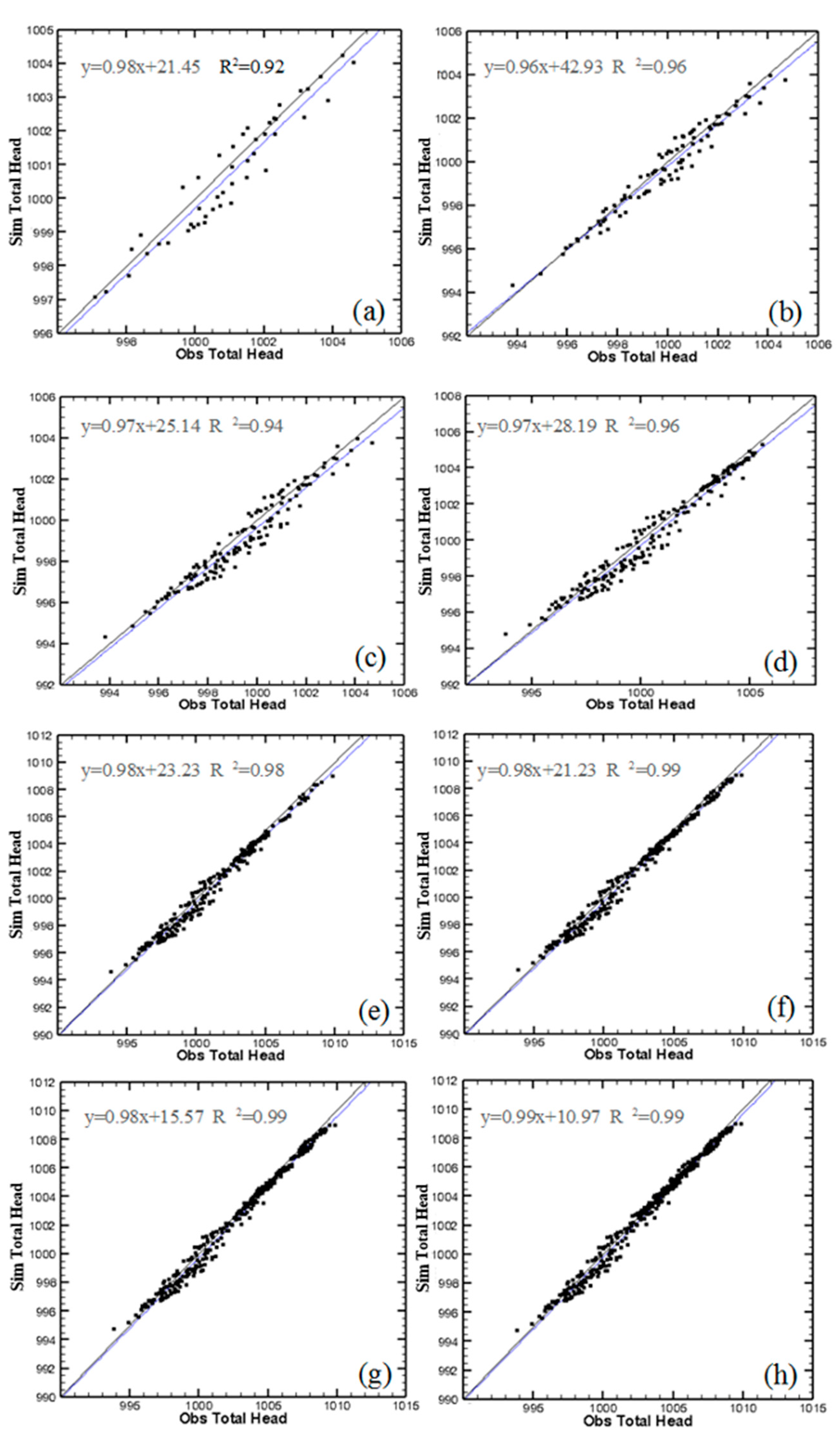
2.2. Pumping Tests
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Equivalent Homogeneous Conceptual Model
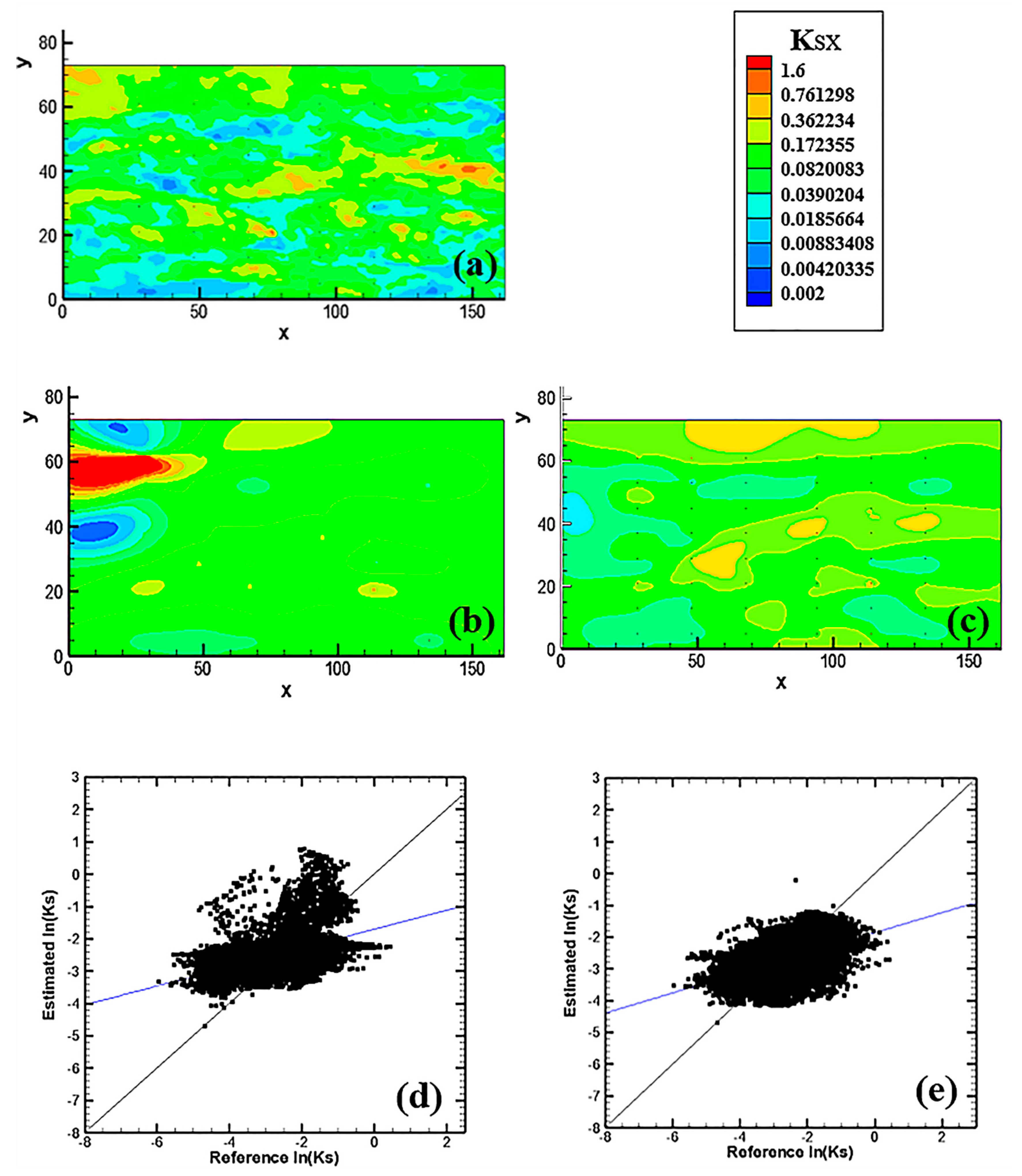
3.2. Heterogeneity Characterization by Kriging
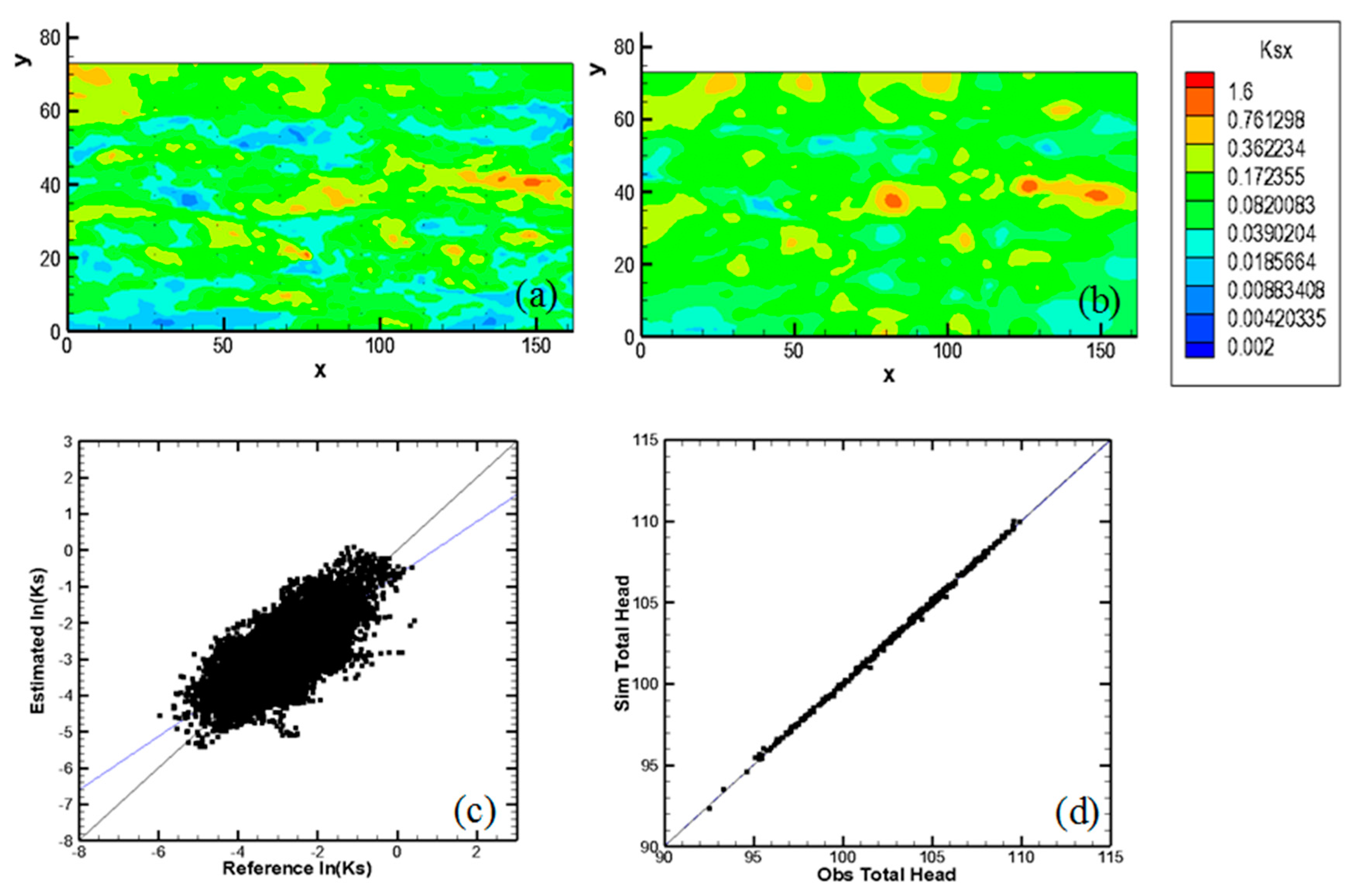
3.3. Heterogeneity Characterization by HT
3.4. Tracer Test
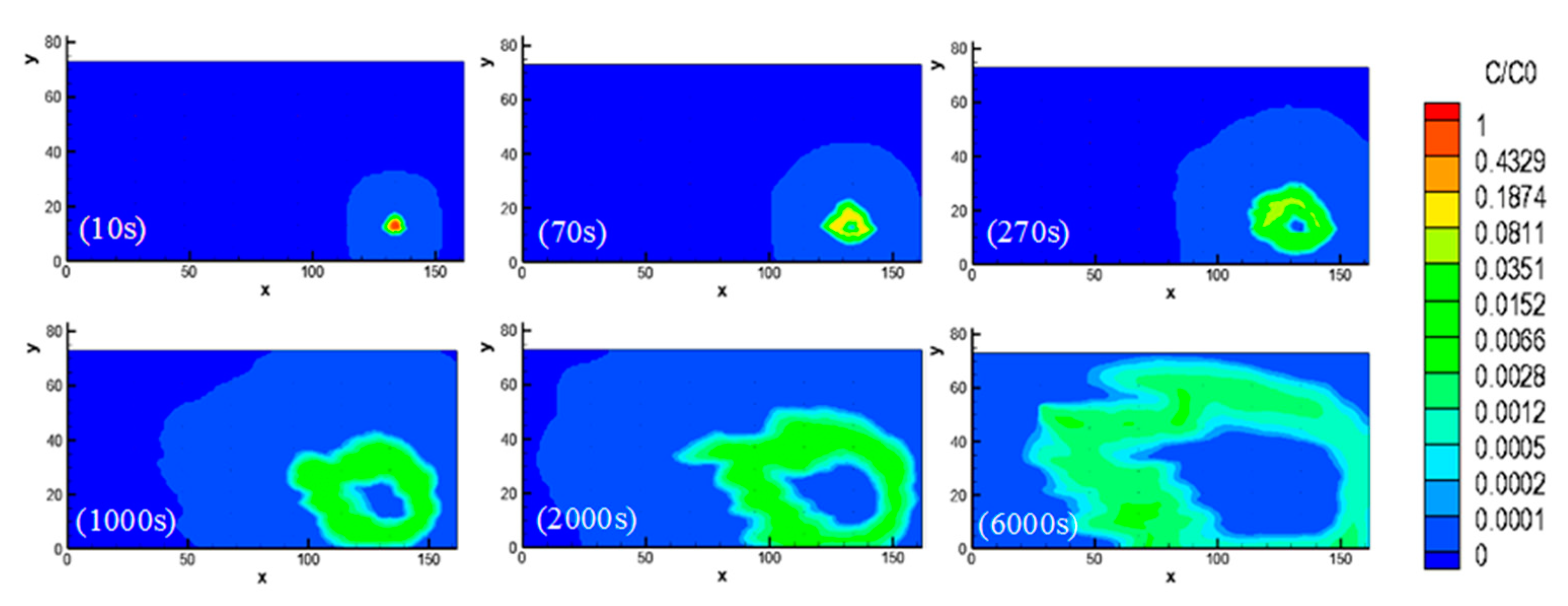
3.4.1. Comparison of Concentration Contours in the Reference Field and the Estimated Field
3.4.2. Mass Conservation of Solute Concentration
3.4.3. Route of Solute Mean Position
4. Conclusions
- As the number of pumping cycles increases, the accuracy of the inversely obtained K field is improved, although this improvement is no longer significant after the 6th pumping test. For specific regional hydrogeological studies, we can use a sufficient number of pumping cycles during a field experiment and determine the number of pumping cycles beyond which the effect of this number is no longer significant, thus providing a reference for determining the number of pumping cycles needed for different hydrogeological points of the same region.
- Incorporation of multilevel a priori geological information improves the accuracy in the estimated K field. When small-level heterogeneity is considered, the accuracy in the characterization of the K field heterogeneity of the aquifer inversely obtained by HT is generally higher than that by kriging.
- The HT-derived optimal estimated K field is able to not only fit head signals very well but also more accurately predict solute transport, suggesting that fine characterization of aquifer heterogeneity is of great importance to the prediction of solute transport.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zech, A.; Attinger, S.; Cvetkovic, V.; Dagan, G.; Teutsch, G. Is unique scaling of aquifer macrodispersivity supported by field data? Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 7662–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copty, N.K.; Findikakis, A.N. Quantitative estimates of the uncertainty in the evaluation of ground water remediation schemes. Groundwater 2010, 38, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslauer, C.P.; Rau, M.; Bárdossy, A.; Sudicky, E.A. Effects of Multidimensional Description of the Spatial Structure of Hydraulic Conductivity on Solute Transport. In Proceedings of the Agu Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Butler, J.J.; Bohling, G.; Reboulet, E.C.; Knobbe, S.; Hyndman, D.W.; Zheng, C. A New Method for Rapid, High-Resolution Characterization of Hydraulic Conductivity: Application to Solute Transport at the MADE Site. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, H21B-0844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Huang, G. Impact of Hydraulic Conductivity on Solute Transport in Highly Heterogeneous Aquifer. In Proceedings of the Computer Computing Technologies in Agriculture Iv-ifip Tc 12 Conference, Nanchang, China, 22–25 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jr, J.J.B.; Healey, J.M. Relationship between pumping-test and slug-test parameters: Scale effect or artifact? Groundwater 2010, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Sihag, P.; Tiwari, N.K.; Ranjan, S. Prediction of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity using adaptive neuro- fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 25, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihag, P. Prediction of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity using fuzzy logic and artificial neural network. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Liu, S. Hydraulic tomography: Development of a new aquifer test method. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Srivastava, R.; Guzman, A.; Harter, T. A Numerical model for water flow and chemical transport in variably saturated porous media. Ground Water 2010, 31, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Liu, X.; Craig, A. Steady-state hydraulic tomography in a laboratory aquifer with deterministic heterogeneity: Multi-method and multiscale validation of hydraulic conductivity tomograms. J. Hydrol. 2007, 341, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Gardiner, R. Effectiveness of hydraulic tomography: Sandbox experiments. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Liu, X.Y.; Takeuchi, S.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Ando, K.; Saegusa, H. Hydraulic tomography in fractured granite: Mizunami Underground Research site, Japan. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W01406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, M.; Barrash, W.; Kitanidis, P.K.; Malama, B.; Revil, A.; Straface, S.; Rizzo, E. A Potential-Based Inversion of Unconfined. Ground Water 2009, 47, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelhar, L.W.; Gutjahr, A.L.; Naff, R.L. Stochastic analysis of macrodispersion in a stratified aquifer. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1643–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Berg, S.J.; Yeh, T.C. Comparison of approaches for predicting solute transport: Sandbox experiments. Ground Water 2011, 50, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z. Hydraulic Tomography in Unconfined Aquifers and the Importance of Geological Data: Laboratory and Field Studies; University of Waterloo: Ontario, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Clyde, M.; George, E.I. Model Uncertainty. Stat. Sci. 2004, 19, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Heitman, J.L. Hartge/Horn: Essential Soil Physics, An Introduction to Soil Processes, Functions, Structure, and Mechanics. Soil Sci. 2017, 182, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Shuai, Y.; Jie, Y.; Heng, M.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yue, X.A. Optimization of Well Spacing to Achieve a Stable Combustion During the THAI Process. Energy 2018, 151, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.L.; Fan, J.W.; Liao, H.M.; Xu, W. Optimization of well spacing for tight sandstone gas reservoirs - case study of eastern sulige gas field. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 616–618, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, K.; Deng, Q.; Dongliang, L.; Branch, T. Research of injection-production system seepage field characteristics and well spacing optimization in bohai m oilfield. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. 2013, 35, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, S.; Zlotnik, V.A.; Tartakovsky, D.M. On the use of analytical solutions to design pumping tests in leaky aquifers connected to a stream. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaoui, Z.K.; Chebbi, A. Comparison of two kriging interpolation methods applied to spatiotemporal rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A. Hydraulic tomography offers improved imaging of heterogeneity in fractured rocks. Groundwater 2013, 52, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Illman, W.A.; Craig, A.J.; Zhu, J.; Yeh, T.C.J. Laboratory sandbox validation of transient hydraulic tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, J.; Dietrich, P. Identification of the permeability distribution in soil by hydraulic tomography. Inverse Probl. 1995, 11, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Craig, A.J.; Liu, X. Practical issues in imaging hydraulic conductivity through hydraulic tomography. Groundwater 2010, 46, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yeh, T.C.; Xiang, J.; Illman, W.A.; Ando, K.; Hsu, K.C.; Lee, C.H. Hydraulic tomography for detecting fracture zone connectivity. Ground Water 2010, 46, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kitanidis, P.K. Large-scale inverse modeling with an application in hydraulic tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W02501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.; Khaleel, R.; Carroll, K.C. Flow through Heterogeneous Geologic Media; Hydrology and Water Resources: World Meteorological Organization Weather: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Brauchler, R.; Herold, M.; Bayer, P. Hydraulic tomography analog outcrop study: Combining travel time and steady shape inversion. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauchler, R.; Hu, R.; Hu, L.; Jimenez, S.; Bayer, P.; Dietrich, P.; Ptak, T. Rapid field application of hydraulic tomography for resolving aquifer heterogeneity in unconsolidated sediments. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


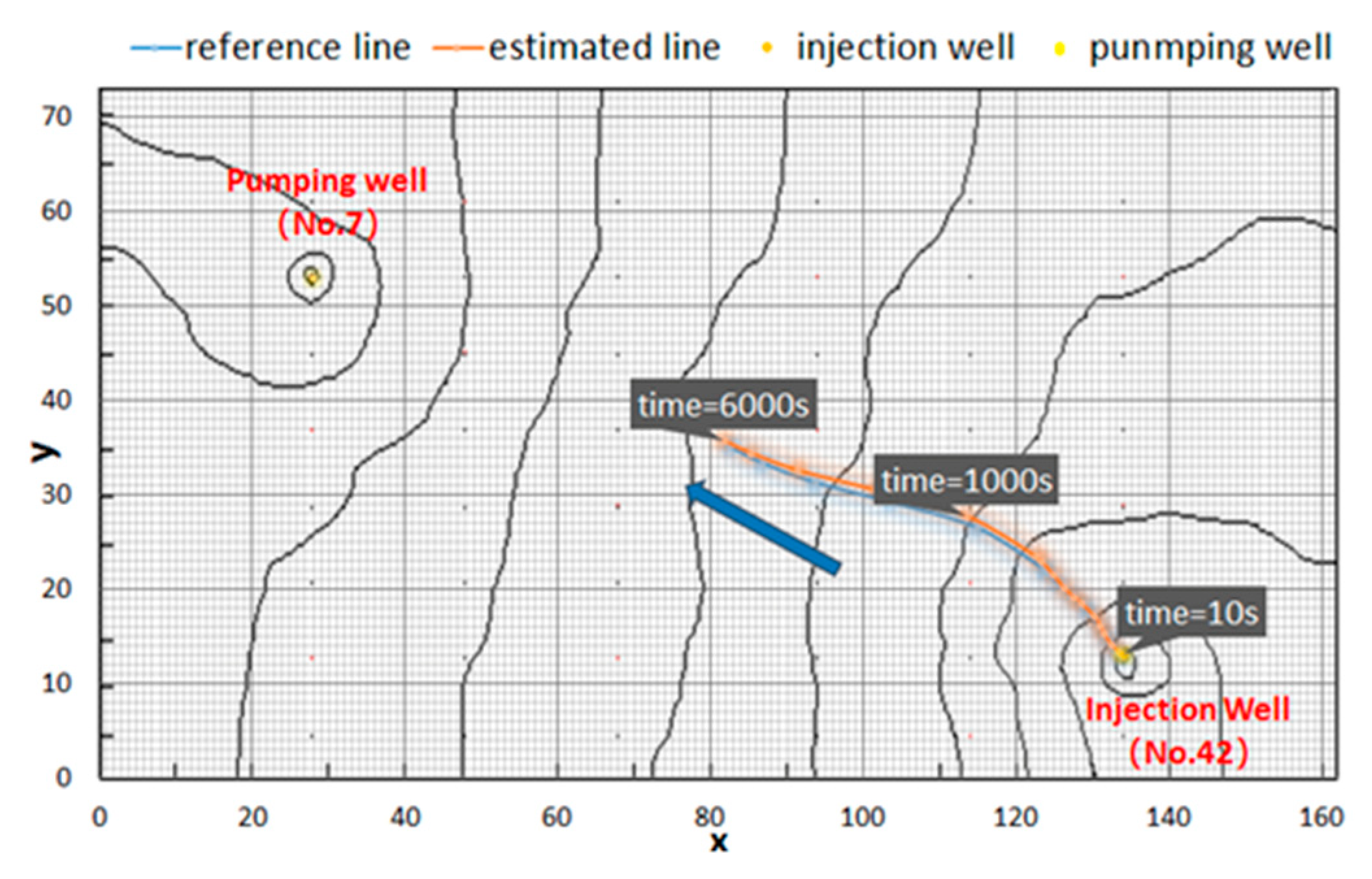
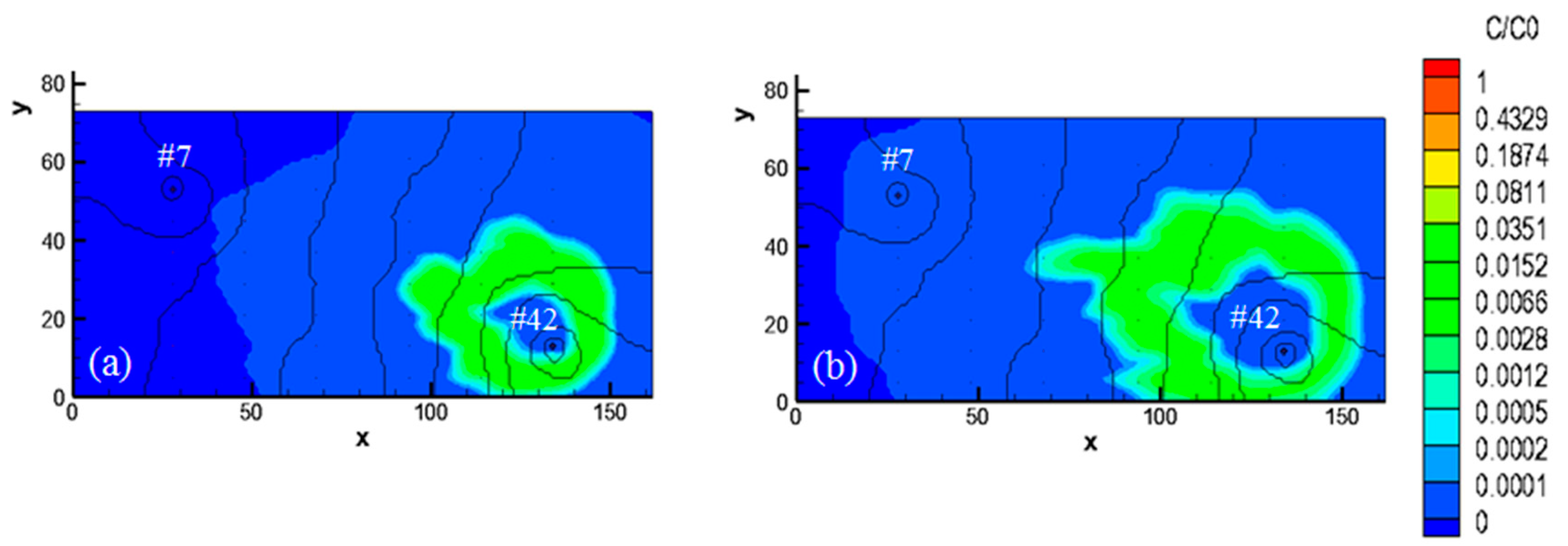
| Time Point (s) | Concentration of Reference Field (mg/mL) Multiplied by Time (s) | Concentration of Estimated Field (mg/mL) Multiplied by Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 12,617.05 | 12,348.89 |
| 70 | 13,389.39 | 13,184.79 |
| 100 | 13,530.88 | 13,437.63 |
| 270 | 13,965.98 | 14,346.23 |
| 500 | 14,235.86 | 14,513.34 |
| 700 | 14,176.88 | 14,257.88 |
| 1000 | 14,047.74 | 14,160.73 |
| 2000 | 14,030.94 | 14,016.92 |
| 3000 | 13,845.20 | 13,828.36 |
| 5000 | 12,698.78 | 12,609.27 |
| 6000 | 11,431.97 | 11,283.76 |
| Time (s) | Displacement of Reference Field (cm) | Velocity of Reference Field (cm/s) | Displacement of Estimated Field (cm) | Velocity of Reference Field (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.23 | 0.0227 | 0.48 | 0.0478 |
| 70 | 2.35 | 0.0310 | 3.38 | 0.0385 |
| 100 | 3.14 | 0.0263 | 4.25 | 0.0289 |
| 270 | 6.36 | 0.0175 | 7.75 | 0.0191 |
| 500 | 9.27 | 0.0118 | 10.58 | 0.0113 |
| 700 | 11.28 | 0.0101 | 12.53 | 0.0097 |
| 1000 | 14.03 | 0.0089 | 15.37 | 0.0094 |
| 2000 | 23.48 | 0.0094 | 25.34 | 0.0099 |
| 3000 | 34.48 | 0.0110 | 36.86 | 0.0115 |
| 5000 | 51.35 | 0.0070 | 53.18 | 0.0064 |
| 6000 | 56.03 | 0.0047 | 57.00 | 0.0038 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, B.X.; Yeh, T.-C.J.; Hao, Y.; Lv, W. Fine Characterization of the Effects of Aquifer Heterogeneity on Solute Transport: A Numerical Sandbox Experiment. Water 2019, 11, 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112295
Zhang Y, Wu C, Hu BX, Yeh T-CJ, Hao Y, Lv W. Fine Characterization of the Effects of Aquifer Heterogeneity on Solute Transport: A Numerical Sandbox Experiment. Water. 2019; 11(11):2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112295
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuefen, Chuanhao Wu, Bill X. Hu, Tian-Chyi Jim Yeh, Yimin Hao, and Wenhan Lv. 2019. "Fine Characterization of the Effects of Aquifer Heterogeneity on Solute Transport: A Numerical Sandbox Experiment" Water 11, no. 11: 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112295
APA StyleZhang, Y., Wu, C., Hu, B. X., Yeh, T.-C. J., Hao, Y., & Lv, W. (2019). Fine Characterization of the Effects of Aquifer Heterogeneity on Solute Transport: A Numerical Sandbox Experiment. Water, 11(11), 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112295





