Assessment of Shallow Groundwater Contamination Resulting from a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill—A Case Study in Lianyungang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Site Description and Hydrogeological Condition
2.1. Site History and Condition
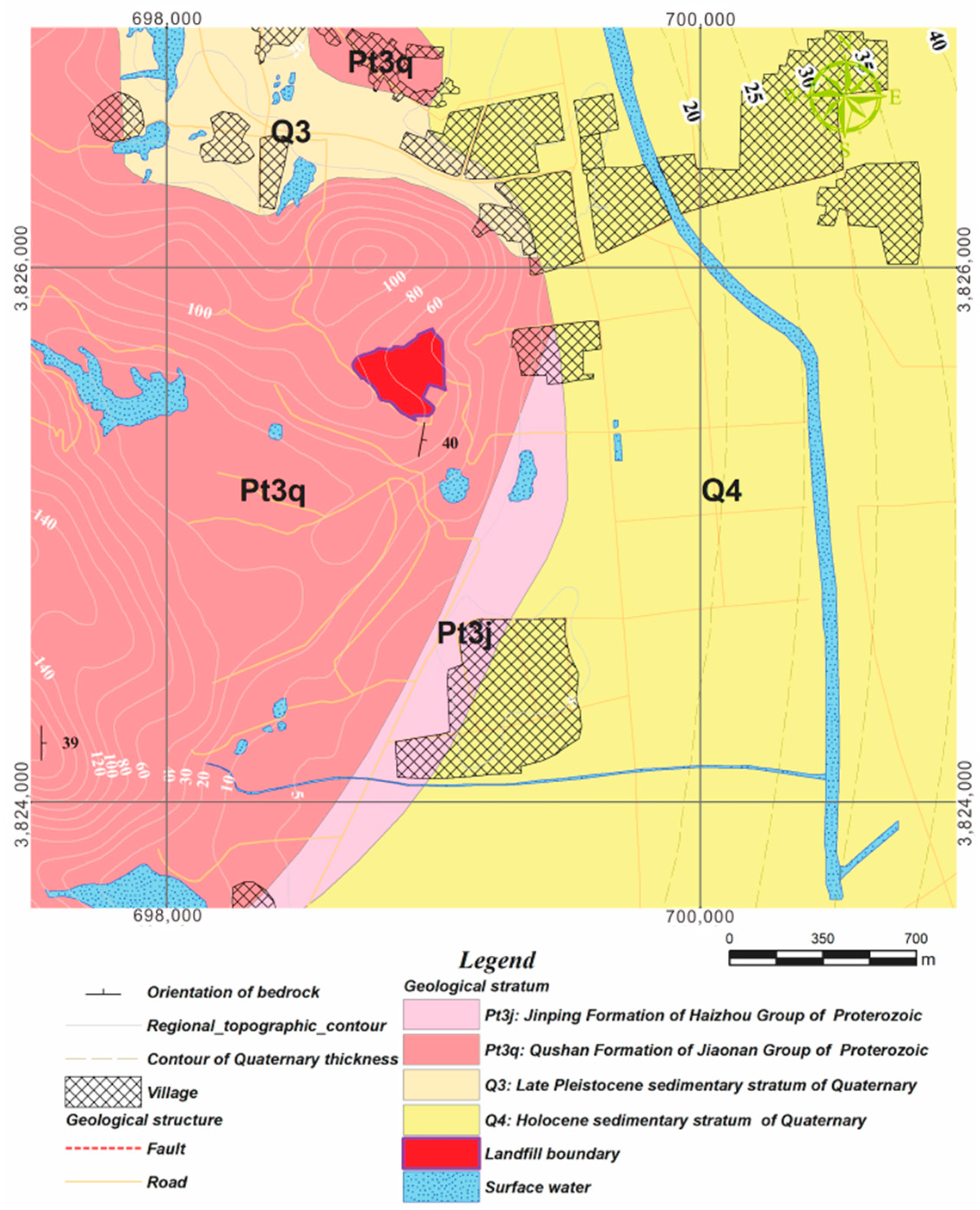
2.2. Geological Background and Hydrogeological Condition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling Sites and Chemical Test
3.2. Factor Analysis and the Nemerow Index Calculation
3.3. Statistical and Spatial Distribution Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Groundwater Quality in the Study Area
4.2. Factor Analysis
4.3. Analysis of Contaminant Transportation and Path
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, S.; Tiwary, D.; Ohri, A.; Agnihotri, A.K. Impact of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill leachate on groundwater quality in Varanasi, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ma, H.; Shi, G.; He, L.; Wei, L.; Shi, Q. A review of groundwater contamination near municipal solid waste landfill sites in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenigül, N.B.; Hensbergen, A.T.; Elfeki, A.M.M.; Dekking, F.M. Detection of contaminant plumes released from landfills: Numerical versus analytical solutions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Geng, Y.; Fujita, T. An overview of municipal solid waste management in China. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Contaminants of emerging concern in landfill leachate in China: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhener, P. Simulating stable carbon and chlorine isotope ratios in dissolved chlorinated groundwater pollutants with BIOCHLOR-ISO. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2016, 195, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, T. Simultaneous chemical oxygen demand removal, methane production and heavy metal precipitation in the biological treatment of landfill leachate using acid mine drainage as sulfate resource. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadder, S.R.; Prabhakar, R.; Khan, D.; Kishan, D.; Chauhan, M.S. Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Barlaz, M.A. Measurement of chemical leaching potential of sulfate from landfill disposed sulfate containing wastes. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, W.; Long, Y.; Wei, F.; Nie, Z.; Fang, C. Fate and migration of arsenic in large-scale anaerobic landfill. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Sappa, G.; Vitale, S.; Parisse, B.; Battistel, M. Soil control of trace metals concentrations in landfills: A case study of the largest landfill in Europe, Malagrotta, Rome. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 143, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, S.; Feng, L.; Chen, X. The effects of aquifer heterogeneity on the 3D numerical simulation of soil and groundwater contamination at a chlor-alkali site in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, M.; Datta, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Sreekrishnan, T.R.; Ramana, G.V. Comprehensive assessment of the leachate quality and its pollution potential from six municipal waste dumpsites of India. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 6, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.K.; De, S.; Hazra, T.; Debsarkar, A.; Dutta, A. Characterization of Leachate and Its Impact on Surface and Groundwater Quality of a Closed Dumpsite–A Case Study at Dhapa, Kolkata, India. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleasant, S.; O’Donnell, A.; Powell, J.; Jain, P.; Townsend, T. Evaluation of air sparging and vadose zone aeration for remediation of iron and manganese-impacted groundwater at a closed municipal landfill. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.M.; Alfaia, R.G.D.S.; Campos, J.C. Landfill leachate treatment in Brazil–An overview. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Beydoun, D.; Amal, R.; Low, G.; Cattle, J. Landfill Management, Leachate Generation, and Leach Testing of Solid Wastes in Australia and Overseas. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Technol. 2005, 35, 239–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chofqi, A.; Younsi, A.; Lhadi, E.K.; Mania, J.; Mudry, J.; Veron, A. Environmental impact of an urban landfill on a coastal aquifer (El Jadida, Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowski, T.; Satora, S. Analysis of the spatial variablity of the concentrations of Na+ and K+ ions in the groundwater sourced in southern Poland. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2016, 42, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotowski, T.; Kachnic, M. The geochemical study of groundwaters from Cenozoic aquifers in the Gwda catchment (Western Pomerania, Poland). Environ Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, I.A.; Atherton, W.; Hashim, K.; Kot, P.; Alkhaddar, R.; Alo, B.I.; Shaw, A. An analyses of the status of landfill classification systems in developing countries: Sub Saharan Africa landfill experiences. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.F.; Yue, X.B.; Cui, Y.J.; Shao, G.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, D.W. Effect of pore water chemistry on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of Lianyungang soft marine clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, S.; Cai, G. Correlations between electrical resistivity and basic engineering property parameters for marine clays in Jiangsu, China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 159, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wilde, S.A.; Liu, F.; Han, J. Zircon U–Pb and Lu–Hf isotope study of the Neoproterozoic Haizhou Group in the Sulu orogen: Provenance and tectonic implications. Lithos 2012, 136, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Seo, I.W.; Choi, S.Y. Assessment of water quality variation of a monitoring network using exploratory factor analysis and empirical orthogonal function. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2017, 94, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Samadi, A.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Ghaemian, N. Impact of the uncontrolled leakage of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill on soil in a cultivated-calcareous environment. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution using stochastic site indicators. Geoderma 2019, 337, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Negi, P.; Khaiwal, R. Assessment of groundwater pollution by landfills in India using leachate pollution index and estimation of error. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Zhu, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Fan, X.; Wu, S.; Shi, J.; Song, J. Effect of the leachate head on the key pollutant indicator in a municipal solid waste landfill barrier system. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salam, M.M.A.; Abu-Zuid, G.I. Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: A case study in Egypt. J. Adv Res. 2015, 6, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapelewska, J.; Kotowska, U.; Karpińska, J.; Astel, A.; Zieliński, P.; Suchta, J.; Algrzym, K. Water pollution indicators and chemometric expertise for the assessment of the impact of municipal solid waste landfills on groundwater located in their area. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Chen, Z. Heavy metal(loid)s and organic contaminants in groundwater in the Pearl River Delta that has undergone three decades of urbanization and industrialization: Distributions, sources, and driving forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kumar, R.N. Assessment of groundwater quality at a MSW landfill site using standard and AHP based water quality index: A case study from Ranchi, Jharkhand, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przydatek, G.; Kanownik, W. Impact of small municipal solid waste landfill on groundwater quality. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smahi, D.; Hammoumi, O.E.; Fekri, A. Assessment of the Impact of the Landfill on Groundwater Quality: A Case Study of the Mediouna Site, Casablanca, Morocco. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talalaj, I.A.; Biedka, P. Use of the landfill water pollution index (LWPI) for groundwater quality assessment near the landfill sites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24601–24613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabian, M.; Hassanzadeh, Y.; Marofi, S. Assessment of landfill leachate in semi-arid climate and its impact on the groundwater quality case study: Hamedan, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, L.; Ding, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.; Shao, W. Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanjai; Sinha, A.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Mugo, S.M. Water Analysis Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand; Worsfold, P., Poole, C., Townshend, A., Miró, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 258–270. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, G.; Kueffer, D.; Davies, J.; Wale, N. Nitrate and nitrite in shallow groundwater. 2005. Available online: http://www.cdhd.idaho.gov/pdfs/eh/land_nitrate.pdf (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Amiri, H.; Zare, M.; Widory, D. Assessing sources of nitrate contamination in the Shiraz urban aquifer (Iran) using the δ 15 N and δ 18 O dual-isotope approach. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 51, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Ge, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Luo, W.; Chang, J. Nitrate in groundwater of China: Sources and driving forces. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.M.; Jones, M.M. A Comparative Study of Nitrate Levels at Three Adjacent Ground-Water Sources in a Chalk Catchment Area West of London. Groundwater 1980, 18, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baedecker, M.J.; Back, W. Modern Marine Sediments as a Natural Analog to the Chemically Stressed Environment of A Landfill. J. Hydrol. 1979, 43, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baedecker, M.J.; Back, W. Hydrogeological Processes and Chemical Reactions at a Landfill. Groundwater 1979, 17, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, F.; Ding, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L. Historical trends in the anthropogenic heavy metal levels in the tidal flat sediments of Lianyungang, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1458–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Misra, A.K. Groundwater quality analysis of Quaternary aquifers in Jhajjar District, Haryana, India: Focus on groundwater fluoride and health implications. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.F.D.; Mlayah, A.; Gomes, C.; Noronha, F.; Charef, A.; Sequeira, C.; Esteves, V.; F, A.R. Marques. Heavy elements in the phosphorite from Kalaat Khasba mine (North-western Tunisia): Potential implications on the environment and human health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnandi, K.; Tobschall, H.J. Heavy metal release from phosphorite tailings into seawater: A simulated laboratory study. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 236, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, O.; Assal, A.; Devlin, H.; Elliot, T.; Kalin, R.M. Performance of a field-scale biological permeable reactive barrier for in-situ remediation of nitrate-contaminated groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglari, H.; Saeidi, M.; Karimyan, K.; Narooie, M.R.; Sharafi, H. Data for factor analysis of hydro-geochemical characteristics of groundwater resources in Iranshahr. Data Brief 2018, 19, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Well ID (Survey Time) | Location | Water Type of Well/Pond | Distance from Leachate Collecting Pond (m) | Hydro-Chemistry Type | pH Value | NH3-N (mg/L) | CODMn (mg/L) | NO2− (mg/L) | Total Hardness | Cl− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | Pb (mg/L) | TDS (mg/L) | Mn (mg/L) | Nemerow Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# (March 2014) | Shantoujiulou | Pore phreatic groundwater | 1141 | SO4–Na | 7.02 | 0.10 | 3.8 | 0.004 | 376 | 100 | 144 | 0.00573 | 715 | 0.0600 | 4.54 |
| 2# (March 2014) | Dongdasha village | Pore phreatic groundwater | 283 | SO4–Ca | 6.87 | 0.12 | 4.0 | 0.008 | 468 | 77 | 150 | 0.00454 | 773 | 0.0302 | 4.56 |
| 2# (July 2017) | HCO3–Ca | 7.43 | 0.20 | 2.0 | 0.035 | 240 | 83 | 68 | 0.00125 | 385 | 0.0092 | 2.26 | |||
| 2#-1 (July 2017) | Dongdasha village | Pore phreatic groundwater | 320 | Cl–Ca | 7.61 | 0.29 | 2.2 | 0.041 | 505 | 258 | 107 | 0.00125 | 632 | 0.0605 | 4.66 |
| 3# (March 2014) | Unicom tower | Deep bedrock fissure groundwater | 663 | Cl–Na | 7.17 | 0.72 | 3.9 | 0.013 | 3490 | 7960 | 356 | 0.00366 | 16,400 | 3.8300 | 8.18 |
| 3# (July 2017) | Cl–Na | 7.47 | 2.36 | 3.0 | 0.004 | 4860 | 5710 | 353 | 0.10400 | 8440 | 0.0089 | 8.49 | |||
| 4# (March 2014) | Office | Pore phreatic groundwater | 644 | Cl–Na | 6.96 | 0.42 | 5.9 | 0.009 | 3200 | 6220 | 553 | 0.00039 | 13,600 | 4.6600 | 8.05 |
| 4# (July 2017) | Cl–Na | 7.52 | 0.59 | 2.1 | 0.016 | 4090 | 5750 | 511 | 0.08910 | 8360 | 0.0072 | 8.15 | |||
| 5# (March 2014) | Qushan middle school | Pore phreatic groundwater | 992 | Cl–Na | 7.06 | 0.40 | 1.7 | 0.006 | 591 | 1100 | 162 | 0.00248 | 2190 | 0.9550 | 7.52 |
| GW05 (July 2017) | Farmland | Pore phreatic groundwater | 470 | Cl–Na | 6.87 | 1.24 | 6.0 | 1.400 | 392 | 394 | 153 | 0.00125 | 1220 | 1.0400 | 7.69 |
| GW06 (July 2017) | Farmland | Pore phreatic groundwater | 428 | Cl–Na | 6.69 | 1.07 | 3.6 | 0.009 | 492 | 292 | 255 | 0.00125 | 986 | 0.0200 | 4.77 |
| GW07 (July 2017) | Farmland | Deep bedrock fissure groundwater | 248 | SO4–Na | 7.44 | 0.94 | 9.9 | 0.474 | 248 | 256 | 356 | 0.00420 | 492 | 0.0038 | 7.59 |
| GW08 (July 2017) | Farmland | Deep bedrock fissure groundwater | 315 | Cl–Ca | 7.52 | 1.05 | 7.6 | 1.350 | 742 | 420 | 297 | 0.00125 | 1130 | 0.8240 | 8.21 |
| GW09 (July 2017) | Orchard | Deep bedrock fissure water | 441 | HCO3–Ca | 7.54 | 1.59 | 2.4 | 0.008 | 224 | 95 | 78 | 0.00125 | 401 | 0.0028 | 7.17 |
| D1# (Feb. 2017) | Taowan village | Pore phreatic groundwater | 1100 | HCO3–Na | 8.34 | 0.05 | 0.6 | 0.008 | 222 | 122 | 132 | 0.01130 | 1004 | 0.0860 | 4.47 |
| D2# (Feb. 2017) | Diaoyu hill | Pore phreatic groundwater | 1020 | Cl–Mg | 7.46 | 0.41 | 1.4 | 0.008 | 320 | 118 | 67 | 0.00125 | 450 | 0.0020 | 2.31 |
| D4# (Feb. 2017) | Near leachate collection pond area | Shallow bed rock fissure groundwater | 16 | Cl–Na | 8.27 | 6.97 | 5.5 | 0.010 | 728 | 333 | 127 | 0.00125 | 1477 | 0.0860 | 7.73 |
| D5# (Feb. 2017) | Taoyuanshan community | Pore phreatic groundwater | 678 | HCO3–Na | 8.24 | 7.92 | 3.8 | 0.009 | 406 | 110 | 134 | 0.00125 | 763 | 0.0840 | 7.32 |
| P-1# (July 2017) | 1# pond | Surface water | 500 | SO4–Ca | 6.52 | 1.03 | 6.4 | 0.021 | 571 | 230 | 478 | 0.00125 | 812 | 0.2000 | 7.82 |
| P-2# (July 2017) | 2# pond | Surface water | 485 | Cl–Na | 6.54 | 0.34 | 5.8 | 0.006 | 253 | 314 | 109 | 0.00125 | 694 | 0.0350 | 4.56 |
| The III standard concentration in GB/T14848-2017 (China) | / | / | 6.5–8.5 | 0.50 | 3.0 | 1.000 | 450 | 250 | 250 | 0.01000 | 1000 | 0.1000 | / | ||
| Parameters | Factor Analysis Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Factor | 2nd Factor | 3rd Factor | 4th Factor | |
| NH3-N | −0.228 | −0.087 | 0.027 | 0.958 |
| CODMn | 0.079 | 0.868 | 0.263 | 0.226 |
| NO2− | −0.128 | 0.775 | 0.416 | −0.158 |
| Total hardness | 0.949 | −0.199 | 0.199 | 0.055 |
| Cl− | 0.986 | −0.070 | −0.074 | 0.038 |
| SO42− | 0.874 | 0.256 | 0.197 | 0.032 |
| Pb | 0.575 | −0.478 | 0.658 | −0.016 |
| TDS | 0.958 | 0.031 | −0.247 | 0.065 |
| Mn | 0.683 | 0.424 | −0.572 | 0.014 |
| Eigenvalue | 4.426 | 1.880 | 1.148 | 1.005 |
| Variance (%) | 49.181 | 20.890 | 12.752 | 11.162 |
| Cumulative variance (%) | 49.181 | 70.071 | 82.824 | 93.985 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shan, X.; Chen, Z. Assessment of Shallow Groundwater Contamination Resulting from a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill—A Case Study in Lianyungang, China. Water 2019, 11, 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122496
Chen G, Sun Y, Xu Z, Shan X, Chen Z. Assessment of Shallow Groundwater Contamination Resulting from a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill—A Case Study in Lianyungang, China. Water. 2019; 11(12):2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122496
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ge, Yajun Sun, Zhimin Xu, Xuekai Shan, and Zhengliang Chen. 2019. "Assessment of Shallow Groundwater Contamination Resulting from a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill—A Case Study in Lianyungang, China" Water 11, no. 12: 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122496
APA StyleChen, G., Sun, Y., Xu, Z., Shan, X., & Chen, Z. (2019). Assessment of Shallow Groundwater Contamination Resulting from a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill—A Case Study in Lianyungang, China. Water, 11(12), 2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122496







