Abstract
A prediction–correction solver is presented here for rapid simulation of free-surface flows in dendritic and looped river networks. Rather than solving a large global algebraic system over the entire domain of river networks, the model solves subsystems for subdomains of branches in two steps: prediction and correction. With the help of the prediction–correction method (PCM), the partial linearization technique, the semi-implicit method, and the Eulerian–Lagrangian method (ELM), the model only needs to solve tridiagonal linear systems for branches and is free of any iteration. The new model was tested using a hypothetical looped river network with regular cross sections, the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) dendritic river network, and the Jing-south looped river system (with seasonally flooding branches). In the first test, a time-step sensitivity study was conducted and the model was revealed to produce accurate simulations at large time steps when the condition for application of the PCM to river networks was satisfied. In the TGR test, the PCM model provided almost the same histories of water levels and discharges as those simulated by the HEC-RAS model. In the Jing-south test, the mean absolute error in simulated water levels was 0.07–0.24 m, and the relative error in simulated cross-section water flux was 0.5–4.9% compared with field data; the conservation error was generally 2 × 10−4 to 3 × 10−4. The PCM model was revealed to be 2–4 times as fast as a reported model, which solves local nonlinear subsystems using two-layer iterations, and 1.2–1.4 times as fast as the HEC-RAS. Using a time step of 1200 s, it took the sequential code 26.8 and 23.1 s to complete a simulation of a one-year unsteady flow process, respectively, in the TGR river networks (with 588 cells) and the Jing-south river system (with 662 cells).
1. Introduction
In river basin management, rapid decisions are required to cope with emergency events such as dangerous floods, power generation (e.g., short-term regulation), and so on. Simulations of hydrodynamics in river networks are often involved. For example, in short-term power generation scheduling of a large river-type reservoir with many tributaries, the hydrodynamic model is expected to generate results for the optimization model that include influences of dynamic capacities in the upper reaches of reservoirs [1]. The optimization model in this case requires thousands of calls for the hydrodynamic model, and it is expected that the latter can run as fast as possible to provide data for the real-time calls of the former.
Unlike a single river, river networks consist of many interconnected branches linked by junctions. The modeling of a river network has the following features. First, flows in all branches of the river networks should be simulated simultaneously to ensure a qualified description of the coupling of the branches. The solution of the coupling of the branches within river networks is often time consuming. Second, the computational cost related to the modeling of large river networks is significant when the number and total length of the branches are large. Real-time simulations of free-surface flows in large river networks are therefore challenging. Significant efforts have been dedicated to developing accurate and efficient solvers [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14] since the 1960s. Implicit discretization methods, which can use large time steps and require a relatively short runtime, are popular in river network modeling. These implicit river network models are briefly reviewed below.
1.1. Existing Implicit Models for River Networks
In terms of the algebraic system constructed for the solution of velocity–pressure coupling, the existing implicit 1D river network models may be divided into three kinds: those that solve a global nonlinear system (GNS) (e.g., [14]), a global linear system (GLS) (e.g., [8]), and local nonlinear subsystems (LNS) (e.g., [4]). Moreover, a so-called “hierarchical solution method” is also often used, for which there is a shrunken linear/nonlinear system (e.g., [2]).
(1) GNS models for river networks: When the nonlinear 1D Saint-Venant equations are solved directly within an implicit numerical formulation, an algebraic system of nonlinear equations is usually constructed and solved. For GNS models, much effort has been devoted to finding ways to eliminate or alleviate the influences of the nonlinear terms in order to reduce the complexity of the algebraic system; a typical GNS model was reported in [14]. With the advection term calculated explicitly by the Eulerian–Lagrangian method (ELM), the model of [14] excludes influences of almost all nonlinear terms except for those arising from the time derivative of the cross-section area in the continuity equation. As a result, in the implicit formulation of [14], velocity–pressure coupling only results a global mildly nonlinear system, which can be solved using a nested Newton-type iterative algorithm [15] at a moderate computational cost.
(2) GLS models for river networks: To circumvent the high cost and the troublesome convergence of iterative methods in nonlinear solutions for the 1D Saint-Venant equations, Preissmann developed a technique for linearizing equations [16]. The linearization technique has been widely used in river network models, which is here called the GLS model. For a single river, the resulting algebraic system of an implicit model often has a banded coefficient matrix and can be solved efficiently using a banded matrix solver [5]. However, for river networks, the velocity–pressure couplings over all of the computational nodes of the branches and the junctions result in an algebraic system with a nonbanded sparse coefficient matrix. As a result, a large amount of computer storage and runtime are required to store and solve the large and complex algebraic system.
Much effort has been put forth to simplify the solution of the coupling of branches within river networks and to minimize the computational cost of the model, such as the special node-numbering method (e.g., [6,7]). Using a special node numbering to define the connections of the branches of river networks can effectively reduce the bandwidth of the resulting coefficient matrix in certain cases. However, as noted in [3], the application of a special node-numbering scheme to general river networks might be difficult, especially when the networks are looped. Alternatively, others resorted to a special storage for the sparse matrix instead of the special node numbering. For instance, the famous HEC-RAS model [8] used a skyline storage algorithm to store the coefficient matrix. The resulting model has a coefficient matrix such that the elements are banded for the branches, but sparse elements appear at junctions.
(3) LNS models for river networks: An LNS model solves subsystems for subdomains of branches instead of a large global algebraic system over the entire domain of river networks. On the one hand, the subsystems for branches can be constructed locally and solved independently, leading to a simpler and more efficient numerical formulation. On the other hand, solutions of the subsystems are essentially decoupled at junctions. An LNS model, therefore, needs additional mechanisms to couple the solutions of the branches of river networks to ensure the accuracy of simulations. The idea of the local subsystem solution method is quite similar to that of the two-layer iteration method [12,13] used in multidimensional models. Relative to the method of solving a global algebraic system for entire river networks, the method that only needs to solve local subsystems has sharply reduced requirements for computer memory and runtime. A typical GNS model was reported in [4].
Zhu et al. [4] solved the subsystems for the branches of river networks using repeatedly updated junction water levels (as the internal boundary conditions), until the required precisions of solutions were reached. The nonlinear subsystem for each branch of the river networks was solved locally by the local layer iterations, the results of which were synchronized for data exchange at junctions by a global layer iteration. The two-layer iterations were alternated until a tolerance was reached. The global layer iteration included a predictor and several corrector steps [4]. Because of the influences of nonlinear terms, iteration solutions for the subsystems were needed. Moreover, Zhu et al. [4] did not study the quantitative relation between the number of correction steps (or the time step) and the convergence of their model. Therefore, the number of corrector steps cannot be explicitly determined in advance. Moreover, global layer iteration, which is time consuming and cannot be well parallelized, may counteract some of the gains in efficiency obtained by the local calculations of branch subsystems.
(4) The hierarchical solution method: A river network model [2,3,5], using the hierarchical solution method, can simulate river networks in three steps. First, for each branch, forward elimination is implemented to reduce the equations of all computational nodes of the branch to the equations of end-nodes of the branch. Second, the end-node equations of all branches are coupled and solved to obtain the end-node variables. Third, for each branch, the end-node variables are back-substituted to obtain the variables at interior nodes independently. The idea of the hierarchical solution method is quite similar to that of the Schur complement method [9,10] used in multidimensional models. The hierarchical solution method only solves a relatively small algebraic system and requires relatively small runtimes, but it may be unstable if the initial conditions are inaccurate or the time step and the subreach length are not carefully chosen [11].
1.2. Objective
The objective of this study was to propose a new model to simulate free-surface flows in dendritic and looped river networks using the basic idea of the prediction–correction method (PCM) [17,18]. Rather than solving a large global algebraic system over the entire domain of river networks, the PCM model solves local linear subsystems (LLS) for subdomains of the branches in two steps: prediction and correction. In terms of the involved algebraic system, the new model can be easily differentiated from existing GNS, GLS, and LNS models and is a fourth kind of river network model: the LLS model.
The first advantage of the new model is its simplicity and efficiency relative to most existing river network models. Relative to a GNS/GLS model, the LLS model does not need to solve a global large nonlinear/linear algebraic system for the entire domain of river networks, and the complex and time-consuming iteration solution can be avoided. Moreover, in the LLS model, special node-numbering or storage algorithms (e.g., skyline storage) are not needed. Relative to an LNS model (the number of global layer iterations may not be determined in advance), the new model uses a two-step solution instead of global layer iteration. Moreover, the new model only needs to solve tridiagonal linear systems for branches and is free of any iterations.
The new model was tested using a hypothetical looped river network with regular cross sections, as well as the real dendritic river networks of the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) and the Jing-south looped river system with frequent dry-and-wet alternations of riverbeds.
2. Methods
The governing equations, the description of river networks, and the numerical formulation of the proposed PCM model for river networks are introduced.
2.1. Governing Equations
The 1D Saint-Venant equations, which consist of continuity and momentum equations, are generally adopted to describe the free-surface flow in 1D open channels. In the continuity equation, the conveyance area (A) of a 1D cell is a nonlinear function of the cell water level (η). To exclude the influences of nonlinear terms, a linearized method [16], which is also adopted by other models (e.g., [8]), is used to locally linearize the continuity equation by transforming the nonlinear term . The governing equations are then taken to be
where u is the cross-section averaged velocity (m/s), A is the wet cross-sectional area (m2), B is the wet surface width of the cross section (m), q is the lateral inflow per unit length (m2/s), g is the gravity acceleration (m/s2), η is the water level measured from an undisturbed reference water surface (m), x is the longitudinal distance along the river (m), t is time (s), nm is Manning’s roughness coefficient (m−1/3s), and R is the hydraulic radius (m).
2.2. Description of River Networks and Computational Grid
The river networks consist of branches linked by junctions. Each branch is divided by a set of 1D cells (elements). The control volume, which is generated for a junction, is defined as the “junction cell” for which the number of connected branches can be arbitrary (see Figure 1). A nonjunction cell only has two cell faces (sides), while a junction cell could have more than two cell faces. The side shared by a junction cell is referred to as the “junction side”. For both nonjunction and junction cells, a cross section with general topographical data is arranged at the center of the cell. The cell at the two ends of an internal branch (defined as the “end-cell”) is either a junction cell or is connected to a junction cell. A junction cell does not stand alone but is arranged as part of the branch that has the largest river width around the junction (as a default arrangement), and we call this branch the “largest-width” branch of the junction. In the model, the junction cell and the other cells of the largest-width branch together contribute to the construction of a subsystem (see Section 2.3).
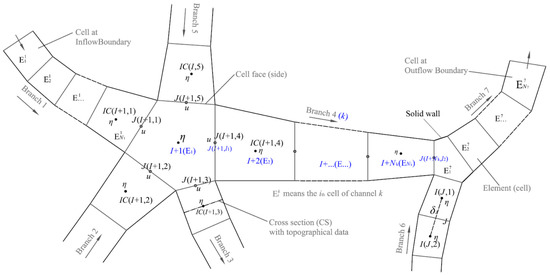
Figure 1.
The topology relations of cells and sides at junctions of river networks and the staggered grid arrangement of variables.
To obtain a graphical description of the river networks, the coordinates of the cell centers in the horizontal plane are required as inputs of the current model. The position of a side is described using its central point, the coordinates of which are interpolated according to those of cell centers. Distances between the centers of cells and sides are calculated from their coordinates and are used in the model computation. A staggered grid of variable arrangement is used (see Figure 1). The velocity u is defined at side centers and the water level η is defined at cell centers. The ne and ns are used to denote the quantities of cells and sides, respectively, in the computational grid. The number of branches of river networks is denoted by NR, and the cell quantities of these branches are sequentially denoted by N1, N2, …, NNR. Every cell/side has a unique global cell/side index.
Branch k is taken as an example to illustrate the relation between the global and local indices. The cells of branch k take up a successive section of the global indices of the cell sequence of river networks (denoted by I + 1, I + 2, …, I + Nk); otherwise, arbitrary numberings are allowed. A mapping is defined between the local indices of the cells (or the sides) in branch k and their global indices. For branch k, the cells with local indices “1, 2, …, Nk” in sequence correspond to the cells with global indices “I + 1, I + 2, …, I + Nk”. Moreover, side J (global index), which is located between cells i and I + 1 (local indices), has a local index of “I + 1/2”.
Because only using the notations with local indices is insufficient to describe the complex topology relations among cells and sides in different branches, the notations with global indices are defined as a supplement: (1) I34(I) is the number of sides of cell I, which is equal to 2 for nonjunction cells and is larger than 2 for junction cells; J(I,l) are the sides of cell I, where l = 1, 2,…, I34(I); IC(I,l) are the cells that have a common side with cell I, where l = 1, 2, …, I34(I); I(J,l) are the two cells that share side J, where l = 1, 2; and (2) sI,l is a sign function associated with the orientation of the normal velocity defined on side l of cell I [17]. Specifically, sI,l = 1/−1 if a positive velocity on side l of cell I corresponds to outflow/inflow (of cell I), and sI,l is defined as
Moreover, the variables, associated with the geometries and the computational grid, are defined as follows. For a given cell I (global index), ΔxI represents the length of the 1D cell. The length of a junction cell is set to the width scale of the neighboring reach in the largest-width branch. All nonjunction and junction cells allow a general cross-sectional bathymetry. BI is the river’s wet surface width and is related to the cell water level that varies with respect to time. The conveyance area (AI) of cell I, which could be obtained by integrating the water depth (related to ηI) along the cross section, is usually a non-negative nonlinear function of ηI for natural rivers and the derivative of AI with respect to ηI is non-negative and nondecreasing. For a given side J (global index) which connects two cells I1 and I2 (global indices), δJ is the distance between the centers of cells I1 and I2. AJ and RJ are the conveyance area and the hydraulic radius at the cross section of side J, respectively, and they are interpolated from those of neighboring cells. When cells I1 and I2 are in the same branch, their global and local indices are both successive. If the local indices of cells I1 and I2 are assumed to be i and i + 1, respectively, δJ, AJ, and RJ can then be described as Δxi+1/2, Ai+1/2, and Ri+1/2.
Dry-and-wet alternation of the grid is simulated using the method of the widely used critical water depths. Applying a stepwise approximation to a cross section, the topography of a subgrid can be approximated by the average elevation of its two nodes [8]. When the water level of a cell is h0 (a critical water depth) higher than the elevation of its lowest subgrid (denoted by “Zblsg”), this cell is defined as wet. Another critical water depth (hk) is defined for the dry-and-wet alternation of subgrids, and a subgrid with a water depth larger than hk is wet. In simulations of real river networks, the h0 is suggested to be set to 0.01 m, while the hk is suggested to be 0.001 m. A flag is defined to record the dry-and-wet state of a cell in the code. The wet cells are included in the computation of the next time step, while the dry ones are not. In the model, the solutions of the governing equations and the simulation of the dry-and-wet alternation of cells are two independent parts, and the latter is done after the former at each time step. For a wet cell, dry-and-wet states of the subgrids are checked using the new cell water level (ηn+1). Conveyance areas of wet subgrids are calculated and then summed to give the total conveyance area of the cross section located in the middle of the cell, while other hydraulic parameters are also updated.
2.3. Numerical Formulation
2.3.1. Discretization of Governing Equations
The momentum equation is discretized using operator-splitting techniques. The advection term is solved by the ELM [19,20]. The backtracking starts at a side center, and the multistep backward Euler technique [20] is performed to backtrack from the known location at time level n + 1 to the unknown foot of the backward trajectory at time level n. The tracking displacement of each substep is given by , where “Nbt” is the number of substeps and is the velocity vector at the starting point of each substep. When a tracking point has been found, the velocities at this point are interpolated based on the velocity field of time level n for calculating the next displacement and searching the next tracking point. Once the location of the foot of the trajectory at time level n is found, the initial condition at that time step is interpolated and recorded as ubt. The cell face velocity is then directly updated with ubt, which means that the advection term is solved.
To eliminate the stability restrictions imposed by rapid gravity waves, the θ semi-implicit method [19,21] is used to discretize the gradient of the free-surface elevation in two parts, where the explicit and implicit parts have weight factors of 1 − θ and θ, respectively. For side J (global index), the discretized momentum equation can be described using notations with global indices:
where θ is the implicit factor, Δt is the time step, superscript n indicates time level n, and the riverbed friction term is discretized using ubt and un+1 to enhance computational stability.
When the explicit terms of the discretized momentum equations are incorporated, the unknowns (cell water levels of time level n + 1, ηn+1) emerge and Equation (4) is then transformed into the following form:
where , and represents the incorporated explicit terms. is regarded as the provisional solution (velocity) by solving the explicit terms.
Without loss of generality, side J is assumed to connect two cells with global indices I1 and I2. When cells I1 and I2 are in different branches, Equation (5) is directly used to represent . When cells I1 and I2 are in the same branch, we set their corresponding local indices to be i and I + 1, respectively. At this time, side J means side I + 1/2. (namely, ) can then be rewritten using notations with local indices:
The linearization of in the continuity equation allows the nonlinear A(η) to be expressed using a linear Bn(ηn+1 − ηn). Moreover, the advection term in the momentum equation is calculated explicitly by the ELM. As a result, the current formulation excludes the influences of all the nonlinear terms, which further allows the construction of linear systems for the solution of velocity–pressure coupling. For a given cell I (global index), the discrete water level ηI is assumed to be constant within the cell. Moreover, the wet surface width of cell I (BI) is assumed to be constant within a time step (Δt) and is explicitly represented by the value of time level n (). From time level n to n + 1, a semi-implicit finite-volume discretization of the linearized continuity equation, for any nonjunction or junction cell I, can be written using global notations as
where l is the side index of cell I, and l = 1, 2, …, I34(I). Within the finite-volume framework, the mass of water is conserved both locally and globally by the unique flux at a cell face.
2.3.2. Solution of Hydrodynamics at Junctions
Strictly speaking, a 2D hydrodynamic problem should be solved at junctions, while the 1D governing equations are only applicable within river reaches [3,5]. To our knowledge, in existing 1D models, there are mainly two ways to solve hydrodynamics at junctions.
The first method defines hydraulic conditions to link flow variables at junctions, which is used in most existing 1D river network models, such as the CE-QUAL-RIV1 [22], the MASCARET [23], the HEC-RAS [8], and others [3,4,5]. As stated by Islam et al. [5], the hydraulic conditions at a junction of a river network are derived by assuming “no change in storage volume within the junction” (continuity assumption) and “the junction losses and the differences in velocity heads at junctions are negligible” (energy assumption). The simplest version of the hydraulic conditions is described by the equations of mass and energy conservation. These two equations are used as a supplement to the 1D Saint-Venant equations to describe the hydrodynamics at junctions.
A limitation of the hydraulic conditions is the absence of a mechanism to govern the partitioning of the discharges among related branches, when they are applied to a junction with multiple inflow branches and multiple outflow branches (called “Multi-IO” junction). A river networks using the method of hydraulic conditions (e.g., the HEC-RAS) often have to stipulate that a junction should be a convergence of several reaches into one reach (or a split of one reach into several reaches), or they split the Multi-IO junction using an artificial cross section.
The second method [14] solves the continuity and the momentum equations at junction cells instead of using hydraulic conditions and is free of the aforementioned limitations brought by the “continuity” or “energy” assumptions. However, the method uses an extended continuity equation at junction cells, such as Equation (7) of this paper and Equation (6) of [14].
The new model uses the second method. Benefiting from domain decomposition and PCM, the implicit solution of a 2D-like velocity–pressure coupling problem at junctions is reduced to solving simple 1D problems. The first method, used by most of existing 1D river network models, is usually reported to be sufficient enough to produce accurate simulations. If the hydraulic conditions are regarded as an extremely simplified version of the continuity and momentum equations, the second method used in this study is much more reasonable in theories than the first method.
2.3.3. Solution of Velocity–Pressure Coupling
Using the basic idea of the PCM [17,18], the proposed model only requires the construction of the subsystems for the branches of river networks to solve the velocity–pressure coupling problem of river networks. The solutions of the subsystems for the branches of river networks are coupled using two steps (namely, prediction and correction steps). The new solver is derived and presented as follows.
Around an end-cell of a branch, all the cells (except for that in this branch) supply water levels as boundary conditions to close the subsystem of this branch. A typical branch “k”, with a junction and a nonjunction end-cell, is taken as an example. The cells of branch k take up a successive section of the global indices of the cell sequence of river networks, which are denoted by I + 1, I + 2, …, I + Nk. Correspondingly, the local indices of the cells of branch k are in the sequence 1, 2, …, Nk. Without loss of generality, end-cell I + 1 (I = 1) is taken to be a junction cell, while end-cell I + Nk (I = Nk) is a nonjunction cell and connects to a cell which belongs to another branch, as shown in Figure 1.
(1) The Prediction Step
At the prediction step, Equations (5)–(7) are rewritten by replacing ηn+1 and un+1 with provisional variables and . For branch k, a subsystem is constructed as follows.
Around the junction end-cell (I = 1) with a global index I + 1, velocity–pressure coupling is performed by substituting Equation (5) into Equation (7) (using and ). The cells (except for cell I + 2) supply water levels of time level n as internal boundary conditions. Variables of cell I + 2 and the side shared by cells I + 1 and I + 2 are rewritten using the notations with local indices. The resulting equation of the velocity–pressure coupling at the junction end-cell (I = 1) is then given by
where , , , IC(I + 1,l1) is equal to I + 2, and side J(I + 1,l1) is the cell face between cells I + 1 and I + 2 (see Figure 1).
At a non-end-cell (I = 2, 3, …, Nk − 1) within branch k, velocity–pressure coupling is performed by substituting Equation (6) into Equation (7) (using and ), which is given by
where , , , and .
Because cell I + Nk is a nonjunction end-cell, I34(I + Nk) is equal to 2. There is only one cell which connects to cell I + Nk and it is not in branch k. Cell IC(I + Nk, l2) represents the cell in another branch, if IC(I + Nk, l3) is equal to I + Nk − 1. Around the nonjunction end-cell (I = Nk) with a global index I + Nk, velocity–pressure coupling is performed by substituting Equation (5) into Equation (7) (using and ). The cell IC(I + Nk, l2) supplies water levels of time level n as internal boundary conditions. Variables of cell I + Nk − 1 and the side shared by cells I + Nk − 1 and I + Nk are rewritten using the notations with local indices. The resulting equation is given by
where , , , and IC(I + Nk, l2) is a neighboring cell of cell I + Nk but not in branch k (see Figure 1).
Equations (8)–(10) form a tridiagonal linear system of Nk equations (I = 1, 2, …, Nk) with cell water levels () as unknowns for branch k. This system has a symmetric and positive definite coefficient matrix and can be solved directly without iterations. For each branch, the matrix and the right-hand side of the subsystem are arranged independently. Then, the resulting subsystems are solved to obtain the provisional solutions ().
(2) The Correction Step
At the correction step, the coefficients of subsystems are kept the same as those at the prediction step, and only the internal boundary conditions are updated. Relative to ηn, the provisional solutions () provide improved and sufficiently accurate internal boundary conditions for the subsystems of branches. The equations solved at the correction step (using ) are updated as follows:
where the coefficients Ca, Cb, and Cc are kept the same as those at the prediction step.
The subsystems for branches are solved to obtain the final solutions (ηn+1). Once the ηn+1 have been obtained, the velocity un+1 defined at a side center is calculated using Equation (5) and the AI and RI are then updated.
(3) Condition for Application of PCM to River Networks
The basic idea of the PCM based on domain decomposition is as follows. For free-surface flows in river networks, the gravity wave propagation over the entire domain is divided into internal and external parts, moving within a branch and across the junction, respectively. The external part is assumed to be well solved at the prediction step; the whole wave propagation is solved accurately at the correction step using the updated end-cell water levels as internal boundary conditions.
The PCM uses a two-step solution of prediction and correction instead of the potential global layer iterations such as that used in [4]. The PCM ensures the accuracy of the solution of the velocity–pressure coupling of river networks, at the expense of using a limited time step. For river networks, the sizes of junction and nonjunction cells are both considered to obtain a composite grid scale to reform the condition for application of the PCM in [17]. When the Δx2 in Equation (17) of [17] is replaced by the product of the river’s width scale (W) and the longitudinal grid size (Δx), a condition for the application of the PCM applied to river networks is derived as
where the left-hand side is the error of the PCM around the interfaces of branches at the prediction step and is denoted by “EP”; LE is a quantitative upper limit imposed on the EP; M1 is represented by the maximum daily variations of water levels per day (unit: m/s); and c is the wave celerity calculated by , where h is the water depth. Generally, the interfaces of subdomains of river networks are located around junctions. Hence, calculation of Equation (14) uses the variables around junctions. According to extensive tests in ideal channels and real alluvial rivers [17,18] and this study, the value of LE is suggested to be 1.5 cm.
2.4. Flowchart of the PCM Model
In the current formulation, the model solves the governing equations in three steps, and the flowchart of one time-stepping is summarized as follows (see Figure 2). First, all the explicit terms in the momentum equation are computed to obtain provisional velocities. Second, the velocity–pressure coupling is solved to obtain new water levels. Third, a back-substitution of the new water levels into the momentum equation is performed to obtain the final velocities.
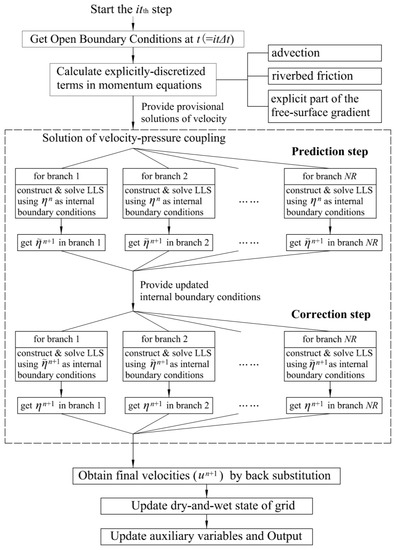
Figure 2.
Flowchart of one time-stepping of the proposed PCM model.
It must be pointed out that the current model is unconditionally stable with respect to wave celerity, advection, and bottom friction due to the use of the semi-implicit method, the ELM, and an implicit discretization of bottom friction. Equation (14) is mainly used to determine proper model parameters to ensure the accuracy of the coupled solutions of the subsystems of the branches of river networks for a given flow condition and mesh.
To quantitatively describe the stability of a numerical simulation, two Courant numbers are defined at cell faces (sides):
where hJ is the average water depth at the center of side J.
Correspondingly, RCFL1>1 (RCFL2>10) is defined as the percent that wet sides of CFL1 > 1 (CFL2 > 10) account for the total sides to describe the CFL level of a simulation. The observed maximum velocity is about 4.0 m/s in the field data of many alluvial rivers and lakes. The “large-u quantity” is defined as the number of sides with a velocity higher than the upper limit (4.0 m/s) and is used as an indicator of instability of the numerical model.
3. Results
3.1. Tests of River Networks with Regular Cross Sections
The hypothetical case of [5] was used to test the PCM model in modeling looped river networks with regular cross sections, for which the parameter (time step) sensitivity study was performed.
3.1.1. Test Conditions and Methods
The characteristics of the tested river networks and the boundary conditions can be found in [4]. This river networks contained 14 branches connected by 6 junctions (see Table 1 and Figure 3). A 1D grid of 100 m was used to divide the branches, and the junctions were covered by polygons of 10–30 m. We then had 300 cells. The grid scale (WΔx) around junctions was calculated as 1000 m2 for the evaluation of EP. The implicit factor θ was set to 0.6 and the sub-time-step for ELM tracking was 10 s.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the channel network of Islam et al. [4,5].
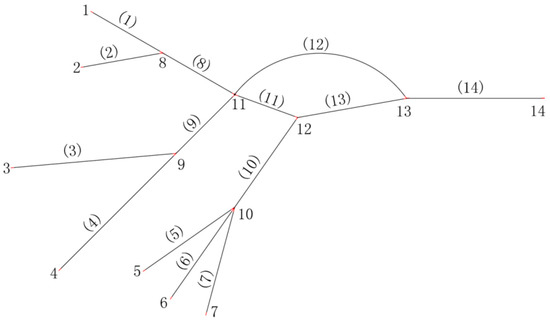
Figure 3.
Channel network with regular cross sections.
In this test, we employed the Manning’s roughness coefficient (nm) used by Islam et al. [5], so the calibration was not included. Then, the model was tested using the appointed unsteady flow process, the inflow discharges and outflow water levels of which were imposed at open boundaries.
3.1.2. Time-Step Sensitivity Study and Results
If the condition for the application of the PCM to river networks is not satisfied, the accuracy of the PCM model may be sensitive to time step. Hence, the PCM model was tested on gradually reduced time steps (Δt), which were sequentially 90, 60, 45, 30, and 15 s, to establish the time step independence of the solutions. Using the PCM model, the simulated histories of water levels and discharges under different time steps were plotted (Figure 4) for nodes 11 and 12. The results of Zhu et al. [4] are almost the same as those of Islam et al. [5] and are not presented in the figures. As the time step decreased, the simulated results of the PCM model approached those of Islam et al. [5]. The time step, which was less than or equal to 60 s, provided time-step-independent results. For each run, the key model parameters and the test results of the 40 h simulations are listed in Table 2.
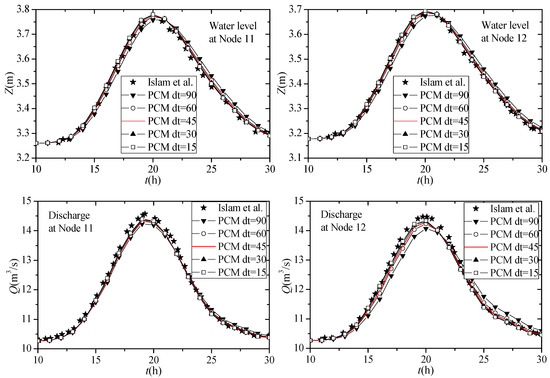
Figure 4.
Simulated histories of water levels and discharges using different Δt (Note: The results of Islam et al. can extracted from [5]).

Table 2.
Model parameters and test results of the 40 h simulations.
3.1.3. Comparison of PCM Model with LNS Model
The PCM model uses a limited time step instead of the multiple correction steps of the LNS model of Zhu et al. [4]. If the condition for application of the PCM to river networks is satisfied, the PCM model is able to ensure accurate simulations under large time steps. For PCM simulations, the time step (60 s), which provided time-step-independent results, was only slightly less than the time step (90 s) used by the model of Zhu et al. [4].
Efficiency tests of the PCM model were conducted using an old processor (Intel I3-3220, made in 2012), such that the runtimes of the PCM model were comparable to those of the LNS model of [4]. Despite the use of a relatively smaller time step, the PCM model (using the I3-3220 processor), which is free of any iteration, could be 1.2–4.5 times as fast as the model of [4].
3.2. Tests of Real Dendritic River Networks
The TGR, located in the upper Yangtze River, was tested. In this test, the Yangtze River and its tributaries formed typical dendritic river networks. As stated in the introduction, this test represented an important real application of the 1D river network model. Performances of the PCM model and the HEC-RAS model were compared in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
3.2.1. Test Conditions and Methods
The computational domain included the upper reach of the Yangtze River from Zhutuo (ZT) to the dam (about 735 km) and its tributaries (see Figure 5). The width of this reach of the Yangtze River varies periodically within 0.7–1.7 km. The hydrology department of the Yangtze River Water Conservancy Commission (YRWCC) provided the surveyed cross sections with a longitudinal interval of 1–2 km. Using these field data, a mesh of 588 cells was generated to cover the computational domain. The PCM model and the HEC-RAS were both tested using three time steps (Δt) of 600, 900, and 1200 s. For the PCM model, a sub-time-step of 100 s was used for ELM tracking, with Δt being equally divided, and the implicit factor θ was set to 0.6.
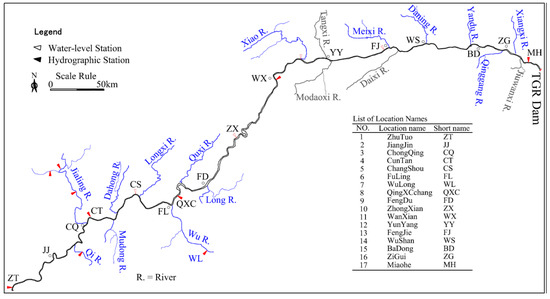
Figure 5.
Computation domain of the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) dendritic river networks.
In this test case, the flow velocity was not sensitive to the Manning’s roughness coefficient (nm) due to the influence of downstream damming. Hence, we calibrated the nm using the flow condition of the flood peak in 2005. The nm was calibrated as 0.05–0.04 from upstream to downstream, and the comparison of the longitudinal profiles for the main channel of the Yangtze River at the flood peak was plotted (Figure 6). Then, the model was tested under unsteady open boundary conditions using the flow condition from 1 January to 31 December 2005. The simulation results were then analyzed to evaluate the accuracy and efficiency of the PCM model in simulating long-term unsteady flows.
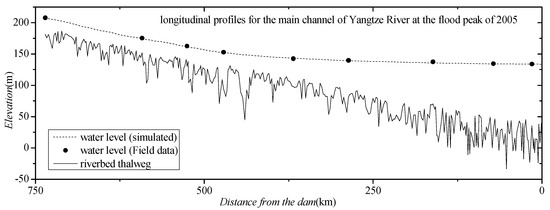
Figure 6.
Comparison of the simulated results with field data in the calibration test.
3.2.2. Test Results and Analysis
The histories of the simulated water levels (Zcs) and discharges (Qcs) agreed with the field data, as shown in Figure 7 (taking stations QingXChang (QXC), Zhongxian (ZX), and Miaohe (MH) as examples). The mean absolute errors in the simulated water levels were generally less than 0.15 m, and the mean absolute relative errors in the simulated cross-sectional discharges were less than 5% compared with field data.
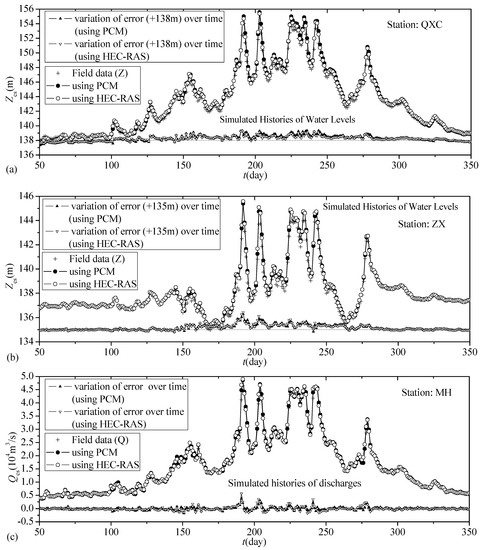
Figure 7.
Comparison of the simulated histories of discharge and water level with field data: (a) water level at Station QXC; (b) water level at Station ZX; (c) discharge at Station MH.
3.2.3. Comparison of PCM Model with HEC-RAS
The Zcs and Qcs histories simulated by the PCM model were almost the same as those simulated by the HEC-RAS (see Figure 7). The difference of the simulated cross-sectional discharge between the PCM and the HEC-RAS simulations was calculated based on all the samples in a one-year simulation (one sample per day), for which the mean absolute error is denoted by EQ1. Similarly, the mean absolute error in water levels is denoted by EZ1. The differences of the simulation results between the two models were minor (see Table 3), even if the two models used different formulations (the PCM model is an LLS model and the HEC-RAS is a GLS model). This also indicates that the PCM model has almost the same predictive capacity as the HEC-RAS model.

Table 3.
Test results of one-year unsteady flow simulations of the TGR river network.
The runtimes of the models are listed in Table 3. Using the E5-2697 processer and a time step of 1200 s, it took 26.8 s for the PCM model and 34.7 s for the HEC-RAS to complete a simulation of a one-year (2005) unsteady flow process in the TGR dendritic river networks. Using different processors and time steps, the PCM model was revealed to be 1.2–1.4 times as fast as the HEC-RAS.
3.3. Tests of Real Looped River Networks
The Jing-south river system, located in the middle Yangtze River, gives a typical example of a looped river network (see Figure 8) and many of its branches experience seasonal floods. In dry seasons, the low water level of the Jing River prevents flows from being diverted into the river network. The Shadaoguan (SDG) and Mituoshi (MTS) branches (and their downstream branches) are dried out when insufficient inflows from the Jing River meet a relatively high riverbed elevation along these branches. In flood seasons, the river network is fully flooded and bidirectional flows are often observed in certain branches (e.g., the Guangyuan (GY) branch). This system, characterized by frequent dry-and-wet alternations of riverbeds, was tested to clarify the stability, accuracy, and efficiency of the PCM model and its ability to simulate dry-and-wet alternations.
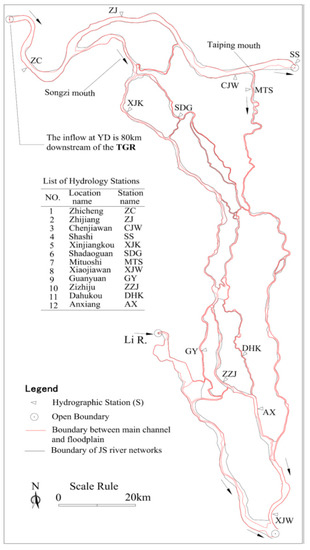
Figure 8.
Computation domain of the Jing-south river networks.
3.3.1. Test Conditions and Methods
The computational domain included a part of the Jing River, the river networks, and a part of the Dongting Lake (see Figure 8). The width of the Jing River is about 2–3 km, and that of the river networks is generally 0.3–0.8 km. The hydrology department of the YRWCC provided the surveyed cross sections with a longitudinal interval of 1–2 km. Using these field data, a mesh of 662 cells was generated to cover the computational domain. Five time steps (Δt) of 600, 900, 1200, 1440, and 1800 s were tested. The Δt was equally divided, and a constant sub-time-step of 100 s was used for the backtracking of the ELM. The implicit factor θ was set to 0.6.
To describe the accuracy of the PCM simulations, three indicators were defined. First, EZ2 is the mean absolute error in water levels compared with field data. Second, it may be difficult to define a relative error in simulated cross-sectional discharges for some seasonally flooding branches because their discharges are zero in dry seasons. Hence, a relative error (EQ2) in cross-sectional annual water flux is used to describe the accuracy of simulated cross-section discharges. Third, an error of mass conservation (Em) is defined as the difference (relative error) between all the inflows and outflows during a given period (e.g., a one-year hydrological process).
We calibrated the nm using the flow condition of the bankfull discharge using the method of [18]. The nm was calibrated as 0.028–0.018 in the Jing-south river system, from upstream to downstream. Then, the model was tested under unsteady open boundary conditions using the flow condition from 1 January to 31 December 2013. The simulation results were analyzed to evaluate the stability, accuracy, and efficiency of the PCM model in simulating long-term unsteady flows.
3.3.2. Test Results and Analysis
The PCM model completed the simulations and provided reasonable results (see Table 4) under a Δt of 600–1800 s. On the one hand, the sides with a large velocity were recorded in simulations using a Δt larger than 1440 s. These unstable sides were generally located on the dry-and-wet fronts, where large gradients of water levels formed due to the discontinuous elevation of riverbeds. These facts imply that dry-and-wet alternations arising from the propagation of unsteady flows help generate unusual velocities, especially when a large Δt is used. On the other hand, the tests also revealed that, for river networks with frequent dry-and-wet alternations, stable PCM simulation can be achieved at large time steps for which the CFL1 > 3 and CFL2 > 20.

Table 4.
Test results of the PCM model in simulating the Jing-south river system.
The histories of the simulated water levels (Zcs) and discharges (Qcs) agreed well with the field data, as shown in Figure 9 (taking station MTS as an example). Moreover, the Zcs and Qcs histories simulated using different time steps overlapped each other and were almost the same. For a stable PCM simulation, the mean absolute error in simulated water levels (EZ2) at 10 gauges was generally 0.07–0.24 m, and the relative error in simulated cross-section annual water flux (EQ2) at 7 cross sections was 0.5–4.9% compared with field data. The conservation error (Em) was generally 2 × 10−4 to 3 × 10−4 in the simulations, and it increased with respect to Δt.
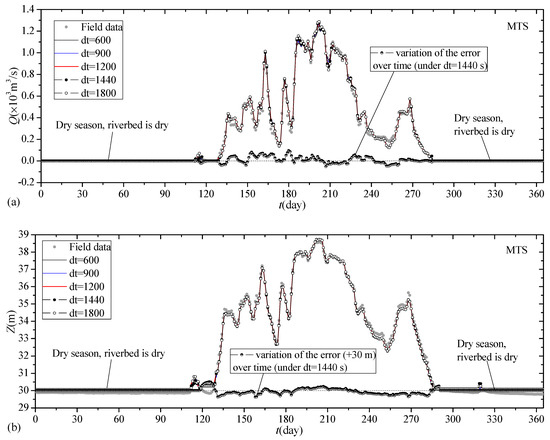
Figure 9.
Comparisons of simulated flow process with field data: (a) Zcs histories at station MTS and (b) Qcs histories at station MTS.
The runtimes of the simulations using the I3-3220 and E5-2697 processers were also recorded. Using a time step of 1200 s and the E5-2697 processor, it took 23.1 s for the PCM model to complete a simulation of a one-year (2013) unsteady flow process in the system. Using different time steps, a run using the E5-2697 processor was 1.3 times faster than a run using the I3-3220 processor.
4. Discussion
With the help of the PCM, the partial linearization technique, the semi-implicit method, and the ELM, the proposed model only needs to solve tridiagonal linear systems (arising from the velocity–pressure coupling) for branches of river networks. These linear systems, characterized by a symmetric and positive definite coefficient matrix, can be directly solved and no iterations are needed. In terms of the involved algebraic system, the new model can be easily differentiated from existing GNS, GLS, and LNS models and is a fourth kind of river network model: the LLS model. The properties of the PCM model are analyzed as follows.
4.1. Advantages of the PCM Model
The first advantage of the new model is its simplicity relative to most existing river network models. Relative to a GNS/GLS model, the LLS model does not need to solve a global large nonlinear/linear algebraic system for the entire domain of river networks, and the complex iteration solution can be avoided. Moreover, in the LLS model, special node-numbering or storage algorithms (e.g., skyline storage) are not needed. Relative to an LNS model (the number of global layer iteration may not be determined in advance), the new model uses a two-step solution instead of global layer iteration. Moreover, the new model only needs to solve tridiagonal linear systems for branches, which can be solved using a direct method.
Second, almost all existing GNS (e.g., [14]), GLS (e.g., [8]), and LNS (e.g., [4]) models require a global layer iteration to solve the global nonlinear/linear system (for river networks) or to synchronize the calculations of local nonlinear subsystems (for branches). These iterations often require a relatively high computation cost, for which, moreover, the calculations generally cannot be well parallelized due to the frequent fork–join. Relatively, the PCM model, which is free of any global or local iteration, was revealed in tests to be efficient.
The model is applicable to both looped and dendritic river networks. Each junction of river networks is covered by a polygonal control volume, for which the number of connected branches can be arbitrary. Both junction and nonjunction cells, with a cross section arranged at its center, allow for a general cross-sectional bathymetry. The model is unconditionally stable with respect to wave celerity, advection, and bottom friction due to the use of the semi-implicit method, the ELM, and an implicit discretization of bottom friction. It is good at simulating river network flows characterized by complex cross-section topographies and frequent dry-and-wet alternations of riverbeds.
In simulating real complex river networks with frequent dry-and-wet alternations, stable PCM simulation can be achieved at large time steps, for which the CFL is much larger than 1. The model was also revealed to achieve high accuracy in conserving mass (mass error was generally 2 × 10−4 to 3 × 10−4). The space–time accumulation of mass errors is so minor that additional correction for the mass error, arising from the dry-and-wet alternations of cells and subgrids, is not necessary.
4.2. Limitations of the PCM Model
The PCM model essentially solves quasi-coupled subsystems of branches of river networks, where only a one-time data exchange is involved in the solution of the subsystems. The condition for the application of the PCM to river networks of alluvial rivers is easily satisfied, so large time steps are allowed. However, according to the condition for application, the time steps may be limited when the PCM model is used to simulate highly unsteady flows (water levels and velocity fields vary quickly with respect to time), such as tidal flows. In this case, the model may, alternatively, resort to global layer iteration, which was used in [4,12,13] to improve the simulation accuracy.
As previously mentioned, an incomplete solution of the advection may happen at junctions in the new model due to the difficulty of further ELM tracking in a junction cell. Despite the simplification, the PCM model has been, in all the tests, revealed to achieve accurate simulations. However, the incomplete solution of the advection term may be a potential source of inaccuracy in case of solving some special flows, for which a further study is expected.
The overlapping halo is a widely used technique for models using domain decompositions in order to improve accuracy by extending subsystems. However, the overlapping halo technique may not be applicable to the PCM model applied to river networks because it will break the matrix structure of the tridiagonal linear systems.
5. Conclusions
A new model was proposed to simulate free-surface flows in dendritic and looped river networks using the basic idea of the PCM. The new model is a fourth kind of river network model (the LLS model), which can be easily differentiated from existing GNS, GLS, and LNS models. With the help of the PCM, the partial linearization technique, the semi-implicit method, and the ELM, the new model solves subsystems for subdomains of branches locally, where only the tridiagonal linear systems for branches of river networks are involved. As a result, it is free of any iterations. The first advantage of the new model is its simplicity (see Section 4.1) and then its efficiency, relative to most existing river network models.
The new model was tested using a hypothetical looped river network with regular cross sections, the TGR dendritic river networks, and the Jing-south looped river system (with seasonally flooding branches), for which a time-step sensitivity study was also conducted. In the tests, the new model produced stable simulations at large time steps, for which the CFL was much larger than 1, and simulated well the dry-and-wet alternations of riverbeds. It achieved almost the same accuracy as the HEC-RAS model. Moreover, the PCM model was revealed to be 2–4 times as fast as a reported model which solves local nonlinear subsystems using two-layer iterations and 1.2–1.4 times as fast as the HEC-RAS. Using a time step of 1200 s, it took the sequential code of the new model 26.8 and 23.1 s to complete a simulation of a one-year unsteady flow process in the TGR river networks (with 588 cells) and the Jing-south river system (with 662 cells), respectively. The new model can achieve high accuracy and efficiency and is robust in simulating real river networks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.H., and C.L.; methodology: D.H., and C.L.; software: D.H., Y.L., C.D., and S.Y. (Shuai Yuan); validation: D.H., C.D., and C.L.; formal analysis: D.H., C.D., S.Y. (Shuai Yuan), and C.L.; investigation: D.H., S.Y. (Shiming Yao), Y.L., and S.Y. (Shuai Yuan); resources: S.Y. (Shiming Yao), and Y.Z.; data curation: S.Y. (Shiming Yao), Y.Z., and D.H.; writing—original draft preparation: D.H., and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing: Y.Z., D.H.; visualization: C.D., and Y.L.; supervision: D.H., and Y.Z.; project administration: S.Y. (Shiming Yao), and Y.Z.; funding acquisition: S.Y. (Shiming Yao), D.H., and Y.Z.
Funding
Financial support from fundamental research funds for the Central Universities (2017KFYXJJ197) and China’s National Natural Science Foundation (51339001, 51779015, and 51479009) is acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, S.H.; Jing, Z.; Yi, Y.J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. The dynamic capacity calculation method and the flood control ability of the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronkers, J.J. Tidal computations for rivers, coastal areas, and seas. J. Hydraul. Div. Proc. 1969, 95, 29–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, D.J.; Garg, N.K. Efficient algorithm for gradually varied flows in channel networks. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2002, 128, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.W. Simple, robust, and efficient algorithm for gradually varied subcritical flow simulation in general channel networks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R.; Sen, D.J. Comparison of gradually varied flow computation algorithms for open-channel network. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2005, 131, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.W.; Molinas, A. Simultaneous solution algorithm for channel networks modeling. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.K.; Kawano, H. Simultaneous solution for flood routing in channel networks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1995, 121, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEC (Hydrologic Engineering Center). River Analysis System, Hydraulics Reference Manual. (Version 4.1); Rep. No. CPD-69; US Army Corps of Engineers: Davis, CA, USA, 2010.
- Papadrakakis, M.; Bitzarakis, S. Domain decomposition PCG methods for serial and parallel processing. Adv. Eng. Softw. 1996, 25, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, R.R.; Storti, M.A. An interface strip preconditioner for domain decomposition methods: Application to hydrology. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2005, 62, 1873–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lv, M.Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhan, J.M. Study of treatment for linking conditions at junction points of river networks. Yellow River 2007, 29, 31–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.; Taylor, R.E. Numerical simulation of fully nonlinear regular and focused wave diffraction around a vertical cylinder using domain decomposition. Appl. Ocean Res. 2007, 29, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Pedersen, G.K.; Langtangen, H.P. A parallel multi-subdomain strategy for solving Boussinesq water wave equations. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, V.; Stelling, G.S. A semi-implicit numerical model for urban drainage systems. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2013, 73, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, V.; Zanolli, P. Iterative solutions of mildly nonlinear systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2012, 236, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggett, J.A.; Cunge, J.A. Numerical methods of solution of the unsteady flow equations. In Unsteady Flow in Open Channels; Mahmood, K., Yevjevich, V., Eds.; Water Resources Publication: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1975; Volume I, Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.C.; Zhong, D.Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, G.Q. Prediction–Correction Method for Parallelizing Implicit 2D Hydrodynamic Models I Scheme. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.C.; Zhong, D.Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Wang, G.Q. Prediction–Correction Method for Parallelizing Implicit 2D Hydrodynamic Models II Application. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141, 06015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Baptista, A.M.; Myers, E.P. A cross-scale model for 3D baroclinic circulation in estuary-plume-shelf systems, I. Formulation and skill assessment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 2187–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, K. 3-D Hybrid Eulerian–Lagrangian/Particle Tracking Model for Simulating Mass Transport in Coastal Water Bodies. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Casulli, V.; Walters, R.A. An unstructured grid, three-dimensional model based on the shallow water equations. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2000, 32, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Waterways Experiment Station. CE-QUAL-RIV1: A Dynamic, One-Dimensional (Longitudinal) Water Quality Model for Streams: User’s Manual; Instruction Report EL-95-2; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Waterways Experiment Station: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1995.
- Goutal, N.; Lacombe, J.-M.; Zaoui, F.; El-Kadi-Adberrezzak, K. MASCARET: A 1-D open-souce software for flow hydrodynamic and water quality in open channel networks. In River Flow; Murillo, Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1169–1174. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).