Sub-Daily Rainfall Intensity Extremes: Evaluating Suitable Indices at Australian Arid and Wet Tropical Observing Sites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Exploring the dependence of the most intense rainfalls on temperature (dry bulb or dew point) and possible secular change of intensity under global warming;
- Climatological description and the provision of necessary intensity and duration information for planning of urban drainage systems, including assessment of secular intensity change;
- To assist in understanding the triggering of mass movements, the drivers of soil erosion, and related phenomena;
- For hydrologic applications, including research on water partitioning, infiltration, canopy interception, and others.
- What diurnal and seasonal variability is shown by intensity data at 5, 15, 30, and 60 min ADs? The objective in exploring this is to document the nature of the population of such intensities, which is the little-explored context (the statistical population) from which measures of extremes are sampled. To what extent do the patterns of variability differ between arid and very wet observing sites?
- Is the widely-used index of extreme rainfall, the 95th percentile of rainfall amounts (or equivalently, intensities) over short ADs [23,39], a meaningful index for application of intensity data to landsurface processes? Might an index based on rainfall amounts delivered above an intensity threshold (RQ95, introduced below) be more informative?
- To what extent can descriptors of extreme rainfall intensity that rely on percentiles of a wide distribution of intensities, and which are therefore not associated with any fixed intensity, be used to compare the rainfall climates of wet and dry locations, or to detect secular change in intensity?
Short AD Rainfall Data as Measures of Rainfall Intensity Extremes: Approaches and Indices
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Sites and Data Collection
2.2. Data Processing
3. Results
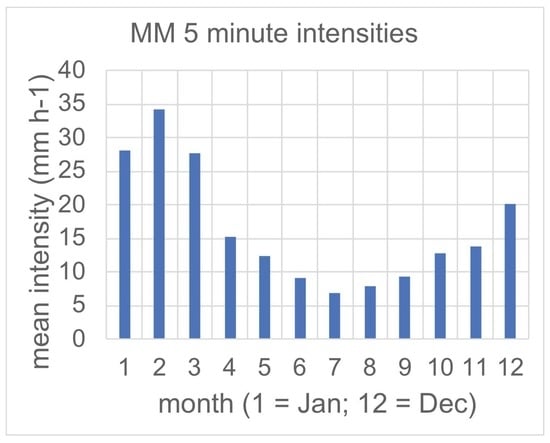
3.1. Seasonal Distributions of Short-AD Rainfall Intensities
3.2. Diurnal Cycle of Short-Duration Intensity Extremes
3.3. The 5-min and Unaggregated ITT Intensity Data: Full Period of Record
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal and Diurnal Variation in Short AD Rainfall Intensities
4.2. What Best Reflects Extremes of Rainfall Intensity
4.3. Data Availability and the Detection of Intensity Extremes
4.4. The Proposed RQ95 Index
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Todeschini, S. Trends in long daily rainfall series of Lombardia (northern Italy) affecting urban stormwater control. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 900–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benestad, R.E. Association between trends in daily rainfall percentiles and the global mean temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 10–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Raffaele, F.; Coppola, E. The response of precipitation characteristics to global warming from climate projections. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2019, 10, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Römkens, M.J.M.; Helming, K.; Prasad, S.N. Soil erosion under different rainfall intensities, surface roughness, and soil water regimes. Catena 2002, 46, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Fei, J.; Liu, D.L.; Yu, Q. Extreme rainfall, rainfall erosivity, and hillslope erosion in Australian Alpine region and their future changes. Int. J. Climatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, T.; Galli, A.; Marsala, V.; Miccadei, V. Analysis of soil erosion induced by heavy rainfall: A case study from the NE Abruzzo Hills area in Central Italy. Water 2009, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Toffol, S.; Laghari, A.N.; Rauch, W. Are extreme rainfall intensities more frequent? Analysis of trends in rainfall patterns relevant to urban drainage systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, J.A.; Burger, G.J. Investigation into increasing short-duration rainfall intensities in South Africa. Water SA 2015, 41, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panthou, G.; Lebel, T.; Vischel, T.; Quantin, G.; Sane, Y.; Ba, A.; Ndiaye, O.; Diongue-Niang, A.; Diopkane, M. Rainfall intensification in tropical semi-arid regions: The Sahelian case. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waal, J.H.; Chapman, A.; Kemp, J. Extreme 1-day rainfall distributions: Analysing change in the Western Cape. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2017, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Mujumdar, P.P. On the relationship of daily rainfall extremes and local mean temperature. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernokulsky, A.; Kozlov, F.; Zolina, O.; Bulygina, O.; Mokhov, I.I.; Semenov, V.A. Observed changes in convective and stratiform precipitation in Northern Eurasia over the last five decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D.L. Rainfall intensity bursts and the erosion of soils: An analysis highlighting the need for high temporal resolution rainfall data for research under current and future climates. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2019, 7, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunkerley, D. How does sub-hourly rainfall intermittency bias the climatology of hourly and daily rainfalls? Examples from arid and wet tropical Australia. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2412–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Effects of rainfall intensity fluctuations on infiltration and runoff: Rainfall simulation on dryland soils, Fowlers Gap, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecham, S.; Chowdhury, R.K. Temporal characteristics and variability of point rainfall: A statistical and wavelet analysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 458–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneepeerakul, C.P.; Muneepeerakul, R.; Huffaker, R.G. Rainfall intensity and frequency explain production basis risk in cumulative rain index insurance. Earth Future 2017, 5, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biasutti, M.; Yuter, S.E. Observed frequency and intensity of tropical precipitation from instantaneous estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9534–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Li, Z. Establishing a rainfall threshold for flash flood warnings in China’s mountainous areas based on a distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarasa-Belmonte, A.M.; Soriano, J. Empirical study of extreme rainfall intensity in a semi-arid environment at different time scales. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 100, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meshgi, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Tay, S.H.X.; Pijcke, G.; Manocha, N.; Ong, M.; Nguyen, M.T.; Babovic, V. Three resampling approaches based on method of fragments for daily-to-subdaily precipitation disaggregation. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, e1119–e1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Yu, Y.-C.; Kung, C.-Y.; Wang, A.-H.; Los, S.A.; Huang, W.-R. Climatology and change of extreme precipitation events in Taiwan based on weather types. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, P.; Haerter, J.O.; Thejll, P.; Piani, C.; Hagemann, S.; Christensen, J.H. Seasonal characteristics of the relationship between daily precipitation intensity and surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-H.; Walther, A.; Nikulin, G.; Chen, D.; Jones, C. Diurnal cycle of precipitation amount and frequency in Sweden: Observation versus model simulation. Tellus A 2011, 63, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, A.G.; Hossain, I.; Perera, B.J.C. Effect of climate change and variability on extreme rainfall intensity–frequency–duration relationships: A case study of Melbourne. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alber, R.; Jaagus, J.; Oja, P. Diurnal cycle of precipitation in Estonia. Est. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 64, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Bárdossy, A.; Seidel, J.; Müller, T.; Sanchis, E.F.; Hauser, A. Statistical analysis of sub-daily precipitation extremes in Singapore. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 3, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brönnimann, S.; Rajczak, J.; Fischer, E.M.; Raible, C.C.; Rohrer, M.; Schär, C. Changing seasonality of moderate and extreme precipitation events in the Alps. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uboldi, F.; Lussana, C. Evidence of non-stationarity in a local climatology of rainfall extremes in northern Italy. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, A.; Fernández-González, S.; García-Ortega, E.; Sánchez, J.L.; López, L.; Gascón, E. Temporal continuity of extreme precipitation events using sub-daily precipitation: Application to floods in the Ebro basin, northeastern Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douka, M.; Karacostas, T. Statistical analyses of extreme rainfall events in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Res. 2018, 208, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.M.; Fowler, H.J.; Blenkinsop, S.; Tye, M.R. A regional frequency analysis of UK sub-daily extreme precipitation and assessment of their seasonality. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4758–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Yuan, W.; Yu, R. Diurnal cycle of rainfall in amount, frequency, intensity, duration, and the seasonality over the UK. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4967–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, I.; Lee, O.; Kim, S. Sensitivity Analysis of Extreme Daily Rainfall Depth in Summer Season on Surface Air Temperature and Dew-Point Temperature. Water 2019, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbero, R.; Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Blenkinsop, S. Is the intensification of precipitation extremes with global warming better detected at hourly than daily resolutions? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokkonen, T.; Koivusalo, H.; Karvonen, T.; Croke, B.; Jakeman, A. Exploring streamflow response to effective rainfall across event magnitude scale. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1467–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Taylor, R.G. Intensive rainfall recharges tropical groundwaters. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Felzer, B.S.; Troy, T.J. Extreme precipitation drives groundwater recharge: The Northern High Plains Aquifer, central United States, 1950–2010. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchoni, D.O.V.; Vouillamoz, J.-M.; Lawson, F.M.A.; Adjomayi, P.; Boukari, M.; Taylor, R.G. Relationships between rainfall and groundwater recharge in seasonally humid Benin: A comparative analysis of long-term hydrographs in sedimentary and crystalline aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calf, G.E.; McDonald, P.S.; Jacobson, G. Recharge mechanism and groundwater age in the Ti-Tree Basin, Northern Territory. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 1991, 38, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.G.; Scanlon, B.; Döll, P.; Rodell, M.; van Beek, R.; Wada, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Leblanc, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Edmunds, M.; et al. Ground water and climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skliris, N.; Zika, J.D.; Nurser, G.; Josey, S.A.; Marsh, R. Global water cycle amplifying at less than the Clausius-Clapeyron rate. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lenderink, G.; Barbero, R.; Loriaux, J.M.; Fowler, H.J. Super-Clausius–Clapeyron scaling of extreme hourly convective precipitation and its relation to large-scale atmospheric conditions. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6037–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochbihler, K.; Lenderink, G.; Siebesma, A.P. Response of extreme precipitating cell structures to atmospheric warming. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6904–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenderink, G.; van Meijgaard, E. Linking increases in hourly precipitation extremes to atmospheric temperature and moisture changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 025208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, C.; Sharma, A.; Johnson, F. Does storm duration modulate the extreme precipitation-temperature scaling relationship? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8783–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasko, C.; Lu, W.T.; Mehrotra, R. Relationship of extreme precipitation, dry-bulb temperature, and dew point temperature across Australia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 074031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasko, C.; Sharma, A. Steeper temporal distribution of rain intensity at higher temperatures within Australian storms. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick Jones, R.; Westra, S.; Sharma, A. Observed relationships between extreme sub-daily precipitation, surface temperature, and relative humidity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, J.; Foster, K. Short-term precipitation extremes in regional climate simulations for Sweden. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 45, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, J.; Södling, J.; Berg, P.; Wern, L.; Eronn, A. Short-duration rainfall extremes in Sweden: A regional analysis. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laz, O.U.; Rahman, A.; Yilmaz, A.; Haddad, K. Trends in sub-hourly, sub-daily and daily extreme rainfall events in eastern Australia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, M.W.; Mekis, E.; Morris, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kilcup, K.; Fleetwood, R. Trends in Canadian short-duration extreme rainfall: Including an intensity–duration–frequency perspective. Atmos. Ocean 2014, 52, 398–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, S.M.; Sarukkalige, R.; Nguyen, V.T.V. Evaluation of empirical relationships between extreme rainfall and daily maximum temperature in Australia. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, C.; Berg, P.; Haerter, J.O. Probing the precipitation life cycle by iterative rain cell tracking. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakob, D.; Karoly, D.J.; Seed, A. Non-stationarity in daily and sub-daily intense rainfall—Part 1: Sydney, Australia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriaux, J.M.; Lenderink, G.; De Roode, S.R.; Siebesma, A.P. Understanding Convective Extreme Precipitation Scaling Using Observations and an Entraining Plume Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 3641–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, E.M.C.; Goodrich, D.; Keefer, T. Frequency analysis of extreme sub-daily precipitation under stationary and non-stationary conditions across two contrasting hydroclimatic environments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 2017, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masud, M.B.; Khaliq, M.N.; Wheater, H.S. Projected changes to short- and long-duration precipitation extremes over the Canadian Prairie Provinces. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 1597–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldini, L.; Darvini, G. Extreme rainfall statistics in the Marche region, Italy. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, D.; Carlino, G.; Blenkinsop, S.; Arnone, E.; Fowler, H.; Noto, L.V. Sensitivity of extreme rainfall to temperature in semi-arid Mediterranean regions. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerter, J.O.; Berg, P.; Hagemann, S. Heavy rain intensity distributions on varying time scales and at different temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haylock, M.; Nicholls, N. Trends in extreme rainfall indices for an updated high quality data set for Australia, 1910–1998. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, H.; Ciampittiello, M.; Dresti, C.; Ghiglieri, G. Observed variability and trends in extreme rainfall indices and Peaks-Over-Threshold series. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2013, 2013, 6049–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeer, K.; Kirchengast, G. Sensitivity of extreme precipitation to temperature: The variability of scaling factors from a regional to local perspective. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 3981–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utsumi, N.; Seto, S.; Kanae, S.; Maeda, E.E.; Oki, T. Does higher surface temperature intensify extreme precipitation? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Bookhagen, B.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J.; Marrengo, J. Complex networks identify spatial patterns of extreme rainfall events of the South American Monsoon System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4386–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paxian, A.; Hertig, E.; Seubert, S.; Vogt, G.; Jacobeit, J.; Paeth, H. Present-day and future Mediterranean precipitation extremes assessed by different statistical approaches. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Marra, F.; Fatichi, S.; Molnar, P.; Morin, E.; Sharma, A.; Burlando, P. Intensification of convective rain cells at warmer temperatures observed from high-resolution weather radar data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.G.; Tank, K.; Zwiers, F.W.; Zhang, X. Guidelines on Analysis of Extremes in a Changing Climate in Support of Informed Decisions for Adaptation; World Meteorological Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkerley, D.L. How do the rain rates of sub-event intervals such as the maximum 5- and 15-min rates (I5 or I30) relate to the properties of the enclosing rainfall event? Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2425–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. What does I30 tell us? An assessment using high-resolution rainfall event data from two Australian locations. Catena 2019, 180, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schär, C.; Ban, N.; Fischer, E.M.; Rajczak, J.; Schmidli, J.; Frei, C.; Giorgi, F.; Karl, T.R.; Kendon, E.J.; Tank, A.M.G.K.; et al. Percentile indices for assessing changes in heavy precipitation events. Clim. Chang. 2016, 137, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weder, C.; Müller, G.; Brümmer, B. Precipitation extremes on time scales from minute to month measured at the Hamburg Weather Mast 1997–2014 and their relation to synoptic weather types. Meteorologische Zeitschrift 2017, 26, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Sub-daily rainfall events in an arid environment with marked climate variability: Variation among wet and dry years at Fowlers Gap, New South Wales, Australia. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 96, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Field Site | MM | FG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentile of | 5-Min AD Intensities (mm h−1) | Unaggregated ITT Intensities (mm h−1) | 5-Min AD Intensities (mm h−1) | Unaggregated ITT Intensities (mm h−1) |
| Q90 | 8 | 48.0 | 15 | 48.7 |
| Q95 | 14 | 65.5 | 20 | 71.2 |
| Q99 | 32 | 119.9 | 40 | 120.0 |
| Q99.5 | 42 | 179.9 | 55 | 133.3 |
| Q99.9 | 68.1 | 240.0 | 90 | 161.1 |
| maximum | 152 | 719.9 | 110 | 211.8 |
| Field Site | MM | FG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity (mm h−1) | Percentile of Rain Depth (RQ) | Percentile of 5-Min ADs (Q) | Percentile of Rain Depth (RQ) | Percentile of 5-Min ADs (Q) |
| ≤2 | 28.91 | 63.1 | - | - |
| ≤5 | 44.24 | 79.86 | 51.87 | 78.88 |
| ≤10 | 66.76 | 93.49 | 66.37 | 89.91 |
| ≤15 | 73.94 | 95.94 | 73.88 | 93.72 |
| ≤20 | 80.46 | 97.56 | 78.74 | 95.57 |
| ≤50 | 95.36 | 99.70 | 94.92 | 99.46 |
| ≤100 | 99.50 | 99.98 | 99.59 | 99.97 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dunkerley, D. Sub-Daily Rainfall Intensity Extremes: Evaluating Suitable Indices at Australian Arid and Wet Tropical Observing Sites. Water 2019, 11, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122616
Dunkerley D. Sub-Daily Rainfall Intensity Extremes: Evaluating Suitable Indices at Australian Arid and Wet Tropical Observing Sites. Water. 2019; 11(12):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122616
Chicago/Turabian StyleDunkerley, David. 2019. "Sub-Daily Rainfall Intensity Extremes: Evaluating Suitable Indices at Australian Arid and Wet Tropical Observing Sites" Water 11, no. 12: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122616
APA StyleDunkerley, D. (2019). Sub-Daily Rainfall Intensity Extremes: Evaluating Suitable Indices at Australian Arid and Wet Tropical Observing Sites. Water, 11(12), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122616