Multi-Satellite Data of Land Surface Temperature, Lakes Area, and Water Level for Hydrological Model Calibration and Validation in the Yangtze River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
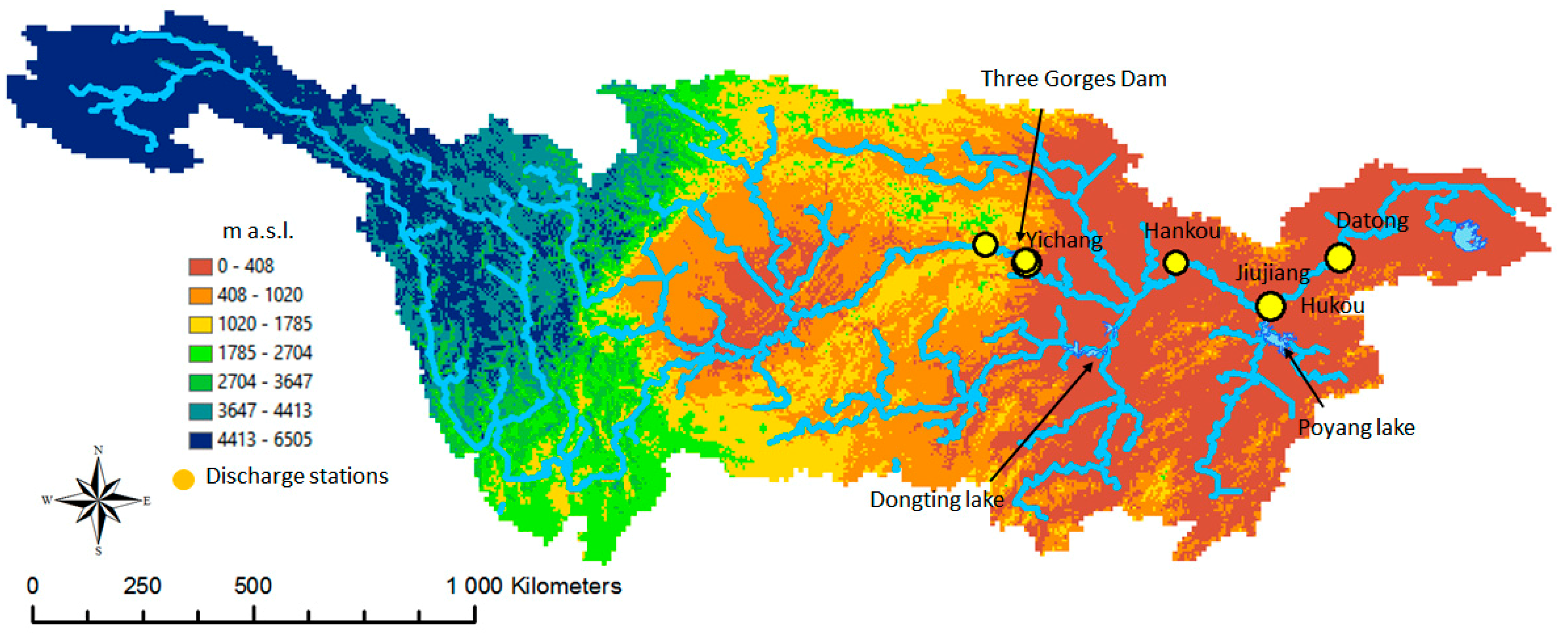
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Hydrological and Meteorological Data
2.2. Soil Type, Land Use, and Hydraulic Properties
2.3. Satellite Data
2.3.1. Vegetation Parameters
2.3.2. Land Surface Temperature
2.3.3. Lake Water Extent
2.3.4. Altimeter Water Level
3. Methodology: FEST-EWB Distributed Hydrological Model
Calibration Methodology with Satellite and Ground Data
4. Results
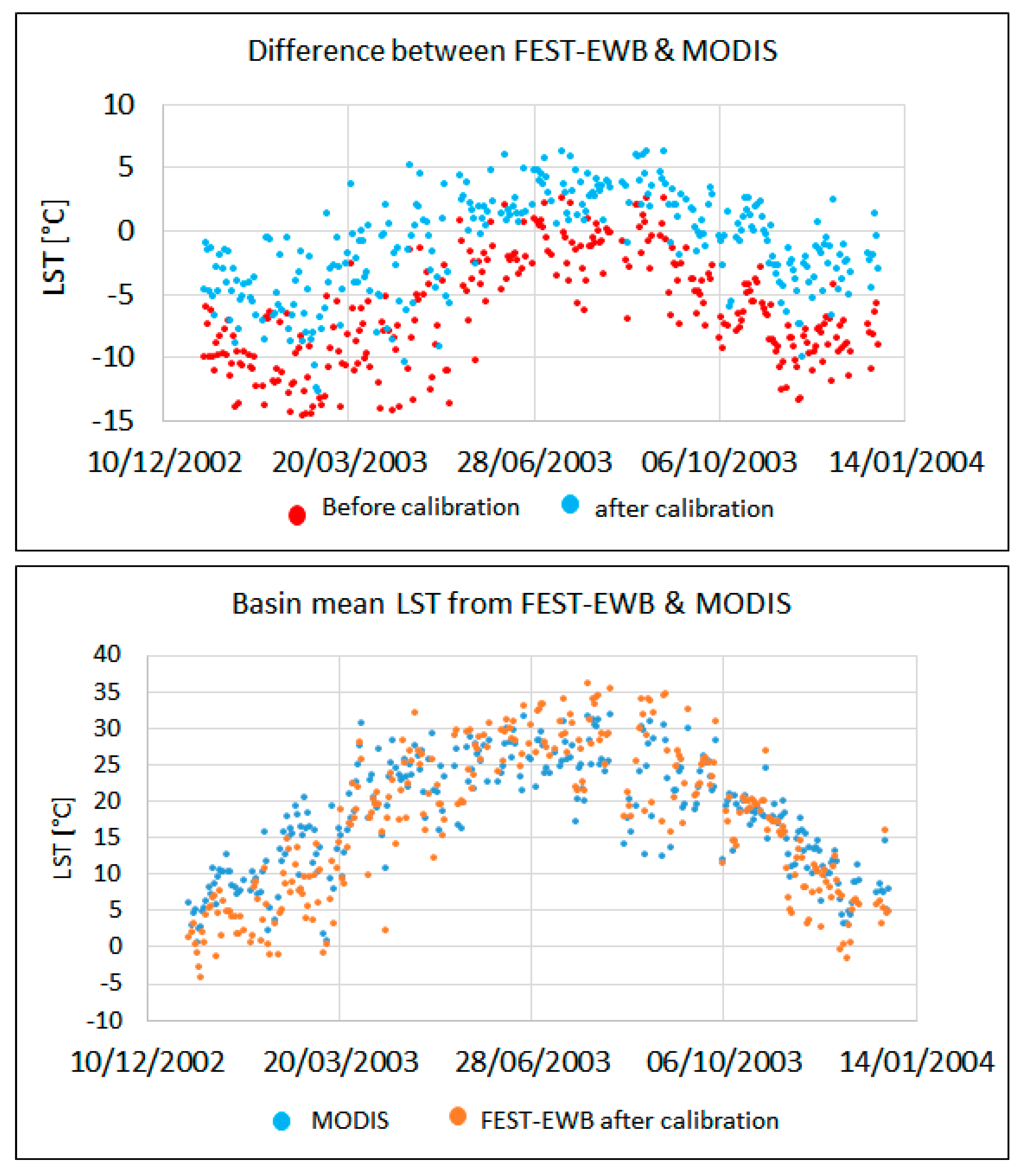
4.1. Calibration and Validation of Soil Surface Parameters from Satellite Data of LST
4.2. Calibration and Validation of Lake Dynamics from Satellite Altimeter and Water Surface Extension
4.3. Calibration of Base Flow Parameters from Ground Discharge Data
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ceola, S.; Montanari, A.; Krueger, T.; Dyer, F.; Kreibich, H.; Westerberg, I.; Carr, G.; Cudennec, C.; Elshorbagy, A.; Savenije, H.; et al. Adaptation of water resources systems to changing society and environment: A statement by the International Association of Hydrological Sciences. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 2803–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivapalan, M. From engineering hydrology to Earth system science: Milestones in the transformation of hydrologic science. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1665–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, M.; Wood, E.F. Data assimilation for estimating the terrestrial water budget using a constrained ensemble Kalman filter. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuffetti, D.; Ravazzani, G.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Verification of operational Quantitative Discharge Forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system-the AMPHORE case studies in the upper Po River. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMillan, H.; Freer, J.; Pappenberger, F.; Krueger, T.; Clark, M. Impacts of uncertain river flow data on rainfall-runoff model calibration and discharge predictions. Hydrol. Processes Int. J. 2010, 24, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Refsgaard, J.C. Discussion of model validation in relation to the regional and global scale. In Model Validation: Perspectives in Hydrological Science; Anderson, M.G., Bates, P.D., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 461–483. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, M.F.; Wood, E.F.; Wójcik, R.; Pan, M.; Sheffield, J.; Gao, H.; Su, H. Hydrological consistency using multi-sensor remote sensing data for water and energy cycle studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Chen, J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Viterbo, P.; Holl, S.; Wilson, C.R. Basin scale estimates of evapotranspiration using GRACE and other observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L20504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramillien, G.; Frappart, F.; Güntner, A.; Ngo-Duc, T.; Cazenave, A.; Laval, K. Time variations of the regional evapotranspiration rate from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite gravimetry. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W10403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheffield, J.; Ferguson, C.; Troy, T.; Wood, E.F.; McCabe, M. Closing the terrestrial water budget from satellite remote sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Tang, Q.; Ferguson, C.R.; Wood, E.F.; Lettermaier, D.P. Estimating the water budget of major US river basins via remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3955–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrini, F.; Castelli, F.; Entekhabi, D. Estimation of surface turbulent fluxes through assimilation of radiometric surface temperature sequences. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J.S.; Wood, E.F. Multiscale modelling of spatially variable water and energy balance processes. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 3061–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbari, C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Mancini, M.; Hidalgo, V. Land surface temperature representativeness in a heterogeneous area through a distributed energy-water balance model and remote sensing data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for GCMs. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 14415–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; Wood, E.F. The assimilation of remotely sensed soil brightness temperature imagery into a land-surface model using ensemble Kalman filtering: A case study based on ESTAR measurements during SGP97. Adv. Water Resour. 2003, 26, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kaleita, A.L. Assimilation of Surface Temperature in a Land-Surface Model, Remote Sensing and Hydrology. In Proceedings of the Symposium Held at Santa Fe, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 28 June–2 July 1999. IAHS Publication no. 267. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Salama, M.S.; Su, Z.; Zheng, D.; Krol, M.S.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Roughness Length Parameterizations on Regional-Scale Land Surface Modeling of Alpine Grasslands in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1069–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M.; Niu, G.-Y.; Zeng, W. Improving the Xin’anjiang Hydrological Model Based on Mass-Energy Balance. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3359–3375. [Google Scholar]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P. Calibration of a distributed hydrological model based on satellite evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, L.; Caparrini, F.; Castelli, F. Use of multi-platform, multi-temporal remote-sensing data for calibration of a distributed hydrological model: An application in the Arno basin, Italy. Hydrol. Processes Int. J. 2006, 20, 2693–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rientjes, T.H.M.; Muthuwatta, L.P.; Bos, M.G.; Booij, M.J.; Bhatti, H.A. Multi-variable calibration of a semi-distributed hydrological model using streamflow data and satellite-based evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Karssenberg, D.; De Roo, A.; de Jong, S.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. The suitability of remotely sensed soil moisture for improving operational flood forecasting. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2343–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Oceans Atmos. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL), 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, E.D.; Small, E.E. A method for the determination of the hydraulic properties of soil from MODIS surface temperature for use in land-surface models. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbari, C.; Mancini, M.; Li, J.; Su, Z. Can satellite land surface temperature data be used similarly to ground discharge measurements for distributed hydrological model calibration? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Calibration and validation of a distributed energy water balance model using satellite data of land surface temperature and ground discharge measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Rodriguez, E.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Measuring surface water from space. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.S.; Matgen, P.; Pappenberger, F. Progress in integration of remote sensing derived flood extent and stage data and hydraulic models. Rev. Geophys. 2009, 47, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, W.A.; Fonstad, M.A. Optical remote mapping of rivers at sub-meter resolutions and watershed extents. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2008, 33, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C. Satellite remote sensing of river inundation area, stage, and discharge: A review. Hydrol. Processes 1997, 11, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwangoy, J.B.; Hansen, M.C.; Roya, D.P.; Grandi, G.D.; Justic, C.O. Wetland mapping in the Congo Basin using optical and radar remotely sensed data and derived topographical indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenridge, R.; Anderson, E. MODIS-based flood detection, mapping and measurement: The potential for operational hydrological applications. In Transboundary Floods: Reducing the Risks Through Flood Management; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Xiong, L.; Guo, C.; Shu, N. Study of Dongting Lake area variation and its influence on water level using MODIS data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2005, 50, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yésou, H.; Huber, C.; Lai, X.; Averty, S.; Li, J.; Daillet, S.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Burnham, J.; et al. Nine years of monitoring of water resource over the Yangtze middle reaches exploiting ENVISAT, MODIS, Beijing 1 time series, altimetric data, and field measurements. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2011, 16, 231–247. [Google Scholar]
- Yesou, H.; Pottier, E.; Mercier, G.; Grizonnet, M.; Haouet, S.; Giros, A.; Faivre, R.; Maxant, J.; Studer, M.; Huber, C. Synergy of Sentinel1 and Sentinel2 imagery for wetland monitoring information extraction from continuous flow of Sentinel images applied to water bodies and vegetation mapping and monitoring. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing (IGARSS), IEEE International Symposium, Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 163–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yésou, H.; HUBER, C.; HAOUET, S.; LAI, X.; HUANG, S.; de FRAIPONT, P.; DESNOS, Y.L. Exploiting Sentinel1 time series to monitor the largest fresh water bodies in PR China, the Poyang lake case. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 36882–36885. [Google Scholar]
- Yésou, H.; Huber, C.; Huang, S.; Studer, M.; Lai, X.; Chen, X.; Daillet, S. Water resource monitoring based on EO data: Gained experience after 10 years of DRAGON programme over the Yangtze middle reaches: From ERS1 to Sentinel 1, and from MERIS to HJ and Pleiades HR. In Proceedings of the Mid Term Results of Dragon III, Chengdu, China, 26–28 May 2014. ESA SPS 742. [Google Scholar]
- Prigent, C.; Matthews, E.; Aires, F.; Rossow, W. Remote sensing of global wetland dynamics with multiple satellite data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 4631–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, D.C.; Horritt, M.S.; Dall’Amico, J.T.; Scott, T.R. Improving River Flood Extent Delineation from Synthetic Aperture Radar Using Airborne Laser Altimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, S.; Fatoyinbo, T.E.; Policelli, F. Flood extent mapping for Namibia using change detection and thresholding with SAR. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingham, D.J.; Rapley, C.G. Saturation effects in the Seasat altimeter receiver. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.S.; Gill, S.K. Evaluation of the TOPEX/POSEIDON altimeter system over the Great Lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1994, 99, 24527–24539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birkett, C.M. Contribution of the Topex NASA radar altimeter to the global monitoring of large rivers and wetlands. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 34, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.A.M.; Garlick, J.D.; Freeman, J.A.; Mathers, E.L. Global inland water monitoring from multi-mission altimetry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretaux, J.-F.; Jelinski, W.; Calmant, S.; Kouraev, A.; Vuglinski, V.; Berge-Nguyen, M.; Gennero, M.-C.; Nino, F.; Abarca Del Rio, R.; Cazenave, A.; et al. SOLS: A lake database to monitor in the Near Real Time water level and storage variations from remote sensing data. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 47, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, F.; Calmant, S.; Cauhope, M.; Seyler, F.; Cazenave, A. Preliminary results of ENVISAT RA-2-derived water levels validation over the Amazon basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leon, J.G.; Calmant, S.; Seyler, F.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Cauhopé, M.; Frappart, F.; Filizola, N.; Fraizy, P. Rating curves and estimation of average water depth at the upper Negro River based on satellite altimeter data and modeled discharges. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Getirana, A.C.V.; Peters-Lidard, C. Estimating water discharge from large radar altimetry datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, A.; Dias de Paiva, R.; Santos daSilva, J.; Medeiros Moreira, D.; Calmant, S.; Garambois, P.-A.; Collischonn, W.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Seyler, F. Stage-discharge rating curves based on satellite altimetry and modeled discharge in the Amazon basin. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3787–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarpanelli, A.; Barbetta, S.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T. River discharge estimation by using altimetry data and simplified flood routing modeling. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4145–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Getirana, A.C.V. Integrating spatial altimetry data into the automatic calibration of hydrological models. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, S.J.; O’Donnell, G.M.; Moore, P.; Kilsby, C.G.; Fowler, H.J.; Berry, P.A.M. Using satellite altimetry data to augment flow estimation techniques on the Mekong River. Hydrol. Processes 2010, 24, 3811–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancamaria, S.; Bates, P.D.; Boone, A.; Mognard, N.M. Large-scale coupled hydrologic and hydraulic modelling of an arctic river: The Ob river in Siberia. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domeneghetti, A.; Tarpanelli, A.; Brocca, L.; Barbetta, S.; Moramarco, T.; Castellarin, A.; Brath, A. The use of remote sensing-derived water surface data for hydraulic model calibration. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbari, C.; Ravazzani, G.; Mancini, M. A distributed thermodynamics model for energy and mass balance computation: FEST-EWB. Hydrol. Processes 2011, 25, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Xu, W.; Gu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, L. Risk perception and hazard mitigation in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Nat. Hazards 2011, 56, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood Frequency in China’s Poyang Lake Region: Trends and Teleconnections. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, T. Observed trends of annual maximum water level and streamflow during past 130 years in the Yangtze River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Gleason, J.C.; Wada, Y. Downstream Yangtze River levels impacted by Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Dai, Z.; van Gelder, P.H.A.J.M.; Gao, J. Linking Three Gorges Dam and downstream hydrological regimes along the Yangtze River, China. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the Three Gorges Dam on Yangtze River flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416–417, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Bi, N. Sedimentation in the Three Gorges Dam and its impact on the sediment flux from the Changjiang (Yangtze River), China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2009, 6, 5177–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on downstream delivery of sediment and its environmental implications, Yangtze River. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Hydrological evidence and causes of seasonal low water levels in a large river-lake system: Poyang Lake, China. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze River flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Lai, X.; Daillet, S.; Li, C.; Huang, S.; Burnham, J.; Uribe, C.; Zhang, W.; et al. Twelve Years of Monitoring from Space the Largest Chinese lakes: Gained Experience in Term of Water Resource, Biodiversity and Public Health and Recommendations in Term of EO Data Resource Access. ESA MOST. In Proceedings of the Dragon Final Symposium, Beijing, China, 25–29 June 2012. ESA SP. 704. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Hong, Y.; Hardy, J.; Sun, Z. Examining the influence of river-lake interaction on the drought and water resources in the Poyang Lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P. Modelling spatial-temporal change of Poyang Lake using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5767–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, J.; XU, K.; YANG, Y.; QI, L.; HAYASHI, S.; WATANABE, M. Measuring water storage fluctuations in lake Dongting, china, by topex/poseidon satellite altimetry. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 115, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fang, J.; Miao, S.; Gu, B.; Tao, S.; Peng, C.; Tang, Z. The 7-Decade Degradation of a Large Freshwater Lake in Central Yangtze River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Yesou, H.; Lai, X. The Change Analysis of Wetland Landscape Based on Remote Sensing Data in Dongting Lake, China. In Proceedings of the Dragon 2 Final Results and Dragon 3 Kickoff Symposium, Beijing, China, 25–29 June 2012; ESA SP-704. ISBN 92-9092-268-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Fang, C.; Cao, W. Shrinking of Dongting Lake and its weakening connection with the Yangtze River: Analysis of the impact on flooding. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2015, 30, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; He, J.; Tang, W.; Qin, J.; Cheng, C.C.K. On downward shortwave and longwave radiations over high altitude regions: Observation and modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmonized World Soil Database (version 1.1); FAO: Rome, Italy; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2009; Available online: https://webarchive.iiasa.ac.at/Research/LUC/External-World-soil-database/HTML/ (accessed on 1 January 2009).
- Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L. Prediction of Soil Water Properties for Hydrologic Modelling. In Proceedings of the Symposium Watershed Management in the Eighties, New York, NY, USA, 30 April–1 May 1985; Jones, E.B., Ward, T.J., Eds.; pp. 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Arino, O.; Gross, D.; Ranera, F.; Bourg, L.; Leroy, M.; Bicheron, P.; Latham, J.; Di Gregorio, A.; Brockman, C.; Witt, R.; et al. GlobCover: ESA service for global land cover from MERIS. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli, R.; Yésou, Y.; Li, J.; Desnos, Y.-L.; Huang, S.; . De Fraipont, P. Poyang Hu (Jiangxi Province, China) area variations between January 2004 and June 2006 using ENVISAT low and medium resolution time series. Ann. GIS 2007, 13, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, J.; Shankman, D.; Wu, G.; Boer, F.W.; Burnham, M.; He, Q.; Yesou, H.; Xiao, J. Strategic assessment of the magnitude and impacts of sand mining in Poyang lake, China. Reg. Env. Chang. 2010, 10, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Lai, X.; Uribe, C.; Huang, S.; Marie, T.; Chen, X.; Andreoli, R.; Li, J.; Yesou, H. Influence of resolution on water detection and on the water height and level relationship, case of Poyang lake (China). In Proceedings of the ESA Living Planet Symposium, Bergen, Norway, 28 June–2 July 2010; ISBN 978-92-9221-250-6. ESA SP-686. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, M. La modellazione distribuita della risposta idrologica: Effetti della variabilità spaziale e della scala di rappresentazione del fenomeno dell’assorbimento. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy, 1990. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Corbari, C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Mancini, M.; Hidalgo, V. Mass and energy flux estimates at different spatial resolutions in a heterogeneous area through a distributed energy-water balance model and remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3208–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbari, C.; Mancini, M. Intercomparison across scales between remotely-sensed land surface temperature and representative equilibrium temperature from a distributed energy water balance model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1830–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravazzani, G.; Mancini, M.; Giudici, I.; Amadio, P. Effects of soil moisture parameterization on a real-time flood forecasting system based on rainfall thresholds. In Quantification and Reduction of Predictive Uncertainty for Sustainable Water Resources Management. In Proceedings of the Symposium HS2004 at IUGG2007, Perugia, Italy, 7–13 July 2007; IAHS: Wallingford, UK; pp. 407–416.
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Tan, Z. Inter-annual variations of Poyang Lake area during dry seasons: Characteristics and implications. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 4, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, X.; Jiang, J.; Liang, Q.; Huang, Q. Large-scale hydrodynamics modeling of the middle Yangtze River Basin with complex river-lake interactions. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooge, J.C.I. Looking for hydrologic laws. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jimènez-Munoz, J.C.; Lee, B.; Gillespie, A.R.; Sabol, D.A.; Gustafson, W.T. Accuracy of ASTER Level-2 thermal-infrared Standard Products of an agricultural area in Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Kharraz, J.E.; Li, Z.-L. Surface temperature and water vapour retrieval from MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 5161–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J.K.; Harlow, R.C.; Scott, R.L.; Best, M.J.; Edwards, J.M.; Thelen, J.-C.; Weeks, M. Evaluating the Met Office Unified Model land surface temperature in Global Atmosphere/Land 3.1 (GA/L3.1), Global Atmosphere/Land 6.1 (GA/L6.1) and limited area 2.2 km configurations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1703–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghent, D.; Kaduk, J.; Remedios, J.; Ardö, J.; Balzter, H. Assimilation of land surface temperature into the land surface model JULES with an ensemble Kalman filter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D19112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancini, M.; Hoeben, R.; Troch, P. Multifrequency radar observation of bare surface soil moisture content: A laboratory experiment. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Scipal, K. Large-Scale Soil Moisture Mapping in Western Africa using the ERS Scatterometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Al-Yaari, A.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Parrens, M.; Molero, B.; Leroux, D.; Bircher, S.; Mahmoodi, A.; Mialon, A.; Richaume, P.; et al. Overview of SMOS performance in terms of global soil moisture monitoring after six years in operation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.P. Uncertainties in the determination of river discharge: A literature review. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1987, 15, 834–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Montanari, A. Uncertainty in river discharge observations: A quantitative analysis. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amengual, A.; Carrió, D.S.; Ravazzani, G.; Homar, V. A comparison of ensemble strategies for flash flood forecasting: The 12 october 2007 case study in Valencia, Spain. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1143–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levenberg, K. A Method for the Solution of Certain Non-Linear Problems in Least Squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1994, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuczera, G. Efficient subspace probabilistic parameter optimization for catchment models. Water Resour Res. 1997, 33, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. Prophesy, reality and uncertainty in distributed hydrological modelling. Adv. Water Resour. 1993, 16, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corbari, C.; Huber, C.; Yesou, H.; Huang, Y.; Su, Z.; Mancini, M. Multi-Satellite Data of Land Surface Temperature, Lakes Area, and Water Level for Hydrological Model Calibration and Validation in the Yangtze River Basin. Water 2019, 11, 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122621
Corbari C, Huber C, Yesou H, Huang Y, Su Z, Mancini M. Multi-Satellite Data of Land Surface Temperature, Lakes Area, and Water Level for Hydrological Model Calibration and Validation in the Yangtze River Basin. Water. 2019; 11(12):2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122621
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorbari, Chiara, Claire Huber, Hervè Yesou, Ying Huang, Zhongbo Su, and Marco Mancini. 2019. "Multi-Satellite Data of Land Surface Temperature, Lakes Area, and Water Level for Hydrological Model Calibration and Validation in the Yangtze River Basin" Water 11, no. 12: 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122621
APA StyleCorbari, C., Huber, C., Yesou, H., Huang, Y., Su, Z., & Mancini, M. (2019). Multi-Satellite Data of Land Surface Temperature, Lakes Area, and Water Level for Hydrological Model Calibration and Validation in the Yangtze River Basin. Water, 11(12), 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122621






