Evaluation of Groundwater Potential by GIS-Based Multicriteria Decision Making as a Spatial Prediction Tool: Case Study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin, Turkey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
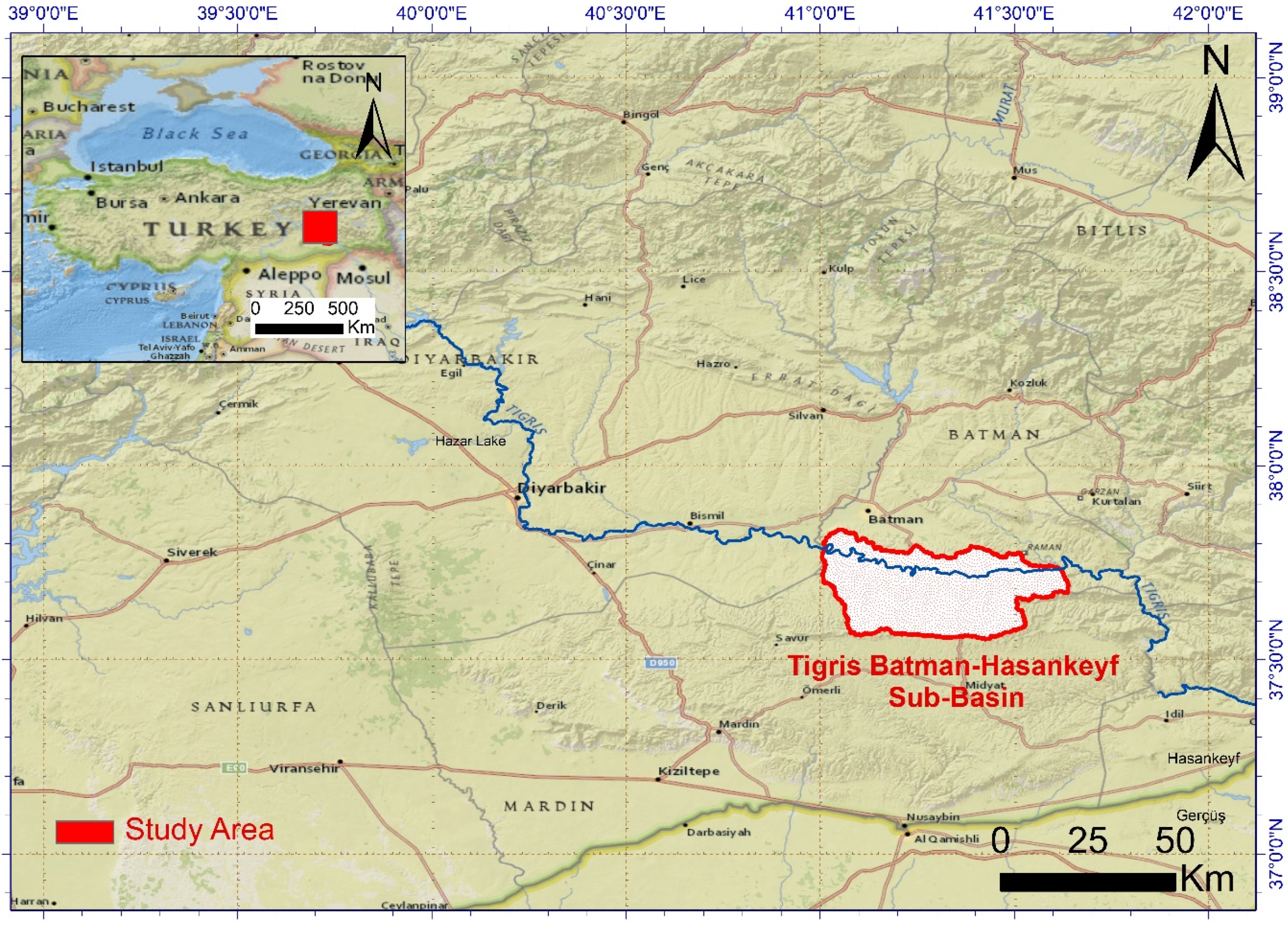
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Method
2.3. GIS-Based AHP Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geomorphology
3.2. Geology
3.3. Lineament Density
3.4. Slope
3.5. Rainfall
3.6. Soil
3.7. Drainage Density
3.8. Land Use
3.9. GWPZ Delination
3.10. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okello, C.; Tomasello, B.; Greggio, N.; Wambiji, N.; Antonellini, M. Impact of population growth and climate change on the freshwater resources of Lamu Island, Kenya. Water 2015, 7, 1264–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantino, C.; Henriques, M.J.; Oliveira, M.M.; Ferreira, J.P.L. Methodologies for pollution risk assessment of water resources systems. IAHS Publ. 2007, 310, 298. [Google Scholar]
- Alessa, L.; Kliskey, A.; Lammers, R.; Arp, C.; White, D.; Hinzman, L.; Busey, R. The arctic water resource vulnerability index: An integrated assessment tool for community resilience and vulnerability with respect to freshwater. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielopol, D.L.; Griebler, C.; Gunatilaka, A.; Notenboom, J. Present state and future prospects for groundwater ecosystems. Environ. Conserv. 2003, 30, 104–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Stefano, L.; Lopez-Gunn, E. Unauthorized groundwater use: Institutional, social and ethical considerations. Water Policy 2012, 14, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C.W. Application of decision-tree model to groundwater productivity-potential mapping. Sustainability 2015, 7, 13416–13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernandez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourtaghi, Z.S.; Pourghasemi, H.R. GIS-based groundwater spring potential assessment and mapping in the Birjand Township, southern Khorasan Province, Iran. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Gupta, S.; Guin, S.; Kaur, H. Assessment of groundwater potential zones using multi-influencing factor (MIF) and GIS: A case study from Birbhum district, West Bengal. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 4117–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K.; Mal, B.C. Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 1359–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Shi, Y.; Niu, H.; Xie, D.; Wei, J.; Lefticariu, L.; Xu, S. A GIS-based model of potential groundwater yield zonation for a sandstone aquifer in the Juye Coalfield, Shangdong, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeih, S.F. An overview of integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater mapping in Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senanayake, I.P.; Dissanayake, D.M.D.O.K.; Mayadunna, B.B.; Weerasekera, W.L. An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saaty, T.L. The Analytic Hierarchy Process; McGrawHill: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Fundamentals of Decision Making and Priority Theory; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Sun, Q.-Y. Applications of AHP method in safety science. J. Saf. Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, G. A GIS-based spatial multi-criteria approach for flood risk assessment in the Dongting Lake Region, Hunan, Central China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 3465–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yi, S.; Xiao, Y. Assessment of flood susceptible areas using spatially explicit, probabilistic multi-criteria decision analysis. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wood, M.D.; Linstead, C.; Maltby, E. Uncertainty analysis in a GIS-based multi-criteria analysis tool for river catchment management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.C.; Srinivas, Y.; Magesh, N.S.; Kaliraj, S. Assessment of groundwater potential zones in Chittar basin, Southern India using GIS based AHP technique. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 15, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, W.; Ghoneim, E.; Shew, R.; LaMaskin, T.; Al-Bloushi, K.; Hussein, S.; AbuBakr, M.; Al-Mulla, E.; Al-Awar, M.; El-Baz, F. Delineation of groundwater potential (GWP) in the northern United Arab Emirates and Oman using geospatial technologies in conjunction with Simple Additive Weight (SAW), Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), and Probabilistic Frequency Ratio (PFR) techniques. J. Arid Environ. 2018, 157, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Mishra, P.; Mahapatra, S.C. Delineation of groundwater potential zone for sustainable development: A case study from Ganga Alluvial Plain covering Hooghly district of India using remote sensing, geographic information system and analytic hierarchy process. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2485–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gdoura, K.; Anane, M.; Jellali, S. Geospatial and AHP-multicriteria analyses to locate and rank suitable sites for groundwater recharge with reclaimed water. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, S.; Hosni, S.; Mannai, H.; Jelassi, F.; Bouri, S.; Anselme, B. GIS-based multi-criteria analysis and vulnerability method for the potential groundwater recharge delineation, case study of Manouba phreatic aquifer, NE Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Rishi, M.S.; Singh, G.; Thakur, S.N. Groundwater potential assessment of an alluvial aquifer in Yamuna sub-basin (Panipat region) using remote sensing and GIS techniques in conjunction with analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and catastrophe theory (CT). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Srivastava, P.K. Integrating GIS and remote sensing for identification of groundwater potential zones in the hilly terrain of Pavagarh, Gujarat, India. Water Int. 2010, 35, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Samani, A.N.; Mahdavi, M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Zeinivand, H. Groundwater potential mapping at Kurdistan region of Iran using analytic hierarchy process and GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 7059–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Shrestha, S.; Babel, M.S.; Ninsawat, S. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in the Comoro watershed, Timor Leste using GIS, remote sensing and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) technique. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murthy, K.S.R. Ground water potential in a semi-arid region of Andhra Pradesh—A geographical information system approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim-Bathis, K.; Ahmed, S.A. Geospatial technology for delineating groundwater potential zones in Doddahalla watershed of Chitradurga district, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2016, 19, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sikdar, P.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Adhya, E.; Paul, P.K. Land use/Land cover changes and groundwater potential zoning in and around Raniganj coal mining area, Bardhaman District, West Bengal—A GIS and Remote Sensing Approach. J. Spat. Hydrol. 2004, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.K.; Mondal, N.C.; Banerjee, P.; Nandakumar, M.V.; Singh, V.S. Deciphering potential groundwater zone in hard rock through the application of GIS. Environ. Geol. 2007, 55, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrucci, V.; Taioli, F.; De Araújo, C.C. Groundwater favorability map using GIS multicriteria data analysis on crystalline terrain, Sao Paulo State, Brazil. J. Hydrol. 2008, 357, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Jha, M.K.; Chowdary, V.M.; Mal, B.C. Integrated remote sensing and GIS-based approach for assessing groundwater potential in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, F.K.; Nazzal, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Naeem, M.; Jafri, M.K. Identification of potential artificial groundwater recharge zones in Northwestern Saudi Arabia using GIS and Boolean logic. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Chowdary, V.M.; Chowdhury, A. Groundwater assessment in Salboni Block, West Bengal (India) using remote sensing, geographical information system and multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1713–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Garg, P.K. Remote sensing and GIS based groundwater potential and recharge zones mapping using multi-criteria decision making technique. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Saxena, R. Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques or generation of groundwater prospect zones towards rural developmentean approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Bhattacharya, A.K. Groundwater assessment through an integrated approach using remote sensing, GIS and resistivity techniques: A case study from a hard rock terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4599–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, N.S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Soundranayagam, J.P. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahunbay, Z.; Balkiz, Ö. Outstanding universal value of Hasankeyf and the Tigris valley. Doğa Deneği. 2009, 22. Available online: https://goo.gl/qZ9tqX (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Miyake, Y.; Maeda, O.; Tanno, K.; Hongo, H.; Gündem, C.Y. New excavations at Hasankeyf Höyük: A 10th millennium cal. BC site on the upper Tigris, southeast Anatolia. Neo Lithics 2012, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, R. Temporal changes in the groundwater level in the Upper Tigris Basin, Turkey, determined by a GIS technique. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 107, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikalovic, A.; Cosic, I.; Lazarevic, D. GIS based multi-criteria analysis for industrial site selection. Procedia Eng. 2014, 69, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmoud, S.H. Delineation of potential sites for groundwater recharge using a GIS-based decision support system. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3429–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenini, I.; Mammou, A.B.; El May, M. Groundwater recharge zone mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria analysis: A case study in Central Tunisia (Maknassy Basin). Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.G.; Bras, R.L.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. A physical basis for drainage density. Geomorphology 1992, 5, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Directorate of Mineral Research on Exploration. Available online: http://yerbilimleri.mta.gov.tr/anasayfa.aspx (accessed on 8 August 2019).
- Mandal, U.; Sahoo, S.; Munusamy, S.B.; Dhar, A.; Panda, S.N.; Kar, A.; Mishra, P.K. Delineation of groundwater potential zones of coastal groundwater basin using multi-criteria decision making technique. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4293–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, F.J.; Batista, F.; Rocha, C.; Mubareka, S. Disaggregating population density of the European Union with CORINE land cover. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 2051–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateşoğlu, A. Havza çalışmalarında kullanılan CORINE 2006 arazi sınıflandırma verilerinin doğruluğunun araştırılması. İstanb. Üniv. Orman Fakültesi Derg. 2016, 66, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, B.V.; Briz-Kishore, B.H. A methodology for locating potential aquifers in a typical semi-arid region in India using resistivity and hydrogeologic parameters. Geoexploration 1991, 27, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S.; Pandey, A.C. Delineation of groundwater potential zone in hard rock terrain of India using remote sensing, geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) techniques. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punniyamoorty, M.; Ponnusamy, M.; Lakshmi, G. A combined application of structural equation modeling (SEM) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in supplier selection. Benchmarking Int. J. 2012, 19, 70–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, V. Benchmarking the service quality of ocean container carriers using AHP. Benchmarking Int. J. 2010, 17, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.; Devillers, R.; Luther, J.E.; Eddy, B.G. GIS-based multiple-criteria decision analysis. Geogr. Compass 2011, 5, 412–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, E.; Sanchez, A. A sensitivity analysis approach for some deterministic multi-criteria decision making methods. Decis. Sci. 1997, 28, 151–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Xu, X.; Dey, P.K. Multi-criteria decision making approaches for supplier valuation and selection: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector necessary. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 145, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.A.; Lamata, M.T. Consistency in the analytic hierarchy process: A new approach. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 2006, 14, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magowe, M.; Carr, J.R. Relationship between lineaments and ground water occurrence in western Botswana. Groundwater 1999, 37, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batelaan, O.; De Smedt, F. Wet Spass: A flexible, GIS based, distributed recharge methodology for regional groundwater modelling. IAHS Publ. 2001, 269, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, G.E.; Bras, R.L. Hillslope processes, drainage density, and landscape morphology. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza, G.A.; Martins, H. Multi-criteria decision analysis in natural resource management: A critical review of methods and new modelling paradigms. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 230, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makropoulos, C.K.; Butler, D. Spatial ordered weighted averaging: Incorporating spatially variable attitude towards risk in spatial multi-criteria decision-making. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 21, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnatak, H.C.; Saran, S.; Bhatia, K.; Roy, P.S. Multicriteria spatial decision analysis in web GIS environment. Geoinformatica 2017, 11, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiat, K.A.N.; Nawawi, M.N.M.; Abdullah, K. Assessing the accuracy of GIS-based elementary multicriteria decision analysis as a spatial prediction tool—A case of predicting potential zones of sustainable groundwater resources. J. Hydrol. 2012, 440, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Moghaddam, M.A.; Monfared, S.A.H. Spatial assessment of the potential of groundwater quality using fuzzy AHP in GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Dahiphale, P.; Yadav, K.K.; Singh, M. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Jaisamand Basin of Udaipur District. In Groundwater; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gnanachandrasamy, G.; Zhou, Y.; Bagyaraj, M.; Venkatramanan, S.; Ramkumar, T.; Wang, S. Remote sensing and GIS based groundwater potential zone mapping in Ariyalur District, Tamil Nadu. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souissi, D.; Msaddek, M.H.; Zouhri, L.; Chenini, I.; El May, M.; Dlala, M. Mapping groundwater recharge potential zones in arid region using GIS and Landsat approaches, southeast Tunisia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Slope | Lineament Density | Geology | Geomorphology | Land Use | Soil | Rainfall | Drainage Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | 1.00 | 1.80 | 1.29 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.29 | 1.00 | 1.29 |
| Lineament dens | 0.56 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 0.71 |
| Geology | 0.78 | 1.40 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 1.00 |
| Geomorphology | 0.89 | 1.60 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 1.14 | 0.89 | 1.14 |
| Land use | 0.56 | 1.20 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.67 | 0.86 |
| Soil | 0.78 | 1.40 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 1.00 |
| Rainfall | 0.89 | 1.80 | 1.29 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.29 | 1.00 | 1.29 |
| Drainage dens | 0.49 | 1.40 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 1.00 |
| Parameters | Slope | Lineament Density | Geology | Geomorphology | Land Use | Soil | Rainfall | Drainage Density | Normalized Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| Lineament dens | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.12 |
| Geology | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| Geomorphology | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.13 |
| Land use | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Soil | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| Rainfall | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| Drainage Dens | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| Weight | Criteria | Sub-Feature | Area Cover (%) | Sub-Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Geomorphology | Alluvion | 1 | 9 |
| Plain | 43 | 7 | ||
| Plateau | 12 | 5 | ||
| Hill | 21 | 3 | ||
| Mountain | 23 | 1 | ||
| 7 | Geology | Shale | 10.9 | 1 |
| Sandstone–conglomerate | 17.1 | 7 | ||
| Evaporites/moraine | 21.7 | 3 | ||
| Clayey limestone/basalt/quartz | 0.6 | 5 | ||
| Pebble–sandstone–conglomerate | 5.0 | 7 | ||
| Limestone | 43.7 | 8 | ||
| Alluvion | 1.0 | 9 | ||
| 5 | Lineament density (%) | 0–0.01 | 93.7 | 1 |
| 0.01–1.5 | 1.4 | 3 | ||
| 1.5–3.5 | 2.6 | 5 | ||
| 3.5–6.50 | 2.3 | 7 | ||
| 9 | Slope (%) | 0–2 | 9 | 9 |
| 2–4 | 6 | 7 | ||
| 4–8 | 12 | 5 | ||
| 8–15 | 25 | 3 | ||
| >15 | 48 | 1 | ||
| 7 | Rainfall (mm/year) | 448–478 | 43.57 | 5 |
| 479–508 | 32.16 | 6 | ||
| 509–548 | 17.08 | 7 | ||
| 549–592 | 7.18 | 8 | ||
| 6 | Soil | Alluvial soil | 0.10 | 9 |
| Brown forestry soil | 56.90 | 6 | ||
| Brown Soil | 41.30 | 4 | ||
| Reddish-brown soil | 1.70 | 3 | ||
| 5 | Drainage density (%) | 0–0.01 | 55.5 | 1 |
| 0.1–2 | 4.1 | 7 | ||
| 2–4.06 | 40.5 | 9 | ||
| Bare rock | 7.23 | 1 | ||
| Discrete rural building | 0.13 | 3 | ||
| Non-irrigated agricultural field/vineyards | 28.92 | 4 | ||
| Agricultural areas with natural vegetation/non-irrigated orchard | 12.32 | 5 | ||
| Sparse plant areas | 30.23 | 6 | ||
| Grassland | 19.79 | 7 | ||
| Irrigated area | 0.17 | 8 | ||
| Water bodies | 1.21 | 9 |
| Evaluation | km2 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Very poor | 262.45 | 19 |
| Poor | 241.71 | 17 |
| Moderate | 484.22 | 34 |
| Good | 234.53 | 17 |
| Very good | 177.09 | 13 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çelik, R. Evaluation of Groundwater Potential by GIS-Based Multicriteria Decision Making as a Spatial Prediction Tool: Case Study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin, Turkey. Water 2019, 11, 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122630
Çelik R. Evaluation of Groundwater Potential by GIS-Based Multicriteria Decision Making as a Spatial Prediction Tool: Case Study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin, Turkey. Water. 2019; 11(12):2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122630
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇelik, Recep. 2019. "Evaluation of Groundwater Potential by GIS-Based Multicriteria Decision Making as a Spatial Prediction Tool: Case Study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin, Turkey" Water 11, no. 12: 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122630
APA StyleÇelik, R. (2019). Evaluation of Groundwater Potential by GIS-Based Multicriteria Decision Making as a Spatial Prediction Tool: Case Study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin, Turkey. Water, 11(12), 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122630





