Key Drivers for Copepod Assemblages in a Eutrophic Coastal Brackish Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
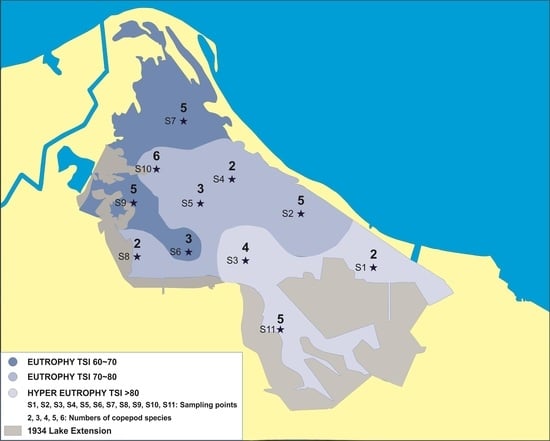
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
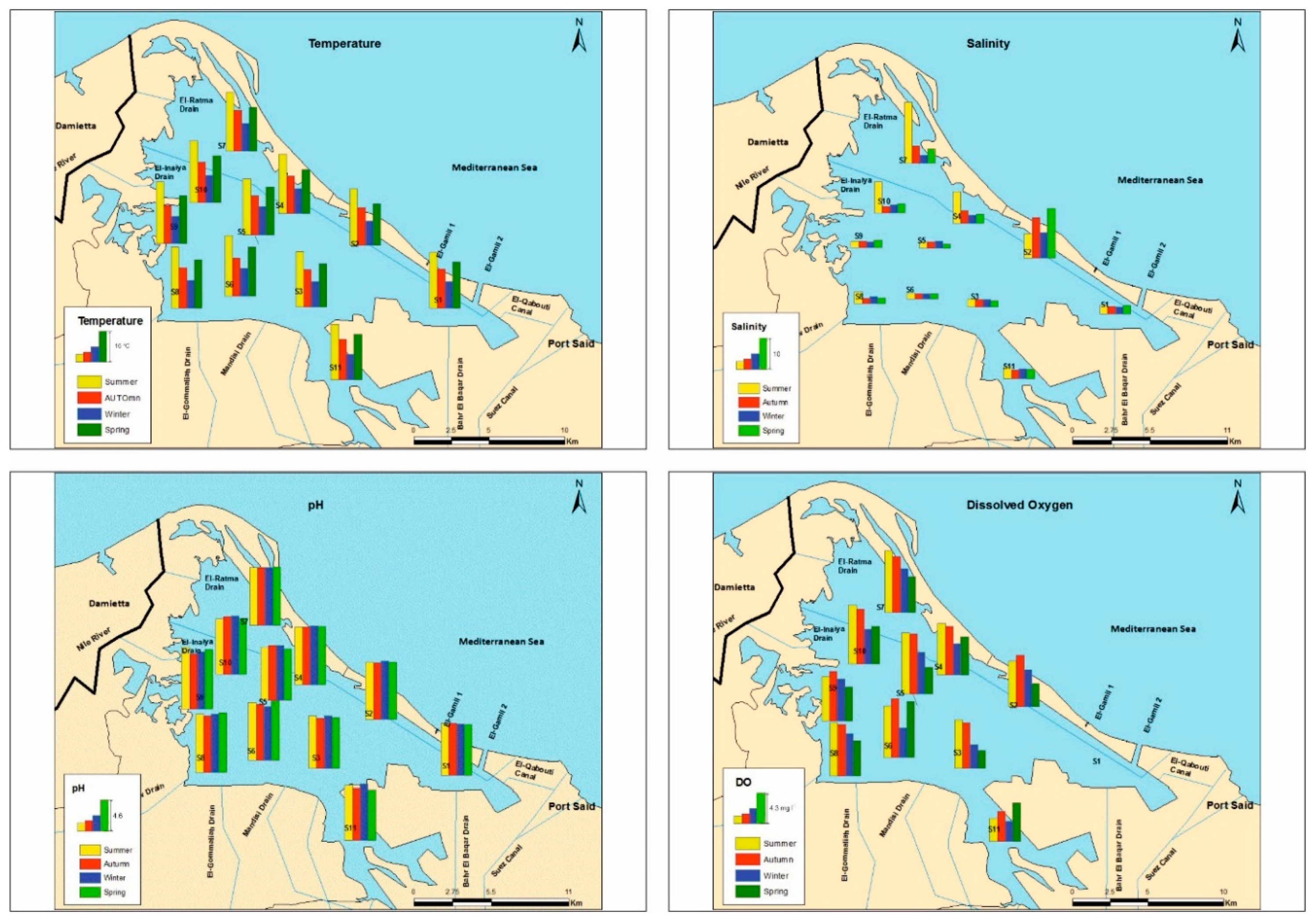
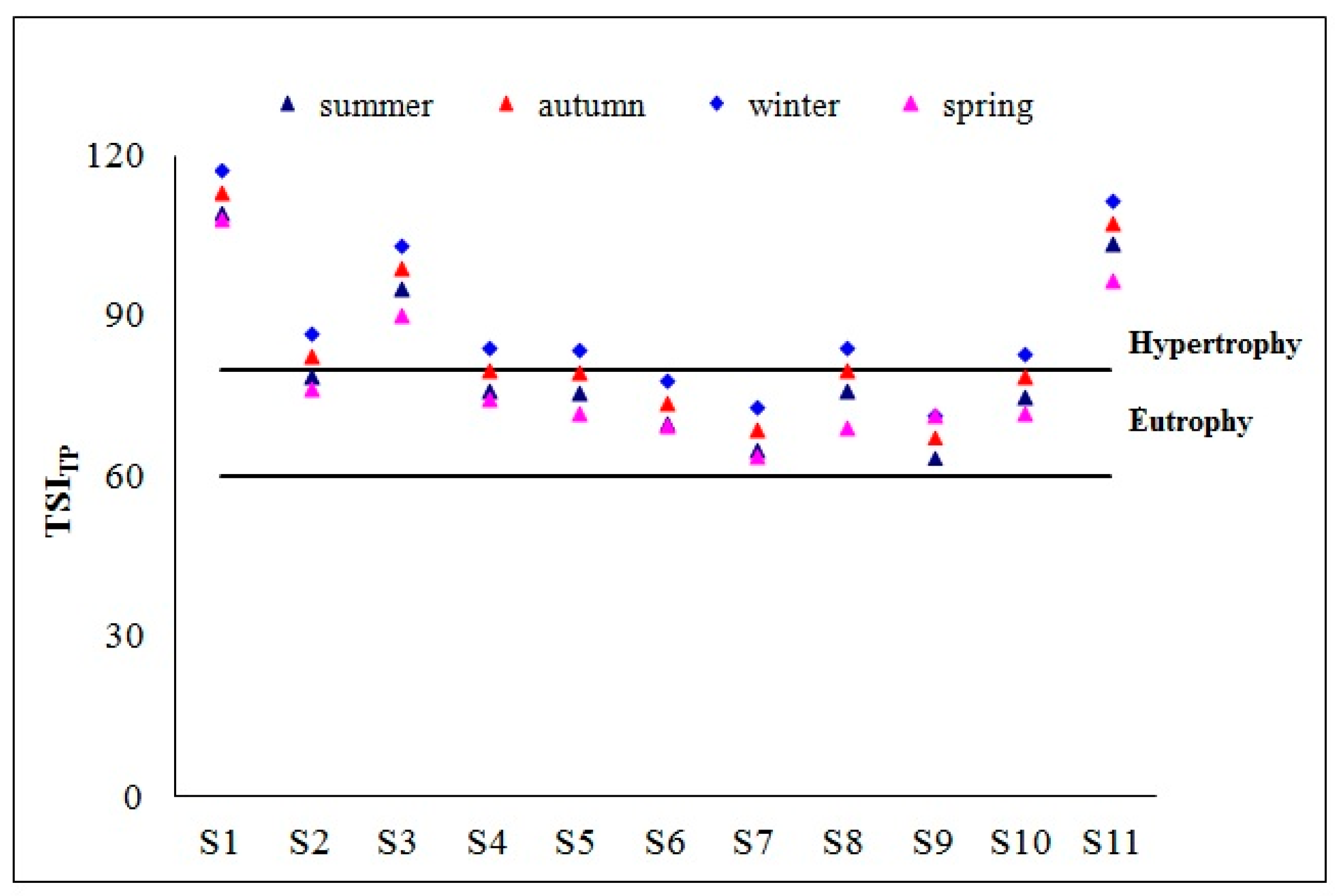
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters and Trophic State
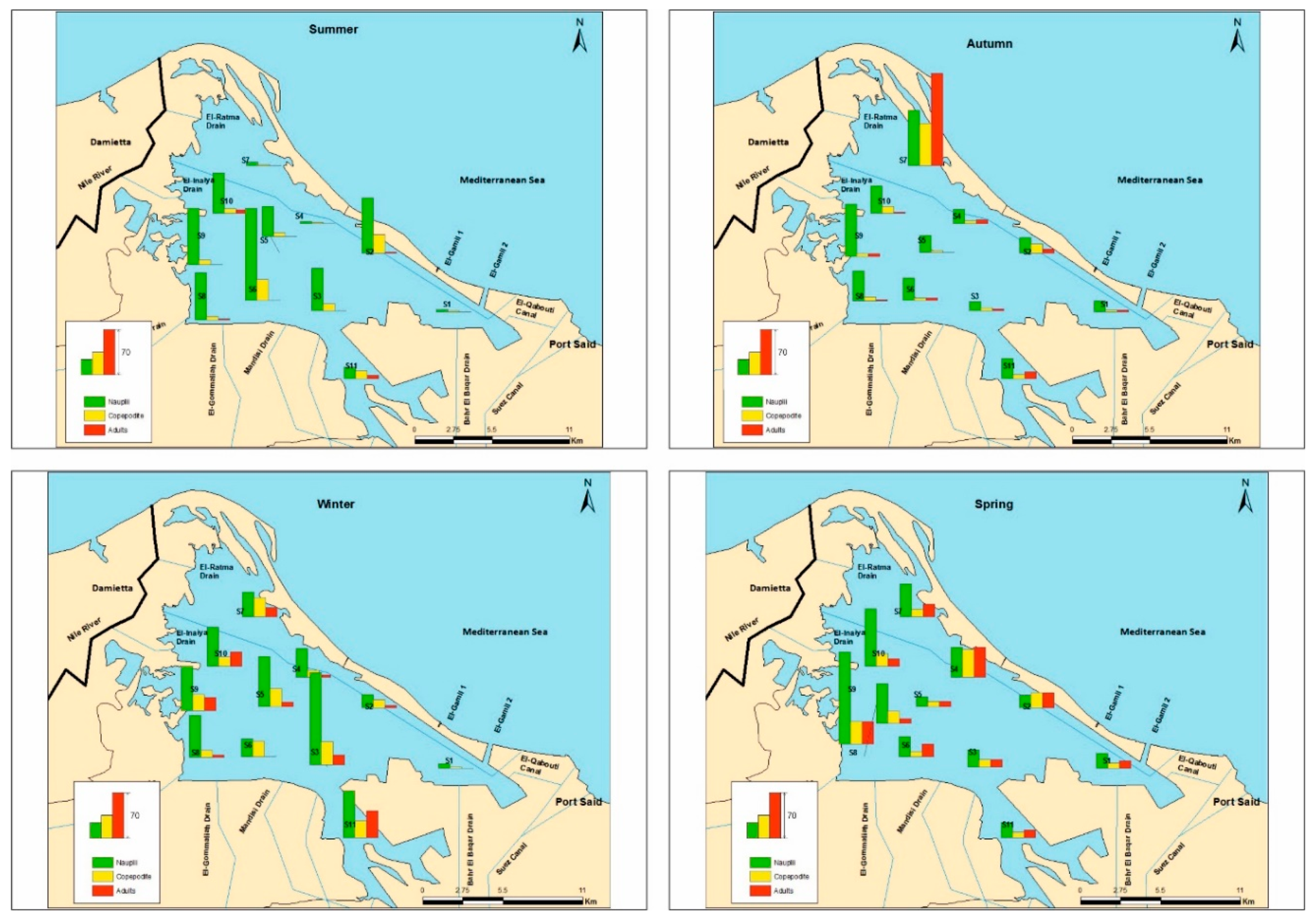
3.2. Copepod Species Composition, Distribution, and Abundance
3.3. Copepod Assemblages and Environmental Conditions
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nixon, S.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, G.M. Eutrophication of Freshwater and Coastal Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.A.; Ansari, A.A. Eutrophication: An ecological vision. Bot. Rev. 2005, 71, 449–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, T.; Huang, D.; Liu, S.M.; Fang, J. Eutrophication and hypoxia and their impacts on the ecosystem of the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent coastal environment. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 154, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.W.; Haisheng, J. Eutrophication model for a coastal bay in Hong Kong. J. Environ. Eng. 1998, 124, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Liu, J.; Irwin, A.J.; Laws, E.A.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, B. Warming and eutrophication combine to restructure diatoms and dinoflagellates. Water Res. 2018, 128, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.D.; Falcao, M.; Nobre, A.; Nunes, J.P.; Ferreira, J.G.; Vale, C. Evaluation of eutrophication in the Ria Formosa coastal lagoon, Portugal. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, P.; Gilpin, L.; Svendsen, H.; Erlandsson, C.P.; Larsso, N.U.; Kratzer, S.; Fouilland, E.; Janzen, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Grenz, C.; et al. Eutrophication and some European waters of restricted exchange. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 1635–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IFREMER. Réseau de Suivi Lagunaire du Languedoc-Roussillon. Available online: http://www.etang-de-l-or.com/uploads/file/Eau/RSL/2009_RapportRSL%20resultats%202008.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2019).
- Bianchi, F.; Acri, F.; Bernardi Aubry, F.; Berton, A.; Boldrin, A.; Camatti, E.; Cassin, D.; Comaschi, A. Can plankton communities be considered as bio-indicators of water quality in the Lagoon of Venice? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S. Seeing red: Alien species along the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Aquat. Invasions 2007, 2, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollens, S.M.; Cordell, J.R.; Avent, S.; Hooff, R. Occurrences, causes and consequences of zooplankton invasions: A brief review, plus two case studies from the northeast Pacific Ocean. Hydrobiologia 2002, 480, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attayde, J.L.; Bozelli, R.L. Assessing the indicator properties of zooplankton assemblages to disturbance gradients by canonical correspondence analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.; Myers, E.E.; Campbell, C.; Webber, D. Phytoplankton and zooplankton as indicators of water quality in Discovery Bay, Jamaica. Hydrobiologia 2005, 545, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Nõges, P.; Davidson, T.A.; Haberman, J.; Nõges, T.; Blank, K.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Søndergaard, M.; Sayer, C.; Laugaste, R.; et al. Zooplankton as indicators in lakes: A scientific-based plea for including zooplankton in the ecological quality assessment of lakes according to the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). Hydrobiologia 2011, 676, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimouni, E.; Pinel-Alloul, B.; Beisner, B.E. Assessing aquatic biodiversity of zooplankton communities in an urban landscape. Urban Ecosyst. 2015, 18, 1353–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbiche-Neves, G.; Saito, V.S.; Previattelli, D.; da Rocha, C.E.F.; Nogueira, M.G. Cyclopoid copepods as bioindicators of eutrophication in reservoirs: Do patterns hold for large spatial extents? Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Papathanassiou, E. Differentiation of zooplankton populations in a polluted area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 76, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, N. An overview of the impacts of eutrophication and chemical pollutants on copepods of the coastal zone. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Siokou-Frangou, I.; Papathanassiou, E.; Lepretre, A.; Frontier, S. Zooplankton assemblages and influence of environmental parameters on them in a Mediterranean coastal area. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 847–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, P. Long-term trends in mesozooplankton biomass development in the southern Baltic. Oceanology 1985, 22, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fransz, H.G.; Gonzalez, S.R.; Cadée, G.C.; Hansen, F.C. Long-term change of Temora longicornis (Copepoda: Calanoida) abundance in a dutch inlet (Marsdiep) in relation to eutrophication. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1992, 30, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uye, S.I. Replacement of large copepods by small ones with eutrophication of embayments: Cause and consequence. Hydrobiologia 1994, 292/293, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.T.; Wong, C.K. Changes in the planktonic copepod community in a landlocked bay in the subtropical coastal waters of Hong Kong during recovery from eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 2011, 666, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.R.; Crisman, T.L. The trophic response of ciliated protozoans in freshwater lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim-Júnior, M.; Perbiche-Neves, G.; Brito, L.; Ghidini, A.R.; Casanova, S.M.C. Spatial-temporal variation of Rotifera in an eutrophic reservoir insouthern Brazil. Iheringia 2010, 100, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallberg, P.; Horppila, S.M.C.; Vaisanen, A.; Nurminen, L. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton and zooplankton along a trophic gradient in a eutrophic lake implication for food web management. Hydrobiologia 1999, 412, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.S.; Marshall, H.G. Estuarine relationships between zooplankton community structure and trophic gradients. J. Plankton Res. 2000, 22, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uye, S.I.; Sano, K. Seasonal reproductive biology of the small cyclopoid copepod Oithona davisae in a temperate eutrophic inlet. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 118, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, T.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J. Eutrophication strengthens the response of zooplankton to temperature changes in a high-altitude lake. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 6690–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.T.; Salib, E.A. Effects of some water quality parameters on fish composition and productivity in Lake Manzalah, Egypt. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1986, 12, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Said, M.A.; Abdel Moati, A.R. Water budget of lake Manzalah. Mahasagar 1995, 28, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Baky, T.E.; Hagras, A.E.; Hassan, S.H.; Zyadah, M.A. Environmental impact assessment of pollution in Lake Manzalah, I-Distribution of some heavy metals in water and sediment. J. Egypt Ger. Soc. Zool. 1998, 26, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, H.Y.; Hussien, M.; Flower, R. Environmental assessment of spatial distribution of zooplankton community in Lake Manzalah, Egypt. Acta Adriat. 2007, 48, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Karim, M.S. Present and long term changes of phytoplankton communities in hypertrophic mediterranean lagoon, Lake Manzalah, Egypt. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Mageed, A. Distribution and long-term historical changes of zooplankton assemblages in Lake Manzalah (South Mediterranean Sea, Egypt). Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2007, 33, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wahby, S.D.; Youssef, S.F.; Bishara, N.F. Further studies on the hydrography and chemistry of Lake Manzalah. Bull. Natl. Inst. Oceanogr. Fish. 1972, 2, 400–422. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rakaiby, M.L.; Youns, H.A. Morphological and temporal studies of Manzalah Lake area and Damietta-Port Said Coast, Egypt using remote sensing Technology. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 1, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; El Leithy, B.; Thompson, J.; Flower, R.; Ramdani, M.; Ayache, F.; Hassan, S. Application of remote sensing to site characterization and environmental change analysis of North Africa coastal lagoons. Hydrobiologia 2009, 622, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rasheed, M.E. Ecological studies on Lake El-Manzalah with special reference to their water quality and sediment productivity. Master’s Thesis, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G. Nutrient Criteria, Technical Guidance Manual; FAO Departments and Offices: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bajkiewicz-Grabowska, E. Zróżnicowanie troficzne jezior—stan obecny, miejsce w klasyfikacji troficznej (Trophic diversity of lakes—present state, the place in trophic classification). Bad. Limnol. 2007, 5, 293–305, (in Polish, English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Bradford-Grieve, J.M.; Markhaseva, E.L.; Rocha, C.E.F.; Abiahy, B. South Atlantic Zooplankton; Backhuys: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Boxshall, G.A.; Halsey, S.H. An Introduction to Copepod Diversity; The Ray Society: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.; Wiener, E. The Mathematical Theory of Communications; Urbana Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- UNDP. Project Document–Lake Manzalah Engineered Wetland. Patent Number EGY/93/G31, 31 March 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Said, M.A.; Abdel Moati, M.A.R. A water budget study of Lake Manzalah, Egypt. Pak. J. Mar. Sci. 1997, 1–2, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, Y.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fetahi, T.; Schagerl, M.; Mengistou, S. Key drivers for phytoplankton composition and biomass in an Ethiopian highland Lake. Limnologica 2014, 46, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, F.R.; Slaboda, M.L.; Stanley, D. Metal pollution loading, Manzalah Lagoon, Nile Delta, Egypt: Implications for aquaculture. Environ. Geol. 1994, 23, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, M.T.; Rippeth, T.P.; Nash, J.D. Turbulence and Stratification in Estuaries and Coastal Seas. Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences. Treatise Estuar. Coast. Sci. 2011, 2, 9–35. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Satar, A.M.; Goher, M.E. Nutrient status and Phosphorus speciation of Manzalah lake sediments. Thalass. Sal. 2009, 32, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, S.; Gamito, S.; Pérez-Ruzafa, A. Trophic state of Foz de Almargem coastal lagoon (Algarve, South Portugal) based on the water quality and the phytoplankton community. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 71, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldívar, J.M.; Cardoso, A.C.; Viaroli, P.; Newton, A.; de Wit, R.; Ibañez, C.; Reizopoulou, S.; Somma, F.; Razinkovas, A.; Basset, A.; et al. Eutrophication in transitional waters: An overview. Transit. Water Monogr. 2008, 1, 11–78. [Google Scholar]
- Nuccio, C.; Melillo, C.; Massi, L.; Innamorati, M. Phytoplankton abundance, community structure and diversity in the eutrophicated Orbetello lagoon (Tuscany) from 1995 to 2001. Oceanol. Acta 2003, 26, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraoui, I.; Grami, B.; Bates, S.S.; Bouchouicha, D.; Chikhaoui, M.A.; Hadj Mabrouk, H.; Sakka Hlaili, A. Response of potentially toxic Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) populations and domoic acid to environmental conditions in a eutrophied, SW Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Tunisia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 102–103, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souchu, P.; Bec, B.; Smith, V.; Laugier, T.; Fiandrino, A.; Benau, L.; Orsoni, V.; Collos, Y.; Vaquer, A. Patterns in nutrient limitation and chlorophyll a along an anthropogenic eutrophication gradient in French Mediterranean coastal lagoons. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 67, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, H.J.; El-Shabrawy, G.M. Seven decades of change in the zooplankton (s.l.) of the Nile Delta lakes (Egypt), with particular reference to Lake Borullus. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, H. The crustacean zooplankton (Copepoda, Branchiopoda, Atyid Decapoda and Syncarida) of the Nile Basin. Nile Monogr. Biol. 2009, 89, 521–545. [Google Scholar]
- Gravili, C.; Belmonte, G.; Cecere, E.; Denitto, F.; Giangrande, F.; Guidetti, P.; Longo, C.; Mastrototaro, F.; Moscatello, S.; Petrocelli, A.; et al. Non-indigenous species (NIS) along the Apulian coast, Italy. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, G.; Potenza, D. Biogeography of the family Acartiidae (Calanoida) in the Ponto-Mediterranean Province. Hydrobiologia 2001, 453/454, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubanova, A. Occurrence of Acartia tonsa Dana in the Black Sea. Was it introduced from the Mediterranean? Mediterr. J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 1, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.A.; Jones, I.D.; Thackeray, S.J. Testing the sensitivity of phytoplankton communities to changes in water temperature and nutrient load, in a temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, V.H.; Adrian, R.; Gerten, D. Phytoplankton response to climate warming modified by trophic state. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Sakai, Y.; Ban, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Ichise, S.; Yamamura, N.; Kumagai, M. Eutrophication and warming effects on long-term variation of zooplankton in Lake Biwa. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, R.; Ráudez, S.; Hooker, E. The Natural Diet of Apocyclops panamensis at a Shrimp Farm on the Pacific Coast of Nicaragua. Zool. Stud. 2004, 43, 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Velde, I. Revision of the African species of the genus Mesocyclops Sars, 1914 (Copepoda: Cyclopidae). Hydrobiologia 1984, 109, 3–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, G.M. Limnological studies on zooplankton and benthos, in the second lake of Wadi El-Rayan, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chertoprud, E.S.; Gheerardyn, H.; Gomez, S. Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Copepoda) of the South China Sea: Faunistic and biogeographical analysis. Hydrobiologia 2011, 666, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, G.M.; Dumont, H.J. Spatial and seasonal variation of the zooplankton in the coastal zone and main khors of Lake Nasser (Egypt). Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, M.M. Ecological studies on zooplankton and macrobenthos of Lake Edku. Ph.D. Thesis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mirabdullayev, I.M.; Defaye, D. On the taxonomy of the Acanthocyclops robustus species complex (Copepoda, Cyclopidae). 1. Acanthocyclops robustus (G. O. Sars, 1863) and Acanthocyclops trajani sp. n. Selevinia 2002, 1, 7–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lescher-Motoué, F. Seasonal variation in size and morphology of Acanthocyclops robustus (Copepoda Cyclopoida). J. Plankton Res. 1996, 8, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramujo, M.J.; Boavida, M.J. Acanthocyclops robustus external morphology: How many morphs? Verh. des Int. Ver. Limnol. 1998, 26, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maghraby, A.M.; Wahby, S.D.; Shaheen, A.H. The ecology of zooplankton in Lake Manzalah. Note Mem. 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, N.; Mageed, A. Some ecological aspects on the zooplankton in Lake Manzalah, Egypt. J. Zool. 2002, 38, 293–307. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.T. The physical and chemical environment of lake Manzalah, Egypt. Hydrobiologia 1990, 196, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.A. Aquatic macrophytes distribution in Lake Manzalah, Egypt. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1997, 5, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, M.; Gauzens, A.L.; Rhineheart, W.K.; White, J. Effects of low oxygen water on Chesapeake Bay zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, H.P. Succession of two Acartia species in estuaries. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1962, 7, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbet, A.; Garrido, S.; Saiz, E.; Alcaraz, M.; Duarte, C.M. Annual zooplankton succession in coastal NW Mediterranean waters: The importance of the smaller size fractions. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffenhöfer, G.A. On the ecology of marine cyclopoid copepods (Crustacea, Copepoda). J. Plankton Res. 1993, 15, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeda, R.; Augustin, C.B.; Alcaraz, M.; Calbet, A.; Saiz, E. Feeding rates and gross growth efficiencies of larval development stages of Oithona davisae (Copepoda, Cyclopoida). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 387, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, G.G.; Barbosa, F.A.R.; Rietzler, A.C.; Maia-Barbosa, P.M. Thermocyclops decipiens (Kiefer, 1929) (Copepoda, Cyclopoida) as indicator of water quality in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.G.; Reis-Oliveira, P.C.; Ybritto, T. Zooplankton assemblages (Copepoda and Cladocera in a cascade of reservoirs of a large tropical river (SE Brazil). Limnetica 2008, 27, 151–170. [Google Scholar]





| Physicochemical Parameters | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | EC mS·cm−1 | Salinity | pH | Oxygen (mg·l−1) | Ammonium (µg·l−1) | Nitrates (µg·l−1) | Nitrites (µg·l−1) | Phosphates (µg·l−1) | Silicates (µg·l−1) | |
| Stations | ||||||||||
| S1 | 17.0 ± 6.4 abc | 5.0 ± 0.3 a | 2.6 ± 0.3 a | 7.7 ± 0.1 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 17264 ± 16874 b | 237.4 ± 59.9 c | 210.7 ± 62.8 c | 383.9 ± 41.2 e | 2.0 ± 0.2 ab |
| S2 | 16.6 ± 6.7 a | 19.3 ± 6.3 c | 11.4 ± 4.0 c | 8.6 ± 0.1 b | 5.5 ± 1.7 bcd | 56.5 ± 9.1 a | 70.0 ± 20.31 ab | 4.4 ± 0.6 a | 72.9 ± 14.2 c | 1.5 ± 0.1 a |
| S3 | 17.0 ± 6.5 a | 5.4 ± 1.5 a | 2.4 ± 0.2 a | 7.7 ± 0.2 a | 4.7 ± 2.2 bc | 399.6 ± 9.7 a | 16.5 ± 3.3 a | 51.8 ± 12.3 b | 160.6 ± 42.6 e | 2.5 ± 0.2 bc |
| S4 | 17.0 ± 7.2 abc | 8.9 ± 5.8 ab | 5.0 ± 3.6 ab | 8.7 ± 0.1 b | 5.9 ± 1.3 cd | 96.6 ± 11.1 a | 59.9 ± 15.7 ab | 4.4 ± 0.9 a | 65.4 ± 16.7 be | 2.9 ± 0.3 c |
| S5 | 18.5 ± 5.9 bcde | 3.9 ± 0.7 a | 1.9 ± 0.4 a | 7.9 ± 0.2 a | 6.6 ± 2. 3 d | 75.4 ± 20.7 a | 83.7 ± 11.9 ab | 6.3 ± 2.9 a | 84.5 ± 10.4 abc | 3.1 ± 0.4 cd |
| S6 | 19.2 ± 6.9 e | 3.3 ± 0.1 a | 1.7 ± 0.1 a | 8.4 ± 0.3 b | 6.8 ± 1.9 d | 72.8 ± 4.8 a | 88.8 ± 4.9 b | 4.7 ± 0.5 a | 32.6 ± 4.8 ab | 2.6 ± 0.4 bc |
| S7 | 18.4 ± 6.6 abcd | 13.8± 12.4 bc | 8.4 ± 7.9 bc | 8.6 ± 0.1 b | 6.9 ± 1.6 d | 82.3 ± 7.9 a | 80.9 ± 39.6 ab | 4.7 ± 1.5 a | 16.9 ± 3.4 a | 3.7 ± 0.5 de |
| S8 | 19.6 ± 7.2 e | 4.6 ± 1.5 a | 2.4 ± 0.9 a | 8.7 ± 0.2 b | 6.4 ± 1.2 cd | 75.5 ± 7.8 a | 81.7 ± 28. 8 ab | 5.5 ± 1.3 a | 49.3 ± 27.5 abc | 3.8 ± 0.9 ef |
| S9 | 19.7 ± 7.3 de | 4.1 ± 0.4 a | 2.1 ± 0.8 a | 8.7 ± 0.4 b | 5.9 ± 0.9 cd | 85.6 ± 19.5 a | 68.9 ± 34.3 ab | 5.9 ± 2.3 a | 23.9 ± 7.4 a | 2.9 ± 0.2 c |
| S10 | 19.7 ± 7.2 cde | 7.9 ± 6.1 ab | 4.5 ± 3.8 ab | 8.5 ± 0.2 b | 6.4 ± 1.7 cd | 84.1 ± 11.1 a | 72.4 ± 34.9 ab | 4.8 ± 0.8 a | 42.7 ± 13.7 abc | 2.9 ± 0.2 c |
| S11 | 18.0 ± 6.3 ab | 5.9 ± 0.6 a | 3.1 ± 0.4 a | 8.9 ± 0.4 a | 3.9 ± 1.2 b | 787.8 ± 234 a | 24.0 ± 7.8 ab | 42.6 ± 10.5 b | 162.1 ± 49.2 d | 4.4 ± 0.5 f |
| F value (df) | 4.9 (10) *** | 4.4 (10) ** | 4.4 (10) ** | 10.6 (10) *** | 12.9 (10) *** | 4.1 (10) ** | 19. 9 (10) *** | 38.9 (10) *** | 91.7 (10) *** | 13.1 (10) *** |
| Seasons | ||||||||||
| Summer | 29.6 ± 1.3 d | 6.2 ± 5.9 | 10.5 ± 8.4 | 8.4 ± 0.4 | 6.3 ± 2.4 b | 477.6 ± 885.1 | 61.9 ± 49.1 a | 28.6 ± 54.3 | 117.1 ± 123.2 b | 3.2 ± 1.1 |
| Autumn | 19.8 ± 0.6 b | 3.7 ± 3.3 | 6.9 ± 5.2 | 8.2 ± 0.4 | 6.4 ± 2.3 b | 2778.7 ± 8281.3 | 100.4 ± 87.5 b | 28.6 ± 54.3 | 94.4 ± 97.6 a | 2.8 ± 0.9 |
| Winter | 13.4 ± 0.6 a | 2.9 ± 1.8 | 5.6 ± 2.9 | 8.4 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 1.7 a | 3295.7 ± 9878.1 | 80.8 ± 49.9 ab | 29.4 ± 52.6 | 81.0 ± 88.4 a | 3.0 ± 0.8 |
| Spring | 23.2 ± 1.2 c | 3.9 ± 4.0 | 6.9 ± 6.4 | 8.3 ± 0.6 | 4.4 ± 1.9 a | 386.7 ± 685.4 | 78.4 ± 51.2 ab | 28.4 ± 46.7 | 92.6 ± 104.5 b | 2.6 ± 0.6 |
| F-value (df) | 969.1 (3) *** | - | - | - | 12.0 (3) *** | - | 4.2 (3) * | - | 4.9 (3) * | - |
| Temperature | EC | Salinity | pH | Oxygen | Silicates | Phosphates | Ammonium | Nitrates | Nitrites | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1 | |||||||||
| EC | −0.480 * | 1 | ||||||||
| Salinity | −0.447 * | 0.998 ** | 1 | |||||||
| pH | 0.459 * | 0.350 | 0.379 | 1 | ||||||
| Oxygen | 0.508 ** | 0.141 | 0.158 | 0.680 ** | 1 | |||||
| Silicates | 0.627 ** | −0.328 | −0.306 | 0.110 | 0.278 | 1 | ||||
| Phosphates | −0.545 ** | −0.184 | −0.204 | −0.757 ** | −0.985 ** | −0.282 | 1 | |||
| Ammonium | −0.400 * | −0.174 | −0.176 | −0.530 ** | −0.907 ** | −0.358 | 0.904 ** | 1 | ||
| Nitrates | −0.207 | −0.117 | −0.100 | −0.218 | −0.637 ** | −0.398 | 0.629 ** | 0.894 ** | 1 | |
| Nitrites | −0.461 * | −0.223 | −0.234 | −0.681 ** | −0.961 ** | −0.309 | 0.971 ** | 0.971 ** | 0.769 ** | 1 |
| Order | Cyclopoida (× 103 ind·m−3) | Calanoida (× 103 ind·m−3) | Harpacticoida (× 103 ind·m−3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Acathocyclops trajani | Thermocyclops consimilis | Mesocyclops ogunnus | Apocyclops panamensis | Oithona nana | Acartia tonsa | Nitocra lacustris | Onychocamptus mohammed | Euterpina acutifrons | H’ |
| Stations | ||||||||||
| S1 | 1.5 ± 2.6 a | 0.5 ± 0.9 ab | - a | - | - | - a | - | - | - | 0.6 a |
| S2 | 1.0 ± 1.0 a | -a | - a | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 3.0 ± 3.0 bc | - | 0.5 ± 0.9 | - | 1.3 b |
| S3 | 2.7 ± 2.8 ab | 1.2 ± 1.3 ab | 0.2 ± 0.4 ab | - | - | - a | 0.2 ± 0.4 | - | - | 1.0 a |
| S4 | 6.5 ± 8.9 ab | -a | - a | - | - | 1.5 ± 1.6 abc | - | - | - | 0.5 a |
| S5 | 0.5 ± 0.9 a | 1.0 ± 1.7 ab | - a | - | - | - a | - | 0.5 ± 0.9 | - | 1.0 a |
| S6 | 1.5 ± 1.6 a | 0.5 ± 0.9 ab | - a | - | - | - a | 1.5 ± 1.6 | - | - | 1.0 a |
| S7 | 0.5 ± 0.9 a | 0.5 ± 0.9 ab | 0.5 ± 0.9 ab | - | - | 37.5 ± 59.2 c | 0.5 ± 0.9 | - | - | 0.2 c |
| S8 | 2.0 ± 1.4 ab | 0.5 ± 0.9 ab | - a | - | - | - a | - | - | - | 0.5 a |
| S9 | 2.0 ± 2.5 a | 1.1 ± 0.9 ab | 1.7 ± 2.1 b | - | - | 0.5 ± 0.9 ab | 2.5 ± 3.8 | - | - | 1.5 b |
| S10 | 1.0 ± 1.0 a | 0.7 ± 1.3 ab | 1.5 ± 2.6 ab | 0.5 ± 0.9 | - | 2.5 ± 0.9 c | - | - | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 1.6 b |
| S11 | 6.2 ± 5.1 b | 3.5 ± 2.6 b | 0.7 ± 1.3 ab | - | - | - a | 0.5 ± 0.9 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | - | 1.1 b |
| F (df) | 3.3 (10) ** | 2.6 (10) * | 2.5 (10) * | - | - | 6.9 (10) *** | - | - | - | 6.6 (10) *** |
| Seasons | ||||||||||
| Summer | 0.2 ± 0.6 a | 0.4 ± 0.8 | - a | - | 0.2 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 1.1 a | 0.2 ± 0.6 | - | - | |
| Autumn | 0.9 ± 1.3 ab | 1.1 ± 1.7 | - a | - | - | 14.0 ± 39.9 b | 0.3 ± 0.6 | - | 0.2 ± 0.6 | |
| Winter | 2.7 ± 4.1 b | 1.6 ± 1.9 | 1.5 ± 2.1 b | - | - | 0.5 ± 1.2 a | 0.2 ± 0.6 | - | - | |
| Spring | 5.4 ± 5.5 c | 0.4 ± 0.8 | 0.2 ± 0.6 a | 0.4 ± 0.8 | - | 1.4 ± 2.3 ab | 1.3 ± 2.4 | 0.5 ± 0.9 | - | |
| F (df) | 16.1 (3) *** | - | 6.5 (3) ** | - | - | 3.8 (3) * | - | - | ||
| Copepod Species | References |
|---|---|
| Acanthocyclops trajani (= A. americanus) | [34,36,76,77] |
| Thermocyclops consimilis | [77] |
| Mesocyclops ougunnus | |
| Apocyclops panamensis | |
| Oithona nana | [34,36] |
| Thermocyclops sp. | [34,36] |
| Nitochra lacustris | [34,36] |
| Onychocamptus mohammed | |
| Euterpina acutifrons | [34,36] |
| Harpacticus sp. | [77,78] |
| Mesochra holdeti | [34,36] |
| Acartia tonsa | |
| Paracalanus parvus | [34,36] |
| Paracartia latisetosa | [76] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Annabi-Trabelsi, N.; El-Shabrawy, G.; Goher, M.E.; Subrahmanyam, M.N.V.; Al-Enezi, Y.; Ali, M.; Ayadi, H.; Belmonte, G. Key Drivers for Copepod Assemblages in a Eutrophic Coastal Brackish Lake. Water 2019, 11, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020363
Annabi-Trabelsi N, El-Shabrawy G, Goher ME, Subrahmanyam MNV, Al-Enezi Y, Ali M, Ayadi H, Belmonte G. Key Drivers for Copepod Assemblages in a Eutrophic Coastal Brackish Lake. Water. 2019; 11(2):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020363
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnnabi-Trabelsi, Neila, Gamal El-Shabrawy, Mohamed E. Goher, Madhavapeddi N. V. Subrahmanyam, Yousef Al-Enezi, Mohammad Ali, Habib Ayadi, and Genuario Belmonte. 2019. "Key Drivers for Copepod Assemblages in a Eutrophic Coastal Brackish Lake" Water 11, no. 2: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020363
APA StyleAnnabi-Trabelsi, N., El-Shabrawy, G., Goher, M. E., Subrahmanyam, M. N. V., Al-Enezi, Y., Ali, M., Ayadi, H., & Belmonte, G. (2019). Key Drivers for Copepod Assemblages in a Eutrophic Coastal Brackish Lake. Water, 11(2), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020363