Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact versus Climate Change on the Succession of the Diatom Community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) Using the Sedimentary Record of Geochemical Elements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Analyses
2.4. Geo-Accumulation Index and Enrichment Factor Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
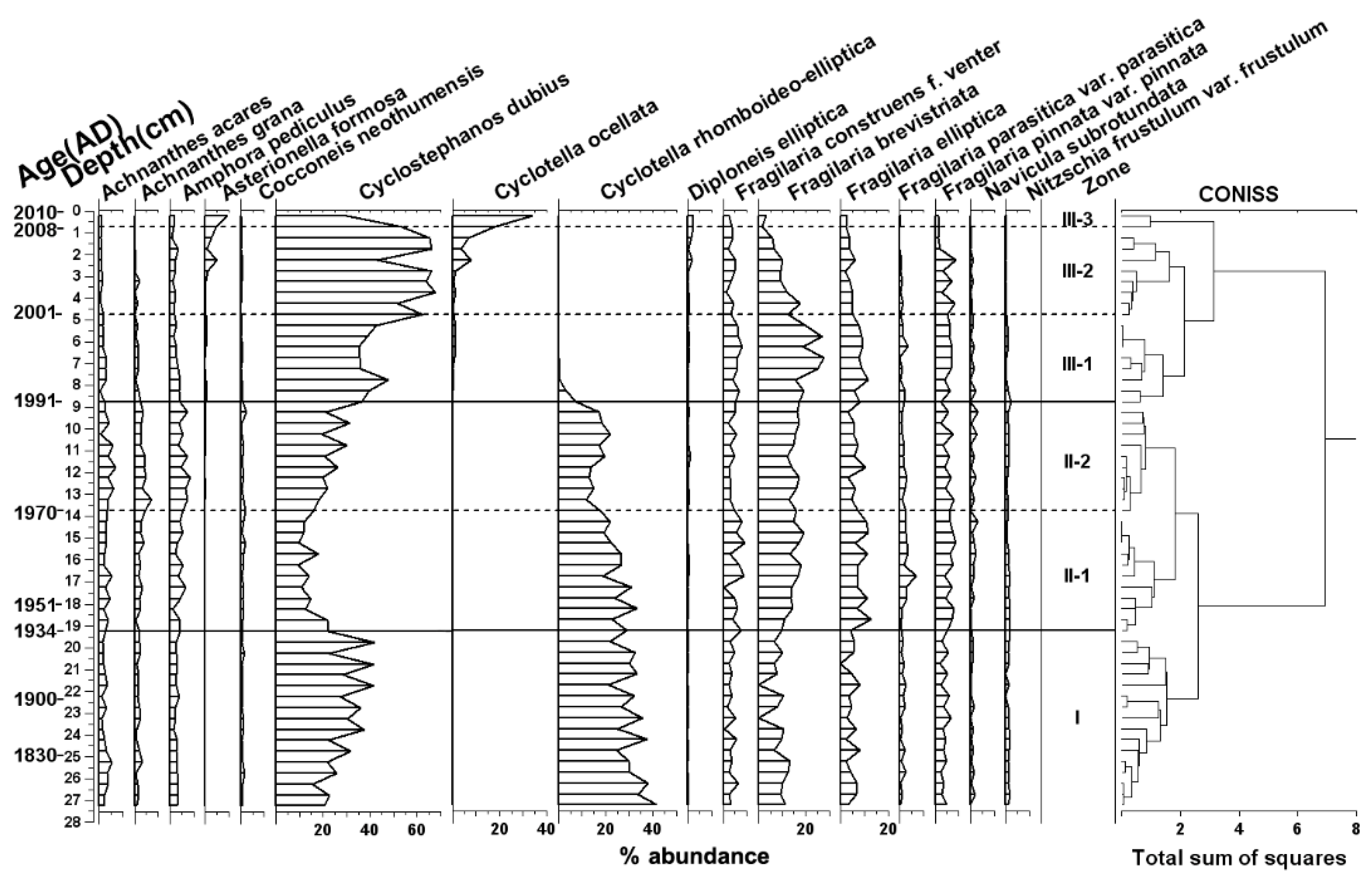
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Records of Geochemical Elements
3.2. Geo-Accumulation Index and Enrichment Factor
4. Discussion
4.1. History of Changes in the Anthropogenic Activities in the Lugu Lake Catchment
4.2. Impact of Human Activity on the Changes of Diatom Assemblages in the Sediments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Mcgowan, S.; Barker, P.; Haworth, E.Y.; Leavitt, P.R.; Maberly, S.C.; Pates, J. Humans and climate as drivers of algal community change in Windermere since 1850. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, S.; Verneaux, V.; Millet, L.; Etienne, D.; Lami, A.; Musazzi, S.; Reyss, J.; Magny, M. Climate and human land-use as a driver of Lake Narlay (Eastern France, Jura Mountains) evolution over the last 1200 years: Implication for methane cycle. J. Paleolimnol. 2016, 55, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, F.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, G. A regional strategy for ecological sustainability: A case study in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 616, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.Z.; Jiang, J.H.; Yang, S. Response of diatom community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) to climate change over the past century. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Anderson, N.J.; Zhang, E.; Li, Y. Diatom response to climate forcing of a deep, alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan, SW China) during the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for understanding regional monsoon variability. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-F.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.-Q. Climate Change in Southwest China during 1961–2010: Impacts and Adaptation. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2013, 4, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, E.; Yu, K.; Xu, H.; Lan, J.; Liu, B.; Che, S. Late Holocene Indian summer monsoon precipitation history at Lake Lugu, northwestern Yunnan Province, southwestern China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 438, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Jin, M. A sediment record of environmental change in and around Lake Lugu, SW China, during the past two centuries. J. Paleolimnol. 2016, 55, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, E.; Zhang, E.; Nath, B.; Shen, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, R. Reconstruction of atmospheric trace metals pollution in Southwest China using sediments from a large and deep alpine lake: Historical trends, sources and sediment focusing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yu, Z.; Moeller, R.E.; Bebout, G.E. Complex trajectories of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem shifts caused by multiple human-induced environmental stresses. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4338–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chraibi, V.L.S.; Kireta, A.R.; Reavie, E.D.; Cai, M.; Brown, T.N. A paleolimnological assessment of human impacts on Lake Superior. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laperriere, L.; Fallu, M.; Hausmann, S.; Pienitz, R.; Muir, D. Paleolimnological evidence of mining and demographic impacts on Lac Dauriat, schefferville (subarctic Quebec, Canada). J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, L.S.; Gussarova, G.; Boessenkool, S.; Olsen, J.; Haile, J.; Schrøder-Nielsen, A.; Ludikova, A.; Hassel, K.; Stenøien, H.K.; Funder, S.; et al. Lake sediment multi-taxon DNA from North Greenland records early post-glacial appearance of vascular plants and accurately tracks environmental changes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 117, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callender, E.; Rice, K.C. The urban environmental gradient: Anthropogenic influences on the spatial and temporal distributions of lead and zinc in sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, M.; Critto, A.; Torresan, S.; Giubilato, E.; Santini, M.; Zirino, A.; Ouyang, W.; Marcomini, A. Modelling climate change impacts on nutrients and primary production in coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 919–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Dou, H.S. Lakes in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; p. 580. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Ma, K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Simulating the impacts of land-use changes on non-point source pollution Lugu Lake watershed. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2008, 15, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, E.; Zhang, E.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Liu, X. Historical variations of atmospheric trace metal pollution in Southwest China: Reconstruction from a 150-year lacustrine sediment record in the Erhai Lake. J. Geochem. Exp. 2017, 172, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ati-Hellal, M.E.; Hellal, F.; Dachraoui, M.; Hedhili, A. Plackett–Burman designs in the pretreatment of macroalgae for Pb, Cr and Al determination by GF-AAS. C. R. Chim. 2007, 10, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audry, S.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Jouanneau, J.M. Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Zheng, L.L.; Liu, B.H.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, X.L. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Sediment of the Main Tributaries of Dongting Lake, China. Water 2018, 10, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Jin, Z.D.; Cao, J.J.; Posmentier, E.S.; An, Z.S. Atmospheric Cu and Pb deposition and transport in lake sediments in a remote mountain area, northern China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 179, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juggins, S. C2 Version 1.5 User Guide: Software for Ecological and Palaeoecological Data Analysis and Visualisatio; University of Newcastle: Newcastle Upon Tyne, UK, 2007; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); Microcomputer Power: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Leps, J.; Smilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; p. 193. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- The R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- Don, R.; Yu, L.; Liu, G. Impact of tourism development on land-cover change in a matriarchal community in the Lugu Lake area. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2008, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F.; Olmos, M.A. Sediment-bound heavy metals as indicators of human influence and biological risk in coastal water bodies. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.A.; Wu, J.L.; Liu, W. Two-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution from Lake Sayram: A deep mountain lake in central Tianshan, China. Quat. Int. 2014, 321, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Zhu, C.Y.; Gao, J.J.; Cheng, K.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.R. Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China: Historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies. Atmosp. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 10127–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.A.; Kahl, J.S. Progress in understanding the chemical stratigraphy of metals in lake sediments in relation to acidic precipitation. Hydrobiologia 1991, 214, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Assessment and Spatial Distribution of Zinc Pollution in Agricultural Soils of Chaoyang, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaalgamaa, S.; Sonninen, E.; Korhola, A.; Weckström, K. Identifying recent sources of organic matter enrichment and eutrophication trends at coastal sites using stable nitrogen and carbon isotope ratios in sediment cores. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.L.; Tang, H.Q.; Cao, Y.M.; Langdon, P.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.D.; Shen, J. The effects of soil erosion on chironomid assemblages in Lugu Lake over the past 120 years. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2013, 98, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, H.; Watanabe, I.; Kuno, K. Investigation of the Heavy Metal Sources in Relation to Automobiles. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 157, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houhou, J.; Lartiges, B.S.; Montargespelletier, E.; Sieliechi, J.; Ghanbaja, J.; Kohler, A. Sources, nature, and fate of heavy metal-bearing particles in the sewer system. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6052–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, N.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Ravisankar, R.; Alagarsamy, R. Statistical assessment to magnetic susceptibility and heavy metal data for characterizing the coastal sediment of East coast of Tamilnadu, India. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2018, 135, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battarbee, R.W. Diatom analysis. In Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology; Berglund, B.E., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1986; p. 527. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, T.J.; Brenner, M.; Jiang, Z.; Curtis, J.H.; Moore, A.M.; Engstrom, D.R.; Wu, Y. Water quality and sediment geochemistry in lakes of Yunnan Province, southern China. Environ. Geol. 1997, 32, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Mu, L.; Dai, L. Water quality of Lugu Lake: Changes, causes and measurements. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2008, 15, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Langdon, P.; Zhang, E. Limnological responses to warming on the Xizang Plateau, Tibet, over the past 200 years. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, H.; Wagner, B. The diatom flora in the ultra-oligotrophic Lake El’gygytgyn, Chukotka. Polar Biol. 2003, 26, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S. Phytoplankton designer—Or how to predict compositional responses to trophic-state change. Hydrobiologia 2000, 424, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Anderson, N.J.; Ji, J. Diatom seasonality and sedimentation in a subtropical alpine lake (Lugu Hu, Yunnan-Sichuan, Southwest China). Antarct. Alp. Res. 2015, 47, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Igeo | Sediment Quality | EF | Sediment Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0 | Unpolluted | <1 | No enrichment |
| 0–1 | Unpolluted to moderately polluted | 1–3 | Minor enrichment |
| 1–2 | Moderately polluted | 3–5 | Moderate enrichment |
| 2–3 | Moderately to highly polluted | 5–10 | Moderately severe enrichment |
| 3–4 | Highly polluted | 10–25 | Severe enrichment |
| 4–5 | Highly to very highly polluted | >25 | Extremely severe enrichment |
| >5 | Very highly polluted |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, S. Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact versus Climate Change on the Succession of the Diatom Community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) Using the Sedimentary Record of Geochemical Elements. Water 2019, 11, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040655
Liu Y, Chen C, Yang S. Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact versus Climate Change on the Succession of the Diatom Community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) Using the Sedimentary Record of Geochemical Elements. Water. 2019; 11(4):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040655
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi, Chuanhong Chen, and Shao Yang. 2019. "Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact versus Climate Change on the Succession of the Diatom Community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) Using the Sedimentary Record of Geochemical Elements" Water 11, no. 4: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040655
APA StyleLiu, Y., Chen, C., & Yang, S. (2019). Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact versus Climate Change on the Succession of the Diatom Community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China) Using the Sedimentary Record of Geochemical Elements. Water, 11(4), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040655





