Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater and Its Suitability for Domestic Uses in Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Iraq
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
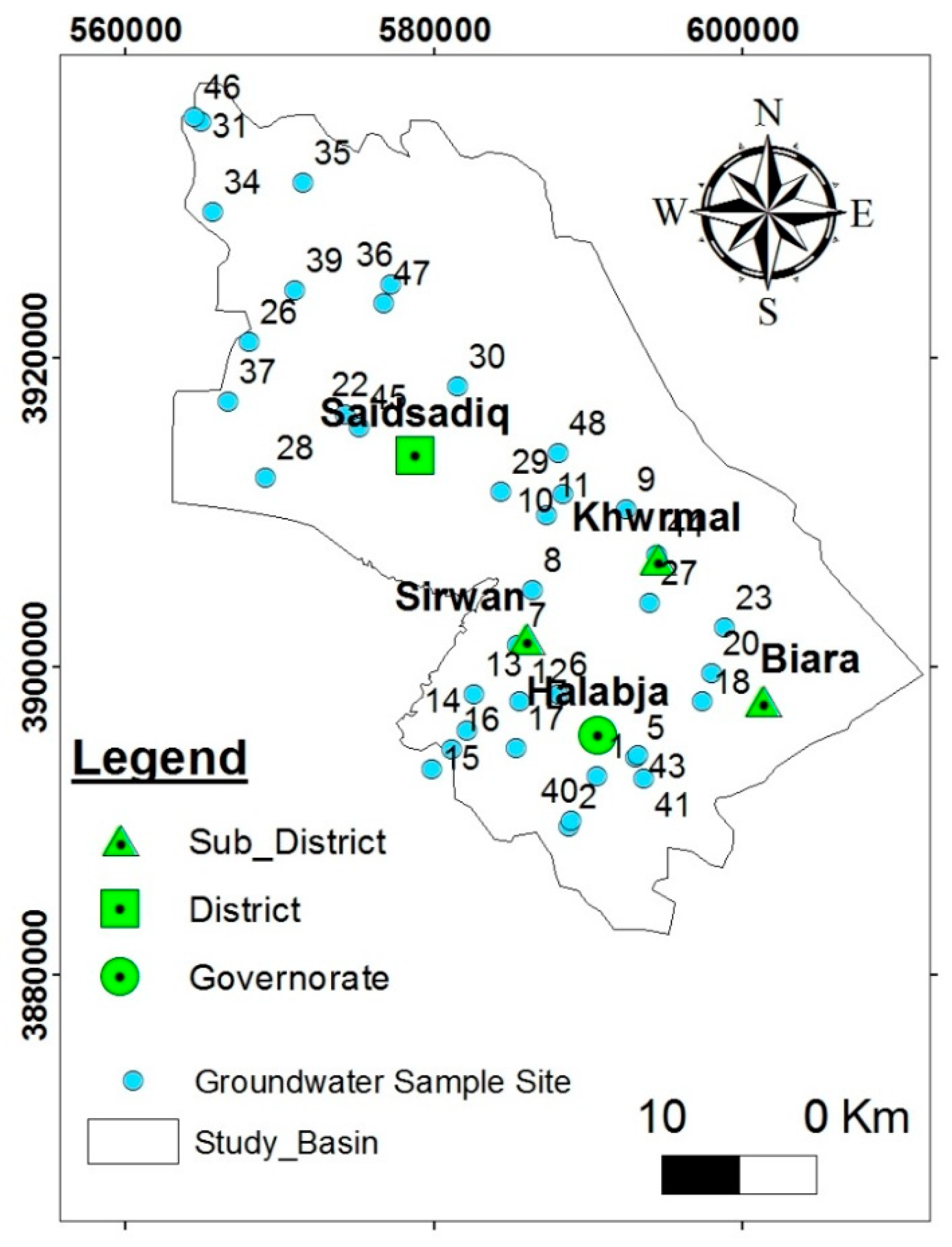
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Hydrogeological Setting
2.3. Uncertainty Measurement of Chemical Analysis
Trueness (Systematic Error) of Chemical Analysis
2.4. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Domestic Purposes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation
Piper Diagram
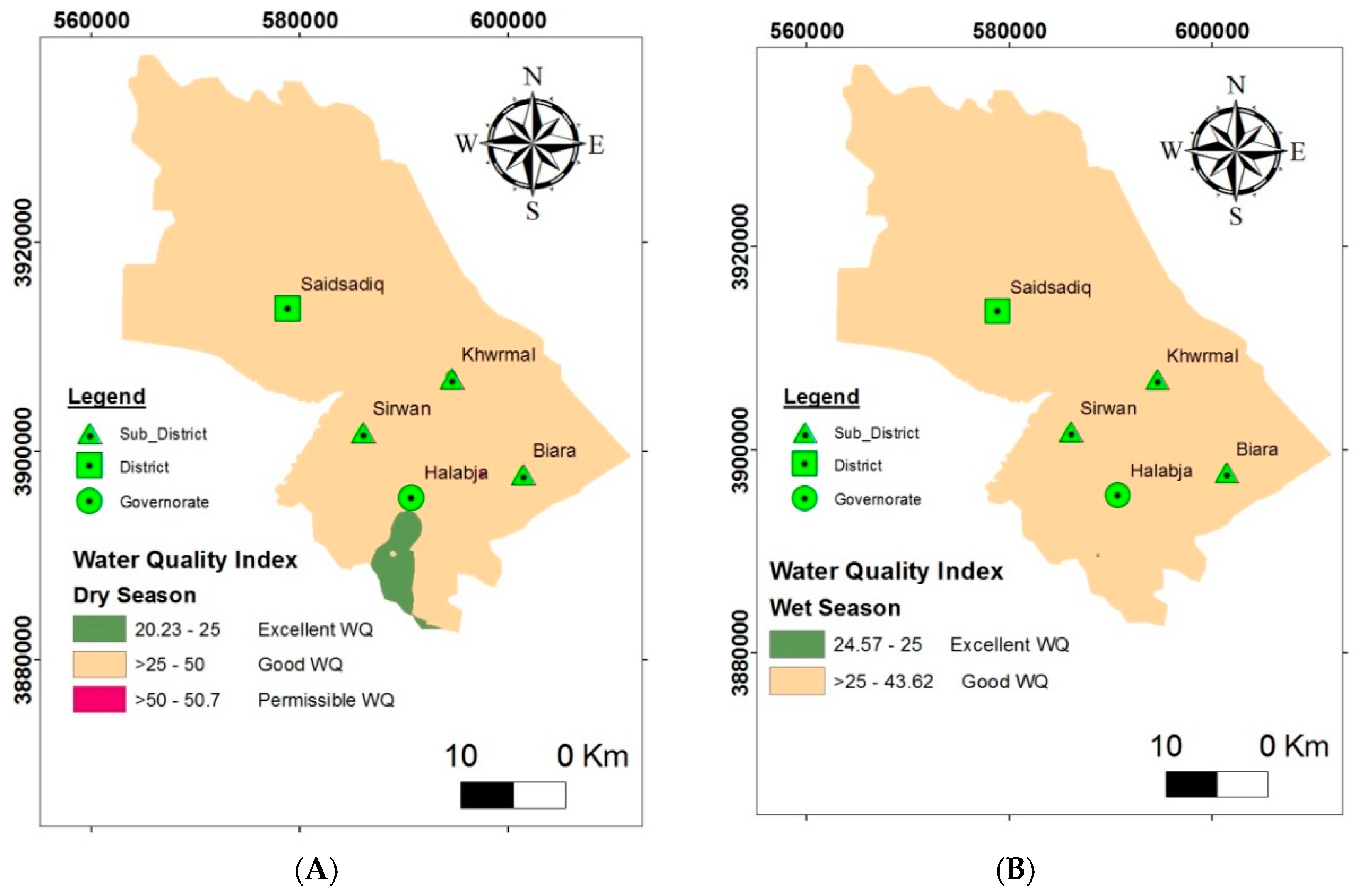
3.2. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Domestic Purposes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mtoni, Y.; Mjemah, I.C.; Bakundukize, C.; Van Camp, M.; Martens, K.; Walraevens, K. Saltwater Intrusion and Nitrate Pollution in the Coastal Aquifer of Dares Salaam, Tanzania. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1091–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakirevich, A.; Weisbrod, N.; Kuznetsov, M.; Rivera Villarreyes, C.A.; Benavent, I.; Chavez, A.M.; Ferrando, D. Modeling the Impact of Solute Recycling on Groundwater Salinization Under Irrigated Lands: A Study of the Alto Piura Aquifer, Peru. J. Hydrol. 2013, 482, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, A.; Hassan, M.Q.; Balke, K.D.; Flegr, M.; Clark, D.W. Groundwater chemistry and occurrence of arsenic in the Meghna flood plain aquifer, southeastern Bangladesh. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, O.; Simsek, C.; Hasozbek, A. Arsenic pollution in the groundwater of Simav plain, Turkey: Its impact on water quality and human health. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 205, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindha, K.; Elango, L. Impact of tanning industries on groundwater quality near ametropolitan city in India. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiem, Z.; Zouari, K.; Chkir, N.; Agoune, A. Geochemical characteristics of arid shallow aquifers in Chott Djerid, south-western Tunisia. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouderbala, A.; Remini, B.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Hydrogeological characterization of the Nador Plio-quaternary aquifer, Tipaza (Algeria). Bol. Geol. Min. 2014, 125, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Houatmia, F.; Azouzi, R.; Charef, A.; Bédir, M. Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical mechanisms evolution in northeastern, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kumar, R.N. Assessment of groundwater quality at a MSW landfill site using standard and AHP based water quality index: A case study from Ranchi, Jharkhand, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Dash, M.K.; Mukherjee, C.K.; Dash, B.; Pokhrel, S. Assessment of water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in the coastal region of Visakhapatnam, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6385–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouderbala, A.; Remini, B.; Saaed, H.A.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Application of multivariate statistical techniques for characterization of groundwater quality in the coastal aquifer of Nador, Tipaza (Algeria). Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 670–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, T.O.; Ali, S.S.; Al-Ansari, N.A.; Knutsson, S. Groundwater Vulnerability Mapping using Lineament Density on Standard DRASTIC Model: Case Study in Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Engineering 2015, 7, 644–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buday, T. Regional Geology of Iraq; Volume 1, Stratigraphy; Kassab, I.I., Jassim, S.Z., Eds.; Directorate General for Geological Survey and Mineral Investigations: Baghdad, Iraq, 1980; p. 445. [Google Scholar]
- Buday, T.; Jassim, S. The Regional Geology of Iraq: Tectonis, Magmatism, and Metamorphism; Kassab, I.I., Abbas, M.J., Eds.; Geological Survey and Mineral Investigations: Baghdad, Iraq, 1987; p. 445. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.S. Geology and Hydrogeology of Sharazoor-Piramagroon Basin in Sulaimani Area, Northeastern Iraq. Unpublished. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade, Beograd, Serbia, 2007; p. 317. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, T.O.; Ali, S.S.; Al-Ansari, N.A. Groundwater assessment of Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Kurdistan region, NE of Iraq using vulnerability mapping. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, S.Z. Geology of Iraq; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2006; p. 340. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, T.O.; Ali, S.S.; Al-Ansari, N.A. Possibility of Groundwater Pollution in Halabja Saidsadiq Hydrogeological Basin, Iraq Using Modified DRASTIC Model Based on AHP and Tritium Isotopes. Geosciences (MDPI) 2018, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A. Geochemical Patterns in the Coachella Valley, California. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1940, 21, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durov, S.A. Natural Waters and Graphic Representation of Their Compositions. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1948, 59, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chadha, D.K. A Proposed New Diagram for Geochemical Classification of Natural Waters and Interpretation of Chemical Data. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods of the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, G. Principles and Application of Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998; p. 600. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines for Drinking–Water Quality, 3rd ed.; WHO: Recommendations, Geneva, 2006; Volume 1, p. 515. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, C.; Raziuddin, M. Studies on the water quality of a water body at Asansol Town, West Bengal. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2007, 6, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Langguth, H.R. Groundwater verhaltisse in Bereiech Des Velberter. In Sattles. Der Minister Fur Eraehrung, Land Wirtsch Forste; NRW: Duesseldorf, Germany, 1966; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Printice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh, R.; Brindha, K.; Elango, L. Groundwater Quality and its Hydrochemical Characteristics in a Shallow Weathered Rock Aquifer of Southern India. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2015, 7, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.K.; Chaudhary, B.S.; Singh, O.; Sethi, G.K.; Thakur, P.K. GIS Based Spatial Distribution Mapping and Suitability Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Domestic and Agricultural Purpose in Kaithal Distirct, Haryana State, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality an Introduction; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; p. 330. [Google Scholar]
- IQS. Iraqi Standards for Drinking Water. Draft of Improving Standards No. 417/1996; Iraqi Government: Baghdad, Iraq, 1996. (in Arabic)
- Brindha, K.; Kavitha, R. Hydrochemical assessment of surface water and groundwater quality along Uyyakondan channel, south India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 73, 5383–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Aquifer | Formation | Thickness (m) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intergranular Aquifer (AIA) | Quaternary deposits | >300 | [12] |
| Fissured Aquifer (CFA) | Balambo Kometan | 250 | [15] |
| Fissured-Karstic Aquifer (CKFA) | Avroman Jurassic formation | 200 80–200 | [17] |
| Karstic Aquifer (TKA) and (JKA) | Avroman Jurassic | 200 80–200 | [17] |
| Non-Aquifer (Aquiclude, Aquitard, and TAT) | Qulqula Shiranish Tanjero | >500 225 2000 | [14] |
| Parameters | Methods |
|---|---|
| TDS | Gravimetric |
| HCO3−, Cl−, TH as CaCO3, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+ | Titration |
| SO42−, NO3− | Colorimetric |
| Parameters | Drinking Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | Weight (wi) | Relative Weight (Wi) | |
| EC (μS/cm) | 1500 | 5 | 0.119 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1000 | 5 | 0.119 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 250 | 5 | 0.119 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 200 | 5 | 0.119 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 150 | 5 | 0.119 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 50 | 5 | 0.119 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 75 | 4 | 0.095 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 100 | 2 | 0.0048 |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 300 | 2 | 0.048 |
| K+ (mg/L) | 12 | 1 | 0.024 |
| pH | 8.5 Total | 3 Ʃwi = 42 | 0.071 Ʃwi = 1 |
| Class | Range of WQI for Drinking Purposes | Type of Water Quality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | <25 | Excellent water quality |
| 2 | 25.1–50 | Good water quality |
| 3 | 50.1–75 | Permissible water quality |
| 4 | 75.1–100 | Doubtful water quality |
| 5 | 100 | Water unsuitable for drinking uses |
| Parameters | Dry Season | Wet Season | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | Min. | Average | SD | Max. | Min. | Average | SD | |
| EC | 1430.00 | 356.00 | 568.03 | 236.21 | 2400.00 | 264.00 | 517.11 | 380.10 |
| TDS | 630.00 | 16.80 | 20.21 | 1.83 | 550.00 | 120.00 | 211.10 | 76.30 |
| TH | 454.60 | 210.00 | 331.20 | 50.60 | 429.00 | 190.40 | 312.30 | 47.60 |
| pH | 8.20 | 7.26 | 7.72 | 0.26 | 8.08 | 6.48 | 7.66 | 0.26 |
| Cl (mg/L) | 49.40 | 17.30 | 33.91 | 8.30 | 45.40 | 14.20 | 29.06 | 7.43 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 116.00 | 5.90 | 34.60 | 30.10 | 110.20 | 4.00 | 30.30 | 28.22 |
| Na (mg/L) | 43.00 | 2.00 | 11.20 | 9.90 | 39.50 | 1.80 | 10.08 | 9.60 |
| NO3 (mg/L) | 51.60 | 0.00 | 11.76 | 13.67 | 58.00 | 6.10 | 31.33 | 15.52 |
| Mg (mg/L) | 79.90 | 4.32 | 31.23 | 14.50 | 76.40 | 3.00 | 28.90 | 14.10 |
| Ca(mg/L) | 145.50 | 38.50 | 78.63 | 23.96 | 140.20 | 34.30 | 75.02 | 23.30 |
| HCO3 (mg/L) | 312.50 | 180.50 | 237.61 | 37.89 | 314.20 | 182.10 | 244.20 | 38.42 |
| K (mg/L) | 6.00 | 0.02 | 2.00 | 1.40 | 4.00 | 0.02 | 1.50 | 1.10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, T.O.; Ali, S.S.; Al-Ansari, N.A.; Knutsson, S. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater and Its Suitability for Domestic Uses in Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Iraq. Water 2019, 11, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040690
Abdullah TO, Ali SS, Al-Ansari NA, Knutsson S. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater and Its Suitability for Domestic Uses in Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Iraq. Water. 2019; 11(4):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040690
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Twana O., Salahalddin S. Ali, Nadhir A. Al-Ansari, and Sven Knutsson. 2019. "Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater and Its Suitability for Domestic Uses in Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Iraq" Water 11, no. 4: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040690
APA StyleAbdullah, T. O., Ali, S. S., Al-Ansari, N. A., & Knutsson, S. (2019). Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater and Its Suitability for Domestic Uses in Halabja Saidsadiq Basin, Iraq. Water, 11(4), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040690







