The System Evaluation of Grain Production Efficiency and Analysis of Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
2.1. DEA Method
2.2. Malmquist Index Method
2.3. LMDI Method
2.4. Construction of the SD Model for Grain Production
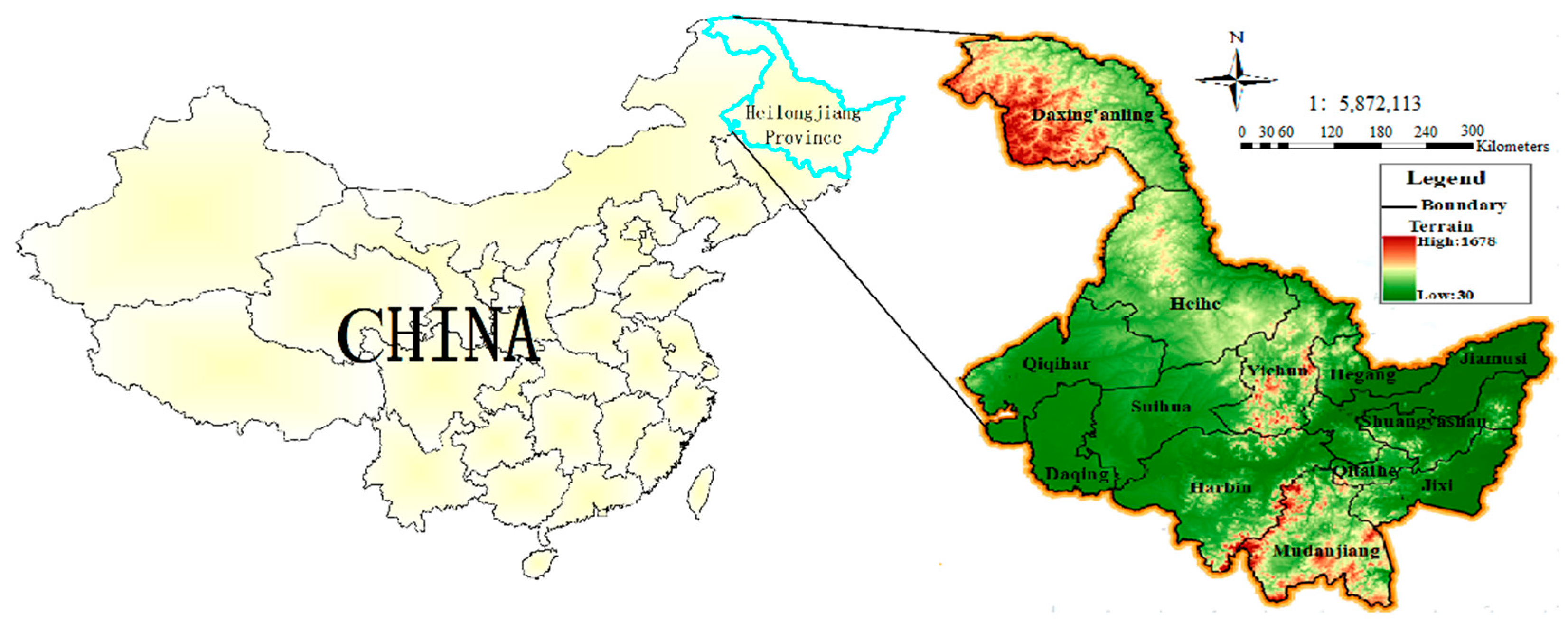
2.5. General Situations of the Study Region and Data Sources
2.5.1. General Situations of the Study Region
2.5.2. Data Sources
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Simulation of the SD Model for Grain Production
3.2. Analysis of Grain Production Efficiency in Heilongjiang Province at the Provincial Level
3.3. Analysis of Grain Production Efficiency in Heilongjiang Province at the National Level
3.4. Grain Production Efficiency Drivers and Forecast
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Fu, Q.; Li, M.; Faiz, M.A.; Khan, M.I.; Li, T.; Cui, S. Construction and application of a refined index for measuring the regional matching characteristics between water and land resources. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, Y. Simulating the Evolution of the Land and Water Resource System under Different Climates in Heilongjiang Province, China. Water 2018, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Clarke-Sather, A.; Ma, J.; Qu, J. Estimating Changes in the Green Water Productivity of Cropping Systems in Northern Shaanxi Province in China’s Loess Plateau. Water 2018, 10, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiertz, J.H.J.; Ewert, F. Crop production and resource use to meet the growing demand for food, feed and fuel: Opportunities and constraints. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2009, 56, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.F.F.P.; Smit, A.L.; Schröder, J.J. Is agricultural intensification in The Netherlands running up to its limits? NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2013, 66, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatemeh, K.; Arjen, H. Informing National Food and Water Security Policy through Water Footprint Assessment: The Case of Iran. Water 2017, 9, 831. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yue, T.; Wang, C.; Wilson, J.P. Using models and spatial analysis to analyze spatio-temporal variations of food provision and food potential across China’s agro-ecosystems. Ecol. Model. 2015, 306, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. A framework of indicator system for zoning of agricultural water and land resources utilization: A case study of Bayan Nur, Inner Mongolia. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosegrant, M.W.; Paisner, M.S.; Meijer, S.; Witcover, J. Global Food Projections to 2020: Emerging Trends and Alternative Futures; Implications Investment vision Discussion Paper; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, I.M.; Parveen, S. Food security in the face of climate change, population growth, and resource constraints: Implications for Bangladesh. Environ. Manag. 2004, 34, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.J.; Li, X.B.; Tan, M.H. Changes of comparative advantages of regional grain production in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 222–227, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J.D. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Irwin-McGraw Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Forrester, J.W. Industrial dynamics. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilmann, C.; Hennersdorf, J.; Lehmann, I.; Reißmann, D. Data envelopment analysis of urban efficiency—Interpretative methods to make DEA a heuristic tool. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanna, C.G.; Stefano, P. Data Envelopment Analysis of sustainability indicators of European agricultural systems at regional level. Agric. Syst. 2013, 118, 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul, W.; Ben, W. Farm household efficiency in Bangladesh: A comparison of stochastic frontier and DEA methods. Appl. Econ. 2000, 32, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar]
- Haji, J. Production efficiency of smallholders’ vegetable-dominated mixed farming system in eastern ethiopia: A non-parametric approach. J. Afr. Econ. 2007, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanopoulos, K.; Abas, Z.; Laga, V.; Hatziminaoglou, I.; Boyazoglu, J. The technical efficiency of transhumance sheep and goat farms and the effect of EU subsidies: Do small farms benefit more than large farms? Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 99, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.L.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L. Application of the DEA on the performance evaluation of the agricultural support policy in China. Agric. Econ. 2017, 63, 510–523. [Google Scholar]
- Atici, K.B.; Podinovski, V.V. Using data envelopment analysis for the assessment of technical efficiency of units with different specialisations: An application to agriculture. Omega 2015, 54, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; He, X.; Li, J. Efficiency change in North-East China agricultural sector: A DEA approach. Agric. Econ. Czech. 2015, 61, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Li, X. The evaluation on agricultural support level of agricultural policy in China. China Soft Sci. 2006, 7, 33–41, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some models for estimating technological and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fare, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Norris, M. Productivity growth, technical progress, and efficiency change in industrialized countries: Reply. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 87, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Yunos, J.M.; Hawdon, D. The efficiency of the National Electricity Board in Malaysia: An intercountry comparison using DEA. Fuel Energy Abstr. 1997, 19, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: Which is the preferred method. Energy Policy 2004, 32, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: A practical guide. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilongjiang Statiscal Bureau. Heilongjiang Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Heilongjiang Water Conservancy Department. Heilongjiang Province Water Resources Bulletin; Heilongjiang People’s Publishing House: Harbin, China, 2016.
- State Statistical Bureau. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Schouten, G.; Vink, M.; Vellema, S. Institutional diagnostics for African food security: Approaches, methods and implications. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2018, 84, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Huo, Y. A study on research hot-spots and frontiers of agricultural science and technology innovation-visualization analysis based on the Citespace III. Agric. Econ. 2016, 62, 429–445. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Nie, P.Y.; Yang, Y.C. Effects of corporate social responsibility on food safety. Agric. Econ. 2017, 63, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Demartini, E.; Gaviglio, A.; Pirani, A. Farmers’ motivation and perceived effects of participating in short food supply chains: Evidence from a North Italian survey. Agric. Econ. 2017, 63, 204–216. [Google Scholar]
- Speelman, S.; Buysse, J.; Farolfi, S.; Frija, A.; D’Haese, M.; D’Haese, L. Estimating the impacts of water pricing on smallholder irrigators in North West Province, South Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Objective | Index | Index Selection Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of food production efficiency | Grain output | Foodstuff output |
| Rural population | Labor force input | |
| Total power of agricultural machinery | Capital input | |
| Agricultural water demand | Water resource input | |
| Sown area of the crops | Land resource input |
| Projects | Units | 2003 | 2005 | 2007 | 2009 | 2011 | 2013 | 2015 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume of water resources | Simulated value | 108 m³ | 245 | 267 | 296 | 308 | 353 | 374 | 348 |
| Actual value | 108 m³ | 246 | 272 | 291 | 316 | 352 | 362 | 355 | |
| Error | % | −0.33 | −1.84 | 1.43 | −2.50 | 0.13 | 3.32 | −2.02 | |
| Quantity of groundwater resources | Simulated value | 108 m³ | 275 | 269 | 222 | 311 | 240 | 379 | 282 |
| Actual value | 108 m3 | 292 | 289 | 233 | 313 | 237 | 382 | 282 | |
| Error | % | −5.70 | −6.78 | −4.49 | −0.86 | 1.37 | −0.57 | −0.11 | |
| Effective irrigated area | Simulated value | 104 hm2 | 225 | 252 | 294 | 355 | 437 | 539 | 551 |
| Actual value | 104 hm2 | 211 | 239 | 295 | 341 | 434 | 534 | 553 | |
| Error | % | 6.55 | 5.34 | −0.28 | 4.25 | 0.69 | 0.83 | −0.35 | |
| GDP | Simulated value | 108 Yuan | 3861 | 5421 | 7015 | 8338 | 13,045 | 15,150 | 15,491 |
| Actual value | 108 Yuan | 4057 | 5514 | 7104 | 8587 | 12,582 | 14,455 | 15,490 | |
| Error | % | −4.85 | −1.68 | −1.25 | −2.90 | 3.68 | 4.81 | 0.01 | |
| Urbanization rate | Simulated value | % | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 57 | 58 | 58 |
| Actual value | % | 53 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 59 | |
| Error | % | −0.20 | 0.40 | 0.41 | −1.31 | 0.94 | 1.10 | −1.04 | |
| Area | Technical Efficiency | Pure Technical Efficiency | Scale Efficiency | Economies of Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbin | 0.991 | 1 | 0.991 | Decreasing |
| Qiqihar | 0.836 | 0.923 | 0.905 | Decreasing |
| Jixi | 1 | 1 | 1 | Constant |
| Hegang | 1 | 1 | 1 | Constant |
| Shuangyashan | 0.924 | 0.927 | 0.997 | Decreasing |
| Daqing | 0.806 | 1 | 0.806 | Increasing |
| Yichun | 1 | 1 | 1 | Constant |
| Jiamusi | 0.821 | 1 | 0.821 | Increasing |
| Qitaihe | 1 | 1 | 1 | Constant |
| Mudanjiang | 0.886 | 1 | 0.886 | Increasing |
| Heihe | 0.733 | 0.74 | 0.991 | Increasing |
| Suihua | 1 | 1 | 1 | Constant |
| Daxing’anling | 1 | 1 | 1 | Constant |
| Provincial average value | 0.923 | 0.968 | 0.954 |
| Rank | Area | Tfpch | Effch | Techch | Pech | Sech | Area | Tfpch | Effch | Techch | Pech | Sech | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shandong | 1.65 | 1.20 | 1.38 | 1.00 | 1.20 | Tibet | 0.94 | 0.69 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 0.69 | 17 |
| 2 | Henan | 1.53 | 1.20 | 1.27 | 1.00 | 1.20 | Xinjiang | 0.91 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 1.04 | 1.00 | 18 |
| 3 | Beijing | 1.51 | 1.11 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 1.11 | Chongqing | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 19 |
| 4 | Hebei | 1.48 | 1.06 | 1.39 | 0.95 | 1.11 | Shanxi | 0.89 | 0.86 | 1.04 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 20 |
| 5 | Tianjin | 1.47 | 1.08 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 1.08 | Jiangxi | 0.88 | 1.13 | 0.78 | 1.13 | 1.00 | 21 |
| 6 | Inner Mongolia | 1.31 | 1.37 | 0.95 | 1.44 | 0.95 | Yunnan | 0.83 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 1.12 | 22 |
| 7 | Shanxi | 1.17 | 0.96 | 1.22 | 1.01 | 0.96 | Hunan | 0.82 | 0.79 | 1.04 | 0.71 | 1.11 | 23 |
| 8 | Zhejiang | 1.07 | 0.79 | 1.36 | 0.80 | 0.98 | Fujian | 0.78 | 0.73 | 1.07 | 0.74 | 0.98 | 24 |
| 9 | Shanghai | 1.05 | 1.40 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.40 | Guangdong | 0.77 | 0.70 | 1.10 | 0.68 | 1.02 | 25 |
| 10 | Jiangsu | 1.03 | 0.91 | 1.13 | 0.80 | 1.14 | Hubei | 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 0.78 | 0.99 | 26 |
| 11 | Liaoning | 1.01 | 0.88 | 1.14 | 0.88 | 1.00 | Hainan | 0.66 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.52 | 1.39 | 27 |
| 12 | Qinghai | 1.00 | 0.74 | 1.36 | 0.64 | 1.16 | Guangxi | 0.62 | 0.58 | 1.08 | 0.59 | 0.98 | 28 |
| 13 | Gansu | 0.99 | 0.95 | 1.04 | 0.95 | 1.00 | Sichuan | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.98 | 29 |
| 14 | Heilongjiang | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 1.03 | Guizhou | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.86 | 0.64 | 1.03 | 30 |
| 15 | Ningxia | 0.98 | 0.83 | 1.19 | 1.57 | 0.53 | Anhui | 0.23 | 0.62 | 0.37 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 31 |
| 16 | Jilin | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | National Average | 0.921 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 1.03 | 0.88 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z. The System Evaluation of Grain Production Efficiency and Analysis of Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province. Water 2019, 11, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051073
Zhao Y, Jiang Q, Wang Z. The System Evaluation of Grain Production Efficiency and Analysis of Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province. Water. 2019; 11(5):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051073
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Youzhu, Qiuxiang Jiang, and Zilong Wang. 2019. "The System Evaluation of Grain Production Efficiency and Analysis of Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province" Water 11, no. 5: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051073
APA StyleZhao, Y., Jiang, Q., & Wang, Z. (2019). The System Evaluation of Grain Production Efficiency and Analysis of Driving Factors in Heilongjiang Province. Water, 11(5), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051073





