Influence of Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbial Ecology and Sanitary Threat in the Final Stretch of the Brda River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Strategy
2.3. Physico-Chemical Parameters of Water
2.4. Abundance of Planktonic Bacteria
- X—number of bacterial cells per 1cm3 of water
- N—number of cells in a field of view
- S—effective area of filtration
- s—analyzed area of the field of view
- V—volume of filtered sample
- R—sample dilution
2.5. Distribution of Faecal Bacteria
2.6. Antimicrobial Resistance
2.7. The Rate of Organic Carbon Oxidation by the Planktonic Bacteria
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A Guide to the Natural History of Freshwater Lake Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Dittel, A.I.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Fischer, D. Changes in bacterial activity and community structure in response to dissolved organic matter in the Hudson River, New York. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiersztyn, B.; Siuda, W.; Chróst, R.J. Persistence of bacterial proteolytic enzymes in lake ecosystems. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2012, 80, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krevš, A.; Kučinskienė, A. Influence of invasive Acer negundo leaf litter on benthic microbial abundance and activity in the littoral zone of a temperate river in Lithuania. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2017, 418, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perliński, P.; Mudryk, Z.J.; Antonowicz, J. Enzymatic activity in the surface microlayer and subsurface water in the harbour channel. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 196, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, N.; Chen, L.; Jiang, C.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Xue, D. Structure and se-asonal dynamics of bacterial communities in three urban rivers in China. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal variation of planktonic and sediment bacterial assemblages in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic status. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4161–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krevš, A.; Kučinskienė, A. Microbial decomposition of sedimentary organic matter in small temperate lakes. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2018, 191, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H. Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 143–169. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.D. Recent findings on the viable but nonculturable state in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.D. The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Senjarini, K.; Karsten, U.; Schumann, R. Application of Fluorescence Markers for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Abundance and Viability in Aquatic Ecosystem. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 3, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, H.; Ren, J.; Song, L.; Sun, S.; An, L. Diverse tetracycline resistant bacteria and resi-stance genes from coastal waters of Jiaozhou Bay. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 55, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.; Manivasagan, S.; Ashokkumar, S.; Rajaram, G.; Mayavu, P. Plasmid profiling and multiple antibiotic resistance of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from Muthupettai mangrove environment, southeast coast of India. Curr. Res. Bacteriol. 2010, 3, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Costanzo, S.D.; Murby, J.; Bates, J. Ecosystem response to antibiotic entering the aquatic environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, G.; Bernaś, R.; Dębowski, P.; Morzuch, J.; Skóra, M. Fish fauna of the Brda river system. Sci. Annu. Pol. Angling Assoc. 2015, 28, 43–84. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9308-1:2014. Water Quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria—Part 1 Membrane Filtration Method for Waters with Low Bacterial Background Flora; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 7899-2:2000. Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Intestinal Enterococci—Part 2: Membrane Filtration Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 8.1. 2018. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Sepers, A.B.J. The aerobic mineralization of organic compounds in the saline Lake Grevelingen (The Netherlands) (VI). Hydrobiol. Bull. 1979, 13, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Mayorga, E.; Raymond, P.A.; Melack, J.M.; Doney, S.C.; Alin, S.R.; Aalto, R.E.; Yoo, K. Riverine coupling of biogeochemical cycles between land, oceans, and atmosphere. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Heinrich, F.; Bertilsson, S. Coherent dynamics and association networks among lake bacterioplankton taxa. ISME J. 2012, 6, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, T.C.; Schmitz Fontes, M.L.; Harrison, D.P.; Van-Dongen-Vogels, V.; Eyre, B.D.; Ralph, P.J.; Seymour, J.R. Bacterioplankton Dynamics within a Large Anthropogenically Impacted Urban Estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, R.L.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Jeffries, T.; Westhorpe, D.; Curlevski, N.; Seymour, J.R. River bacterioplankton community responses to a high inflow event. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 75, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmysłowska, I.; Gołaś, I. Sanitary and bacteriological examinations of lake Oświn water. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2003, 12, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Mao, G.; Liu, J.; Gao, G.; Zou, C.; Bartlam, M.G.; Wang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Chan-ges of Bacterioplankton Community along an Exhorheic River. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donderski, W.; Wilk, I. The Sanitary State of Water in the River Vistula between Wyszogród and Toruń. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2002, 11, 509–515. [Google Scholar]
- Strauch, A.M. Seasonal variability in faecal bacteria of semiarid rivers in the Serengeti National Park, Tanzania. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela-Alonso, P.; Pérez-Uz, B.; Sanchez-Jimenez, A.; Murciano, A.; Centeno, J.D.; García-Rodríguez, M.; Montero, E.; Muñoz, B.; Olmedo, C.; Refoyo, P.; et al. Complexity of river ciliate communities at a national park highlights the need for microbial conservation. Aquat. Conserv.: Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleò, M.M.; Benedetti, D.; Tafi, M.C.; Signoretto, C.; Canepari, P. Inhibition of the resusci-tation from the viable but non-culturable state in Enterococcus faecalis. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, T.; Ghosh, A.; Pazhani, G.P.; Shinoda, S. Current perspectives on viable but non-culturable (VBNC) pathogenic bacteria. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, P.; Schmidt-Emrich, S.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Critical aspects of using bac-terial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perliński, P.; Skórczewski, P.; Zdanowicz, M.; Mudryk, Z. Participation of MEM + bacte-ria in the bacterioplankton community in Ustka harbor, the River Słupia estuary, Southern Baltic Sea. Eur. J. Biol. Res. 2015, 5, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Haglund, A.L.; Lantz, P.; Törnblom, E.; Tranvik, L. Depth distribution of active bacteria and bacterial activity in lake sediment. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 2003, 46, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.; Diaper, J.; Edwards, C.; Pickup, R. Direct Measurements of Natural Planktonic Bacterial Community Viability by Flow Cytometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2783–2786. [Google Scholar]
- Swiontek-Brzezinska, M.; Lalke-Porczyk, E.; Donderski, W.; Walczak, M. Occurrence and activity of microorganisms in shrimp waste. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, M.; Freese, H.M.; Schumann, R. Bacterial Activity and Bacterioplankton Diversity in the Eutrophic River Warnow-Direct Measurement of Bacterial Growth Efficiency and Its Effect on Carbon Utilization. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdanowicz, M.; Mudryk, Z.J. Abundance, production and respiration of bacterioneu-ston and bacterioplankton in the coastal lake Dołgie Wielkie. Balt. Coast. Zone 2017, 21, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kubera, Ł.; Donderski, W. Distribution and activity of benthic bacteria in four lakes in the Bory Tucholskie National Park (Poland). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 79, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, C.; Gould, T.J.; Wang, P.; Phillips, J.; Cotner, J.B.; Sadowsky, M.J. Species sorting and seasonal dynamics primarily shape bacterial communities in the Upper Mississippi River. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance; Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Park, M.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, Y.H. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli fecal isolates from healthy persons and patients with diarrhea. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2011, 2, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudryk, Z.J.; Perliński, P.; Robak, D. Antibiotic resistance of fecal coliform bacteria in-habiting sea water and sand of marine recreation beach in the southern Baltic Sea. Balt. Coast. Zone 2016, 20, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda-Jauregui, A.; Hoyos-Santillan, J.; Gutierrez-Mendieta, F.J.; Torres-Alvarado, R.; Dendooven, L.; Thalasso, F. The impact of anthropogenic pollution on limnological characteristics of a subtropical highland reservoir “Lago de Guadalupe”, Mexico. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2013, 410, 04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boon, P.I.; Cattanach, M. Antibiotic resistance of native and faecal bacteria isolated from rivers, reservoirs and sewage treatment facilities in Victoria, south-eastern Australia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 28, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, A.; Cole, Z.; Bhattacharya, A.; Oyibo, O. Presence of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents Utilized as Water Reuse for Irrigation. Water 2018, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
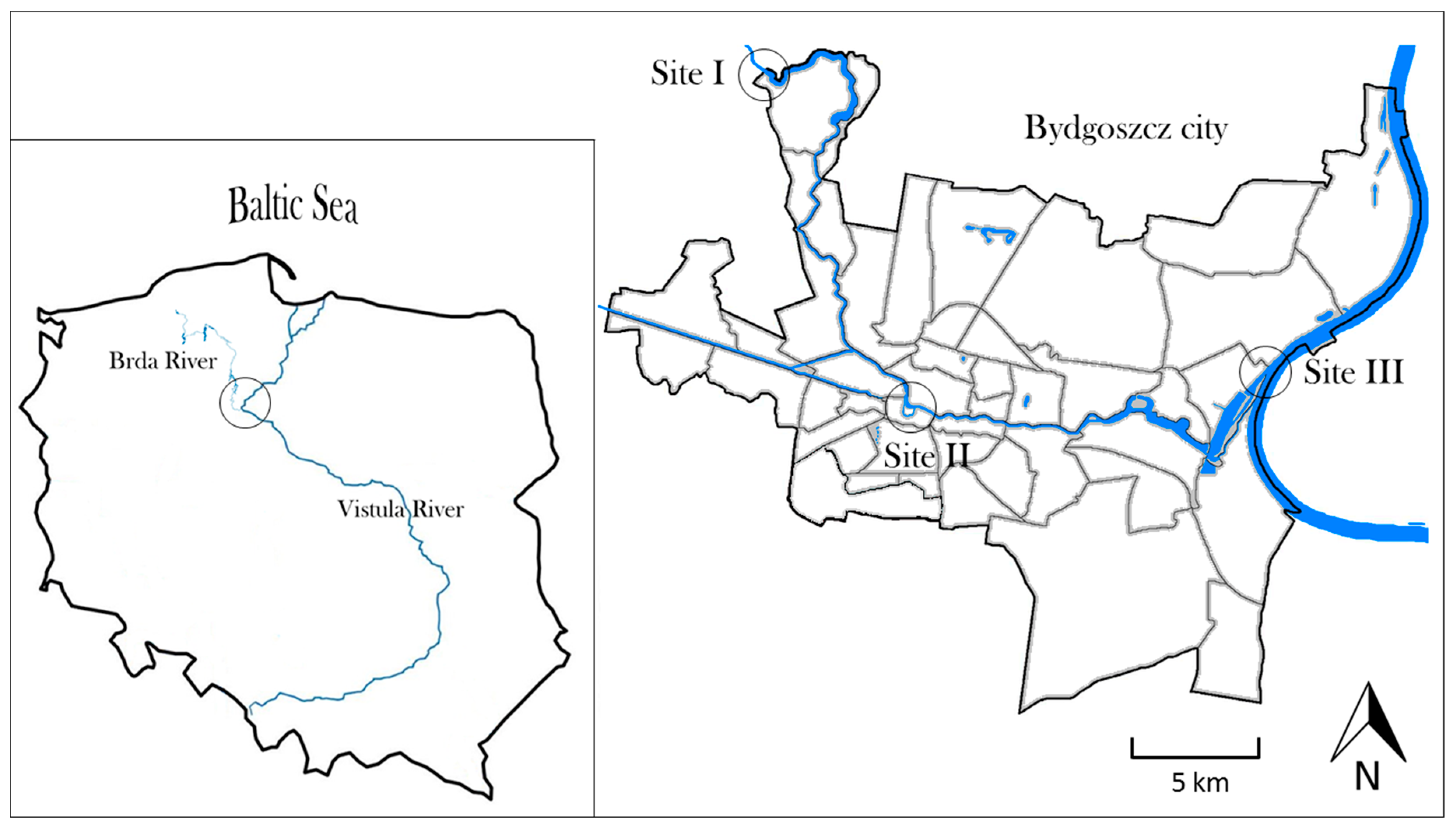
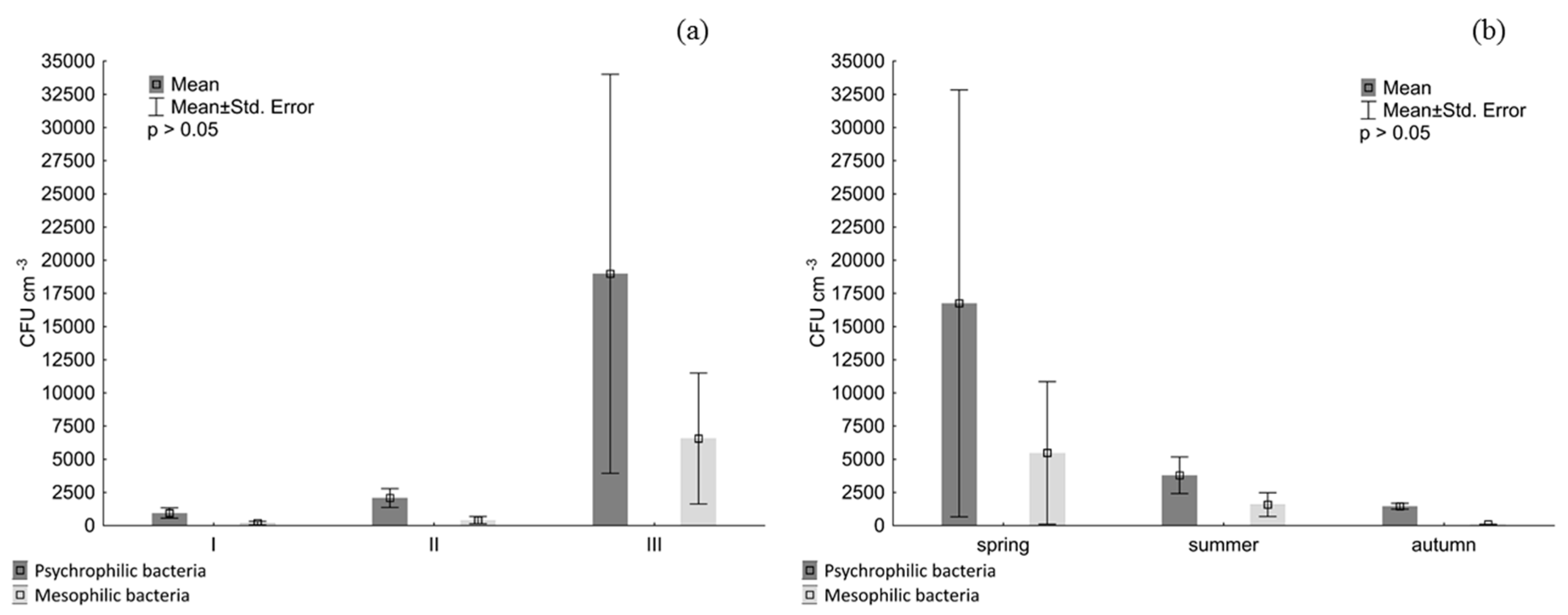
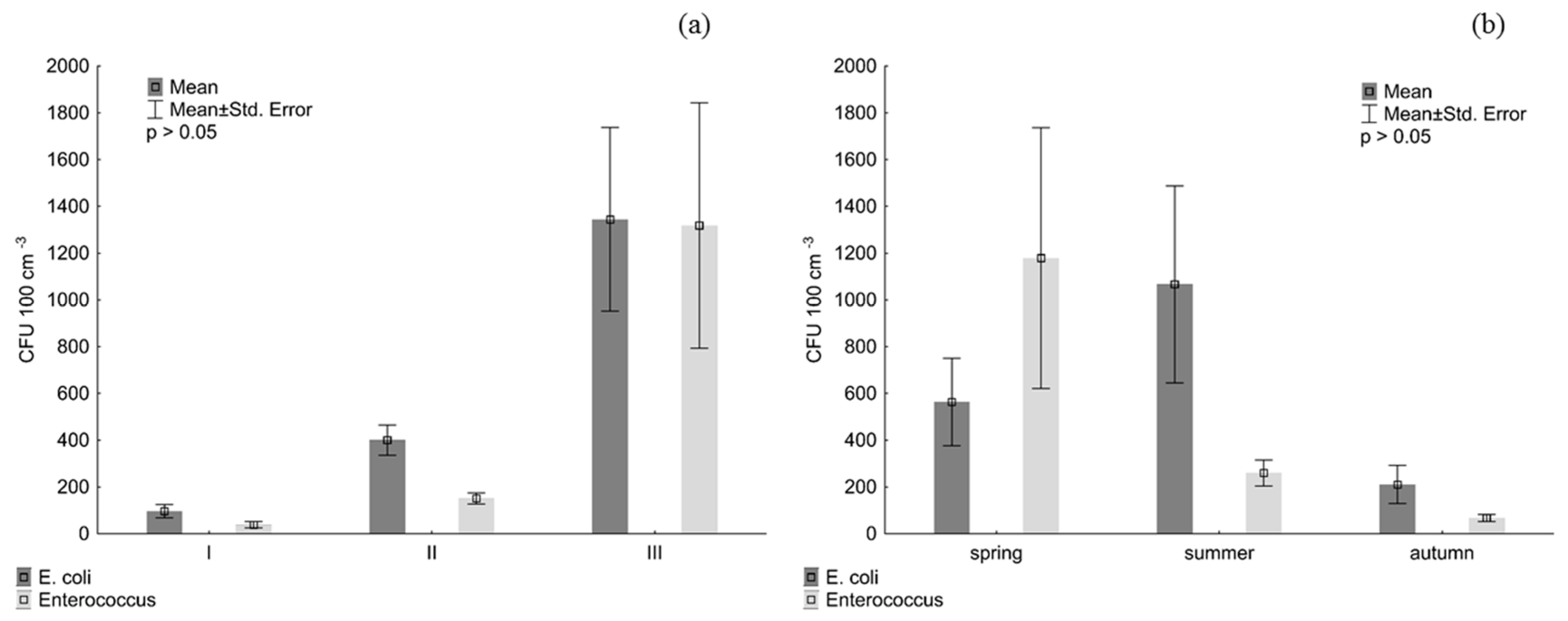
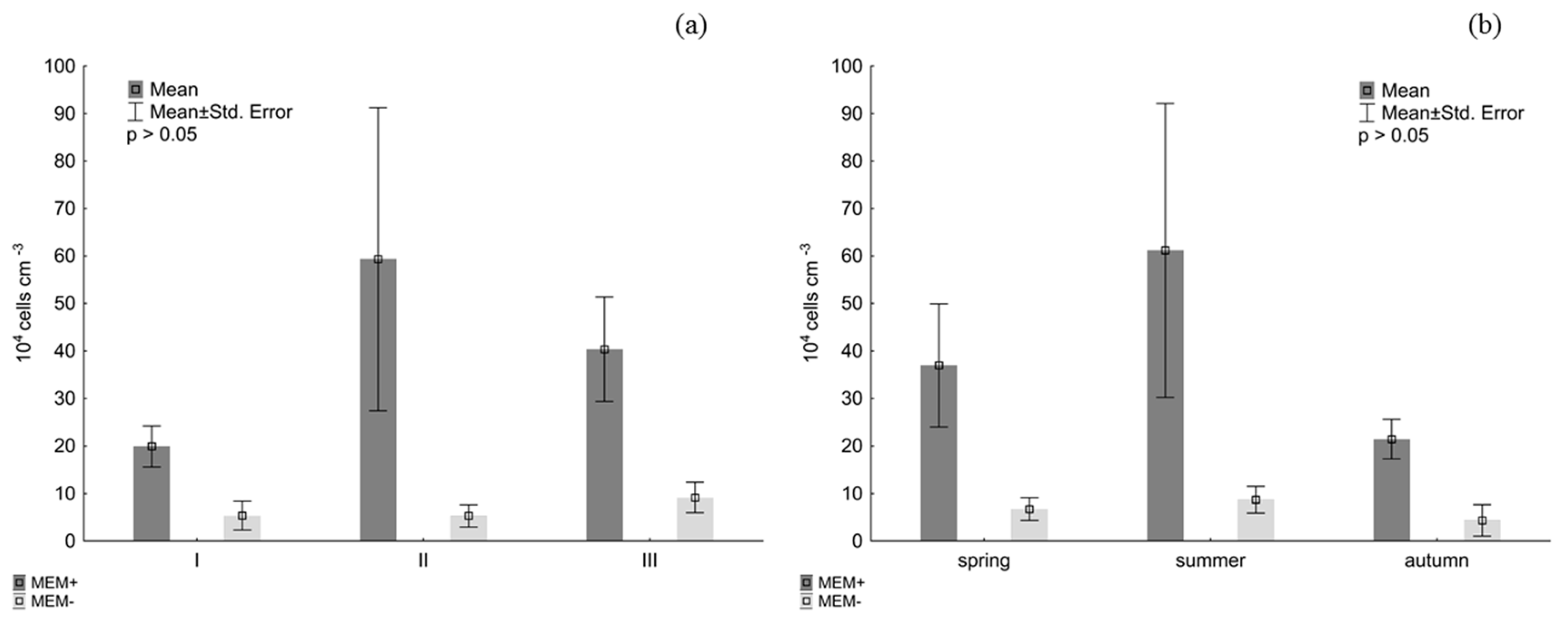


| Site | Location | T (°C) | pH | EC (µS cm−1) | OC (mg dm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 53°12′16,86″ N | 15.7 ± 5.66 | 7.6 ± 0.58 | 350.4 ± 36.93 | 5.4 ± 0.96 |
| 17°56′20,19″ E | (8.8–22.1) | (6.6–8.0) | (303.0–390.0) | (4.1–5.7) | |
| II | 53°7′25,48″ N | 15.0 ± 5.02 | 7.7 ± 0.45 | 360.1 ± 21.71 | 5.8 ± 0.83 |
| 17°59′53,81″ E | (8.6–20.8) | (7.0–8.0) | (331.0–382.0) | (4.6–6.5) | |
| III | 53°7′22,28″ N | 14.8 ± 4.92 | 7.5 ± 0.32 | 367.7 ± 20.92 | 5.7 ± 0.7 |
| 18°5′14,65″ E | (8.7–20.7) | (7.1–7.9) | (339.0–397) | (4.8–6.5) |
| Class of Antibiotic | Type of Antibiotic | Symbol of Disc | Concentration (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbapenems | Imipenem | IMP | 10 |
| Fluoroquinolones | Levofloxacin | LEV | 5 |
| Tetracyclines | Tigecycline | TGC | 15 |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin * | VA | 5 |
| Penicillins | Ampicillin * | AM | 2 |
| Piperacillin ** | PRL | 30 | |
| Cephalosporins | Cefoxitin ** | FOX | 30 |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin ** | CN | 10 |
| Escherichia coli | Enterococcus spp. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | I | II | III | |
| I | ||||||
| II | * | * | ||||
| III | ** | ns | *** | ns | ||
| T (°C) | pH | EC (μS cm−1) | OC (mg dm−3) | Corg (dm3 24 h−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation (r) | |||||
| Psychrophilic bacteria | 0.17 | −0.01 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.57 |
| Mesophilic bacteria | 0.21 | −0.05 | 0.21 | 0.4 | 0.59 |
| Escherichia col | 0.33 | −0.34 | −0.08 | 0.22 | 0.48 |
| Enterococcus spp. | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.24 | 0.4 | 0.59 |
| Abundance of bacteria | 0.44 | −0.47 | −0.31 | 0.5 | 0.76 * |
| Corg (dm3 24 h−1) | 0.67 | −0.35 | −0.21 | 0.8* | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubera, Ł.; Małecka-Adamowicz, M.; Jankowiak, E.; Dembowska, E.; Perliński, P.; Hejze, K. Influence of Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbial Ecology and Sanitary Threat in the Final Stretch of the Brda River. Water 2019, 11, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050922
Kubera Ł, Małecka-Adamowicz M, Jankowiak E, Dembowska E, Perliński P, Hejze K. Influence of Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbial Ecology and Sanitary Threat in the Final Stretch of the Brda River. Water. 2019; 11(5):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050922
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubera, Łukasz, Marta Małecka-Adamowicz, Emilia Jankowiak, Ewa Dembowska, Piotr Perliński, and Karolina Hejze. 2019. "Influence of Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbial Ecology and Sanitary Threat in the Final Stretch of the Brda River" Water 11, no. 5: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050922
APA StyleKubera, Ł., Małecka-Adamowicz, M., Jankowiak, E., Dembowska, E., Perliński, P., & Hejze, K. (2019). Influence of Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors on Microbial Ecology and Sanitary Threat in the Final Stretch of the Brda River. Water, 11(5), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050922







