Effects of Bridge Piers on Flood Hazards: A Case Study on the Jialing River in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
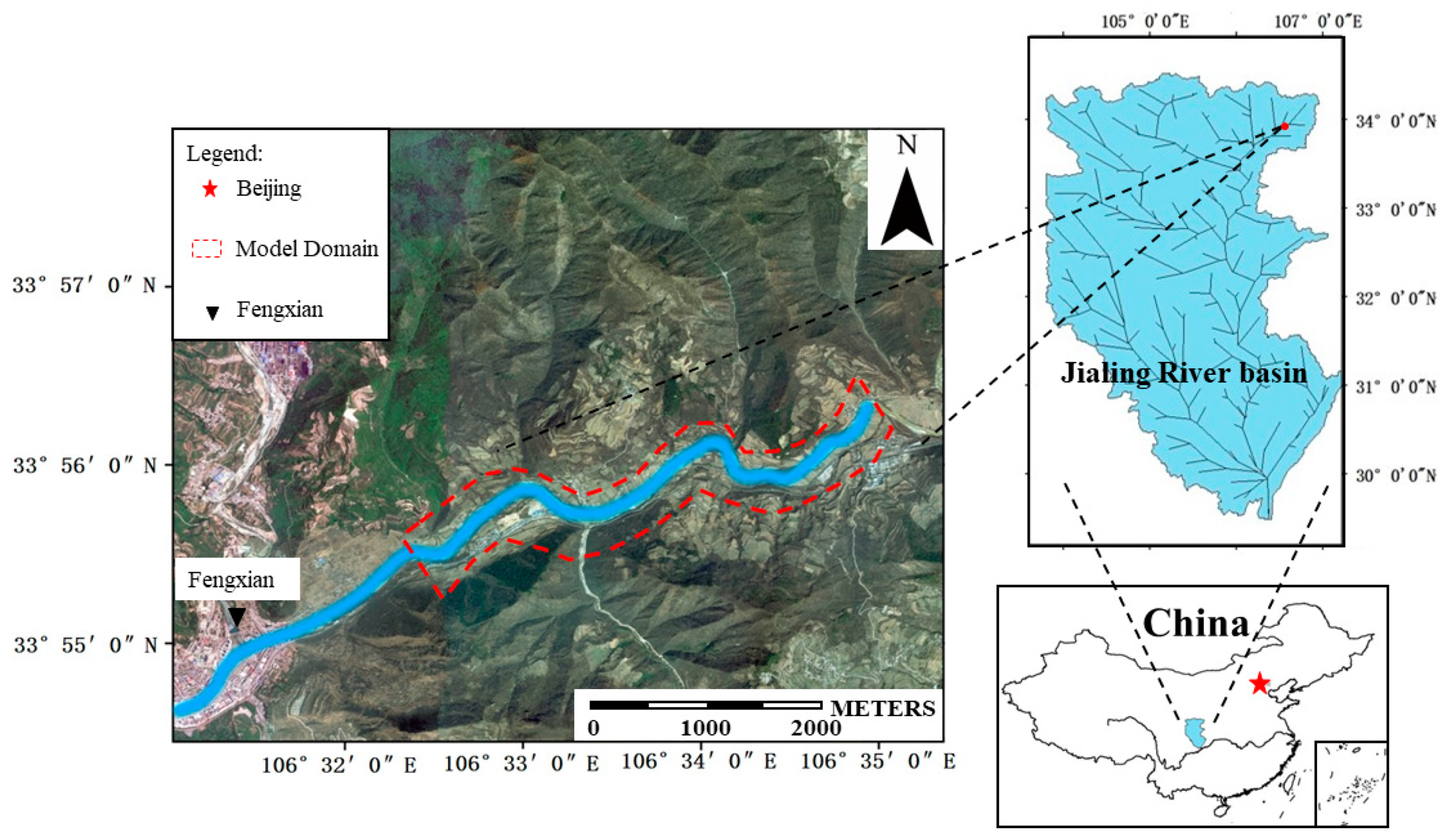
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Model Description
2.3. Mesh Generation and Model Parameters
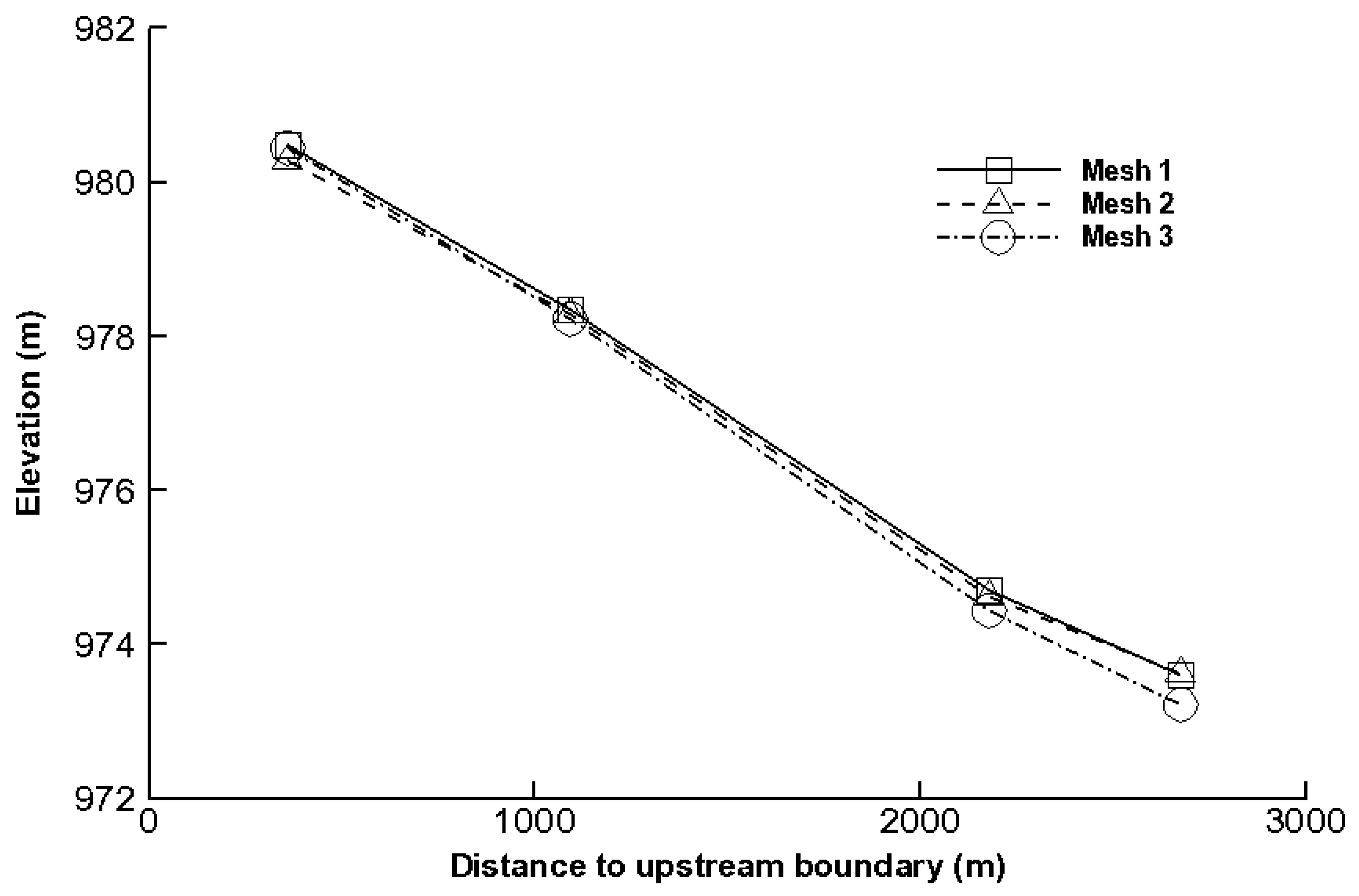
2.4. Sensitivity Analysis
2.5. Validation of the Numerical Model
3. Results and Discussion
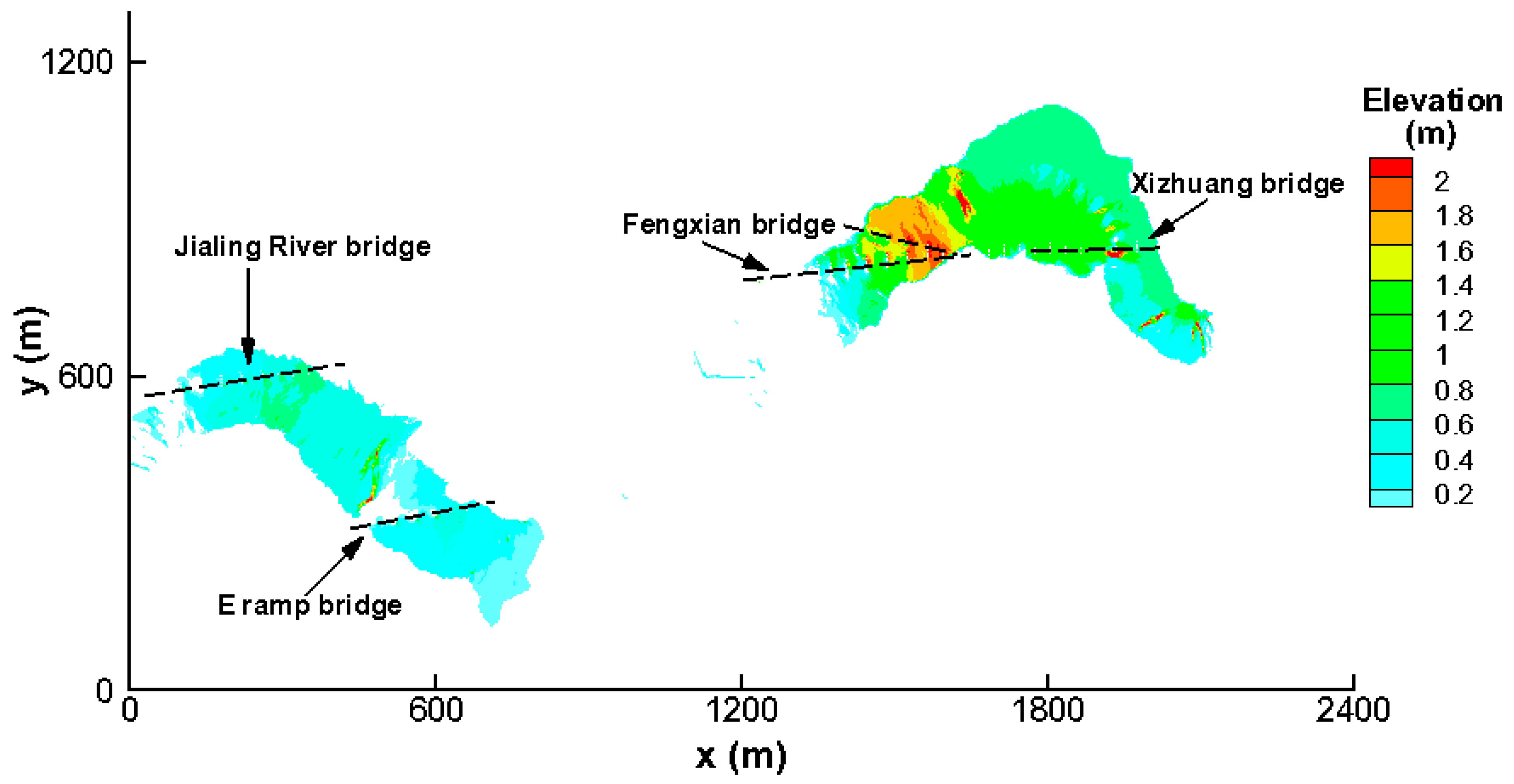
3.1. Backwater Effects of Bridge Piers
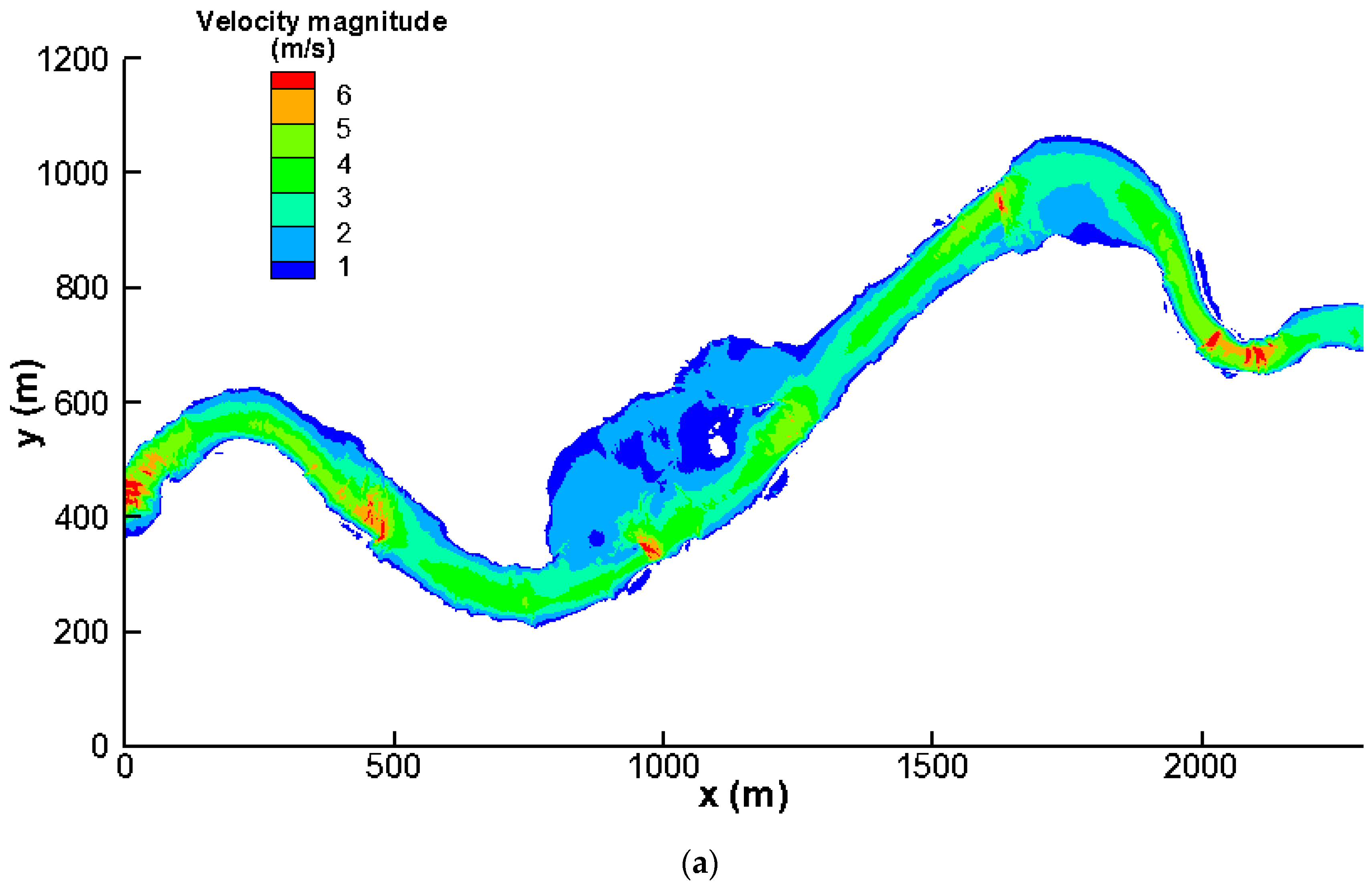
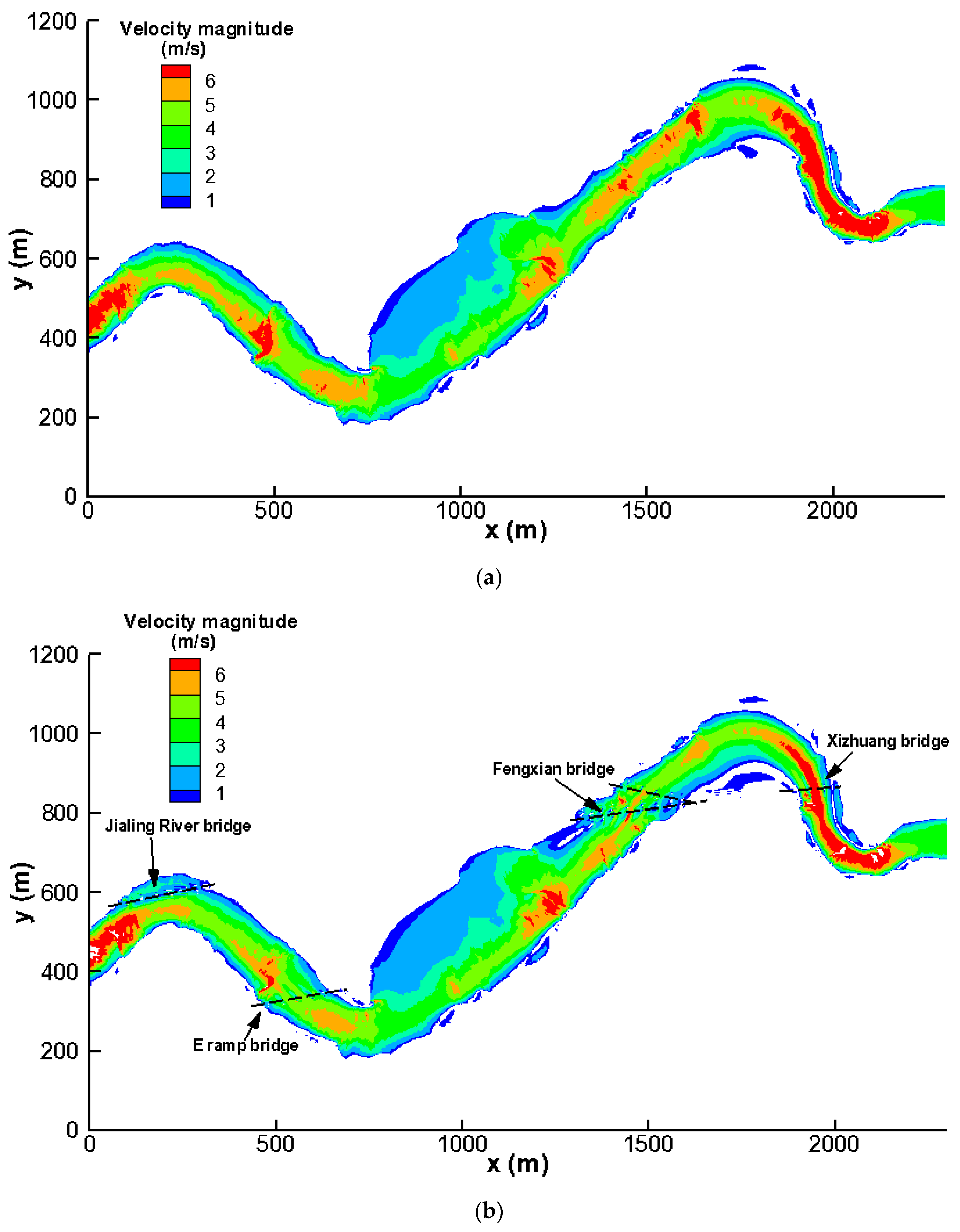
3.2. Effects on Flow Velocity Fields
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, P.; Zhou, M.; Deng, H.; Lyu, J.; Cao, W.; Takara, K.; Nover, D.; Schladow, S.G. Impact of forest maintenance on water shortages: Hydrologic modeling and effects of climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davor, K.; Roger, A.F.; Michaela, B. Flood hazard assessment for extreme flood events. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 1569–1599. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Beniston, M. Trends in joint quantiles of temperature and precipitation in Europe since 1901 and projected for 2100. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horritt, M.; Bates, P. Evaluation of 1D and 2D numerical models for predicting river flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 268, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkuryeva, G.; Merkuryev, Y.; Sokolov, B.V.; Potryasaev, S.; Zelentsov, V.A.; Lektauers, A. Advanced river flood monitoring, modelling and forecasting. J. Comput. Sci. 2015, 10, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.; Dutta, D.; Kim, S. Flood inundation modelling: A review of methods, recent advances and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossi, K.; Jeffrey, N.; Mark, A.T.; Bernd, D. Modelling of flood hazard extent in data sparse areas: A case study of the Oti River basin, West Africa. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 10, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Wang, T.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Hinkelmann, R. An implicit friction source term treatment for overland flow simulation using shallow water flow model. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.L.; Liang, Q.H.; Ming, X.D.; Hou, J.M. An efficient and stable hydrodynamic model with novel source term discretization schemes for overland flow and flood simulations. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 3730–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Li, G.D. Fast simulation of large-scale floods based on GPU parallel computing. Water 2018, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, J.; Choo, Y.; Jo, D. Application of flood nomograph for flood forecasting in urban areas. Water 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasz, D.; Joanna, W.; Mariusz, S. Assessment of the impact of new investments on flood hazard-study case: the bridge on the Warta River near Wronki. Water 2015, 7, 5752–5767. [Google Scholar]
- Costabile, P.; Macchione, F. Enhancing river model set-up for 2-D dynamic flood modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 67, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglari, B.; Sturm, T.W. Numerical modeling of flow around bridge abutments in compound channel. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, L.T.; Shigeko, H.; Nhan, N.H.; Cong, T.T. Infrastructure effects on floods in the Mekong River Delta in Vietnam. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siregar, R.I. Hydraulic modeling of flow impact on bridge structures: A case study on Citarum bridge. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 309, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petaccia, G.; Natale, E. ORSADEM: A one-dimensional shallow water code for flood inundation modelling. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 62, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Macchione, F.; Natale, L.; Petaccia, G. Flood mapping using LIDAR DEM Limitations of the 1-D modeling highlighted by the 2-D approach. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Macchione, F.; Natale, L.; Petaccia, G.; Schleiss, A.J.; De Cesare, G.; Franca, M.J.; Pfister, M. Representing skewed bridge crossing on 1-D and 2D flood propagation models: Compared analysis in practical studies. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics (River Flow), Lausanne, Switzerland, 3–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gallegos, H.A.; Schubert, J.E.; Sanders, B.F. Two-dimensional, high-resolution modeling of urban dam-break flooding: A case study of Baldwin Hills, California. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Mu, D.; Xue, H.; Thanh, N.; Kha, D.; Kaoru, T.; Daniel, N.; Groffrey, S. Flood inundation assessment for the Hanoi Central Area, Vietnam under historical and extreme rainfall conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.H.; Smith, L.S. A high-performance integrated hydrodynamic modelling system for urban flood simulations. J. Hydroinform. 2015, 17, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesuk, V.; Vojinovic, Z.; Mynett, A.E.; Abdullah, A.F. Urban flood modelling combining top-view LiDAR data with ground-view SfM observations. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 75, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kawaike, K.; Seo, D.J. Hyper-resolution 1D-2D urban flood modelling using LiDAR data and hybrid parallelization. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 103, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.M.; Liang, Q.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Hinkelmann, R. An efficient unstructured MUSCL scheme for solving the 2D shallow water equations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 66, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costabile, P.; Macchione, F.; Natale, L.; Petaccia, G. Comparison of scenarios with and without bridges and analysis of backwater effect in 1-D and 2-D river flood modeling. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2015, 109, 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Two-dimensional unstructured finite volume model for bridge pier flow. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2008, 4, 015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Wen, C. Application of 2D flow mathematical model in flood control evaluation of Tongjiang River Bridge. J. Water Resour. Archit. Eng. 2012, 6, 028. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Xiong, Y.; Nover, D.; Duan, W.; Fukushi, K. Historical assessment of Chinese and Japanese flood management policies and implications for managing future floods. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 48, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Li, T.S. Study on the Historic Flood in Jialing River Basin. J. Catastrophol. 2005, 20, 113–115. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute. MIKE 21& MIKE 3 Flow Model FM Hydrodynamic and Transport Module: Scientific Documentation; Danish Hydraulic Institute: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Ai, N.S.; Huang, Z.W.; Yi, C.B.; Qin, F.C. Meanders of the Jialing River in China: morphology and formation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Mesh | Number of Elements | Smallest Allowable Angle | Maximum Element Area (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14,412 | 29° | 200 |
| 2 | 33,865 | 29° | 80 |
| 3 | 41,524 | 29° | 50 |
| Location | Distance to the Upstream Boundary (m) | Designed Elevations at the Top of Levees (m) | Computed (with Piers) Elevations at the Top of Levees (m) | Differences (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xizhuang Bridge | 631 | 978.83 | 978.98 | −0.15 |
| Fengxian Bridge | 1220 | 976.64 | 976.97 | −0.33 |
| E Ramp Bridge | 2400 | 973.24 | 973.6 | −0.36 |
| Jialing River Bridge | 2856 | 971.03 | 971.38 | −0.35 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhou, K.; Jing, H.; Zuo, J.; Li, P.; Li, Z. Effects of Bridge Piers on Flood Hazards: A Case Study on the Jialing River in China. Water 2019, 11, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061181
Wang W, Zhou K, Jing H, Zuo J, Li P, Li Z. Effects of Bridge Piers on Flood Hazards: A Case Study on the Jialing River in China. Water. 2019; 11(6):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061181
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wen, Kaibo Zhou, Haixiao Jing, Juanli Zuo, Peng Li, and Zhanbin Li. 2019. "Effects of Bridge Piers on Flood Hazards: A Case Study on the Jialing River in China" Water 11, no. 6: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061181
APA StyleWang, W., Zhou, K., Jing, H., Zuo, J., Li, P., & Li, Z. (2019). Effects of Bridge Piers on Flood Hazards: A Case Study on the Jialing River in China. Water, 11(6), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061181






