Estuarine Macrofauna Affects Benthic Biogeochemistry in a Hypertrophic Lagoon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Intact Core Collection and Benthic Flux Measurement
2.2. Denitrification Measurement with Isotope Pairing Technique
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.4. Multivariate Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bottom Water and Sediment Features at the Sampling Sites
3.2. Benthic Macrofauna
3.3. Benthic Metabolism and Respiration
3.4. Benthic Nutrient Fluxes
3.5. Macrofauna Community, Functional Traits and Benthic Ecosystem Functioning
4. Discussion
4.1. Physico-Chemical Zonation and Macrofauna Composition
4.2. Macrofauna Affect Benthic Metabolim and N-Cyling across Sites
4.3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hargrave, B. Oxidation-Reduction Potentials, Oxygen Concentration and Oxygen Uptake of Profundal Sediments in a Eutrophic Lake. Oikos 1972, 23, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.; Hupfer, M. Effect of macrozoobenthos on two-dimensional small-scale heterogeneity of pore water phosphorus concentrations in lake sediments: A laboratory study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkenborn, N.; Polerecky, L.; Hedtkamp, S.I.C.; van Beusekom, J.E.; De Beer, D. Bioturbation and bioirrigation extend the open exchange regions in permeable sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1898–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, E.; Penha-Lopes, G.; Delefosse, M.; Valdemarsen, T.; Quintana, C.O.; Banta, G.T. What is bioturbation? The need for a precise definition for fauna in aquatic sciences. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaller, J. Bioturbation/bioirrigation by Chironomus plumosus as main factor controlling elemental remobilization from aquatic sediments? Chemosphere 2014, 107, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aller, R.C.; Aller, J.Y. The effect of biogenic irrigation intensity and solute exchange on diagenetic reaction rates in marine sediments. J. Mar. Res. 1998, 56, 905–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Hansen, K. Transport of carbon dioxide and ammonium in bioturbated (Nereis diversicolor) coastal, marine sediments. Biogeochemistry 1999, 45, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaglia, S.; Nascimento, F.A.; Bartoli, M.; Klawonn, I.; Brüchert, V. Meiofauna increases bacterial denitrification in marine sediments. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carstensen, J.; Conley, D.J.; Bonsdorff, E.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Hietanen, S.; Janas, U.; Reed, D.C. Hypoxia in the Baltic Sea: Biogeochemical cycles, benthic fauna, and management. Ambio 2014, 43, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geert Hiddink, J.; Wynter Davies, T.; Perkins, M.; Machairopoulou, M.; Neill, S.P. Context dependency of relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning is different for multiple ecosystem functions. Oikos 2009, 118, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, M.; Benelli, S.; Bondavalli, C.; Bartoli, M.; Christian, R.R.; Bodini, A. Benthic N pathways in illuminated and bioturbated sediments studied with network analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, S68–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, D.K.; Allen, B.J. Paradigm lost: Reconsidering functional form and group hypotheses in marine ecology. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 250, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverock, B.; Tait, K.; Gilbert, J.A.; Osborn, A.M.; Widdicombe, S. Impacts of bioturbation on temporal variation in bacterial and archaeal nitrogen-cycling gene abundance in coastal sediments. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foshtomi, M.Y.; Braeckman, U.; Derycke, S.; Sapp, M.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Sabbe, K.; Vanaverbeke, J. The link between microbial diversity and nitrogen cycling in marine sediments is modulated by macrofaunal bioturbation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130116. [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez-Cardenas, D.; Quintana, C.O.; Meysman, F.J.; Kristensen, E.; Boschker, H.T. Species-specific effects of two bioturbating polychaetes on sediment chemoautotrophic bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 549, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauppi, L.; Bernard, G.; Bastrop, R.; Norkko, A.; Norkko, J. Increasing densities of an invasive polychaete enhance bioturbation with variable effects on solute fluxes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, T.C.; Smaal, A.C.; Dame, R.F. A review of the feedbacks between bivalve grazing and ecosystem processes. Aquat. Ecol. 1997, 31, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakenkamp, C.C.; Palmer, M.A. Introduced bivalves in freshwater ecosystems: The impact of Corbicula on organic matter dynamics in a sandy stream. Oecologia 1999, 119, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegri, S.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Bioturbation effects of the amphipod Corophium volutator on microbial nitrogen transformations in marine sediments. Mar. Biol. 1994, 121, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegri, S.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Effect of bioturbation by Nereis sp., Mya arenaria and Cerastoderma sp. on nitrification and denitrification in estuarine sediments. Ophelia 1995, 42, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, D.; Matschonat, G. Limitations of controlled experimental systems as models for natural systems: A conceptual assessment of experimental practices in biogeochemistry and soil science. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 277, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaglia, S. Benthic Metabolism and Sediment Nitrogen Cycling in Baltic Sea Coastal Areas: The Role of Eutrophication, Hypoxia and Bioturbation. Licentiate Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2012. Available online: http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:su:diva-85261 (accessed on 18 December 2018).
- Stocum, E.T.; Plante, C.J. The effect of artificial defaunation on bacterial assemblages of intertidal sediments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 337, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammal, J.; Norkko, J.; Pilditch, C.A.; Norkko, A. Coastal hypoxia and the importance of benthic macrofauna communities for ecosystem functioning. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammal, J.; Järnström, M.; Bernard, G.; Norkko, J.; Norkko, A. Environmental Context Mediates Biodiversity—Ecosystem Functioning Relationships in Coastal Soft-sediment Habitats. Ecosystems 2019, 22, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogina, M.; Lipka, M.; Woelfel, J.; Liu, B.; Böttcher, M.E.; Zettler, M.L. In search of a field-based relationship between benthic macrofauna and biogeochemistry in a modern brackish coastal sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Zilius, M.; Saltyte-Vaisiauske, L.; Bartoli, M. Recent trends (2012–2016) of N, Si, and P export from the Nemunas River Watershed: Loads, unbalanced stoichiometry, and threats for downstream aquatic ecosystems. Water 2018, 10, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, M.J. Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 341–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.E.; Nizzoli, D.; Bartoli, M.; Smyth, A.R.; Castaldelli, G.; Anderson, I.C. Variation in benthic metabolism and nitrogen cycling across clam aquaculture sites. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmala, E.; Carstensen, J.; Conley, D.J.; Slomp, C.P.; Stadmark, J.; Voss, M. Efficiency of the coastal filter: Nitrogen and phosphorus removal in the Baltic Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, S222–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilius, M.; Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Vaiciute, D.; Petkuviene, J.; Zemlys, P.; Liskow, I.; Bukaveckas, P.A. The influence of cyanobacteria blooms on the attenuation of nitrogen throughputs in a Baltic coastal lagoon. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, R.F. The role of bivalve filter feeder material fluxes in estuarine ecosystems. In Bivalve Filter Feeders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 245–269. [Google Scholar]
- Lohrer, A.M.; Thrush, S.F.; Gibbs, M.M. Bioturbators enhance ecosystem function through complex biogeochemical interactions. Nature 2004, 431, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stief, P. Stimulation of microbial nitrogen cycling in aquatic ecosystems by benthic macrofauna: Mechanisms and environmental implications. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7829–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, P.C.; Zilius, M.; Benelli, S.; Bartoli, M. Nitrification and denitrification in estuarine sediments with tube-dwelling benthic animals. Hydrobiologia 2018, 819, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Nizzoli, D.; Viaroli, P.; Turolla, E.; Castaldelli, G.; Fano, E.A.; Rossi, R. Impact of Tapes philippinarum farming on nutrient dynamics and benthic respiration in the Sacca di Goro. Hydrobiologia 2001, 455, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaroli, P.; Azzoni, R.; Bartoli, M.; Giordani, G.; Tajé, L. Evolution of the trophic conditions and dystrophic outbreaks in the Sacca di Goro lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea). In Mediterranean Ecosystems; Springer: Milano, Italy, 2001; pp. 467–475. [Google Scholar]
- Viaroli, P.; Bartoli, M.; Azzoni, R.; Giordani, G.; Mucchino, C.; Naldi, M.; Tajé, L. Nutrient and iron limitation to Ulva blooms in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzoli, D.; Bartoli, M.; Viaroli, P. Nitrogen and phosphorous budgets during a farming cycle of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum: An In Situ experiment. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilius, M.; Giordani, G.; Petkuviene, J.; Lubiene, I.; Ruginis, T.; Bartoli, M. Phosphorus mobility under short-term anoxic conditions in two shallow eutrophic coastal systems (Curonian and Sacca di Goro lagoons). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 164, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naldi, M.; Viaroli, P. Nitrate uptake and storage in the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh in relation to nitrate availability and thallus nitrate content in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Po River Delta, Italy). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 269, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccherelli, V.U.; Ceccherelli, G.C.; Reggiani, G.; Caramori, V.; Gaiani, C.; Corazza, C. Le comunità macrobentoniche della Sacca di Goro e gli effetti di disturbo ambientale; Risultate di due anni d’indagine (Dicembre 1987–Dicembre 1989). In Sacca di Goro: Studio Integrato Sull’ecologia; FrancoAngeli: Milano, Italy, 1994; pp. 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Mistri, M.; Rossi, R.; Fano, E.A. Structure and secondary production of a soft bottom macrobenthic community in a brackish lagoon (Sacca di Goro, north-eastern Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, D.; Zaldívar, J.M.; Norro, A.; Giordani, G.; Viaroli, P. Integrated modelling in coastal lagoons: Sacca di Goro case study. Hydrobiologia 2008, 611, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viaroli, P.; Giordani, G.; Bartoli, M.; Naldi, M.; Azzoni, R.; Nizzoli, D.; Ferrari, I. The Sacca di Goro lagoon and an arm of the Po River. In Estuaries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 197–232. [Google Scholar]
- Nizzoli, D.; Bartoli, M.; Cooper, M.; Welsh, D.T.; Underwood, G.J.; Viaroli, P. Implications for oxygen, nutrient fluxes and denitrification rates during the early stage of sediment colonisation by the polychaete Nereis spp. in four estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.T.; Nizzoli, D.; Fano, E.A.; Viaroli, P. Direct contribution of clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) to benthic fluxes, nitrification, denitrification and nitrous oxide emission in a farmed sediment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistri, M.; Fano, E.A.; Rossi, R. Redundancy of macrobenthos from lagoonal habitats in the Adriatic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 215, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalsgaard, T.; Nielsen, L.P.; Brotas, V.; Viaroli, P.; Underwood, G.; Nedwell, D.; Dong, L. Protocol Handbook for NICE-Nitrogen Cycling in Estuaries: A Project under the EU Research Programme: Marine Science and Technology (MAST III); Ministry of Environment and Energy National Environmental Research Institute: Silkeborg, Denmark, 2000; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, L.P. Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1992, 9, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kana, T.M.; Darkangelo, C.; Hunt, M.D.; Oldham, J.B.; Bennett, G.E.; Cornwell, J.C. Membrane inlet mass spectrometer for rapid high-precision determination of N2, O2, and Ar in environmental water samples. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 4166–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassshoff, K. Determination of nitrate. In Methods of Seawater Analysis; Grassoff, K., Ehrhardt, M., Kremling, K., Eds.; Verlag Chemie: Weinheimm, Germany, 1982; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Complex ecological data sets. In Developments in Environmental Modelling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 24, pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zuur, A.; Ieno, E.N.; Smith, G.M. Analyzing Ecological Data; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.B.; Nielsen, L.P.; Sørensen, J.; Revsbech, N.P. Denitrification in nitrate-rich streams: Diurnal and seasonal variation related to benthic oxygen metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norling, K.; Rosenberg, R.; Hulth, S.; Grémare, A.; Bonsdorff, E. Importance of functional biodiversity and species-specific traits of benthic fauna for ecosystem functions in marine sediment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 332, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeckman, U.; Provoost, P.; Gribsholt, B.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Middelburg, J.J.; Soetaert, K.; Vanaverbeke, J. Role of macrofauna functional traits and density in biogeochemical fluxes and bioturbation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 399, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.J.; Näslund, J.; Elmgren, R. Meiofauna enhances organic matter mineralization in soft sediment ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 57, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, A.; Eyre, B. Interaction of benthic microalgae and macrofauna in the control of benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes and denitrification in a shallow sub-tropical coastal embayment (western Moreton Bay, Australia). Biogeochemistry 2013, 112, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, N.A.; Jackson, C.R.; McDonnell, J.J.; Klaus, J.; Du, E.; Bitew, M.M. Dual nitrate isotopes clarify the role of biological processing and hydrologic flow paths on nitrogen cycling in subtropical low-gradient watersheds. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbahi, N.; Blanchet, H.; Lavesque, N.; De Montaudouin, X.; Dauvin, J.C.; Neifar, L. Main Ecological Features of Benthic Macrofauna in Mediterranean and Atlantic Intertidal Eelgrass Beds: A Comparative Study. J. Mar. Biol. Oceanogr. 2017, 6, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, W.P. Disturbance in marine intertidal boulder fields: The nonequilibrium maintenance of species diversity. Ecology 1979, 60, 1225–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, W.P. Experimental investigations of disturbance and ecological succession in a rocky intertidal algal community. Ecol. Monogr. 1979, 49, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, B.M.; Keeley, N.B.; Hopkins, G.A.; Webb, S.C.; Clement, D.M. Bivalve aquaculture in estuaries: Review and synthesis of oyster cultivation effects. Aquaculture 2009, 298, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Castaldelli, G.; Nizzoli, D.; Fano, E.A.; Sousa, P. Manila clam introduction in the Sacca di Goro Lagoon (Northern Italy): Ecological implications. Bull. Jpn. Fish. Res. Educ. Agen. 2016, 42, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.J. Physical disturbance and marine benthic communities: Life in unconsolidated sediments. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1994, 32, 179–239. [Google Scholar]
- Norkko, A.; Thrush, S.F.; Hewitt, J.E.; Cummings, V.J.; Norkko, J.; Ellis, J.I.; MacDonald, I. Smothering of estuarine sandflats by terrigenous clay: The role of wind-wave disturbance and bioturbation in site-dependent macrofaunal recovery. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 234, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, D.M.; Rodi, A.J.; Ranasinghe, J.A. Effects of low dissolved oxygen events on the macrobenthos of the lower Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 1992, 15, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilius, M.; Bartoli, M.; Bresciani, M.; Katarzyte, M.; Ruginis, T.; Petkuviene, J.; Razinkovas-Baziukas, A. Feedback mechanisms between cyanobacterial blooms, transient hypoxia, and benthic phosphorus regeneration in shallow coastal environments. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Rosenberg, R.; François-Carcaillet, F.; Norling, K.; Mauclaire, L. Influence of bioturbation by three benthic infaunal species on microbial communities and biogeochemical processes in marine sediment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, C.O.; Hansen, T.; Delefosse, M.; Banta, G.; Kristensen, E. Burrow ventilation and associated porewater irrigation by the polychaete Marenzelleria viridis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 397, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamdrup, B.; Fossing, H.; Jørgensen, B.B. Manganese, iron and sulfur cycling in a coastal marine sediment, Aarhus Bay, Denmark. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 5115–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, A.; Jørgensen, B.B. Oxidation of pyrite and iron sulfide by manganese dioxide in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzoni, R.; Giordani, G.; Viaroli, P. Iron-sulphur-phosphorus interactions: Implications for sediment buffering capacity in a mediterranean eutrophic lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy). Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegri, S.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Effects of Tubifex tubifex (Oligochaeta: Tubificidae) on N-mineralization in freshwater sediments, measured with 15N isotopes. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1995, 9, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, P.; Montani, S.; Takada, C.; Tsutsumi, H. Temporal scaling and relevance of bivalve nutrient excretion on a tidal flat of the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 198, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, G.; Rosenberg, R. Bioresuspension and biodeposition: A review. J. Mar. Syst. 1997, 11, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundbäck, K.; Miles, A.; Göransson, E. Nitrogen fluxes, denitrification and the role of microphytobenthos in microtidal shallow-water sediments: An annual study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
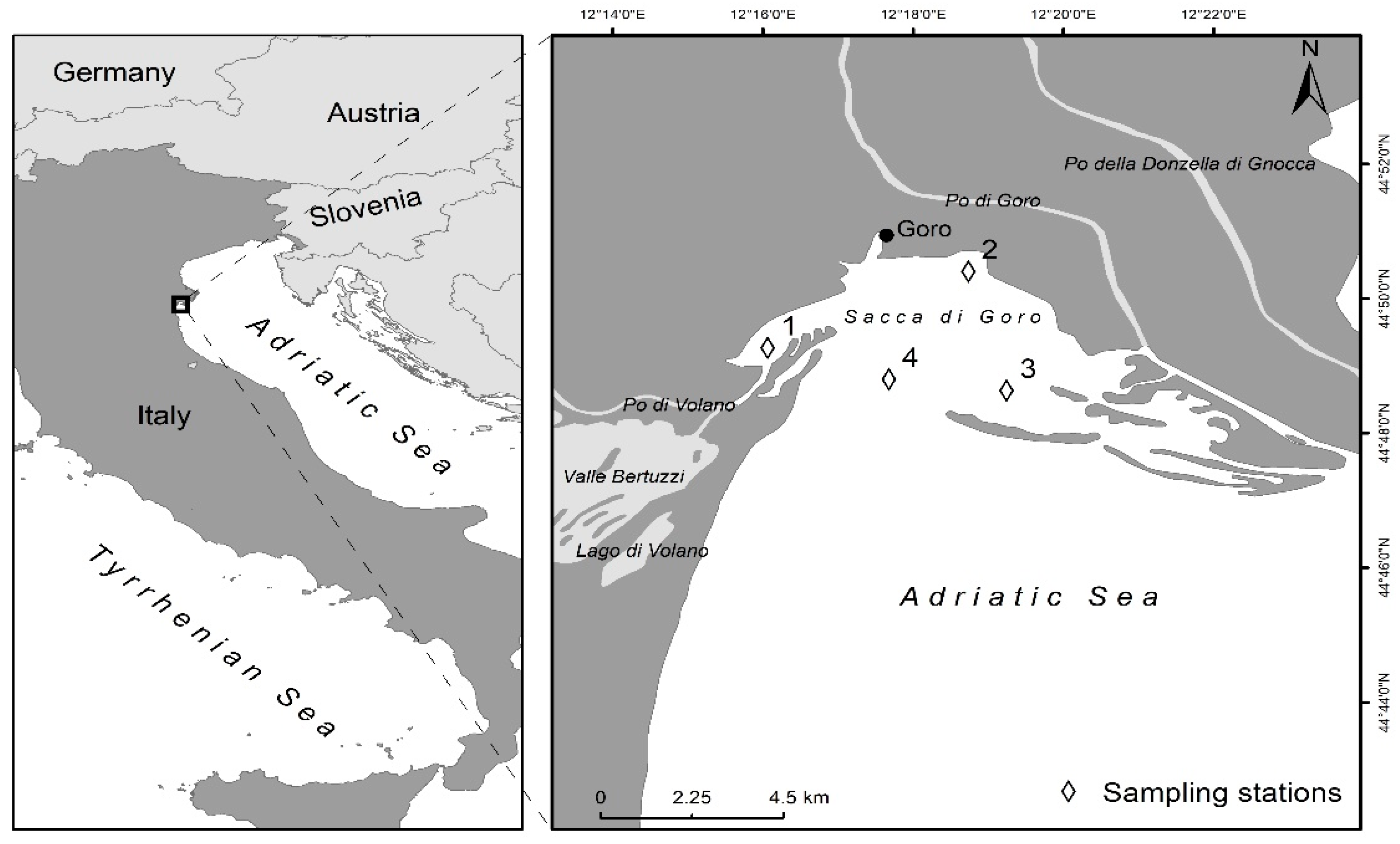




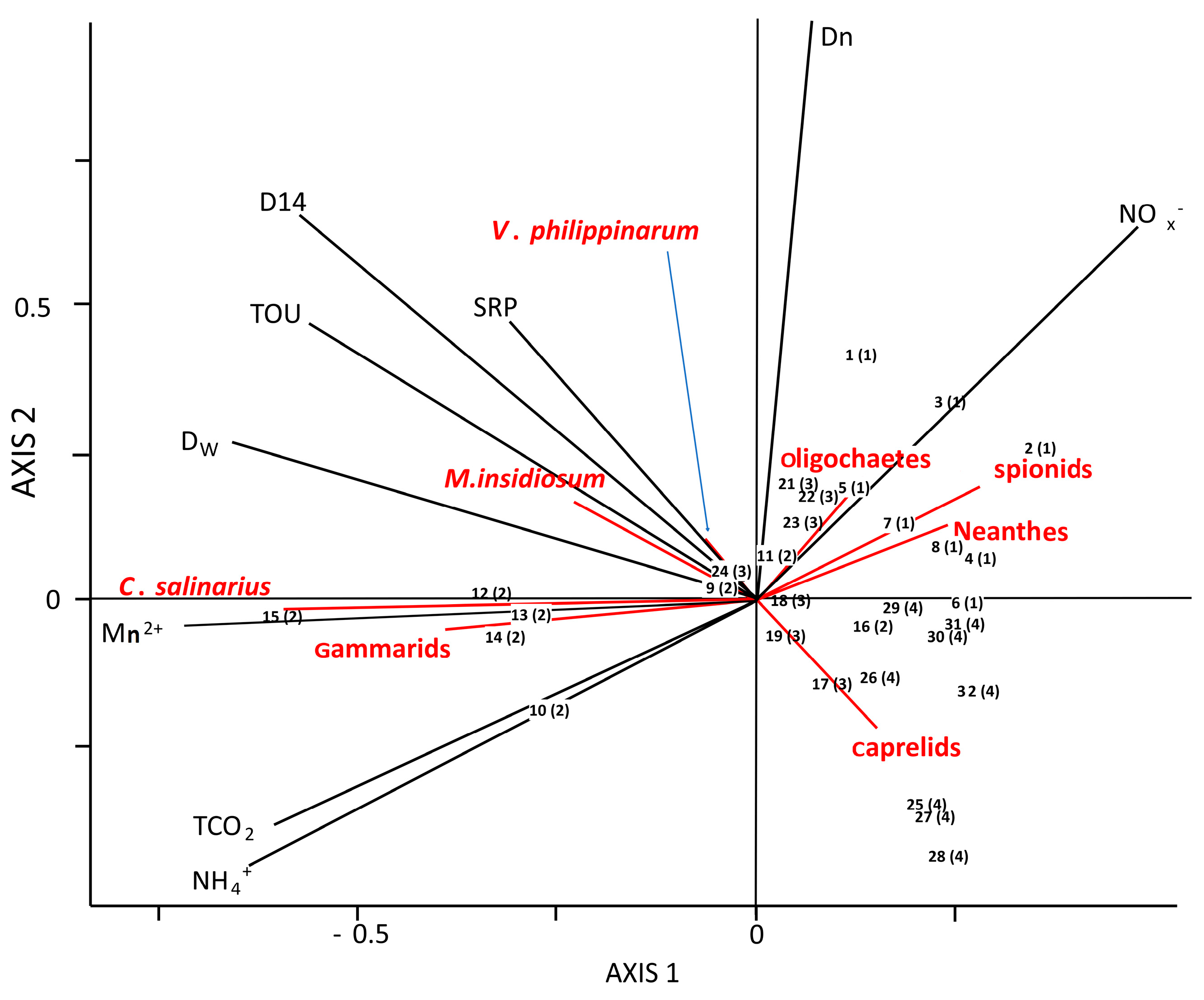

| PARAMETERS | SITE 1 | SITE 2 | SITE 3 | SITE 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water column | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | 21 | 21 | 19 | 19 |
| Salinity (PSU) | 5 | 12 | 12 | 7 |
| TCO2 (mmol L−1) | 5.2 ± 0.01 | 3.3 ± 0.01 | 2.6 ± 0.01 | 2.6 ± 0.01 |
| NH4+ (µmol L−1) | 7.1 ± 0.12 | 32.1 ± 0.17 | 31.9 ± 0.17 | 19.1 ± 0.69 |
| NOx− (µmol L−1) | 114.7 ± 4.45 | 40.8 ± 1.67 | 56.5 ± 2.02 | 52.3 ± 3.93 |
| SRP (µmol L−1) | 2.2 ± 0.02 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 1.1 ± 0.01 | 0.5 ± 0.01 |
| Sediment | ||||
| Type | Clayish mud | Detrital mud | Muddy sand | Fine sand |
| Porosity | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.03 |
| Density (g cm−3) | 1.16 ± 0.01 | 1.12 ± 0.02 | 1.83 ± 0.02 | 1.78 ± 0.02 |
| Corg (%) | 4.02 ± 0.27 | 7.48 ± 0.26 | 1.29 ± 0.14 | 1.42 ± 0.14 |
| TN (%) | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| C:N (mass) | 11.8 | 8.8 | – | – |
| Predictors and Covariables | Df | Sum of All Canonical Eigenvalues (%) |
|---|---|---|
| (Species effect ∪ Site effect) = [A+B+C] | 9 | 74 |
| Species | Site effect = [A] (Site effect as covariable) | 6 | 19 |
| Site effect | species = [C] (Species as covariable) | 3 | 8 |
| Species effect ∩ Site effect = [(Species effect ∪ Site effect) – (Species effect | Site effect) − (Site effect | Species effect)] = [B] | 0 | 74 – (19) – (8) = 47 |
| Residuals = [Total inertia – (Species effect ∪ Site effect)] | 0 | 100 – 74 = 26 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Politi, T.; Zilius, M.; Castaldelli, G.; Bartoli, M.; Daunys, D. Estuarine Macrofauna Affects Benthic Biogeochemistry in a Hypertrophic Lagoon. Water 2019, 11, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061186
Politi T, Zilius M, Castaldelli G, Bartoli M, Daunys D. Estuarine Macrofauna Affects Benthic Biogeochemistry in a Hypertrophic Lagoon. Water. 2019; 11(6):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061186
Chicago/Turabian StylePoliti, Tobia, Mindaugas Zilius, Giuseppe Castaldelli, Marco Bartoli, and Darius Daunys. 2019. "Estuarine Macrofauna Affects Benthic Biogeochemistry in a Hypertrophic Lagoon" Water 11, no. 6: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061186
APA StylePoliti, T., Zilius, M., Castaldelli, G., Bartoli, M., & Daunys, D. (2019). Estuarine Macrofauna Affects Benthic Biogeochemistry in a Hypertrophic Lagoon. Water, 11(6), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061186







