Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Mixing Phenomena in Double-Tee Junctions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
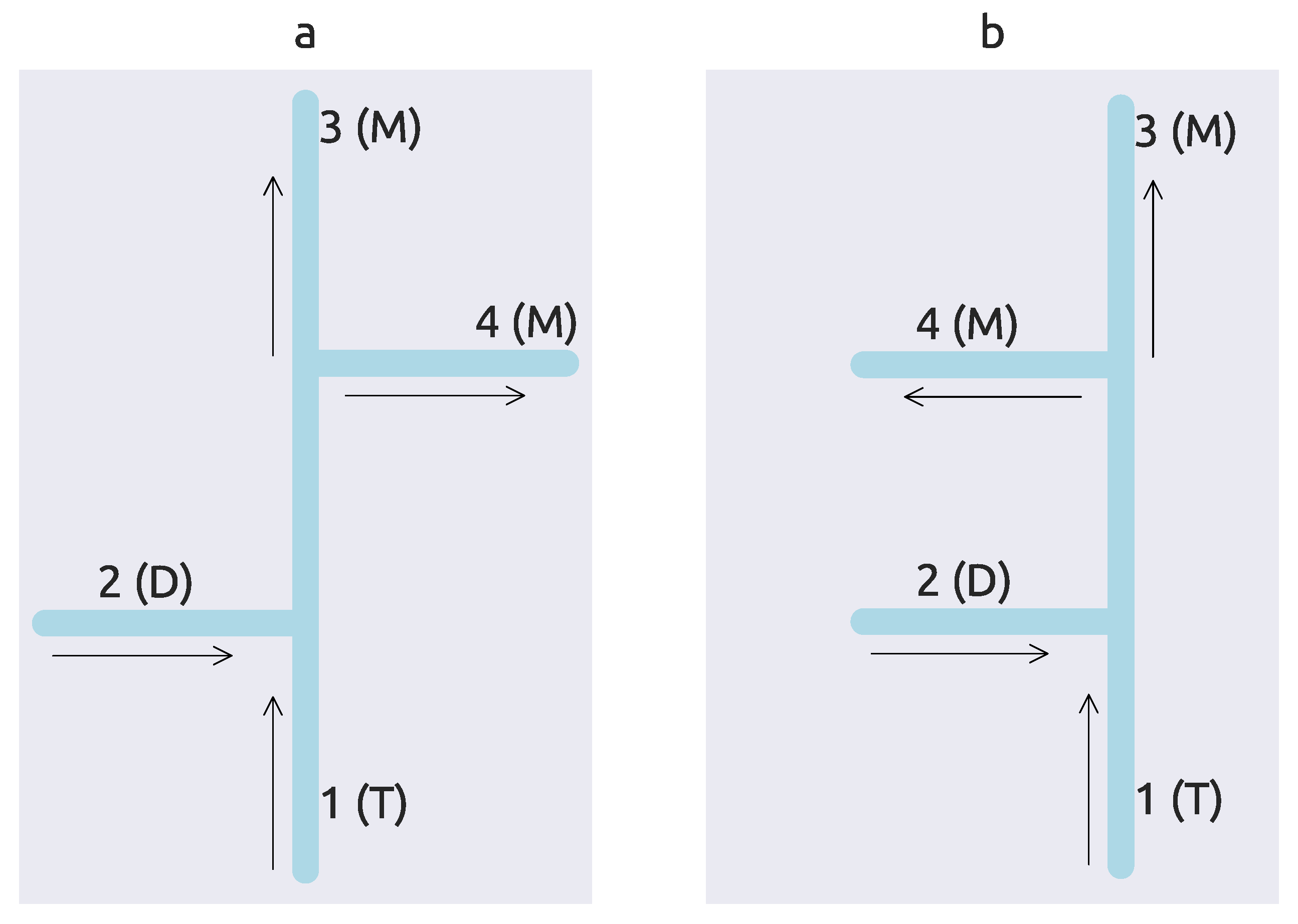
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Measurement Procedure and Apparatus
2.3. Numerical Modeling
2.3.1. Passive Scalar Model
2.3.2. Multiphase Model
3. Results and Discussion
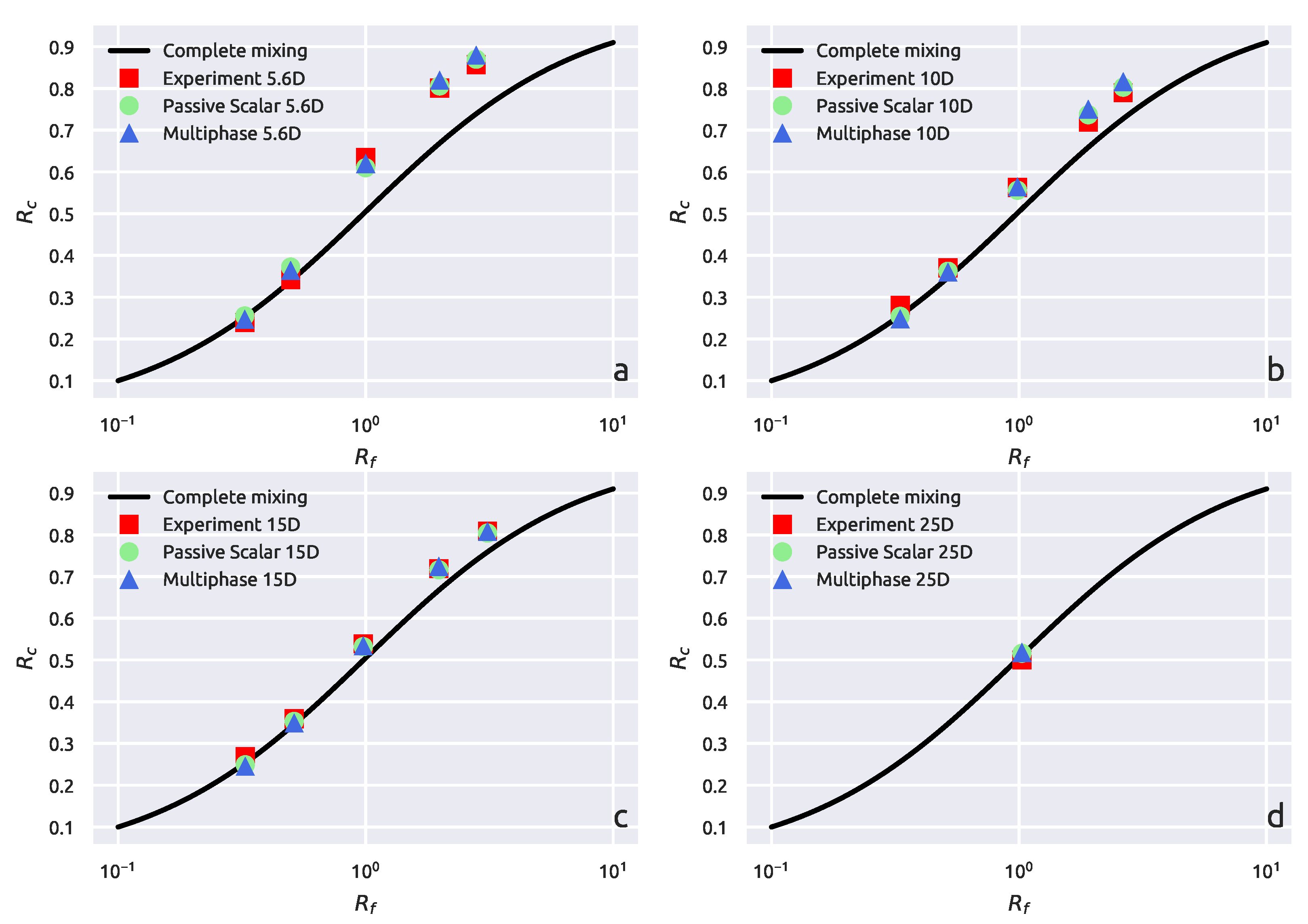
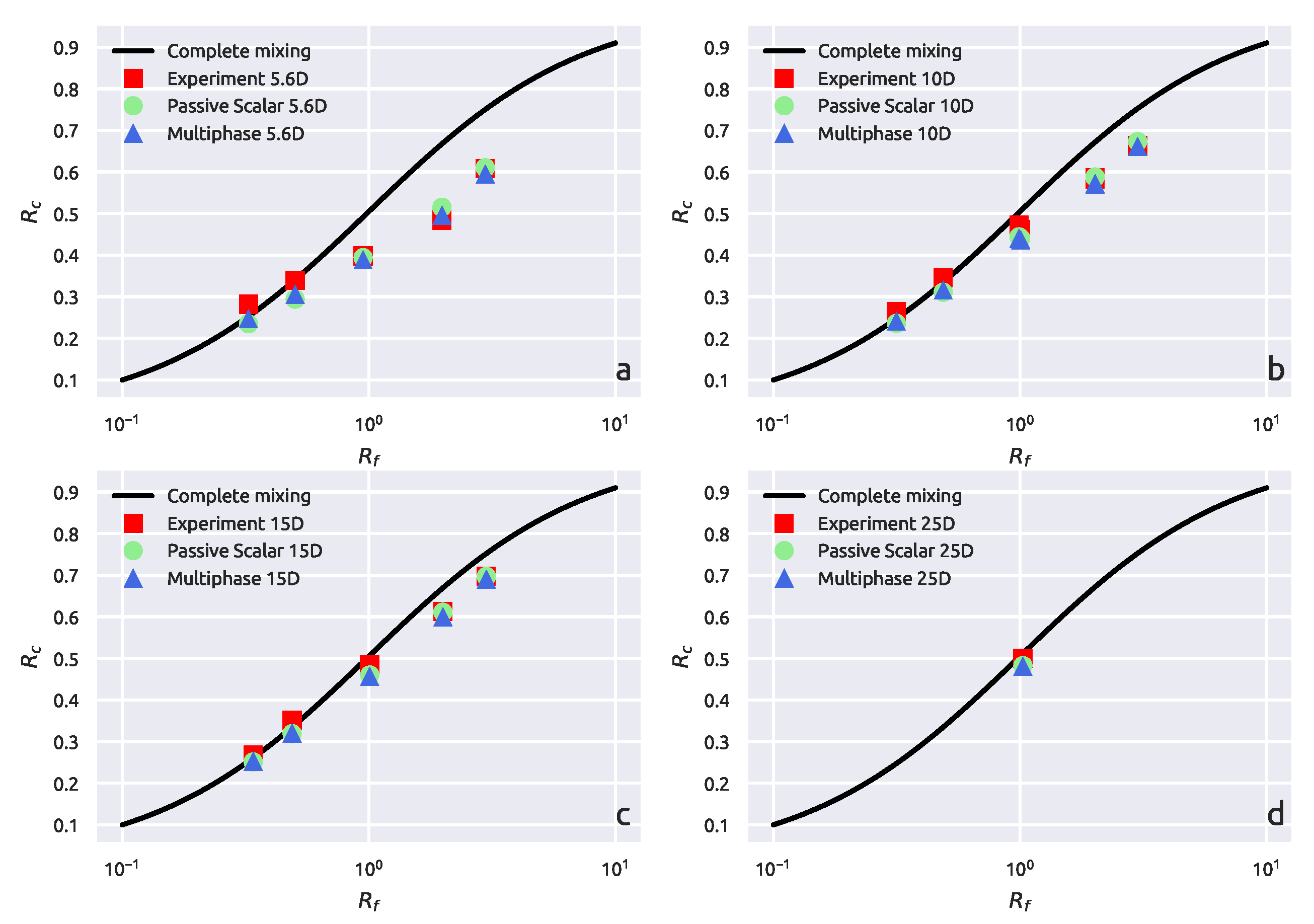
3.1. Experimental Results
3.1.1. Complete Mixing
3.2. CFD Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossman, L.A. EPANET 2: Users Manual; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2000.
- Ostfeld, A.; Uber, J.G.; Salomons, E.; Berry, J.W.; Hart, W.E.; Phillips, C.A.; Watson, J.P.; Dorini, G.; Jonkergouw, P.; Kapelan, Z.; et al. The battle of the water sensor networks (BWSN): A design challenge for engineers and algorithms. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Harrison, K.W. Improving efficiency of the Bayesian approach to water distribution contaminant source characterization with support vector regression. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2012, 140, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhao, J.; Yan, X.; Zeng, D.; Guo, S. A MapReduce based Parallel Niche Genetic Algorithm for contaminant source identification in water distribution network. Ad Hoc Netw. 2015, 35, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.; Klise, K.A.; Siirola, J.D.; Haxton, T.; Laird, C.D. Testing contamination source identification methods for water distribution networks. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjčević, L.; Čavrak, M.; Šestan, M. Contamination source detection in water distribution networks. Eng. Rev. 2010, 30, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, J.; Hu, C.; Zeng, D. Multimodal optimization problem in contamination source determination of water supply networks. Swarm Evolut. Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.A.; Orear, L.; Wright, J. Experimental determination of solute mixing in pipe joints. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2007: Restoring Our Natural Habitat, Tampa, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2007; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Gomez, P.; Choi, C.; van Bloemen Waanders, B.; McKenna, S. Transport phenomena at intersections of pressurized pipe systems. In Proceedings of the Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, R.; Waanders, B.V.B.; McKenna, S.; Choi, C. Mixing at cross junctions in water distribution systems. II: Experimental study. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.K. Solute mixing models for water-distribution pipe networks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.K.; O’Rear, L., Jr. Evaluation of solute mixing in water distribution pipe junctions. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2009, 101, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, T.; Shen, C. Experimental testing and modeling analysis of solute mixing at water distribution pipe junctions. Water Res. 2014, 56, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Tao, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, T. Experimental study of solute mixing at double-Tee junctions in water distribution systems. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2015, 15, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Qiu, H.; Yang, J.; Shao, Y.; Tao, L. Mixing at double-Tee junctions with unequal pipe sizes in water distribution systems. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Romero-Gomez, P.; Andrade, M.A.; Mondaca, M.; Choi, C.Y. Mixing at junctions in water distribution systems: an experimental study. Urban Water J. 2018, 15, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasak, H.; Jemcov, A.; Tukovic, Z. OpenFOAM: A C++ library for complex physics simulations. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Coupled Methods in Numerical Dynamics, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 19–21 September 2007; Volume 1000, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, R. Self-diffusion in normal and heavy water in the range 1–45. deg. J. Phys. Chem. 1973, 77, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. In Numerical Prediction of Flow, Heat Transfer, Turbulence and Combustion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; pp. 96–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gualtieri, C.; Angeloudis, A.; Bombardelli, F.; Jha, S.; Stoesser, T. On the values for the turbulent Schmidt number in environmental flows. Fluids 2017, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, D.; Bung, D.B. Sensitivity of turbulent Schmidt number and turbulence model to simulations of jets in crossflow. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 82, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, D.; Bung, D.; Oertel, M. Turbulent dispersion in bounded horizontal jets: RANS capabilities and physical modeling comparison. In Sustainable Hydraulics in the Era of Global Change, Proceedings of the 4th IAHR Europe Congress, Liege, Belgium, 27–29 July 2016; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.K.; Wright, J.L.; McKenna, S.A.; Orear, L., Jr. Contaminant Mixing at Pipe Joints: Comparison between Laboratory Flow Experiments and Computational Fluid Dynamics Models; Technical Report; Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM): Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, S.W.; van Bloemen Waanders, B.G. High fidelity computational fluid dynamics for mixing in water distribution systems. In Proceedings of the Eight Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 39, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Law, A.W.K.; Zhao, B. Large eddy simulations of 45 inclined dense jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Law, A.W.K.; Lai, A.C. Turbulence characteristics of 45 inclined dense jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krpan, R.; Končar, B. Simulation of turbulent wake at mixing of two confined horizontal flows. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2018, 2018, 5240361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Internal pipe diameter (D) | 18 | (mm) |
| Inlet pipes length | 20D | (-) |
| Outlet pipes length | 40D | (-) |
| Tee distances | 5.6D, 10D, 15D, 20D, 25D, 30D, 70D, 120D, 130D, 150D | (-) |
| Inlet flow range | 0.08–0.43 | (l/s) |
| Reynolds number range | 6000–30,000 | (-) |
| Inlet flow ratios (5.6D, 10D, 15D) | 3:1, 2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 3:1 | (-) |
| Inlet flow ratios (20D, 25D, 30D, 70D, 120D, 130D, 150D) | 1:1 | (-) |
| Variable | Inlets | Outlets | Pipe Walls |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | p | ||
| c | c | ||
| k | k | ||
| Variable | Inlets | Outlets | Pipe Wall |
|---|---|---|---|
| p | p | ||
| k | k | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grbčić, L.; Kranjčević, L.; Lučin, I.; Čarija, Z. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Mixing Phenomena in Double-Tee Junctions. Water 2019, 11, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061198
Grbčić L, Kranjčević L, Lučin I, Čarija Z. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Mixing Phenomena in Double-Tee Junctions. Water. 2019; 11(6):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061198
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrbčić, Luka, Lado Kranjčević, Ivana Lučin, and Zoran Čarija. 2019. "Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Mixing Phenomena in Double-Tee Junctions" Water 11, no. 6: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061198
APA StyleGrbčić, L., Kranjčević, L., Lučin, I., & Čarija, Z. (2019). Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Mixing Phenomena in Double-Tee Junctions. Water, 11(6), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061198