Stable Isotope Ratios in Tap Water of a Riverside City in a Semi-Arid Climate: An Application to Water Source Determination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Sample Acquisition
2.2. Isotope Analysis
2.3. Other Data
3. Result
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Isotopes in Tap Water
3.1.1. Local Tap Water Line
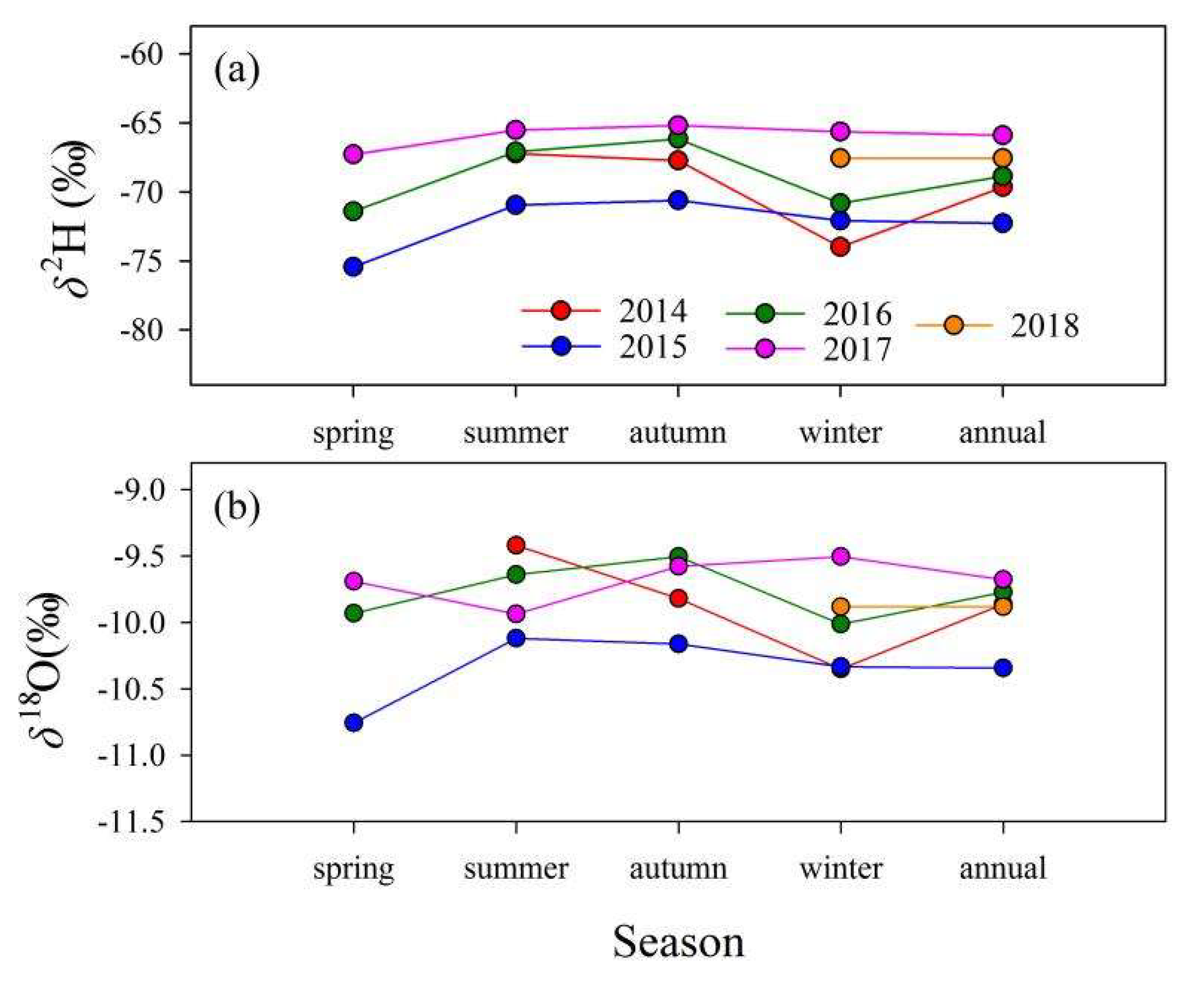
3.1.2. Temporal Variations of Isotopes in Tap Water
3.1.3. Differences of Isotopes in Tap Water at Each Sampling Site
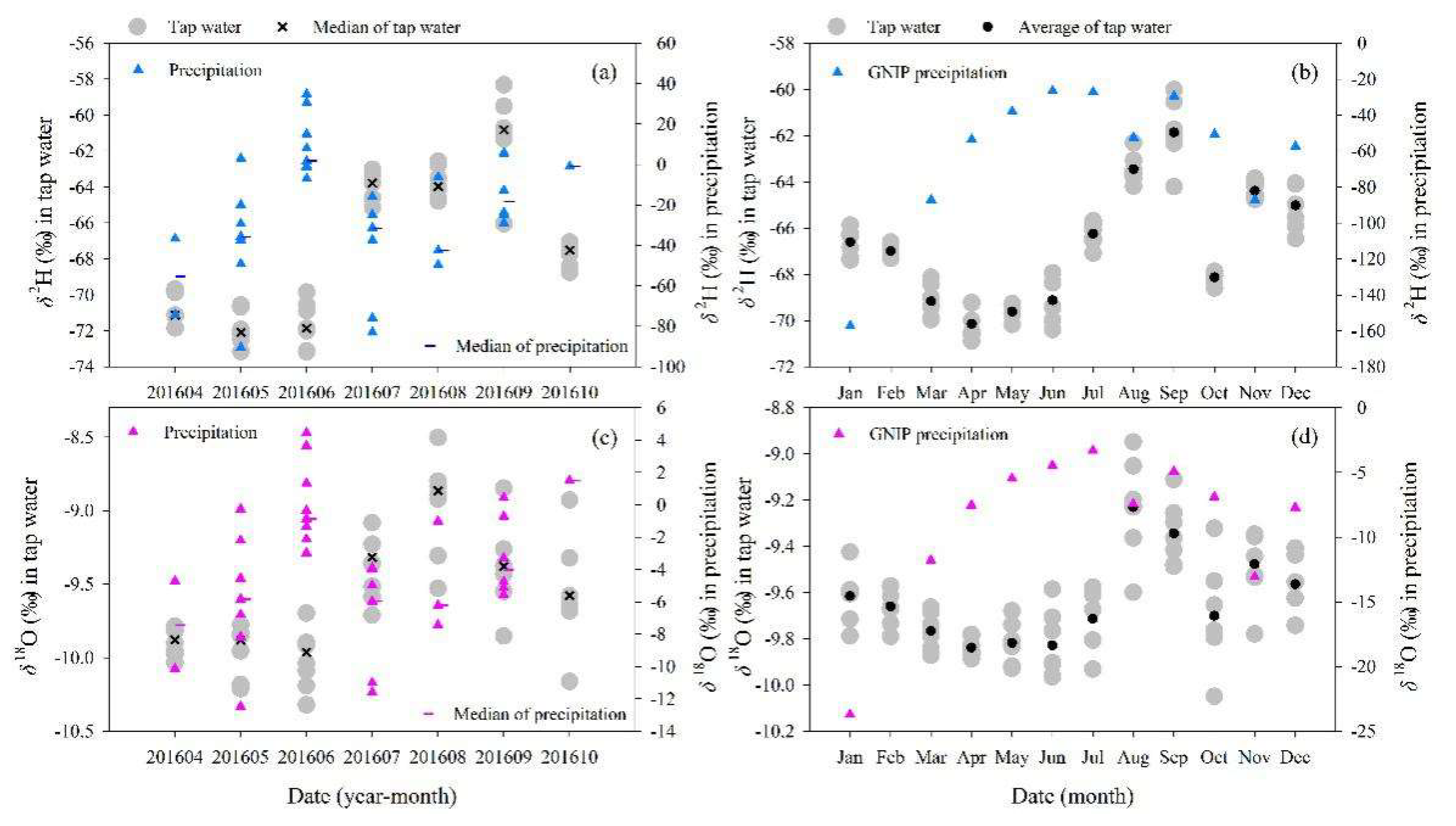
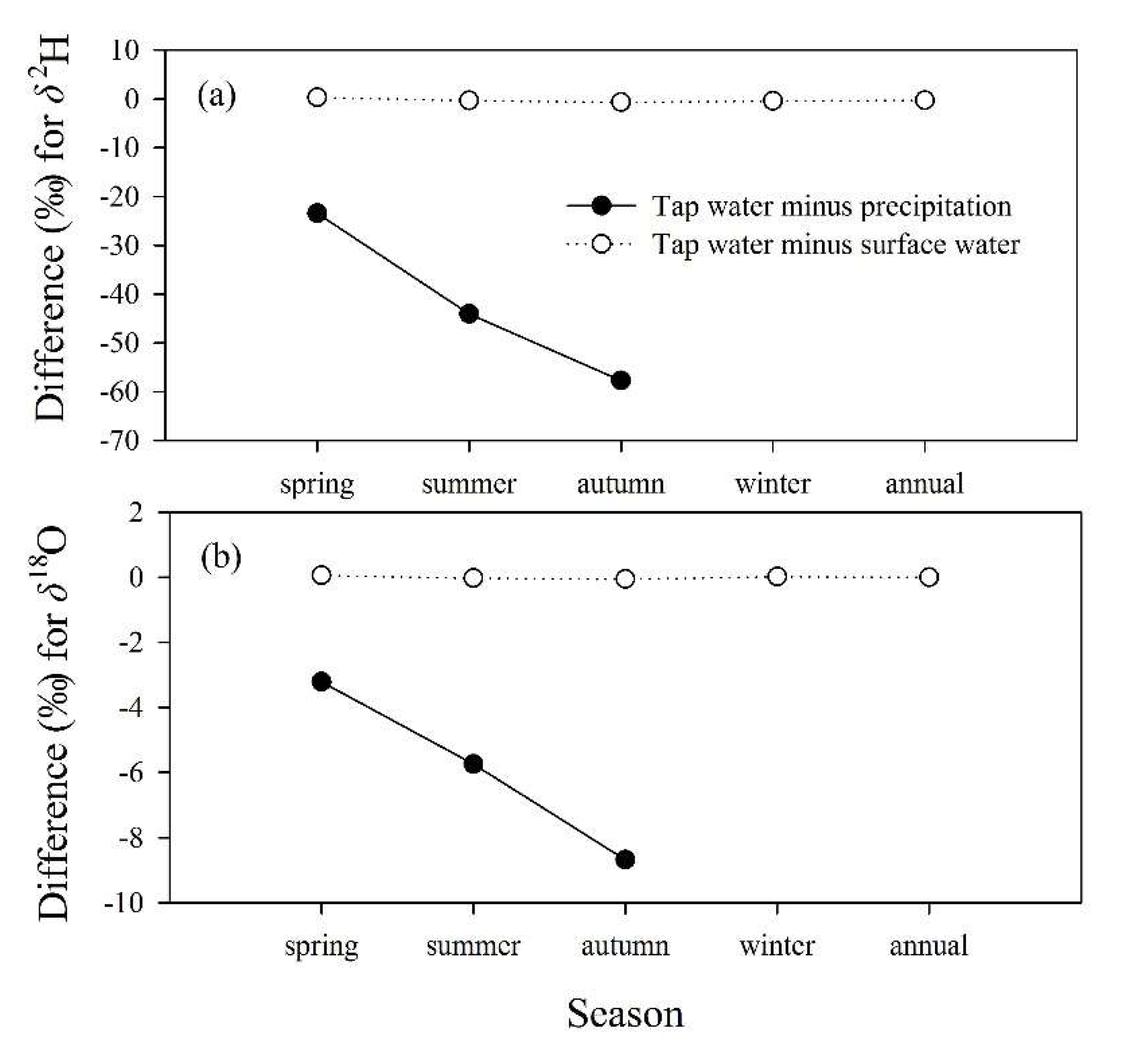
3.2. Comparison of Isotopes in Tap Water with Those in Precipitation and Surface Water
4. Discussion
4.1. Representation of Isotope Data at a Single Sampling Site
4.2. Determination of Tap Water Source Based on Isotope Data
4.3. Change of Isotopes from Raw Water to Tap Water
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Killingley, J.S.; Newman, W.A. 18O fractionation in barnacle calcite: A barnacle paleotemperature equation. J. Mar. Res. 1982, 40, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1996, 24, 225–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, J.S.; Lin, G.G.; Ehleringer, J.R. A mechanistic model for interpretation of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in tree-ring cellulose. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepez, E.A.; Williams, D.G.; Scott, R.L.; Lin, G. Partitioning overstory and understory evapotranspiration in a semiarid savanna woodland from the isotopic composition of water vapor. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 119, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.G.; Cable, W.; Hultine, K.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Yepez, E.A.; Simonneaux, V.; Er-Raki, S.; Boulet, G.; de Bruin, H.A.R.; Chehbouni, A. Evapotranspiration components determined by stable isotope, sap flow and eddy covariance techniques. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 125, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, F.E.; Sibray, S.S. Delineating ground water recharge from leaking irrigation canals using water chemistry and isotopes. Ground Water 2001, 39, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.B.; Bowen, G.J.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Stable isotopes as one of nature’s ecological recorders. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Bowen, G.J.; Chesson, L.A.; West, A.G.; Podlesak, D.W.; Cerling, T.E. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in human hair are related to geography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.W.; Mullins, H.T.; Patterson, W.P. Relationship between atmospheric circulation and winter precipitation delta O-18 in central New York State. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L22209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Kennedy, C.D.; Henne, P.D.; Zhang, T. Footprint of recycled water subsidies downwind of Lake Michigan. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; Hultine, K.R.; Burtch, K.G.; Ehleringer, J.R. Seasonal variations in moisture use in a pinon-juniper woodland. Oecologia 2007, 153, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, H.; Hettasch, H.; West, A.G.; Cramer, M.D. Hydraulic redistribution by Protea “Sylvia” (Proteaceae) facilitates soil water replenishment and water acquisition by an understorey grass and shrub. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienen, R.J.W.; Helle, G.; Pons, T.L.; Guyot, J.L.; Gloor, M. Oxygen isotopes in tree rings are a good proxy for Amazon precipitation and El Nino-Southern Oscillation variability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16957–16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K.A.; Atwell, L.; Wassenaar, L.I. Influence of drinking water and diet on the stable-hydrogen isotope ratios of animal tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8003–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Global application of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to wildlife forensics. Oecologia 2005, 143, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Heaton, K.; Hoogewerff, J. Tracing the geographical origin of food: The application of multi-element and multi-isotope analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Streamside trees that do not use streamwater. Nature 1991, 350, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Dawson, T.E. Water uptake by plants: Perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Revenaugh, J. Interpolating the isotopic composition of modern meteoric precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Levin, N.E.; Chesson, L.A. Continental scale variation in 17O-excess of meteoric waters in the United States. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 164, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; February, E.C.; Bowen, G.J. Spatial analysis of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes (“isoscapes”) inground water and tap water across South Africa. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 145, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, Y.; Brewer, S.; Good, S.P.; Tipple, B.J.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Bowen, G.J. Tap water isotope ratios reflect urban water system structure and dynamics across a semi-arid metropolitan area. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; McDonnell, J.J. Ecohydrologic separation of water between trees and streams in a Mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gat, J.R.; Bowser, C.J.; Kendall, C. The contribution of evaporation from the Great Lakes to the continental atmosphere: Estimate based on stable isotope data. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Edwards, T.W.D. Regional water balance trends and evaporation-transpiration partitioning from a stable isotope survey of lakes in northern Canada. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.J.; McDonnell, J.J.; Weiler, M.; Kendall, C.; McGlynn, B.L.; Welker, J.M.; Seibert, J. The role of topography on catchment–scale water residence time. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, J.; Noone, D.; Bowman, K.; Beer, R.; Eldering, A.; Fisher, B.; Gunson, M.; Goldman, A.; Herman, R.; Kulawik, S.S.; et al. Importance of rain evaporation and continental convection in the tropical water cycle. Nature 2007, 445, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Winter, D.A.; Spero, H.J.; Zierenberg, R.A.; Reeder, M.D.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios of bottled waters of the world. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenčič, M.; Vreča, P. Identification of sources and production processes of bottled waters by stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 3205–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bong, Y.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Lee, K.S. Characterizing the origins of bottled water on the South Korean market using chemical and isotopic compositions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 631, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesson, L.A.; Valenzuela, L.O.; O’Grady, S.P.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope ratios of milk in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesson, L.A.; Valenzuela, L.O.; O’Grady, S.P.; Cerling, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Links between purchase location and stable isotope ratios of bottled water, soda, and beer in the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7311–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotsika, E.; Poutoukis, D.; Raco, B.; Psomiadis, D. Stable isotope composition of Hellenic bottled waters. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.E.; Shin, W.J.; Ryu, J.S.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, K.S. Identification of the origin and water type of various Korean bottled waters using strontium isotopes. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipple, B.J.; Jameel, Y.; Chau, T.H.; Mancuso, C.J.; Bowen, G.J.; Dufour, A.; Chesson, L.A.; Ehleringer, J.R. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of tap water reveal structure of the San Francisco Bay Area’s water system and adjustments during a major drought. Water Res. 2017, 119, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hu, H.; Tian, F.; Tie, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C. Divergence of stable isotopes in tap water across China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Chesson, L.A.; Stange, E.; Cerling, T.E. Stable isotope ratios of tap water in the contiguous United States. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwehr, J.M.; Coplen, T.B.; Stewart, D.W. Spatial, seasonal, and source variability in the stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of tap waters throughout the USA. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 5382–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Kennedy, C.D.; Stalker, J.C.; Chesson, L.A.; Valenzuela, L.O.; Beasley, M.M.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Bowen, G.J. Patterns of local and nonlocal water resource use across the western US determined via stable isotope intercomparisons. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8034–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Bowen, G.J.; Liu, X.; Du, M.; Chen, F.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L.; Che, Y.; Zhao, G. Water source signatures in the spatial and seasonal isotope variation of Chinese tap waters. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 9131–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.R.; Barnette, J.E.; Jameel, Y.; Tipple, B.J.; Bowen, G.J. Urban water–a new frontier in isotope hydrology. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2016, 52, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, M.; Bell, L.S. A city-wide investigation of the isotopic distribution and source of tap waters for forensic human geolocation ground-truthing. J. Forens. Sci. 2017, 62, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, G.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hendry, M.J. High-precision laser spectroscopy D/H and 18O/16O measurements of microliter natural water samples. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, S.W.; Desilets, S.L.E.; Troch, P.A. A tale of two isotopes: Differences in hydrograph separation for a runoff event when using δD versus δ18O. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA/WMO (International Atomic Energy Agency/World Meteorological Organization). Water Isotope System for Data Analysis, Visualization and Electronic Retrieval (WISER). 2017. Available online: https://nucleus.iaea.org/wiser (accessed on 2 June 2018).
- Craig, H. Standard for reporting concentration of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural waters. Science 1961, 113, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. Standard for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds. Nature (Lond.) 1978, 271, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, E.; Dall’ Olio, A.; Matsui, E.; Gat, J.R. Recycling of water in the Amazon basin: An isotopic study. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansu Provincial Water Conservancy Department. Gansu Water Resources Bulletin in 2015; Gansu Water Resources Bulletin; Gansu Provincial Water Conservancy Department: Lanzhou, China, June 2016.
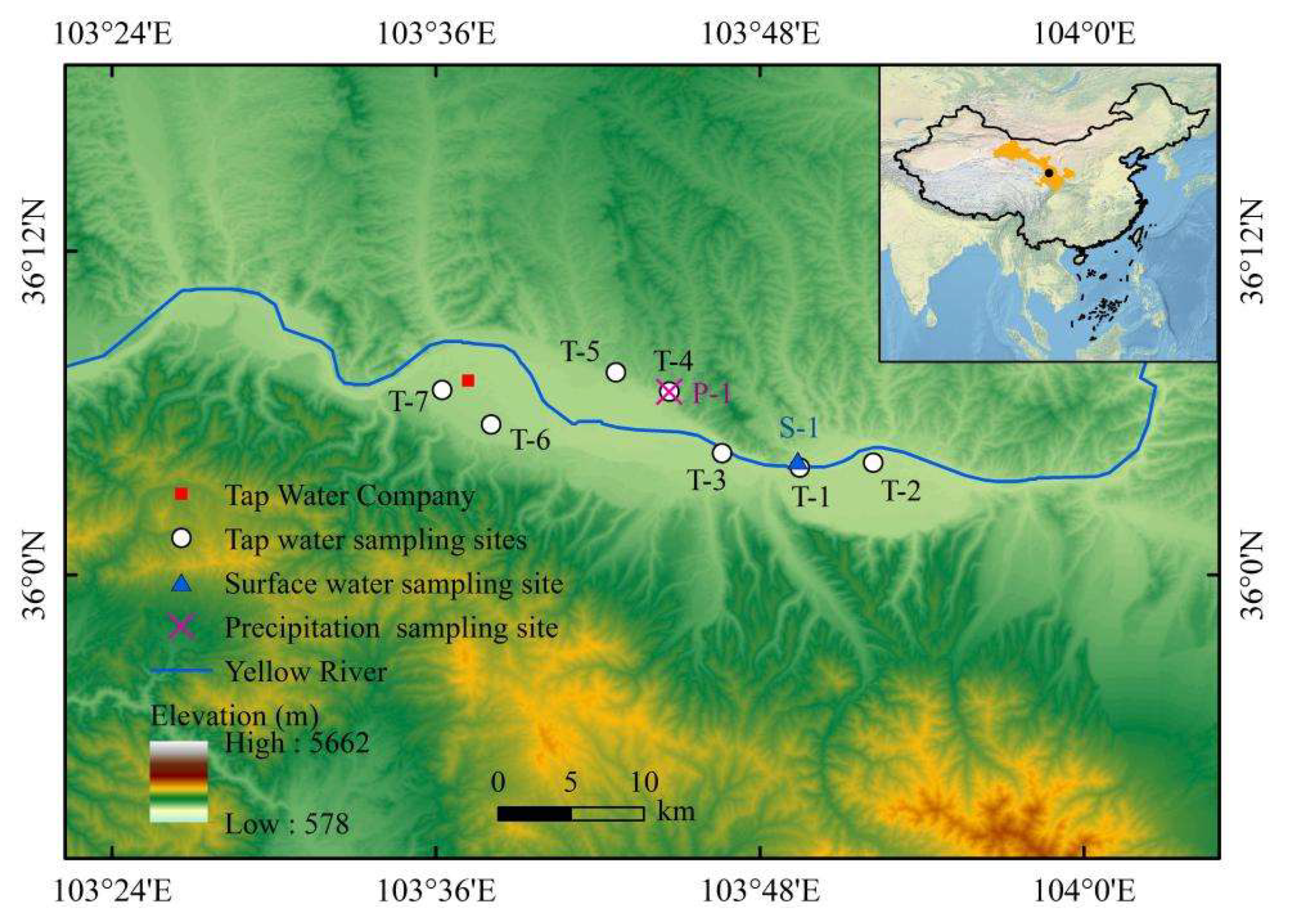







| Type | Code | Name of Sampling Sites | Longitude (°) | Latitude (°) | Elevation (m) | Sampling Period | Number of Samples (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water sampling sites | T-1 | Xiguan | 103.825 | 36.066 | 1533 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 |
| T-2 | Tanjianzi | 103.870 | 36.069 | 1517 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 | |
| T-3 | Xizhan | 103.777 | 36.075 | 1543 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 | |
| T-4 | Qiujiawan | 103.744 | 36.113 | 1545 | August 2014–February 2018 1 March 2018–31 March 2018 11 March 2018, 00:30–23:30 | 98 | |
| T-5 | Shijiawan | 103.711 | 36.125 | 1550 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 | |
| T-6 | Jincheng | 103.634 | 36.093 | 1586 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 | |
| T-7 | Sunjiazhuang | 103.604 | 36.114 | 1542 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 | |
| Precipitation sampling site | P-1 | Qiujiawan | 103.744 | 36.113 | 1545 | April 2016–October 2016 | 35 |
| Surface water sampling site | S-1 | Zhongshan Bridge | 103.823 | 36.071 | 1551 | March 2016–February 2018 | 24 |
| Isotope and SD | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ2H (‰) | −69.6 | −66.3 | −64.8 | −66.2 | −66.7 |
| SD for δ2H (‰) | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 1 |
| δ18O (‰) | −9.8 | −9.6 | −9.5 | −9.6 | −9.6 |
| SD for δ18O (‰) | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 1 |
| Type of Water | Seasonal or Annual Mean Value | δ2H (‰) | SD for δ2H (‰) | δ18O (‰) | SD for δ18O (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation | spring | −46.2 | 13.1 | −6.6 | 1.1 |
| summer | −22.2 | 27.4 | −3.9 | 3.6 | |
| autumn | −7.1 | 8.7 | −0.8 | 3.3 | |
| Surface water | spring | −70.0 | 0.4 | −9.9 | 0.1 |
| summer | −65.9 | 2.3 | −9.6 | 0.4 | |
| autumn | −64.1 | 3.0 | −9.5 | 0.2 | |
| winter | −65.8 | 0.8 | −9.6 | 0.1 | |
| annual | −66.5 | 1.2 1 | −9.6 | 0.2 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y. Stable Isotope Ratios in Tap Water of a Riverside City in a Semi-Arid Climate: An Application to Water Source Determination. Water 2019, 11, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071441
Du M, Zhang M, Wang S, Chen F, Zhao P, Zhou S, Zhang Y. Stable Isotope Ratios in Tap Water of a Riverside City in a Semi-Arid Climate: An Application to Water Source Determination. Water. 2019; 11(7):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071441
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Mingxia, Mingjun Zhang, Shengjie Wang, Fenli Chen, Peipei Zhao, Su’e Zhou, and Yaning Zhang. 2019. "Stable Isotope Ratios in Tap Water of a Riverside City in a Semi-Arid Climate: An Application to Water Source Determination" Water 11, no. 7: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071441
APA StyleDu, M., Zhang, M., Wang, S., Chen, F., Zhao, P., Zhou, S., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Stable Isotope Ratios in Tap Water of a Riverside City in a Semi-Arid Climate: An Application to Water Source Determination. Water, 11(7), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071441







