Classification of Synoptic Conditions of Summer Floods in Polish Sudeten Mountains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Area of the Study
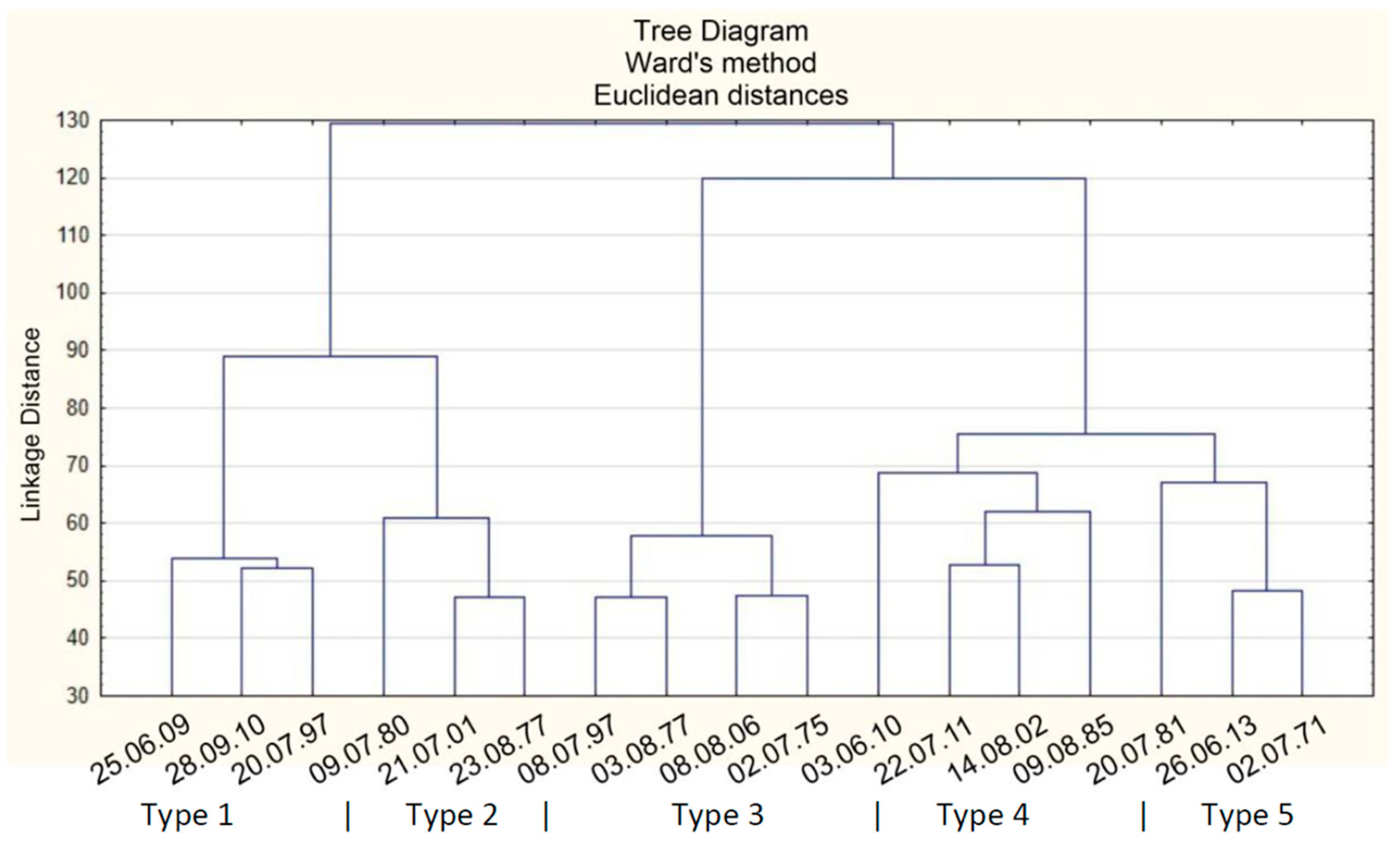
3. Data and Methods
4. Results
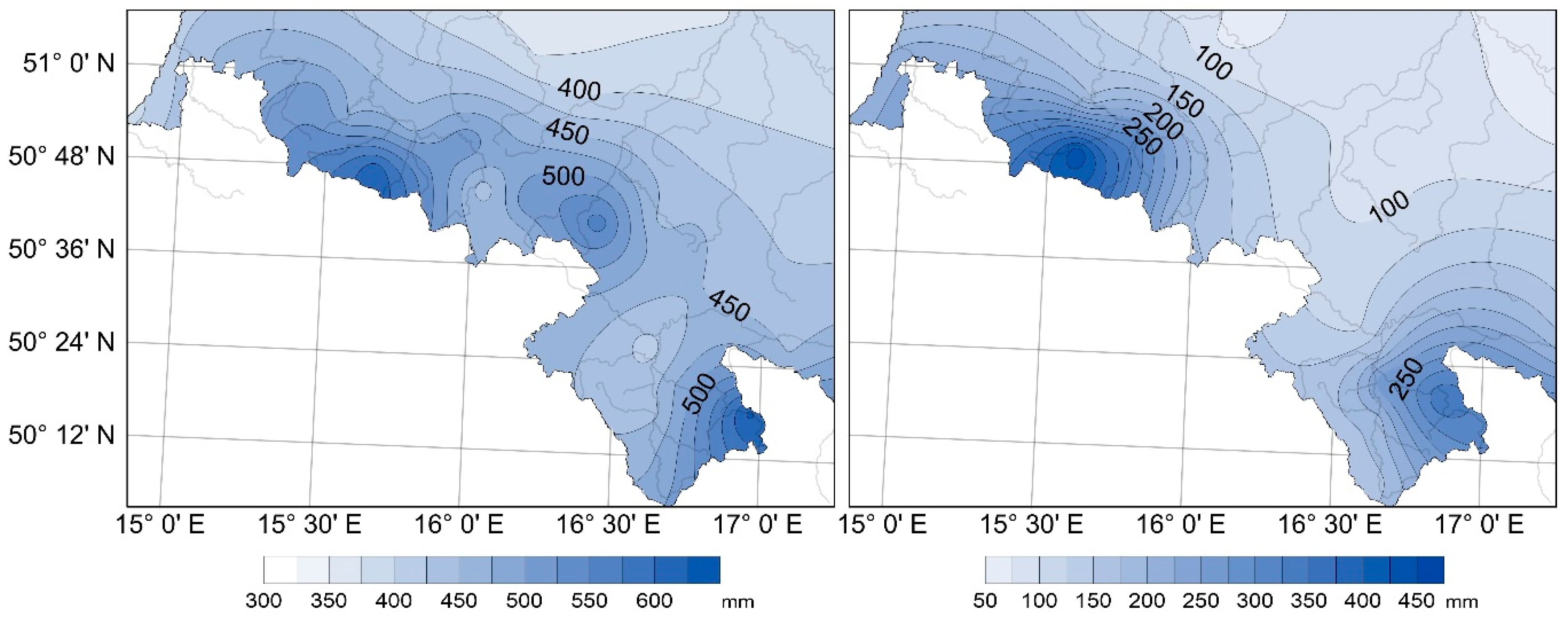
4.1. Average Hydrometeorological Conditions in the Study Area
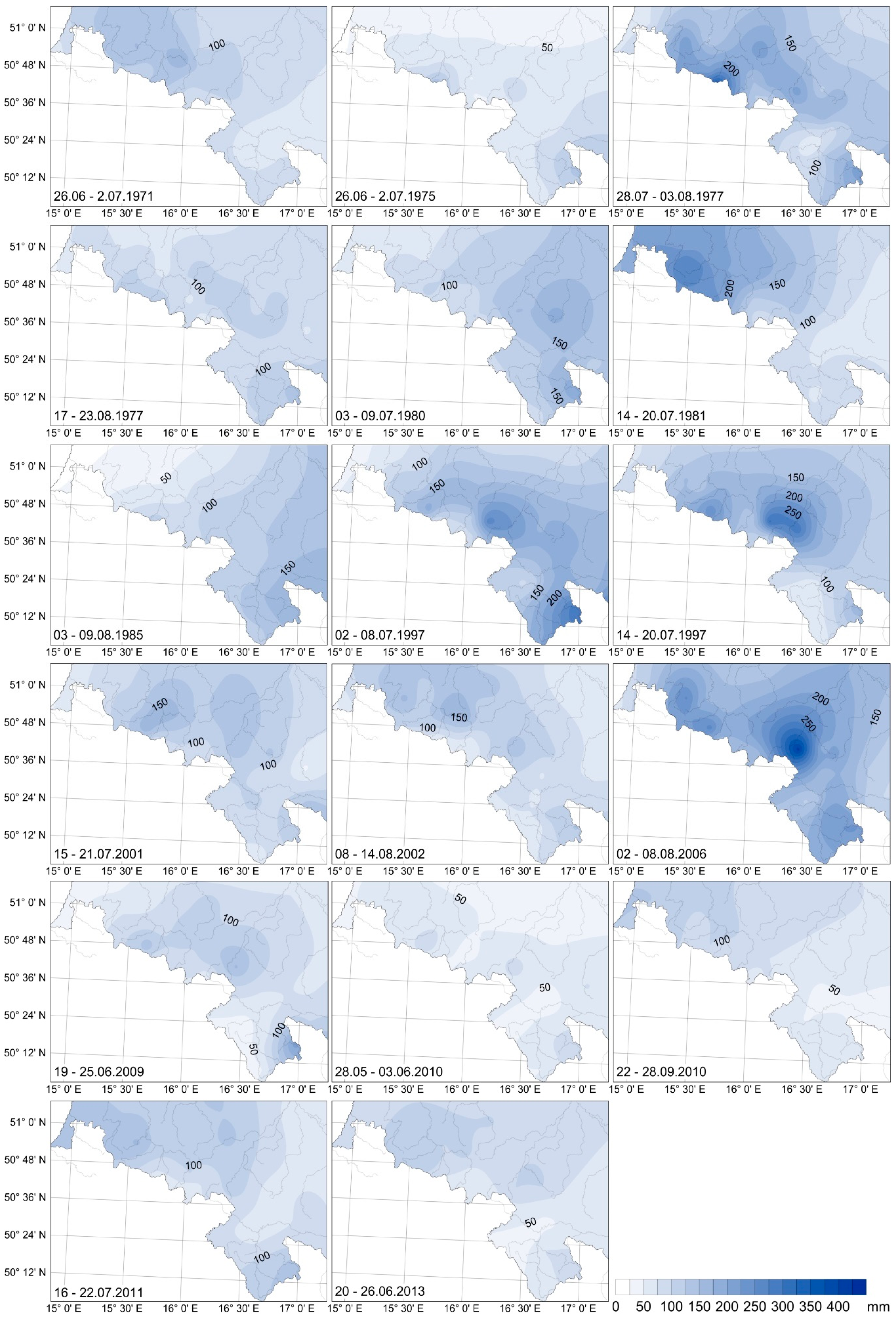
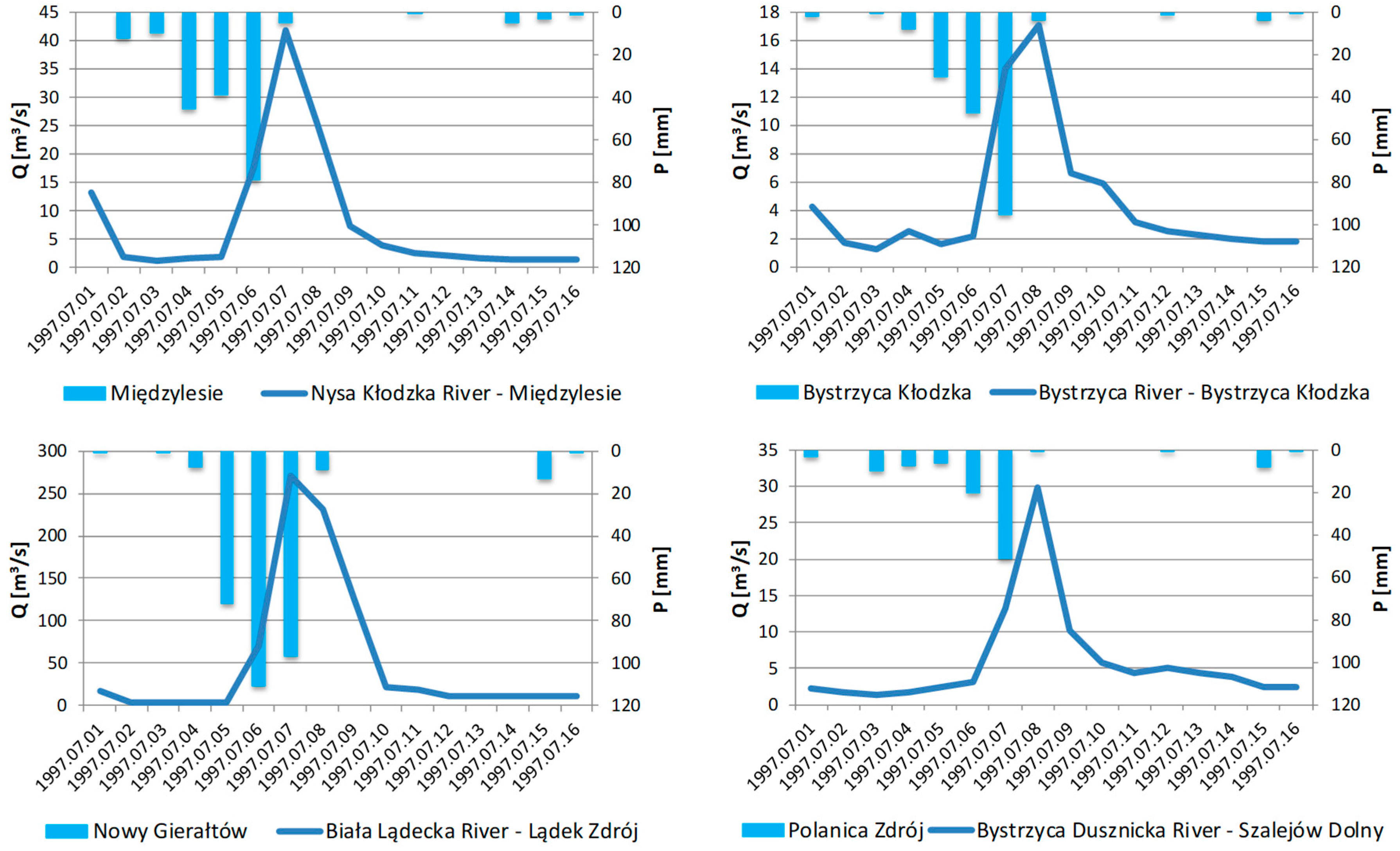
4.2. Hydrometeorological Conditions during Flood Events
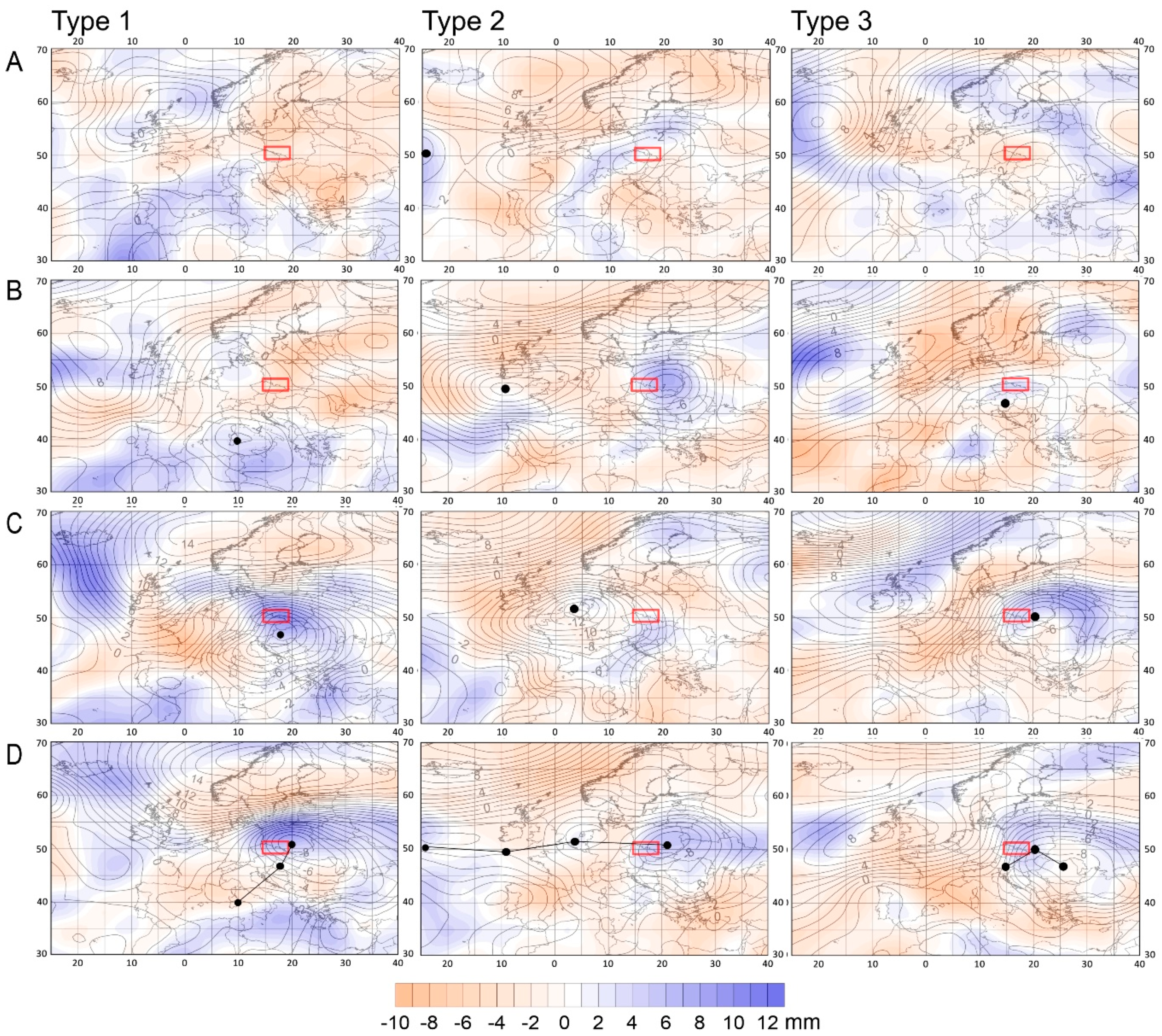
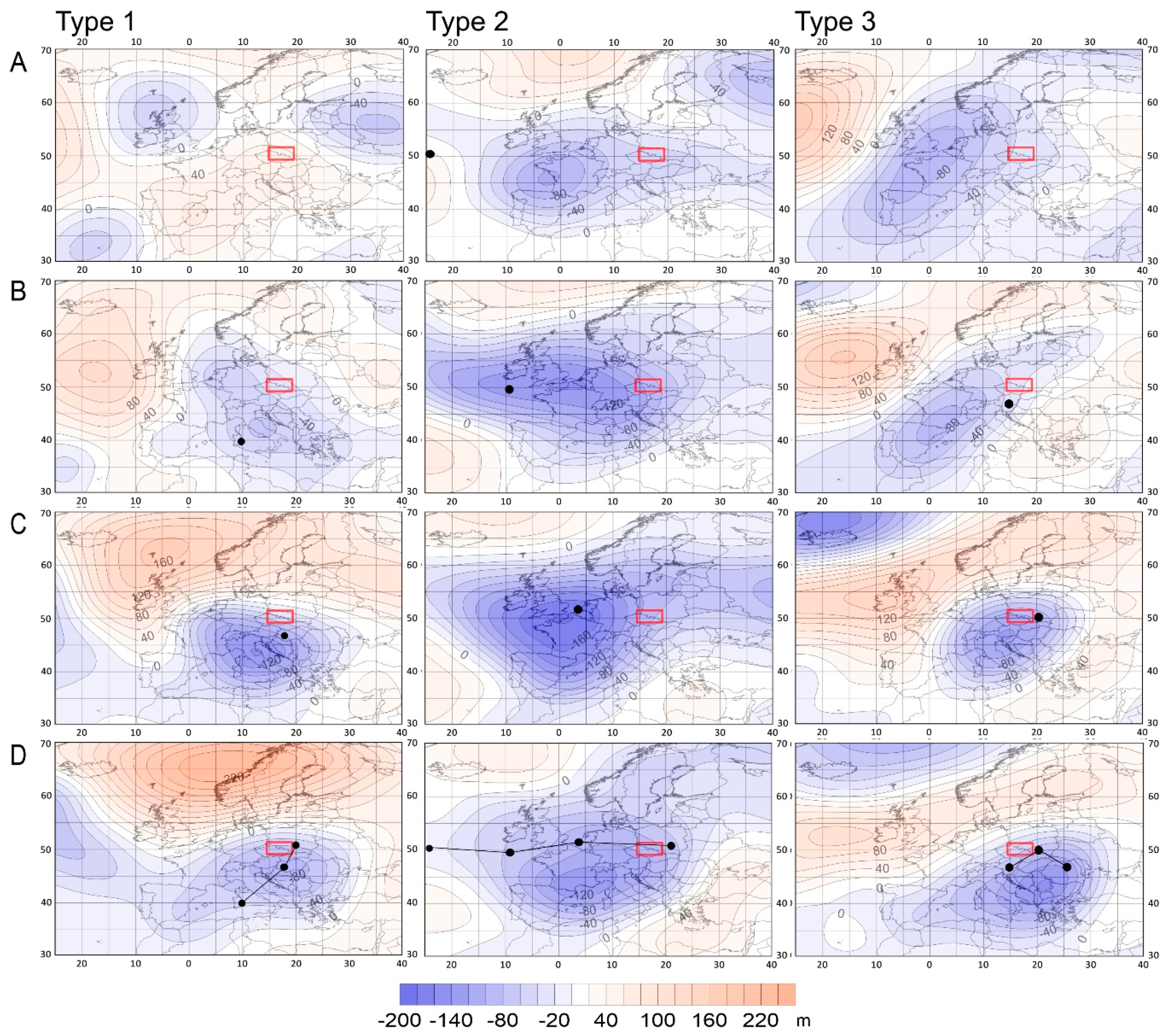
4.3. Pressure Patterns and Precipitable Water Content over Euro-Atlantic Sector during Flood Events
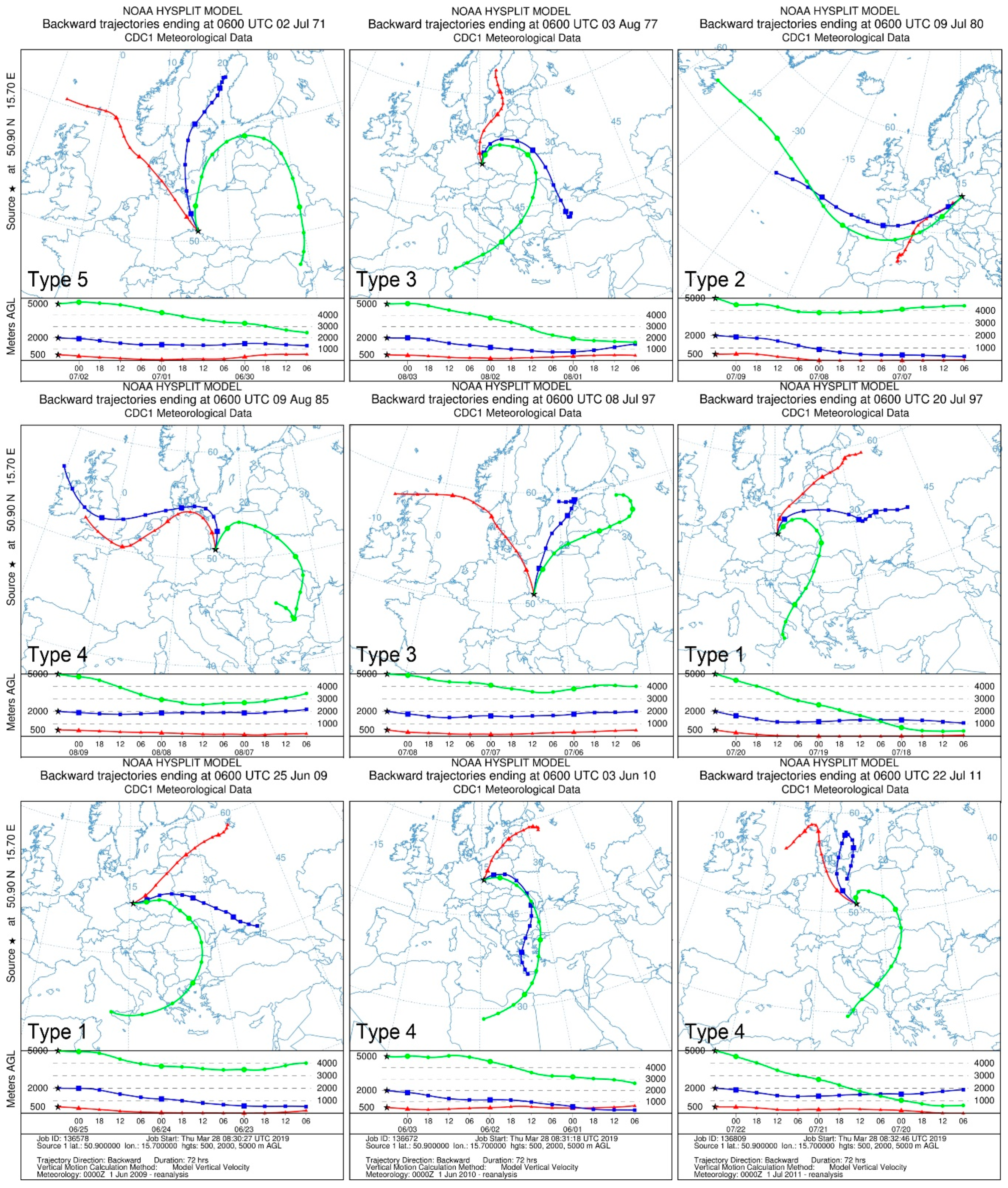
4.4. Trajectories of Air Masses before Flood Events
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Type | Beginning | End | Max Precipitation (mm) | Name of Station |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 26.06.1971 | 02.07.1971 | 170.7 | Ciechanowice |
| 3 | 26.06.1975 | 02.07.1975 | 141.2 | Śnieżka |
| 3 | 28.07.1977 | 03.08.1977 | 345.6 | Śnieżka |
| 2 | 17.08.1977 | 23.08.1977 | 138.9 | Jarnołtówek |
| 2 | 03.07.1980 | 09.07.1980 | 199.1 | Nowy Gierałtów |
| 5 | 14.07.1981 | 20.07.1981 | 266.4 | Rębiszów |
| 4 | 03.08.1985 | 09.08.1985 | 174.3 | Nowy Gierałtów |
| 3 | 02.07.1997 | 08.07.1997 | 312.8 | Jarnołtówek |
| 1 | 14.07.1997 | 20.07.1997 | 305.7 | Boguszów-Gorce |
| 2 | 15.07.2001 | 21.07.2001 | 172.4 | Przesieka |
| 4 | 08.08.2002 | 14.08.2002 | 179.5 | Ciechanowice |
| 3 | 02.08.2006 | 08.08.2006 | 412.6 | Walim |
| 1 | 19.06.2009 | 25.06.2009 | 211.5 | Nowy Gierałtów |
| 4 | 28.05.2010 | 03.06.2010 | 98.4 | Nowy Gierałtów |
| 1 | 22.09.2010 | 28.09.2010 | 126.0 | Bierna |
| 4 | 16.07.2011 | 22.07.2011 | 156.1 | Stara Kamienica |
| 5 | 20.06.2013 | 26.06.2013 | 122.3 | Stara Kamienica |
References
- Mudelsee, M.; Börngen, M.; Tetzlaff, G.; Grünewald, U. No upward trends in the occurrence of extreme floods in central Europe. Nature 2003, 425, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudelsee, M.; Börngen, M.; Tetzlaff, G.; Grünewald, U. Extreme foods in central Europe over the past 500 years: Role of cyclone pathway “Zugstrasse Vb”. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D23101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Krysanova, V.; Dankers, R.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Kanae, S.; Hattermann, F.; Huang, S.; Milly, P.; Stoffel, M.; Driessen, P.; et al. Differences in flood hazard projections in Europe—Their causes and consequences for decision making. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Pińskwar, I.; Brakenridge, G.R. Changes in river flood hazard in Europe: A review. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 49, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Graczyk, D.; Maurer, T.; Pinskwar, I.; Radziejewski, M.; Svensson, C.; Szwed, M. Trend detection in river flow time series: 1. Annual maximum flow. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2005, 50, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Pinskwar, I.; Brakenridge, R.G. Large floods in Europe, 1985–2009. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Kanae, S.; Emori, S.; Oki, T.; Kimoto, M. Global projections of changing risks of floods and droughts in a changing climate. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Doswell, C.A., III; Brooks, H.E.; Maddox, R.A. Flash Flood Forecasting: An Ingredients-Based Methodology. Weather Forecast. 1996, 11, 560–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzenli, E.; Tabari, H.; Willems, P.; Yilmaz, M.T. Decadal variability analysis of extreme precipitation in Turkey and its relationship with teleconnection patterns. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3513–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadehtalaei, P.; Tabari, H.; Willems, P. Uncertainty assessment for climate change impact on intense precipitation: How many model runs do we need? Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panziera, L.; James, C.N.; Germann, U. Mesoscale organization and structure of orographic precipitation producing flash floods in the Lago Maggiore region. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A.; Filiz, F. Identification of flood producing atmospheric circulation patterns. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Borga, M.; Morin, E.; Delrieu, G. Analysis of flash flood regimes in the north-western and south-eastern Mediterranean regions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armon, M.; Dente, E.; Smith, J.A.; Enzel, Y.; Morin, E. Synoptic-Scale Control over Modern Rainfall and Flood Patterns in the Levant Drylands with Implications for Past Climates. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 1077–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzi, A.; Tartaglione, N.; Malguzzi, P. Numerical simulations of the 1994 Piedmont flood: Role of orography and moist processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedźwiedź, T.; Łupikasza, E.; Pińskwar, I.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Stoffel, M.; Małarzewski, Ł. Variability of high rainfalls and related synoptic situations causing heavy floods at the northern foothills of the Tatra Mountains. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Smull, B.F.; Houze, R.A., Jr.; Steiner, M. Cross-barrier flow during orographic precipitation events: Results from MAP and IMPROVE. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 3580–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapero, L.; Bech, J.; Duffourg, F.; Esteban, P.; Lorente, J. Mesoscale numerical analysis of the historical November 1982 heavy precipitation event over Andorra (Eastern Pyrenees). Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. 2013, 13, 2969–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niedźwiedź, T. Extreme precipitation events on the northern side of the Tatra Mountains. Geogr. Pol. 2003, 76, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Stoffel, M.; Kaczka, R.J.; Wyżga, B.; Niedźwiedź, T.; Pińskwar, I.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Łupikasza, E.; Czajka, B.; Ballesteros-Canovas, J.A.; et al. Floods at the northern foothills of the Tatra Mountains-a Polish-Swiss research project. Acta Geophys. 2014, 62, 620–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, A.; Ustrnul, Z.; Czekierda, D.; Palarz, A.; Sulikowska, A. Extreme precipitation events in the Polish Carpathians and their synoptic determinants. Időjárás 2018, 122, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska-Horawska, M. Meteorologiczne przyczyny powodzi w Polsce południowej w lipcu 1970 roku (Meteorological reasons of flood in southern Poland in July 1970). Przeglad Geofizyczny 1971, 4, 299–315. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dubicki, A.; Słota, H.; Zieliński, J. Dorzecze Odry: Monografia Powodzi Lipiec 1997 (Odra Basin: Monograph of the Flood in July 1997); IMGW: Warszawa, Poland, 1999. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Świątek, M. Advection of air masses responsible for extreme rainfall totals in Poland, as exemplified by catastrophic floods in Racibórz (July 1997) and Dobczyce (May 2010). Acta Agrophys. 2013, 20, 481–494. [Google Scholar]
- Szalińska, W.; Otop, I.; Tokarczyk, T. Precipitation extremes Turing flooding in the Odra River Basin in May–June 2010. Meteorol. Hydrol. Water Manag. Res. Oper. Appl. 2014, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubicki, A.; Malinowska-Małek, J.; Strońska, K. Flood hazards in the upper and middle Odra River basin—A short review over the last century. Limnologica 2005, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, M. Wezbrania i powodzie na rzekach Dolnego Śląska. In Wyjątkowe Zdarzenia Przyrodnicze na Dolnym Śląsku i Ich Skutki (Surges and Floods on Rivers of Lower Silesia and Their Effects); Migoń, P., Ed.; Rozprawy Naukowe Instytutu Geografii i Rozwoju Regionalnego 14, Uniwersytet Wrocławski: Wrocław, Poland, 2010. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dubicki, A. Przebieg wezbrania w lipcu 1979 r. w dorzeczu Odry (Course of the surge in July 1979 in the Odra basin). In Powódź w Lipcu 1970 r. Monografia; IMGW: Warszawa, Poland, 1972; pp. 100–112. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wrona, B. Meteorologiczne i morfologiczne uwarunkowania ekstremalnych opadów atmosferycznych w dorzeczu górnej i środkowej Odry (Meteorological and morphological conditions of extreme precipitation in lower and middle Odra basin); Materiały Badawcze, Seria: Meteorologia 41; IMGW: Warszawa, Poland, 2008. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Yarnal, B. Synoptic Climatology in Environmental Analysis; Belhaven Press: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yarnal, B.; Comrie, A.C.; Frakes, B.; Brown, D.P. Developments and prospects in synoptic climatology. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1923–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Tubia, A.; Levy, I. On the importance of synoptic classification methods with respect to environmental phenomena. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamistu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NMC/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Meteorological Society. Glossary of Meteorology. 2017. Available online: http://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/climatology (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Kalkstein, L.S.; Tan, G.; Skindlov, J.A. An evaluation of three Clustering procedures for use in synoptic climatological classification. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1987, 26, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rolph, G.D. Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display System (READY); NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012. Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D. HYSPLIT Model Access via NOAA ARL READY; NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012. Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Dynowska, I. Reżim odpływu rzecznego. In Atlas Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej; Główny Geodeta Kraju: Warszawa, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wrzesiński, D. Use of entropy in the assessment of uncertainty of river runoff regime in Poland. Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jania, J.; Zwoliński, Z. Ekstremalne zdarzenia meteorologiczne, hydrologiczne i geomorfologiczne w Polsce (Extreme meteorological, hydrological and geomorphological events in Poland). Landf. Anal. 2011, 15, 51–64. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Migoń, P. Wyjątkowe Zdarzenia Przyrodnicze na Dolnym Śląsku i Ich Skutki (Extreme Environmental Events in Lower Silesia and Their Effects); Rozprawy Naukowe Instytutu Geografii i Rozwoju Regionalnego 14, Uniwersytet Wrocławski: Wrocław, Poland, 2010; Available online: http://rtarka.ing.uni.wroc.pl/badania/rozprawy_14.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2019). (In Polish)
- Qian, W.H.; Yu, T.T.; Du, J. A unified approach to trace surface heat and cold events by using height anomaly. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 4, 1647–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Qian, W. Anomaly based analysis of extreme heat waves in Eastern China during 1981–2013. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.M.; Bednorz, E.; Sulikowska, A. Cold spells in Poland and Germany and their circulation conditions. Int. J. Climatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.M.; Bednorz, E. Heat waves in Central Europe and tropospheric anomalies of temperature and geopotential heights. Int. J. Climatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmendžić, J.; Kożuchowski, K. Szlaki niżów śródziemnomorskich nad Europą Środkowo-Wschodnią a opady w Polsce (tracks of Mediterranean Lows over Central Europe versus precipitation in Poland). Przegląd Geograficzny 2015, 87, 477–496. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bebber, W.J. Die Zugstrassen der barometrischen Minima. Meteorol. Z. 1891, 8, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Seibert, P.; Frank, A.; Formayer, H. Synoptic and regional patterns of heavy precipitation in Austria. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007, 87, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R.; Vázquez, M.; Lavers, D.A. Atmospheric rivers: A mini-review. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, D.A.; Villarini, G. The nexus between atmospheric rivers and extreme precipitation across Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 40, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavers, A.D.; Villarini, G. The contribution of atmospheric rivers to precipitation in Europe and the United States. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Martins, M.J.; Tomé, R.; Trigo, R.M. Extreme Precipitation Events in Summer in the Iberian Peninsula and Its Relationship with Atmospheric Rivers. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; Wick, G.A.; Lundquist, J.D.; Dettinger, M.D. Meteorological Characteristics and Overland Precipitation Impacts of Atmospheric Rivers Affecting the West Coast of North America Based on Eight Years of SSM/I Satellite Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, A.J.; Allan, R.P.; Lavers, D.A. Atmospheric rivers do not explain UK summer extreme rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 6731–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosart, L.F.; Moore, B.J.; Cordeira, J.M.; Archambault, H.M. Interactions of North Pacific tropical, midlatitude, and polar disturbances resulting in linked extreme weather events over North America in October 2007. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 1245–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.J.; Keyser, D.; Bosart, L.F. Rossby Wave Breaking and Extreme Precipitation Events in the Central and Eastern United States. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Atmospheric Rivers Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–28 June 2018; Available online: http://cw3e.ucsd.edu/ARconf2016/Presentations/Wednesday/S3_TheoryStructureProcesses1/Moore_IAR C2016.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Webb, J.D.C. The great summer heatwaves of 1975–1976 in the UK, and some violent storms. Int. J. Meteorol. 2011, 36, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, J.D.C.; Elsom, D.M.; Reynolds, D.J. Climatology of severe hailstorms in Great Britain. Atmos. Res. 2011, 56, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.A.; Vavrus, S.J. Evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in mid-latitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L06801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.A.; Vavrus, S.J. Evidence for a wavier jet stream in response to rapid Arctic warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.A.; Vavrus, S.J.; Cohen, J. 2017 Amplified Arctic warming and midlatitude weather: New perspectives on emerging connections. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bednorz, E.; Wrzesiński, D.; Tomczyk, A.M.; Jasik, D. Classification of Synoptic Conditions of Summer Floods in Polish Sudeten Mountains. Water 2019, 11, 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071450
Bednorz E, Wrzesiński D, Tomczyk AM, Jasik D. Classification of Synoptic Conditions of Summer Floods in Polish Sudeten Mountains. Water. 2019; 11(7):1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071450
Chicago/Turabian StyleBednorz, Ewa, Dariusz Wrzesiński, Arkadiusz M. Tomczyk, and Dominika Jasik. 2019. "Classification of Synoptic Conditions of Summer Floods in Polish Sudeten Mountains" Water 11, no. 7: 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071450
APA StyleBednorz, E., Wrzesiński, D., Tomczyk, A. M., & Jasik, D. (2019). Classification of Synoptic Conditions of Summer Floods in Polish Sudeten Mountains. Water, 11(7), 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071450





