Development of a Contaminant Distribution Model for Water Supply Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Works
3. Proposed Model Formulation
3.1. Hydraulic Model
3.2. Formulation of the Proposed Contaminant Distribution Model
4. Application of the Developed Model on WDNs
4.1. Model Programming Procedures
- Get the network analysis solution
- Prepare the Structure
- Get the pipe flows
- Get supplies and demands
- Get injections at the supply nodes
- Get contamination at supply nodes
- Compute the sum input flows to the nodes
- Build matrices for equation as function of gamma, .
- Compute contamination at the nodes
- Get contamination in the pipes, .
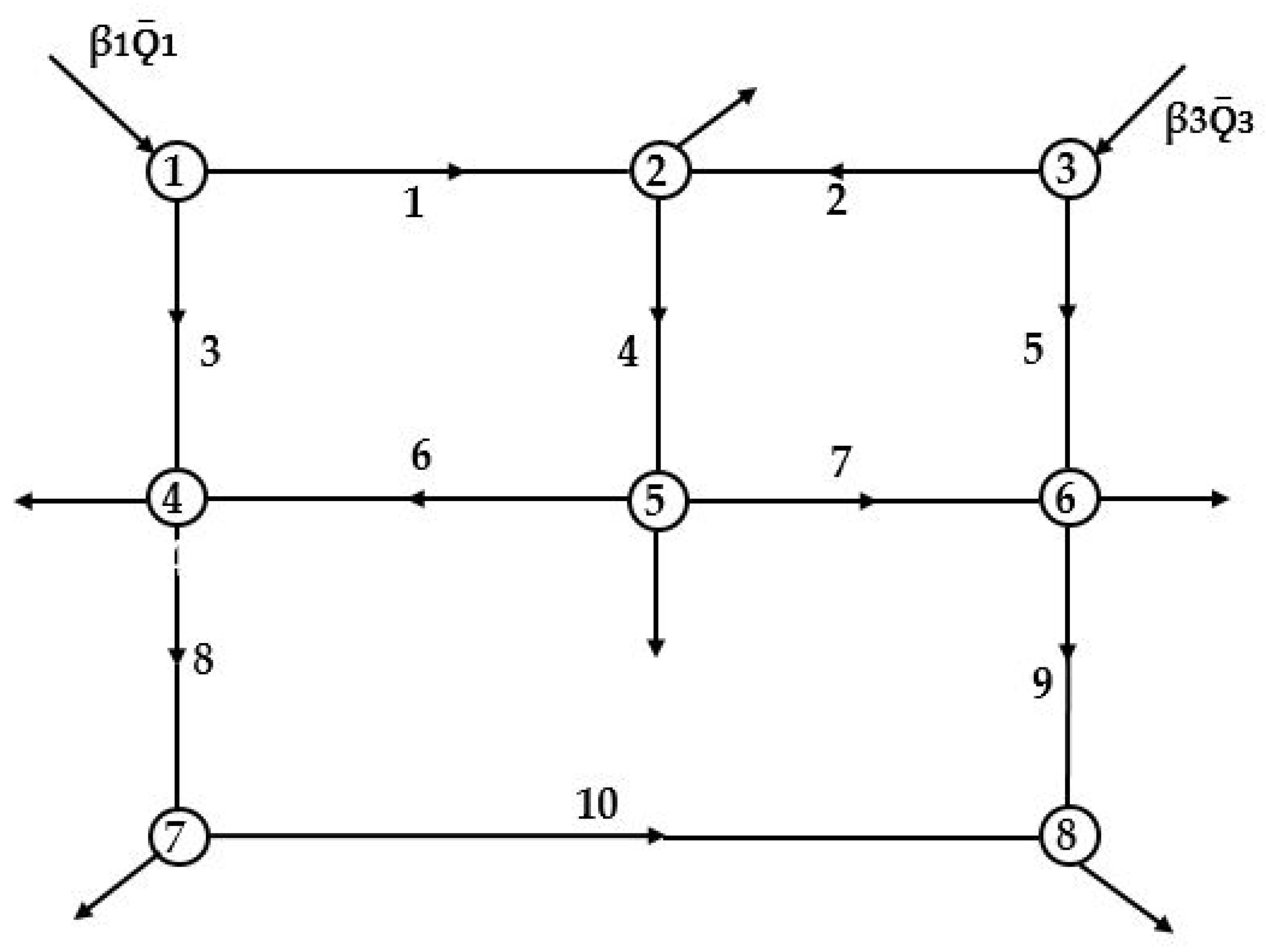
4.2. Illustrative Example 1
4.3. Illustrative Example 2
4.4. Illustrative Example 3
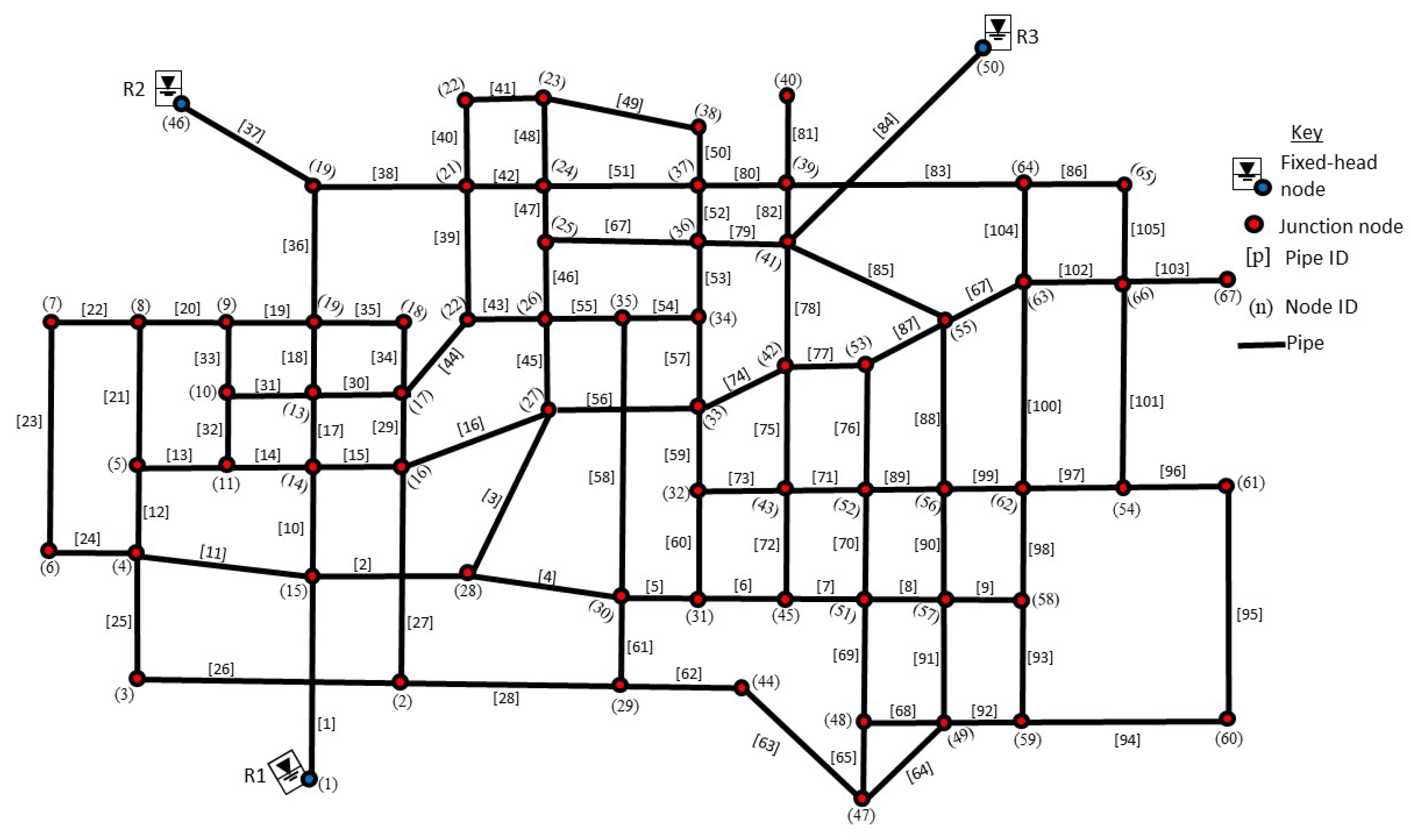
4.5. Illustrative Example 4
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Results and Discussions for Illustrative Example 1
5.2. Results and Discussions for Illustrative Example 2
5.3. Results and Discussions for Illustrative Example 3
5.4. Results and Discussions for Illustrative Example 4
6. Conclusions and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sdgreport. The Sustainable Development Goals 2015. 2015. Available online: www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sustainable-development-goals/goal-6-clean-water-and-sanitation.html (accessed on 18 May 2019).
- Clark, R.M.; Grayman, W.M.; Males, R.M. Contaminant propagation in distribution systems. J. Environ. Eng. 1988, 114, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.M.; Deininger, R.A. Protecting the nation’s critical infrastructure: The vulnerability of US water supply systems. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2000, 8, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmeyer, G.J.; Martel, K. Pathogen Intrusion into the Distribution System; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adedoja, O.S.; Hamam, Y.; Khalaf, B.; Sadiku, R. Towards Development of an Optimization Model to Identify Contamination Source in a Water Distribution Network. Water 2018, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Kenzie, W.R.; Hoxie, N.J.; Proctor, M.E.; Gradus, M.S.; Blair, K.A.; Peterson, D.E.; Kazmierczak, J.J.; Addiss, D.G.; Fox, K.R.; Rose, J.B.; et al. A massive outbreak in Milwaukee of Cryptosporidium infection transmitted through the public water supply. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corso, P.S.; Kramer, M.H.; Blair, K.A.; Addiss, D.G.; Davis, J.P.; Haddix, A.C. Costs of illness in the 1993 waterborne Cryptosporidium outbreak, Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, W.J. Responding to crisis: The West Virginia chemical spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, J.W.; Fleischer, L.; Hart, W.E.; Phillips, C.A.; Watson, J.P. Sensor placement in municipal water networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2005, 131, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.; Carr, R.D.; Hart, W.E.; Leung, V.J.; Phillips, C.A.; Watson, J.P. Designing contamination warning systems for municipal water networks using imperfect sensors. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2009, 135, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, A.; Salomons, E. Optimal layout of early warning detection stations for water distribution systems security. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, A.; Salomons, E. Optimal early warning monitoring system layout for water networks security: Inclusion of sensors sensitivities and response delays. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2005, 22, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propato, M. Contamination warning in water networks: General mixed-integer linear models for sensor location design. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, M.; Dorji, T.; Chandniha, S.K. Design scheme for water quality monitoring in a distribution network. Int. J. Environ. Dev. 2012, 9, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Afshar, A.; Khombi, S.M. Multiobjective optimization of sensor placement in water distribution networks; dual use benefit approach. Int. J. Optim. Civil. Eng. 2015, 5, 315–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, L.; Mucherino, C.; Pianese, D.; Pirozzi, F. Positioning, within water distribution networks, of monitoring stations aiming at an early detection of intentional contamination. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2006, 23, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, A.; Uber, J.G.; Salomons, E.; Berry, J.W.; Hart, W.E.; Phillips, C.A.; Watson, J.P.; Dorini, G.; Jonkergouw, P.; Kapelan, Z.; et al. The battle of the water sensor networks (BWSN): A design challenge for engineers and algorithms. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, C.D.; Biegler, L.T.; van Bloemen Waanders, B.G.; Bartlett, R.A. Contamination source determination for water networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2005, 131, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gong, W.; Wu, Q. Contaminant source identification of water distribution networks using cultural algorithm. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2017, 29, e4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechman, E.M.; Ranjithan, S.R. Evolutionary computation-based methods for characterizing contaminant sources in a water distribution system. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2009, 135, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, A.; Boccelli, D.; Shang, F.; Uber, J. Probabilistic approach to characterize contamination sources with imperfect sensors. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2008, Ahupua’A, HI, USA, 13–16 May 2008; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ranjithan, S.R.; Mahinthakumar, G. Contamination source identification in water distribution systems using an adaptive dynamic optimization procedure. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2010, 137, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zechman, E.M.; Brill, E.D., Jr.; Mahinthakumar, G.; Ranjithan, S.; Uber, J. Adaptive contamination source identification in water distribution systems using an evolutionary algorithm-based dynamic optimization procedure. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Adedeji, K.B.; Hamam, Y.; Abe, B.T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Leakage Detection and Estimation Algorithm for Loss Reduction in Water Piping Networks. Water 2017, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamam, Y.; Brameller, A. Hybrid method for the solution of piping networks. In Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers; IET: London, UK, 1971; Volume 118, pp. 1607–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Hamam, Y.; Hindi, K. Optimised on-line leakage minimisation in water piping networks using neural nets. In Proceedings of the IFIP Working Conference, Dagschul, Germany, 28 September–1 October 1992; Volume 28, pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Todini, E. A unifying view on the different looped pipe network analysis algorithms. In Computing and Control for the Water Industry; Research Studies Press Ltd.: Baldock, UK, 1999; pp. 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- De Sanctis, A.E.; Shang, F.; Uber, J.G. Real-time identification of possible contamination sources using network backtracking methods. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2009, 136, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Harrison, K.W. Improving efficiency of the Bayesian approach to water distribution contaminant source characterization with support vector regression. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2012, 140, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; McBean, E.A.; James, W. Multi-objective optimization for monitoring sensor placement in water distribution systems. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bloemen Waanders, B.G.; Bartlett, R.A.; Biegler, L.T.; Laird, C.D. Nonlinear programming strategies for source detection of municipal water networks. In Proceedings of the World Water & Environmental Resources Congress 2003, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–26 June 2003; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Laird, C.D.; Biegler, L.T.; van Bloemen Waanders, B.G. Real-time, large-scale optimization of water network systems using a subdomain approach. In Real-Time PDE-Constrained Optimization; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Preis, A.; Ostfeld, A. A contamination source identification model for water distribution system security. Eng. Optim. 2007, 39, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A. EPANET 2: Users Manual; National Risk Management Research Laboratory, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2000.
- Preis, A.; Ostfeld, A. Multiobjective sensor design for water distribution systems security. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, J.; Hu, C.; Wu, Q. Contaminant source identification in water distribution network based on hybrid encoding. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2016, 16, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawsey, W.J.; Minsker, B.S.; VanBlaricum, V.L. Bayesian belief networks to integrate monitoring evidence of water distribution system contamination. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Huang, H.D.; Xin, K.L.; Liu, S.M. Identification of contamination source in water distribution network based on consumer complaints. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2012, 19, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupauer, R.M.; Records, M.K.; Ashwood, W.H. Backward probabilistic modeling to identify contaminant sources in water distribution systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2009, 136, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, S. Contamination source identification based on sequential Bayesian approach for water distribution network with stochastic demands. IISE Trans. 2017, 49, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barandouzi, M.; Kerachian, R. Probabilistic Contaminant Source Identification in Water Distribution Infrastructure Systems. Civ. Eng. Infrastruct. J. 2016, 49, 311–326. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Guida, M.; Musmarra, D. Water network protection from intentional contamination by sectorization. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Choi, C.Y.; Gerba, C.P. Source tracking of microbial intrusion in water systems using artificial neural networks. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zechman, E.M.; Mahinthakumar, G.; Ranji Ranjithan, S. Identifying contaminant sources for water distribution systems using a hybrid method. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2012, 29, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zechman, E.M.; Mahinthakumar, G.; Ranjithan, S.R. Coupling of logistic regression analysis and local search methods for characterization of water distribution system contaminant source. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumbelow, K.; Torres, J.; Guikema, S.; Bristow, E.; Kanta, L. Virtual cities for water distribution and infrastructure system research. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2007: Restoring our Natural Habitat, Tampa, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Adedeji, K. Development of a Leakage Detection and Localisation Technique for Real-Time Applications in Water Distribution Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Tshawane University of Technology, Pretoria, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, H.; Kassab, B. Analysis of water distribution systems using a perturbation method. Appl. Math. Model. 1996, 20, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockling, M.; Allen, J.; Smits, A. Roughness effects in turbulent pipe flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 564, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozger, S.S.; Mays, L. A Semi-Pressure-Driven Approach to Reliability Assessment of Water Distribution Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.M.; Narasimhan, S.; Bhallamudi, S.M. State estimation in water distribution networks using graph-theoretic reduction strategy. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Pipe ID | Length (m) | D (mm) | C (H-W) | Node ID | Elevation (m) | Demand (CMH) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 609.60 | 762 | 130 | 1 | 27.43 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 243.80 | 762 | 128 | 2 | 33.53 | 212.4 |
| 3 | 1524.00 | 609 | 126 | 3 | 28.96 | 212.4 |
| 4 | 1127.76 | 609 | 124 | 4 | 32.00 | 640.8 |
| 5 | 1188.72 | 406 | 122 | 5 | 30.48 | 212.4 |
| 6 | 640 | 406 | 120 | 6 | 31.39 | 684.0 |
| 7 | 762.00 | 254 | 118 | 7 | 29.56 | 640.8 |
| 8 | 944.88 | 254 | 116 | 8 | 31.39 | 327.6 |
| 9 | 1676.40 | 381 | 114 | 9 | 32.61 | 0.0 |
| 10 | 883.92 | 305 | 112 | 10 | 34.14 | 0.0 |
| 11 | 883.92 | 305 | 110 | 11 | 35.05 | 108.0 |
| 12 | 1371.60 | 381 | 108 | 12 | 36.58 | 108.0 |
| 13 | 762.00 | 254 | 106 | 13 | 33.53 | 0.0 |
| 14 | 822.96 | 254 | 104 | RES | 60.96 | N/A |
| 15 | 944.88 | 305 | 102 | RES | 60.96 | N/A |
| 16 | 579.00 | 305 | 100 | |||
| 17 | 487.68 | 203 | 98 | |||
| 18 | 457.20 | 152 | 96 | |||
| 19 | 502.92 | 203 | 94 | |||
| 20 | 883.92 | 203 | 92 | |||
| 21 | 944.88 | 305 | 90 |
| Pipe ID | Pipes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Pipes (L/s) | % of Contaminant in Pipes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 625.874 | 18.776 | 0.030 |
| 2 | 625.874 | 18.776 | 0.030 |
| 3 | 336.585 | 10.098 | 0.030 |
| 4 | 219.708 | 6.591 | 0.030 |
| 5 | 18.485 | 0.369 | 0.020 |
| 6 | 248.126 | 4.963 | 0.020 |
| 7 | 60.193 | 1.758 | 0.029 |
| 8 | 57.877 | 1.736 | 0.030 |
| 9 | 151.430 | 4.542 | 0.030 |
| 10 | 10.287 | 0.308 | 0.030 |
| 11 | 84.557 | 1.691 | 0.020 |
| 12 | 86.082 | 1.721 | 0.020 |
| 13 | 34.961 | 0.699 | 0.020 |
| 14 | 21.021 | 0.631 | 0.030 |
| 15 | 78.858 | 2.365 | 0.030 |
| 16 | 45.785 | 1.373 | 0.030 |
| 17 | 33.072 | 0.992 | 0.030 |
| 18 | 3.0726 | 0.0921 | 0.030 |
| 19 | 26.927 | 0.807 | 0.030 |
| 20 | 18.858 | 0.565 | 0.030 |
| 21 | 51.120 | 1.022 | 0.020 |
| Node ID | Node Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Nodes (L/s) | % of Contaminant at Nodes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 625.874 | 18.776 | 0.030 |
| 2 | 625.874 | 18.776 | 0.030 |
| 3 | 336.585 | 10.098 | 0.030 |
| 4 | 238.193 | 6.955 | 0.029 |
| 5 | 248.125 | 4.962 | 0.020 |
| 6 | 190.000 | 4.465 | 0.024 |
| 7 | 209.307 | 6.279 | 0.030 |
| 8 | 91.000 | 2.220 | 0.024 |
| 9 | 45.785 | 1.373 | 0.030 |
| 10 | 78.858 | 2.365 | 0.030 |
| 11 | 33.072 | 0.992 | 0.030 |
| 12 | 30 | 0.900 | 0.030 |
| 13 | 86.082 | 1.721 | 0.020 |
| 14 | 625.874 | 18.776 | 0.030 |
| 15 | 248.125 | 4.962 | 0.0200 |
| Pipe ID | Pipes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Pipes (L/s) | Pipe ID | Pipes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Pipes (L/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88.879 | 4.444 | 37 | 0.277 | 0.014 |
| 2 | 61.733 | 3.086 | 38 | 0.034 | 0.017 |
| 3 | 58.003 | 2.900 | 39 | 6.542 | 0.327 |
| 4 | 24.731 | 1.236 | 40 | 1.493 | 0.075 |
| 5 | 22.966 | 1.148 | 41 | 0.117 | 0.006 |
| 6 | 7.490 | 0.374 | 42 | 2.167 | 0.108 |
| 7 | 6.545 | 0.327 | 43 | 0.498 | 0.025 |
| 8 | 5.880 | 0.294 | 44 | 0.831 | 0.042 |
| 9 | 4.805 | 0.240 | 45 | 3.818 | 0.191 |
| 10 | 3.415 | 0.171 | 46 | 2.335 | 0.117 |
| 11 | 2.530 | 0.126 | 47 | 1.452 | 0.073 |
| 12 | 1.865 | 0.093 | 48 | 3.376 | 0.169 |
| 13 | 0.733 | 0.037 | 49 | 1.790 | 0.089 |
| 14 | 22.758 | 1.137 | 50 | 0.632 | 0.032 |
| 15 | 5.362 | 0.268 | 51 | 0.482 | 0.241 |
| 16 | 2.266 | 0.113 | 52 | 2.080 | 0.104 |
| 17 | 0.776 | 0.038 | 53 | 14.962 | 0.748 |
| 18 | 8.014 | 0.401 | 54 | 5.924 | 0.296 |
| 19 | 2.479 | 0.124 | 55 | 5.734 | 0.286 |
| 20 | 1.6445 | 0.082 | 56 | 25.816 | 1.290 |
| 21 | 0.685 | 0.034 | 57 | 9.850 | 0.493 |
| 22 | 1.8360 | 0.092 | 58 | 3.660 | 0.183 |
| 23 | 0.479 | 0.024 | 59 | 7.967 | 0.398 |
| 24 | 0.043 | 0.002 | 60 | 7.398 | 0.369 |
| 25 | 5.029 | 0.252 | 61 | 7.490 | 0.374 |
| 26 | 1.313 | 0.065 | 62 | 6.545 | 0.327 |
| 27 | 0.942 | 0.471 | 63 | 5.880 | 0.294 |
| 28 | 0.401 | 0.020 | 64 | 4.805 | 0.240 |
| 29 | 1.913 | 0.095 | 65 | 3.415 | 0.171 |
| 30 | 0.809 | 0.040 | 66 | 2.530 | 0.126 |
| 31 | 0.264 | 0.013 | 67 | 1.865 | 0.093 |
| 32 | 2.832 | 0.141 | 68 | 1.797 | 0.089 |
| 33 | 0.137 | 0.007 | 69 | 0.117 | 0.006 |
| 34 | 0.509 | 0.025 | 70 | 11.606 | 0.580 |
| 35 | 0.345 | 0.017 | 71 | 10.778 | 0.538 |
| 36 | 1.025 | 0.051 |
| Node ID | Node Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Nodes (L/s) | Node ID | Nodes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Nodes (L/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 88.879 | 4.444 | 24 | 3.227 | 0.161 |
| 2 | 88.879 | 4.444 | 25 | 1.749 | 0.087 |
| 3 | 61.732 | 3.086 | 26 | 0.665 | 0.033 |
| 4 | 58.003 | 2.900 | 27 | 2.970 | 0.148 |
| 5 | 44.303 | 2.215 | 28 | 1.024 | 0.051 |
| 6 | 41.143 | 2.057 | 29 | 0.786 | 0.039 |
| 7 | 14.980 | 0.749 | 30 | 0.378 | 0.018 |
| 8 | 13.090 | 0.654 | 31 | 6.542 | 0.327 |
| 9 | 11.760 | 0.588 | 32 | 1.493 | 0.074 |
| 10 | 9.610 | 0.481 | 33 | 2.400 | 0.120 |
| 11 | 6.830 | 0.342 | 34 | 3.818 | 0.191 |
| 12 | 5.060 | 0.253 | 35 | 1.330 | 0.066 |
| 13 | 3.730 | 0.186 | 36 | 4.828 | 0.241 |
| 14 | 2.530 | 0.126 | 37 | 2.335 | 0.116 |
| 15 | 22.757 | 1.137 | 38 | 5.734 | 0.287 |
| 16 | 5.362 | 0.268 | 39 | 2.272 | 0.113 |
| 17 | 2.266 | 0.113 | 40 | 0.632 | 0.032 |
| 18 | 0.820 | 0.041 | 41 | 14.962 | 0.748 |
| 19 | 8.014 | 0.401 | 42 | 2.080 | 0.104 |
| 20 | 4.315 | 0.215 | 43 | 25.816 | 1.290 |
| 21 | 2.123 | 0.106 | 44 | 5.924 | 0.296 |
| 22 | 0.685 | 0.034 | 45 | 9.850 | 0.492 |
| 23 | 5.029 | 0.251 | 46 | 3.660 | 0.183 |
| Pipe ID | Pipes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Pipes (L/s) | % in Pipes | Pipe ID | Pipes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Pipes (L/s) | % in Pipes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 333.826 | 13.353 | 0.0400 | 54 | 3.202 | 0.096 | 0.0300 |
| 2 | 203.906 | 8.156 | 0.0400 | 55 | 0.872 | 0.026 | 0.0300 |
| 3 | 80.237 | 3.209 | 0.0400 | 56 | 13.062 | 0.522 | 0.0400 |
| 4 | 123.668 | 4.946 | 0.0400 | 57 | 2.922 | 0.087 | 0.0300 |
| 5 | 77.794 | 3.097 | 0.0398 | 58 | 2.329 | 0.069 | 0.0300 |
| 6 | 74.988 | 2.985 | 0.0398 | 59 | 7.701 | 0.275 | 0.0358 |
| 7 | 71.229 | 2.836 | 0.0398 | 60 | 2.805 | 0.112 | 0.0398 |
| 8 | 27.487 | 1.094 | 0.0398 | 61 | 8.204 | 0.326 | 0.0398 |
| 9 | 13.357 | 0.527 | 0.0395 | 62 | 12.085 | 0.481 | 0.0399 |
| 10 | 68.823 | 2.752 | 0.0400 | 63 | 2.914 | 0.115 | 0.0397 |
| 11 | 51.096 | 2.043 | 0.0400 | 64 | 8.716 | 0.347 | 0.0397 |
| 12 | 21.911 | 0.876 | 0.0400 | 65 | 4.198 | 0.166 | 0.0396 |
| 13 | 14.557 | 0.582 | 0.0400 | 66 | 3.970 | 0.158 | 0.0398 |
| 14 | 23.466 | 0.938 | 0.0400 | 67 | 12.686 | 0.505 | 0.0398 |
| 15 | 7.850 | 0.314 | 0.0400 | 68 | 26.055 | 1.037 | 0.0398 |
| 16 | 21.783 | 0.871 | 0.0400 | 69 | 12.558 | 0.437 | 0.0348 |
| 17 | 37.507 | 1.500 | 0.0400 | 70 | 3.759 | 0.149 | 0.0398 |
| 18 | 11.772 | 0.473 | 0.0420 | 71 | 10.506 | 0.387 | 0.0368 |
| 19 | 4.206 | 0.192 | 0.0458 | 72 | 6.717 | 0.201 | 0.0300 |
| 20 | 3.183 | 0.145 | 0.0458 | 73 | 8.292 | 0.248 | 0.0300 |
| 21 | 16.468 | 0.658 | 0.0400 | 74 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.0300 |
| 22 | 9.651 | 0.395 | 0.0409 | 75 | 40.705 | 1.221 | 0.0300 |
| 23 | 0.348 | 0.014 | 0.0400 | 76 | 55.714 | 1.671 | 0.0300 |
| 24 | 10.348 | 0.414 | 0.0400 | 77 | 42.031 | 1.261 | 0.0300 |
| 25 | 3.837 | 0.153 | 0.0400 | 78 | 26.066 | 1.007 | 0.0387 |
| 26 | 1.1627 | 0.046 | 0.0400 | 79 | 10.000 | 0.352 | 0.0353 |
| 27 | 10.043 | 0.401 | 0.0400 | 80 | 16.945 | 0.508 | 0.0300 |
| 28 | 3.881 | 0.155 | 0.0400 | 81 | 23.012 | 0.811 | 0.0353 |
| 29 | 19.590 | 0.783 | 0.0400 | 82 | 125.101 | 3.753 | 0.0300 |
| 30 | 4.332 | 0.181 | 0.0419 | 83 | 10.408 | 0.312 | 0.0300 |
| 31 | 10.067 | 0.404 | 0.0402 | 84 | 40.708 | 1.221 | 0.0300 |
| 32 | 8.909 | 0.356 | 0.0458 | 85 | 4.481 | 0.134 | 0.0300 |
| 33 | 1.023 | 0.046 | 0.0458 | 86 | 23.611 | 0.901 | 0.0382 |
| 34 | 6.834 | 0.286 | 0.0419 | 87 | 3.467 | 0.127 | 0.0369 |
| 35 | 8.165 | 0.373 | 0.0458 | 88 | 12.597 | 0.497 | 0.0395 |
| 36 | 15.599 | 0.780 | 0.0500 | 89 | 7.369 | 0.291 | 0.0396 |
| 37 | 76.072 | 3.803 | 0.0500 | 90 | 0.354 | 0.014 | 0.0395 |
| 38 | 60.472 | 3.023 | 0.0500 | 91 | 7.723 | 0.305 | 0.0396 |
| 39 | 6.170 | 0.308 | 0.0500 | 92 | 2.724 | 0.107 | 0.0396 |
| 40 | 10.570 | 0.528 | 0.0500 | 93 | 7.276 | 0.271 | 0.0373 |
| 41 | 5.570 | 0.278 | 0.0500 | 94 | 8.547 | 0.319 | 0.0373 |
| 42 | 43.732 | 2.186 | 0.0500 | 95 | 3.003 | 0.118 | 0.0395 |
| 43 | 5.407 | 0.214 | 0.3970 | 96 | 14.625 | 0.539 | 0.0369 |
| 44 | 11.577 | 0.523 | 0.0452 | 97 | 4.080 | 0.152 | 0.0373 |
| 45 | 25.390 | 1.015 | 0.0400 | 98 | 1.271 | 0.047 | 0.0373 |
| 46 | 20.857 | 0.827 | 0.3970 | 99 | 28.454 | 0.874 | 0.0307 |
| 47 | 14.500 | 0.500 | 0.3450 | 100 | 30.000 | 0.931 | 0.0310 |
| 48 | 35.090 | 1.619 | 0.0461 | 101 | 12.261 | 0.376 | 0.0307 |
| 49 | 20.660 | 0.964 | 0.0467 | 102 | 0.273 | 0.009 | 0.0337 |
| 50 | 5.660 | 0.264 | 0.0467 | 103 | 36.635 | 1.099 | 0.0300 |
| 51 | 8.142 | 0.375 | 0.0461 | 104 | 5.273 | 0.177 | 0.0337 |
| 52 | 12.263 | 0.367 | 0.0300 | 105 | 23.644 | 0.709 | 0.0300 |
| 53 | 6.124 | 0.183 | 0.0300 |
| Node ID | Nodes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Nodes (L/s) | % in Nodes | Node ID | Nodes Flow Rate (L/s) | Contaminant in Nodes (L/s) | % in Nodes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 333.826 | 13.353 | 0.0400 | 35 | 3.202 | 0.096 | 0.0300 |
| 2 | 10.043 | 0.402 | 0.0400 | 36 | 42.013 | 1.261 | 0.0300 |
| 3 | 5.000 | 0.200 | 0.0400 | 37 | 26.066 | 1.008 | 0.0387 |
| 4 | 51.096 | 2.044 | 0.0400 | 38 | 20.660 | 0.964 | 0.0467 |
| 5 | 36.486 | 1.458 | 0.0400 | 39 | 43.012 | 1.516 | 0.0353 |
| 6 | 10.348 | 0.414 | 0.0400 | 40 | 10.000 | 0.353 | 0.0353 |
| 7 | 10.000 | 0.409 | 0.0409 | 41 | 125.101 | 3.753 | 0.0300 |
| 8 | 19.651 | 0.804 | 0.0409 | 42 | 55.714 | 1.671 | 0.0300 |
| 9 | 4.206 | 0.193 | 0.0458 | 43 | 22.558 | 0.785 | 0.0348 |
| 10 | 19.999 | 0.808 | 0.0404 | 44 | 15.000 | 0.597 | 0.0398 |
| 11 | 23.466 | 0.939 | 0.0400 | 45 | 74.072 | 2.985 | 0.0398 |
| 12 | 27.371 | 1.253 | 0.0458 | 46 | 76.072 | 3.804 | 0.0500 |
| 13 | 41.840 | 1.682 | 0.0402 | 47 | 12.914 | 0.513 | 0.0397 |
| 14 | 68.823 | 2.753 | 0.0400 | 48 | 12.686 | 0.505 | 0.0398 |
| 15 | 333.826 | 13.353 | 0.0400 | 49 | 16.567 | 0.655 | 0.0396 |
| 16 | 29.633 | 1.185 | 0.0400 | 50 | 125.101 | 3.753 | 0.0300 |
| 17 | 31.167 | 1.306 | 0.0419 | 51 | 71.229 | 2.836 | 0.0398 |
| 18 | 15.000 | 0.660 | 0.0440 | 52 | 38.617 | 1.475 | 0.0382 |
| 19 | 76.070 | 3.804 | 0.0500 | 53 | 40.705 | 1.221 | 0.0300 |
| 20 | 11.577 | 0.523 | 0.0452 | 54 | 8.547 | 0.319 | 0.0373 |
| 21 | 60.472 | 3.024 | 0.0500 | 55 | 51.117 | 1.534 | 0.0300 |
| 22 | 10.570 | 0.529 | 0.0500 | 56 | 28.092 | 1.036 | 0.0369 |
| 23 | 40.660 | 1.897 | 0.0467 | 57 | 30.954 | 1.222 | 0.0395 |
| 24 | 58.232 | 2.687 | 0.0461 | 58 | 13.352 | 0.527 | 0.0395 |
| 25 | 44.500 | 1.536 | 0.0345 | 59 | 7.723 | 0.305 | 0.0396 |
| 26 | 26.263 | 1.042 | 0.0397 | 60 | 7.723 | 0.305 | 0.0396 |
| 27 | 80.237 | 3.209 | 0.0400 | 61 | 10.000 | 0.379 | 0.0379 |
| 28 | 203.906 | 8.156 | 0.0400 | 62 | 17.628 | 0.658 | 0.0373 |
| 29 | 12.085 | 0.482 | 0.0399 | 63 | 40.716 | 1.251 | 0.0307 |
| 30 | 125.998 | 5.016 | 0.0398 | 64 | 35.273 | 1.188 | 0.0337 |
| 31 | 77.793 | 3.097 | 0.0398 | 65 | 5.273 | 0.177 | 0.0337 |
| 32 | 10.506 | 0.387 | 0.0358 | 66 | 30.000 | 0.931 | 0.0310 |
| 33 | 22.701 | 0.811 | 0.0300 | 67 | 30.000 | 0.931 | 0.0310 |
| 34 | 6.124 | 0.184 | 0.0300 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adedoja, O.S.; Hamam, Y.; Khalaf, B.; Sadiku, R. Development of a Contaminant Distribution Model for Water Supply Systems. Water 2019, 11, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071510
Adedoja OS, Hamam Y, Khalaf B, Sadiku R. Development of a Contaminant Distribution Model for Water Supply Systems. Water. 2019; 11(7):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071510
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdedoja, Oluwaseye S., Yskandar Hamam, Baset Khalaf, and Rotimi Sadiku. 2019. "Development of a Contaminant Distribution Model for Water Supply Systems" Water 11, no. 7: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071510
APA StyleAdedoja, O. S., Hamam, Y., Khalaf, B., & Sadiku, R. (2019). Development of a Contaminant Distribution Model for Water Supply Systems. Water, 11(7), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071510






