Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
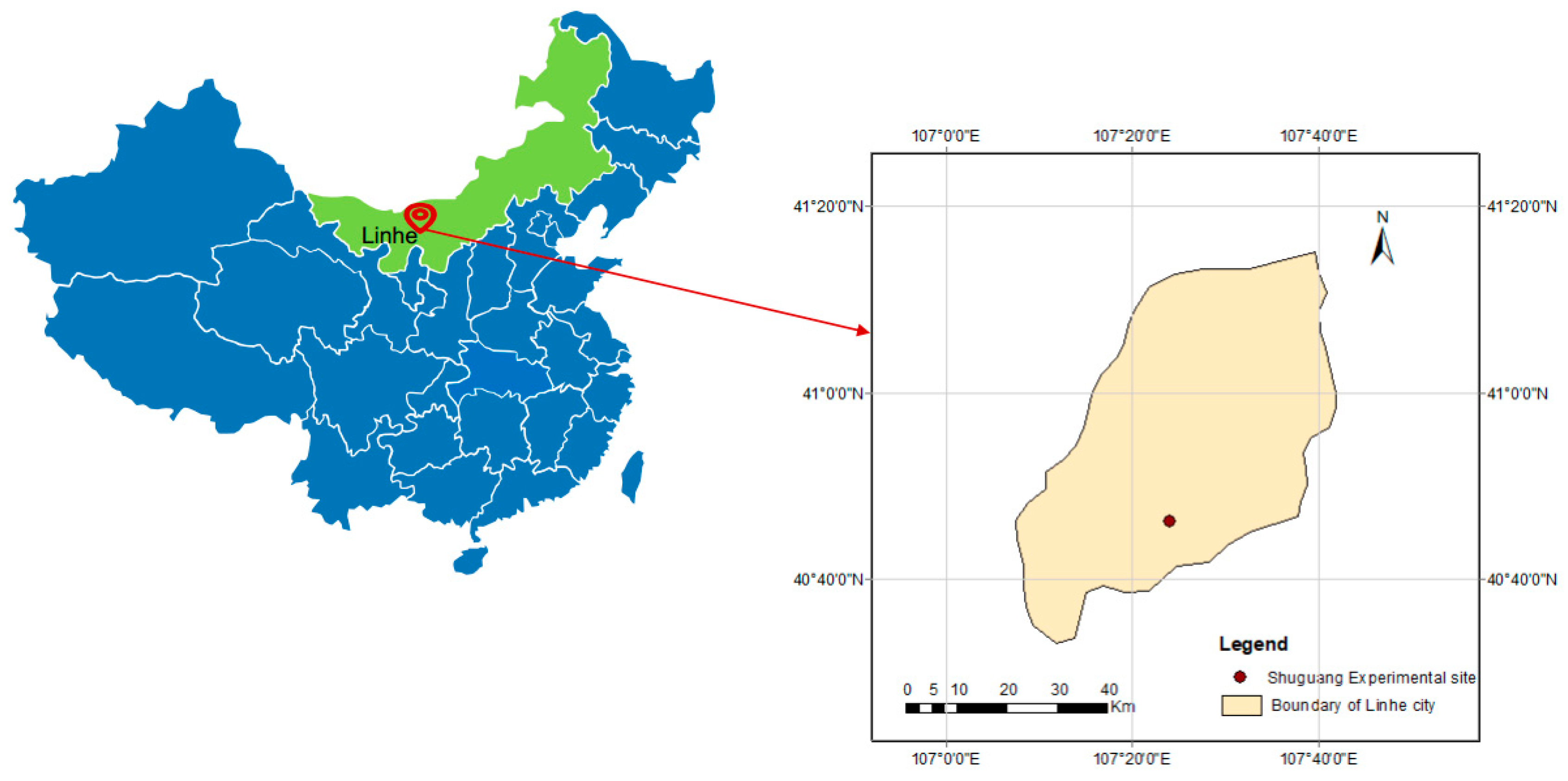
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.3. Measurement Method
2.3.1. Soil N2O Emission
2.3.2. Soil Properties
2.3.3. Spring Maize Yield and IWUE
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Water Content
3.2. Soil Salinity
3.3. Soil pH Value
3.4. Soil NO3− Content
3.5. Saturated Soil Hydraulic Conductivity
3.6. Soil N2O Emission Flux
3.6.1. Seasonal N2O Emission Flux
3.6.2. Seasonal N2O Emission Flux from Different Locations
3.6.3. N2O Cumulative Flux
3.7. Spring Maize Yield and IWUE
3.8. Correlation Analysis among Irrigation Water Salinity, Soil Properties, N2O Emissions and Maize Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Properties
4.2. Soil N2O Emission Dynamics
4.3. Effect of Irrigation Water Salinity on N2O Emissions
4.4. Effect of Different Location on N2O Emissions
4.5. Effect of Irrigation Water Salinity on Spring Maize Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.M.; Xiong, Y.W.; Huang, G.H.; Xu, X.; Huang, Q.Z. Effects of water stress on processing tomatoes yield, quality and water use efficiency with plastic mulched drip irrigation in sandy soil of the Hetao Irrigation District. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, P.L.; Ren, S.M.; Li, Y.K.; Jiang, G.Y.; Li, L.H. Quantitative response of oil sunflower yield to evapotranspiration and soil salinity with saline water irrigation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Rubino, P.; Caliandro, A. Effects of irrigation water with different salt concentrations and SAR values on soil salinisation and sodification. Ital. J. Agron. 2003, 7, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Huang, G.H.; Yang, J.G.; Wang, J.; Tai, R.K.; Meng, L.G. Effect of irrigation with saline water on water-salt dynamic and spring wheat yield. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.J.; Chen, Z.D.; Chen, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.H.; Wen, X.Y.; Gao, H.Y.; Chen, A.P. Analysis of maize salt tolerance in Hetao irrigation district and its ecological adaptable region. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.J.; Shan, Y.Y. Review of research development on water and soil regulation with brackish water irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, B.; Shalhevet, J.; Shimshi, D. Patterns of salt distribution under trickle Irrigation. In Physical Aspects of Soil Water and Salts in Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1973; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, N.F.Y. Effects of wastewater discharge on microbial populations and enzyme activities in mangrove soils. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Honna, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Eneji, A.E.; Yamasaki, N. Nitrogen mineralization under saline conditions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W. Nitrous oxide (N2O): The dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century. Science 2009, 326, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Xu, J.Z.; Liao, L.X.; Li, Y.W.; Wang, H.Y.; Rahim, S.F. Water salinity should be reduced for irrigation to minimize its risk of increased soil N2O emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, G.; Bhatia, A.; Pathak, H.; Prasad, S.; Jain, N.; Singh, J. Mitigating nitrous oxide and methane emissions from soil in rice–wheat system of the Indo-Gangetic plain with nitrification and urease inhibitors. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozlu, E.; Kumar, S. Response of surface GHG fluxes to long-term manure and inorganic fertilizer application in corn and soybean rotation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechler, M.A.A.; Jiang, R.W.; Silverthorn, T.K.; Oelbermann, M. Impact of biochar on soil characteristics and temporal greenhouse gas emissions: A field study from southern Canada. Biomass Bioenerg 2018, 118, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, S.C.; Teira-Esmatges, M.R.; Català, M.M. Influence of irrigation frequency on greenhouse gases emission from a paddy soil. Paddy Water Environ. 2016, 14, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitombo, L.M.; Cantarella, H.; Packer, A.P.C.; Ramos, N.P.; Do Carmo, J.B. Straw preservation reduced total N2O emissions from a sugarcane field. Soil Use Manag. 2017, 33, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.W.; Li, Q.; Liao, N.; Guo, H.J.; Min, W.; Ma, L.J.; Ye, J.; Hou, Z.A. Saline water irrigation stimulate N2O emission from a drip-irrigated cotton field. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2016, 66, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, U.; Thapa, R.; Desutter, T.; Yangbo, H.; Chatterjee, A. Saline–sodic soils: Potential sources of nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide emissions? Pedosphere 2017, 27, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Zhang, Y.; McDaniel, M.D.; Borin, M.; Adams, M.A. Short-term effects of biochar and salinity on soil greenhouse gas emissions from a semi-arid Australian soil after re-wetting. Geoderma 2017, 307, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.H.; Ren, S.M.; Yang, P.L.; Niu, Y.T.; Zou, T. Effects of reclaimed water irrigation and brackish water irrigation on soil greenhouse gas emissions. J. Irrig. Drain. 2014, 33, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Song, L.P.; Wang, B.C.; Shao, H.B.; Zhang, L.W.; Qin, X.C. Co-effects of salinity and moisture on CO2 and N2O emissions of laboratory-incubated salt-affected soils from different vegetation types. Geoderma 2018, 332, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Müller, C. Effect of sodium chloride on denitrification in glucose amended soil treated with ammonium and nitrate nitrogen. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopoulou, C.K.; Bilalis, D.; Pappa, V.A.; Rees, R.M.; Savvas, D. Effects of organic farming practices and salinity on yield and greenhouse gas emissions from a common bean crop. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 183, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inubushi, K.; Barahona, M.A.; Yamakawa, K. Effects of salts and moisture content on N2O emission and nitrogen dynamics in Yellow soil and Andosol in model experiments. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 29, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Yang, P.L.; Su, Y.P.; Shang, F.Z.; Wei, C.C.; Ren, S.M. Effects of alternative irrigation between brackish water and fresh water on CO2 and N2O emission from spring maize soil. J. China Agric. Univ. 2018, 23, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Liu, H.J.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhang, R.H. Climate change trend and its effects on reference evapotranspiration at Linhe Station, Hetao Irrigation District. Water Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.F.; He, J.Q.; Qi, Z.J.; Dyck, M.; Zou, Y.F.; Zhang, T.B.; Feng, H. Effects of lateral spacing for drip irrigation and mulching on the distributions of soil water and nitrate, maize yield, and water use efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Qu, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Jin, Q. Effect of different thresholds of drip irrigation using saline water on soil salt transportation and maize yield. Water 2018, 10, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.S.; Qu, Z.Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, A.Q. Interactive effects of nitrogen fertilization and irrigation on grain yield, water use efficiency and nitrogen use efficiency of mulched drip-irrigated maize in Hetao Irrigation District, China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Shi, H.B.; Li, R.P.; Zhao, J.D.; Feng, Y.Y. The effects of water and nitrogen coupling on photosynthetic characteristics under mulched drip irrigation. Water Sav. Irrig. 2017, 42, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.W.; Gao, X.P.; Tenuta, M.; Kuang, W.N.; Gui, D.W.; Zeng, F.J. Urea fertigation sources affect nitrous oxide emission from a drip-fertigated cotton field in northwestern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ye, X.H.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lin, X.G.; Zou, H.T. The effects of different irrigation regimes on nitrous oxide emissions and influencing factors in greenhouse tomato fields. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Liang, Y.P.; Zhang, Q.; Jha, S.K.; Gao, Y.; Shen, X.J.; Sun, J.S.; Duan, A.W. Mitigated CH4 and N2O emissions and improved irrigation water use efficiency in winter wheat field with surface drip irrigation in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 163, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.J.; Fang, F.L.; Lin, W.; Qiang, X.J.; Xu, C.Y.; Mao, L.L.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, Y.Z. N2O emissions and source partitioning using stable isotopes under furrow and drip irrigation in vegetable field of North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.F.; Wang, X.F.; Du, H.Y.; Shen, S.Z.; Liu, C.R.; Zhang, K.Q.; Li, W.C. N2O and CO2 emissions, nitrogen use efficiency under biogas slurry irrigation: A field study of two consecutive wheat-maize rotation cycles in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wan, C.Y.; Lu, P.R.; Bakour, A. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil salinity and yield of summer maize(zea mays L.) in subsurface drainage system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlberg, L.; Rockström, J.; Annandale, J.G.; Steyn, J.M. Low-cost drip irrigation—A suitable technology for southern Africa? An example with tomatoes using saline irrigation water. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, B.L.; Coleman, N.T. Effect of solution composition on soil hydraulic conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1966, 30, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, J.D.; Schroer, F.W. Infiltration as Influenced by irrigation water quality. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1979, 43, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, C.; Wassmann, R.; Kienzler, K.; Ibragimov, N.; Eschanov, R. Nitrous oxide emissions from fertilized, irrigated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) in the Aral Sea Basin, Uzbekistan: Influence of nitrogen applications and irrigation practices. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, H.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qaisar, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Cai, H.J. The effects of aeration and irrigation regimes on soil CO2 and N2O emissions in a greenhouse tomato production system. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.Z.; Xu, C.; Wu, J.W.; Huang, J.S.; Ma, T. Effect of salinity on soil respiration and nitrogen dynamics. Ecol. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 20, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyailo, O.V.; Stepanov, A.L.; Umarov, M.M. The transformation of nitrous oxide by denitrifying bacteria in Solonchaks. Eurasian Soil Sci. 1997, 30, 178–180. [Google Scholar]
- Heincke, M.; Kaupenijohann, M. Effects of soil solution on the dynamics of N2O emissions: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 1999, 55, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, H.J.; Cai, H.J.; Zhu, Y. Soil N2O emission characteristics of greenhouse tomato fields under aerated irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Komada, M.; Takebe, M.; Yonemura, S.; Kato, N. Nitrous oxide evolved from soil covered with plastic mulch film in horticultural field. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.L.; Lv, W.; Huang, M.Y.; Zhai, Y.M.; Qiang, C. Effects of biochar on coastal reclaimed soil salinity distribution and maize growth with cycle fresh and saline water irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.L.; Qiang, C.; Huang, M.Y.; Zhai, Y.M.; Lv, W. Effect of alternate irrigation with fresh and slight saline water on physiological growth of summer maize in coastal reclamation area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Physiological processes limiting plant growth in saline soils: Some dogmas and hypotheses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 16, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Soil | Soil Texture | Soil Bulk | Field | Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity | Ec1:5 | pH | Soil NO3− | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Density | Capacity | (10−5·cm·s−1) | (uS·cm−1) | -N | ||||
| Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | (g·cm−3) | (g·g−1) | (mg·kg−1) | ||||
| Silty loam | 7.694 | 62.379 | 29.927 | 1.5 | 0.198 | 5.11 | 393 | 8.21 | 33.38 |
| Salinity | Iron Contents (mg·L−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg·L−1) | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | Cl− | CO32− | SO42− | HCO3− |
| 1157 | 90.2 | 48.6 | 152.6 | 41.2 | 141.8 | 0 | 240.2 | 442.4 |
| 2000 | 90.2 | 48.6 | 355.0 | 212.8 | 610.8 | 0 | 240.2 | 442.4 |
| 3500 | 90.2 | 48.6 | 715.2 | 518.4 | 1445 | 0 | 240.2 | 442.4 |
| 5000 | 90.2 | 48.6 | 1075.8 | 823.8 | 2279 | 0 | 240.2 | 442.4 |
| Variables | IWS | SWC | EC1:5 | pH | NO3−–N | N2O | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IWS | 1 | ||||||
| SWC | 0.788 ** | 1 | |||||
| EC1:5 | 0.934 ** | 0.933 ** | 1 | ||||
| pH | 0.706 * | 0.638 * | 0.720 ** | 1 | |||
| NO3−–N | −0.097 | 0.315 | 0.185 | −0.088 | 1 | ||
| N2O | 0.753 ** | 0.756 ** | 0.802 ** | 0.672 * | −0.030 | 1 | |
| Yield | −0.877 ** | −0.677 * | −0.811 ** | −0.571 | 0.219 | −0.767 ** | 1 |
| Variables | Ksat | IWS | SWC | EC1:5 | pH | NO3−–N | N2O | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ksat | 1 | |||||||
| IWS | −0.826 ** | 1 | ||||||
| SWC | −0.347 | 0.783 ** | 1 | |||||
| EC1:5 | −0.630 * | 0.948 ** | 0.905 ** | 1 | ||||
| pH | −0.833 ** | 0.991 ** | 0.743 ** | 0.925 ** | 1 | |||
| NO3−–N | 0.625 * | −0.259 | 0.142 | −0.040 | −0.269 | 1 | ||
| N2O | −0.619 * | 0.837 ** | 0.674 * | 0.799 ** | 0.803 ** | −0.133 | 1 | |
| Yield | 0.875 ** | −0.885 ** | −0.530 | −0.751 ** | −0.898 ** | 0.367 | −0.630 * | 1 |
| Current Research | Wang’s Research [26] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | N2O Flux (ug·m−2·h−1) | Treatment | N2O Flux (ug·m−2·h−1) | Treatment | N2O Flux (ug·m−2·h−1) |
| 2.0 g·L−1 | 52.30 | 2.0 g·L−1 1:1 | 47.96 | 2.0 g·L−1 1:2 | 44.86 |
| 3.5 g·L−1 | 51.10 | 3.5 g·L−1 1:1 | 46.95 | 3.5 g·L−1 1:2 | 41.73 |
| 5.0 g·L−1 | 78.17 | 5.0 g·L−1 1:1 | 44.52 | 5.0 g·L−1 1:2 | 40.66 |
| Current Research | Wang’s Research [26] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Yield (kg·ha−1) | Treatment | Yield (kg·ha−1) | Treatment | Yield (kg·ha−1) |
| 2.0 g·L−1 | 13,434 | 2.0 g·L−1 1:1 | 14,651 | 2.0 g·L−1 1:2 | 13,914 |
| 3.5 g·L−1 | 12,822 | 3.5 g·L−1 1:1 | 13,208 | 3.5 g·L−1 1:2 | 13,636 |
| 5.0 g·L−1 | 11,060 | 5.0 g·L−1 1:1 | 12,957 | 5.0 g·L−1 1:2 | 12,449 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Li, F.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wei, R.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Water 2019, 11, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081548
Wei C, Li F, Yang P, Ren S, Wang S, Wang Y, Xu Z, Xu Y, Wei R, Zhang Y. Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Water. 2019; 11(8):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081548
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Chenchen, Fahu Li, Peiling Yang, Shumei Ren, Shuaijie Wang, Yu Wang, Ziang Xu, Yao Xu, Rong Wei, and Yanxia Zhang. 2019. "Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation" Water 11, no. 8: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081548
APA StyleWei, C., Li, F., Yang, P., Ren, S., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Xu, Z., Xu, Y., Wei, R., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Properties, N2O Emission and Yield of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Water, 11(8), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081548





