Reconciling High Glacier Surface Melting in Summer with Air Temperature in the Semi-Arid Zone of Western Himalaya
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
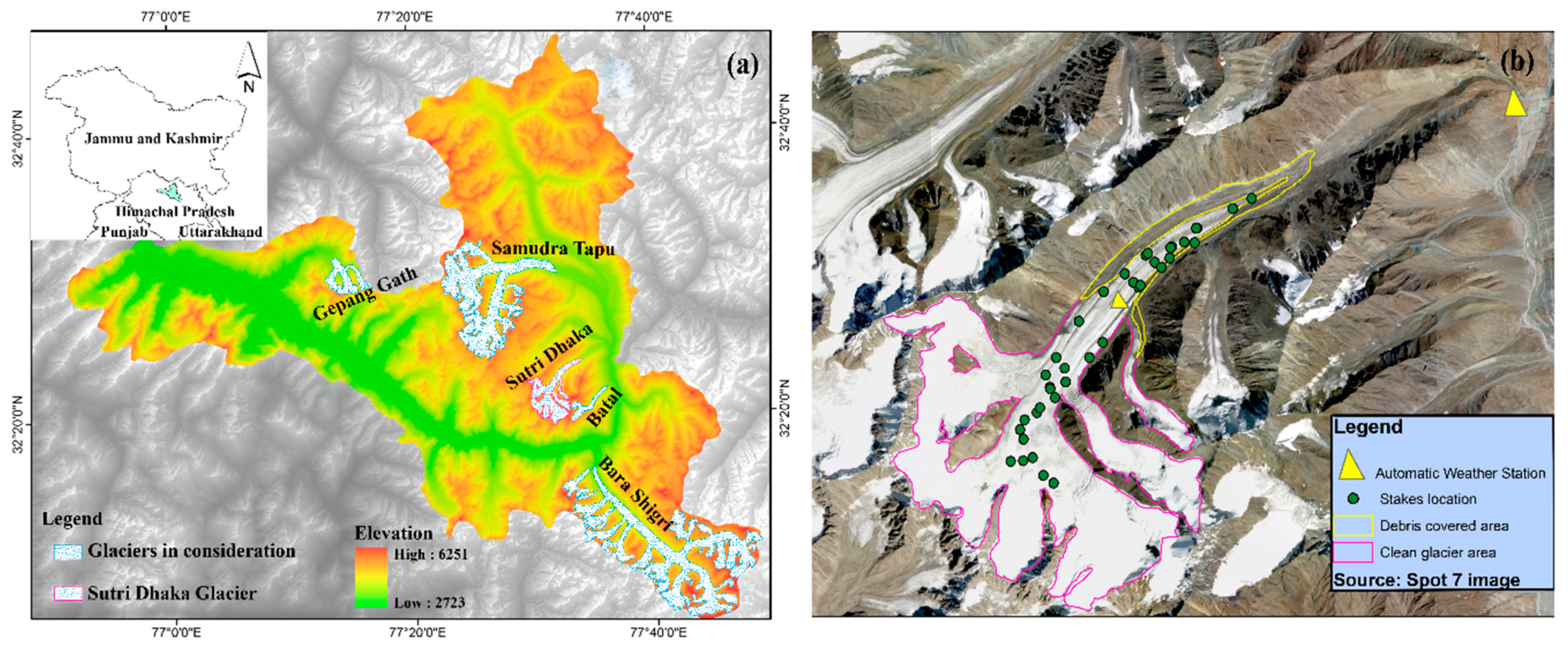
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Installation of AWS and Data Collection
- (i)
- (ii)
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Analysis of Air Temperature Lapse Rate (tlr)
2.3.2. Extrapolation of Average Air Temperature
2.4. Measurement of Glacier Surface Ablation
2.5. Temperature-Index Model for Ice Melt
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Air Temperature and Temperature Lapse Rate (tlr)
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Air Temperature
3.3. Seasonal Variability in Surface Melting
3.4. Evaluation of Modeled and Observed Melting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhambri, R.; Bolch, T.; Kawishwar, P.; Dobhal, D.P.; Srivastava, D.; Pratap, B. Heterogeneity in glacier response in the upper Shyok valley, northeast Karakoram. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Kulkarni, A.; Kaab, A.; Huggel, C.; Paul, F.; Cogley, J.G.; Frey, H.; Kargel, J.S.; Fujita, K.; Scheel, M.; et al. The State and Fate of Himalayan Glaciers. Science 2012, 336, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, K. The Karakoram anomaly? Glacier expansion and the ‘elevation effect,’ Karakoram Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 2005, 25, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaab, A.; Berthier, E.; Nuth, C.; Gardelle, J.; Arnaud, Y. Contrasting patterns of early twenty-first-century glacier mass change in the Himalayas. Nature 2012, 488, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Bengtsson, L. Hydrological sensitivity of a large Himalayan basin to climate change. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2363–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.F.; Wagnon, P.; Berthier, E.; Vincent, C.; Fujita, K.; Kargel, J.S. Review of the status and mass changes of Himalayan-Karakoram glaciers. J. Glaciol. 2018, 64, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nuimura, T. Spatially heterogeneous wastage of Himalayan glaciers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14011–14014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, B.; Dobhal, D.P.; Bhambri, R.; Mehta, M.; Tewari, V.C. Four decades of glacier mass balance observations in the Indian Himalaya. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.; Ramanathan, A.; Wagnon, P.; Dobhal, D.P.; Linda, A.; Berthier, E.; Sharma, P.; Arnaud, Y.; Azam, M.F.; Jose, P.G.; et al. Balanced conditions or slight mass gain of glaciers in the Lahaul and Spiti region (northern India, Himalaya) during the nineties preceded recent mass loss. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Tian, L.; Nüsser, M. No significant mass loss in the glaciers of Astore Basin (North-Western Himalaya), between 1999 and 2016. J. Glaciol. 2019, 65, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambri, R.; Bolch, T. Glacier mapping: A review with special reference to the Indian Himalayas. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 672–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Shukla, A.; Jasrotia, A.S. Influence of topography on glacier changes in the central Himalaya, India. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 155, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.V.; Bahuguna, I.M.; Rathore, B.P.; Singh, S.K.; Randhawa, S.S.; Sood, R.K.; Dhar, S. Glacial retreat in Himalaya using Indian Remote Sensing satellite data. Curr. Sci. 2007, 92, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Mir, R.A.; Jain, S.K.; Lohani, A.K.; Saraf, A.K. Glacier recession and glacial lake outburst flood studies in Zanskar basin, western Himalaya. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Climate Change Will Affect the Asian Water Towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nye, J. The mechanics of glacier flow. J. Glaciol. 1952, 2, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, S.; Syed, T.H.; Arendt, A.A.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Sinha, D. Assessing controls on mass budget and surface velocity variations of glaciers in Western Himalaya. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogley, J.G. Present and future states of Himalaya and Karakoram glaciers. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.F.; Dyurgerov, M.B.; Rick, U.K.; O’Neel, S.; Pfeffer, W.T.; Anderson, R.S.; Anderson, S.P.; Glazovsky, A.F. Glaciers dominate Eustatic sea-level rise in the 21st century. Science 2007, 317, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Kayastha, R.B. Mass and Energy Balance Estimation of Yala Glacier (2011–2017), Langtang Valley, Nepal. Water 2018, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Verma, A.; Gokhale, A.A.; Bhambri, R.; Misra, A.; Sundriyal, S.; Dobhal, D.P.; Kishore, N. Hydrometeorological assessments and suspended sediment delivery from a central Himalayan glacier in the upper Ganga basin. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2018, 33, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.F.; Wagnon, P.; Vincent, C.; Ramanathan, A.; Linda, A.; Singh, V.B. Reconstruction of the annual mass balance of Chhota Shigri glacier, Western Himalaya, India, since 1969. Ann. Glaciol. 2014, 55, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawde, S.A.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Bala, G. An estimate of glacier mass balance for the Chandra basin, western Himalaya, for the period 1984-2012. Ann. Glaciol. 2017, 58, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiyani, M.R. Mass-balance studies on Siachen Glacier in the Nubra valley, Karakoram Himalaya, India. J. Glaciol. 1999, 45, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiyani, M.R.; Kale, V.S.; Pawar, N.J. Climate change and the precipitation variations in the northwestern Himalaya: 1866-2006. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, M.S.; Chand, H.; Kumar, S.; Srinivasan, K.; Ganju, A. Climate-change studies in the western Himalaya. Ann. Glaciol. 2010, 51, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.F.; Wagnon, P.; Vincent, C.; Ramanathan, A.; Favier, V.; Mandal, A.; Pottakkal, J.G. Processes governing the mass balance of Chhota Shigri Glacier (western Himalaya, India) assessed by point-scale surface energy balance measurements. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 2195–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, J.M.; Wagnon, P.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Biron, R.; Brun, F.; Pellicciotti, F. A comparative high-altitude meteorological analysis from three catchments in the Nepalese Himalaya. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2015, 31, 174–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.S.; Pratap, B.; Gupta, A.K.; Dobhal, D.; Yadav, R.; Tiwari, S.K. Spatio-temporal variability of near-surface air temperature in the Dokriani glacier catchment (DGC), central Himalaya. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 136, 1513–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhananga, N.S.; Kayastha, R.B.; Bhattarai, B.C.; Adhikari, T.R.; Pradhan, S.C.; Devkota, L.P.; Shrestha, A.B.; Mool, P.K. Estimation of discharge from Langtang River basin, Rasuwa, Nepal, using a glacio-hydrological model. Ann. Glaciol. 2014, 55, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.F.; Pellicciotti, F. Variability of air temperature over a debris-covered glacier in the Nepalese Himalaya. Ann. Glaciol. 2016, 57, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, T.R.; Humes, K.S.; Harshburger, B.J.; Moore, B.C.; Walden, V.P.; Ye, H.C. Seasonal and synoptic variations in near-surface air temperature lapse rates in a mountainous basin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.J.; Sharp, M.J.; Burgess, D.O.; Anslow, F.S. Near-surface-temperature lapse rates on the Prince of Wales Icefield, Ellesmere Island, Canada: Implications for regional downscaling of temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, D.B.; Yao, T.; Panday, P.K. Near-surface air temperature lapse rate in a humid mountainous terrain on the southern slopes of the eastern Himalayas. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 132, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, D.B.; Yao, T.D.; Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Tian, L.D. Comparison of temperature lapse rates from the northern to the southern slopes of the Himalayas. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 4431–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.; Maruthi, K. Detailed glaciological studies on Hamtah Glacier. Lahaul Spiti Dist. HP Geol. Surv. India 2008, 140, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Topography, relief, and TRMM-derived rainfall variations along the Himalaya. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayyen, R.; Gergan, J. Role of glaciers in watershed hydrology: A preliminary study of a “Himalayan catchment”. Cryosphere 2010, 4, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenek, L.; Bhawan, V. Recent and past glaciation of Lahaul. Indian Geogr. J. 1945, 3, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mayewski, P.A.; Jeschke, P.A. Himalayan and Trans-Himalayan glacier fluctuations since AD 1812. Arct. Alp. Res. 1979, 11, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Venkataraman, G. Changes in the glaciers of ChandraBhaga basin, Himachal Himalaya, India, between 1980 and 2010 measured using remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5584–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Patel, L.K.; Ravindra, R.; Singh, A.; Mahalinganathan, K.; Thamban, M. Role of debris cover to control specific ablation of adjoining Batal and Sutri Dhaka glaciers in Chandra Basin (Himachal Pradesh) during peak ablation season. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 125, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, L.A.; Derbyshire, E.; Richardson, S.; Benn, D.I.; Evans, D.J.A.; Mitchel, W.A. The quaternary glacial history of the Lahul Himalaya, Northern India. J. Quat. Sci. 1996, 11, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, M.; Celleri, R.; Shellito, C.J.; Orellana-Alvear, J.; Abril, A.; Carrillo-Rojas, G. Near-surface air temperature lapse rate over complex terrain in the Southern Ecuadorian Andes: Implications for temperature mapping. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2016, 48, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Rustad, L.E.; Porter, J.H.; Taylor, J.R.; Dereszynski, E.W.; Shanley, J.B.; Gries, C.; Henshaw, D.L.; Martin, M.E.; Sheldon, W.M.; et al. Quantity is Nothing without Quality: Automated QA/QC for Streaming Environmental Sensor Data. Bioscience 2013, 63, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, N.; Losleben, M. Climate change in the Colorado Rocky Mountains: Free air versus surface temperature trends. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.; Pellicciotti, F.; Juszak, I.; Carenzo, M.; Brock, B. Suitability of a constant air temperature lapse rate over an Alpine glacier: Testing the Greuell and Bohm model as an alternative. Ann. Glaciol. 2013, 54, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.R.; Mote, P.W.; Lundquist, J.D. Surface temperature lapse rates over complex terrain: Lessons from the Cascade Mountains. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, C.; Kaser, G. Ventilated and unventilated air temperature measurements for glacier-climate studies on a tropical high mountain site. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicciotti, F.; Helbing, J.; Rivera, A.; Favier, V.; Corripio, J.; Araos, J.; Sicart, J.E.; Carenzo, M. A study of the energy balance and melt regime on Juncal Norte Glacier, semi-arid Andes of central Chile, using melt models of different complexity. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3980–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østrem, G.; Stanley, A. Glacier mass-balance measurements: A manual for field and office work; Canadian Department of Energy, Mines and Resources: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1969; Volume 66. [Google Scholar]
- Cogley, J.; Hock, R.; Rasmussen, L.; Arendt, A.; Bauder, A.; Braithwaite, R.; Jansson, P.; Kaser, G.; Möller, M.; Nicholson, L. Glossary of Glacier Mass Balance and Related Terms, IHP-VII Technical Documents in Hydrology No. 86, IACS Contribution No. 2; UNESCO-IHP: Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fountain, A.G.; Vecchia, A. How many stakes are required to measure the mass balance of a glacier? Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 1999, 81, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, R. Temperature index melt modelling in mountain areas. J. Hydrol. 2003, 282, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, N.; Arora, M. Degree-day factors for snow and ice for Dokriani Glacier, Garhwal Himalayas. J. Hydrol. 2000, 235, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Kumar, A.; Verma, A.; Swaroop, S. Analysis of Climate and Melt-runoff in Dunagiri Glacier of Garhwal Himalaya (India). Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 3035–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Pieczonka, T.; Ghosh, S.; Bolch, T. Glacier mass budget and climate reanalysis data indicate a climatic shift around 2000 in Lahaul-Spiti, western Himalaya. Clim. Chang. 2018, 148, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijampurkar, V.N.; Bhandari, N.; Borole, D.V.; Bhattacharya, U. Radiometric Chronology of changme-khangpu glacier, sikkim. J. Glaciol. 1985, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoti, I.; Kesarwani, K.; Mehta, M.; Dobhal, D.P. Extended T-index models for glacier surface melting: A case study from Chorabari Glacier, Central Himalaya, India. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heynen, M.; Miles, E.; Ragettli, S.; Buri, P.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Pellicciotti, F. Air temperature variability in a high-elevation Himalayan catchment. Ann. Glaciol. 2016, 57, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijampurkar, V.N.; Rao, D.K. Accumulation and flow-rates of ice on chhota shigri glacier, central himalaya, using radio active and stable isotopes. J. Glaciol. 1992, 38, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, F.; Rasul, G. Estimation of water discharge from Gilgit Basin using remote sensing, GIS and runoff modeling. Pak. J. Meteorol. 2010, 6, 97–113. [Google Scholar]
- Karakoti, I.; Kesarwani, K.; Mehta, M.; Dobhal, D.P. Modelling of meteorological parameters for the Chorabari Glacier valley, Central Himalaya, India. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.F.; Casassa, G.; Quintana, J. Changes of the 0 degrees C isotherm and the equilibrium line altitude in central Chile during the last quarter of the 20th century. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2005, 50, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragettli, S.; Pellicciotti, F.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Miles, E.S.; Petersen, L.; Heynen, M.; Shea, J.M.; Stumm, D.; Joshi, S.; Shrestha, A. Unraveling the hydrology of a Himalayan catchment through integration of high resolution in situ data and remote sensing with an advanced simulation model. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 78, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayyen, R.J.; Gergan, J.; Dobhal, D. Slope lapse rates of temperature in Din Gad (Dokriani glacier) catchment, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Bull. Glaciol. Res. 2005, 22, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Haritashya, U.K.; Kumar, N. Meteorological study for Gangotri Glacier and its comparison with other high altitude meteorological stations in central Himalayan region. Nord. Hydrol. 2007, 38, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, D.I.; Bolch, T.; Hands, K.; Gulley, J.; Luckman, A.; Nicholson, L.I.; Quincey, D.; Thompson, S.; Toumi, R.; Wiseman, S. Response of debris-covered glaciers in the Mount Everest region to recent warming, and implications for outburst flood hazards. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 114, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobhal, D.P.; Mehta, M.; Srivastava, D. Influence of debris cover on terminus retreat and mass changes of Chorabari Glacier, Garhwal region, central Himalaya, India. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, B.; Dobhal, D.P.; Mehta, M.; Bhambri, R. Influence of debris cover and altitude on glacier surface melting: A case study on Dokriani Glacier, central Himalaya, India. Ann. Glaciol. 2015, 56, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, R.; Patel, N.; Krishna, A.P. Effects of terrain attributes on snow-cover dynamics in parts of Chenab basin, western Himalayas. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1861–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Negi, H.S.; Kumar, A.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Dewali, S.K.; Datt, P.; Ganju, A.; Kumar, S. Estimation of snow accumulation on Samudra Tapu glacier, Western Himalaya using airborne ground penetrating radar. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Chaudhary, B.S. Using RESOURCESAT-1 data for determination of snow cover and snowline altitude, Baspa Basin, India. Ann. Glaciol. 2010, 51, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagnon, P.; Linda, A.; Arnaud, Y.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.; Vincent, C.; Pottakkal, J.G.; Berthier, E.; Ramanathan, A.; Hasnain, S.I.; et al. Four years of mass balance on Chhota Shigri Glacier, Himachal Pradesh, India, a new benchmark glacier in the western Himalaya. J. Glaciol. 2007, 53, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, J.; Hoogendoorn, N. Mass-balance gradients and climatic change. J. Glaciol. 1989, 35, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Region | Glacier Catchment | Elevation Range (m asl) | Year | Near-Surface (Slope) Lapse Rate °C km−1 | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| December, January, February | March, April, May | June, July, August, September | October, November | ||||||
| Winter | Pre-Monsoon | Monsoon | Post-Monsoon | Annual | |||||
| Chandra Basin, LahaulSpiti | Hamtah Glacier | 3330–3940 | 2002–2006 | - | - | 11.4 | - | - | [36] |
| Chandra River, Himachal Himalaya | Chhota Shigri, Lahaul-Spiti | - | - | - | - | 3.8–6.7 | [61] | ||
| 1092–4863 | 2009–2012 | - | - | 6.4 | [22] | ||||
| Gilgit-Baltistan, Karakoram Himalaya | Baltoro Glacier | 3048–4050 | 2003 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 7.2 | 8.8 | 7.5 | [62] |
| Chandra Basin | Sutri Dhaka Glacier | 4052–4864 | 2015–16 2016–17 | 0.35 ± 0.3 2.5 ± 1.9 | 3.8 ± 1.2 2.8 ± 1.3 | 5.6 ± 0.8 6.8 ± 0.1 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 2.4 4.6 ± 2.5 | Present study |
| Year/Period of Measurements | No of Stakes | Winter Ablation (m w.e.) | Summer Ablation (m w.e.) | Annual Ablation (m w.e.) | ELA (m asl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015–16 Winter:
| 24 | −0.46 ± 0.09 | −3.74 ± 0.74 | −4.20 ± 0.84 | 5410 |
| 2016–17 Winter:
| 28 | −0.38 ± 0.07 | −2.71 ± 0.54 | −3.09 ± 0.62 | 5320 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pratap, B.; Sharma, P.; Patel, L.; Singh, A.T.; Gaddam, V.K.; Oulkar, S.; Thamban, M. Reconciling High Glacier Surface Melting in Summer with Air Temperature in the Semi-Arid Zone of Western Himalaya. Water 2019, 11, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081561
Pratap B, Sharma P, Patel L, Singh AT, Gaddam VK, Oulkar S, Thamban M. Reconciling High Glacier Surface Melting in Summer with Air Temperature in the Semi-Arid Zone of Western Himalaya. Water. 2019; 11(8):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081561
Chicago/Turabian StylePratap, Bhanu, Parmanand Sharma, Lavkush Patel, Ajit T. Singh, Vinay Kumar Gaddam, Sunil Oulkar, and Meloth Thamban. 2019. "Reconciling High Glacier Surface Melting in Summer with Air Temperature in the Semi-Arid Zone of Western Himalaya" Water 11, no. 8: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081561
APA StylePratap, B., Sharma, P., Patel, L., Singh, A. T., Gaddam, V. K., Oulkar, S., & Thamban, M. (2019). Reconciling High Glacier Surface Melting in Summer with Air Temperature in the Semi-Arid Zone of Western Himalaya. Water, 11(8), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081561





