The Development of a Calculation Model for the Instantaneous Pressure Head of Oscillating Water Flow in a Pipeline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiments
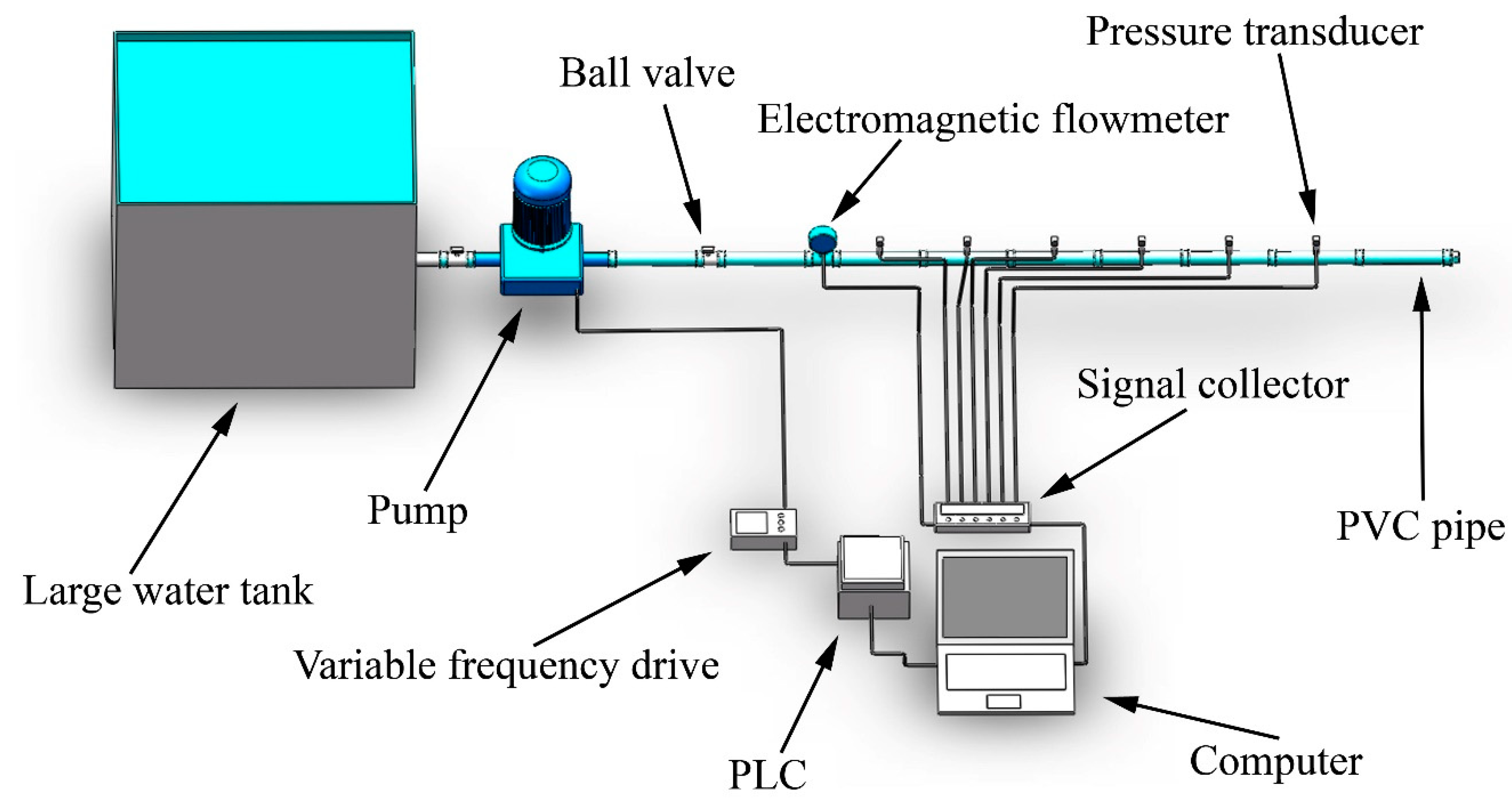
2.1.1. Experimental Equipment and Procedure
2.1.2. Experimental Setup
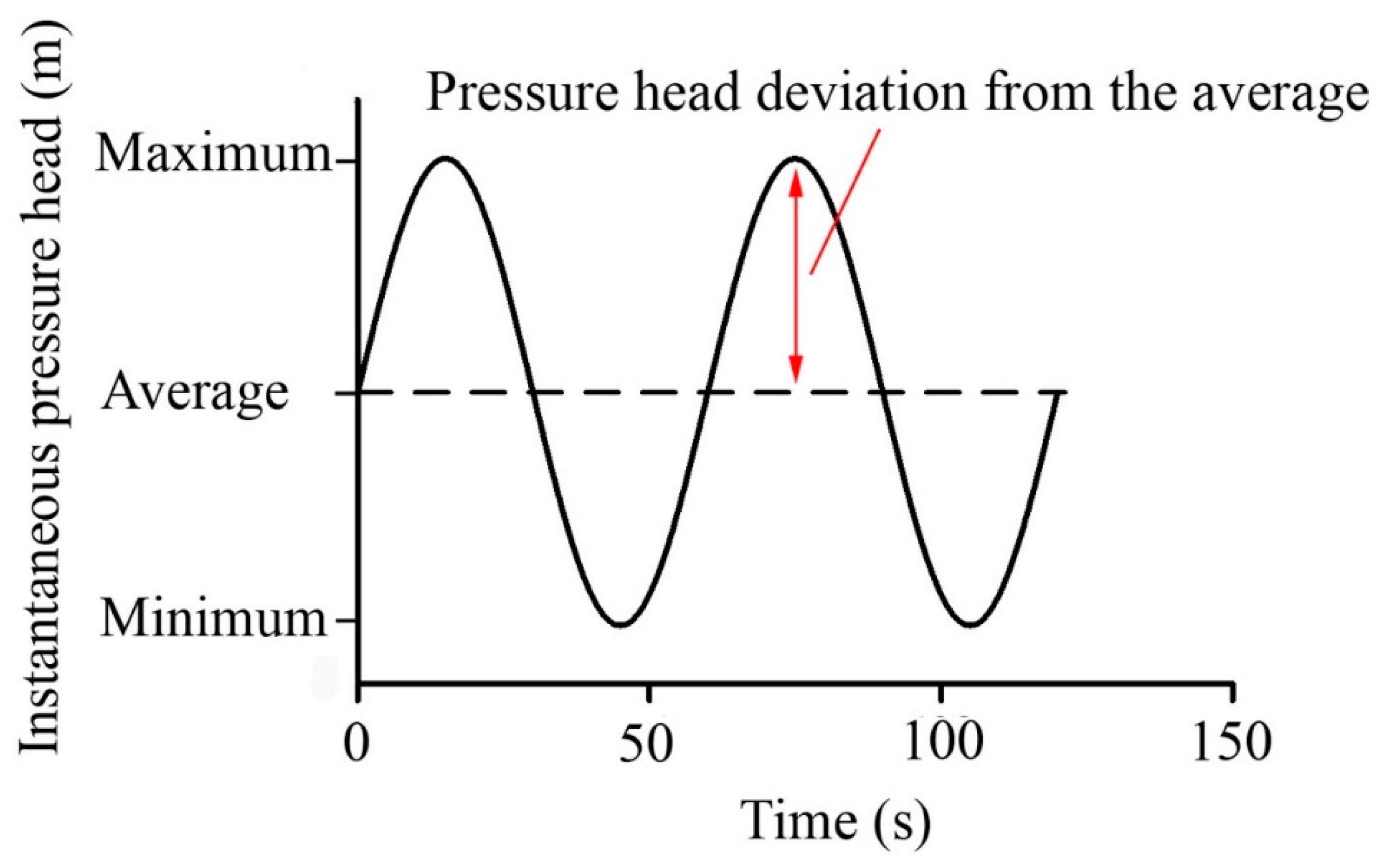
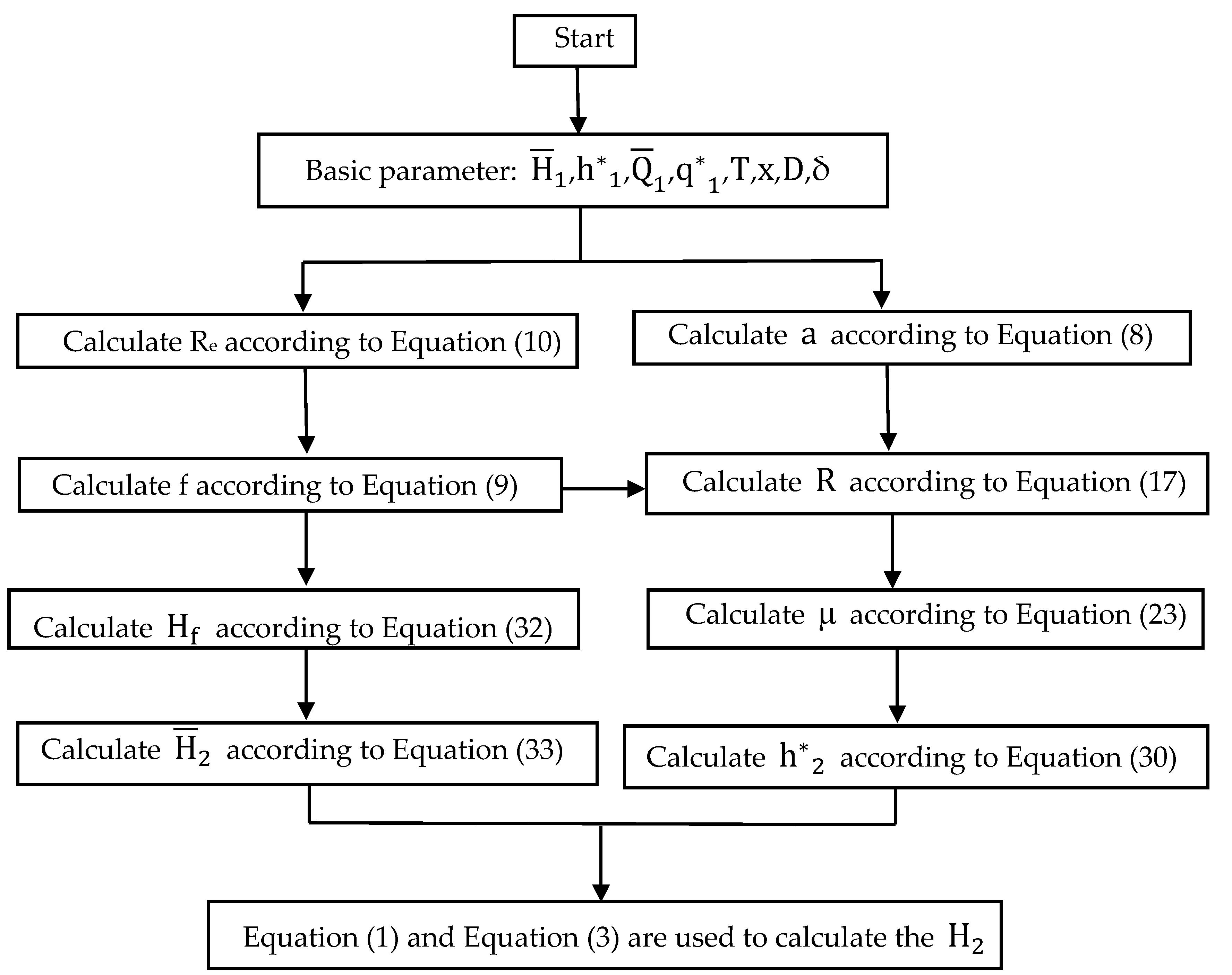
2.2. Calculation Model
2.2.1. The Calculation of the Amplitude of the Pressure Head
2.2.2. The Calculation of the Average Instantaneous Pressure Head
3. Results and Discussion
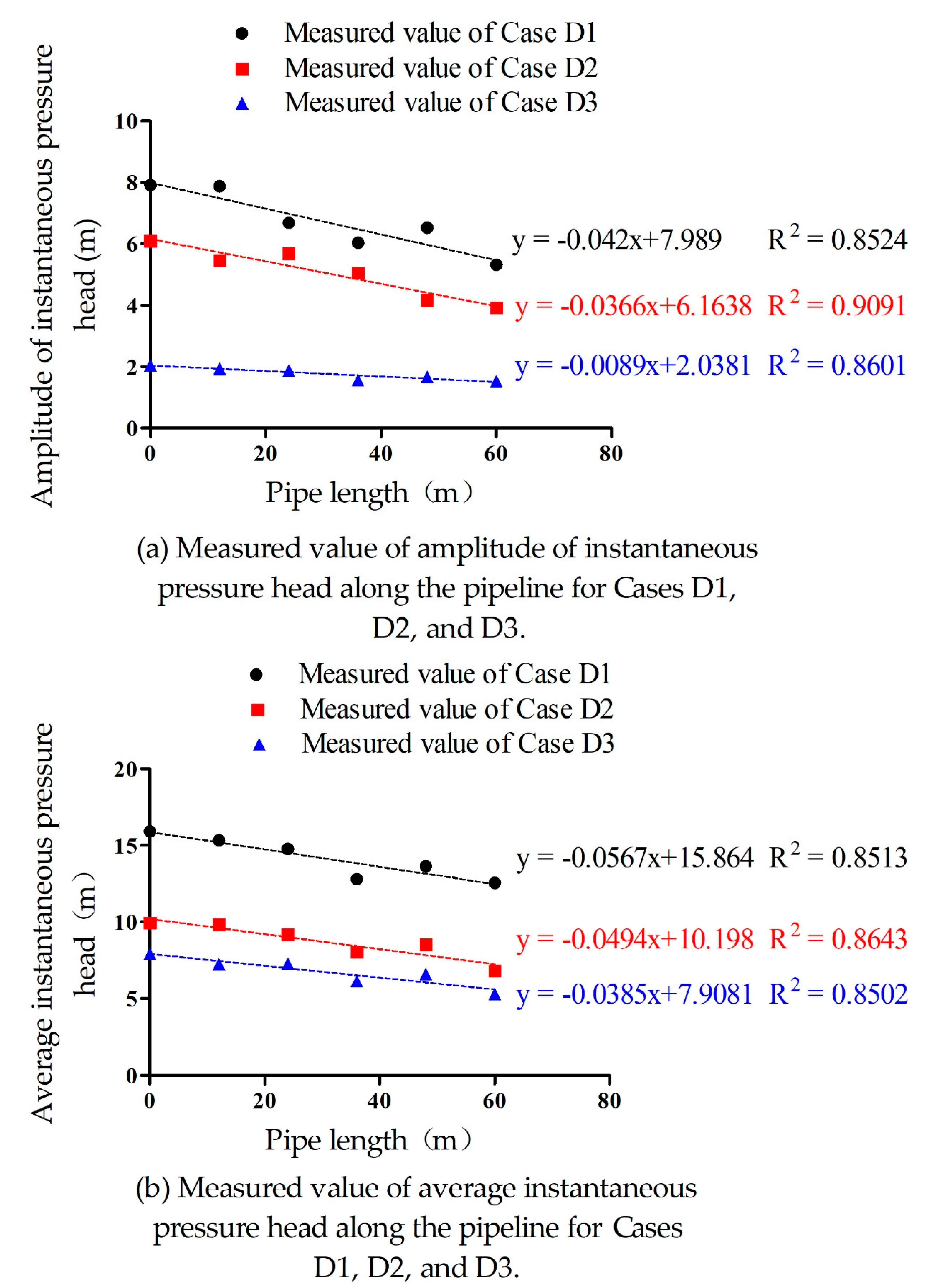
3.1. Results
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woltering, L.; Ibrahim, A.; Pasternak, D.; Ndjeunga, J. The economics of low pressure drip irrigation and hand watering for vegetable production in the Sahel. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsh, B.; Dowgert, M.; Hutmacher, R.; Phene, C.J. Low-pressure drip system in reduced tillage cotton. WIT Ecol. Environ. 2007, 103, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kranz, W.L.; Eisenhauer, D.E.; Retka, M.T. Water and energy-conservation using irrigation scheduling with center-pivot irrigation systems. Agric. Water Manag. 1992, 22, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Evett, S.R.; Andrade, M.A.; Workneh, F.; Price, J.A.; Rush, C.M. Site-specific variable-rate irrigation as a means to enhance water use efficiency. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Sharma, S.P.; Upadhyaya, A.; Rahman, A.; Sikka, A.K. Performance of low energy water application device. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.S.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.S.; Dong, W.C.; Huang, S.H. Evaluations of emitter clogging in drip irrigation by two-phase flow simulations and laboratory experiments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 63, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Oron, G.; Demalach, J.; Hoffman, Z.; Cibotaru, R. Subsurface microirrigation with effluent. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. ASCE 1991, 117, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.L.; Lv, M.C.; Wang, H.; Xiang, H.A. Plugging of microirrigation system and its prevention. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1999, 15, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Shamshery, P.; Winter, A.G. Shape and form optimization of on-line pressure-compensating drip emitters to achieve lower activation pressure. J. Mech. Design 2018, 140, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyadi, H.; Nazemi, A.H.; Sadraddini, A.A.; Delirhasannia, R. Characterising droplets and precipitation profiles of a fixed spray-plate sprinkler. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 119, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seginer, I.; Kantz, D.; Nir, D. The distortion by wind of the distribution patterns of single sprinklers. Agric. Water Manag. 1991, 19, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Alam, M.; Zhao, G.Y. Influence of geometrical parameters of labyrinth flow path of drip emitters on hydraulic and anti-clogging performance. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.M.; Li, N.; Liu, X.G.; Yang, Q.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Long, J. Influence of dentation angle of labyrinth channel of drip emitters on hydraulic and anti-clogging performance. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 68, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.H.; Tang, Y.P.; Lu, B.H. Anti-clogging performance evaluation and parameterized design of emitters with labyrinth channels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 74, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.H.; Tang, Y.P.; Lu, B.H. Structural optimization of labyrinth-channel emitters based on hydraulic and anti-clogging performances. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, X. Combination uniformity improvement of impact sprinkler. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. Effect on hydraulic performance of low-pressure sprinkler by an intermittent water dispersion device. Trans. ASABE 2016, 59, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Xiang, Q. Structure design and experiments on the water distribution of the variable-rate sprinkler with non-circle nozzle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, C. Effect of oscillating pressure on labyrinth emitter clogging. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, P.T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.L.; Zhao, X.; An, B.D. Particles movement characteristics in labyrinth channel under different dynamic water pressure modes. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mac. 2017, 48, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.M.; Li, N.; Liu, X.G.; Yang, Q.L.; Long, J. Influence of flushing pressure, flushing frequency and flushing time on the service life of a labyrinth-channel emitter. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, B.; Zhu, D. The influence of sinusoidal oscillating water flow on sprinkler and impact kinetic energy Intensities of laterally-moving sprinkler irrigation systems. Water 2019, 11, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, D.J.; Silveira, R.C.M.; Wallender, W.W. Oscillating pressure for improving application uniformity of spray emitters. Trans. ASABE 1986, 29, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, D.J.; Gu, Y.P.; Wallender, W.W. Sprinkler uniformity for oscillating low water-pressure. Trans. ASABE 1987, 30, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchin, A.J.; Pons, S.J.; Hills, D.; Abudu, S. Improving Water Application Efficiency in the Landscape through Pressure Oscillation. April 2004. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237342500 (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Tijsseling, A.S. Water hammer with fluid–structure interaction in thick-walled pipes. Comput. Struct. 2007, 85, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidaoui, M.S.; Mansour, S.G.S.; Zhao, M. Applicability of quasisteady and axisymmetric turbulence models in water hammer. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wan, W.; Shi, M. Experimental and numerical simulation of water hammer in gravitational pipe flow with continuous air entrainment. Water 2018, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochupillai, J.; Ganesan, N.; Padmanabhan, C. A new finite element formulation based on the velocity of flow for water hammer problems. Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip. 2005, 82, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharat, M.; Teresa, V.M.; Ramos, H. Experimental study of air vessel behavior for energy storage or system protection in water hammer events. Water 2017, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, P.T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.L.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.Y. Flow characteristics in labyrinth channel under dynamic water pressure. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mac. 2015, 46, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wylie, E.B.; Streeter, V.L.; Suo, L. Fluid Transients in Systems; Prentice Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, A.R. Velocity of a water-hammer wave in an elastic pipe. J. Hydraul. Div. 1963, 89, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Young, W.C.; Budynas, R.G.; Sadegh, A.M. Roark’s Formulas for Stress and Strain; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkinen, J.; Piche, R.; Ellman, A. Fluid transmission line modeling using a variational method. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. ASME 2000, 122, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capponi, C.; Zecchin, A.C.; Ferrante, M.; Gong, J.Z. Numerical study on accuracy of frequency-domain modelling of transients. J. Hydraul. Res. 2017, 55, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, H.M. Applied Hydraulic Transients; Van Nostrand Reinhold, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G. Relating the Hazen-Williams and Darcy-Weisbach friction loss equations for pressurized irrigation. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1996, 12, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Case | Average Pressure Head (m) | Amplitude of Pressure Head (m) | Average Discharge (m3/h) | Amplitude of Discharge (m3/h) | Period (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 16 | 8 | 5.71 | 1.56 | 40 |
| D2 | 10 | 6 | 4.33 | 1.51 | 60 |
| D3 | 8 | 2 | 4.02 | 0.52 | 80 |
| Pipe Length (m) | D1 | D2 | D3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated Value (m) | Measured Value (m) | Relative Error (%) | Calculated Value (m) | Measured Value (m) | Relative Error (%) | Calculated Value (m) | Measured Value (m) | Relative Error (%) | |
| 0 | 8.00 | 7.91 | 1.14 | 6.00 | 6.10 | 1.64 | 2.00 | 2.05 | 2.44 |
| 12 | 7.54 | 7.88 | 4.31 | 5.63 | 5.46 | 3.11 | 1.88 | 1.94 | 3.09 |
| 24 | 7.07 | 6.69 | 5.68 | 5.27 | 5.69 | 7.38 | 1.76 | 1.88 | 6.38 |
| 36 | 6.61 | 6.04 | 9.44 | 4.90 | 5.05 | 2.97 | 1.64 | 1.56 | 5.13 |
| 48 | 6.15 | 6.53 | 5.82 | 4.54 | 4.17 | 8.87 | 1.52 | 1.67 | 8.98 |
| 60 | 5.69 | 5.32 | 6.95 | 4.18 | 3.93 | 6.36 | 1.41 | 1.53 | 7.84 |
| Pipe Length (m) | D1 | D2 | D3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated Value (m) | Measured Value (m) | Relative Error (%) | Calculated Value (m) | Measured Value (m) | Relative Error (%) | Calculated Value (m) | Measured Value (m) | Relative Error (%) | |
| 0 | 16.00 | 15.91 | 0.57 | 10.00 | 9.94 | 0.60 | 8.00 | 7.92 | 1.01 |
| 12 | 15.15 | 15.32 | 1.11 | 9.48 | 9.83 | 3.56 | 7.54 | 7.26 | 3.86 |
| 24 | 14.30 | 14.76 | 3.12 | 8.95 | 9.18 | 2.51 | 7.08 | 7.28 | 2.75 |
| 36 | 13.45 | 12.79 | 5.16 | 8.43 | 8.02 | 5.11 | 6.62 | 6.14 | 7.82 |
| 48 | 12.60 | 13.65 | 7.69 | 7.90 | 8.52 | 7.28 | 6.16 | 6.61 | 6.81 |
| 60 | 11.74 | 12.54 | 6.38 | 7.38 | 6.81 | 8.37 | 5.70 | 5.30 | 7.55 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Song, B.; Zhu, D. The Development of a Calculation Model for the Instantaneous Pressure Head of Oscillating Water Flow in a Pipeline. Water 2019, 11, 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081583
Zhang K, Song B, Zhu D. The Development of a Calculation Model for the Instantaneous Pressure Head of Oscillating Water Flow in a Pipeline. Water. 2019; 11(8):1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081583
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kai, Bo Song, and Delan Zhu. 2019. "The Development of a Calculation Model for the Instantaneous Pressure Head of Oscillating Water Flow in a Pipeline" Water 11, no. 8: 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081583
APA StyleZhang, K., Song, B., & Zhu, D. (2019). The Development of a Calculation Model for the Instantaneous Pressure Head of Oscillating Water Flow in a Pipeline. Water, 11(8), 1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081583





