The Effect of Modifying a CFD-AB Approach on Fish Passage through a Model Hydraulic Dam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
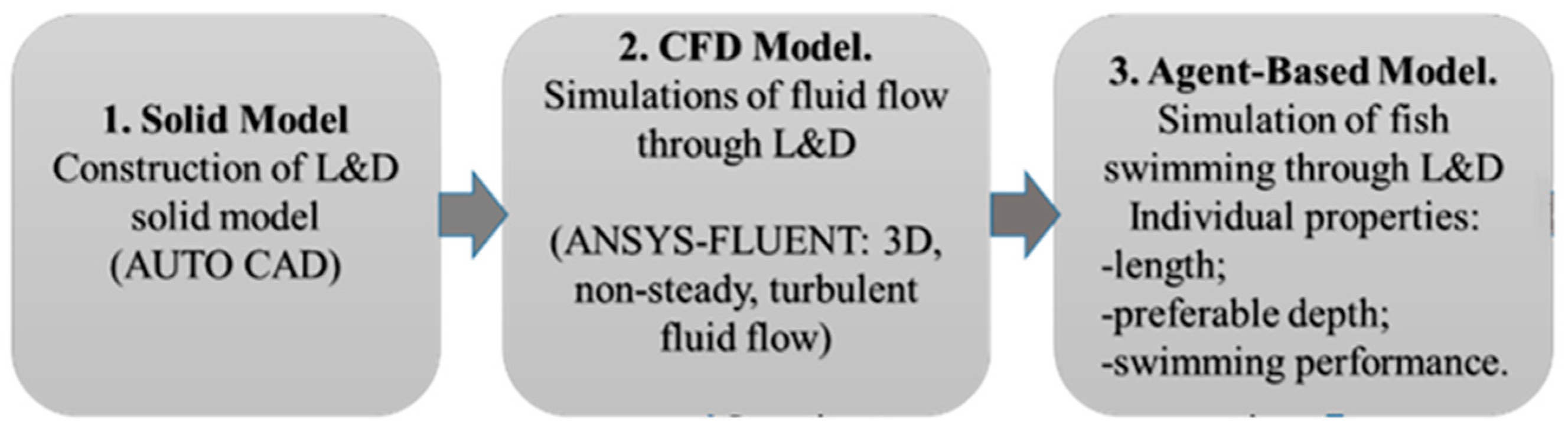
2. Methods
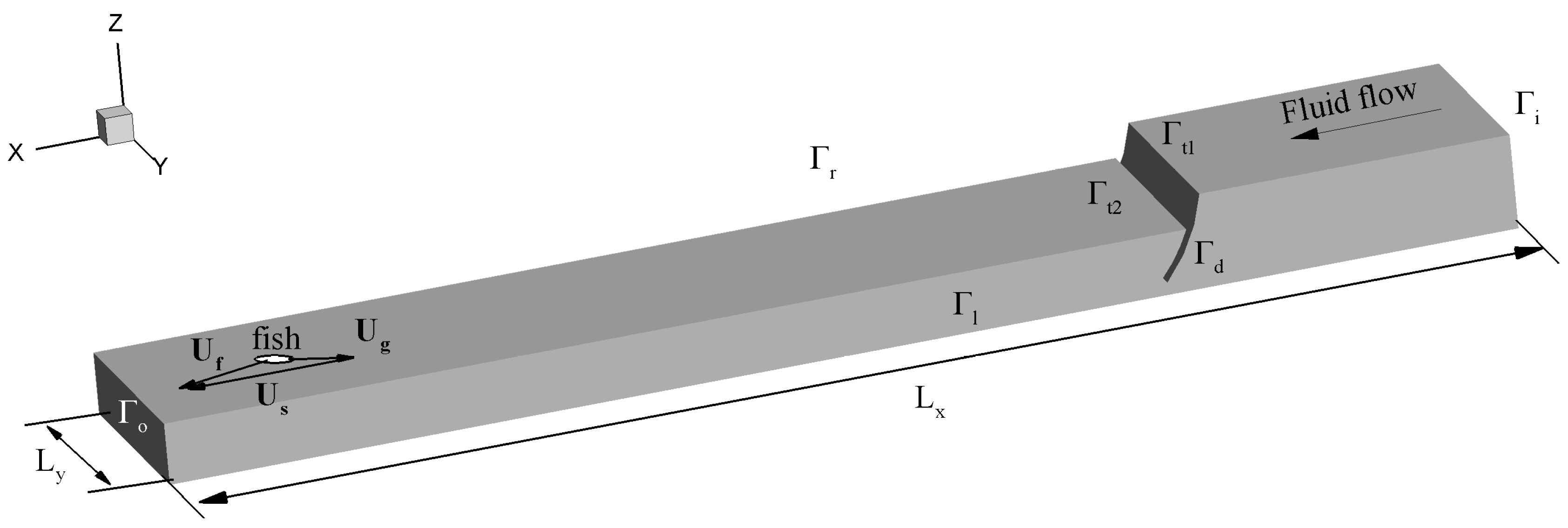
2.1. Fluid Equations
2.2. Agent-Based Model
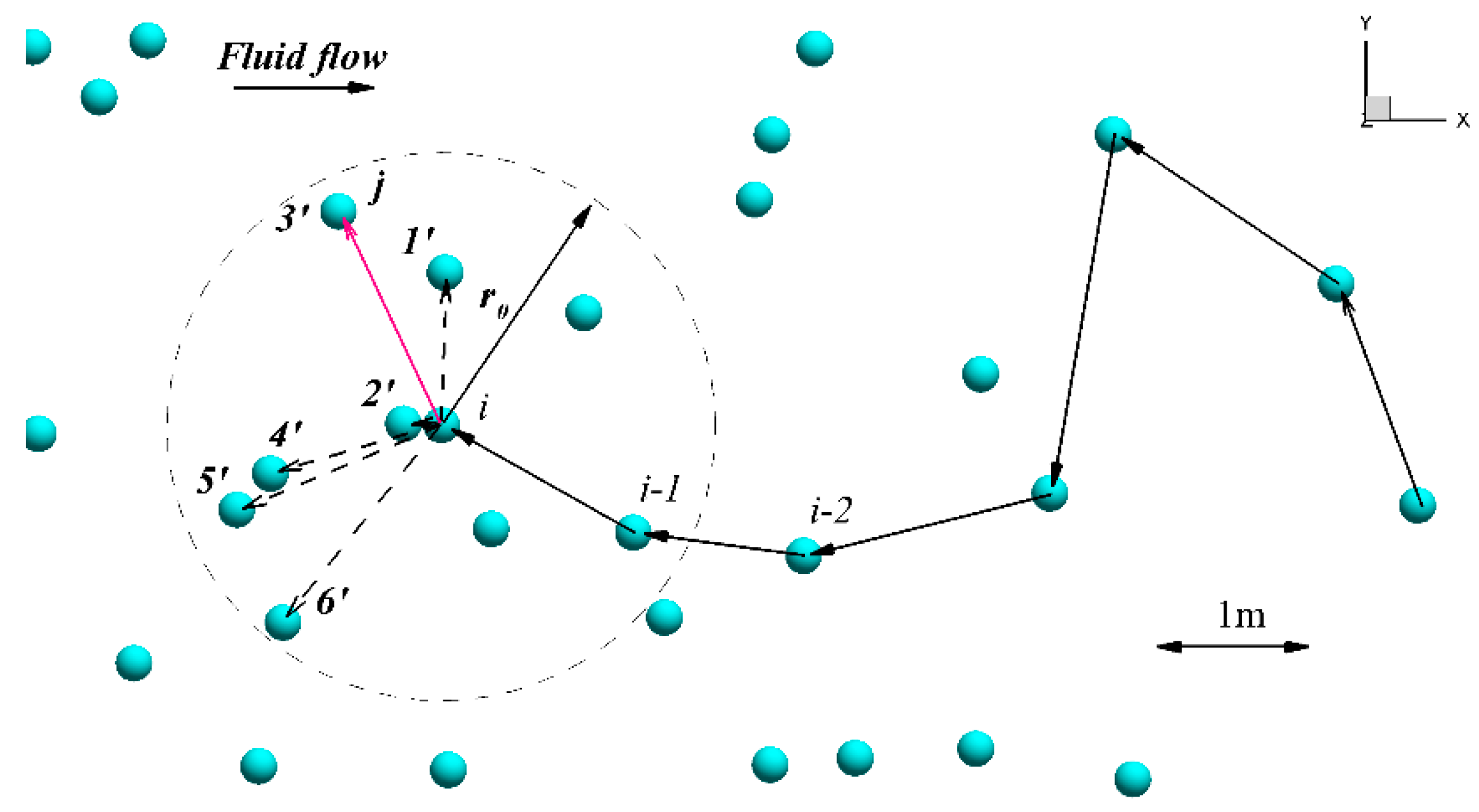
2.2.1. Main Assumptions and Algorithm of the Agent-Based (AB) Model
- (a)
- The main assumptions of the original AB fish passage model used by Zielinski et al. (2018) [4] to simulate fish passing through a LD are as follows:
- (b)
- Fish only swim upstream;
- (c)
- fish swim in the direction that minimizes energy expenditure (minimal fatigue);
- (d)
- changes of fish velocity from a sustained mode to an unsustained (prolonged) speed and vice-versa are attached to the fluid velocity at the fish’s position (Equation (9));
- (e)
- at unsustainable swimming speeds, fish swim at a theoretical distance-maximizing ground speed (Equation (10));
- (f)
- fish try to maintain a species-specific depth that is determined using the best available data;
- (g)
- all fish swim until they pass through the dam or are completely exhausted.
2.2.2. The Modification of the Original Algorithm of the Agent-Based Model
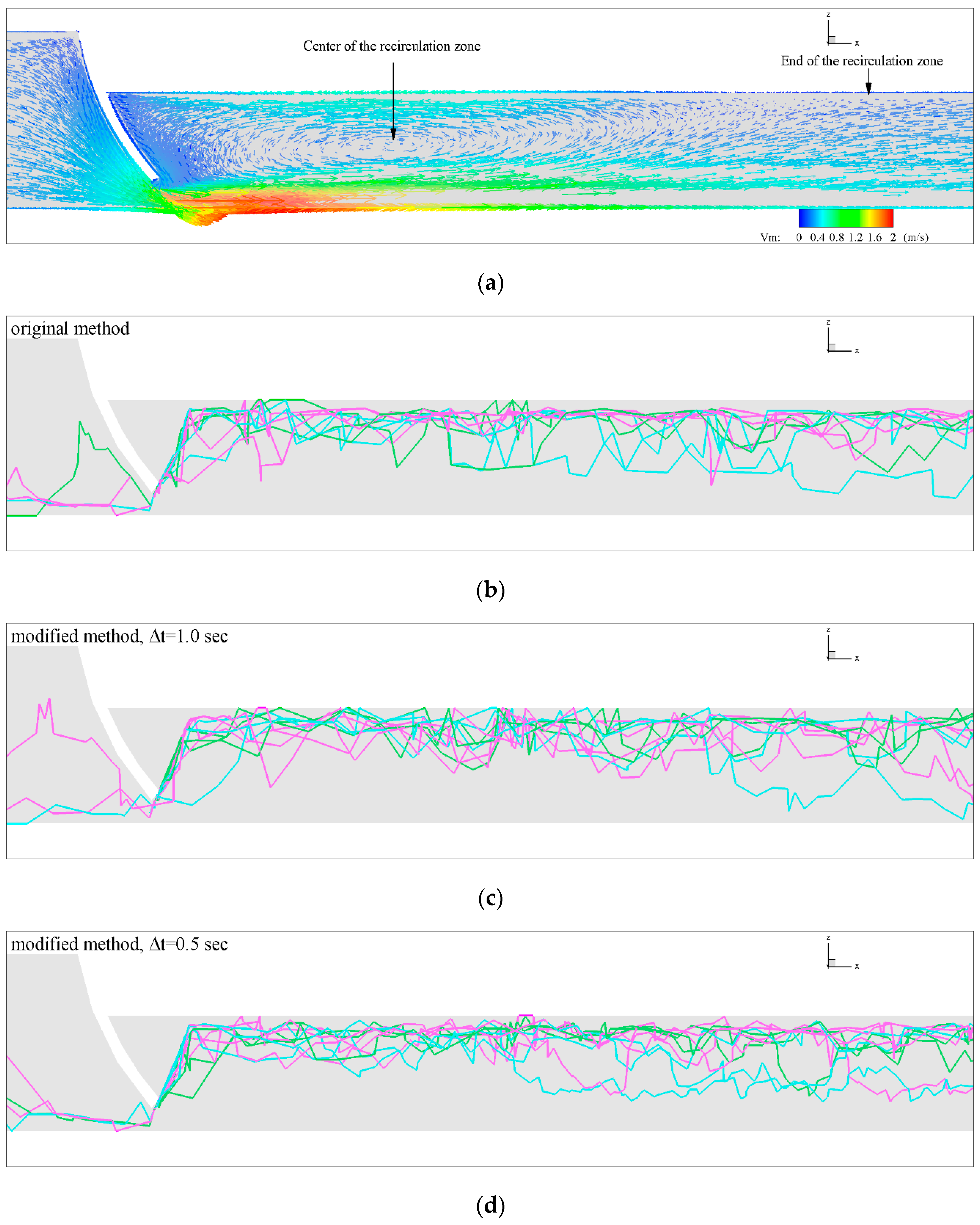
2.3. Comparison of Methods
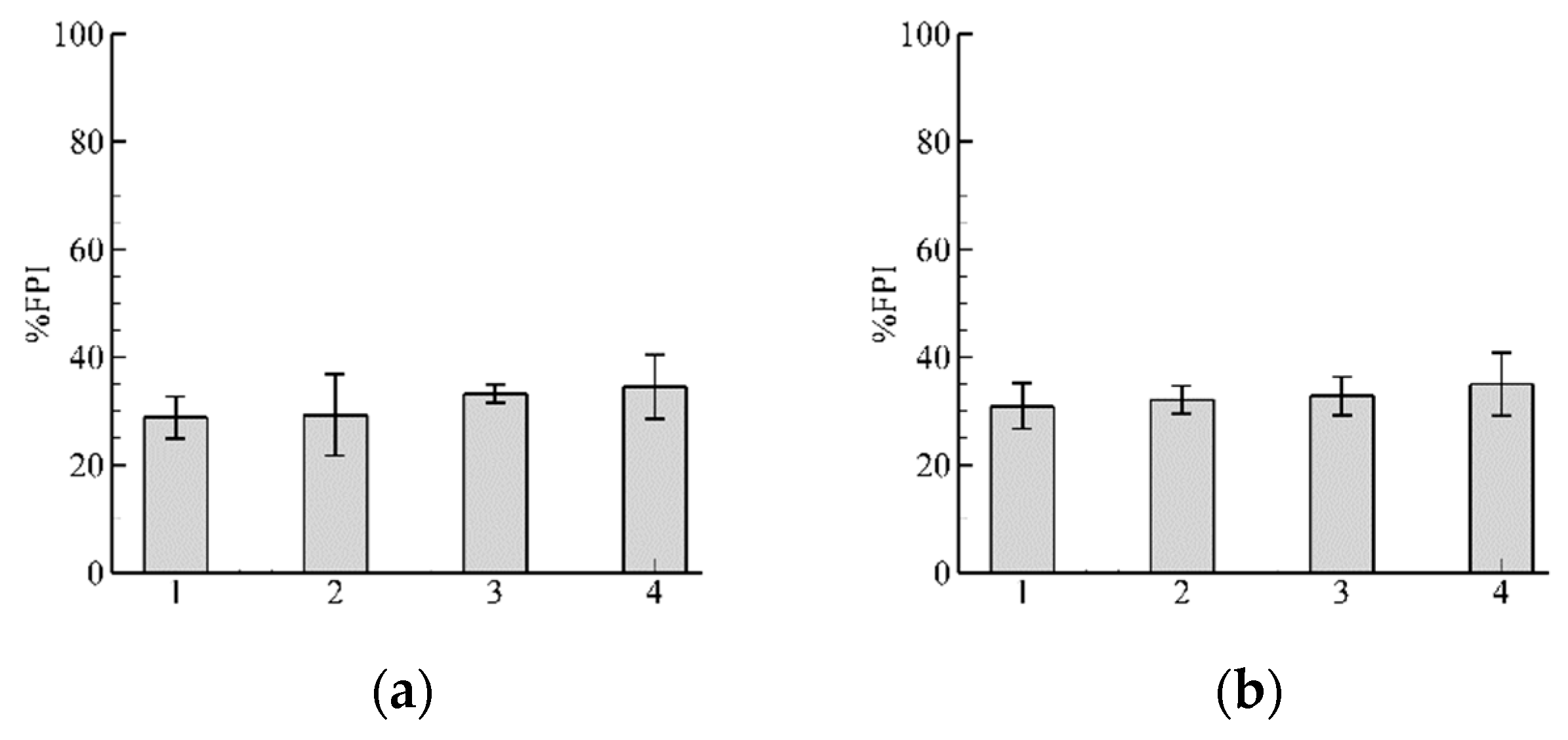
2.3.1. Role of and in Algorithm Performance
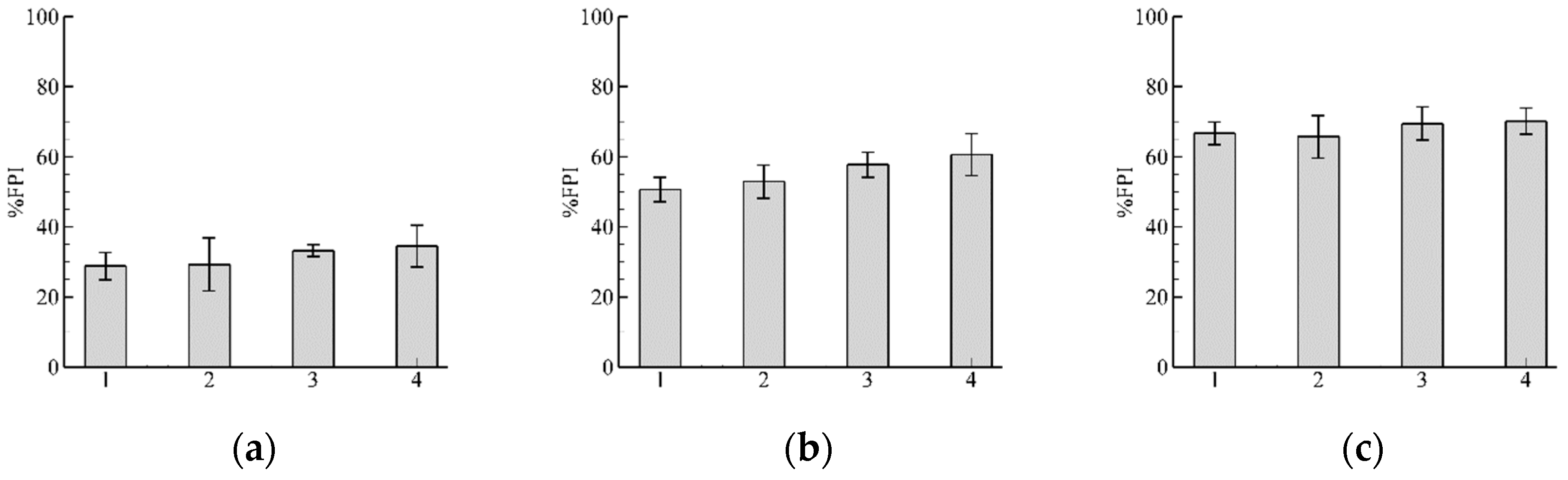
2.3.2. Influence of Discharge
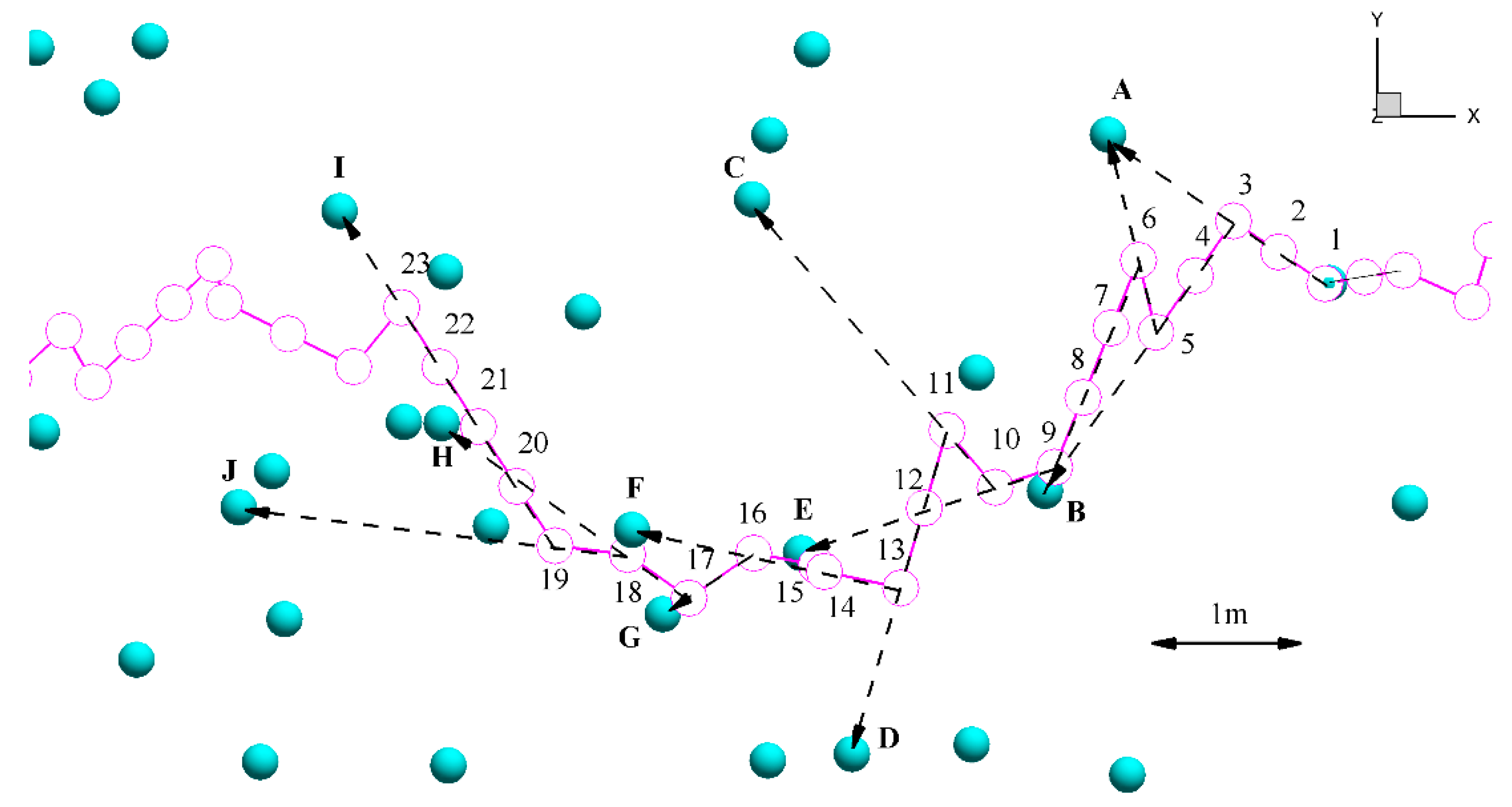
2.3.3. Pathway Characteristics
3. Results
3.1. Role of and in Algorithm Performance for
3.2. Influence of Discharge
3.3. Pathway Characteristics
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larson, J.H.; Knights, B.C.; McCalla, S.G.; Monroe, E.; Tuttle-Lau, M.; Chapman, D.C.; George, A.E.; Vallazza, J.M.; Amberg, J. Evidence of Asian Carp Spawning Upstream of a Key Choke Point in the Mississippi River. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2017, 37, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokotovich, A.; Andow, D.; Aadland, L.; Bertrand, K.; Coulter, A.; Frohnauer, N.; Hoff, M.; Hoxmeier, J.; O’Hara, M.; Phelps, Q.; et al. Minnesota Bigheaded Carps Risk Assessment; Minnesota Department of Natural Resource: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Upper Mississippi River Asian Carp Partnership. Upper Mississippi River Basin Asian Carp Control Strategy Framework; Jackson, N., Runstrom, A., Eds.; Upper Mississippi River Conservation Committee Fisheries Technical Section: Marion, IL, USA, 2018; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zielinski, D.P.; Voller, V.R.; Sorensen, P.W. A physiologically inspired agent-based approach to model fish swimming fatigue and its application to upstream passage of invasive fish at a lock and dam. Ecol. Modeling 2018, 382, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, B.C.; Vallazza, J.M.; Zigler, S.J.; Dewey, M.R. Habitat and movement of lake sturgeon in the upper Mississippi River system. USA Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2002, 131, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigler, S.J.; Dewey, M.R.; Knights, B.C.; Runstrom, A.L.; Steingraeber, M.T. Movement and habitat use by radio-tagged paddlefish in the upper Mississippi River and tributaries. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2003, 23, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, N.E.; Kessel, S.T.; Aarestrup, K.; Cooke, S.J.; Cowley, P.D.; Fisk, A.T.; Whoriskey, F.G. Aquatic animal telemetry: A panoramic window into the underwater world. Science 2015, 348, 1255642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessel, S.T.; Cooke, S.J.; Heupel, M.R.; Hussey, N.E.; Simpfendorfer, C.A.; Vagle, S.; Fisk, A.T. A review of detection range testing in aquatic passive acoustic telemetry studies. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2014, 24, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.; Lucas, M.C.; Castro-Santos, T.; Katopodis, C.; Baumgartner, L.J.; Thiem, J.D.; Aarestrup, K.; Pompeu, P.; O’Brien, G.C.; Braun, D.C.; et al. The future of fish passage science, engineering, and practice. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 340–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Santos, T.; Haro, A. Fish guidance and passage at barriers. In Fish Locomotion: An Eco-Ethological Perspective; Domenici, P., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2010; pp. 62–89. [Google Scholar]
- McElroy, B.; Delonay, A.; Jacobson, R. Optimum swimming pathways of fish spawning migrations in rivers. Ecology 2012, 93, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiem, J.D.; Dawson, J.W.; Hatin, D.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Dumont, P.; Gleiss, A.C.; Wilson, R.P.; Cooke, S.J. Swimming activity and energetic costs of adult lake sturgeon during fishway passage. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2534–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammer, C. Fatigue and exercise tests with fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1995, 112, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaut, I. Critical swimming speed: Its ecological relevance. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2001, 131, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, C.S.; He, P. Burst swimming speeds of mackerel. J. Fish Biol. 1988, 32, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, R. Speed and stamina in three fish. J. Exp. Biol. 1960, 37, 129–153. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, F.W.H. Swimming performance of three southwest Pacific fishes. Mar. Biol. 1984, 79, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, P.; Johnson, L.; Darby, C. The swimming performance of nine species of common California in-shore fishes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1979, 108, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videler, J.J. Fish Swimming; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Santos, T. Optimal swim speeds for traversing velocity barriers: An analysis of volitional high-speed swimming behavior of migratory fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, J.J.; Zielinski, D.P.; Sorensen, P.W. Swimming performance of adult silver and bighead carp. J. Appl. Ichth. 2017, 33, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, W. The effects of exercise training on teleost fish, a review of recent literature. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1997, 117, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, J.D. Limits to exhaustive exercise in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2000, 126, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.A.; Nestler, J.M.; Anderson, J.J.; Weber, L.J.; Loucks, D.P. Forecasting 3-D fish movement behavior using a Eulerian–Lagrangian–agent method (ELAM). Ecol. Model. 2006, 192, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.L.; Goodwin, R.A.; Nestler, J.M. Relating turbulence and fish habitat: A new approach for management and research. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2014, 22, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, J.W.; Bowen, M.D. Physical-based model of fish movement in fish extraction facilities. Ecol. Model. 2002, 152, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, A.; Politano, M.; Weber, L.; Timko, M. Analysis of movements and behavior of smolts swimming in hydropower reservoirs. Ecol. Modeling 2015, 312, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, J.H.; Evans, A.N.; Schreck, C.B. Migratory Patterns of Wild Chinook Salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha Returning to a Large, Free-Flowing River Basin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123127. [Google Scholar]
- Furniss, M.; Love, M.; Firor, S.; Moynan, K.; Llanos, A.; Guntle, J.; Gubernick, R. FishXing: Software and Learning Systems for Fish Passage Through Culverts, Version 3.0. U.S. Forest Service; San Dimas Technology and Development Center: San Dimas, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Andersson, H.I.; Dai, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, L. A new Eulerian-Lagrangian agent method to model fish paths in a vertical slot fishway. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalart, P.R. Strategies for turbulence modelling and simulations. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, J.R. The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 1964, 21, 1183–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, J.R. Swimming performance of sockeye salmon in relation to fatigue time and temperature. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1967, 24, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P.W. Response latencies to postural disturbances in three species of teleostean fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Grosse, E.; Shyu, W.M. Local regression models. In Chapter 8 of Statistical Models in S; Chambers, J.M., Hastie, T.J., Eds.; Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, P.W.; Cotel, A.J.; Meadows, L.A. Waves and eddies: effects on fish behaviour and habitat distribution. In Fish Locomotion: An Eco-ethological Perspective; Domenici, P., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2010; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, P.D.; Osborn, J.F. Analysis of Barrier to Upstream Fish Migration; Contract DE-A179-82BP36523, Project 82-14; Albrock Hydraulics Laboratory: Pullman, WA, USA, 1985. Available online: http://www.efw.bpa.gov/Publications/U36523–1.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2019).



| Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear function | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.45 | 0.43 |
| LOWESS smoother | 0.65 | 0.84 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilmanov, A.; Zielinski, D.; Voller, V.; Sorensen, P. The Effect of Modifying a CFD-AB Approach on Fish Passage through a Model Hydraulic Dam. Water 2019, 11, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091776
Gilmanov A, Zielinski D, Voller V, Sorensen P. The Effect of Modifying a CFD-AB Approach on Fish Passage through a Model Hydraulic Dam. Water. 2019; 11(9):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091776
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilmanov, Anvar, Daniel Zielinski, Vaughan Voller, and Peter Sorensen. 2019. "The Effect of Modifying a CFD-AB Approach on Fish Passage through a Model Hydraulic Dam" Water 11, no. 9: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091776
APA StyleGilmanov, A., Zielinski, D., Voller, V., & Sorensen, P. (2019). The Effect of Modifying a CFD-AB Approach on Fish Passage through a Model Hydraulic Dam. Water, 11(9), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091776






