Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
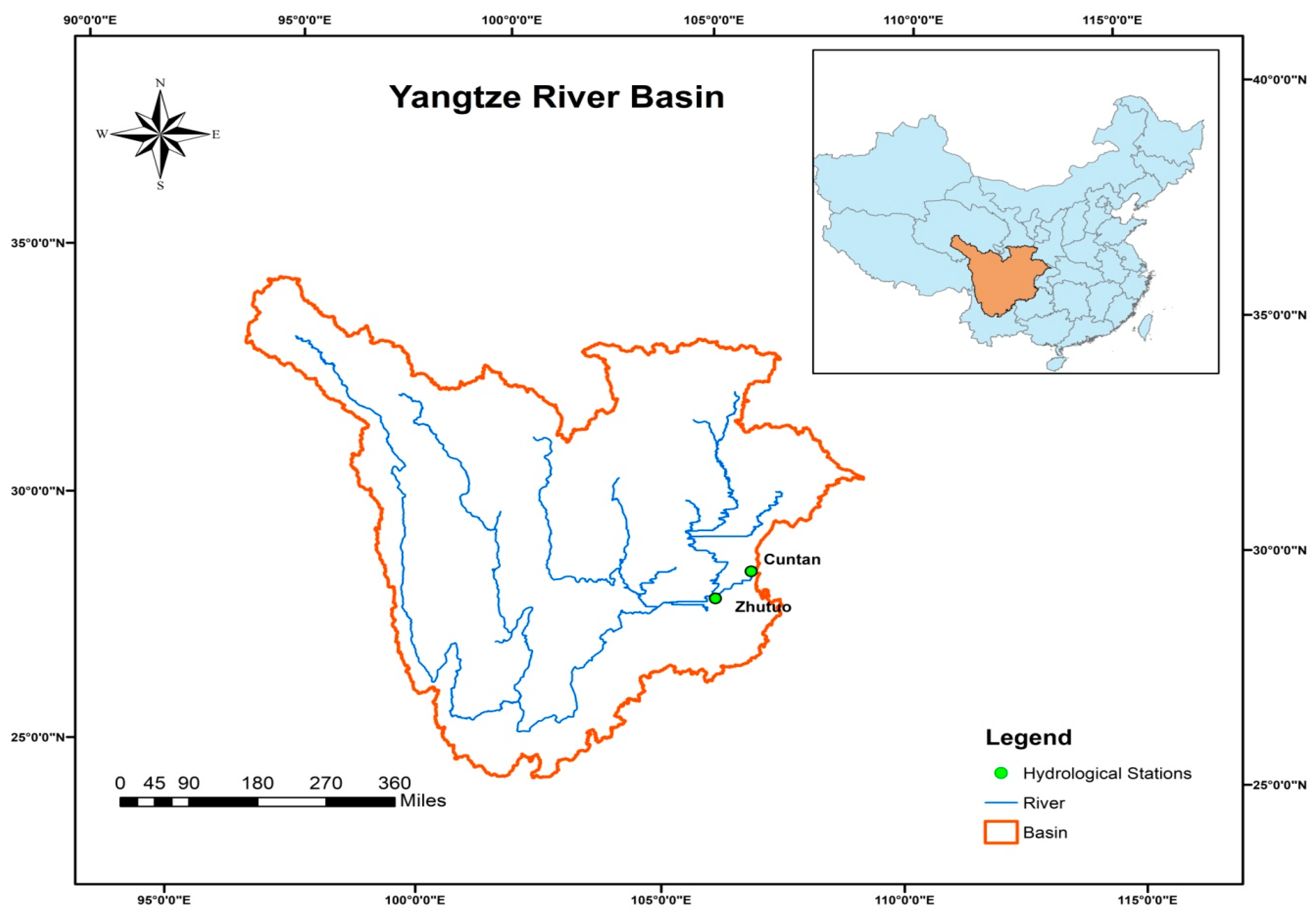
2. Case Study and Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Distributional Analysis
3.2. Estimation of Magnitude of Change
3.3. Mann–Kendall Trend Test
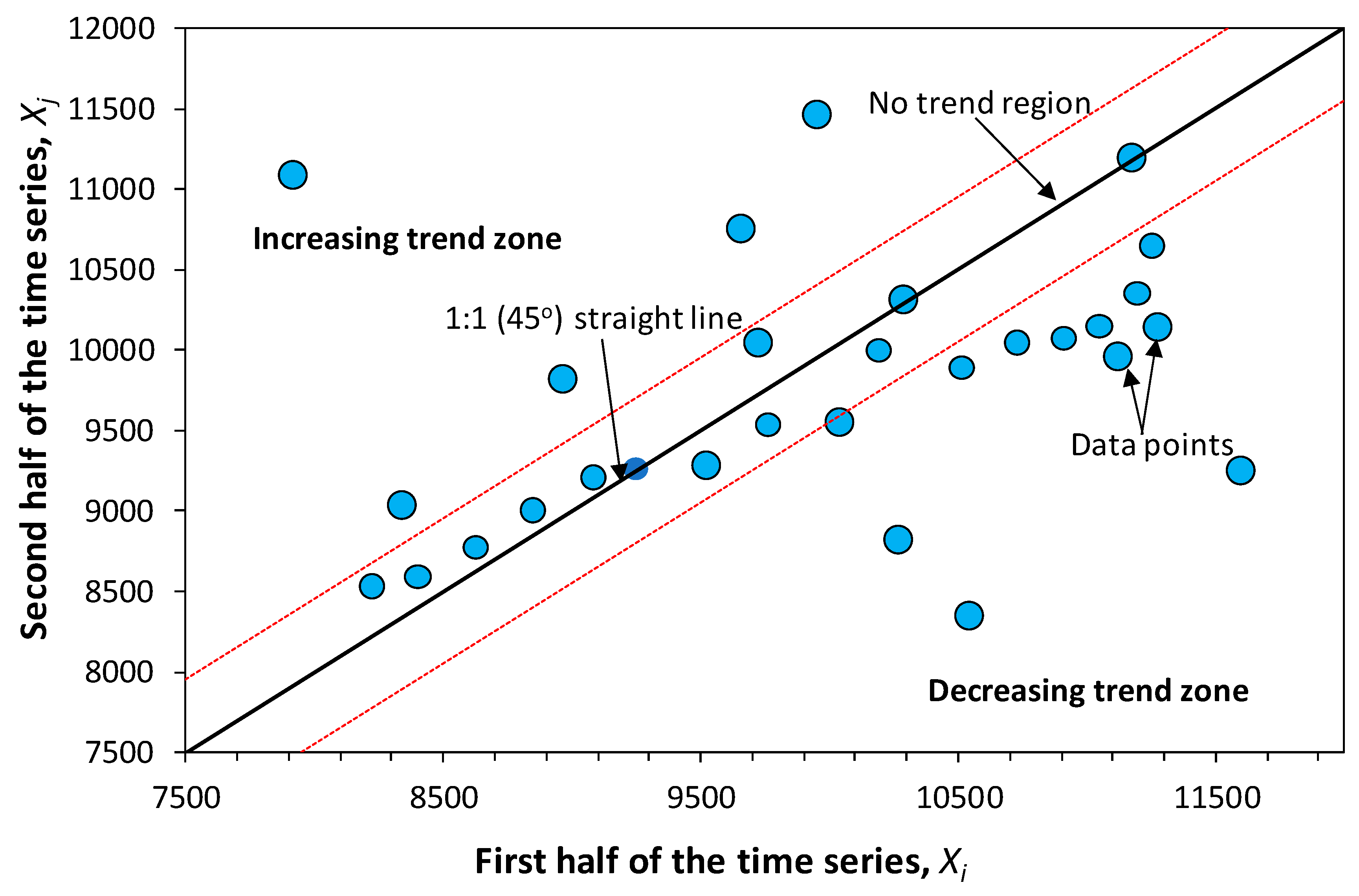
3.4. Innovative Trend Analysis (ITA) Method
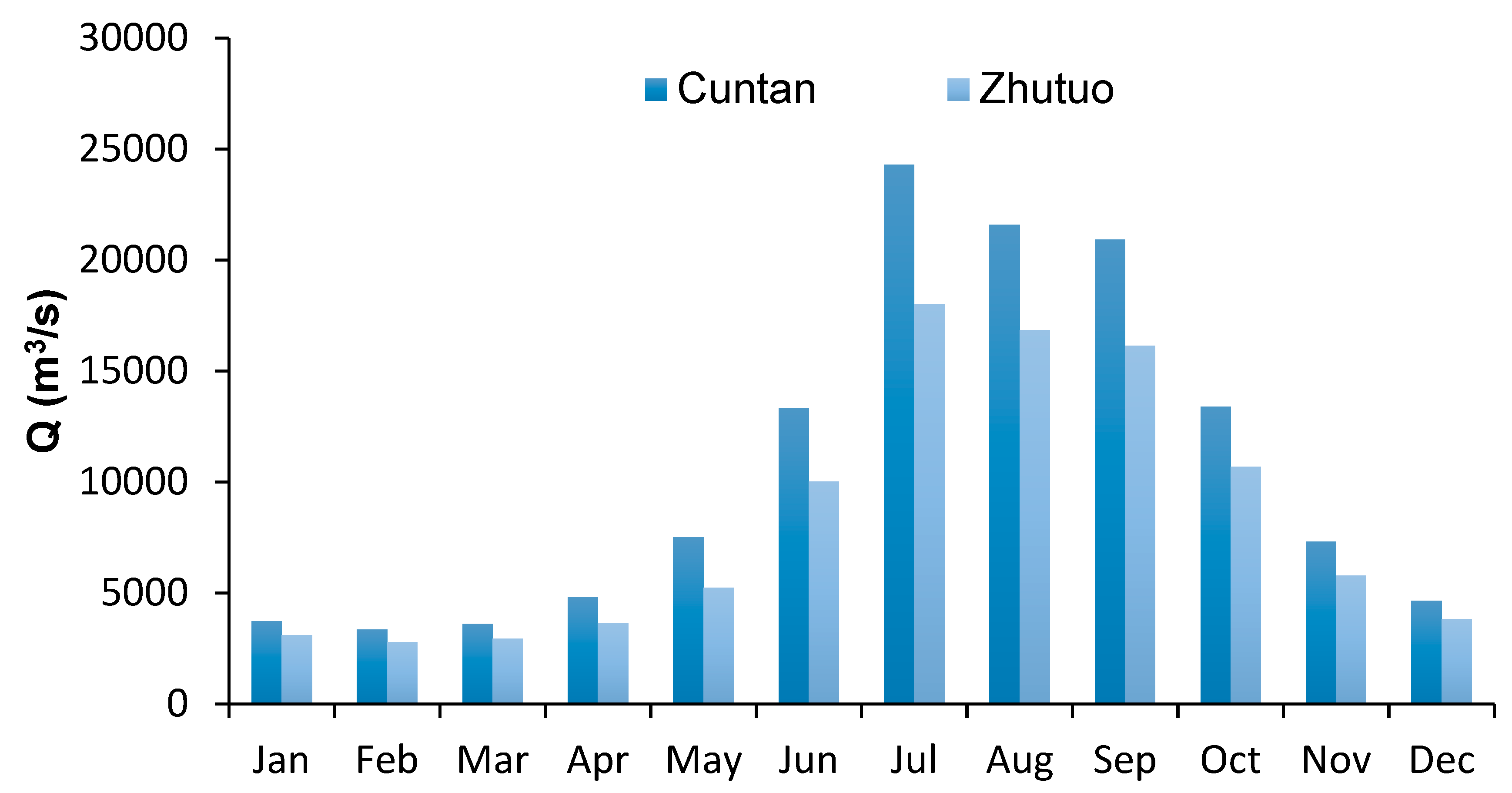
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Distributional Analysis
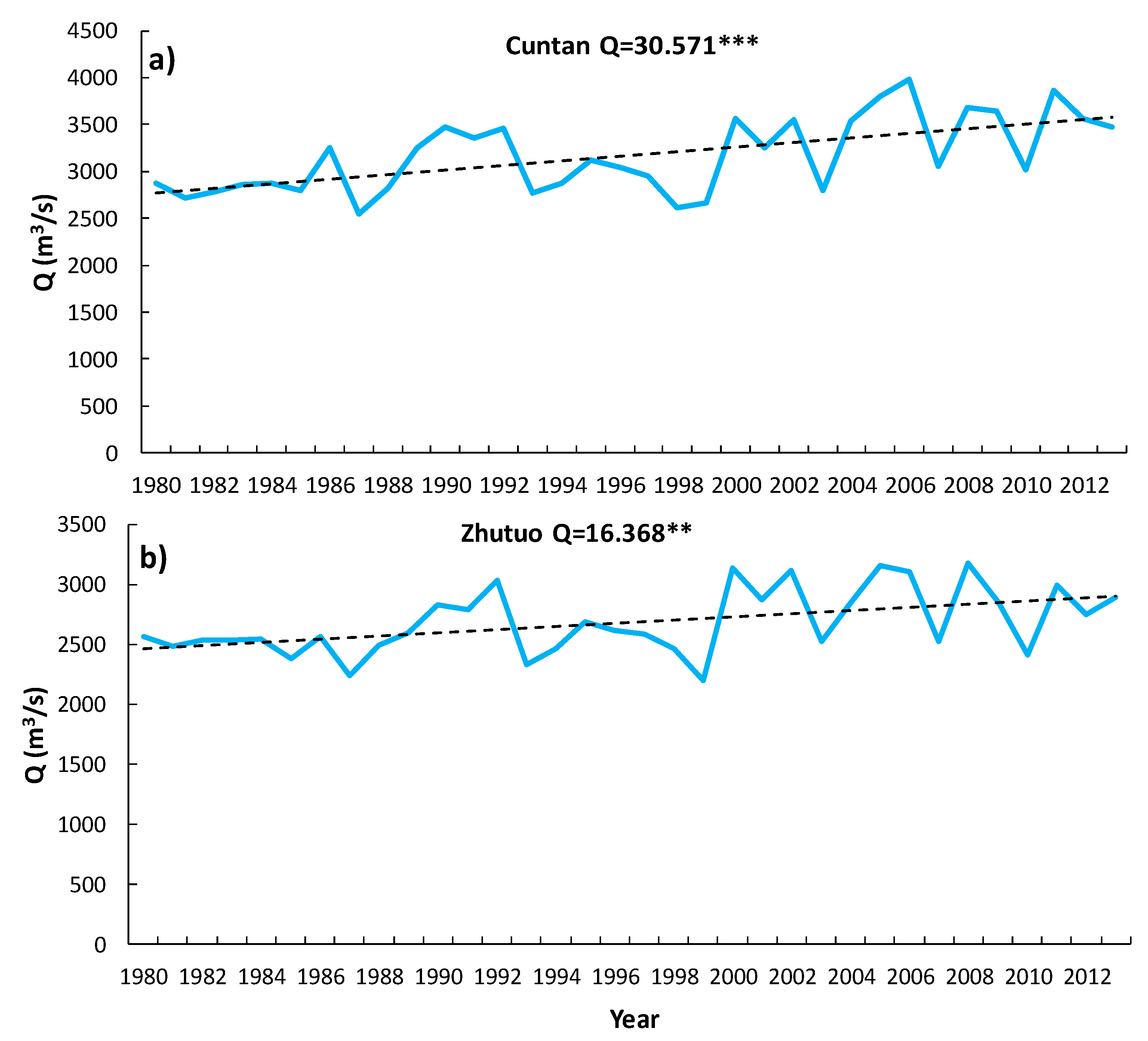
4.2. Mann–Kendall Trends Analysis
4.3. Innovative Trend Analysis (ITA) Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Ahmed, K.; Wang, X.J. Selection of climate models for projection of spatiotemporal changes in temperature of Iraq with uncertainties. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Chung, E.S.; Wang, X.J.; Harun, S.B. Climate change uncertainties in seasonal drought severity-area-frequency curves: Case of arid region of Pakistan. J. Hydrol. 2019, 570, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Ismael, A.; Heryansyah, A.; Nawaz, N. Long term historic changes in the flow of lesser zab river, iraq. Hydrology 2019, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geest, K.; de Sherbinin, A.; Kienberger, S.; Zommers, Z.; Sitati, A.; Roberts, E.; James, R. The impacts of climate change on ecosystem services and resulting losses and damages to people and society. In Loss and Damage from Climate Change: Concepts, Methods and Policy Options; Mechler, R., Bouwer, L.M., Schinko, T., Surminski, S., Linnerooth-Bayer, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ahmed, K.; Ismail, T.; Nawaz, N. Spatial distribution of the trends in precipitation and precipitation extremes in the sub-Himalayan region of Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adi, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.S.; Wang, X.J. Distributional changes in rainfall and river flow in Sarawak, Malaysia. Asia Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 53, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adi, Z.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.S.; Wang, X.J. Trends analysis of rainfall and rainfall extremes in Sarawak, Malaysia using modified Mann–Kendall test. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegerl, G.C.; Black, E.; Allan, R.P.; Ingram, W.J.; Polson, D.; Trenberth, K.E.; Chadwick, R.S.; Arkin, P.A.; Sarojini, B.B.; Becker, A.; et al. Challenges in Quantifying Changes in the Global Water Cycle. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1097–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asefa, T.; Clayton, J.; Adams, A.; Anderson, D. Performance evaluation of a water resources system under varying climatic conditions: Reliability, Resilience, Vulnerability and beyond. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Modeling climate change impacts on precipitation in arid regions of Pakistan: A non-local model output statistics downscaling approach. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanova, A.; Liersch, S.; Nunes, J.P.; Didovets, I.; Stagl, J.; Huang, S.; Koch, H.; Rivas López, M.d.R.; Maule, C.F.; Hattermann, F.; et al. Hydrological impacts of moderate and high-end climate change across European river basins. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigizoglu, H.; Bayazit, M.; Önöz, B. Trends in the maximum, mean, and low flows of Turkish rivers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemans, H.; Speelman, L.H.; Ludwig, F.; Moors, E.J.; Wiltshire, A.J.; Kumar, P.; Gerten, D.; Kabat, P. Future water resources for food production in five South Asian river basins and potential for adaptation--a modeling study. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 468–469, S117–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qutbudin, I.; Shiru, M.S.; Sharafati, A.; Ahmed, K.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X. Seasonal Drought Pattern Changes Due to Climate Variability: Case Study in Afghanistan. Water 2019, 11, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiru, M.S.; Shahid, S.; Alias, N.; Chung, E.S. Trend Analysis of Droughts during Crop Growing Seasons of Nigeria. Sustainability 2018, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Influence of hydrologically based environmental flow methods on flow alteration and energy production in a run-of-river hydropower plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Trade-off between environmental flow policy and run-of-river hydropower generation in Mediterranean climate. Eur. Water 2017, 60, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abghari, H.; Tabari, H.; Hosseinzadeh Talaee, P. River flow trends in the west of Iran during the past 40years: Impact of precipitation variability. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 101, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A.A.; Hasanzadeh, Y.; Besalatpour, A.A.; Pourreza-Bilondi, M. Climate change forecasting in a mountainous data scarce watershed using CMIP5 models under representative concentration pathways. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 129, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardıçlıoğlu, M.; Kuriqi, A. Calibration of channel roughness in intermittent rivers using HEC-RAS model: Case of Sarimsakli creek, Turkey. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramagamage, P. Spatial and temporal variation of rainfall trends of Sri Lanka. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzo, L.; Bono, E.; Sammartano, V.; Freni, G. Analysis of spatial and temporal rainfall trends in Sicily during the 1921–2012 period. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 126, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döll, P.; Fiedler, K.; Zhang, J. Global-scale analysis of river flow alterations due to water withdrawals and reservoirs. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 2413–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Q.; Costa, V.; Wang, X. A hierarchical Bayesian model for decomposing the impacts of human activities and climate change on water resources in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tang, G.; Jones, P. Climatic warming in China during 1901–2015 based on an extended dataset of instrumental temperature records. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L. Probabilistic projections of climate change over China under the SRES A1B scenario using 28 AOGCMs. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4741–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W. A CMIP5 multimodel projection of future temperature, precipitation, and climatological drought in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2059–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fang, X.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Ma, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, L. Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Impacts of Sediment Variations in Downstream of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Kong, F.; Fang, J.; Zhao, L. Observed changes in hydrological extremes and flood disaster in Yangtze River Basin: Spatial–temporal variability and climate change impacts. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, D.; Zhao, T.; Yang, H. Changes in the eco-flow metrics of the Upper Yangtze River from 1961 to 2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Ardiçlioǧlu, M. Investigation of hydraulic regime at middle part of the Loire River in context of floods and low flow events. Pollack Period. 2018, 13, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Ardiçlioglu, M.; Muceku, Y. Investigation of seepage effect on river dike’s stability under steady state and transient conditions. Pollack Period. 2016, 11, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Innovative trend analysis methodology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 17, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosunoglu, F.; Kisi, O. Trend Analysis of Maximum Hydrologic Drought Variables Using Mann–Kendall and Şen’s Innovative Trend Method. River Res. Appl. 2017, 33, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Taye, M.T.; Willems, P. Statistical assessment of precipitation trends in the upper Blue Nile River basin. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, V.; Kisi, O. Comparison of Mann-Kendall and innovative trend method (Şen trend) for monthly total precipitation (Middle Black Sea Region, Turkey). In Proceedings of the Conference 3rd International Balkans Conference on Challenges of Civil Engineering, 3-BCCCE, Tirana, Albania, 19–21 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dabanlı, İ.; Şen, Z.; Yeleğen, M.Ö.; Şişman, E.; Selek, B.; Güçlü, Y.S. Trend Assessment by the Innovative-Şen Method. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 5193–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztopal, A.; Şen, Z. Innovative Trend Methodology Applications to Precipitation Records in Turkey. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qian, H. Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2582–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O. An innovative method for trend analysis of monthly pan evaporations. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Kumar, A.; Guhathakurta, P.; Kisi, O. Spatial-temporal trend analysis of seasonal and annual rainfall (1966–2015) using innovative trend analysis method with significance test. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanikhani, H.; Kisi, O.; Mirabbasi, R.; Meshram, S.G. Trend analysis of rainfall pattern over the Central India during 1901–2010. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Jiang, T.; Jin, W. Recent trends in observed temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 83, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Lewis, Q.W.; Wu, J.; Huang, F. A framework to assess the cumulative impacts of dams on hydrological regime: A case study of the Yangtze River. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.D.; Liu, C.L.; Lin, H. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation maxima during 1960–2005 in the Yangtze River basin and possible association with large-scale circulation. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollert, H. Processes and environmental quality in the Yangtze River system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6904–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.S.; Shahid, S.; Sung, J. Uncertainty in Rainfall Intensity Duration Frequency Curves of Peninsular Malaysia under Changing Climate Scenarios. Water 2018, 10, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Ahmed, K.; Nawaz, N. Trends in heat wave related indices in Pakistan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 33, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.B.; Wang, X.J. Spatial distribution of unidirectional trends in temperature and temperature extremes in Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranuthi, G.; Dubey, S.; Tripathi, S.; Chandniha, S. Trend and change point detection of precipitation in urbanizing Districts of Uttarakhand in India. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Nawaz, N. Impacts of climate variability and change on seasonal drought characteristics of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannaford, J.; Buys, G. Trends in seasonal river flow regimes in the UK. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piniewski, M.; Marcinkowski, P.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Trend detection in river flow indices in Poland. Acta Geophys. 2018, 66, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X.J.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Spatiotemporal Changes in Aridity of Pakistan during 1901-2016. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Chung, E.S.; Ismail, T.; Wang, X.J. Spatial distribution of secular trends in annual and seasonal precipitation over Pakistan. Clim. Res. 2017, 74, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S. Spatial distribution of unidirectional trends in climate and weather extremes in Nile river basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 137, 1181–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonali, P.; Nagesh Kumar, D. Review of trend detection methods and their application to detect temperature changes in India. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S.; Rahim, N.A. Unidirectional trends in annual and seasonal climate and extremes in Egypt. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 136, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Innovative trend significance test and applications. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 127, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Gullà, G.; Nanni, T.; Simolo, C. Precipitation variability and change in the Calabria region (Italy) from a high resolution daily dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, M.; Kisi, O. Investigation of trend analysis of monthly total precipitation by an innovative method. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 120, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E. Application of the Innovative Trend Analysis Method for the Trend Analysis of Rainfall Anomalies in Southern Italy. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 4971–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E. Analysis of Monthly Rainfall Trend in Calabria (Southern Italy) through the Application of Statistical and Graphical Techniques. Proceedings 2018, 2, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü, Y.S.; Dabanlı, İ.; Şişman, E.; Şen, Z. Air quality (AQ) identification by innovative trend diagram and AQ index combinations in Istanbul megacity. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Balasmeh, O.; Babbar, R.; Karmaker, T. Trend analysis and ARIMA modeling for forecasting precipitation pattern in Wadi Shueib catchment area in Jordan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, L.; Lai, Z.; Tian, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal air temperature and rainfall in the Yangtze River Basin, China during 1960–2015. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2017, 164, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Month/Season | Cuntan | Zhutuo | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | Gen. Extreme Value | Normal | Gamma | Gen. Extreme Value | Normal | |
| January | 0.135 | 0.089 | 0.157 | 0.091 | 0.065 | 0.106 |
| February | 0.128 | 0.107 | 0.149 | 0.101 | 0.083 | 0.108 |
| March | 0.123 | 0.088 | 0.144 | 0.117 | 0.085 | 0.137 |
| April | 0.114 | 0.072 | 0.148 | 0.114 | 0.060 | 0.143 |
| May | 0.100 | 0.077 | 0.129 | 0.070 | 0.063 | 0.084 |
| June | 0.122 | 0.098 | 0.138 | 0.095 | 0.087 | 0.096 |
| July | 0.075 | 0.078 | 0.079 | 0.103 | 0.076 | 0.126 |
| August | 0.127 | 0.127 | 0.159 | 0.151 | 0.132 | 0.125 |
| September | 0.191 | 0.124 | 0.159 | 0.192 | 0.108 | 0.160 |
| October | 0.093 | 0.097 | 0.109 | 0.093 | 0.078 | 0.120 |
| November | 0.077 | 0.541 | 0.099 | 0.112 | 0.069 | 0.133 |
| December | 0.140 | 0.112 | 0.141 | 0.082 | 0.061 | 0.076 |
| Mean annual | 0.068 | 0.077 | 0.075 | 0.092 | 0.093 | 0.089 |
| Annual Maximum flow | 0.088 | 0.085 | 0.089 | 0.125 | 0.123 | 0.121 |
| Annual Minimum flow | 0.068 | 0.077 | 0.075 | 0.154 | 0.119 | 0.166 |
| Spring | 0.126 | 0.075 | 0.152 | 0.105 | 0.086 | 0.124 |
| Summer | 0.108 | 0.108 | 0.105 | 0.129 | 0.119 | 0.113 |
| Autumn | 0.144 | 0.083 | 0.120 | 0.136 | 0.091 | 0.111 |
| Winter | 0.184 | 0.096 | 0.200 | 0.078 | 0.063 | 0.088 |
| Cuntan | Zhutuo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Series | MK | Significance | Sen’s Slope | MK | Signific. | Sen’s Slope |
| January | 4.81 | *** | 36.15 | 4.30 | *** | 20.14 |
| February | 3.50 | *** | 27.51 | 3.17 | *** | 16.87 |
| March | 3.61 | *** | 42.67 | 3.09 | *** | 24.47 |
| April | 1.87 | * | 32.03 | 1.32 | 18.10 | |
| May | −0.29 | −11.31 | −1.13 | −17.83 | ||
| June | −1.19 | −48.48 | −1.51 | −54.48 | ||
| July | −1.02 | −113.48 | −1.73 | * | −112.65 | |
| August | −1.21 | −112.07 | −0.48 | −25.77 | ||
| September | −1.16 | −98.08 | −0.91 | −52.83 | ||
| October | −1.81 | * | −71.12 | −1.84 | * | −87.04 |
| November | −0.67 | −16.12 | −1.02 | −11.35 | ||
| December | 0.99 | 8.61 | 0.91 | 5.43 | ||
| Maximum | −0.64 | −82.39 | −1.24 | −50.88 | ||
| Minimum | 4.13 | *** | 30.57 | 3.23 | *** | 16.37 |
| Annual | −1.19 | −26.76 | −1.40 | −17.36 | ||
| Spring | 1.46 | 21.74 | 1.19 | 9.54 | ||
| Summer | −1.21 | −65.90 | −1.35 | −56.53 | ||
| Autumn | −1.68 | * | −61.03 | −1.81 | * | −55.78 |
| Winter | 3.99 | *** | 23.49 | 3.75 | *** | 13.65 |
| Season | Method | Station | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cuntan | Zhutuo | ||
| Annual | ITA | 0.05 | −0.01 |
| β | −26.8 | −17.4 | |
| MK | −1.19 | −1.40 | |
| Spring | ITA | 0.28 | 0.17 |
| β | 21.74 | 9.55 | |
| MK | 1.46 | 1.19 | |
| Summer | ITA | 0 | 0.02 |
| β | −65.9 | −56.5 | |
| MK | −1.21 | −1.35 | |
| Autumn | ITA | −0.15 | −0.39 |
| β | −61.03 | −55.78 | |
| MK | −1.68 | −1.81 | |
| Winter | ITA | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| β | 23.5 | 13.66 | |
| MK | 3.99 | 3.75 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, R.; Kuriqi, A.; Abubaker, S.; Kisi, O. Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method. Water 2019, 11, 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091855
Ali R, Kuriqi A, Abubaker S, Kisi O. Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method. Water. 2019; 11(9):1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091855
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Rawshan, Alban Kuriqi, Shadan Abubaker, and Ozgur Kisi. 2019. "Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method" Water 11, no. 9: 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091855
APA StyleAli, R., Kuriqi, A., Abubaker, S., & Kisi, O. (2019). Long-Term Trends and Seasonality Detection of the Observed Flow in Yangtze River Using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s Innovative Trend Method. Water, 11(9), 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091855







