Functionalized Leather: A Novel and Effective Hazardous Solid Waste Adsorbent for the Removal of the Diazo Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
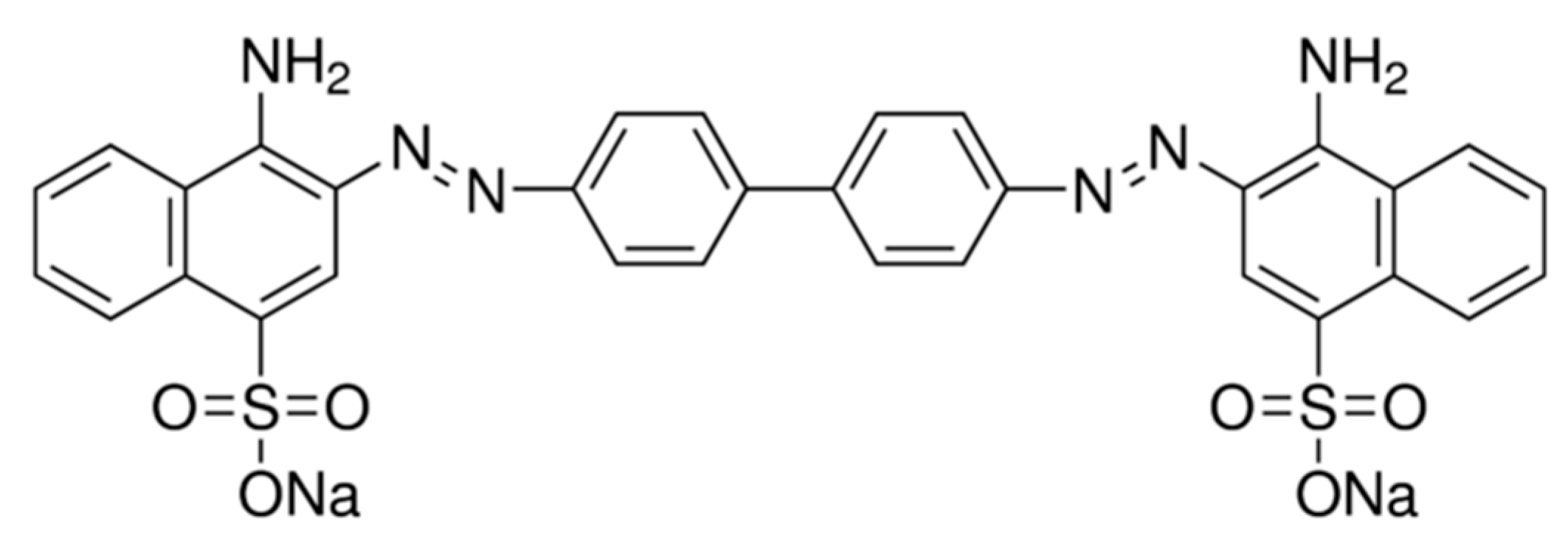
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Adsorbents
2.3. Surface Functionalization
2.4. Retention Time Test of Adsorbents
2.5. Dye Adsorption Tests
2.6. Effect of pH on Dye Adsorption
2.7. Life Cycle Determination
2.8. Phytotoxicity Test
2.9. Microscopic Examination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Functionalization
3.2. Retention Time Tests of Adsorbents
3.3. Effect of The Adsorbents on Dye Removal
3.4. Dye Absorption on Different pH
3.5. Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherm Models
3.6. Kinetics of the Adsorption Process
3.7. Intra-Particle Diffusion Study
3.8. Life Cycle
3.9. Phytotoxicity
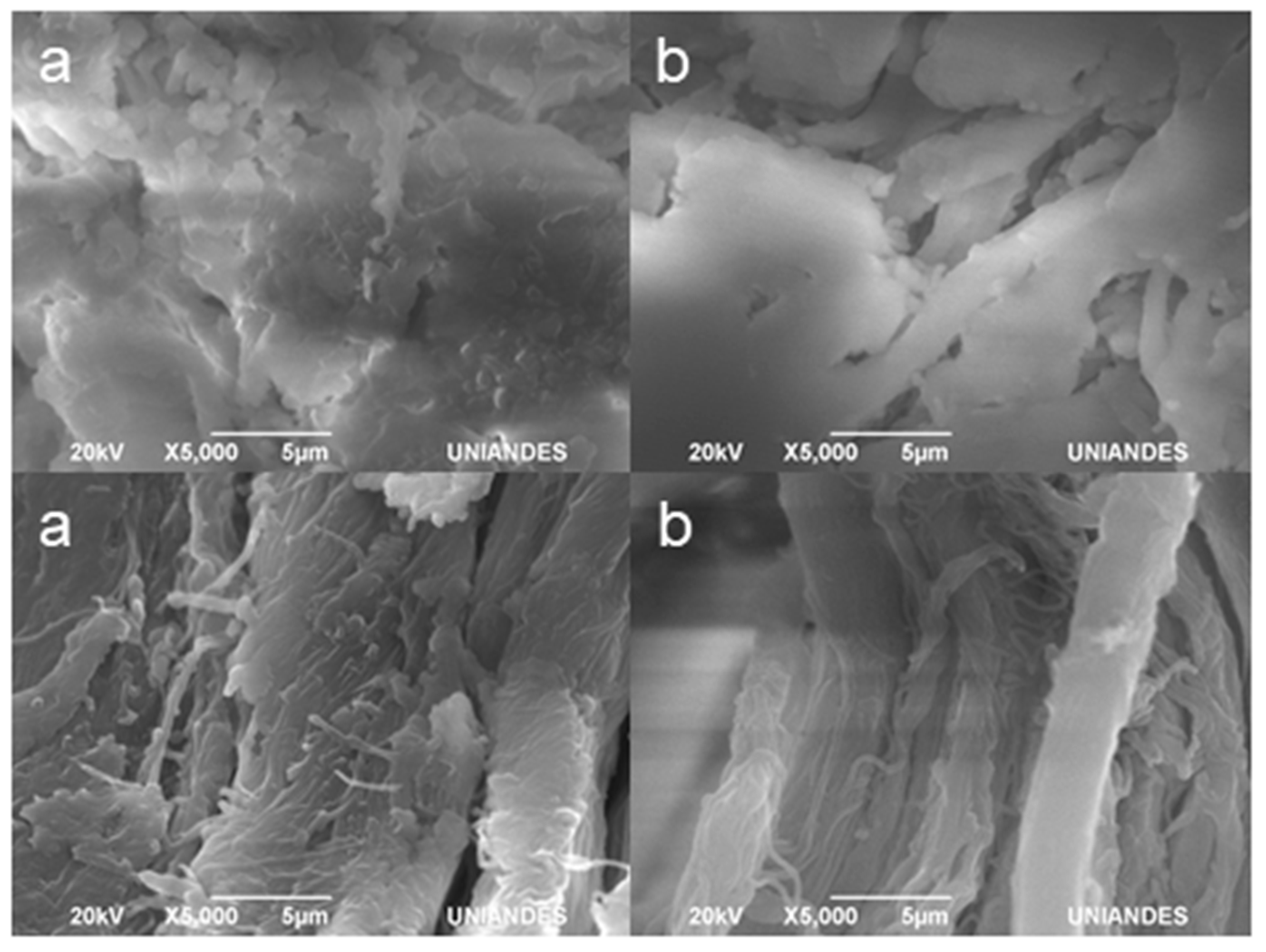
3.10. SEM Photographs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosari, S.; Ardiansyah, T. Degradation of Methylene Blue and Congo-Red Dyes Using Fenton, PhotoFenton, Sono-Fenton, and Sonophoto-Fenton Methods in the Presence of Iron (II, III) Oxide/Zinc Oxide/Graphene (Fe3O4/ZnO/Graphene) Composites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.M.; Khan, A.; Hasmath Farzana, M.; Hwang, G.C.; Lee, W.; Lee, G. Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Oxide-Doped Nano-Hydroxyapatite and Its Adsorption Performance of Toxic Diazo Dyes from Aqueous Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermatt, F.; Joss, A.; Eggen, R.I.L.; Stamm, C.; Reyes, M.; Räsänen, K.; Focks, A.; Munz, N.A.; Burdon, F.J. Agriculture versus Wastewater Pollution as Drivers of Macroinvertebrate Community Structure in Streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 659, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, L.R.G.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Dallago, R.M.; Guerreiro, M.C.; Oliveira, D.Q.L.; Gonçalves, M. Solid Waste from Leather Industry as Adsorbent of Organic Dyes in Aqueous-Medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 141, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, C.; Soontarapa, K.; Jyothi, M.S.; Balakrishna, R.G. Environmental Friendly and Cost Effective Caramel for Congo Red Removal, High Flux, and Fouling Resistance of Polysulfone Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadinia, T.; Behnam, B.; Allahresani, A. Removal of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Znfe2o4/Sio2 Tragacanth Gum Magnetic Nanocomposite as a Novel Adsorbent, Surfaces and Interfaces. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 14, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J. Adsorption of Congo Red Dye on FexCo3-XO4 Nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wu, P.; Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Ruan, B.; Hu, H.; Zhu, N.; Lin, Z. FeOOH-Loaded MnO2 Nano-Composite: An Efficient Emergency Material for Thallium Pollution Incident. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selcuk, H. Decolorization and Detoxification of Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Coagulation Processes. Dye. Pigment. 2005, 64, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Najafi, F.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Malachite Green Dye Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions on Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Kim, E.J.; Yang, J.-W.; Shin, H.-J. Removal of Malachite Green by Adsorption and Precipitation Using Aminopropyl Functionalized Magnesium Phyllosilicate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Sharif, M.; Iqbal, M. Application Potential of Grapefruit Peel as Dye Sorbent: Kinetics, Equilibrium and Mechanism of Crystal Violet Adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdy, A.; Fouad, Y.O.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Konsowa, A.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4/Kaolin Magnetic Nanocomposite and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I. Reactive Dye Removal in Dye/Salt Mixtures by Nanofiltration Membranes Containing Vinylsulphone Dyes: Effects of Feed Concentration and Cross Flow Velocity. Desalination 2002, 143, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Choi, S.-P.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Shim, W.-G.; Moon, H. Submerged Microfiltration Membrane Coupled with Alum Coagulation/Powdered Activated Carbon Adsorption for Complete Decolorization of Reactive Dyes. Water Res. 2006, 40, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Enhanced and Suppressed Effects of Ionic Liquid on the Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2. Adsorption 2013, 19, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemlikchi, W.; Drouiche, N.; Belaicha, N.; Oubagha, N.; Baaziz, B.; Mecherri, M.O. Kinetic Study of the Adsorption of Textile Dyes on Synthetic Hydroxyapatite in Aqueous Solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 32, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Abdou, A.E.H.; Shehata, A.K.; Header, H.M.A.; Hamed, E.A. Sustainable Super Fast Adsorptive Removal of Congo Red Dye from Water by a Novel Technique Based on Microwave-Enforced Sorption Process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 57, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkait, M.; Maiti, A.; DasGupta, S.; De, S. Removal of congo red using activated carbon and its regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi Khaniabadi, Y.; Mohammadi, M.; Shegerd, M.; Sadeghi, S.; Basiri, H. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions by a low-cost adsorbent: Activated carbon prepared from Aloe vera leaves shell. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2016, 4, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S.; Sivaramakrishna, L.; Reddy, A.V. The use of an agricultural waste material, Jujuba seeds for the removal of anionic dye (Congo red) from aqueous medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 203–204, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wanyonyi, W.C.; Onyari, J.M.; Shiundu, P.M. Adsorption of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Roots of Eichhornia Crassipes: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaniabadi, Y.O.; Basiri, H.; Nourmoradi, H.; Mohammadi, M.J.; Yari, A.R.; Sadeghi, S.; Amrane, A. Adsorption of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Montmorillonite as a Low-Cost Adsorbent. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneip, M.; Danisch, P. Water Repellent Treatment of Leather and Skins with Polysiloxanes Functionalized with Carboxyl Groups in a Comb-like Manner. United States patent US 5,702,490, 6 February 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Eckert, G.; Bergold, W. Hydrophobization of Leather, Pelts and Leather Substitute Materials with Carboxyl-Containing Polysiloxanes. United States patent US 4,931,062, 10 January 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yan, J.; Yan, W. Aqueous Polyurethane Leather Finishing and Preparation Method. CN 102,796,447, 12 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Li, G.L.; Liu, R.Q.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, X.D. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Dispersible and Spherical Nano-SiO2@Copolymer Nanocomposite in Leather Tanning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Ferdov, S.; Mansilla, C.; Marques, S.M.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Pastrana, L.M.; Henriques, M.; Gaidau, C.; Ferreira, P.; Carvalho, S. Development of Antimicrobial Leather Modified with Ag–TiO2 Nanoparticles for Footwear Industry. Sci. Technol. Mater. 2018, 30, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Luo, X.; Yan, T.; Lin, X. Recovery of Cesium from Saline Lake Brine with Potassium Cobalt Hexacyanoferrate-Modified Chrome-Tanned Leather Scrap Adsorbent. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lladó, J.; Gil, R.R.; Lao-Luque, C.; Solé-Sardans, M.; Fuente, E.; Ruiz, B. Highly Microporous Activated Carbons Derived from Biocollagenic Wastes of the Leather Industry as Adsorbents of Aromatic Organic Pollutants in Water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Daniels-Race, T. Electrophoretic Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes on 3-Amino-Propyl-Triethoxysilane (APTES) Surface Functionalized Silicon Substrates. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syga, Ł.; Spakman, D.; Punter, C.; Poolman, B. Method for immobilization of living and synthetic cells for high-resolution imaging and single-particle tracking. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, R.; Song, Q.; Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; Gu, X. Hydrophobic modification of SAPO-34 membranes for improvement of stability under wet condition. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingan, H.; Mengjun, J.; Yanyan, Z.; Ling, H. A silica/PVA adhesive hybrid material with high transparency, thermostability and mechanical strength. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osma, J.F.; Saravia, V.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; Couto, S.R. Sunflower Seed Shells: A Novel and Effective Low-Cost Adsorbent for the Removal of the Diazo Dye Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagusiak, A.; Pańczyk, T. Interaction of Congo Red, Evans Blue and Titan Yellow with Doxorubicin in Aqueous Solutions. A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 279, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.; Morris, J. Advances in Water Pollution Research: Removal of Biologically Resistant Pollutant from Waste Water by Adsorption. In International Conference on Water Pollution Symposium; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1962; pp. 231–266. [Google Scholar]













| L1 | L2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Isotherm Parameters | Values | Isotherm Parameters | Values |
| Qm(mg g-1) | 3831 | Qm (mg g-1) | 746.27 |
| KL (L mg-1) | 0.001659 | KL(L mg-1) | 0.000080 |
| RL | 0.9095 | RL | 0.9952 |
| R2 | 0.99 | R2 | 0.99 |
| L1 | L2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Isotherm Parameters | Values | Isotherm Parameters | Values |
| n | 1.015 | n | 1.003 |
| Kf | 0.30 | Kf | 0.30 |
| R2 | 0.99 | R2 | 0.99 |
| Parameters | L1 | L2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH3 | pH4 | pH5 | pH6 | pH7 | pH8 | pH3 | pH4 | pH5 | pH6 | pH7 | pH8 | |
| qecalculated | 3.18 | 3.30 | 2.44 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 3.04 | 3.32 | 2.38 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.06 |
| K1calculated | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| qeexperimental | 0.17 | 0.48 | 1.49 | 3.31 | 3.23 | 3.48 | 0.11 | 0.54 | 1.57 | 3.11 | 3.25 | 3.56 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.68 | 0.94 | 0.76 | 0.19 |
| Parameters | L1 | L2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH3 | pH4 | pH5 | pH6 | pH7 | pH8 | pH3 | pH4 | pH5 | pH6 | pH7 | pH8 | |
| qecalculated | 0.18 | 0.48 | 1.54 | 3.32 | 3.24 | 3.49 | 0.11 | 0.55 | 1.62 | 3.12 | 3.26 | 3.56 |
| K2 calculated | 0.00 | 0.12 | 1.18 | 5.50 | 5.24 | 6.07 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 2.63 | 1.70 | 12.93 | 19.70 |
| qeexperimental | 0.17 | 0.48 | 1.49 | 3.31 | 3.23 | 3.48 | 0.11 | 0.54 | 1.57 | 3.11 | 3.25 | 3.56 |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Parameters | L1 | L2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH3 | pH4 | pH5 | pH6 | pH7 | pH8 | pH3 | pH4 | pH5 | pH6 | pH7 | pH8 | |
| kp1 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.002 | −0.014 | −0.008 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| kp2 | 0.464 | 0.145 | 0.052 | 0.003 | 0.030 | 0.002 | 0.517 | 0.080 | 0.046 | 0.013 | −0.001 | 0.002 |
| kp3 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.001 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clavijo, C.; Osma, J.F. Functionalized Leather: A Novel and Effective Hazardous Solid Waste Adsorbent for the Removal of the Diazo Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Solution. Water 2019, 11, 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091906
Clavijo C, Osma JF. Functionalized Leather: A Novel and Effective Hazardous Solid Waste Adsorbent for the Removal of the Diazo Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Solution. Water. 2019; 11(9):1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091906
Chicago/Turabian StyleClavijo, Camila, and Johann F. Osma. 2019. "Functionalized Leather: A Novel and Effective Hazardous Solid Waste Adsorbent for the Removal of the Diazo Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Solution" Water 11, no. 9: 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091906
APA StyleClavijo, C., & Osma, J. F. (2019). Functionalized Leather: A Novel and Effective Hazardous Solid Waste Adsorbent for the Removal of the Diazo Dye Congo Red from Aqueous Solution. Water, 11(9), 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11091906






