Abstract
Rainfall simulators are useful tools for controlling the main variables that govern natural rainfall. In this study, a new drop-forming rainfall simulator, which consists of pressure-compensating dripper grids above a horizontal mesh that breaks and distributes raindrops, was developed to be applied in wash-off experiments in a large-scale physical model of 36 m2. The mesh typology and size, and its distance to drippers, were established through a calibration where rain uniformity and distributions of raindrop sizes and velocities were compared with local natural rainfall. Finally, the rain properties of the final solution were measured for the three rain intensities that the rainfall simulator is able to generate (30, 50 and 80 mm/h), obtaining almost uniform rainfalls with uniformity coefficients of 81%, 89% and 91%, respectively. This, together with the very suitable raindrop size distribution obtained, and the raindrop velocities of around 87.5% of the terminal velocity for the mean raindrop diameter, makes the proposed solution optimal for wash-off studies, where rain properties are key in the detachment of particles. In addition, the flexibility seen in controlling rain characteristics increases the value of the proposed design in that it is adaptable to a wide range of studies.
1. Introduction
Urban areas of cities are expected to continue to grow significantly over the forthcoming decades [1]. The sustainable development of cities, respect for the surrounding environment, and ensuring healthy living conditions are thus all significant challenges for current science and engineering. Regarding urban stormwater, increases in the percentage of impervious areas in urbanization processes leads not only to higher runoff volumes and flow discharges, but also to an increase in the total load and peak concentration of mobilized pollutants. These contaminants, such as heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and microplastics, accumulate in urban catchments during dry weather and can be washed off during rain events and transported by stormwater runoff into drainage systems, and eventually into aquatic media [2,3,4]. Since the impact of these pollutants in receiving environments represents one of the most urgent environmental issues in urban areas [5,6], a thorough understanding of processes involved in wash-off and sediment transport is essential in estimating pollution loads and concentrations toward designing treatment and management measures that promote the sustainable growth of towns and cities.
Pollutant wash-off is a complex phenomenon which is influenced by highly variable processes such as rainfall and sediment build-up [7], limiting the prediction accuracy of current wash-off models [8,9]. In this context, rainfall simulators offer a means of controlling the main variables that govern natural rainfall, and are often used in laboratory and field studies [10,11,12,13] to increase the understanding of pollutant wash-off processes in urban catchments. The use of rainfall simulators with suitable rain uniformity and with drop size and velocity distributions similar to real rain is crucial for the reliability and transferability of experimental results. However, the difficulties in replicating natural rain lead to a wide range of designs, these falling into two main groups in terms of the way in which the raindrops are produced: (i) pressurized nozzle simulators, and (ii) drop-forming simulators, with no definitive solution having been identified [14,15]. Both typologies have been used not only in wash-off studies but also in soil erosion studies, and both present benefits and drawbacks that must be considered during experimental design, in light of the objectives of a particular study. Moreover, the variety of designs makes the measurement of rain properties such as uniformity, intensity, and raindrop size and velocity distribution essential to ensure the comparability of experimental results.
Pressurized nozzle simulators are commonly preferred for studies with simulated rainfall due to their simple design and installation. Generated raindrops emerge from nozzles with a considerable initial velocity, so this typology produces satisfactory raindrop velocity distributions at lower fall heights, reaching terminal drop velocities as in natural rain. A disadvantage here is that nozzles require a relatively large orifice to generate a mean raindrop similar to real rain, and this results in a high intensity storm if the nozzle sprays continuously [16]. An oscillating bar [17,18,19,20] or a solenoid-controlled simulator [21] can be used to pause the spray and hence reduce the rainfall intensity. However, Armstrong and Quinton [22] examined the effect of intermittent rain in runoff sediment concentrations, concluding that results can be affected. When the spray stops, water depths decrease over the street surface and the sediments are more exposed to the next period of high intensity rain, causing a greater detachment of soil particles.
These nozzle-based designs can generate rainfalls with suitable spatial uniformity in small-scale catchments, which is the case in most studies carried out to date [5,11,12,13,23] covering areas smaller than 10 m2. However, the use of several nozzles to cover larger areas makes it difficult to maintain spatial uniformity [24]. In addition, as seen in Naves et al. [25] where four nozzles were used to simulate rain in a 36 m2 physical model, non-uniform rain significantly affects the mobilization of sediment particles through these large-scale catchments, thus compromising the reliability of wash-off results. As an alternative, drop-forming simulators have been seen to result in a better control of physical rain parameters than nozzle simulators [26,27,28,29]. The spatial uniformity of simulated rain benefits from the use of these kinds of simulators, because of the increase in the number of points where drops are generated, but the complex assembly of existing drop-forming simulators, which use needles to generate raindrops, have also limited their application to small-scale studies of a few square meters.
This study focuses on the development of a new drop-forming rainfall simulator to study wash-off and sediment transport processes in the 36 m2 urban drainage physical model presented in Naves et al. [25]. The proposed rainfall simulator uses pressure-compensating irrigation drippers to simplify the generation of raindrops, being capable of covering large areas and maintaining the appropriate spatial uniformity associated with drop-forming simulators. In the remainder of the article, the calibration of this rainfall simulator will be presented, looking at spatial uniformities and size distributions of the raindrops generated. Then, the rain properties of the definitive solution are characterized in detail and compared with local rain measurements.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rainfall Simulator Description
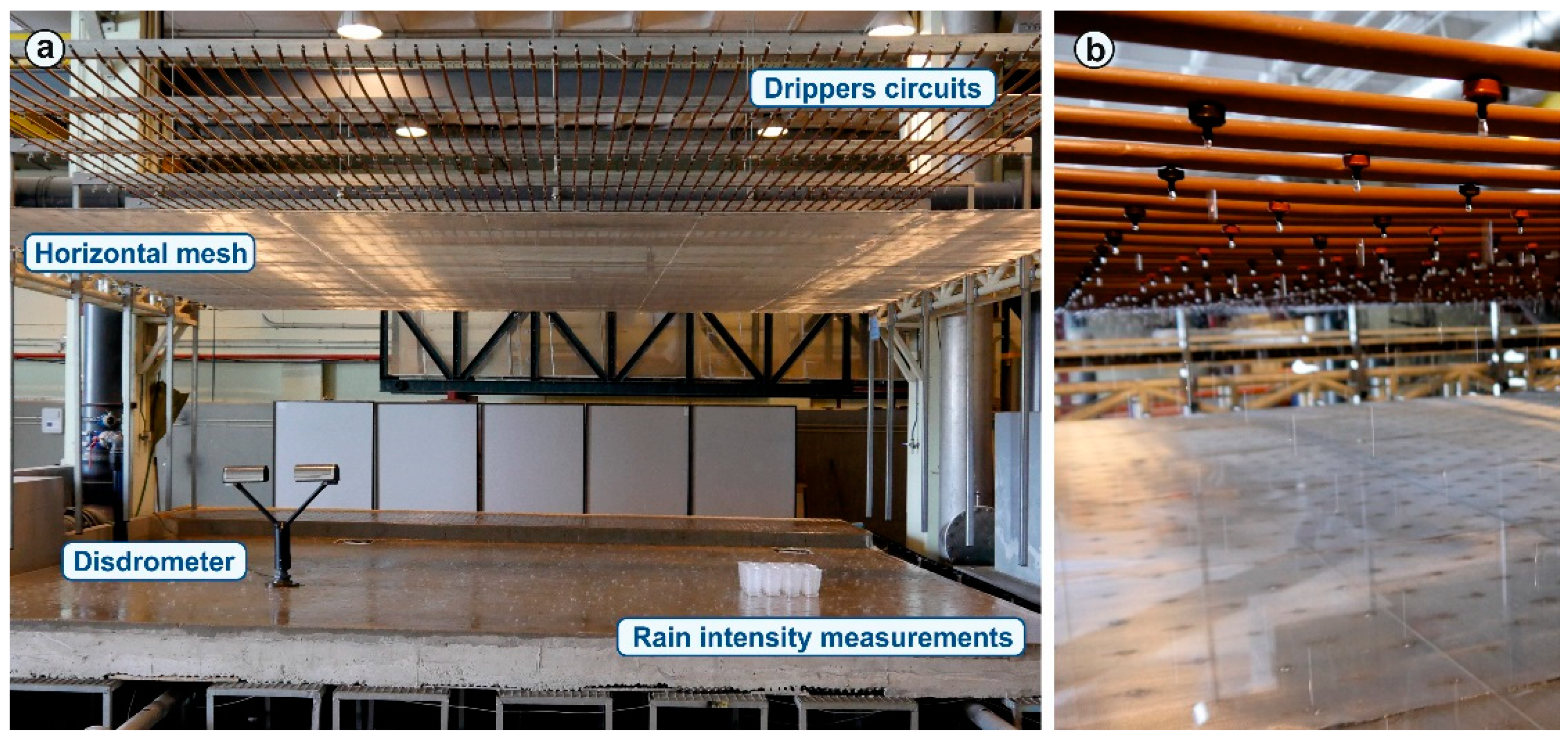
The rainfall simulator that has been developed is located in the Hydraulic Laboratory of the Centre of Technological Innovation in Construction and Civil Engineering (CITEEC) at the University of A Coruña. It consist of two hose circuits placed above an urban drainage physical model with an approximate surface of 36 m2. PCJ-CNL drippers (Netafim, Tel Aviv, Israel) of 1.2 and 2 L/h are inserted in each circuit forming two grids of drippers with longitudinal and transversal separation of 0.20 m. Using this layout, the density of drippers in each circuit is 25 per m2. Therefore, the simulator is able to generate rain intensities of 30 mm/h, 50 mm/h and, if both circuits are working at the same time, 80 mm/h. Pressure-compensating and anti-drain drippers have been chosen to avoid changes in flow rates due to pressure variations and to avoid water losses once the pressure is decreased below a certain value. The generated raindrops always fall on the same point of the model surface and have an approximate diameter of 4 mm, which is very high compared to natural rain. To fix this problem, a horizontal mesh is installed bellow the dripper circuits in order to break and distribute these uniform drops, improving rain uniformity and achieving heterogeneous drop size distribution. Figure 1 shows a general view of the simulator in its final configuration, and a detail of the drippers inserted in the circuits.

Figure 1.
(a) General image of the rainfall simulator in its final configuration above the urban drainage physical model. Disdrometer and vessels for measuring rain intensity are also shown. (b) Detail of both types of drippers inserted in the circuits above the horizontal mesh.
2.2. Calibration Procedure
Rain intensity, spatial uniformity, and the kinetic energy of raindrops, which depends on their size and velocity, are the key rain variables that affect the wash-off process in the detachment of particles. Therefore, these variables were considered during the calibration process in a comparison with natural rain. First, as seen in Naves et al. [25], non-uniform simulated rain can modify surface sediment transport and lead to unreliable results in wash-off experiments. Therefore, the main objective during the calibration of this new rainfall simulator was to achieve a high rain spatial uniformity across the entire physical model surface, as occurs with natural rain [15]. In addition, a realistic raindrop size distribution was also sought during the calibration process. Finally, the rainfall generator was installed and fixed as high as possible, approximately 2.6 m from the model surface, to allow larger raindrops to achieve their terminal velocity.
The calibration focused on establishing the optimal typology and position of the horizontal mesh that breaks and distributes generated raindrops. Rain intensity, spatial uniformity, and mean drop size and velocity were analyzed for nine different combinations of mesh size, material, and distance to drippers in order to simulate rainfall with a high spatial uniformity and realistic raindrop size distribution. In these tests, rain intensity was set firstly at the lowest rain intensity that it is possible to generate (30 mm/h), since this is expected to be the most demanding case in terms of rain uniformity. Then, configurations with better performance were also analyzed for the rain intensities 50 and 80 mm/h. The typologies and ranges tested during the calibration process are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Typologies and ranges considered during rainfall simulator calibration.
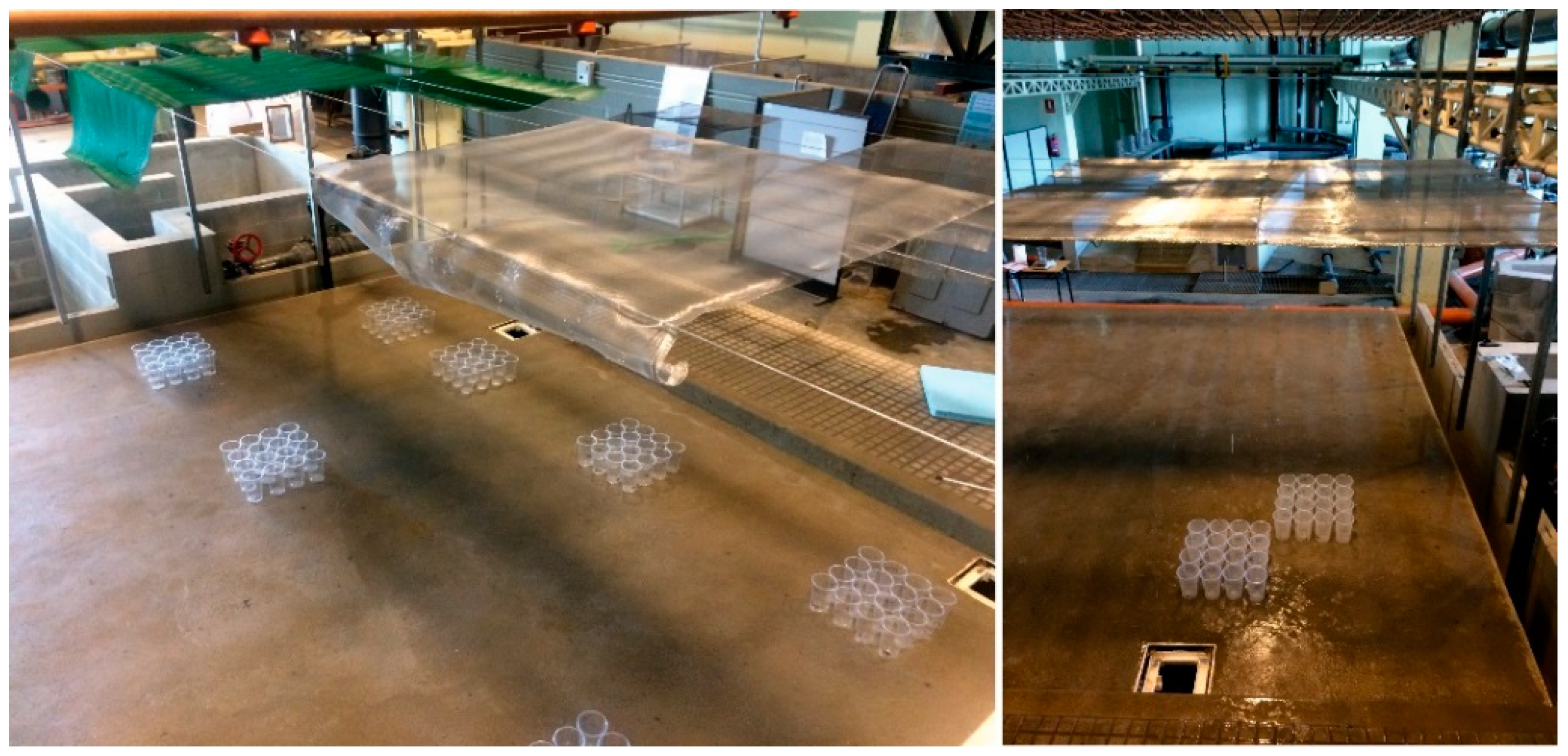
Rain intensity and uniformity were measured in each case using 16 vessels of 0.1 m in diameter as rain gauges, disposed together in a 4 × 4 grid covering a total surface area of 0.16 m2 (Figure 2). Rain intensity was obtained from the water mass collected by each vessel during a 15 min period of rain, and the result was then used to determine the Christiansen’s uniformity coefficients (UC) [30] as:
where is the rain intensity in each vessel, their average, and the total number of vessels.

Figure 2.
Vessels disposed over the model surface to measure rain intensity and uniformity for different mesh types and distances to drippers during calibration.
A laser Parsivel2 disdrometer (OTT HydroMet, Kempten, Germany) was used during calibration (Figure 1a) to measure the mean diameter and velocity of raindrops. This equipment provides the number of raindrops that pass through a horizontal laser surface of approximately 54 cm2 and classify them into 32 diameters and 32 velocity non-uniform ranges measuring the magnitude and the duration of signal attenuations [31]. In view of the wide variability of natural rain found in the literature [32,33,34,35,36], with mean raindrop diameters from 0.63 to 2.49 mm, raindrop size and velocity distributions of local natural rain were also measured as a means of establishing reference values for the comparison of the different configurations tested during calibration. For this, the disdrometer was installed in February 2017 on the roof of the laboratory of CITEEC (A Coruña, Spain) with a sample frequency of 10 s.
2.3. Rain Properties of Calibrated Rainfall Simulator
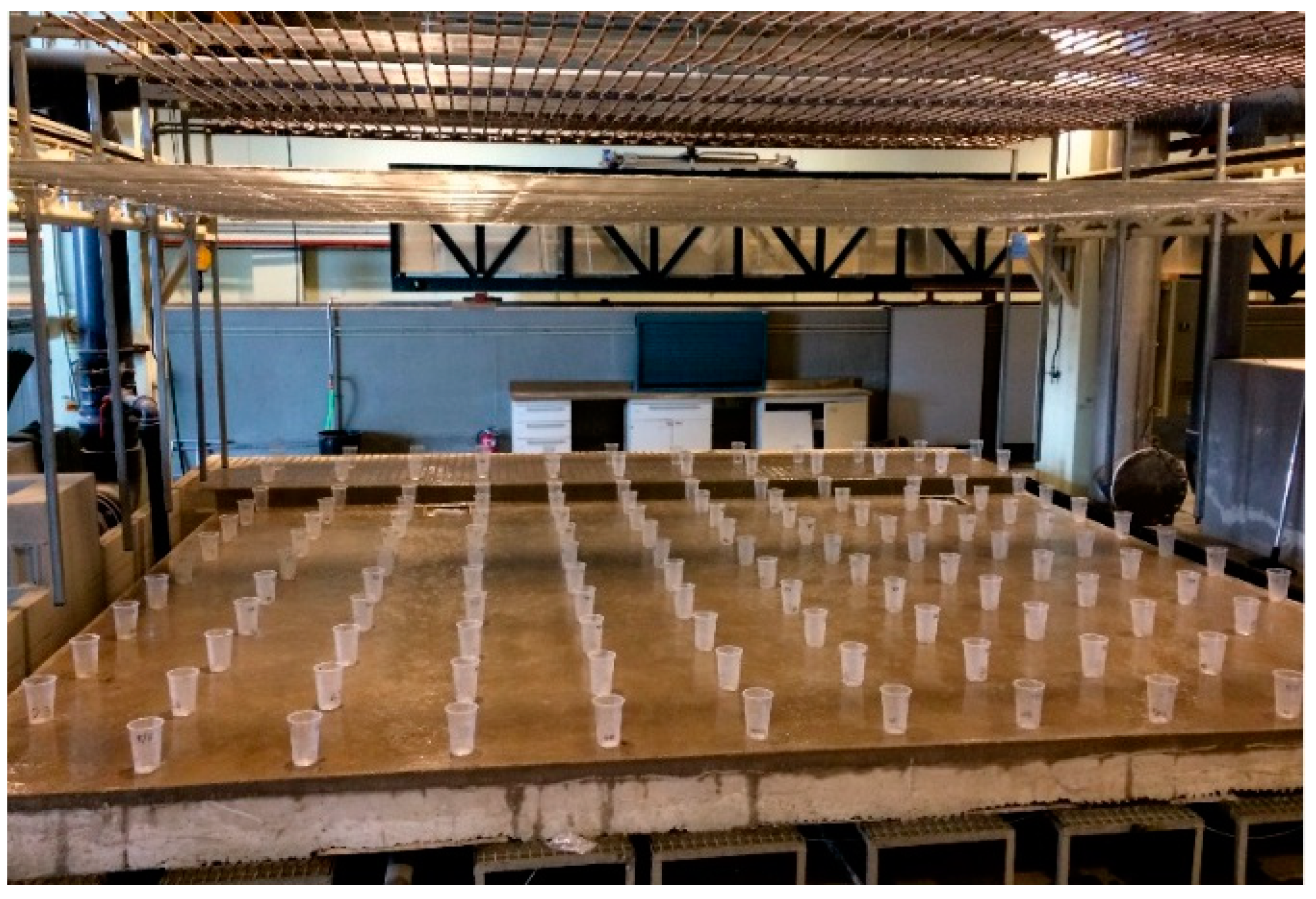
Once the simulator had been calibrated, rain intensity, spatial uniformity, and raindrop size and velocity distribution were measured for the three rain intensities that it is able to generate. In a way similar to the calibration methodology, rain intensity and uniformity were obtained from the water collected in 144 vessels placed over the full physical model surface in a 0.5 m × 0.5 m grid for a 5 min period of rain (Figure 3). Finally, disdrometer measurements were used to register 10 s measurements of raindrop size and velocity distributions over 2 min.

Figure 3.
Vessels disposed over the entire model surface in a 0.5 m × 0.5 m grid to measure rain intensity and uniformity.
3. Results
3.1. Local Natural Rain Properties Recorded
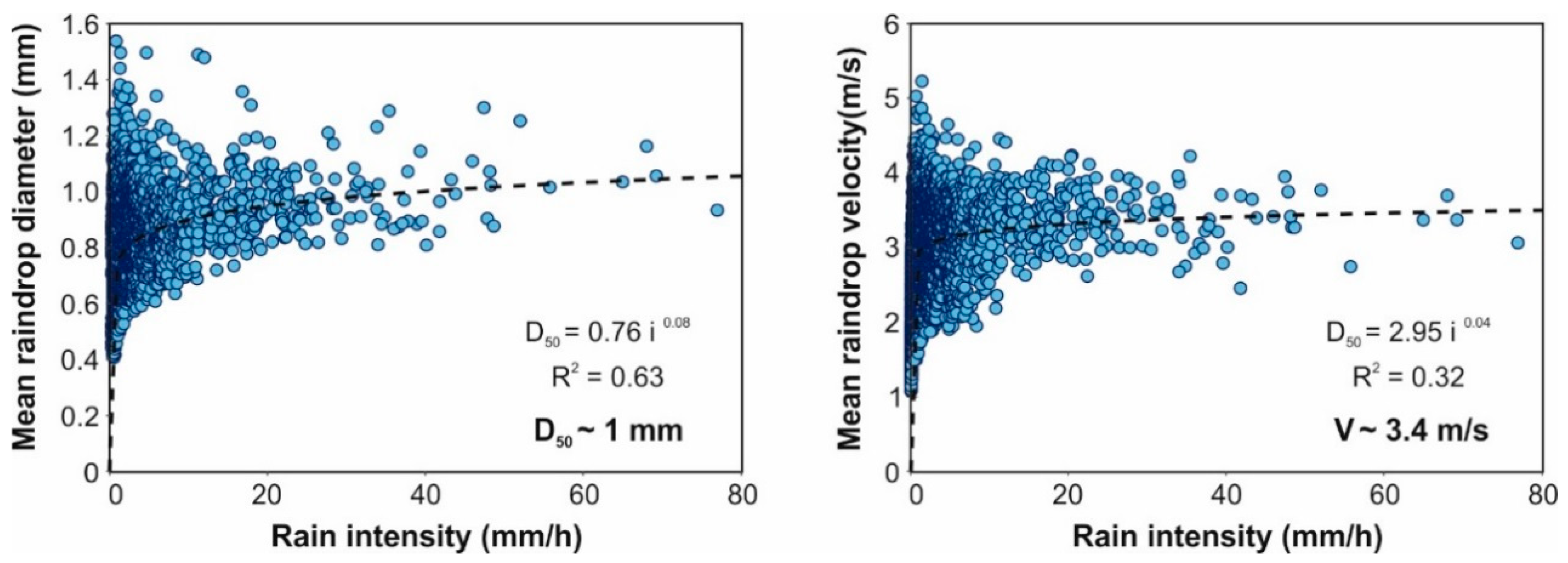
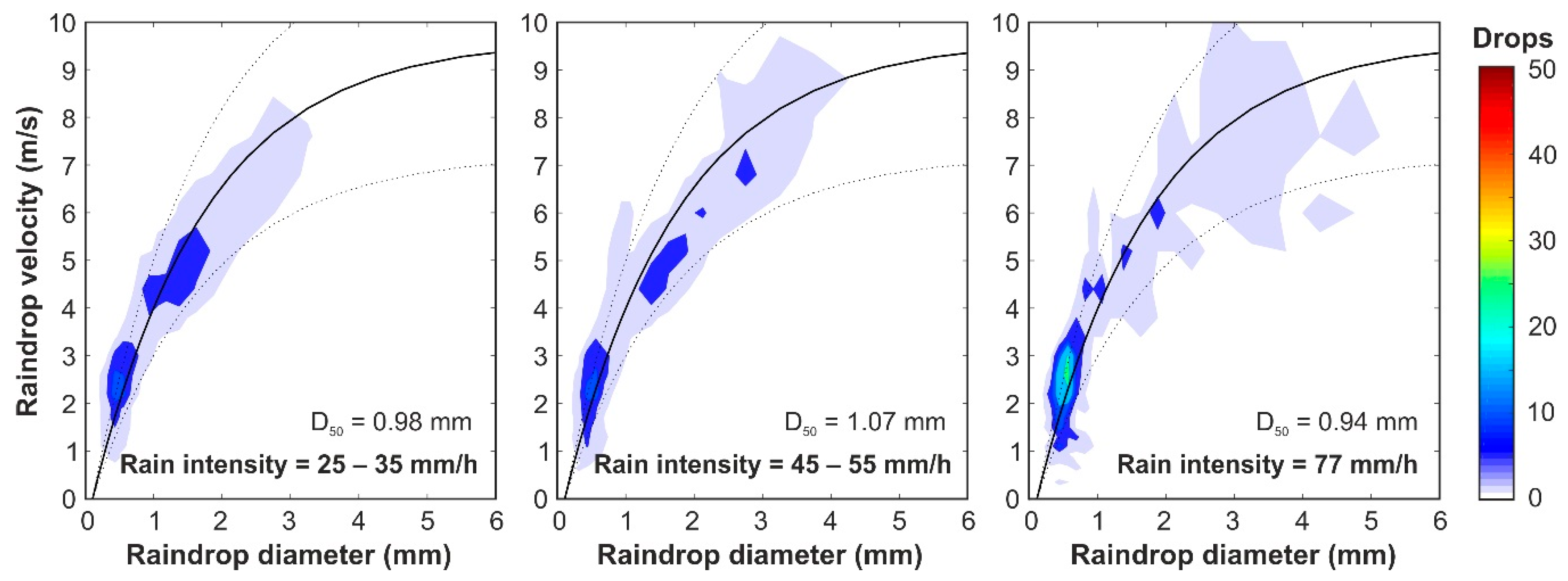
Firstly, local rain properties registered by the disdrometer are presented here to be used as reference values to compare the different configurations tested during calibration. Plots in Figure 4 show the mean raindrop diameters and velocities measured according to their rain intensities. The results show that mean raindrop diameters registered were between 0.75 and 1.3 mm in the case of rain intensities over 20 mm/h, which are within the ranges found in the literature [32,33,34,35,36]. In addition, mean raindrop velocities match the corresponding terminal velocities of the measured raindrop diameters. This can also be observed in the raindrop size and velocity distributions shown in Figure 5, which shows the mean of 33 disdrometer measurements of natural rainfall with intensities ranging from 25 to 35 mm/h, 8 measurements between 45 and 55 mm/h, and one measurement of 77 mm/h, respectively. These plots represent the mean number of raindrops registered in 10 s, classified into sizes and velocities and compared with the experimental relation between diameter and terminal velocity [37]. It can also be noted that, as reported in Tokay et al. [38], the maximum drop diameter rarely exceeded 4 mm, even in heavy rainfall with an increased presence of large drops. In addition, very few raindrops larger than 3 mm were measured in the three cases presented. These characteristics, considering a mean raindrop diameter of 1 mm and a mean velocity of 3.4 m/s, are established as objective values for the rainfall simulator under study here.
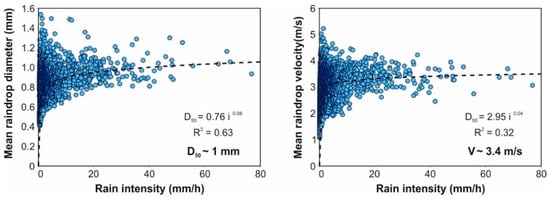
Figure 4.
Relation of raindrop mean diameter and velocity with respect to the rain intensity measured by the disdrometer.
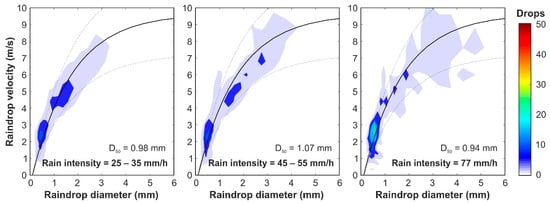
Figure 5.
Raindrop size and velocity distribution of natural rainfalls with intensities ranging from 25 to 35 mm/h (33 measurements), 45 to 55 mm/h (8 measurements) and a measurement of 77 mm/h, respectively. The mean of the raindrops registered by the disdrometer classified in sizes and velocities is compared with experimental relation between diameter and terminal velocity [37], which is represented by the solid curve and its 25% of variation by the dotted curves.
3.2. Calibration Results
In this section, the rain properties obtained for the different configurations tested during the calibration process are shown. Table 2 includes mean rain intensities, uniformity coefficients, mean raindrop diameters, and mean velocities measured for the different configurations tested. In the first set of configurations using plastic mesh, it can be seen that larger mesh sizes of 4.5 mm (tests #1 and #2) produced uniformity coefficients of around 65% and mean raindrop sizes of around 0.85 mm, which is slightly lower than that observed in natural rain, for mesh-drippers distances of 0.45 and 0.70 m. In this case, the mesh size is similar to the diameter of the raindrops and a small distribution area is observed when raindrops pass through the mesh and break, decreasing uniformity.

Table 2.
Configurations and results of the tests performed during the rainfall simulator calibration.
If the mesh size is reduced (tests #3–#5 with 2 and 1 mm mesh sizes), mean raindrop sizes decrease but raindrops are distributed in a larger area by the mesh and the uniformity coefficient is significantly increased to over 83%. In these tests, it can also be observed that increasing dripper-mesh distance improves rain uniformity, but also leads to smaller diameters and lower velocities of raindrops. Summarizing, the results obtained from tests with plastic meshes (tests #1–#5) showed that it is necessary to decrease mesh-size and increase dripper-mesh distance in order to improve rainfall uniformity, but maintaining an equilibrium without reducing mean raindrop sizes and velocities. Since it was observed that measured mean rain intensities decreases in the case of more suitable solutions for plastic meshes (tests #3–#5), perhaps due to the fact that the coarse mesh plastic wires retain water easily, metallic meshes were used in the following tests to avoid this issue.
In tests #6–#8, a 2 mm metallic mesh was used to assess the influence of dripper–mesh distance in the results with values of 0.45, 0.60 and 0.70 m, respectively. These tests illustrated the importance of ensuring that there is enough distance between the mesh and the dripper grids to allow raindrops to reach a higher velocity before the impact against the mesh, achieving a larger distribution area of raindrops and improving rain uniformity above 85%. In view of the solid performance of tests in which the mesh was placed 0.60 and 0.70 m from the drippers, and also the simpler installation of the second option, the distance of 0.70 m was selected to compare the 2 mm metallic mesh with a 3 mm mesh for the three intensities that the simulator is able to generate (tests #9–#13). The possibility of increasing mean raindrop size to the reference value was thus assessed, achieving a slightly better behavior for the 3 mm mesh in terms of rain uniformity and mean drop size. Greater mesh sizes were not considered because, as seen in tests #1 and #2, uniformity is significantly reduced for mesh sizes over 4 mm. Therefore, the 3 mm metallic mesh installed 0.70 m below the drippers was selected as the optimal solution.
3.3. Measured Rain Properties of the Developed Rainfall Simulator
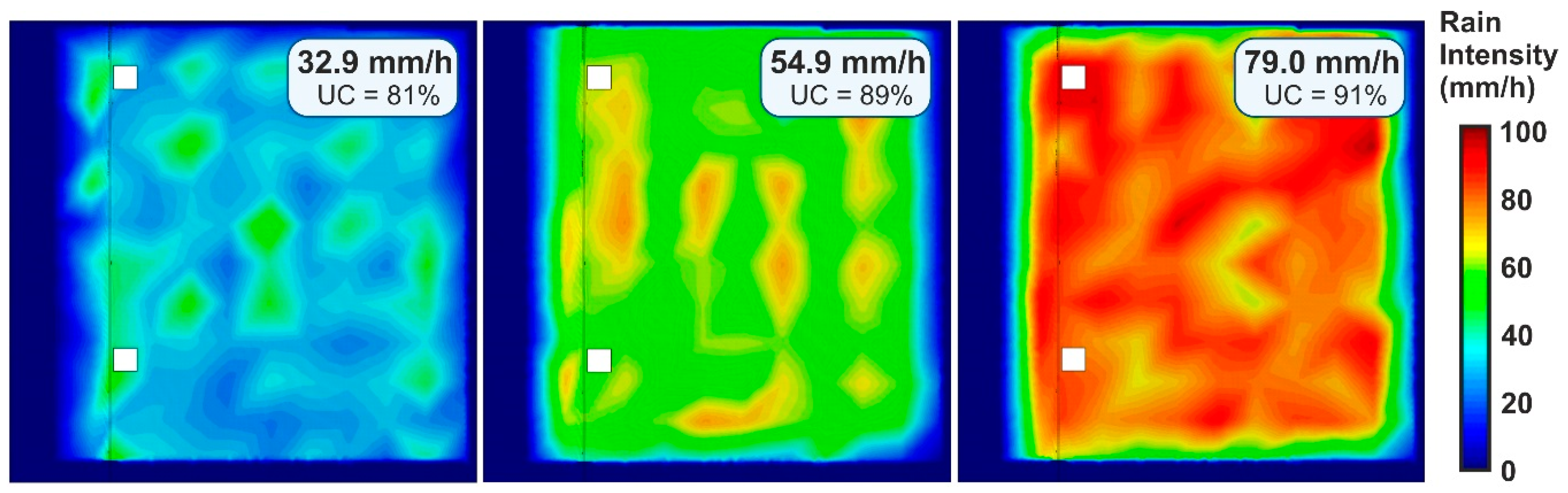
Rain intensity, uniformity, and raindrop size and velocity distributions were measured with the configuration resulting from the calibration, and for the three rain intensities that it was possible to generate. Figure 6 shows rain intensity maps and the uniformity coefficients, with values over 81%, which means almost uniform rain and a very significant improvement in uniformity compared to most medium- and large-scale rainfall simulators in the literature.
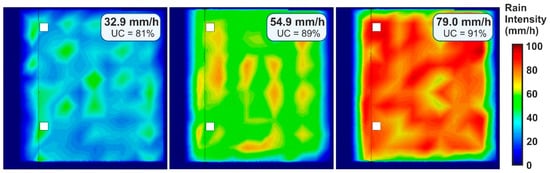
Figure 6.
Rain intensity map of the physical model surface, which has an approximate area of 36 m2, for the three intensities that the rainfall simulator is able to generate. Plots include the mean rainfall intensity measured and the Christiansen’s uniformity coefficient (UC) resulted.
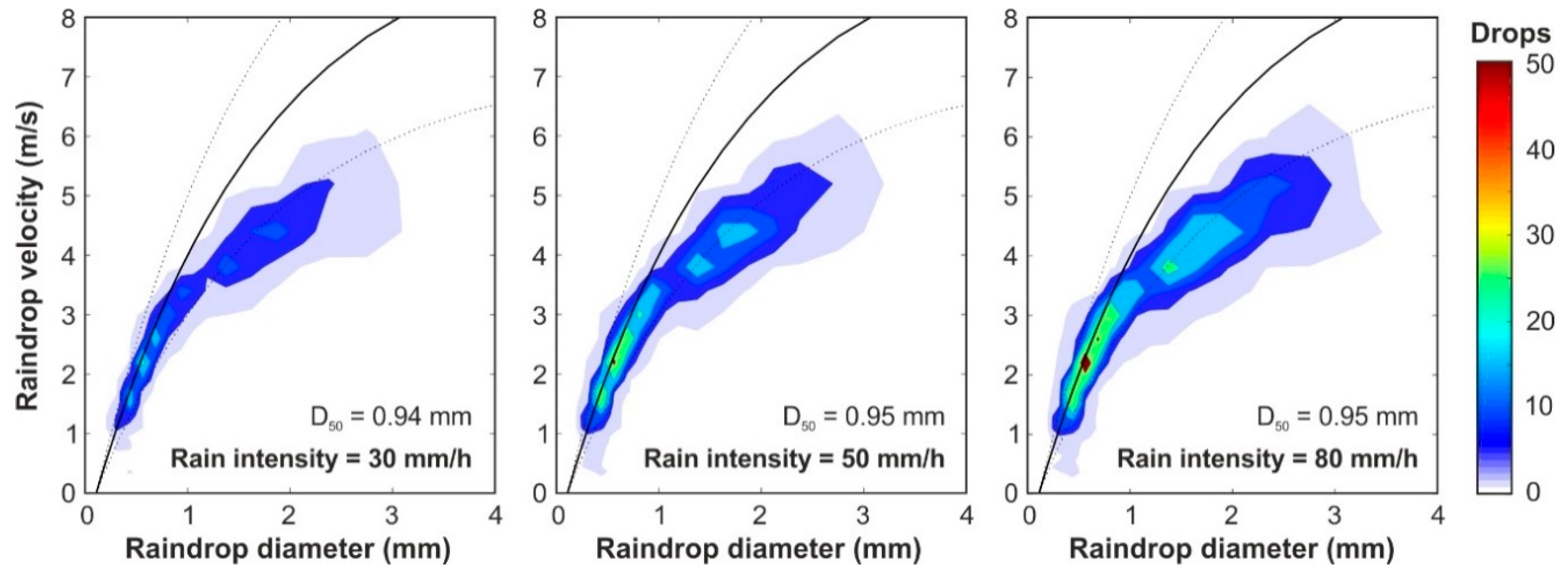
The mean number of raindrops detected by the disdrometer in 10 s measurements over 2 min, classified in sizes and velocities for the three rain intensities, are presented in Figure 7. The mean raindrop sizes obtained over 0.94 mm and the heterogeneous distributions of sizes up to 3 mm are very close to those established as the objective from natural rain measurements with a mean raindrop size of 1 mm (Figure 5). Regarding velocity distributions, larger raindrops (around 2 mm) develop slightly lower velocities than the corresponding terminal velocity, which are represented by the solid curve in Figure 7, which is in accordance with Gunn and Kinzer [37]. In the following section, a more detailed comparison between simulated and natural rain is made.
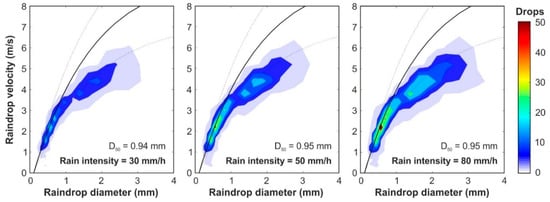
Figure 7.
Number of raindrops, classified according their diameter and velocity, obtained by the disdrometer in an interval of 10 s and for the three rain intensities that it is possible to generate (30, 50 and 80 mm/h respectively). The experimental relation between diameter and terminal velocity [37] was represented by the solid and dots (±25%) curves.
3.4. Simulated and Natural Rain Comparison
The main objective in the development of this simulator was to achieve rain properties as close as possible to local natural rain. In this section, a comparison of rain uniformity and raindrop size and velocity distribution is made between simulated and natural rain measurements. Regarding rain uniformity, the measured intensity maps showed almost uniform simulated rainfalls with UC of 81%, 89% and 91% for rain intensities of 30, 50 and 80 mm/h, respectively, which are very close to the mean value of 96% measured by Kathiravelu et al. [15] for natural rain. This is a notable achievement here, considering the large area covered by the simulator.
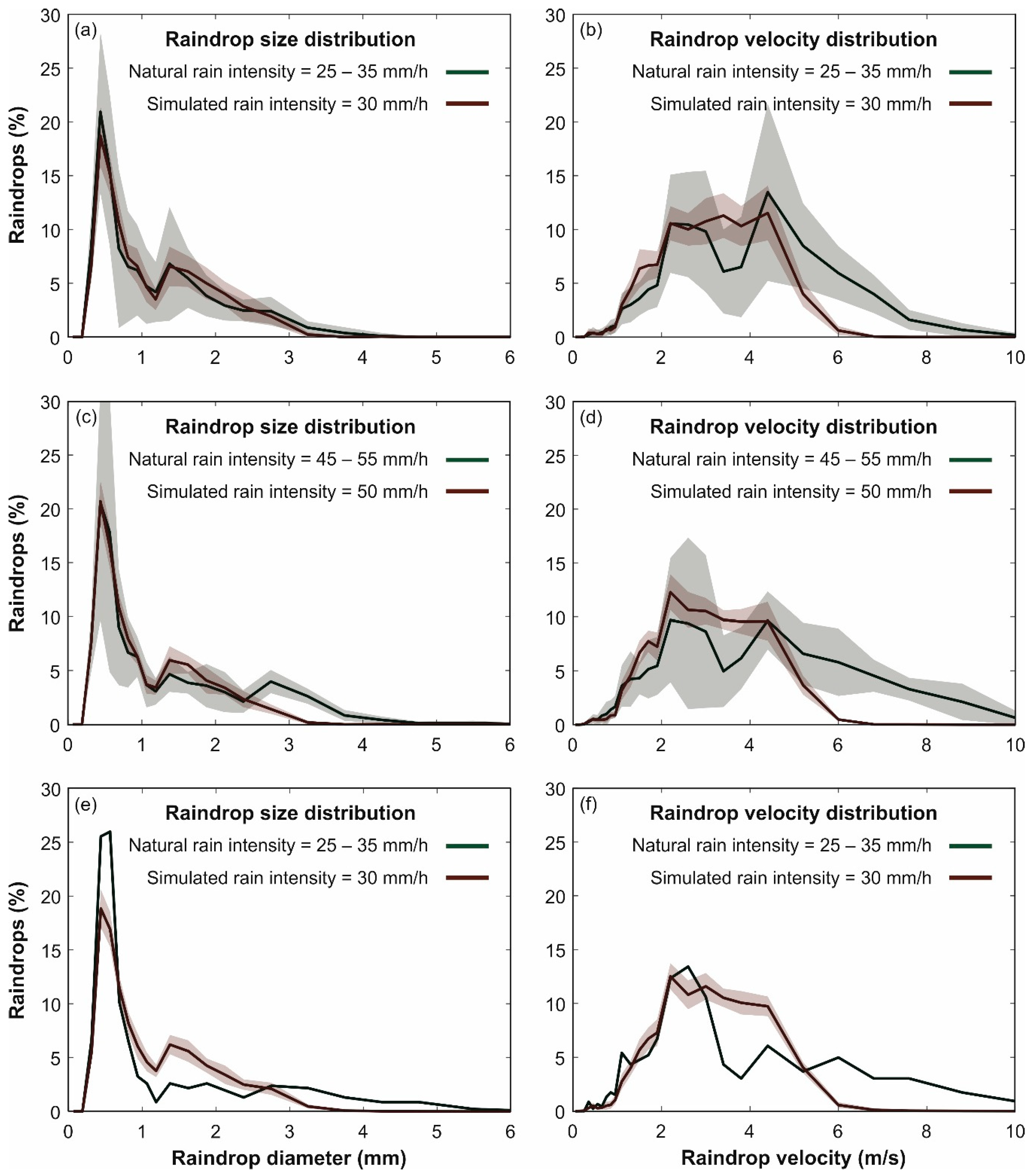
In addition, this uniformity was obtained while maintaining suitable size and velocity distributions of raindrops, which ensures similar behavior to natural rain in the detachment of surface particles by raindrop impacts in wash-off studies. In Figure 8, the raindrop size and velocity distributions measured by disdrometer for each rain intensity that the simulator can generate were compared to those obtained from natural rain in Section 3.1. The lowest simulated rain intensity (30 mm/h) was compared with the mean of 33 disdrometer measurements of natural rain between 25 and 35 mm/h. In the case of the intermediate rain, the comparison was performed using 8 measurement between 45 and 55 mm/h. Finally, the 80 mm/h intensity rain was compared with a unique natural rain measurement of 77 mm/h.
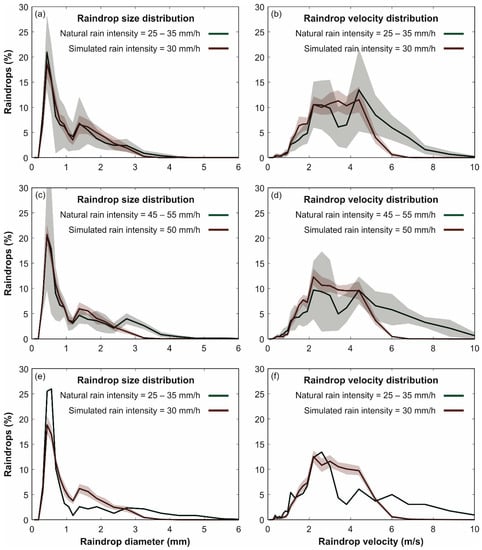
Figure 8.
Comparison of mean distributions of raindrop sizes (plots a, c and e) and velocities (plots b, d and f) between natural (green) and simulated (red) rainfall measurements for the three rain intensities that the rainfall simulator can generate. Contours represent standard deviation of disdrometer measurements both for natural and simulated rain.
Regarding the raindrop size distributions showed in Figure 8, it can be seen that the horizontal mesh selected from the calibration generates a very satisfactory raindrop size distribution, which accurately fitted natural rain measurements for all the intensities. In the case of the highest rain intensity, and in view of the high variability shown by natural rain for the rest of the intensities, the availability of only one natural raindrop size distribution produced a slightly worse fit for the peak of the raindrop diameter distribution. It can also be observed that the distributions of raindrop sizes, both natural and simulated, were similar for all the intensities, the rain intensity thus varying according to the total number of drops. The mean difference observed is the presence, in the intermediate and highest natural rainfall, of a few raindrops with diameters above 3 mm. These sizes cannot be generated by the rainfall simulator here because of the chosen mesh size of 3 mm, but this is only a modest disadvantage considering their low percentage with respect to the total amount of raindrops and the satisfactory uniformity and raindrop size distribution achieved by the mesh.
In Figure 8, natural and simulated raindrop velocity distributions showed a very good fit up to roughly 3 m/s, which correspond with the terminal velocity of particles up to around 1 mm. From this value, while the natural raindrops followed the experimental relation between diameter and terminal velocity proposed in Gunn and Kinzer [37] (Figure 5), simulated raindrops drifted away from the corresponding terminal velocity as their diameter increased (Figure 7) because the drop height was not enough to develop their terminal falling velocities. The percentage of simulated raindrops with higher velocities than 3 m/s are thus accumulated between roughly 3 and 6 m/s and the highest velocities are not developed in the rainfall simulator. However, due to the geometry involved, disdrometer measurements of raindrop size and velocity distributions were registered at 0.6 m from the model surface, and raindrop velocities could still increase before impacting the model surface for sizes that have not yet reached terminal velocity.
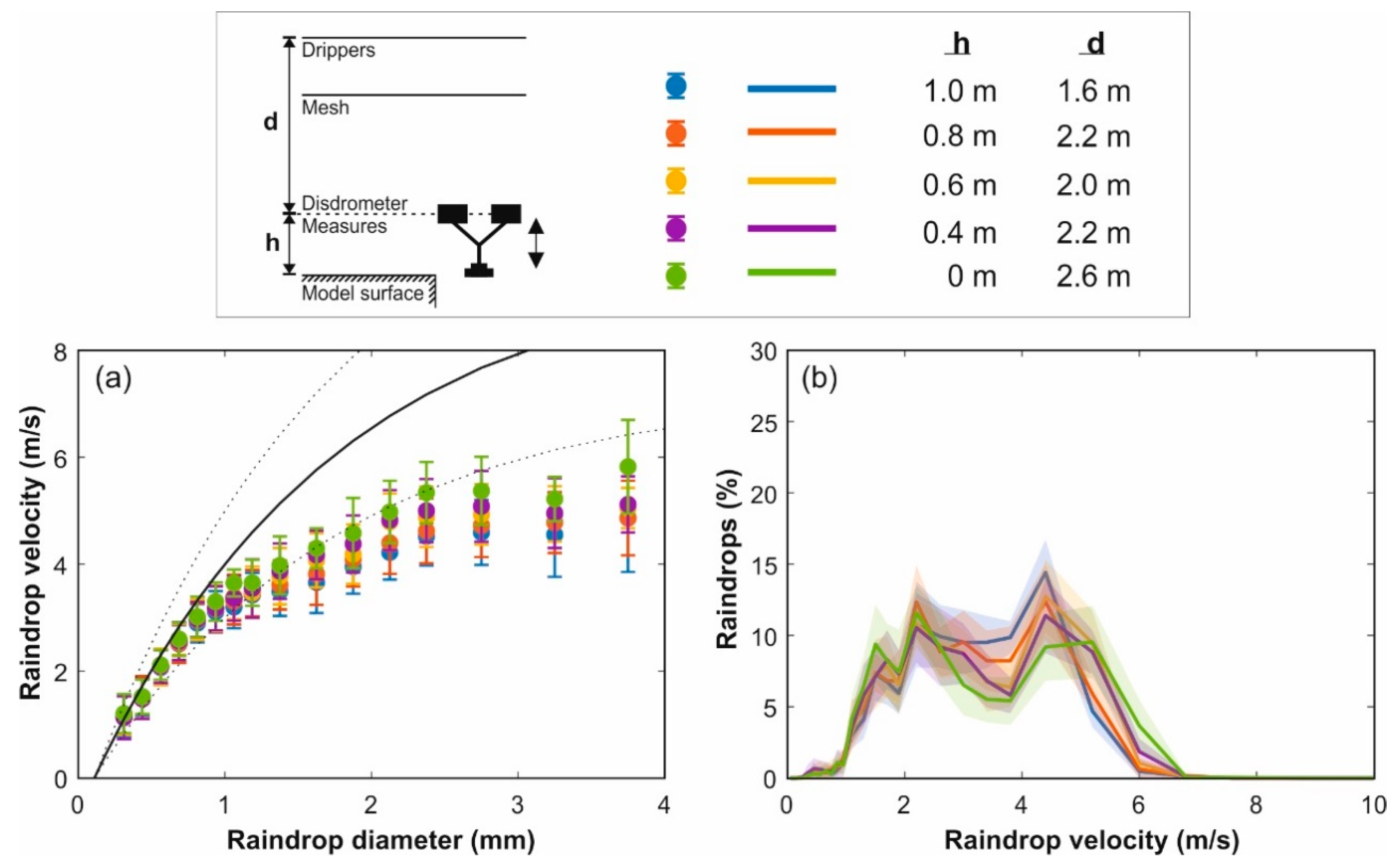
New raindrop size and velocity distributions were thus measured by a disdrometer in an extension of the rainfall simulator outside the physical model surface to estimate the impact velocity at the model surface and to assess the variation of velocities according to drop heights and raindrop sizes. In these tests, the disdrometer measuring point was placed at different heights between 0 and 1 m from the model surface and the size and velocity distributions produced by one dripper were registered for 2 min at 0.1 Hz. The relation between raindrop sizes and velocities, and the velocity distribution of raindrops for each drop height, are included in Figure 9. In these results, the impact velocity of raindrops at the model surface corresponds with the measurements obtained at h = 0 m, with h = 0.6 m being the measurement height of the disdrometer when it was placed on the physical model to register simulated rain properties in Section 3.3.
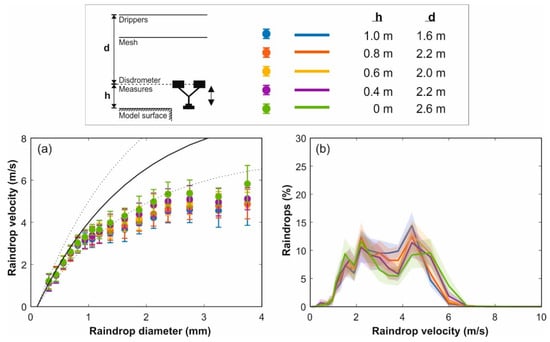
Figure 9.
(a) Mean velocity of simulated raindrops for each diameter class and considering different measuring heights. Velocity errors represent standard deviation. The experimental relation between diameter and terminal velocity [37] was represented by the solid and dots (±25%) curves. (b) Raindrop velocity distributions for different measuring heights. Contours represents standard deviation of disdrometer measurements.
Figure 9a shows the increase of raindrop velocities for greater drop heights depending on the raindrop size. Due to the asymptotic behavior of the phenomenon [39], the velocity of raindrops with diameters smaller than 1.5 mm did not vary when the drop distance was increased since they had almost reached the terminal velocity. In fact, the mean velocity value for the mean raindrop size obtained in Section 3.3 is around the 87.5% of terminal velocity for the measuring heights considered. In the case of larger raindrops, their mean velocity was significantly increased for measurement points closer to the model surface, where velocities of approximately 75% of terminal velocities were achieved for raindrops with diameters up to 3 mm. This effect was also observed in the raindrop velocity distributions included in Figure 9b, where larger percentages of raindrops with high velocities were registered as the measuring point was displaced towards the model surface. The few raindrops with diameters above 3 mm make their mean velocity values negligible in terms of obtaining the potential detachability of particles by rain in wash-off studies. In sum, then, the new rainfall simulator developed in this study is able to generate an almost uniform rain covering a surface of 36 m2, with a raindrop size distribution very similar to local natural rain, and presenting suitable raindrops velocities above 75% of terminal velocities and up to 87.5% in the case of the mean raindrop diameter.
4. Discussion
Rain uniformity and raindrop size and velocity distributions are key in the detachment and transport of surface particles during wash-off processes, so the suitable rain properties obtained here make the presented rainfall simulator a very suitable tool for urban wash-off studies. First, the simulator achieved an impressive uniformity for three different rain intensities, 30, 50 and 80 mm/h, covering a large area of around 36 m2. The use of drippers is simpler than existing drop-forming rainfall simulators [26,27,28,29] and allows the use of this typology in large-scale studies, being characterized by a better control of rain properties. In addition, the studied area can easily be extended while maintaining uniformity if the water supply pressure is inside the operating range of pressure-compensating drippers. This addresses the issue raised in the Introduction relating to the importance of spatial uniformity in the reliability of wash-off results and the difficulties of simulating uniform rain in large areas using several nozzles [24]. In addition, although the simulator does not allow us to generate complex synthetic rainfall events as in a recent study by Nielsen et al. [40], it is feasible to simulate a wide range of constant intensities and keeping suitable uniformities by changing the spatial density of drippers and their flow discharges. This design is thus a suitable alternative for the simulation of lower rain intensities with appropriate raindrop size distributions, which is a clear improvement over nozzle-based simulators that have to resort to intermittent rain [19].
It was also demonstrated that it is possible to generate different raindrop size distributions by changing the mesh size and its distance from drippers in order to adapt simulated rain to the required rain properties. Finally, the weak point of drop-forming rainfall simulators is that they generate drops with a null initial velocity, and that raindrops need to fall a considerable distance to reach their terminal velocity. As reported in Laws [39], 1.17-mm-size raindrops (slightly larger than our mean raindrop diameters) and 2.3-mm-size raindrops (the order of magnitude of our largest ones) require up to 5 and 13 m of fall, respectively, before attaining their terminal velocity completely, heights which are not practicable in a laboratory facility. However, due to the asymptotic behavior of the phenomenon, 90% of terminal velocity can be achieved with considerably less fall heights, of 2 and 4 m, respectively. In the present study, the simulator was installed as high as possible, at 2.6 m from the model surface, obtaining raindrop impact velocities of around 87.5% of their terminal velocities for the mean raindrop diameter, and 75% for raindrops with larger diameters, up to 3 mm. These results are already very satisfactory considering the almost uniform rain and the very suitable raindrop size distributions obtained, but a significant improvement in the velocity of larger raindrops could be achieved through increasing the simulator’s total height. Following the results reported in Laws [39], and considering that the horizontal mesh slightly reduces raindrop velocities, an optimal installation height of roughly 4.5 m can be estimated. From this point, a large increase in height would be required to achieve only a slight increase in raindrop velocity.
Due to the high variability of natural rain properties and the different typologies of rainfall simulators in use, the measurement of raindrop size and velocity distributions by disdrometers in field and laboratory studies [41] should become a standard procedure to ensure the comparability and transferability of wash-off and sediment transport results. Therefore, the accurate characterization of rain properties carried out in this study is a significant contribution, enhancing derived results and showing the performance of the rainfall simulator when it is calibrated using natural rain measurements. The initial results obtained using this simulator involved an accurate definition of the runoff flow generated, plus a series of wash-off and sediment transport experiments using the three rain intensities analyzed in this article and five different sediment granulometries, which were initially distributed over the model surface [42]. The experimental dataset obtained is described and openly available at the Zenodo [43] repository, where the quality of the experimental results obtained using this rainfall simulator can be confirmed. In addition, these experimental results were used to obtain a detailed representation of the overland runoff though a 2D shallow water model [44] and to analyze the performance of a novel physically-based urban wash-off model [45].
The work carried out to date has focused on analyzing total suspended solids mobilization through the different parts of an urban drainage physical model, so tap water was used directly from the laboratory water supply. This prevents blockages and provides suitable pressure within the operating range of the pressure-compensating drippers. However, the rainfall simulator might be adapted for the use of distilled water through a tank and a pumping system to analyze, for example, dissolved solids or heavy metals wash-off. For this, with 5-min-long experiments, as in the case of the wash-off experiments already performed, a volume of around 90, 150 and 240 L would be necessary for each rain intensity that the simulator can generate (30, 50 and 80 mm/h). This solution, using a pumping system, would be also suitable as a means of adapting the simulator design for field applications. Whereas it is true that a large infrastructure is required in the case of large areas, as indeed has been shown in the application of the simulator in the present study, areas of a few square meters, common in applications of this kind [5,11,13], can be covered with a far more affordable and simpler structure, similar to that presented in Clarke and Walsh [28]. The main benefit of the present simulator would be reduced in such cases, since nozzles can also achieve very suitable spatial uniformities in reduced areas. However, the non-intermittent rain produced, the suitable raindrop size distribution obtained, and the greater height available in field applications, all mean that this new alternative is also of great potential use in such studies. Finally, due to the similarities between urban wash-off and soil erosion processes, in which rain properties are key in the detachment of surface particles and their subsequent transport by the generated runoff, the rainfall simulator developed here can also be useful for analyzing rain-driven soil erosion in rural catchments.
So, the rainfall simulator design presented and calibrated in this study is a new alternative for the simulation of rainfall for a wide range of studies, offering very good spatial uniformity and raindrop size distribution. The total cost of the simulator was around 3500 € (97 €/m2), which includes the construction of 7 metallic porticoes (2500 €) to sustain hose circuits. In addition, no maintenance costs were incurred over almost three years of intensive use.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a new drop-forming rainfall simulator was developed to be applied in wash-off and sediment transport studies in a street-scale laboratory physical model. To this end, the proposed simulator design, which consists of pressure-compensating dripper grids above a horizontal mesh that breaks and distributes raindrops, was calibrated using natural rain as a reference. The mesh typology, mesh size and mesh-drippers distance that best fitted natural rain measurements, were established in consideration of rain intensity, rain uniformity, and raindrop size and velocity distributions. Finally, the rain properties of the selected solution were measured for the three rain intensities that the rainfall simulator is able to generate. In light of the results obtained, the following three main conclusions were drawn:
- Modifying the density of drippers and their flow rate makes possible the precise generation of a wide range of rainfalls with different intensities, maintaining suitable uniformities and raindrop diameter distributions. This design has been presented as a suitable solution for simulating low rain intensities, which is a clear improvement on nozzles-based simulators that have to resort to intermittent rains.
- Very good spatial uniformity of rain intensities was obtained covering an area of 36 m2, both for high-resolution measurements during calibration (10 cm resolution) and for large-scale measurements during rain characterization of the final solution (resolution of 50 cm). The Christiansen’s UC obtained of 81%, 89% and 91% for the rain intensities of 30, 50 and 80 mm/h, respectively, showed almost uniform rainfalls, which confirms a good transferability of the experimental results that will be obtained when using the simulator.
- This rainfall simulator design allowed for controlling rain properties from the calibration of the mesh typology, mesh size, and mesh-drippers distance. The calibration performed in this study has achieve a very accurate representation of raindrop size distribution using local natural rain measurements as a reference, and maintaining good rain uniformity. In this study, the simulator was installed as high as possible, at 2.6 m, achieving suitable raindrop impact velocities of around 87.5% of their terminal velocities for the mean raindrop diameter and 75% for larger raindrops of up to 3 mm. This impact velocity of large raindrops could be further improved by increasing the simulator height to roughly 4.5 m.
Considering the difficult challenge of simulating rain that is as real as possible, the results achieved here have been very satisfactory. The almost uniform rain uniformity and the suitable drop size and velocity distributions indicate that the rainfall simulator developed is optimal for wash-off experiments. In addition, the flexibility seen in controlling rain characteristics increases the value of the proposed design, in that it is adaptable to a wide range of studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P., J.A., J.S. and J.N.; methodology, J.N. and J.A.; investigation, J.N.; resources, J.A., J.P. and J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.; writing—review and editing, J.A.; supervision, J.A., J.P. and J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The first author was in receipt of a Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities predoctoral grant FPU14/01778. The project was partially funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities under POREDRAIN project RTI2018-094217-B-C33 (MINECO/FEDER-EU).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Population Division the World’s Cities in 2018—Data Booklet (ST/ESA/SER.A/417); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Akan, A.O.; Houghtalen, R.J. Urban Hydrology, Hydraulics, and Stormwater Quality: Engineering Applications and Computer Modelling; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Anta, J.; Peña, E.; Suárez, J.; Cagiao, J. A BMP selection process based on the granulometry of runoff solids in a separate urban catchment. Water SA 2006, 32, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zafra, C.; Temprano, J.; Suárez, J. A simplified method for determining potential heavy metal loads washed off by stormwater runoff from road-deposited sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egodawatta, P.; Thomas, E.; Goonetilleke, A. Mathematical interpretation of pollutant wash-off from urban road surfaces using simulated rainfall. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, D.; Digman, C.J.; Makropoulos, C.; Davies, J.W. Urban Drainage, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesiri, B.; Egodawatta, P.; McGee, J.; Goonetilleke, A. Incorporating process variability into stormwater quality modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellart, A.N.A.; Tait, S.J.; Ashley, R.M. Towards quantification of uncertainty in predicting water quality failures in integrated catchment model studies. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, A.; Bombardelli, F.A.; Pitton, B.J.; Oki, L.R.; Haver, D.L.; Young, T.M. Uncertainty in the parameterization of sediment build-up and wash-off processes in the simulation of sediment transport in urban areas. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 111, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, J.D.; Boyd, G.B. Water Pollution Aspects of Street Surface Contaminants. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA-R2-72-081; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Al Ali, S.; Bonhomme, C.; Dubois, P.; Chebbo, G. Investigation of the wash-off process using an innovative portable rainfall simulator allowing continuous monitoring of flow and turbidity at the urban surface outlet. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, M.; Tait, S.J.; Schellart, A.N.A.; Beg, M.N.A.; Carvalho, F.R.; de Lima, J.L.M.P. Improving understanding of the underlying physical process of sediment wash-off from urban road surfaces. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoon, A.A.; Jahan, S.; He, X.; Joergensen, N.E.; Rahman, A. First flush analysis using a rainfall simulator on a micro catchment in an arid climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grismer, M.E. Rainfall Simulation Studies—A Review of Designs, Performance and Erosion Measurement Variability. 2011. Available online: http://ucanr.org/sites/californiaagriculture/files/145682.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Kathiravelu, G.; Lucke, T.; Nichols, P. Designing the Perfect Rainfall Simulator for Urban Stormwater Studies: An Impossible Dream? In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Sarawak, Malaysia, 7–12 September 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Isidoro, J.M.G.P.; de Lima, J.L.M.P.; Leandro, J. Influence of wind-driven rain on the rainfall-runoff process for urban areas: Scale model of high-rise buildings. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, R.J.; Robotham, B.G.; Zeller, L.; Masterman, N.; Orange, D.N.; Bridge, B.J.; Sheridan, G.; Bourke, J.J. A multi-purpose rainfall simulator for field infiltration and erosion studies. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, G.B.; Stone, J.J.; Smith, J.R.; Kennedy, J.R. The Walnut Gulch rainfall simulator: A computer-controlled variable intensity rainfall simulator. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2004, 20, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herngren, L.; Goonetilleke, A.; Sukpum, R.; Silva, D.Y. de Rainfall Simulation as a Tool for Urban Water Quality Research. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 22, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, H.; Unal, N.E.; Cokgor, S.; Gedikli, A.; Yoon, J.; Koca, K.; Inci, S.B.; Eris, E. A rainfall simulator for laboratory-scale assessment of rainfall-runoff-sediment transport processes over a two-dimensional flume. CATENA 2012, 98, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, S.S.; Siqueira, E.Q. Development and calibration of a rainfall simulator for urban hydrology research. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 11–16 September 2011; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, A.; Quinton, J.N. Pumped rainfall simulators: The impact of rain pulses on sediment concentration and size. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaze, J.; Chiew, F.H. Study of pollutant washoff from small impervious experimental plots. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassu, T.; Seeger, M.; Peters, P.; Keesstra, S.D. The Wageningen rainfall simulator: Set-up and calibration of an indoor nozzle-type rainfall simulator for soil erosion studies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, J.; Jikia, Z.; Anta, J.; Puertas, J.; Suárez, J.; Regueiro-Picallo, M. Experimental study of pollutant washoff on a full-scale street section physical model. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.H.; Meyer, B.; Frede, H.G. A portable rainfall simulator for studying factors affecting runoff, infiltration and soil loss. CATENA 1985, 12, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battany, M.C.; Grismer, M.E. Development of a portable field rainfall simulator foruse in hillside vineyard runoff and erosion studies. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.A.; Walsh, R.P.D. A portable rainfall simulator for field assessment of splash and slopewash in remote locations. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 2052–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elbasit, M.A.; Yasuda, H.; Salmi, A.; Anyoji, H. Characterization of rainfall generated by dripper-type rainfall simulator using piezoelectric transducers and its impact on splash soil erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 35, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.E. Irrigation by Sprinkling, No. 04; USDA, REPORT 1532; Agricultural Experiment Station, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A. Evaluation of the New Version of the Laser-Optical Disdrometer, OTT Parsivel2. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2014, 31, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, M.A.; Tomás, P.P. Characterization of raindrop size distributions at the Vale Formoso Experimental Erosion Center. CATENA 1995, 25, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedich, K.; Gochis, D.; Kucera, P.A.; Ikeda, K.; Sun, J. Raindrop Size Distribution and Rain Characteristics during the 2013 Great Colorado Flood. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Porcù, F.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A. A Field Study of Footprint-Scale Variability of Raindrop Size Distribution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 3165–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Raindrop Size Distribution Measurements at 4,500 m on the Tibetan Plateau During TIPEX-III. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11,092–11,106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; D’Adderio, L.P.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W.A. Development and Evaluation of the Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters for the NASA Global Precipitation Measurement Mission Ground Validation Program. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, R.; Kinzer, G.D. The terminal velocity of fall for water droplets in stagmant air. J. Meteorol. 1949, 6, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Bashor, P.G.; Habib, E.; Kasparis, T. Raindrop size distribution measurements in tropical cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, J.O. Measurements of the fall-velocity of water -drops and raindrops. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1941, 22, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.T.; Moldrup, P.; Thorndahl, S.; Nielsen, J.E.; Duus, L.B.; Rasmussen, S.H.; Uggerby, M.; Rasmussen, M.R. Automated rainfall simulator for variable rainfall on urban green areas. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 3364–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserloh, T.; Fister, W.; Seeger, M.; Willger, H.; Ries, J.B. A small portable rainfall simulator for reproducible experiments on soil erosion. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, J.; Anta, J.; Suárez, J.; Puertas, J. Hydraulic, wash-off and sediment transport experiments in a full-scale urban drainage physical model. Sci. Data 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Naves, J.; Anta, J.; Suárez, J.; Puertas, J. [Dataset] WASHTREET Hydraulic, wash-off and sediment transport experimental data in an urban drainage physical model. Zenodo 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, J.; Anta, J.; Puertas, J.; Regueiro-Picallo, M.; Suárez, J. Using a 2D shallow water model to assess Large-Scale Particle Image Velocimetry (LSPIV) and Structure from Motion (SfM) techniques in a street-scale urban drainage physical model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, J.; Rieckermann, J.; Cea, L.; Puertas, J.; Anta, J. Global and local sensitivity analysis to improve the understanding of physically-based urban wash-off models from high-resolution laboratory experiments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).