Evidence of Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Rainwater Trace Metal Geochemistry in Central Mexico: A Statistical Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
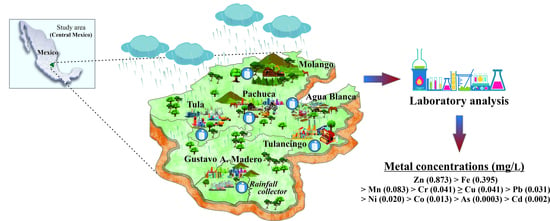
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Characteristics
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.4. Data Assessment
2.4.1. Statistical Analysis
2.4.2. Enrichment Factor
2.4.3. Elemental Ratios
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Trace Metals in Rainwater
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.3. Enrichment Factor
- Gustavo A. Madero: Cd (4095) > Zn (2475) > Cu (296) > Pb (201) > Co (39) > Cr (30) > As (13) > Mn (11).
- Tula: Cd (2798) > Cu (367) > Zn (264) > Pb (232) > Co (82) > Ni (66) > Cr (38) > As (18) > Mn (14).
- Pachuca: Cd (2700) > Zn (1656) > Cu (415) > Pb (212) > Co (105) > Cr (42) > Ni (37) > As (24) > Mn (14).
- Tulancingo: Zn (4155) > Cd (2402) > Cu (385) > Pb (228) > Co (94) > Cr (38) > Ni (27) > Mn (18) > As (16)
- Agua Blanca: Cd (2314) > Zn (766) > Pb (287) > Cu (267) > Co (91) > Ni (67) > Cr (44) > As (20) > Mn (12).
- Molango: Cd (1754) > Zn (461) > Cu (376) > Pb (236) > Co (66) > Cr (36) > Ni (24) > Mn (19) > As (11).
3.4. Elemental Ratios
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goni, I.B.; Fellman, E.; Edmunds, W.M. Rainfall geochemistry in the Sahel region of the Northern Nigeria. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 3, 4331–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khare, P.; Goel, A.; Patel, D.; Behari, J. Chemical characterization of rainwater at a developing urban habitat of Northern India. Atmos. Res. 2004, 69, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacardit, M.; Camarero, L. Fluxes of Al, Fe, Ti, Mn, Pb, Cd, Zn, Ni, Cu, and As in monthly bulk deposition over the Pyrenees (SW Europe): The influence of meteorology on the atmospheric component of trace element cycles and its implications for high mountain lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114, G00D02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreda-Piñeiro, J.; Alonso-Rodríguez, E.; Moscoso-Pérez, C.; Blanco-Heras, G.; Turnes-Carou, I.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. Influence of marine, terrestrial and anthropogenic sources on ionic and metallic composition of rainwater at a suburban site (northwest coast of Spain). Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Kang, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tripathee, L.; Sillanpää, M. Seasonal variations of trace elements in precipitation at the largest city in Tibet, Lhasa. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Qin, D.; Qin, X.; Cui, J.; Kang, S. Changes in precipitating snow chemistry with seasonality in the remote Laohugou glacier basin, western Qilian Mountains. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11404–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-mayor, R.; Fernández-Espinosa, A.J.; Seijo-Delgado, I.; Ternero-Rodríguez, M. Determination of soluble ultra-trace metals and metalloids in rainwater and atmosphere deposition fluxes: A 2-year survey and assessment. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Gong, G.C.; Shiah, F.K.; Huang, Y.T.; Kao, S.J.; Tsai, F.J.; Lung, S.C.C.; Lin, F.J.; Lin, I.I.; et al. Sources, solubility, and dry deposition of aerosol trace elements over the East China Sea. Mar. Chem. 2010, 120, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.B.; Dadashazar, H.; Chuang, P.Y.; Crosbie, E.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Jonsson, H.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Sorooshian, A. Characteristic vertical profiles of cloud water composition in marine stratocumulus clouds and relationships with precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3704–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, T.F.M.; Fontenele, A.P.G.; Pedrotti, J.J.; Fornaro, A. Composicao ionica majoritaria de aguas de chuva no centro da cidade de Sao Paulo. Quim. Nova 2004, 27, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Sterren, M.; Rahman, A.; Dennis, G. Quality and quantity monitoring of five rainwater tanks in Western Sydney, Australia. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Tiwari, S.; Sarkar, C.; Das, S.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Raha, S. Precipitation chemistry over urban, rural and high altitude Himalayan Stations in Eastern India. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siudek, P.; Frankowski, M. The effect of sources and air mass transport on the variability of trace element deposition in Central Poland: A cluster-based approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 23026–23028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colin, J.L.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Pinart, J.; Roulette-Cadene, S. Sequential sampling of snow in a rural area. Experimentation and identification of the acidifying agents. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1987, 21, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Ma, C.T.; Padilla, H.; Belmont, R.; Azpra, E.; Arcega-Cabrera, F.; Baez, A. Measurement of chemical elements in rain from Rancho Viejo, a rural wooded area in the State of Mexico. Mex. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6088–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.C.; You, C.F. Sources of major ions and heavy metals in rainwater associated with typhoon events in southwestern Taiwan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 105, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J. Global inventory of natural and anthropogenic emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere. Nature 1979, 279, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.; Pacyna, J.M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 1988, 333, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrie, L.A.; Lindberg, S.E.; Chan, W.H.; Ross, H.B.; Arimoto, R.; Church, T.M. On the concentration of trace metals in precipitation. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1987, 21, 1133–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Thornton, J.D.; Norton, S.A.; Volchok, H.L.; McLean, R.A.N. Trace metals in atmospheric deposition: A review and assessment. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1982, 16, 1677–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Røyset, O.; Steinnes, E. Trace elements in atmospheric precipitation at Norwegian background stations (1989–1990) measured by ICP-MS. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 3519–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Scurdlark, J.R.; Church, T.M. Atmospheric wet deposition of trace elements to Chesapeake and Delaware Bays. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguillaume, L.; Maud, L.; Karine, D.; Gilles, M.; Christian, G.; Nadine, C. Transition metals in atmospheric liquid phases: Sources, reactivity, and sensitive parameters. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3388–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Diaz-de-Quijano, M.; Monna, F.; Marielle Franchi, M.; Toussaint, M.; Gilbert, D.; Bernard, N. Characterisation and distribution of deposited trace elements transported over long and intermediate distance in northeastern France using Sphagnum peatlands as a sentinel ecosystem. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlastos, D.; Antonopoulou, M.; Lavranou, A.; Efthimiou, I.; Dailianis, S.; Helas, D.; Lambropoulou, D.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Kassomenos, P. Assessment of the toxic potential of rainwater precipitation: First evidence from a case study in three Greek cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehr, M.R.; Keshavarzi, B.; Sorooshran, A. Influence of natural and urban emissions on rainwater chemistry at a Southwestern Iran coastal site. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gispert, M.I.; Armienta Herandez, M.A.; Lomnitz Climent, E.; Torregrosa Flores, M.F. Rainwater harvesting as a drinking water option for Mexico City. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrow, A.; Coombes, P.; Dunstan, H.; Evans, C.; Martin, A. Elements in Tank Water—Comparisons with mains water & effects of locality & roofing materials. In Proceedings of the Rainwater and Urban Design Conference, Sydney, Australia, 21–23 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Eletta, O.A.A.; Oyeyipo, J.O. Rain Water Harvesting: Effect of Age of Roof on Water Quality. Int. J. Appl. Chem. 2008, 4, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, R.; Chan, Y.; Chapman, H.; Gardner, T.; Shaw, G. Source apportionment of heavy metals and ionic contaminants in rainwater tanks in a subtropical urban area in Australia. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gichuki, S.W.; Mason, R.P. Mercury and metals in South African precipitation. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbers, G.-J.; Sebesvari, Z.; Rechenburg, A.; Renaud, F.G. Effects of local and spatial conditions on the quality of harvested rainwater in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobbina, S.J.; Agoboh, Y.P.; Duwiejuah, A.B.; Bakobie, N. Evaluation of Stored Rainwater Quality in Basic Schools in the Tamale Metropolis, Ghana. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2015, 7, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetangula, G.N.; Wamalwa, H.M. Trace elements in rainfall collected around Menengai Area Kenya. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Melbourne, Australia, 19–24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tubek, S.; Bunio, A.; Szyguła, R.; Tubek, A. Frequency of hospitalization for angina pectoris, stroke, and peripheral venous thrombosis and its relationship to elements in rainwater in Opole Voivodship, Poland, during 2000–2002. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 133, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Báez, A.P.; De González, O.G.; Solono, F.; Belmont, R. Determinación de plomo, cadmio y cromo en la precipitación pluvial de algunos lugares de la República Mexicana (Parte 1). Medio Ambiente 1980, 2, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- García, J.A.; Gallego, M.C.; Serrano, A.; Vaquero, J.M. Trends in block-seasonal extreme rainfall over the Iberian Peninsula in the second half of the twentieth century. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez, A.; Belmont, R.; Garcia, R.; Padilla, H.; Torres, M.C. Chemical composition of rainwater collected at a southwest site of Mexico City, Mexico. Atmos. Res. 2007, 86, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, A.P.; Belmont, R.D.; Padilla, H.G. Chemical composition of precipitation at two sampling sites in Mexico: A 7—Year study. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Báez, A.P.; Belmont, R.D.; García, R.M.; Torres, M.C.B.; Padilla, H.G. Rainwater chemical composition at two sites in Central Mexico. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 80, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Belmont, R.; Padilla, H.; Torres, M.C.B.; Báez, A.P. Determination of inorganic ions and trace elements in total suspended particles at three urban zones in the Mexico City metropolitian area and one rural site. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 94, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INEGI. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Panorama socio-demográfico de México. 2015. Available online: http://www.inegi.org.mx (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Saavedra Silva, E.E.; Sánchez Salazar, M.T. Minería y espacio en el distrito minero Pachuca-Real del Monte en el siglo XIX. Boletín del Instituto de Geografía de la UNAM 2008, 65, 82–101. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, S.L.M. La productividad de la industria manufacturera como determinante del crecimiento económico: Estado de Hidalgo, 1999–2004; UAEH: Pachuca, Mexico, 2010; 25p. [Google Scholar]
- INEGI. Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía. Marco Geoestadístico Municipal. 2010. Available online: http://www.inegi.org.mx (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- US EPA. Method 7000B—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. 2007; rev.02, 72p. Available online: www.epa.gov/epaoswer/hazwaste/test/pdfs/7000b.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Tsarpali, V.; Dailianis, S. Investigation of landfill leachate toxic potency: An integrated approach with the use of stress indices in tissues of mussels. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 124–125, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabukdhara, M.; Nema, A.K. Heavy metals assessment in urban soil around industrial clusters in Ghaziabad, India: Probabilistic health risk approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, H.; Gonzales, C.; Smith, M.; Mielke, P. The urban environment and children’s health: Soils as an integrator of lead, zinc, and cadmium in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Environ. Res. 1999, 81, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lu, W.; Long, Y.; Bao, X.; Yang, Q. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 108, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Wei, Y.; Pan, Z.; Meng, X.-Z.; Hung, Q.; Li, W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface soil of Shanghai, China: Concentrations, distribution and sources. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loredo, J.; Ordóñez, A.; Charlesworth, S.; De Miguel, E. Influence of industry on the geochemical urban environment of Mieres (Spain) and associated health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2003, 25, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynam, M.M.; Dvonch, J.T.; Hall, N.L. Trace elements and major ions in atmospheric wet and dry deposition across central Illinois, USA. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1985; 330p. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Luo, T.-C.; Zhang, B.-R.; Zhang, H.-F.; Han, Y.-W.; Hu, Y.-K.; Zhao, Z.-D. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in east China. Geochim. Cosmochim. 1998, 62, 1959–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediagbonya, T.F. Enrichment Factor of atmospheric trace metal using Zirconium, Titanium Iron and Copper as Reference Element. Niger. J. Technol. 2016, 35, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—Weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerks, P.L.; Levinton, J.S. Rapid evolution of metal resistance in a benthic oligochaete inhabiting a metal—Polluted site. Biol. Bull. 1989, 176, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.A.; Tolosa, C.A.; Tack, F.M.G.; Verloo, M.G. Characterization of selected element concentrations and enrichment ratios in background and anthropogenically impacted roadside areas. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongming, H.; Peixuan, D.; Junji, C.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xían, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lee, S.-L.; Wong, S.-C.; Shi, W.; Thornton, I. The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environ. Poll. 2004, 129, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ljung, K.; Selinus, O.; Otabbong, E.; Berglund, M. Metal and arsenic distribution in soil particle sizes relevant to soil ingestion by children. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliardi, I.; Buttafuoco, G.; Cicchella, D.; De Rosa, R. A multivariate approach for anomaly separation of potentially toxic trace elements in urban and peri-urban soils: An application in a southern Italy area. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Kato, J.; Mori, J.; Tenmoku, M.; Suda, Y.; Tanaka, S.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Yang, F.; Yu, X. Daily concentrations of trace metals in aerosols in Beijing, China, determined by using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry equipped with laser ablation analysis, and source identification of aerosols. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 330, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, M.; Asakura, K. Factors contributing to seasonal variations in wet deposition fluxes of trace elements at sites along Japan Sea coast. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3867–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başak, B.; Alagha, O. Trace metals solubility in rainwater: Evaluation of rainwater quality at a watershed area, Istanbul. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 167, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulou, E. Determination of heavy metals in wet deposition of Athens. Glob. Nest J. 2001, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Momani, I.F. Trace elements in atmospheric precipitation at Northern Jordan measured by ICPMS: Acidity and possible sources. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4507–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.; Rodrigo, A. Trace metals fluxes in bulk deposition, throughfall and stemflow at two evergreen oak stands n NE Spain subject to different exposure to the industrial environment. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melidis, P.; Akraatos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Trikilidou, E. Characterization of rain and roof drainage water quality in Xanthi, Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Li, G.; Yan, P.; Ren, J.; Zheng, L.; Han, D.; Sun, S.; Huang, S.; Zhong, Y. Removal of metals from lead-zinc mine tailings using bioleaching and followed by sulfide precipitation. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbič, A.; Gorjanc, M.; Simončič, B. Zinc oxide for functional textile coatings: Recent advances. Coatings 2019, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Servicio Geológico Mexicano. Cartografía Geoquímica escala 1:250,000. 2017. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/sgm (accessed on 25 March 2019).
- Liu, B.; Zhnag, Y.; Lu, M.; Su, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Extraction and separation of manganese and iron from ferruginous manganese ores: A review. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, R.J.; Wiley, J.D.; Zvalaren, S.D. Chromium speciation in rainwater: Temporal variability and atmospheric deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 5321–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.L.; Pan, Y.P.; Wang, Y.S. Size-resolved source apportionment of particulate matter in urban Beijing during haze and non-haze episodes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mihajlidi-Zelić, A.; Deršek-Timotić, I.; Relić, D.; Popović, A.; Đorđević, D. Contribution of marine and continental aerosols to the content of major ions in the precipitation of the central Mediterranean. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Belmont, R.; Padilla, H.; Torres, M.C.; Baez, A. Trace metals and inorganic ion measurements in rain from Mexico City and a nearby rural area. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 25, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Atmospheric wet deposition of trace elements to central Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsoy, T.; Ornektekin, S. Trace elements in urban and suburban rainfall, Mersin, northeastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khashman, O.A. Chemical characteristics of rainwater collected at a western site of Jordan. Atmos. Res. 2009, 91, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ni, Z.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, X. Atmospheric deposition of trace elements to Daya Bay, South China Sea: Fluxes and sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Duan, L.; Qu, B. Atmospheric wet deposition of dissolved trace elements to Jiaozhou Bay, North China: Fluxes, sources and potential effects on aquatic environments. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T.; Li, Y.; Wai, K.M.; Wang, W. Origin and distribution of trace elements in high-elevation precipitation in southern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3389–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOM-127-SSA1-1994. Límites permisibles de calidad y tratamientos a que debe someterse el agua para su potabilización. Secr. Medio Ambient. y Recur. Nat. D. Of. la Fed. 1994. Available online: http://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/105139/Normas_Oficiales_Mexicanas.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2018).
- Zalakeviciute, R.; Lopez-Vilalda, J.; Rybarczyk, Y. Contrasted effects of relative humidity and precipitation on urban PM 2.5 pollution in high elevation urban areas. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owoade, O.K.; Olise, F.S.; Ogundele, L.T.; Fawole, O.G.; Olaniyi, H.B. Correlation between particulate matter concentrations and meteorological parameters at a site in Ile-Ife, Nigeria. Ife J. Sci. 2012, 14, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, A.D.; Van Zyl, P.G.; Berkes, J.P.; Joseipovic, M.; Hendricks, J.; Vakkari, V.; Loakso, L. Atmospheric trace metals measured at a regional background site (Welgegund) in South Africa. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4251–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dao, L.; Morrison, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, I. Influences of traffic on Pb, Cu and Zn concentrations in roadside soils of urban park in Dublin, Ireland. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubaka, C.E.; Whiley, H.; Edwards, J.W.; Ross, K.E. Lead, Zinc, Copper and Cadmium content of water from South Australian rainwater tanks. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cipurkovic, A.; Trumic, I.; Hodzic, Z.; Selimbasic, V.; Djozic, A. Distribution of heavy metals in Portland cement production process. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Missimer, T.M.; Teaf, C.M.; Beeson, W.T.; Maliva, R.G.; Woolschlager, J.; Covert, D.J. Natural background and anthropogenic arsenic enrichment in Florida soils, surface water and groundwater. A review with a discussion on Public health risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chileshe, M.N.; Syampungani, S.; Festin, E.S.; Tigabu, M.; Daneshvar, A.; Oden, P.C. Physico chemical characteristics and heavy metal concentrations of copper mine wastes in Zambia: Implications for pollution risk and restoration. J. For. Res. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sungur, S.; Gülmez, F. Determination of metal contents of various fibers used in textile industry by MP-AES. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krook, J.; Martensson, A.; Eklund, M. Source of heavy metal contamination in Swedish wood waste used for combustion. J. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Gao, Y. Chemical characteristics of precipitation at metropolitan Newark in the US East Coast. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4903–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyep, P.A.; Chuma, A.G.; Awodi, S.; Nok, A.J. Biosorption of Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu and Pb metals from petroleum refinery effluent by calcium alginate immobilized mycelia of Polyporus squamosus. Sci. Res. Essay 2007, 2, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Rai, V. Assessment of rainwater chemistry in the Lucknow metropolitan city. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskin, A.; Gaspar, D.J.; Wang, W.H.; Hunt, S.W.; Cowin, J.P.; Colson, S.D.; Finlayson-Pits, B.T. Reactions at interfaces as a source of sulfate formation in sea-salt particles. Science 2003, 301, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Shen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Insight into generation and evolution of sea-salt aerosols from field measurements in diversified marine and coastal atmospheres. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouli, P.C.; Mohan, S.V.; Reddy, S.J. Chemical composition of atmospheric aerosol (PM10) at a semi-arid urban site: Influence of terrestrial sources. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 117, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, M.; Heikkinen, L.; Bell, D.M.; Peräkylä, O.; Zha, Q.; Schallart, S.; Rissanen, M.P.; Imre, D.; Petäjä, T.; Thornton, J.A.; et al. Chemical transformations in monoterpene-derived organic aerosol enhanced by inorganic composition. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabas, A.; Lefevre, R.A. Chemistry and atmospheric particulates at Delos (Cyclades—Greece). Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, J.D.; Inscore, M.T.; Kieber, R.J.; Skrabal, S.A. Manganese in coastal rainwater: Speciation, photochemistry and deposition to seawater. J. Atmos. Chem. 2009, 62, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, S.; Adler, B.; Cuxart, J.; De Wekker, S.F.J.; Gohm, A.; Grisogono, B.; Kalthoff, N.; Kirshbaum, D.J.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmidli, J.; et al. Exchange Processes in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Over Mountainous Terrain. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoigné, J.; Bader, H. Ozonation of water: “Oxidation-competition values” of different types of waters used in Switzerland. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1979, 1, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toui, S. The Oxidation of Manganese and Disinfection by Ozonation in Water Purification Processing. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1991, 13, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabla-Hernández, J.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, P.F.; Hernandez-Ramirez, A.G.; Mendoza-Pérez, J.A.; Cano-Aznar, E.R.; Martínez-Tavera, E. Treatment of Eutrophic Water and Wastewater from Valsequillo Reservoir, Puebla, Mexico by Means of Ozonation: A Multiparameter Approach. Water 2018, 10, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Agricultura y la Alimentación (FAO). Manual de Captación y aprovechamiento del agua de lluvia. Experiencias en América Latina 2015, 13, 235. [Google Scholar]



| Location | Altitude (masl) | Average Temperature (°C/year) | Average Rainfall (mm/year) | Population | Geology | Industries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gustavo A. Madero | 2240 | 16 | 893 | 1,164,477 | Igneous rocks (basalts) | Food products Textile, leather Wood Paper Chemical Nonmineral products Metal industries |
| Tula | 2020 | 17.6 | 438 | 109,093 | Igneous rocks (tuffs, andesites, rhyolites); Sedimentary rocks (sandstone, limestone) | Refinery and Thermoelectric Plant Chemical Cement Metalworking |
| Pachuca | 2382 | 15.5 | 574 | 277,375 | Extrusive rocks (rhyolites and andesites) | Silver mining Manufacturing |
| Tulancingo | 2181 | 14 | 532 | 161,069 | Extrusive igneous rocks (acid and basalt tuffs) | Textile Clothing and leather Food products, beverages, and tobacco Nonmetallic mineral products and basic metal industries. |
| Agua Blanca | 2100 | 14.2 | 1061 | 9116 | Igneous rocks (basalts and acid tuffs) | Food products Wood Production of nonmetallic and metallic minerals |
| Molango | 1620 | 17 | 1438 | 11,587 | Igneous rocks (basalt, acid tuff and traquita); Metamorphic rocks (gneiss); Sedimentary rocks (limestones, shales and sandstones) | Manufacturing Manganese extraction |
| Locations | Years | Description | Fe | Mn | Cr | Cu | Ni | Co | Pb | Zn | Cd | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nam Co a* | 2007–2008 | Remote | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.006 | 0.000004 | - |
| Mexico City b* | 2001–2002 | Urban | - | 0.008 | 0.0003 | - | 0.003 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.0004 | - |
| Pretoria c* | 2007–2009 | Rural | 0.045 | 0.001 | - | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.00003 | - |
| Cape Point d* | 2007–2009 | Urban | 0.049 | 0.002 | - | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.057 | 0.00002 | - |
| Mersin e* | 2003–2005 | Urban | 0.743 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.050 | 0.0008 | - |
| S. Jordan f* | 2003–2004 | Rural | 0.022 | - | - | 0.04 | 0.002 | - | 0.051 | 0.032 | 0.042 | - |
| Matsuura g* | 2003–2005 | Remote | - | 0.003 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | - | 0.004 | 0.011 | 0.0002 | 0.0005 |
| Daya Bay h* | 2015–2017 | Urban | 1.13 | 0.23 | 0.016 | 0.025 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.040 | 0.51 | 0.008 | 0.020 |
| Jiaozhou Bay i* | 2015–2016 | Urban | 0.017 | 0.028 | 0.001 | - | - | 0.0001 | 0.003 | 0.028 | 0.0002 | - |
| Mt Heng j* | 2009 | Urban | 0.118 | 0.013 | 0.001 | - | - | - | 0.008 | - | 0.0007 | - |
| Present Study + | 2016–2017 | |||||||||||
| Gustavo A. Madero | Urban | 0.371 | 0.044 | 0.035 | 0.037 | 0.019 | 0.009 | 0.033 | 0.952 | 0.004 | 0.003 | |
| Tula | Industrial | 0.472 | 0.074 | 0.036 | 0.045 | 0.033 | 0.015 | 0.028 | 0.137 | 0.002 | 0.004 | |
| Pachuca | Urban/Mining | 0.292 | 0.075 | 0.030 | 0.041 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 1.174 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Tulancingo | Peri-urban | 0.406 | 0.098 | 0.038 | 0.046 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.031 | 1.892 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| Agua Blanca | Rural/Remote | 0.379 | 0.059 | 0.058 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.014 | 0.045 | 0.799 | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| Molango | Rural | 0.448 | 0.148 | 0.055 | 0.047 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.031 | 0.282 | 0.001 | 0.002 | |
| Permissible limits | ||||||||||||
| Mexico k | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 2 | - | - | 0.025 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.005 | ||
| Total Metal Burden (TMB) | Precipitation (P) | Wind Velocity (WV) | Air Temperature (AT) | Relative Humidity (RH) | Barometric Pressure (BP) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gustavo A. Madero (n = 7) | ||||||
| Total Metal burden | 1.00 | |||||
| Precipitation | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Wind velocity | - | - | 1.00 | |||
| Air temperature | 0.52 | - | - | 1.00 | ||
| Relative humidity | -0.56 | - | - | −0.64 | 1.00 | |
| Barometric pressure | 0.65 | - | −0.65 | 0.71 | −0.89 | 1.00 |
| Tula (n = 8) | ||||||
| Total Metal burden | 1.00 | |||||
| Precipitation | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Wind velocity | 0.91 | - | 1.00 | |||
| Air temperature | - | - | - | 1.00 | ||
| Relative humidity | −0.90 | - | −0.88 | −0.66 | 1.00 | |
| Barometric pressure | −0.77 | - | −0.70 | −0.64 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| Pachuca (n = 6) | ||||||
| Total Metal burden | 1.00 | |||||
| Precipitation | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Wind velocity | - | −0.65 | 1.00 | |||
| Air temperature | 0.78 | - | - | 1.00 | ||
| Relative humidity | - | 0.92 | - | - | 1.00 | |
| Barometric pressure | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 |
| Tulancingo (n = 10) | ||||||
| Total Metal burden | 1.00 | |||||
| Precipitation | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Wind velocity | - | - | 1.00 | |||
| Air temperature | 0.65 | - | - | 1.00 | ||
| Relative humidity | - | 0.60 | −0.91 | - | 1.00 | |
| Barometric pressure | - | - | −0.92 | - | 0.84 | 1.00 |
| Agua Blanca (n = 10) | ||||||
| Total Metal burden | 1.00 | |||||
| Precipitation | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Wind velocity | - | - | 1.00 | |||
| Air temperature | - | - | 0.66 | 1.00 | ||
| Relative humidity | - | 0.76 | −0.80 | - | 1.00 | |
| Barometric pressure | - | - | −0.89 | −0.69 | 0.70 | 1.00 |
| Molango (n = 11) | ||||||
| Total Metal burden | 1.00 | |||||
| Precipitation | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Wind velocity | - | - | 1.00 | |||
| Air temperature | 0.66 | - | - | 1.00 | ||
| Relative humidity | - | 0.66 | - | - | 1.00 | |
| Barometric pressure | - | - | −0.65 | - | 0.86 | 1.00 |
| Cu | Cd | Cr | Ni | Pb | Zn | Co | Fe | Mn | As | Cu | Cd | Cr | Ni | Pb | Zn | Co | Fe | Mn | As | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agua Blanca (n = 10) | Cu | 1.00 | Molango (n = 11) | Cu | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cd | 0.58 | 1.00 | Cd | −0.58 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cr | 0.55 | 0.71 | 1.00 | Cr | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ni | 0.69 | - | - | 1.00 | Ni | - | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Pb | 0.65 | 0.90 | 0.64 | - | 1.00 | Pb | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Zn | 0.71 | 0.97 | 0.77 | - | 0.93 | 1.00 | Zn | 0.58 | −0.50 | 0.59 | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Co | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | Co | - | - | - | - | 0.56 | - | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Fe | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.85 | - | 0.84 | 0.84 | −0.62 | 1.00 | Fe | 0.59 | - | 0.86 | - | - | 0.70 | - | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mn | 0.93 | 0.51 | - | 0.82 | 0.56 | 0.61 | - | - | 1.00 | Mn | 0.63 | - | - | - | - | 0.77 | - | 0.63 | 1.00 | ||||
| As | −0.52 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.57 | −0.53 | - | 1.00 | As | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | ||
| Gustavo A. Madero (n = 7) | Cu | 1.00 | Tula (n = 8) | Cu | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cd | - | 1.00 | Cd | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cr | - | - | 1.00 | Cr | - | 0.66 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ni | 0.64 | - | - | 1.00 | Ni | 0.70 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Pb | −0.76 | - | −0.63 | −0.52 | 1.00 | Pb | −0.64 | −0.71 | - | −0.62 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Zn | - | - | 0.51 | - | −0.73 | 1.00 | Zn | 0.85 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.93 | −0.70 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Co | - | - | - | - | - | 0.57 | 1.00 | Co | - | - | −0.60 | −0.66 | - | −0.58 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Fe | - | - | - | - | 0.57 | −0.84 | −0.56 | 1.00 | Fe | 0.75 | - | 0.83 | 0.84 | - | 0.80 | - | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mn | 0.83 | 0.58 | - | - | −0.94 | 0.76 | - | −0.58 | 1.00 | Mn | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.96 | −0.67 | 0.99 | −0.55 | 0.86 | 1.00 | ||||
| As | −0.69 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | As | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.92 | - | 0.84 | −0.58 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 1.00 | ||
| Pachuca (n = 6) | Cu | 1.00 | Tulancingo (n = 10) | Cu | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cd | - | 1.00 | Cd | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cr | - | - | 1.00 | Cr | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ni | - | - | 0.94 | 1.00 | Ni | 0.72 | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Pb | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | Pb | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Zn | 0.77 | - | 0.87 | 0.83 | - | 1.00 | Zn | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Co | - | 0.83 | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | Co | −0.81 | 0.58 | - | −0.61 | - | −0.53 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Fe | 0.76 | −0.56 | 0.67 | 0.60 | - | 0.90 | - | 1.00 | Fe | - | - | - | - | - | 0.52 | - | 1.00 | ||||||
| Mn | 0.84 | −0.53 | 0.69 | 0.59 | - | 0.94 | −0.65 | 0.94 | 1.00 | Mn | 0.62 | - | - | 0.69 | - | 0.81 | - | 0.60 | 1.00 | ||||
| As | - | - | - | - | 0.73 | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | As | - | - | - | - | - | −0.76 | - | - | −0.57 | 1.00 |
| Gustavo A. Madero | Tula | Pachuca | ||||||||
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | ||
| Cu | - | 0.97 | - | - | - | 0.74 | - | - | - | |
| Cd | - | - | 0.88 | - | - | - | −0.92 | - | - | |
| Cr | - | - | - | 0.93 | 0.93 | - | - | - | 0.96 | |
| Ni | - | 0.70 | - | - | 0.77 | - | - | - | 0.98 | |
| Pb | - | - | - | - | - | −0.98 | - | −0.89 | - | |
| Zn | 0.85 | - | - | - | - | 0.74 | - | - | 0.87 | |
| Co | 0.75 | - | - | - | - | - | −0.87 | - | - | |
| Fe | −0.95 | - | - | - | 0.86 | 0.71 | - | - | - | |
| Mn | - | 0.70 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| As | - | −0.80 | - | - | 0.92 | - | - | - | - | |
| Expl. Var | 2.99 | 3.10 | 1.65 | 1.79 | 4.74 | 3.66 | 2.96 | 2.31 | 3.73 | |
| Prp. Totl | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.47 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.37 | |
| Tulancingo | Agua Blanca | Molango | ||||||||
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | |
| Cu | - | −0.75 | - | - | 0.78 | - | 0.86 | - | - | - |
| Cd | - | - | - | 0.92 | - | - | - | - | −0.75 | - |
| Cr | - | - | - | 0.79 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.93 |
| Ni | - | - | - | - | 0.98 | - | - | 0.83 | - | - |
| Pb | - | - | 0.85 | 0.93 | - | - | - | 0.81 | - | - |
| Zn | 0.86 | - | - | 0.94 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Co | - | - | - | - | - | −0.88 | - | - | - | - |
| Fe | - | - | - | 0.82 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.88 |
| Mn | 0.89 | - | - | - | 0.90 | - | 0.77 | - | - | - |
| As | −0.83 | - | - | - | - | −0.80 | - | - | −0.86 | - |
| Expl. Var | 3.29 | 2.90 | 1.40 | 4.46 | 2.57 | 1.94 | 2.73 | 1.85 | 1.52 | 2.36 |
| Prp. Totl | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.45 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.24 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivera-Rivera, D.M.; Escobedo-Urías, D.C.; Jonathan, M.P.; Sujitha, S.B.; Chidambaram, S. Evidence of Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Rainwater Trace Metal Geochemistry in Central Mexico: A Statistical Approach. Water 2020, 12, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010192
Rivera-Rivera DM, Escobedo-Urías DC, Jonathan MP, Sujitha SB, Chidambaram S. Evidence of Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Rainwater Trace Metal Geochemistry in Central Mexico: A Statistical Approach. Water. 2020; 12(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivera-Rivera, D. M., D. C. Escobedo-Urías, M. P. Jonathan, S. B. Sujitha, and S. Chidambaram. 2020. "Evidence of Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Rainwater Trace Metal Geochemistry in Central Mexico: A Statistical Approach" Water 12, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010192
APA StyleRivera-Rivera, D. M., Escobedo-Urías, D. C., Jonathan, M. P., Sujitha, S. B., & Chidambaram, S. (2020). Evidence of Natural and Anthropogenic Impacts on Rainwater Trace Metal Geochemistry in Central Mexico: A Statistical Approach. Water, 12(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010192