Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Procedures
2.3. Water Quality Index
2.4. Geostatistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydro-Chemical Characterization
3.2. Water Quality
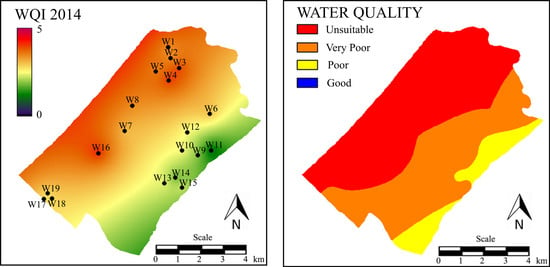
3.3. Water Quality Mapping
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foster, S.; Hirata, R.; Gomes, D.; D’Elia, M.; Paris, M. Groundwater Quality Protection: A Guide for Water Utilities, Municipal Authorities, and Environment Agencies; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; 114p. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, I.S.; Rajaveni, S.P.; Schneider, M.; Elango, L. Geochemical and isotopic signatures for the identification of seawater intrusion in an alluvial aquifer. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartram, J.; Ballance, R. Water Quality Monitoring—A Practical Guide to the Design and Implementation of Freshwater Quality Studies and Monitoring Programs; World Health Organization, United Nations Environment Programme, E. & F.N. Spon: London, UK, 1996; 383p. [Google Scholar]
- Shomar, B. Groundwater of the Gaza Strip: Is it drinkable? Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf and Eddy Inc. Coastal Aquifer Management Program (Camp); Integrated Aquifer Management Plan (Gaza Strip); The United States Agency for International Development and Palestinian Water Authority: Gaza, Palestine, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ghabayen, S.; McKee, M.; Kemblowski, M. Ionic and isotopic ratios for identification of salinity sources and missing data in the Gaza aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2006, 318, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, M.; Ghabayen, S. Analysis of nitrate contamination of Gaza coastal aquifer, Palestine. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aish, A.M. Drinking water quality assessment of the Middle Governorate in the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Water Resour. Ind. 2013, 4, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Barbieri, M.; Battistel, M.; Brattini, G.; Garone, A.; Parisse, B. Water quality in the Gaza Strip: The present scenario. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastal, K.M.; Alagha, J.S.; Abuhabib, A.A.; Ababou, R. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index (WQI) approach: Gaza Coastal aquifer case study. J. Eng. Res. Tech. 2015, 2, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- PWA (Palestinian Water Authority). Water Resources Status Summary Report/Gaza Strip; Palestinian Water Authority: Ramallah, Palestine, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-alnaeem, M.F.; Yusoff, I.; Ng, T.F.; Alias, Y.; Raksmey, M. Assessment of groundwater salinity and quality in Gaza coastal aquifer, Gaza Strip, Palestine: An integrated statistical, geostatistical and hydrogeochemical approaches study. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 972–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Poll. Cont. Fed. 1965, 37, 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. J. Am. Water Res. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Sikdar, P.K. Hydrochemical framework of the aquifer in and around East Kolkata wetlands, West Bengal, India. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketata, M.; Gueddari, M.; Bouhlila, R. Use of geographical information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in El Khairat deep aquifer (Enfidha, Central East Tunisia). Ara. J. Geos. 2012, 5, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeiy, R.E. Assessment and modeling of groundwater quality using WQI and GIS in Upper Egypt area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawo, N.S.; Karuppannan, S. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index and GIS technique in Modjo River Basin, central Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Affairs (MEnA). Palestinian Environmental Action Plan; Ministry of Environmental Affairs: Gaza, Palestine, 2001; pp. 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- El Baba, M.; Kayastha, P.; De Smedt, F. Landfill site selection using multi-criteria evaluation in the GIS interface: A case study from the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Ara. J. Geos. 2015, 8, 7499–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeid, K.F. The nature of the Pleistocene-Holocene palaeosols in the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Geologos 2011, 17, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; 1368p. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Vol. 2, Health Criteria and other Supporting Information, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; 973p. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; 824p. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. EoS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; 542p. [Google Scholar]
- Pebesma, E.J. Multivariable geostatistics in S: The gstat package. Com. Geos. 2004, 30, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräler, B.; Pebesma, E.; Heuvelink, G. Spatio-Temporal interpolation using gstat. R J. 2016, 8, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nessim, R.B.; Tadros, H.R.Z.; Taleb, A.E.A.; Moawad, M.N. Chemistry of the Egyptian Mediterranean coastal waters. Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahman, K.; Larabi, A. Evaluation and numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in the Gaza aquifer (Palestine). Hydrogeo. J. 2006, 14, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, S.; Fischbach, J.R.; Blum, I.; Karimov, R.I.; Moore, M. The Public Health Impacts of Gaza’s Water Crisis: Analysis and Policy Options; RAND Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2018; 87p. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Securing Water for Development in West Bank and Gaza; International Bank for Reconstruction and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; 30p. [Google Scholar]







| Chemical Parameter | Unit | Standard | Weight | Relative Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Wi | wi | ||
| pH | - | 6.5–8.5 | 3 | 0.103 |
| TDS | mg/L | 500 | 5 | 0.172 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 75 | 2 | 0.069 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 50 | 2 | 0.069 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 200 | 3 | 0.103 |
| K+ | mg/L | 12 | 1 | 0.034 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 120 | 2 | 0.069 |
| SO42– | mg/L | 250 | 3 | 0.103 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 250 | 3 | 0.103 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 45 | 5 | 0.172 |
| Total | 29 | 1.000 |
| WQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|
| Range | Class |
| <0.5 | Excellent |
| 0.5–1 | Good |
| 1–2 | Poor |
| 2–3 | Very poor |
| >3 | Unsuitable |
| Well | pH | TDS | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | HCO3− | SO42– | Cl− | NO3− | E | WQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | % | Score | Class | |
| W1 | 7.40 | 3241 | 190 | 105 | 670 | 5.7 | 273 | 265 | 1126 | 139 | 3.76 | 3.15 | Unsuitable |
| W2 | 7.10 | 2737 | 161 | 103 | 480 | 7.9 | 574 | 267 | 920 | 200 | −7.97 | 3.18 | Unsuitable |
| W3 | 7.30 | 2912 | 182 | 132 | 524 | 8.1 | 421 | 252 | 987 | 191 | −0.14 | 3.22 | Unsuitable |
| W4 | 7.60 | 3493 | 226 | 125 | 640 | 14.5 | 323 | 204 | 1269 | 183 | 1.49 | 3.54 | Unsuitable |
| W5 | 7.10 | 3108 | 160 | 141 | 600 | 7.5 | 268 | 380 | 1140 | 147 | −0.99 | 3.18 | Unsuitable |
| W6 | 7.60 | 2877 | 131 | 86 | 775 | 5.5 | 231 | 272 | 1028 | 54 | 9.34 | 2.62 | Very poor |
| W7 | 7.00 | 2779 | 174 | 128 | 620 | 5.1 | 286 | 241 | 973 | 113 | 8.64 | 2.82 | Very poor |
| W8 | 7.10 | 2597 | 160 | 139 | 660 | 9.1 | 370 | 511 | 821 | 132 | 7.04 | 2.96 | Very poor |
| W9 | 7.90 | 1953 | 86 | 57 | 480 | 4.0 | 233 | 204 | 662 | 38 | 4.54 | 1.82 | Poor |
| W10 | 7.80 | 2198 | 111 | 71 | 520 | 4.2 | 246 | 209 | 759 | 62 | 5.11 | 2.11 | Very poor |
| W11 | 8.00 | 715 | 62 | 31 | 130 | 1.2 | 201 | 60 | 172 | 50 | 5.43 | 0.92 | Good |
| W12 | 7.60 | 1932 | 112 | 58 | 460 | 11.1 | 323 | 186 | 655 | 99 | 2.33 | 2.12 | Very poor |
| W13 | 7.50 | 2114 | 80 | 35 | 440 | 2.6 | 266 | 186 | 717 | 61 | −6.02 | 1.94 | Poor |
| W14 | 7.30 | 1631 | 84 | 38 | 310 | 2.8 | 360 | 65 | 552 | 42 | −5.96 | 1.57 | Poor |
| W15 | 7.60 | 2002 | 74 | 53 | 400 | 4.1 | 254 | 227 | 632 | 43 | −3.53 | 1.81 | Poor |
| W16 | 7.20 | 3598 | 165 | 123 | 780 | 17.4 | 427 | 511 | 1160 | 190 | −0.64 | 3.77 | Unsuitable |
| W17 | 7.50 | 2100 | 138 | 73 | 360 | 6.7 | 248 | 128 | 681 | 102 | 2.05 | 2.12 | Very poor |
| W18 | 7.50 | 2233 | 121 | 60 | 455 | 5.1 | 273 | 156 | 681 | 120 | 3.41 | 2.27 | Very poor |
| W19 | 7.50 | 2436 | 150 | 97 | 370 | 7.7 | 278 | 407 | 698 | 120 | –4.37 | 2.49 | Very poor |
| Mean | 7.45 | 2456 | 135 | 87 | 509 | 6.9 | 308 | 249 | 823 | 110 | 1.24 | 2.51 | |
| SD | 0.28 | 700 | 45 | 37 | 163 | 4.0 | 90 | 126 | 265 | 55 | 5.08 | 0.75 |
| Well | pH | TDS | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | HCO3− | SO42– | Cl− | NO3− | E | WQI | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | % | Score | Class | |
| W1 | 7.95 | 3409 | 207 | 117 | 760 | 6.0 | 328 | 312 | 1279 | 144 | 2.80 | 3.43 | Unsuitable |
| W2 | 7.76 | 2912 | 176 | 116 | 560 | 6.3 | 598 | 331 | 1032 | 211 | −6.91 | 3.44 | Unsuitable |
| W3 | 7.50 | 3493 | 198 | 147 | 660 | 6.8 | 578 | 353 | 1179 | 236 | −2.89 | 3.91 | Unsuitable |
| W4 | 7.65 | 3514 | 243 | 168 | 760 | 15.2 | 397 | 273 | 1389 | 233 | 3.73 | 4.01 | Unsuitable |
| W5 | 7.54 | 3395 | 179 | 162 | 740 | 7.7 | 281 | 413 | 1272 | 171 | 2.64 | 3.57 | Unsuitable |
| W6 | 7.71 | 3031 | 155 | 98 | 863 | 5.6 | 271 | 329 | 1259 | 72 | 5.44 | 2.97 | Very poor |
| W7 | 7.53 | 2968 | 185 | 137 | 674 | 5.7 | 313 | 273 | 1124 | 122 | 5.80 | 3.06 | Unsuitable |
| W8 | 8.16 | 3003 | 189 | 146 | 720 | 5.4 | 409 | 535 | 1022 | 169 | 3.43 | 3.42 | Unsuitable |
| W9 | 7.77 | 1862 | 96 | 59 | 509 | 4.2 | 246 | 241 | 708 | 47 | 3.43 | 1.90 | Poor |
| W10 | 7.51 | 2359 | 132 | 86 | 634 | 5.7 | 323 | 277 | 853 | 79 | 6.42 | 2.45 | Very poor |
| W11 | 7.66 | 774.2 | 64 | 44 | 164 | 1.4 | 216 | 71 | 191 | 62 | 10.16 | 1.04 | Poor |
| W12 | 7.61 | 2170 | 136 | 74 | 503 | 6.1 | 382 | 262 | 794 | 118 | −1.56 | 2.45 | Very poor |
| W13 | 8.20 | 2464 | 98 | 53 | 523 | 3.7 | 304 | 218 | 893 | 83 | −5.80 | 2.35 | Very poor |
| W14 | 8.10 | 1729 | 97 | 58 | 398 | 3.7 | 394 | 103 | 623 | 52 | 0.01 | 1.81 | Poor |
| W15 | 7.09 | 2366 | 91 | 67 | 530 | 4.5 | 360 | 277 | 777 | 55 | −1.84 | 2.22 | Very poor |
| W16 | 7.90 | 3906 | 169 | 136 | 860 | 20.0 | 456 | 554 | 1326 | 204 | −1.84 | 4.11 | Unsuitable |
| W17 | 8.00 | 2954 | 153 | 92 | 461 | 7.5 | 293 | 154 | 998 | 126 | −3.72 | 2.77 | Very poor |
| W18 | 8.10 | 2975 | 133 | 83 | 630 | 6.1 | 311 | 182 | 977 | 133 | 3.06 | 2.87 | Very poor |
| W19 | 7.68 | 2618 | 169 | 106 | 503 | 6.8 | 311 | 442 | 872 | 132 | –2.26 | 2.81 | Very poor |
| Mean | 7.80 | 2732 | 151 | 103 | 603 | 6.8 | 356 | 295 | 977 | 129 | 1.06 | 2.87 | |
| SD | 0.30 | 749 | 47 | 39 | 170 | 4.2 | 101 | 129 | 293 | 62 | 4.51 | 0.81 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Baba, M.; Kayastha, P.; Huysmans, M.; De Smedt, F. Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine. Water 2020, 12, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010262
El Baba M, Kayastha P, Huysmans M, De Smedt F. Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine. Water. 2020; 12(1):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010262
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Baba, Moustafa, Prabin Kayastha, Marijke Huysmans, and Florimond De Smedt. 2020. "Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine" Water 12, no. 1: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010262
APA StyleEl Baba, M., Kayastha, P., Huysmans, M., & De Smedt, F. (2020). Evaluation of the Groundwater Quality Using the Water Quality Index and Geostatistical Analysis in the Dier al-Balah Governorate, Gaza Strip, Palestine. Water, 12(1), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010262