Abstract
The territory of Lithuania is characterized by a prevailing moisture excess, therefore in order to timely remove excess water from arable lands, the drainage systems have long been installed. In order to drain excess water people used to dig trenches, to regulate (deepen or straighten) natural streams. The length of regulated streams has reached 46,000 km and they are deteriorated ecosystems. Investigations showed that the self-purification of streams from nitrates and phosphates is more effective in natural stretches than in stretches regulated for drainage purposes. Decrease in the average concentration of nitrates in natural and regulated stretches are 8.8 ± 5.0 and 3.0 ± 2.9 mg L−1, respectively. The average coefficient of nitrate self-purification, at a confidence level of 95% in natural stream stretches is 0.50 ± 0.22, and in regulated is −0.15 ± 0.21 km−1, and this difference is essential. The change in the average concentration of phosphates in natural and regulated stretches is almost the same, 0.2 ± 0.1 and 0.2 ± 0.2 mg L−1, respectively. The average coefficient of phosphate self-purification, at a confidence level of 95%, in natural stream stretches is 0.28 ± 0.12, in regulated −0.14 ± 0.12 km−1, and this difference is not essential. In terms of the need for the renovation of drainage systems it is suggested that soft naturalization measures are first applied in the streams of Western (Samogitian) Highlands, Coastal Lowlands, and South-Eastern Highlands to improve their self-purification processes.
1. Introduction
Small-sized rivers, their headwaters, and wetlands have a significant effect on the adjustment of river flow, retention of outwash and pollutants, and preservation of biological diversity. Unfortunately, intensive urbanization affects the channels of small rivers and adjacent ecosystems and strongly influences their ecological status [1]. Intensive use of European rivers for human purposes in the last hundred years has changed natural water flows, their physical and chemical properties, channel morphology, and species composition of local flora and fauna. The former natural, curving river channels were straightened and deepened, artificial slopes were formed having nothing to do with nature. Seeking to adjust flow rate, and due to recreational purposes, people built dams, and sometimes water energy was used in hydropower engineering [2,3,4].
At the end of the 20th century, with a constant growth of world population the cereals production almost doubled, the use of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) fertilizers, related to the increasing food demand, has grown by 6.9 and 3.5 times. From environmental point of view, a large amount of N and P fertilizers was used improperly in the lands of agricultural designation and has essentially changed biogeochemical cycles of these two main nutrients [5]. The expanded network of small rivers and trenches was filled with a large amount of pollutants, including nutrients, pesticides, heavy metals, and soil particles washed out from adjacent fields. Due to the physical and chemical impact on river channel and its water flow, part of local flora and fauna species became extinct, and part of them were replaced by invasive or introduced species [1].
Baczyk A. et al. [6] maintains that this negative anthropogenic effect has been widely described in many world-wide countries and even 96% of the articles analyzed reported a unilateral negative anthropogenic impact on water ecosystems, especially on invertebrates and fishes.
The territory of Lithuania is characterized by a prevailing moisture excess; the average annual amount of precipitation reaches 750 mm, evaporation comes to 512 mm [7,8], and therefore, the excess water is frequently accumulating in the soils of low-gradient and heavier gradation soils (clays, loam) of plains and depressions of hilly relief, due to low infiltration. To timely remove excess water from arable lands the drainage systems has long been installed, i.e., a complex of functionally related hydraulic structures located at the territory to be drained and intended for adjusting the soil moisture regime and creating favorable growing conditions for vegetation.
At the beginning of the 19th and 20th century, the largest attention when draining lands was paid to the regulation of rivers and streams and to digging of discharge trenches. Until 1958, lands were still drained by trenches, but later people started using drainage, since this was a world-recognized and more effective draining method. For the streams to be regulated, water intakes are usually curved, waterlogged, overgrown with water plants, having the already formed natural riparian lanes. Water depth and flow rate in these channels are usually low, water lies close to the surface, and floods take a long period.
Human activities, aimed to increase used agricultural and wooded areas, most of all changed small streams and the upper reaches of rivers: they were regulated to remove excess water collected by drainage, straightened to increase the flow rate and water capacity, or deepened to accommodate for at least 1.50 m depth of the river channel required for installing drainage system.
Thus, the regulated stream does not differ from a trench that was dug. The regulated streams and trenches served as a draining network.
During almost 100 years of land drainage in Lithuania, the streams were regulated, trenches were dug, and drainage systems were installed. Within this period, the area of drained land reached 3.02 million ha (47% of the total area of the country), of which 2.62 million ha were drained with the help of drainage, and 52,454 km of main drainage trenches were regulated and dug.
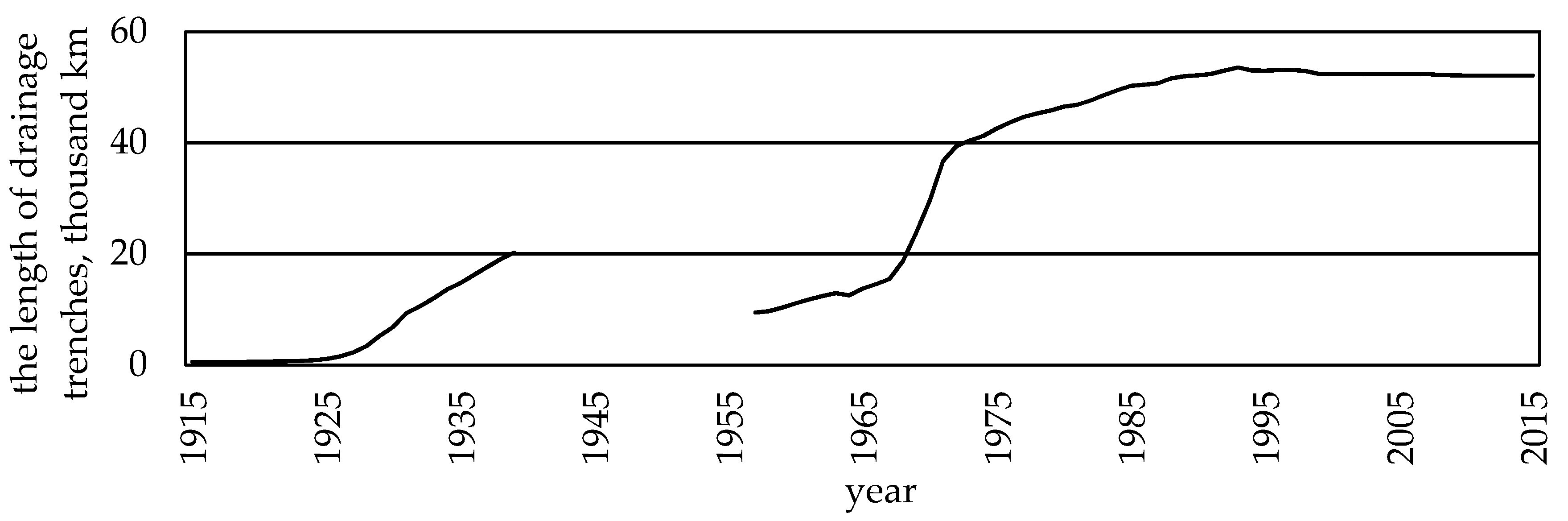
Land drainage has changed landscape structure, especially by a majority of newly dug trenches (Figure 1). The lowest density of trenches was found in plain regions where the most fertile clayey soils were drained. In hilly relief conditions the density of trenches remained higher.
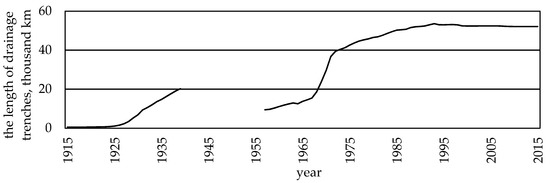
Figure 1.
Dynamics in regulated stream channels and main drainage trenches in Lithuania.
The length of drainage trenches had an effect on the density of the total Lithuanian hydrographic network. What concerns the total length of trenches in the territory of Lithuania it was obviously increasing. In 1930, the density of trenches was 0.1 km/km2, in 1945—0.34, in 1960—0.69, in 1975—0.76, and in 1999 even 0.96 km/km2. Such density of ditches was determined by the deepening, widening and straightening of natural stream channels, i.e., after they became main drainage trenches, and later—regulated streams. In such a way the length of regulated streams reached 46,000 km [8,9].
If the concept of regulated stream can be related to the adaptation of stream to serve draining function (to timely discharge certain amount of excess water necessary to drain the area), from the ecological point of view this is a deregulation of the natural stream and should be related to the destruction of the stream’s ecosystem.
When carrying out regulation of streams the fact of deepening and straightening of natural stream channels used to be emphasized, though at the same time the riparian zones of streams were destroyed. There are not many studies focused on the retention processes of biogenic materials in protective riparian zones. Results of nitrogen retention in protective riparian zones are different [10,11,12,13], however water running through the ecosystem of riparian zone is able to retain up to 74% ± 4% of nitrogen. Data shows that with the increasing width of protective riparian zone the retention efficiency also increases [14], however this relationship is statistically stronger when the zone between the cultivated land and the river border >50 m.
Some authors argue that the efficiency of protective zones in retaining phosphorus is highly dependent on parameters such as vegetation cover type and density, topography, soil, climatic conditions, however, it is of short-term, seasonal in character, as long as plant vegetation continues [11]. The largest amount of total phosphorus is washed out in early spring before the start of vegetation. At that time, the efficiency of protective zone is poor, especially in the case where riversides are overgrown mostly with grass. The outwash is slightly better retained in protective zones overgrown with trees and bushes, though due to decomposition of organic material the amount of mobile phosphorus in these zones is increased [15]. Despite this, many agricultural consultants, planners and practitioners recommend the grass-overgrown protective riparian zones as a measure to settle phosphorus compounds in the areas of intensive agriculture.
There have been various recommendations for defining the main parameter of protective zones, i.e., width [16,17,18]. It was proven that a long-term efficiency can be reached where the zones are wider, 30 m-wide. In agricultural landscape, as suggested by foreign authors, the absolute minimum width should be 10 m. When designing protective riparian zones, it is necessary to take into account not only width requirements but also no less important parameters, such as vegetation species and distribution, slope gradients, soil types, topography, rainfalls [19,20].
In Lithuania, the minimum required depth of stream channel for the installation of drainage systems was about 1.5 m. In the upstream, where the basin area is not large, the stream channel has excessive depth and water collected from the area to be drained does not fill the whole cross-section area with water. Thus, there is a possibility to the improve ecological situation by growing bushes and small trees on the upper part of channel slope, and to manage the lower part of channel in a way that channel capacity corresponds to the requirements for draining function.
The authors suggest an alternative way of maintaining regulated streams (trenches): to allow the overgrowing of slopes with woody vegetation, the crowns of which would shadow the channel and strengthen the slopes [8,21,22]. Depending on the tendencies of species distribution in landscape and in cross-section of the trench, the restoration of dendrology in a desirable direction can be promoted artificially by planting special species or correcting their varietal composition in slopes, also by forming protective zones. This makes it possible when operating trenches to develop their natural functions and to also preserve drainage functions. The process of overgrowing of drainage network with trees can be assessed with ambiguity: reduces hydraulic capacity but makes a positive effect on landscape structure, reduces deflation probability, accumulation of outwash, and pollution of water bodies. Once the right of land ownership was given back to people, the land use intensity started to change. In less-favored areas for developing agriculture the drainage systems is used not intensively. Still, there are locations where drainage systems are outdated, their condition is bad. More than 45% of drainage systems are older than 40 years [23].
Over the last few decades, the number of projects of river naturalization has highly increased in most developed countries in Europe and all over the world [24,25,26,27]. Implementation of river naturalization projects is usually very expensive and the real benefit is not always evident. The analysis, carried out by German specialists [28], showed that the accomplished naturalization processes made no improvements to the population of benthic invertebrates. It was also reported that restoration of this population depends on whether there are any specimens of this species in adjacent waters. This research shows that the processes are not yet fully investigated and that slightly different results may be obtained under different natural conditions.
A very important indicator, showing an overall ecological status of the river, is self-purification [29]. It occurs due to water attenuation with surface and ground waters or due to certain hydrological, biological and chemical processes, such as sedimentation, coagulation, evaporation, sedimentation of colloidal and their further consolidation on the bottom of water body or, finally, due to pollutants assimilation with the living organisms. The level of self-purification in each water body depends on certain factors, such as temperature, water level, river flow rate, hydrological regime, tidal regime, amount of inorganic compounds in water, sediment characteristics, amount of pollutants, phytoplankton, benthic invertebrate fauna, fish fauna, and algae species, and their distribution [30,31].
The aim of the research is to determine the distribution of nitrate and phosphate concentrations in the water of natural and regulated for drainage streams and the influence of regulation on the self-purification efficiency of the streams.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location, Sampling Points
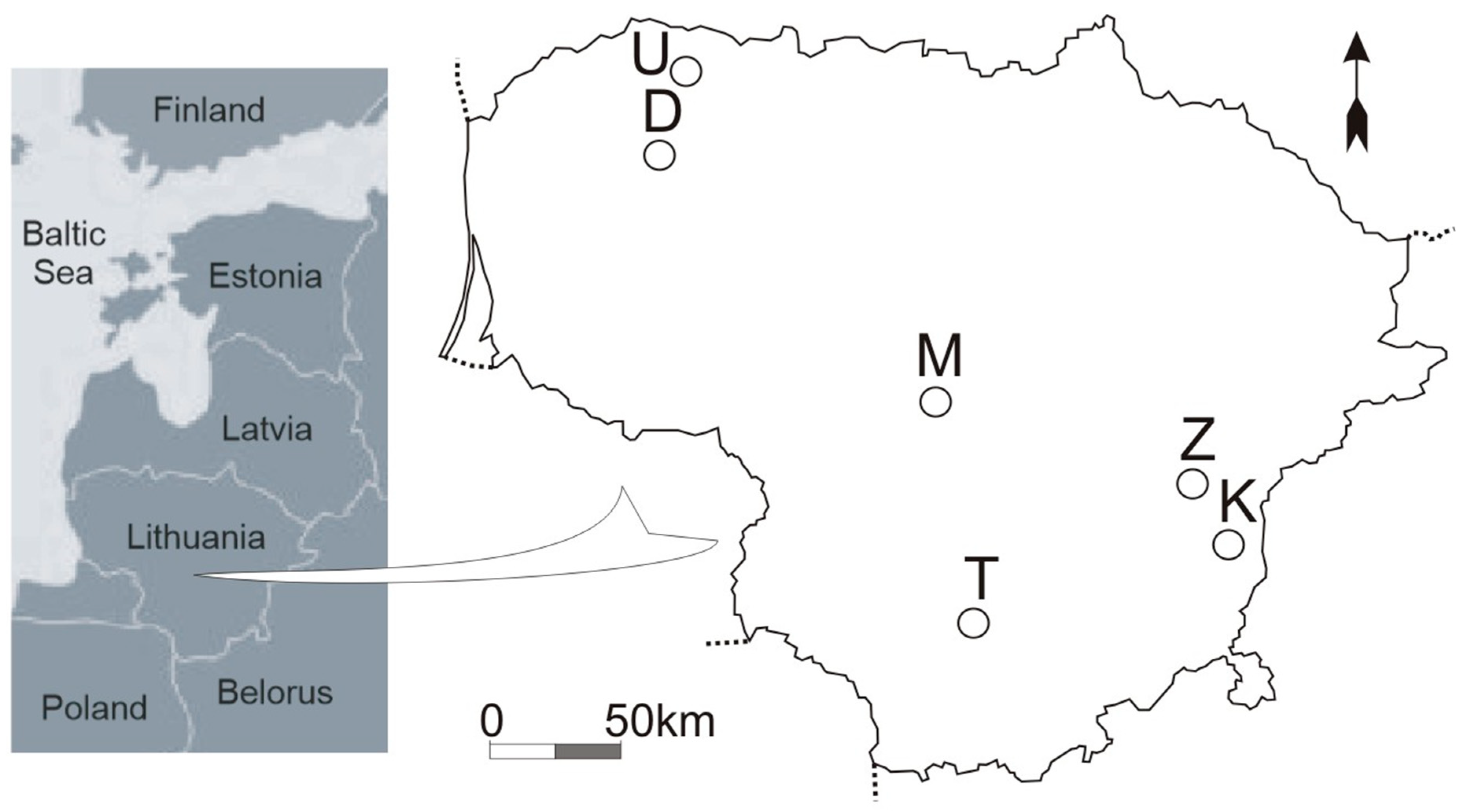
The research was carried out in Lithuania, in the Baltic Sea region, in the Nemunas and Venta river basins. The research included regulated and unregulated stretches of the following streams: Terpinė (T), Žalesa (Z), Kuosinė (K), Mėkla (M), Durbinis (D), and Uogis (U). Distribution of the relevant stretches in the territory of Lithuania is given in Figure 2 and Table 1. The relevant stretches were coded. The first letter indicates the relevant stream according to the first letter of its name. The second letter indicates whether the stream is regulated or natural (the sampling place in the natural stream channel is marked by N, in the regulated—by R). The beginning of the stretch is marked by s; the end—by e.
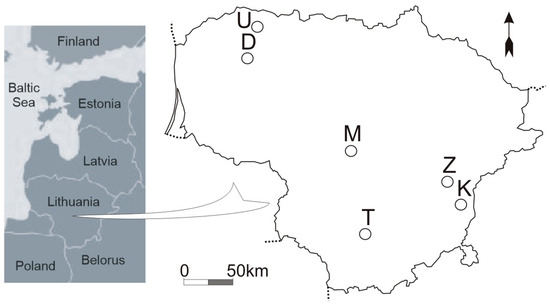
Figure 2.
Distribution of the relevant stretches in the territory of Lithuania.

Table 1.
Characteristics of used streams.
2.2. Time of Research, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations
Water samples for water quality analysis were taken in accordance with the sampling standard [32] taking into consideration all the water sampling aspects. Water samples were taken once per month in the period from August 2013 to February 2019. The investigation in different stretches lasted 12–24 months. Concentrations of nitrates () and phosphates () were determined. The amount of nitrates in water was measured by the photometer HANNA HI 83,205 using the cadmium reduction method and HI 93728-01 reagents. Concentrations of nitrates and phosphates in the samples taken were determined in the Laboratory of Hydraulics of Vilnius Gediminas Technical University.
According to the average annual value of each index a water body is attached to one of the five classes of ecological status. The obtained average annual values were compared to the values presented in the ecological status classification according to the physicochemical quality elements (Table 2) [33,34,35].

Table 2.
Ecological status classification according to the physicochemical quality elements [33,34,35].
In the assessment many parameters (physicochemical, hydromorphological, biological) are used to determine the ecological status class. In the given article we have only rated according to two of them, and .
For the assessment of river self-purification from biogenic substances, the following simplified river purification formula was used [36]:
where: C0—concentration of chemical material at the beginning of the relevant river stretch mg L−1; CL—concentration of chemical material at the end of the relevant river stretch mg L−1; L—length of river stretch km; α-river purification coefficient km−1.
The statistical method of one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), at confidence level of 95%, was used to determine whether the mean values of the self-purification coefficients for natural and regulated streams differed significantly. SPSS Statistics software was used for statistical processing.
2.3. Distribution of Sediment and Used Agricultural Areas
Distribution of sediment and used agricultural areas in the relevant river basins was studied according to the information provided in the Spatial Information Portal of Lithuania [37]. The portal provides data about typological units and gradation of the analyzed soil contour of the used agricultural area, also about land irrigation status and water logging, variety of soil cover, climatic conditions, soil stoniness, agrochemical properties, base index, and soil productivity index of the analyzed soil contour. However, the determination of the agents influencing the self-purification intensity of the stretches of the studied streams is very complex, due to the abundance and diversity of the factors and will be probably addressed in the future.
3. Results
According to the Spatial Information Portal of Lithuania, the main sediment in the relevant river basins is sandy loam and light loam which are prevailing in all basins. The river basins also contain light and medium loam, adhesive sand, light and average clay, and peat. Distribution of the used agricultural areas within the river basins showed that the largest part of the river basins is taken up by permanent grasslands, arable lands, forests, urbanized territory, and pastures (Table 3).

Table 3.
Soil gradation, used agricultural areas and soil productivity index of the river basins.
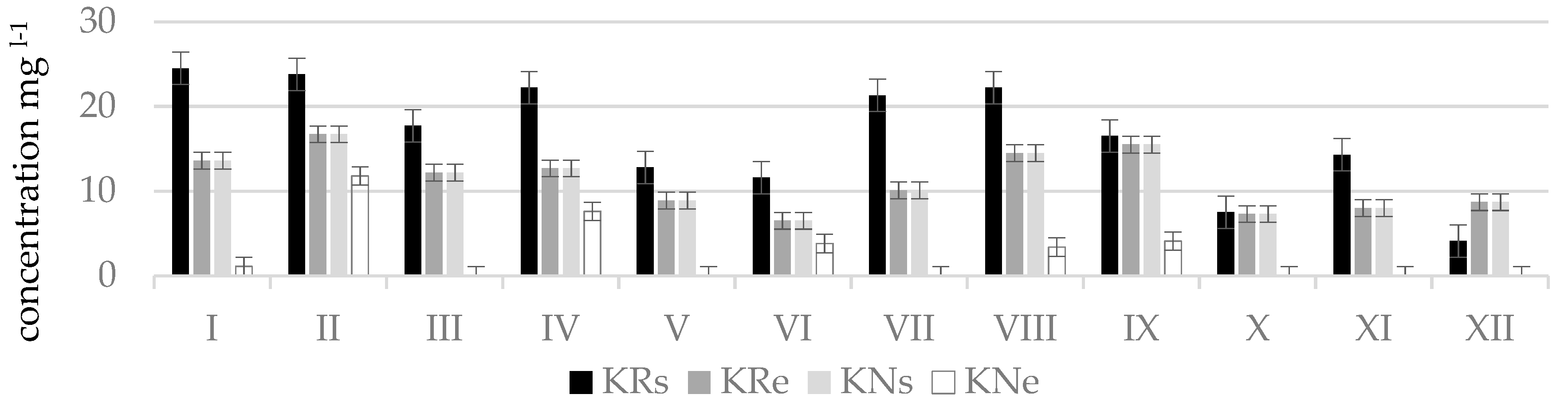
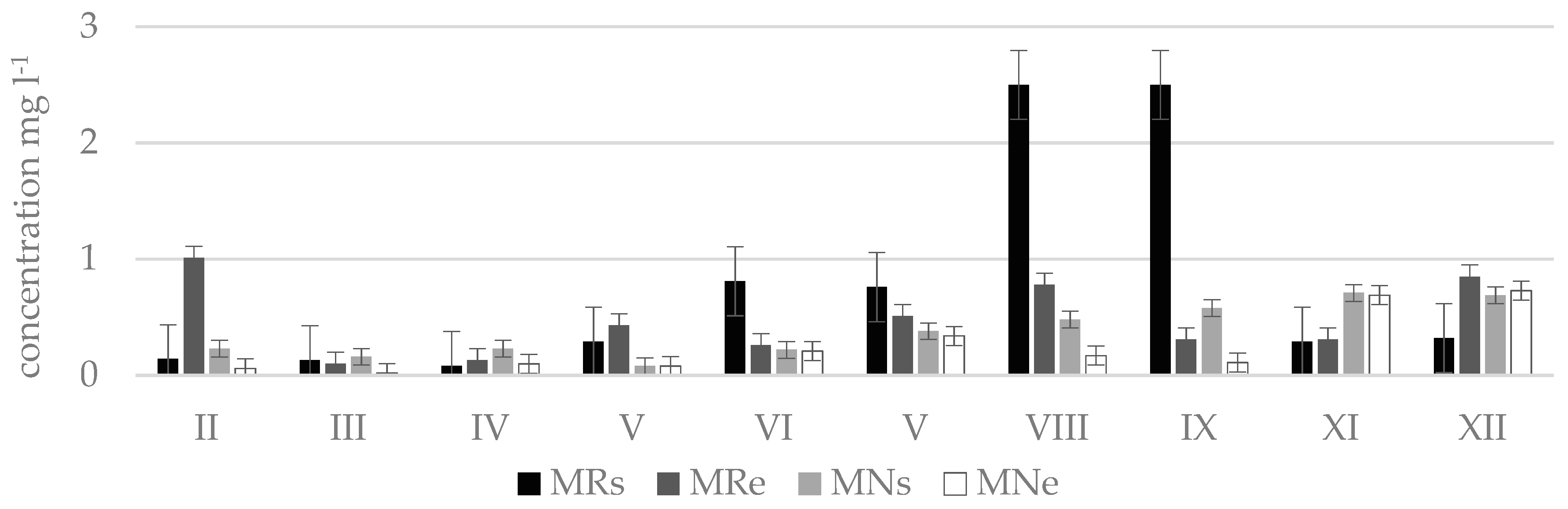
The research and analysis of results showed that nitrate concentrations according to their amount and period are distributed rather differently. Many results showed that water quality in the relevant streams exceeded the limit value of good ecological status (nitrate concentrations 10.18 mg L−1) and could be attributed to moderate and poor ecological status. The worst results were represented by Terpinė, Mėkla, and Kuosinė streams. The best ecological status was found in Žalesa stream [38].
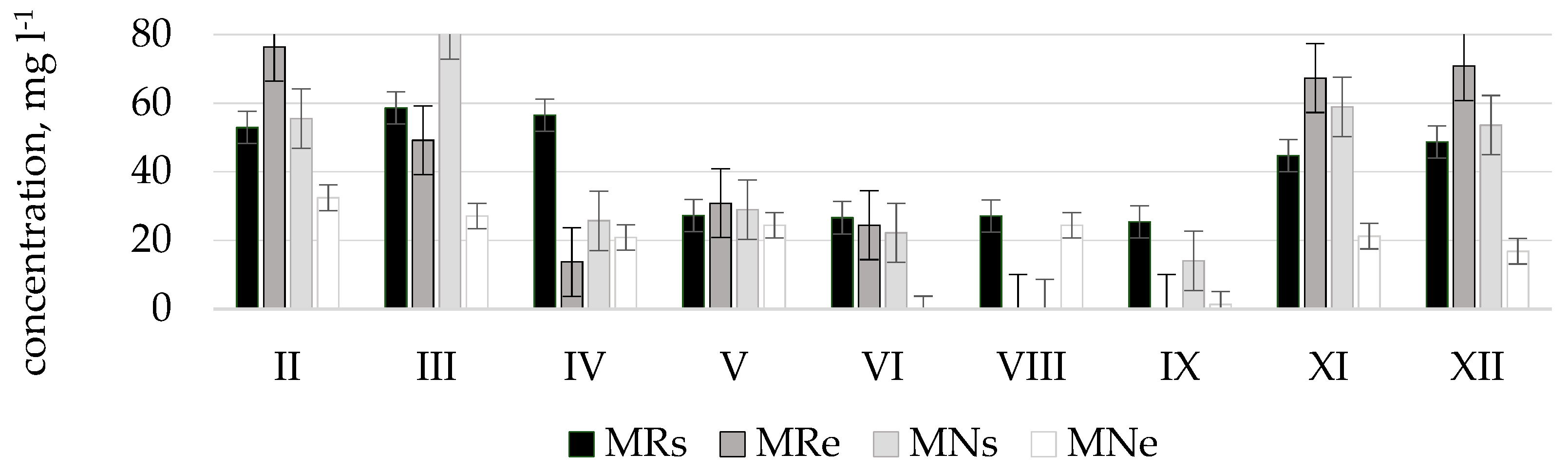
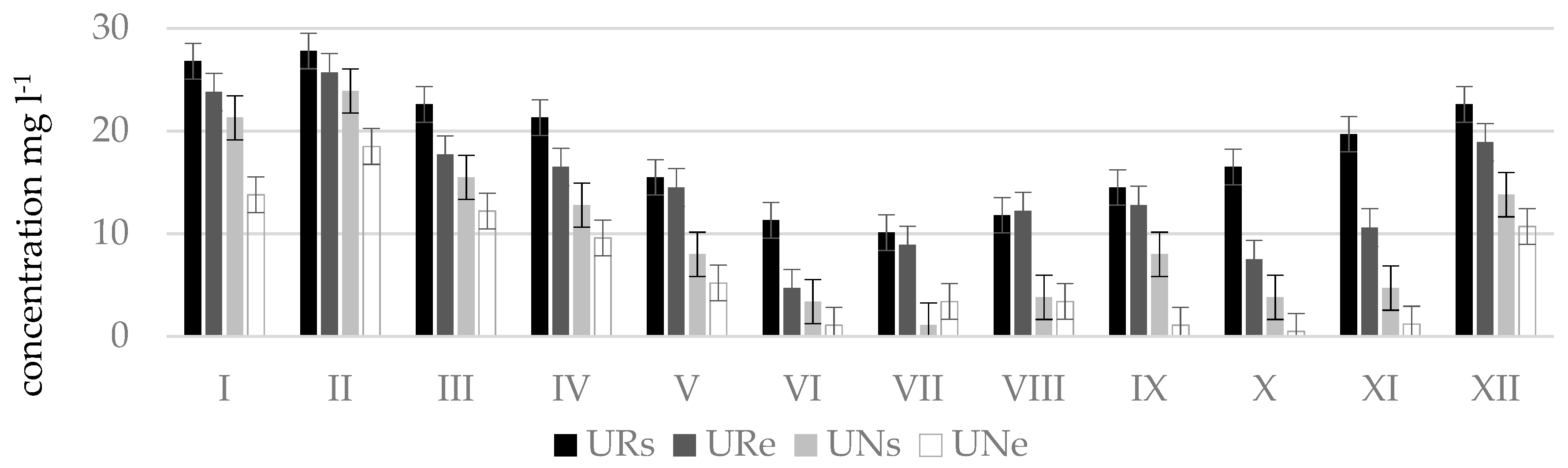
The worst water quality was observed in winter months since at this time of the year maximum concentrations of nitrogen oxides were determined which corresponded to the poor or bad ecological status: in Terpinė stream, at point TRe (41.5 mg L−1, in December); in Mėkla stream, at point MNs (81.4 mg L−1, in March); MRe (76.4 mg L−1, in February); in Kuosinė stream, at point KRs (24.5 mg L−1, in January); in Durbinis stream, at point DRe (26.1 mg L−1, in December). During vegetation period nitrate concentrations were lower. This was especially characteristic of the Durbinis, Mėkla (Figure 3), and Uogis streams (Figure 4). However, in the Kuosinė (Figure 5) and Terpinė streams the relatively large nitrate concentrations were measured even in vegetation period. This could be caused by a more abundant fertilization of arable lands in summer and autumn. The average annual consumption of fertilizers in Lithuanian agriculture in recent years (2016–2018) is 162,000 tons of nitrogen (N) and 52,000 t of phosphorus (P2O5). Winter crops were fertilized with 100–150 kg (N) ha−1 and 50–75 kg (P2O5) ha−1, sugar beet 100–130 kg (N) ha−1, and 80–90 kg (P2O5) ha−1 [39]. As a result, a higher amount of nitrate pollutants is washed out into the rivers. In summer time, due to a shallow water the river water is less diluted.
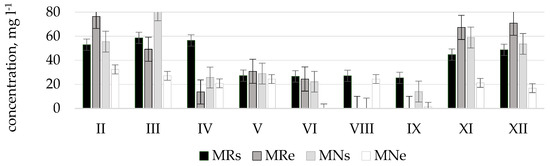
Figure 3.
Nitrate concentrations () in natural (N) and regulated (R) stretches of Mėkla stream.
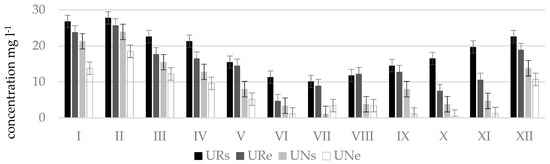
Figure 4.
Nitrate concentrations () in natural (N) and regulated (R) stretches of Uogis stream.
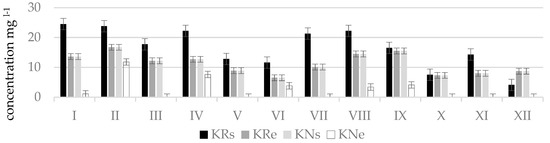
Figure 5.
Nitrate concentrations () in natural (N) and regulated (R) stretches of Kuosinė stream.
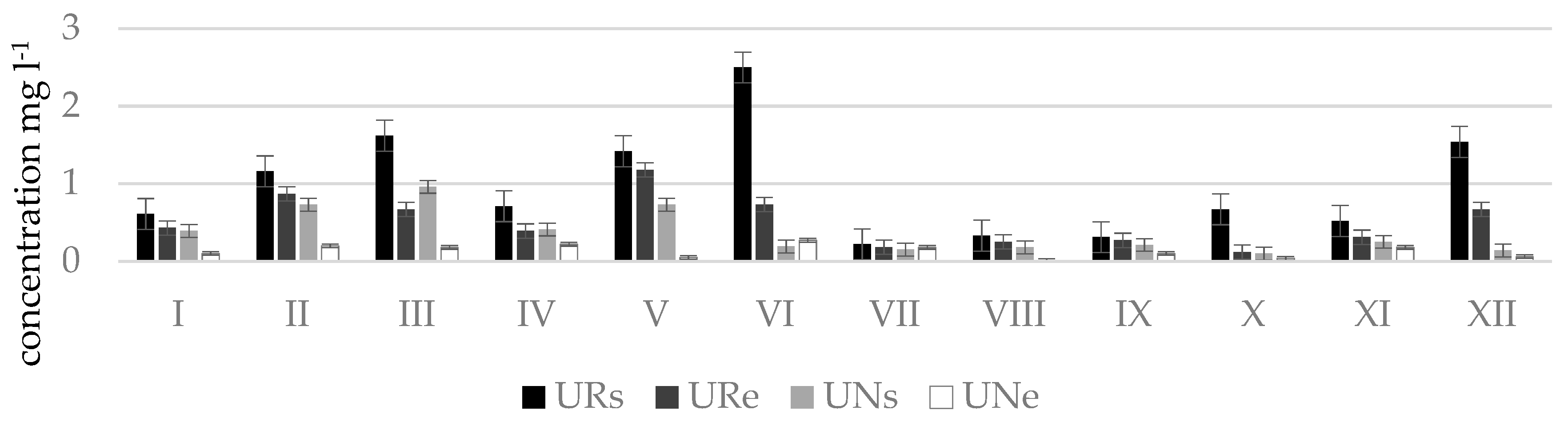
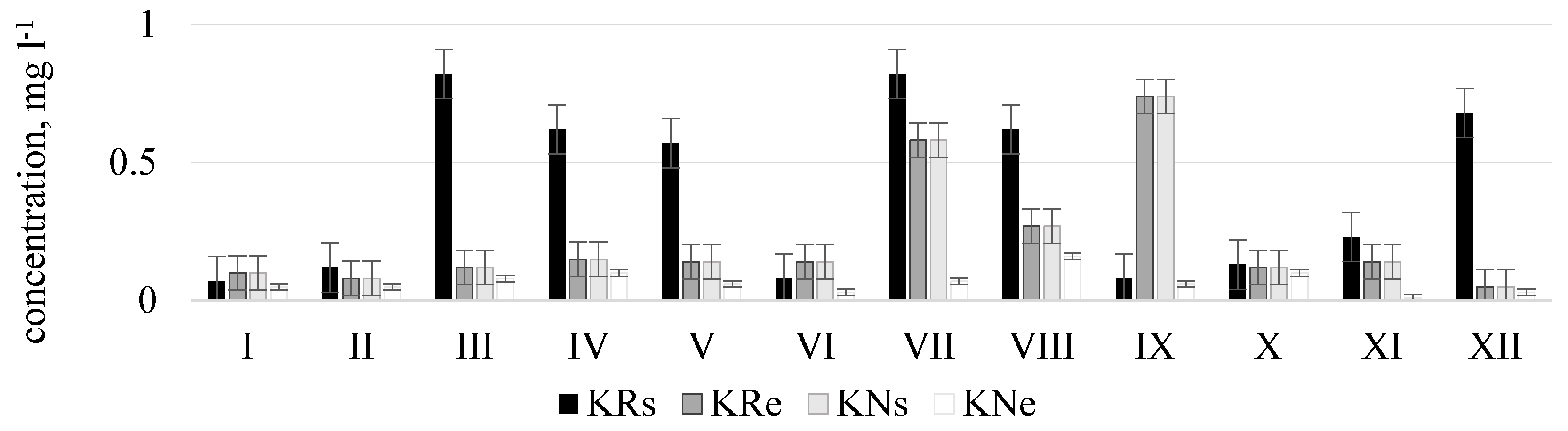
The measurement results showed that phosphate concentrations according to their amount and period, same like nitrates, are distributed rather differently and water quality in streams frequently exceeded the limit value for good ecological status (phosphate concentrations 0.28 mg L−1) and corresponded to the poor or bad ecological status (Figure 6). Very high phosphate concentrations were measured in the Durbinis stream where no seasonality was observed since phosphate concentrations were very high during all months. The maximum concentration measured was 2.5 mg L−1. Based on this concentration the river water corresponded to the bad ecological status (>1.23 mg L−1). In Uogis stream (Figure 7), according to phosphate concentrations in water in a period of even four moths (March, May, June, and December) at the beginning of regulated stretch (point Urs) the ecological status of the stream was bad, however at the end of natural stretch (point Une) in a period of six months (March, April, June, July, November, and February) the stream had a prevailingly good ecological status, and in the remaining six months (May, August, September, October, December, and January) high ecological status. According to phosphate concentrations the Kuosinė stream (Figure 8) represented high ecological status of water quality in January, February, June, and October as well as poor ecological status in December, March, and July in KRs stretches
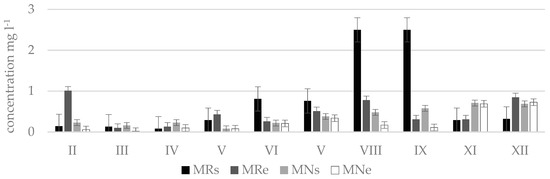
Figure 6.
Phosphate concentrations () in natural (N) and regulated (R) stretches of Mėkla stream.
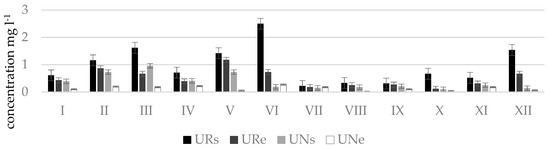
Figure 7.
Phosphate concentrations () in natural (N) and regulated (R) stretches of Uogis stream.
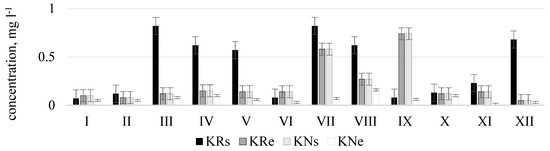
Figure 8.
Phosphate concentrations () in natural (N) and regulated (R) stretches of Kuosinė stream.
Based on the measured concentrations of nitrates and phosphates the average values at the end of stretches and self-purification coefficients were calculated in order to find out how the river is able to purify itself from pollutants. The average concentration of nitrates in natural stretches was twice lower than that in regulated stretches, i.e., 9.3 ± 2.7 and 18.5 ± 6.1 mg L−1, respectively. The average concentration of phosphates in natural stretches was also lower than that in regulated stretches, i.e., 0.4 ± 0.2 and 0.7 ± 0.2 mg L−1, respectively.
The average change of concentrations, determined at the beginning and at the end of river stretches, and the calculated self-purification coefficients showed that streams purify better in natural stretches, further research into organic matter could, of course, further substantiate the purification efficiency. Decrease in nitrate concentrations in natural stretches was 8.8 ± 5.0, in regulated−3.0 ± 2.9 mg L−1, decrease in phosphate concentrations was 0.2 ± 0.1 and 0.2 ± 0.2 mg L−1, respectively (Table 4). The average nitrate self-purification coefficient of all streams was 0.50 ± 0.22 km−1 in unregulated stretches, and 0.15 ± 0.21 km−1 in regulated stretches. The average phosphate self-purification coefficient in natural stretches was 0.28 ± 0.12 km−1, in regulated −0.14 ± 0.12 km−1.

Table 4.
Average decrease in nitrate and phosphate concentrations in natural and regulated stream stretches and self-purification coefficients (R-regulated stretch, N-natural stretch).
What concerns separate streams, the best phosphate self-purification coefficient was determined in natural stretches of Uogis (0.74 ± 0.34 km−1) and Žalesa (0.32 ± 0.61 km−1). The nitrate self-purification coefficient in the natural stretch of Žalesa even reached 1.01 ± 0.38 km−1, and in the natural stretch of Kuosinė −0.99 ± 0.41 km−1. The negative values of self-purification coefficient were calculated in the regulated stretches of Terpinė stream (Table 4).
A high value of self-purification coefficient in the natural stretch of Žalesa stream could be influenced by the adjacent permanent grasslands and forests. Decrease in pollutant concentrations can also be determined by the dilution of polluted water with surface and underground waters. It should be mentioned that the right tributary flows into the Žalesa in the stretch ZNs–ZNe. The inflowing stream water could dilute the nitrate-polluted water of the Žalesa and thus contribute to the decrease in nitrate concentrations. The natural stretch of the Kuosinė stream is surrounded by forests. The self-purification was influenced not only by a natural river stretch but also by the adjacent used agricultural land, since it was likely that the access of nitrates into water was limited.
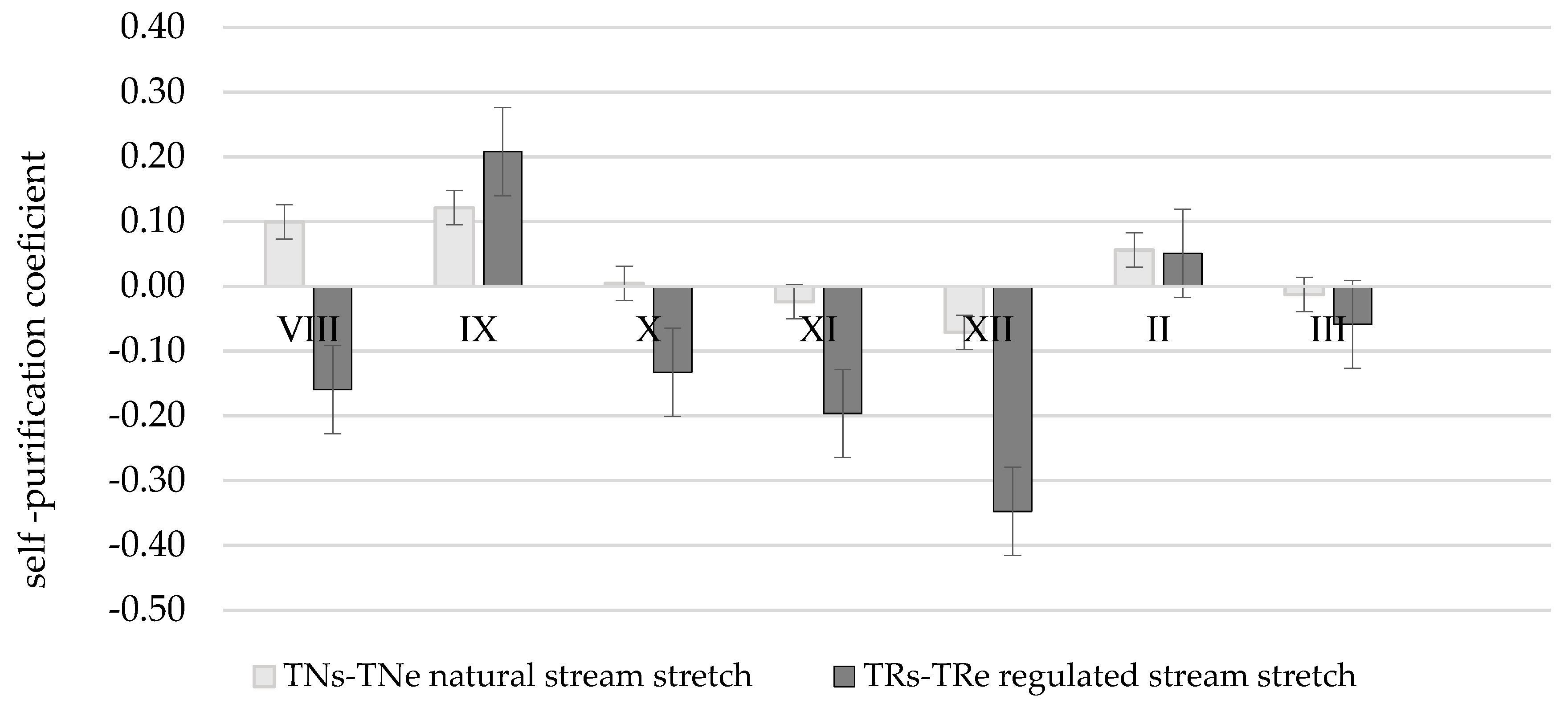
Nitrate self-purification coefficients are obviously different when comparing natural and regulated stretches of Terpinė stream (Table 4; Figure 9).
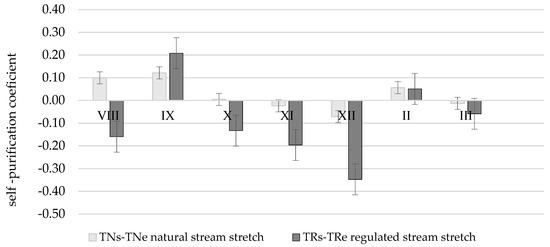
Figure 9.
Nitrate () self-purification coefficient in Terpinė stream.
The whole TNs-TNe stretch is a natural part of the Terpinė stream abundant in meanders thus the river flow rate is lower and detention of nitrates is higher. Nitrate () self-purification coefficient α in a vegetation period (stretch TNs-TNe) is positive α = 0.10; 0.12 km−1. In winter season due to rotting vegetation and frozen land the increase in the amount of nitrates could be noticed in the stretch of natural channel α = −0.02; −0.07 km−1.
In the regulated part of stream, the amount of nitrates is frequently increasing in a flowing direction. In spite of that, in the samples of TRs the least amount of nitrates was determined in the whole period of research. This phenomenon could be explained by the fact that there is a dam before the stretch TRs–TRe and the existing pond operates as a settler, therefore retention of nitrates takes place all year round. The average self-purification coefficient of the stretch α is equal to 0.10 km−1. The slopes of the stretch TRs–TRe are very high and steep, a sharply descending relief increases river flow rate thus causing intensive bank erosion and slope landslips, whereas vegetation prevails on the upper part of the slope and in a protective riparian zone [40]. The average self-purification coefficient of the stretch α = −0.09 km−1.
The one-factorial dispersion analysis showed that the average self-purification coefficients, at a confidence level of 95%, vary essentially in the Žalesa, Terpinė, and Kuosinė streams. The average self-purification coefficients, with a confidence level of 95%, do not essentially vary in the Durbinis, Mėkla, and Uogis streams. Phosphate self-purification coefficient in regulated and natural river stretches, at a confidence level of 95%, is not essential in the Kuosinė, Durbinis, Mėkla, Žalesa, and Terpinė streams, though it varies essentially in Uogis stream. The results obtained show that nitrate self-purification is more effective than phosphate self-purification. The average nitrate concentration in natural stretches is lower than that in regulated stretches, 9.3 ± 2.7 and 18.5 ± 6.1 mg L−1, respectively. Decrease in the average nitrate concentration in natural and regulated stretches is 8.8 ± 5.0 and 3.0 ± 2.9 mg L−1, respectively. The average nitrate self-purification coefficient, at a confidence level of 95%, in natural stretches is 0.50 ± 0.22 km−1, in regulated stretches −0.15 ± 0.21 km−1, and this difference is essential.
The average phosphate concentration in natural stretches is also lower than that in regulated stretches, 0.4 ± 0.2 and 0.7 ± 0.2 mg L−1, respectively. The change in the average phosphate concentration in natural and regulated stretches is almost the same, 0.2 ± 0.1 and 0.2 ± 0.2 mg L−1, respectively. The average phosphate self-purification coefficient, at a confidence level of 95%, in natural stretches is 0.28 ± 0.12 km−1, in regulated stretches −0.14 ± 0.12 km−1, and this difference is not essential.
The distribution of nitrate and phosphate concentrations in rivers is also influenced by the underground water, which we consider relatively small and similar, unfortunately it is not analyzed in detail in our research. However, in the future, in order to get a more detailed analysis of nitrate and phosphate changes, a more detailed assessment of groundwater (underground water fluxes, quantify the nutrient fluxes) should be carried out.
4. Discussion
The research results show that nitrate and phosphate self-purification in the regulated stretches of separate streams takes place slower or not at all since the self-purification coefficients were negative. Negative self-purification rates indicate that larger amounts of nitrate and phosphate pollutants are sometimes discharged into the river, although the inflow from the surrounding areas is similar but still variable, so regulated streams, sometimes natural also fail to treat itself. Seeking to prevent pollutants from getting into the rivers the protective riparian zones are defined along the riverbanks [41]. Industrial activities, carried out in protective riparian zones, has a direct, usually negative impact on water quality, therefore it is very important that they are observed. In order to improve water quality in rivers and streams of Lithuania it is suggested to naturalize them to the extent possible. After getting into the rivers and streams of Lithuania, nitrates and phosphates are better self-purified in natural than in regulated stretches. In order to restore a disturbed hydrological and environmental balance of regulated streams it is important to retain their drainage function without increasing maintenance costs. Therefore, seeking to improve self-purification of streams the so-called soft naturalization measures are suggested: to allow woody vegetation grow on river slopes, to form natural obstacles for water flow, and other elements in flood plains that are characteristic to wetlands [2,42]. The research evaluates the water quality of streams only in terms of nitrate and phosphate concentrations in water, but many other physicochemical, hydro morphological, and biological parameters, for instance organic fraction of nutrients that also have a significant impact on a river′s ecological status should be taken into consideration to fully assess the ecological status of the river and differences in the ecological status of natural and regulated streams.
Nitrate and phosphate concentrations are greatly influenced by man-or animal-made dams. The formed ponds act as precipitators, resulting that significantly less nitrate concentrations flow out from the pond [43]. Research in the Nevėžis River Basin [22] shows that beaver ponds (comparing annual concentrations of inputs and outflows) retain relatively more phosphorus than nitrogen and more soluble mineral N and P compounds: on average 28% nitrate and ammoniacal nitrogen and 43% of orthophosphate phosphorus. But organic forms are much less retained. The retention of total N and total P is therefore 7% and 27%, respectively.
When planning renovation of drainage systems, the authors Šaulys and Barvidienė [44] suggest to take into consideration the Lithuanian hydrological regime, and natural and industrial conditions. Though the territory of Lithuania is relatively small, due to a variety of factors, which form and redistribute run-off, the feeding type and hydrological regime of surface water bodies are rather different. Lithuanian surface water bodies are divided into three hydrological regions based on relief, precipitation and soil [45,46]. Moreover, having taken into consideration the increase in soil productivity index due to drainage, abandoned agricultural land, possible breakdown of drainage systems, and dynamics in crop production, it was determined that the highest need for drainage systems renovation is in the Middle Lithuania region, the average in the Coastal Lowlands and South-Eastern Highlands, and the lowest in the Western (Samogitian) Highlands.
In terms of the need for renovation of drainage systems it is suggested that soft naturalization measures are first applied in the regulated stretches of the Durbinis and Uogis streams, and in other regulated streams of Western (Samogitian) Highlands. A more intensive application of naturalization measures is suggested for the Žalesa, Kuosinė, and Terpinė streams, and other regulated streams of South-Eastern Highlands, since the mentioned streams are crossing territories where the prevailing soil is sand and sandy loam, moreover, the soil productivity index is relatively low.
The works focused on mechanical naturalization of regulated streams in Lithuania have already started [47], though mechanical naturalization of regulated streams financially is rather expensive, the benefit for water quality and ecological diversity has not yet been comprehensively investigated and scientifically justified [24,48,49]. Therefore, no intensive mechanical naturalization works are proposed so far for the regulated streams of Lithuania. In the future, the ecological status of regulated rivers should be studied and evaluated in as many parameters as possible, at the same time contributing to the broader public awareness of the rationalization of the application of naturalization processes.
5. Conclusions
It was determined that the self-purification of streams from nitrates and phosphates is more effective in natural stretches than in stretches regulated for drainage purposes.
Decrease in the average nitrate () concentration in natural and regulated stream stretches was 8.8 ± 5.0 and 3.0 ± 2.9 mg L−1, respectively. The average nitrate self-purification coefficient, at a confidence level of 95%, in natural stretches was 0.50 ± 0.22, in regulated stretches −0.15 ± 0.21 km−1, and this difference is essential.
The change in the average phosphate concentration in natural and regulated stream stretches is almost the same, 0.2 ± 0.1 and 0.2 ± 0.2 mg L−1, respectively. The average phosphate self-purification coefficient, at a confidence level of 95%, in natural stretches is 0.28 ± 0.12, in regulated stretches −0.14 ± 0.12 km−1, and this difference is not essential.
During the warm vegetation period, concentrations of nitrates in water were (could be) in most cases lower than during the cold period of the year. Increased concentrations of nitrates could be caused by fertilization of arable lands. Increased nitrate concentrations could also be affected by the adjacent communities of garden-plots, this is a possible unevenness of inflow from surrounding areas.
In terms of the need for renovation of drainage systems it is suggested that soft naturalization measures are first applied in the streams of Western (Samogitian) Highlands, Coastal Lowlands, and South-Eastern Highlands to improve their self-purification processes and where the need for renovation of drainage systems is low.
Author Contributions
V.Š. conceived the study; O.S. and R.S. procured and analyzed the data, prepared the illustrations and wrote the manuscript under the supervision of V.Š. All authors contributed with ideas to the analysis, discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Riley, W.D.; Potter, E.C.E.; Biggs, J.; Collins, A.L.; Jarvie, H.P.; Jones, J.I.; Kelly-Quinn, M.; Ormerod, S.J.; Sear, D.A.; Wilby, R.L.; et al. Small water bodies in Great Britain and Ireland: Ecosystem function, human-generated degradation, and options for restorative action. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1598–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, M. The passive river restoration approach as an efficient tool to improve the hydromorphological diversity of rivers—Case study from two river restoration projects in the German lower mountain range. Geomorphology 2017, 293, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, D.; Marchese, E.; Theule, J.I.; Comiti, F. Channel degradation and restoration of an Alpine river and related morphological changes. Geomorphology 2014, 221, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, K.J. The human role in changing river channels. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, M.E.; Hinsingerc, P.; Harmanda, J.M. Nitrogen and phosphorus economy of a legume tree-cereal intercropping system under controlled conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 434, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bączyk, A.; Wagner, M.; Okruszko, T.; Grygoruk, M. Influence of technical maintenance measures on ecological status of agricultural lowland rivers—Systematic review and implications for river management. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithuanian Hydrometeorological Service. Available online: http://www.meteo.lt/en/precipitation (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Šaulys, V. Open Channel Hydraulics, 2nd ed.; Technika: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2016; p. 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povilaitis, A.; Taminskas, J.; Gulbinas, Z.; Linkevičienė, R.; Pileckas, M. Lithuanian Wetlands and Their Water Protective Importance, 4th ed.; Apyaušris: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2011; p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Hickey, M.B.C.; Bruce, D. A review of the efficiency of buffer strips for the maintenance and enhancement of riparian ecosystems. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2004, 39, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søvik, A.K.; Syversen, N. Retention of particles and nutrients in the root zone of a vegetative buffer zone—Effect of vegetation and season. Boreal Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Dosskey, M.G.; Vidon, P.; Gurwick, N.P.; Allan, C.J.; Duval, T.P.; Lowrance, R. The role of riparian vegetation in protecting and improving chemical water quality in streams. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.J.; Clausen, J.C.; Kuzovkina, Y. Water quality changes in a short-rotation woody crop riparian buffer. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 107, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Reynolds, S.K.; McCutchen, M.D.; Canfield, T.J. Meta-Analysis of Nitrogen Removal in Riparian Buffers. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorioz, J.M.; Wang, D.; Poulenard, J.; Trévisan, D. The effect of grass buffer strips on phosphorus dynamics—A critical review and synthesis as a basis for application in agricultural landscapes in France. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 117, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, T.R.; Rasera, K.; Parron, L.M.; Brito, A.G.; Ferreira, M.T. Nutrient removal effectiveness by riparian buffer zones in rural temperate watersheds: The impact of no-till crops practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, K.J.; Vose, J.M. Effects of riparian zone buffer widths on vegetation diversity in southern Appalachian headwater catchments. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Jacobson, P. Effectiveness of natural riparian buffers to reduce subsurface nutrient losses to incised streams. Catena 2014, 114, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, P.; Chambers, J.M.; Bell, R.W. Understanding the characteristics of riparian zones in low relief, sandy catchments that affect their nutrient removal potential. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 258, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilen, A.D.; Chen, C.R.; Parker, B.M.; Faggotter, S.J.; Burford, M.A. Differences in nitrate and phosphorus export between wooded and grassed riparian zones from farmland to receiving waterways under varying rainfall conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastienė, N.; Kirstukas, J. Principles and priorities of riparian strips rehabilitation. Water Environ. Eng. 2010, 37, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lamsodis, R.; Morkūnas, V.; Poškus, V.; Povilaitis, A. Ecological approach to management of open drains. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziliauskas, A.; Morkūnas, V.; Rimkus, Z.; Šaulys, V. Economic incentives in land reclamation sector in Lithuania. J. Water Land Dev. 2007, 11, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, J.; Wilkes, M.A. Does river restoration work? Taxonomic and functional trajectories at two restoration schemes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillex, A.; Schuwirth, N.; Lorenz, A.W.; Januschke, K.; Peter, A.; Reichert, P. Integrating and extending ecological river assessment: Concept and test with two restoration projects. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kail, J.; Brabec, K.; Poppe, M.; Januschke, K. The effect of river restoration on fish, macroinvertebrates and aquatic macrophytes: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Atique, U.; An, K.G. Long-term ecological health assessment of a restored urban stream based on chemical water quality, physical habitat conditions and biological integrity. Water 2019, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundemann, A.; Stoll, S.; Haase, P. River restoration success depends on the species pool of the immediate surroundings. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, Z.; Shang, H. Study on the Self-purification of Juma River. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 11, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifabiyi, I.P. Self-purification of a freshwater stream in Ile-Ife: Lessons for water management. J. Hum. Ecol. 2008, 24, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, A.A.A.; Khalil, M.K. Study on stream ability for self-purification process in receiving domestic wastewater. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2016, 22, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Quality—Sampling—Part 1: Guidance on the Design of Sampling Programmes and Sampling Techniques; International Standardisation Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; LST EN ISO 5667-1:2007/AC:2007.
- Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 327, 1–73. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/policy-documents/directive-2000-60-ec-of (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Grizzetti, B.; Pistocchi, A.; Liquete, C.; Udias, A.; Bouraoui, F.; van de Bund, W. Human pressures and ecological status of European rivers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Department under the Ministry of Environment. Available online: https://aad.lrv.lt/en/ (accessed on 25 May 2019).
- Tumas, R. Water Ecology; Naujasis Lankas: Kaunas, Lithuania, 2003; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- The Manager of the Spatial Information Portal of Lithuania. Available online: https://www.geoportal.lt/geoportal/en/web/en (accessed on 10 April 2019).
- Survilė, O.; Šaulys, V.; Stanionytė, A. An assessment of self-purification of regulated and natural streams. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference Environmental Engineering, Vilnius, Lithuania, 27–28 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lithuanian Official Statistics Portal. Available online: https://osp.stat.gov.lt/statistiniu-rodikliu-analize?theme=all#/ (accessed on 12 December 2019).
- Burneika, A.; Barvidiene, O. The influence of naturalization processes on water quality in regulated part of Terpine stream. In Proceedings of the 17th Conference for Junior Researchers, Vilnius, Lithuania, 10 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil, O.; Merot, P.; Marmonier, P. Estimation of nitrate removal by riparian wetlands and streams in agricultural catchments: Effect of discharge and stream order. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 2305–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survilė, O.; Šaulys, V.; Bagdžiūnaitė-Litvinaitienė, L.; Stankevičienė, R.; Litvinaitis, A.; Stankevičius, M. Assessment and research of river restoration processes in regulated streams of Southeastern Lithuania. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winton, R.S.; Calamita, E.; Wehrli, B. Reviews and syntheses: Dams, water quality and tropical reservoir stratification. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šaulys, V.; Barvidienė, O. Substantiation of the expediency of drainage systems renovation in Lithuania. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference Environmental Engineering, Vilnius, Lithuania, 22–23 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Soils of Lithuania, 2nd ed.; Lithuanian Science: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2001; Book 32; p. 1244.
- Gailiušis, B.; Jablonskis, J.; Kovalenkovienė, M. Lithuanian Rivers: Hydrography and Runoff, 2nd ed.; Lithuanian Energy Institute: Kaunas, Lithuania, 2001; p. 792. [Google Scholar]
- The Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: http://vanduo.gamta.lt. (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Friberg, N.; Bonada, N.; Bradley, D.C.; Dunbar, M.J.; Edwards, F.K.; Grey, J.; Hayes, R.B.; Hildrew, A.G.; Lamouroux, N.; Trimmer, M.; et al. Biomonitoring of human impacts in natural ecosystems: The good, the bad and the ugly. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2011, 44, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logar, I.; Brouwer, R.; Paillex, A. Do the societal benefits of river restoration outweigh their costs? A cost-benefit analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 323, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).