Applicability of Benthic Diatom Indices Combined with Water Quality Valuation for Dish Lake from Nanjishan Nature Reserve, Lake Poyang
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
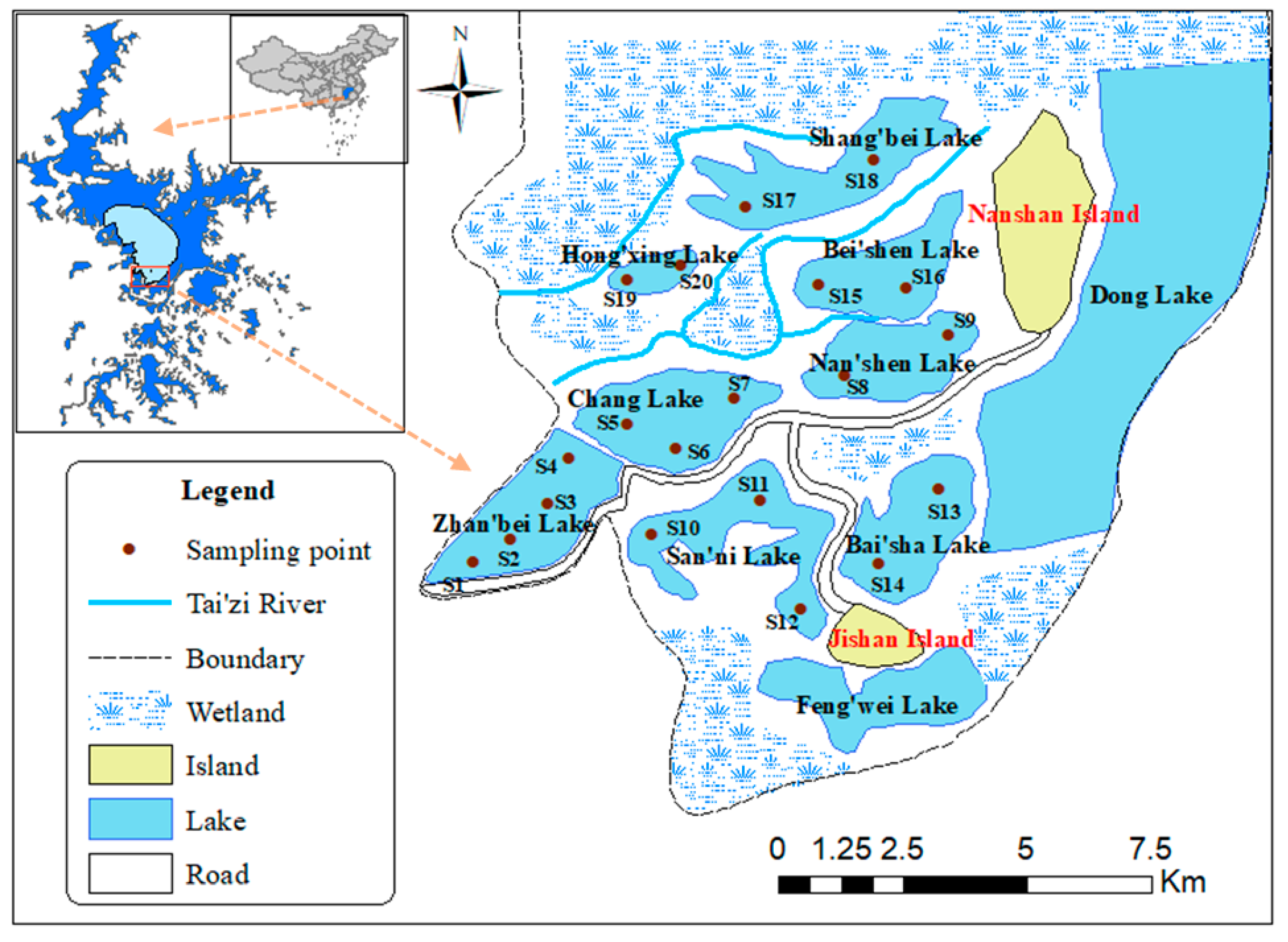
2.2. Sampling Sites
2.3. Water Sampling
2.4. Diatom Sampling
2.5. Diatom Identification
2.6. Diatom Indices Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Classification of Water Quality
3.2. Diatom Communities Structure
3.3. Applicability of Diatom Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, X.; Ma, P.; Bunn, S.E.; Zhang, Q.F. Development of a benthic diatom index of biotic integrity (BD-IBI) for ecosystem health assessment of human dominant subtropical rivers, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.W.; Fa, Y.L. The application of benthic macroinvertebrates in aquatic ecosystem health assessment. J. Meteorol. Environ. 2012, 28, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, N. Biomonitoring of human impacts on freshwater ecosystems: The good, the bad and the ugly. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2011, 44, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.W.; Cao, R.; Mao, J.Z.; Sheng, X.; Wang, X.T.; Deng, P.Y. Study of proper diatom-based indices for bioassessment of water quality in Beijiang Watershed. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 275–284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, S.F.P.; Elias, C.; Ferreira, J.; Tomes, E.; Puccinelli, C.; Delmas, F.; Doerflinger, G.; Urbanic, G.; Marcheggiani, S.; Rosebery, J. Water quality assessment of rivers using diatom metrics across Mediterranean Europe: A methods intercalibration exercise. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignata, C.; Morin, S.; Scharl, A.; Traversi, D.; Schiliò, T.; Degan, R.; Bartley, P.; Tu, M.; Liu, H.; Peres, F. Application of European biomonitoring techniques in China: Are they a useful tool? Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.Y.; Lei, Y.D.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.T. Exploration of benthic diatom indices to evaluate water quality in rivers in the Dongjiang Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 5014–5024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belore, M.L.; Winter, J.G.; Duthie, H.C. Use of Diatoms and Macroinvertebrates as Bioindicators of Water Quality in Southern Ontario Rivers. Can. Water Resour. J. 2002, 27, 457–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karr, J.R.; Chu, E.W. Introduction: Sustaining living rivers. Hydrobiologia 2000, 422, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowe, K.; Harding, J. Development of two diatom-based indices: A biotic and a multimetric index for assessing mine impacts in New Zealand streams. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 48, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.K.; Stevenson, R.J.; Metzmeier, L. Development and evaluation of a diatom-based Index of Biotic Integrity for the Interior Plateau Ecoregion, USA. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 990–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.F.; Xu, Z.X.; Yin, X.W.; Wu, W.; Min, W.W. Assessing water quality with diatom indices in the Wei River Basin. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2016, 52, 317–321. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Zheng, B.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cheng, P.X. Assessment of Aquatic Ecosystem Health of the Wutong River Based on Benthic Diatoms. Water 2019, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, G.; Toja, J.; Sala, S.E.; Fernández, M.D.L.R.; Reyes, I.; Casco, M.A. Application of diatom biotic indices in the Guadalquivir River Basin, a Mediterranean basin. Which one is the most appropriated? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Grover, S.; Verma, J.; Khan, S.A. Applicability and efficacy of diatom indices in water quality evaluation of the Chambal River in Central India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25955–25976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela-Cruz, J.; Pritchard, T.; Gordon, G.; Ajani, P. The use of periphytic diatoms as a means of assessing impacts of point source inorganic nutrient pollution in south-eastern Australia. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédéric, R. Recent views on river pollution and diatoms. Hydrobiologia 2012, 683, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, I.; Campeau Stéphane Zugic-Drakulic, N.; Winter, J.G.; Fortin, C. Using diatoms to monitor stream biological integrity in Eastern Canada: An overview of 10 years of index development and ongoing challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 475, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse-Lototskaya, A.; Verdonschot, P.F.M.; Coste, M.; Vijver, B.V.D. Evaluation of European diatom trophic indices. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, M.; Lavoie, I.; Rousseau, A.N.; Campeau, S. Defining ecological thresholds to determine class boundaries in a bioassessment tool: The case of the Eastern Canadian Diatom Index (IDEC). Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimet, F.; Bouchez, A.; Montuelle, B. Benthic diatoms and phytoplankton to assess nutrients in a large lake: Complementarity of their use in Lake Geneva (France-Switzer-land). Ecol. Indic. 2015, 53, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, H.V.; Mertens, A.; Sinkeldam, J. A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from The Netherlands. Aquat. Ecol. 1994, 28, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atazadeh, I.; Sharifi, M.; Kelly, M.G. Evaluation of the Trophic Diatom Index for assessing water quality in River Gharasou, western Iran. Hydrobiologia 2007, 589, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, C.; Pardo, I.; García, L. A multimetric diatom index to assess the ecological status of coastal Galician rivers (NW Spain). Hydrobiologia 2010, 644, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kow, L. Applicability of a generic index for diatom assemblages to monitor pollution in the tropical River Tsanwun, Taiwan. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trábert, Z.; Tihamér Kiss, K.; Várbíró, G.; Dobosy, P.; Grigorszky, I.; Ács, É. Comparison of the utility of a frequently used diatom index (IPS) and the diatom ecological guilds in the ecological status assessment of large rivers. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2017, 189, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.W.; Qu, X.D.; Li, Q.N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Using periphyton assemblages to assess stream conditions of Taizi River Basin, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 1677–1691. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kalyoncu, H.; Şerbetci, B. Applicability of Diatom-Based Water Quality Assessment Indices in Dari Stream, Isparta Turkey. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Environ. Chem. Ecol. Geol. Geophys. Eng. 2013, 7, 386–394. [Google Scholar]
- Pipp, E. A regional diatom-based trophic state indication system for running water sites in Upper Austria and its overregional applicability. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 2001, 27, 3376–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Zalack, J.T.; Wolin, J. A multimetric index of lake diatom condition based on surface-sediment assemblages. Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 1005–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.C.; Van Vuuren, M.S.; Pieterse, A.J. The application and testing of diatom-based indices in the Vaal and Wilge Rivers, South Africa. Water SA 2009, 33, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zgrundo, A.; Bogaczewiczadamczak, B. Applicability of diatom indices for monitoring water quality in coastal streams in the Gulf of Gdansk Region, Northern Poland. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2004, 33, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Whitton, B.A. The Trophic Diatom Index: A new index for monitoring eutrophication in rivers. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.G. Use of the trophic diatom index to monitor eutrophication in rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Dong, X.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Yang, X.D.; Xu, M.; Davidson, T.A.; Jeppesen, E. Hydrological alterations as the major driver on environmental change in a floodplain Lake Poyang (China): Evidence from monitoring and sediment records. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, K.M.; Chen, Y.W. Effects of water level fluctuations on phytoplankton in a Changjiang River floodplain lake (Poyang Lake): Implications for dam operations. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.W.; Li, X.L.; Wu, D.D.; Liu, J.L.; Li, J. Analysis of heavy metals in the surface sediments of shallow lakes in Nanjishan (Poyang Lake) Natural Wetland in China. J. Environ. Biol. 2017, 38, 561–570. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.S. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods, 4th ed.; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Bennett, C.; Coste, M.; Delgado, C.; Delmas, F.; Denys, L.; Ector, L.; Fauville, C.; Ferréol, M.; Golub, M. A comparison of national approaches to setting ecological status boundaries in phytobenthos assessment for the European Water Framework Directive: Results of an intercalibration exercise. Hydrobiologia 2009, 621, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.; Bennion, H.; Burgess, A.; Ellis, J.; Juggins, S.; Guthrie, R. Uncertainty in ecological status assessments of lakes and rivers using diatoms. Hydrobiologia 2009, 633, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, I.; Campeau, S.; Grenier, M.; Dillon, P.J. A diatom-based index for the biological assessment of eastern Canadian rivers: An application of correspondence analysis (CA). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 1793–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.; Marvan, P. Zur Przisierung der biologischen Klassifikation des Reinheit fliessender Gewsser. Archiv für. Hydrobiologie 1961, 57, 389–407. [Google Scholar]
- Fulazzaky, M.A. Water quality evaluation system to assess the Brantas River water. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 3019–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A.F.; Song, W.; Zhang, C.Z. The fisheries characters and resource status of Nanjishan natural reserve in Poyang lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2005, 14, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.M.; Tang, C.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Ma, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.M. The diatoms: Applications for the environmental and earth sciences. J. Biol. Educ. 2012, 46, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancheva RSheath, R.G. The diatoms: Applications for the environmental and earth sciences. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatli, C.; Solak, C.N.; Yilmaz, E. Water Quality Assessment by Means of Bio-Indication: A Case Study of Ergene River Using Biological Diatom Index. Aquat. Sci. Eng. 2020, 36, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Zhu, W.B.; Wu, P.J.; Gao, G.Q. Effects of substrate types on the growth of typical submerged vegetation in Poyang Lake. J. Nanchang Inst. Technol. 2018, 37, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bere, T.; Mangadze, T.; Mwedzi, T. The application and testing of diatom-based indices of stream water quality in Chinhoyi Town, Zimbabwe. Water SA 2014, 40, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Ma, P.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Q.F. Spatial Pattern of Benthic Diatoms and Water Quality Assessment Using Diatom Indices in a Subtropical River, China. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, M.T.M.P.S.; Scalize, P.S.; Kraus, C.N.; da Silva, W.J.; Garnier, J.; da Motta Marques, D.; de Souza Nogueira, I. Biological index based on epiphytic diatom assemblages is more restrictive than the physicochemical index in water assessment on an Amazon floodplain, Brazil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrisi, M.; Dell’Uomo, A. Biological monitoring of some Apennine rivers (central Italy) using the diatom-based eutrophication/pollution index (EPI-D) compared to other European diatom indices. Diatom Res. 2006, 21, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Uomo, A.; Torrisi, M. The Eutrophication/Pollution Index-Diatom based (EPI-D) and three new related indices for monitoring rivers: The case study of the river Potenza (the Marches, Italy). Plant. Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. Asp. Plant. Biol. 2011, 145, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prygiel, J.; Carpentier, P.; Almeida, S.; Coste, M.; Druart, J.; Ector, L.; Guillard, D.; Honore, M.; Iserentant, R.; Ledeganck, P.; et al. Determination of the biological diatom index (IBD NF T 90–354): Results of an intercomparison exercise. J. Appl. Phycol. 2002, 14, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Group | Lake | Sites | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | TSS (mg/L) | Chl (ug/L) | NH4+ (mg/L) | PC1 | PC2 | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Shang’bei lake | S17 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 11 | 12.7 | 4230 | 0.17 | −1.823 | −0.148 | −1.667 |
| S18 | 0.2 | 0.03 | 7.2 | 10.8 | 4800 | 0.15 | −1.662 | 0.2 | −1.302 | ||
| Hong’xing lake | S19 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 4860 | 0.16 | −0.993 | −0.419 | −1.575 | |
| S20 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 10 | 10.1 | 4730 | 0.2 | −1.414 | −0.654 | −1.496 | ||
| A2 | Nan’shen lake | S8 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 17 | 14.5 | 5100 | 0.26 | −1.418 | 0.047 | −1.249 |
| S9 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 12 | 15 | 4380 | 0.24 | −0.545 | −0.762 | −0.718 | ||
| Bei’shen lake | S15 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 12 | 15 | 5020 | 0.19 | −1.012 | −0.512 | −1.063 | |
| S16 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 15 | 16.5 | 4980 | 0.26 | −1.581 | 0.033 | −1.37 | ||
| A3 | Chang lake | S5 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 16 | 14.5 | 5970 | 0.26 | −0.75 | 0.235 | −0.359 |
| S6 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 13 | 17 | 5610 | 0.24 | −0.64 | −0.222 | −0.276 | ||
| S7 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 14 | 18.5 | 5840 | 0.27 | −0.472 | 0.166 | −0.542 | ||
| A4 | Zhan’bei lake | S1 | 0.57 | 0.06 | 21.2 | 20.2 | 8210 | 0.37 | 1.508 | 0.542 | 1.421 |
| S2 | 0.53 | 0.07 | 17.9 | 25.7 | 7360 | 0.3 | 1.364 | 1.534 | 1.416 | ||
| S3 | 0.48 | 0.06 | 19.8 | 18.3 | 8350 | 0.39 | 1.217 | 1.196 | 1.204 | ||
| S4 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 15.7 | 19.7 | 9200 | 0.32 | 0.896 | 0.586 | 0.718 | ||
| San’ni lake | S10 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 21 | 17.3 | 6980 | 0.36 | 0.726 | 0.869 | 0.831 | |
| S11 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 28.3 | 15.5 | 7680 | 0.26 | 0.575 | 0.922 | 0.887 | ||
| S12 | 0.42 | 0.04 | 20.6 | 18.9 | 9350 | 0.38 | 1.063 | 1.323 | 1.293 | ||
| Bai’sha lake | S13 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 20.1 | 18.5 | 8670 | 0.32 | 1.014 | 0.404 | 0.985 | |
| S14 | 0.52 | 0.05 | 22 | 17.9 | 6390 | 0.29 | 0.649 | 0.56 | 0.605 | ||
| Reference | 0.2 | 0.01 | 15 | - | - | 0.15 | - | - | - |
| Latin Name | Abbreviation | Dominant Index |
|---|---|---|
| Melosira varians | MVAR | 0.137 |
| Gomphonema gracile | GGRA | 0.051 |
| Pinnularia viridis | PVFM | 0.049 |
| Synedra acus | SACU | 0.043 |
| Cymbella tumida | CTUM | 0.043 |
| Synedra tabulata | STTG | 0.041 |
| Nitzschia gracilis | NIGF | 0.037 |
| Synedra ulna | SULN | 0.036 |
| Gomphonema olivaceum | GOLA | 0.036 |
| Fragilaria capucina | FCRP | 0.034 |
| Cyclotella meneghiniana | CMEN | 0.028 |
| Tabellaria flocculosa | TFAM | 0.027 |
| Eunotia lunaris | ELUN | 0.026 |
| Navicula amphibola | NAPH | 0.024 |
| Navicula capitata | NCAP | 0.024 |
| Eunotia arcus | EARC | 0.022 |
| Caloneis hyaline | CHYA | 0.022 |
| Cocconeis placentula | CPTG | 0.021 |
| Gomphonema constrictum | GCST | 0.020 |
| Neidium affine var | NAUC | 0.020 |
| Navicula veneta | NVEN | 0.020 |
| Cymbella cymbiformis | CCYM | 0.020 |
| Navicula trivialis | NTVT | 0.020 |
| Items | IDAP | SHE | IPS | IDSE | TDI | IDP | EPI-D | DI-CH | SLA | IDG | %PT | ROTTtroph | IBD | WAT | DES | CEE | LOBO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHE | −0.104 | ||||||||||||||||
| IPS | 0.515 * | 0.064 | |||||||||||||||
| IDSE | 0.144 | 0.506 * | 0.300 | ||||||||||||||
| TDI | 0.282 | 0.185 | 0.664 ** | 0.479 * | |||||||||||||
| IDP | 0.217 | 0.196 | −0.023 | 0.151 | 0.186 | ||||||||||||
| EPID | −0.225 | 0.084 | 0.415 | 0.388 | 0.162 | −0.280 | |||||||||||
| DICH | 0.387 | 0.381 | 0.606 ** | 0.643 ** | 0.764 ** | 0.461 * | 0.169 | ||||||||||
| SLA | 0.600 ** | −0.189 | 0.366 | −0.015 | 0.037 | 0.383 | 0.061 | 0.042 | |||||||||
| IDG | 0.177 | 0.15338 | 0.305 | 0.373 | 0.329 | −0.373 | 0.098 | 0.432 * | −0.549 ** | ||||||||
| PT | 0.019 | −0.447 * | −0.400 | −0.439 * | −0.621 ** | −0.085 | −0.040 | −0.570 ** | 0.371 | −0.427 * | |||||||
| ROTTtroph | 0.674 ** | 0.081 | 0.547 ** | 0.605 ** | 0.458 * | 0.341 | 0.171 | 0.537 ** | 0.659 ** | −0.030 | −0.155 | ||||||
| IBD | 0.679 ** | −0.037 | 0.794 ** | 0.081 | 0.489 * | −0.055 | 0.112 | 0.529 * | 0.302 | 0.384 | −0.269 | 0.514 * | |||||
| WAT | 0.100 | 0.351 | −0.292 | −0.199 | −0.395 | 0.196 | −0.229 | −0.349 | 0.415 | −0.626 ** | 0.228 | 0.125 | −0.139 | ||||
| DES | −0.007 | 0.187 | 0.326 | 0.473 * | 0.361 | −0.415 | 0.319 | 0.475 * | −0.607 ** | 0.938 ** | −0.467 * | −0.002157 | 0.356 | −0.654 ** | |||
| CEE | 0.103 | 0.461 * | −0.015 | −0.367 | −0.211 | −0.122 | −0.226 | −0.218 | 0.049 | −0.191 | 0.018 | −0.195 | 0.152 | 0.722 ** | −0.253 | ||
| LOBO | 0.341 | −0.373 | 0.050 | −0.784 ** | −0.340 | −0.054 | −0.340 | −0.348 | 0.242 | −0.155 | 0.456 * | −0.309 | 0.229 | 0.161 | −0.344 | 0.457 * | |
| ROTTsap | 0.355 | 0.234 | 0.591 ** | 0.820 ** | 0.653 ** | 0.143 | 0.339 | 0.701 ** | 0.223 | 0.789 ** | −0.285 | 0.686 ** | 0.316 | −0.497 * | 0.826 ** | −0.433 * | −0.445 * |
| TN | −0.409 | 0.081 | −0.455 * | −0.049 | 0.548 * | −0.455 * | −0.475 * | 0.050 | −0.134 | 0.053 | −0.285 | 0.142 | 0.905 ** | 0.232 | 0.152 | 0.205 | 0.450 * |
| TP | −0.515 * | −0.050 | −0.535 * | 0.458 * | 0.206 | −0.028 | −0.018 | 0.112 | −0.157 | 0.626 * | −0.269 | −0.028 | 0.725 ** | 0.044 | 0.107 | 0.535 * | 0.106 |
| COD | −0.077 | −0.218 | −0.137 | −0.151 | −0.450 * | −0.264 | 0.097 | −0.306 | 0.142 | −0.117 | 0.661 ** | −0.163 | −0.226 | −0.001 | −0.102 | 0.004 | 0.226 |
| TSS | −0.080 | −0.260 | −0.133 | −0.175 | −0.301 | −0.301 | 0.065 | −0.368 | 0.010 | 0.036 | −0.013 | −0.281 | −0.326 | −0.216 | −0.056 | −0.119 | 0.359 |
| Chl | 0.214 | −0.002 | 0. 406 * | 0.517 ** | 0.221 | 0.248 | −0.190 | 0.058 | 0.214 | −0.120 | 0.575 ** | 0.096 | 0.493 * | 0.001 | −0.264 | −0.059 | 0.085 |
| NH4+ | −0.030 | −0.153 | −0.206 | 0.345 | 0.095 | 0.276 | 0.161 | 0.002 | 0.285 | −0.285 | 0.060 | 0.293 | −0.381 | 0.043 | −0.285 | −0.505 * | −0.471 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Ji, Y.; Yan, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, N.; Wang, K. Applicability of Benthic Diatom Indices Combined with Water Quality Valuation for Dish Lake from Nanjishan Nature Reserve, Lake Poyang. Water 2020, 12, 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102732
Yang J, Ji Y, Yan R, Liu X, Zhang J, Wu N, Wang K. Applicability of Benthic Diatom Indices Combined with Water Quality Valuation for Dish Lake from Nanjishan Nature Reserve, Lake Poyang. Water. 2020; 12(10):2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102732
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Junfei, Yong Ji, Ruyu Yan, Xingchen Liu, Jie Zhang, Naichen Wu, and Kai Wang. 2020. "Applicability of Benthic Diatom Indices Combined with Water Quality Valuation for Dish Lake from Nanjishan Nature Reserve, Lake Poyang" Water 12, no. 10: 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102732
APA StyleYang, J., Ji, Y., Yan, R., Liu, X., Zhang, J., Wu, N., & Wang, K. (2020). Applicability of Benthic Diatom Indices Combined with Water Quality Valuation for Dish Lake from Nanjishan Nature Reserve, Lake Poyang. Water, 12(10), 2732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102732





