Impact Assessment and Geochemical Background Analysis of Surface Water Quality of Catchments Affected by the 2017 Portugal Wildfires
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area Description
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Field Parameters
2.2.2. Laboratory Analysis and Quality Assurance
2.2.3. Determination of Geochemical Backgrounds
3. Results
3.1. Field Parameters
3.2. Major Ions
3.3. Trace Elements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho, J.; Lopes, J. Classificação de Incêndios Florestais. Manual do Utilizador; Direcção-Geral das Florestas: Lisboa, Portugal, 2001. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, M.C.; Vasconcelos, M.J.; Pereira, J.M.; Dasgupta, N.; Alldredge, R.J.; Rego, F.C. Land cover type and fire in Portugal: Do fires burn land cover selectively? Landsc. Ecology 2005, 20, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, P.; Fernandes, P.M. Forest fires in Portugal: Dynamics, causes and policies. In Forest Context and Policies in Portugal: Present and Future Challenges; Reboredo, F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2014; pp. 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Tedim, F.; Remelgado, R.; Carvalho, S.; Martins, J. The largest forest fires in Portugal: The constraints of burned area size on the comprehension of fire severity. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.N.; Lourenço, L.; Meira, A.C. Exploring spatial patterns and drivers of forest fires in Portugal (1980–2014). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.N. Regional variability and driving forces behind forest fires in Portugal an overview of the last three decades (1980–2009). Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Leite, F.; Bento-Gonçalves, A.; Vieira, A.; Nunes, A.; Lourenço, L. Incidence and recurrence of large forest fires in mainland Portugal. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.G.; Trigo, R.M.; da Camara, C.C.; Pereira, J.M.; Leite, S.M. Synoptic patterns associated with large summer forest fires in Portugal. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 129, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, A.; Palutikof, J.; Holt, T. The climate system. In The Physical Geography of the Mediterranean; Woodward, J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Moriondo, M.; Good, P.; Durao, R.; Bindi, M.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Corte-Real, J. Potential impact of climate change on fire risk in the Mediterranean area. Clim. Res. 2006, 31, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.; Jerez, S.; Augusto, S.; Tarín-Carrasco, P.; Ratola, N.; Jiménez-Guerrero, P.; Trigo, R.M. Climate drivers of the 2017 devastating fires in Portugal. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J.R.; Meireles, C.I.R.; Gomes, C.J.P.; de Almeida Ribeiro, N.M.C. The Evolution of Climate Change in Portugal. In Climate Change Impact on Environmental Variability in the Forest; Nunes, L.J.R., Meireles, C.I.R., Gomes, C.J.P., de Almeida Ribeiro, N.M.C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 19–67. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, F.; Vaz, P.; Catry, F.; Silva, J.S. Regional variations in wildfire susceptibility of land-cover types in Portugal: Implications for landscape management to minimize fire hazard. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakesby, R.A. Post-wildfire soil erosion in the Mediterranean: Review and future research directions. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 105, 71–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.N.; De Almeida, A.C.; Coelho, C.O. Impacts of land use and cover type on runoff and soil erosion in a marginal area of Portugal. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Úbeda, X.; Martin, D.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerdà, A.; Burguet, M. Wildfire effects on extractable elements in ash from a Pinus pinaster forest in Portugal. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3681–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausas, J.G. Changes in fire and climate in the eastern Iberian Peninsula (Mediterranean basin). Clim. Chang. 2004, 63, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, F.; Louro, G.; Constantino, L. The impact of changing wildfire regimes on wood availability from Portuguese forests. For. Policy Econ. 2013, 29, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Valente, S.; Coelho, C.; Figueiredo, E. A look at forest fires in Portugal: Technical, institutional, and social perceptions. Scand. J. For. Res. 2015, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areia, N.; Intrigliolo, D.; Tavares, A.O.; Mendes, J.M.; Sequeira, M.D. The role of media between expert and lay knowledge: A study of Iberian media coverage on climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.X. Wildfires in Portugal. Fire Res. 2018, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.G.; Sheridan, G.J.; Lane, P.N.; Nyman, P.; Haydon, S. Wildfire effects on water quality in forest catchments: A review with implications for water supply. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, C.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Silins, U.; Doerr, S.H. The influence of wildfire on water quality and watershed processes: New insights and remaining challenges. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2019, 28, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakesby, R.A.; Doerr, S.H. Wildfire as a hydrological and geomorphological agent. Earth Sci. Rev. 2006, 74, 269–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.E.; Benito, E.; Keizer, J.J. Effects of wildfire and laboratory heating on soil aggregate stability of pine forest in Galicia: The role of lithology, soil organic matter content and water repellency. Catena 2010, 83, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.; Abrantes, N.; Pereira, P.; Micaelo, A.C.; Vale, C.; Keizer, J.J. Forest fires as potential triggers for production and mobilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to the terrestrial ecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2360–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.F.; Versfeld, D.B.; Lesch, W. Erosion and sediment yield in relation to afforestation and fire in the mountains of the Western Cape Province, South Africa. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 1998, 80, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J.J.; Doerr, S.H.; Malvar, M.C.; Prats, S.A.; Ferreira, R.S.V.; Oñate, M.G.; Coelho, C.O.A.; Ferreira, A.J.D. Temporal variation in topsoil water repellency in two recently burnt eucalypt stands in north-central Portugal. Catena 2008, 74, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, S.R.; Blinn, D.W. Effects of wildfire ash on water chemistry and biotain South-Western USA stream. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1015–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, P.N.J.; Sheridan, G.J.; Noske, P.J.; Sherwin, C.B. Phosphorus and nitrogen exports from SE Australian forests following wildfire. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mast, M.A.; Clow, D.W. Effects of 2003 wildfires on stream chemistry in Glacier National Park. Montan. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 5013–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallaher, B.; Koch, R. Quality of Storm Water Runoff at Los Alamos National Laboratory in 2000 with Emphasis on the Impact of the Cerro Grande Fire. Los Alamos National Laboratory LA-13926. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/45db/26759a2b60debfb6ce5ee1d0fc487ca7889d.pdf?_ga=2.131141005.348100239.1582302245-895007879.1582302245 (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Sequeira, M.D.; Castilho, A.M.; Tavares, A.O.; Dinis, P. Assessment of superficial water quality of small catchment basins affected by Portuguese rural fires of 2017. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.R.; Calvão, A.R.; Aranha, J. Linking wildfire effects on soil and water chemistry of the Marão River watershed, Portugal, and biomass changes detected from Landsat imagery. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 44, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilha, C.; Duarte, C.G.; Melo, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Flores, D.; Marques, J.E. Impact of wildfire on water quality in Caramulo Mountain ridge (Central Portugal). Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z. Geochemical background-an environmental perspective. Mineralogia 2011, 42, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, H.E.; Webb, J.S. Geochemistry in mineral exploration. Soil Sci. 1963, 95, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G. Background and threshold: Critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrone, D.; Ghergo, S.; Preziosi, E. A multi-method approach for the assessment of natural background levels in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, K.A.; Cooke, M.P. A comparison of methods used to calculate normal background concentrations of potentially toxic elements for urban soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, D.X.; Figueiredo Almeida, M.; Ribeiro, L.M.; Raposo, J.; Viegas, M.T.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, D.; Pinto, C.; Jorge, H.; Rodrigues, A.; et al. O complexo de incêndios de Pedrógão Grande e concelhos limítrofes, iniciado a 17 de junho de 2017. Centro de Estudos sobre Incêndios Florestais da Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia da Universidade de Coimbra. Available online: https://www.portugal.gov.pt/download-ficheiros/ficheiro.aspx?v=3bb9773b-59fb-4099-9de5-a22fdcad1e3b (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Viegas, D.X.; Almeida, M.F.; Ribeiro, L.M. Análise dos incêndios florestais ocorridos a 15 de outubro de 2017. Análise dos incêndios florestais ocorridos a 15 de outubro de 2017. Centro de Estudos sobre Incêndios Florestais da Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia da Universidade de Coimbra. Available online: https://www.portugal.gov.pt/pt/gc21/comunicacao/documento?i=analise-dos-incendios-florestais-ocorridos-a-15-de-outubro-de-2017 (accessed on 7 January 2020).
- DGAPPF. Relatório Provisório de Incêndios Florestais: 2017. Instituto da Conservação da Natureza e das Florestas. Available online: www.icnf.pt/portal/florestas/dfci/Resource/doc/rel/2017/10-rel-prov-1jan-31out-2017.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2020).
- Ferreira, V.; Graça, M.A.; Feio, M.J.; Mieiro, C. Water quality in the Mondego river basin: Pollution and habitat heterogeneity. Limnetica 2004, 23, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis, P.A.; Sequeira, M.; Tavares, A.O.; Carvalho, J.; Castilho, A.; Pinto, M.C. Post-wildfire denudation assessed from compositional features of river sediments (Central Portugal). Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 193, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AdCL. Relatório e Contas. Águas do Centro Litoral Grupo Águas de Portugal. Available online: http://www.aguasdocentrolitoral.pt/pt/menu-de-topo/comunicacao/publicacoes/downloads/pub_pdf23_pt.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- IPMA Clima Normais. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt (accessed on 5 January 2020).
- IPMA Boletim Climatológico Setembro 2017 Mensal e Ano Hidrológico Portugal Continental. Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P., Divisão de Clima e Alterações Climáticas. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- ISO Standard No. 5667-1. Water Quality–Sampling–Part 1: Guidance on the Design of Sampling Programmes and Sampling Techniques; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Standard No. 5667-3. Water quality–Sampling–Part 3: Guidance on the Preservation and Handling of Water Samples; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO Standard No. 9963-1. Water quality–Determination of Alkalinity-Part 1: Determination of Total and Composite Alkalinity; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pedro, R.; Castilho, A.; Tavares, A. Surface water quality in a contrasted land-use river catchment. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the World Multidisciplinary Earth Sciences Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 3–7 September 2018; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Otero MSantos, E.B.H.; Duarte, A.C. Chemical composition of rainwater at a coastal town on the southwest of Europe: What changes in 20 years? Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3548–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; De Caritat, P. Chemical Elements in the Environment: Factsheets for the Geochemist and Environmental Scientist; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rulli, M.C.; Rosso, R. Modeling catchment erosion after wildfires in the San Gabriel Mountains of southern California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Dowling, K.; Florentine, S. Risk of post-fire metal mobilization into surface water resources: A review. Sci. Total Env 2017, 599, 1740–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.K.; Raison, R.J. Effect of fire intensity on solution chemistry of surface soil under a Eucalyptus pauciflora forest. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1986, 24, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Coelho, C.; Boulet, A.K.; Lopes, F.P. Temporal patterns of solute loss following wildfires in Central Portugal. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, J.G.; Rivero, V.C.; Lopez, T.I. Forms of Mn in soils affected by a forest fire. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 181, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, C.A.; Hoefen, T.M.; Plumlee, G.S.; Baumberger, K.L.; Backlin, A.R.; Gallegos, E.; Fisher, R.N. Trace elements in stormflow, ash, and burned soil following the 2009 Station Fire in Southern California. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidy, A.R.; Smernik, R.J.; Baldock, J.A.; Kaiser, K.; Sanderman, J. Microbial degradation of organic carbon sorbed to phyllosilicate clays with and without hydrous iron oxide coating. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
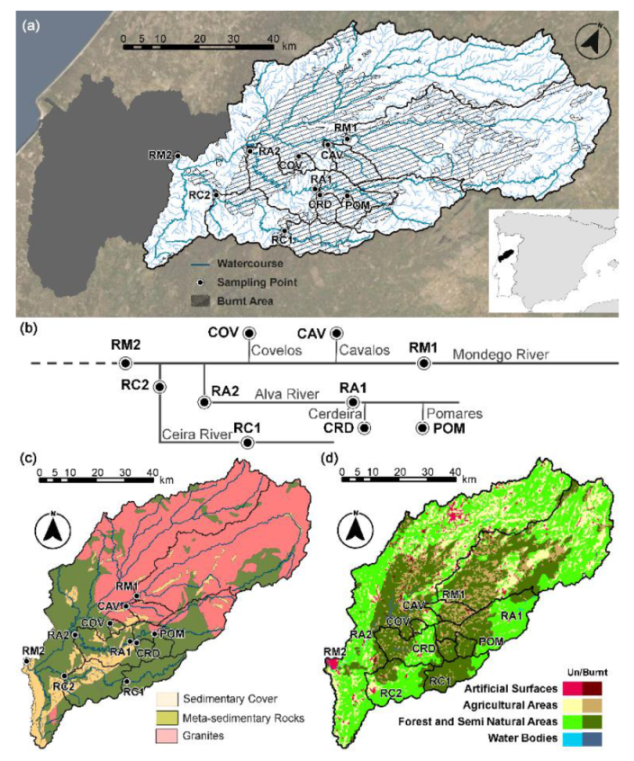

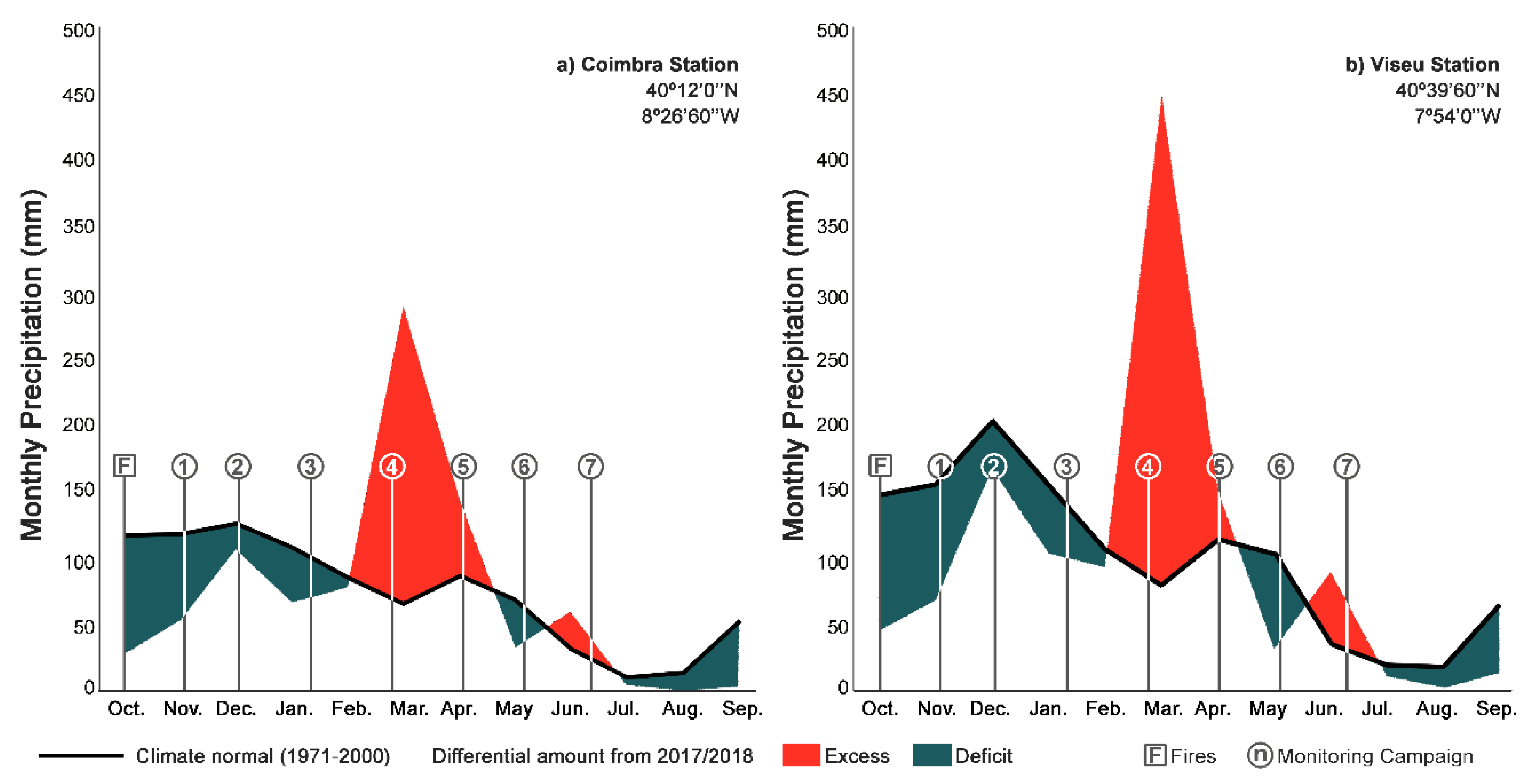
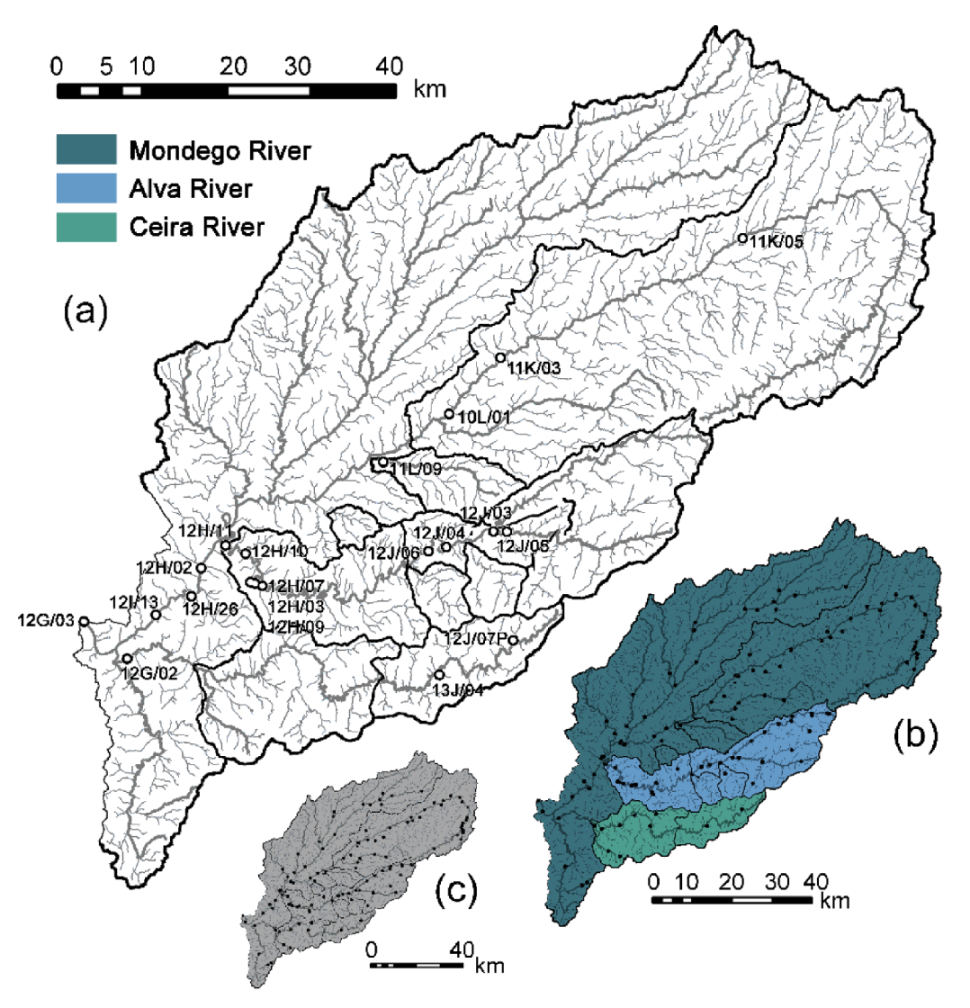

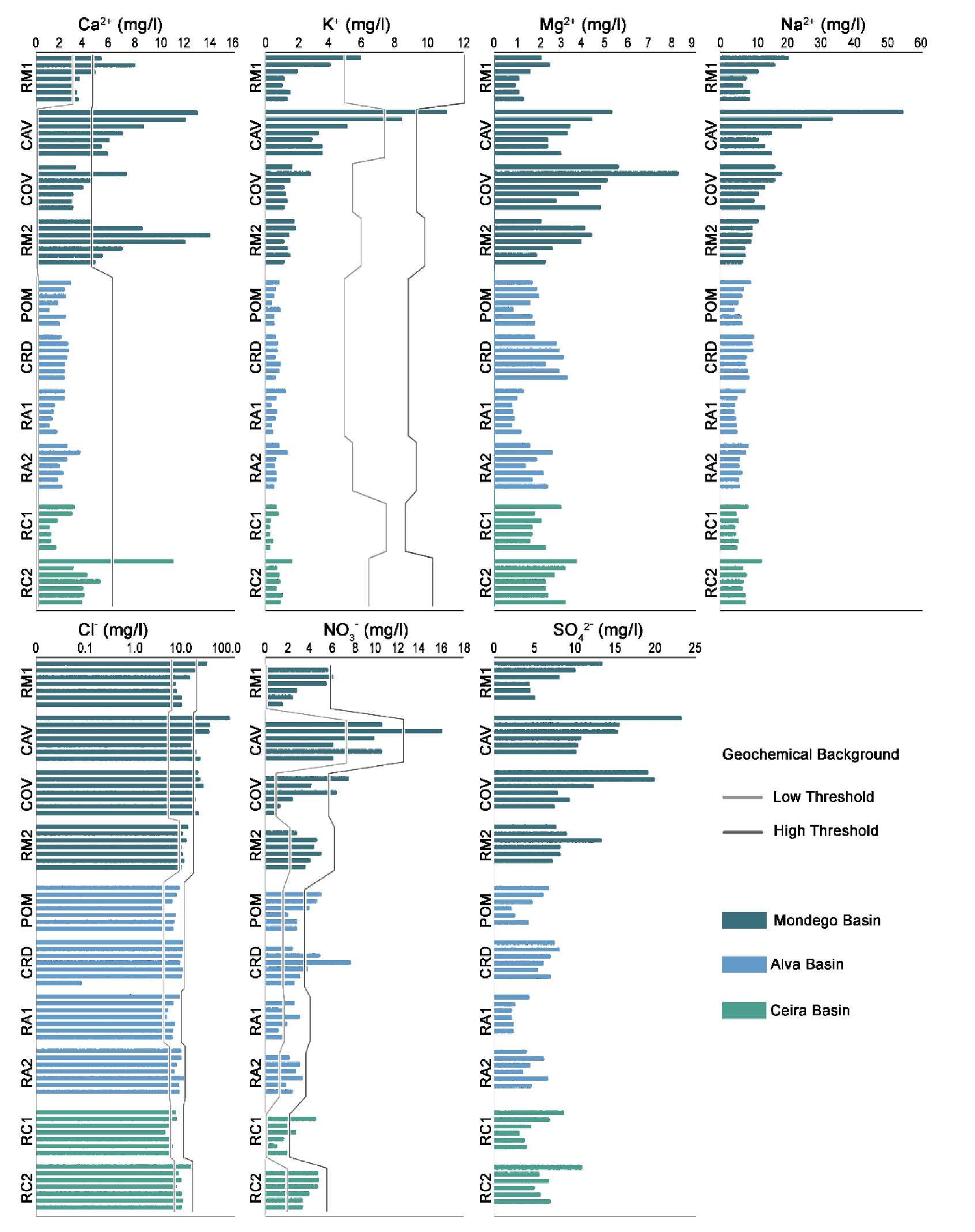
| Watercourse | Ref. | Latitude | Longitude | Av. Slp (°) | Area (km2) | Spr. (km) | B.A. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mondego 1 | RM1 | 40°24′09.36″ N | 7°59′09.26″ W | 6.7 | 1421.6 | 124.1 | 44.2 |
| Cavalos | CAV | 40°22′28.74″ N | 7°59′35.23″ W | 4.5 | 86.8 | 13.4 | 83.6 |
| Covelo | COV | 40°19′40.22″ N | 8°05′36.89″ W | 4.1 | 20.9 | 3.5 | 68.3 |
| Pomares | POM | 40°17′32.14″ N | 7°54′13.21″ W | 18.3 | 44.7 | 10.8 | 99.2 |
| Cerdeira | CRD | 40°15′58.21″ N | 7°59′14.21″ W | 14.0 | 43.0 | 9.7 | 99.2 |
| Alva 1 | RA1 | 40°16′12.83″ N | 7°59′18.64″ W | 14.9 | 433.3 | 50.0 | 52.0 |
| Alva 2 | RA2 | 40°17′42.47″ N | 8°14′43.94″ W | 12.2 | 705.9 | 107.6 | 49.8 |
| Ceira 1 | RC1 | 40°08′19.72″ N | 7°59′54.69″ W | 17.7 | 159.4 | 39.1 | 82.7 |
| Ceira 2 | RC2 | 40°09′42.88″ N | 8°16′40.08″ W | 14.6 | 412.6 | 85.9 | 48.6 |
| Mondego 2 | RM2 | 40°12′03.38″ N | 8°25′39.83″ W | 7.6 | 4905.6 | 188.5 | 39.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sequeira, M.D.; Castilho, A.M.; Dinis, P.A.; Tavares, A.O. Impact Assessment and Geochemical Background Analysis of Surface Water Quality of Catchments Affected by the 2017 Portugal Wildfires. Water 2020, 12, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102742
Sequeira MD, Castilho AM, Dinis PA, Tavares AO. Impact Assessment and Geochemical Background Analysis of Surface Water Quality of Catchments Affected by the 2017 Portugal Wildfires. Water. 2020; 12(10):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSequeira, Mário David, Ana Maria Castilho, Pedro Alexandre Dinis, and Alexandre Oliveira Tavares. 2020. "Impact Assessment and Geochemical Background Analysis of Surface Water Quality of Catchments Affected by the 2017 Portugal Wildfires" Water 12, no. 10: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102742
APA StyleSequeira, M. D., Castilho, A. M., Dinis, P. A., & Tavares, A. O. (2020). Impact Assessment and Geochemical Background Analysis of Surface Water Quality of Catchments Affected by the 2017 Portugal Wildfires. Water, 12(10), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102742






