Water and Land as Shared Resources for Agriculture and Aquaculture: Insights from Asia
Abstract
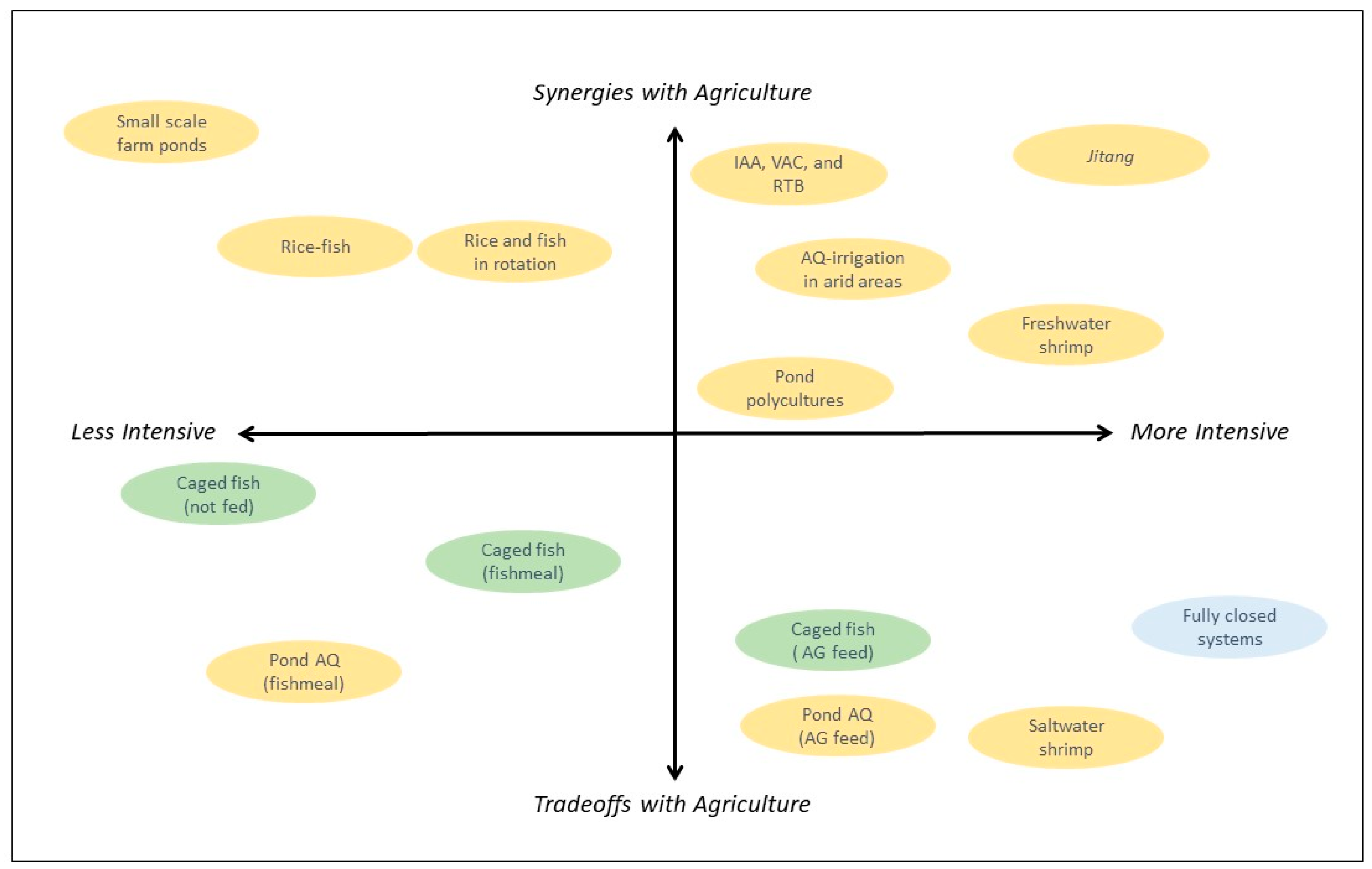
:1. Introduction
2. Tradeoffs over Shared Resources
2.1. Tradeoffs between Agriculture and Open Aquaculture
2.2. Tradeoffs between Semi-Closed Aquaculture and Agriculture
2.3. Indirect Tradeoffs between Agriculture and Aquaculture
3. Synergies between Aquaculture and Agriculture
3.1. Rice–Fish Systems
3.2. IAA Involving Crops, Livestock, and Aquaculture
3.3. IAA in Arid Asia
4. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; de Varies, W.; de Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Do Rosário Cameira, M.; Pereira, S. Innovation issues in water, agriculture and food. Water 2019, 11, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Odorico, P.; Davis, K.F.; Rosa, L.; Carr, J.A.; Chiarelli, D.; Dell’Angelo, J.; Gephart, J.; MacDonald, G.K.; Seekell, D.A.; Suweis, S.; et al. The global food-energy-water nexus. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 456–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Crootof, A.; Scott, C.A. The water-energy-food nexus: A systematic review of methods for nexus assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, G.B.; Jewitt, G.P.W. The water-energy-food nexus in the Anthropocene: Moving from ‘nexus thinking’ to ‘nexus action. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2019, 40, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geressu, R.; Siderius, C.; Harou, J.J.; Kashaigili, J.; Pettinotti, L.; Conway, D. Assessing river basin development given water-energy-food-environment interdependencies. Earth’s Future 2020, 7, e2019EF001464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.; Pilgrim, S. The new competition for land: Food, energy, and climate change. Food Policy 2011, 36, S40–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zou, S.; Nover, D. Managing the water-climate-food nexus for sustainable development in Turkmenistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laspidou, C.S.; Mellios, N.; Kofinas, D. Towards ranking the water-energy-food-land use-climate nexus interlinkages for building a nexus conceptual model with a heuristic algorithm. Water 2019, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, N.; Thompson, S.; Glaser, M. Global aquaculture productivity, environmental sustainability, and climate change adaptability. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troell, M.; Naylor, R.L.; Metian, M.; Beveridge, M.; Tyedmers, P.H.; Folke, C.; Arrow, K.J.; Barrett, S.; Crepin, A.-S.; Ehrlich, P.R.; et al. Does aquaculture add resilience to the global food system? Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13257–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Béné, C.; Barange, M.; Subasinghe, R.; Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Merino, G.; Hemre, G.-I.; Williams, M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050 – Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Béné, C.; Arthur, R.; Norbury, H.; Allison, E.H.; Beveridge, M.; Bush, S.R.; Campling, L.; Leschen, W.; Little, D.; Squires, D.; et al. Contribution of fisheries and aquaculture to food security and poverty reduction: Assessing the current evidence. World Devel. 2016, 79, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhongjie, L.; Gui, J.; Liu, J.; Ye, S.; Yuan, J.; De Silva, S.S. Paradigm changes in freshwater aquaculture practices in China: Moving towards achieving environmental integrity and sustainability. AMBIO 2018, 47, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, J.L.; Watson, R.A.; Fulton, E.A.; Cottrell, R.S.; Nash, K.L.; Bryndum-Buchholz, A.; Büchner, M.; Carozza, D.A.; Cheung, W.W.; Elliott, J.; et al. Linked sustainability challenges and trade-offs among fisheries, aquaculture and agriculture. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prein, M. Integration of aquaculture into crop-animal systems in Asia. Agric. Syst. 2002, 71, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretty, J. Agricultural sustainability: Concepts, principles and evidence. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 2007, 363, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Garlock, T.; Asche, F.; Anderson, J.; Bjørndal, T.; Kumar, G.; Lorenzen, K.; Ropicki, A.; Smith, M.D.; Tveterås, R. A global blue revolution: Aquaculture growth across regions, species, and countries. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2020, 28, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev-Yadun, S.; Gopher, A.; Abbo, S. The cradle of agriculture. Science 2000, 288, 1602–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, B.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Geographic distribution of major crops across the world. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, GB1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, P. The Evolution of Agricultural Productivity; Brittanica Educational Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Miao, W.; Cai, J.; Yuan, X. Contribution of Chinese agriculture to the sector, globally, and to overall food security. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends, 1st ed.; Gui, J.-F., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., De Silva, S.S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Li, X. Review of rice-fish-farming systems in China—One of the Globally Important Ingenious Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS). Aquaculture 2006, 260, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harland, J. The origins of aquaculture. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1378–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, J.S.; Egna, H.S.; Chopin, T.; Peterson, M.S.; Cao, L.; Pomeroy, R.; Verdegem, M.; Slack, W.T.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Cabello, F. Responsible aquaculture in 2050: Valuing local conditions and human innovations will be key to success. BioScience 2013, 4, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, P. Traditional Asian aquaculture. In New Technologies in Aquaculture, Improving Production, Efficiency, Quantity and Environmental Management; Burnell, G., Allan, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 1029–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Waite, R.; Beveridge, M.; Brummett, R.; Castine, S.; Chaiyawannakarn, N.; Kaushik, S.; Munkung, R.; Nawapakpilai, S.; Phillips, M. Improving Productivity and Environmental Performance of Aquaculture; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Little, D.C.; Newton, R.W.; Beveridge, M.C.M. Aquaculture: A rapidly growing and significant source of sustainable food? Status, transitions and potential. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.L.; Goldburg, R.J.; Primavera, J.H.; Kautsky, N.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Clay, J.; Folke, C.; Lubchenco, J.; Mooney, H.; Troell, M. Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 2000, 405, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, J.P.; Love, D.C.; Macdonald, G.K.; West, P.C.; Engstrom, P.M.; Nachman, K.E.; Lawrence, R.S. Environmental health impacts of feeding crops to farmed fish. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tidwell, J.H. Characteristics and categories of aquaculture production systems. In Aquaculture Production Systems; Tidwell, J.H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 64–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Guo, L.; Han, C.-C. Inland fisheries in China: Past, present, and future. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2017, 25, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P. Aquaculture environment interactions: Past, present and likely future trends. Aquaculture 2015, 447, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pierce, B. Environmental impacts of nutrients from aquaculture: Towards the evolution of sustainable aquaculture systems. In Aquaculture and Water Resource Management; Baird, D.J., Beveridge, M.C.M., Kelly, L.A., Eds.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 81–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Ward, J.D.; Saint, C.P. Can integrated aquaculture-agriculture (IAA) produce “more crop per drop”? Food Secur. 2014, 6, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Halwart, M. Cage aquaculture: A global overview. In FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No. 498, Cage Aquaculture—Regional Reviews and Global Overview; Halwart, M., Soto, D., Arthur, J.R., Eds.; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2007; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Klinger, D.; Naylor, R. Searching for solutions in aquaculture; Charting a sustainable course. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resourc. 2012, 37, 247–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belton, B.; Little, D.C. Immanent and interventionist inland Asian aquaculture development and its outcomes. Devel. Policy Rev. 2011, 29, 459–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ye, S.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhongjie, L. Development of lake and reservoir aquaculture related practices in China. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends, 1st ed.; Gui, J.-F., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., De Silva, S.S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 599–610. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Li, Z. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus from fish cage-culture on the communities of a shallow lake in middle Yangtze River basin of China. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Overbeek, C.C.; Bureau, D.P.; Pawlowski, M.; Glibert, P.M. Hindcasts and future projections of global inland and coastal nitrogen and phosphorus loads due to finfish aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 112–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.-F.; Gu, X.; Ye, Y.; Yang, C.; Dai, X.; Chen, N.; Yang, C. Assessment of pollutant loads discharged from aquaculture ponds around Taihu Lake, China. Aquacult. Res. 2012, 44, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottinger, M.; Clauss, K.; Kuenzer, C. Aquaculture: Relevance, distribution, impacts and spatial assessments—A review. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2016, 119, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Porchas, M.; Martinez-Cordova, L.R. World aquaculture: Environmental impacts and troubleshooting alternatives. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 389623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Chapra, S.C.; Wedepohl, R.; Sims, J.T.; Daniel, T.C.; Reddy, K.R. Managing agricultural phosphorus for protection of surface waters: Issues and options. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Geng, N.; Lu, D.; Zhu, L.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Dissanayake, P.D.; Rinklebe, J.; Yang, X.; et al. Recent advances in control technologies for non-point source pollution with nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural runoff: Current practices and future prospects. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, L.; Lebel, P.; Chuah, C.J. Water use by inland aquaculture in Thailand: Stakeholder perceptions, scientific evidence, and public policy. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneres, M.N.P.; Medeiros, M.V.; Camargo, A.F.M. Overview of strategies that contribute to the environmental sustainability of pond aquaculture: Rearing systems, residue treatment, and environmental assessment tools. Rev. Aquacult. 2019, 12, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, W.C.; Kimpara, J.M.; de, L.; Preto, B.; Moraes-Valenti, P. Indicators of sustainability to assess aquaculture systems. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, T.; Zhao, N.; Ni, Y.; Yi, J.; Wilson, J.P.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, C.; et al. China’s improving inland surface water quality since 2003. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaau3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Qin, B.; Horst, B.; Huang, W. Nitrogen surplus of upstream agriculture land of Lake Taihu and eutrophication impact. J. Lake Sci. 2006, 18, 395–400. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Strokal, M.; Burek, P.; Kroeze, C. Excess nutrient loads to Lake Taihu: Opportunities for nutrient reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueppke, S.G.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Chen, D.; Ou, W. An integrative framework to control nutrient loss: Insights from two hilly basins in China’s Yangtze River delta. Water 2019, 11, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; De Silva, S.S. Inland aquaculture: Trends and prospects. In Aquaculture in China: Success Stories and Modern Trends, 1st ed.; Gui, J.-F., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., De Silva, S.S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- MOA. Zero Growth in Synthetic Fertilizer Use from 2020 Onwards; Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, L.; Fu, B.; Gao, G. Redlines for the greening of China. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 79, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delang, C.O.; Yuan, Z. China’s Grain for Green Program; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–213. [Google Scholar]
- Subasinghe, R. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1135/5, Regional Review on Status and Trends in Aquaculture Development in Asia-2015; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Du, P.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Guo, S. Monitoring human-induced surface water disturbance around Taihu Lake since 1984 by time series Landsat images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 3780–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangwei, Z.; Weimin, C.; Hengpeng, L.; Li, R.; Zhao, G.; Linlin, Z.; Yongxia, G.; Ran-Ran, H.; Yunlin, Z.; Yang, C. Response of water quality to the catchment development and protection in Tianmuhu Reservoir, China. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 809–817. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Cui, Y.; Han, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, M.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; Chen, W. Response of phytoplankton to nutrient reduction in Shahe Reservoir, Taihu catchment, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, F.; Perera, H.A.C.C. Status of reservoir fisheries in China and their effect on environment. In Tropical and Sub-Tropical Reservoir Limnology in China; Han, B.-P., Liu, Z., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Mims, S.D. Paddlefish: International status. In Paddlefish Aquaculture; Mims, S.D., Shelton, W.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 153–178. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Choi, C.-Y. Policy-driven changes in enclosure fisheries of large lakes in the Yangtze plain: Evidence from satellite imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 688, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Zhang, Y.; Paudel, B.; Li, S.; Khanal, N.R. A synthesis of studies on land use and land cover dynamics during 1930-2015 in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Primavera, J.H. Overcoming the impacts of aquaculture on the coastal zone. Ocean. Coastal Manag. 2006, 49, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, B.; Hein, A.; Htoo, K.; Kham, L.S. MSU International Development Working Paper 140, Aquaculture in Transition: Value Chain Transformation, Fish. and Food Security in Myanmar; Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty, M.; Szuster, B.; Miller, P. Low salinity inland shrimp farming in Thailand. AMBIO 2000, 29, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Thompson, S. The blue dimensions of aquaculture: A global synthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipski, M.; Belton, B. Give a man a fishpond: Modeling the impacts of aquaculture in the rural economy. World Devel. 2018, 110, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.S. Aquaculture: A newly emergent food production sector—And perspectives of its impacts on biodiversity and conservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 21, 3187–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Brown, G.; Liu, Y.; Searle, G. An evaluation of contemporary China’s land use policy—The Link Policy: A case study from Ezhou, Hubei Province. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, X. Cultivated land and food supply in China. Land Use Policy 2000, 17, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Rao, S.; Zhao, S. Human-induced long-term changes in the lakes of the Jianghan plain, central Yangtze. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 23, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Fang, J.; Ma, S.; Cai, Q.; Xiong, X.; Tian, D.; Zhao, X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Changes in China’s lakes: Climate and human impacts. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Fang, J.; Ji, W.; Tang, Z. Lake restoration from impoldering: Impact of land conversion on riparian landscape in Honghu Lake area, central Yangtze. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 95, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G. Fisheries development in Xinjiang, China. In FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No. 430, Fisheries in Irrigation Systems in Arid Asia; Petr, T., Ed.; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 2003; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lebel, L.; Lebel, P.; Chuah, C.J. Governance of aquaculture water use. Int. J. Water Res. Devel. 2018, 35, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.D.; Do, L.H. Mangrove forests and aquaculture in the Mekong river delta. Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Lorica, M.H. Improving developing country food security through aquaculture development—Lessons from Asia. Food Policy 2002, 27, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braaten, R.O.; Flaherty, M. Hydrology of inland brackishwater shrimp ponds in Chachoengsao, Thailand. Aquacult. Eng. 2000, 23, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poapongsakorn, N.; Ruhs, M.; Tangjitwisuth, S. Problems and outlook of agriculture in Thailand. Tdri Quart. Rev. 1998, 13, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Vandergeest, P.; Flaherty, M.; Miller, P. A political ecology of shrimp aquaculture in Thailand. Rural Soc. 2009, 64, 573–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, M.; Vandergeest, P.; Miller, P. Rice paddy or shrimp pond: Tough decisions in rural Thailand. World Devel. 1999, 27, 2045–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, B.; Halls, A.; Barr, J. Rice versus fish revisited: On the integrated management of floodplain resources in Bangladesh. Nat. Res. Forum 2004, 28, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.K.; Jensen, K.R.; Lin, C.K. Coastal aquaculture development in Bangladesh: Unsustainable and sustainable experiences. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Tabeta, S. Shrimp vs prawn-rice farming in Bangladesh: A comparative impacts study on local environments and livelihoods. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 168, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Milstein, A.; Wahab, M.A.; Kamal, A.H.M.; Dewan, S. Production and economic return of shrimp aquaculture in coastal ponds of different sizes and with different management regimes. Aquacult. Int. 2005, 13, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Lohano, H.D.; Shyamsundar, P. Production externalities of shrimp aquaculture on paddy farming in coastal Bangladesh. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 238, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, G.A.; Ali, H.; Fujita, K.; Abedin, A.; Habiba, U.; Shaw, R. Land use change in southwestern coastal Bangladesh: Consequence to food and water supply. In Land Use Management in Disaster Risk Reduction; Banba, M., Shaw, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 381–401. [Google Scholar]
- Bernier, Q.; Sultana, P.; Bell, A.R.; Ringler, C. Water management and livelihood choices in southwestern Bangladesh. J. Rural Stud. 2016, 45, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.G.; Vogl, C.R. Impacts of shrimp farming in Bangladesh: Challenges and alternatives. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S. From rice to prawns: Economic transformation and agrarian structure in rural Bangladesh. J. Peasant Stud. 2002, 29, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Shivakoti, G.P.; Salaquzzaman, M. A conceptual framework for the sustainability assessment procedures of the shrimp aquaculture industry in coastal Bangladesh. Int. J. Agric. Resour. Gov. Ecol. 2006, 5, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R. Present status and strategies for future development of shrimp farming in Bangladesh. In Environmental and Socio-Economic Impacts of Shrimp-Farming in Bangladesh; Wahab, M.A., Ed.; BARC Centre: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, M.A. Environmental impacts of shrimp farming in the coastal areas of Bangladesh. In Environmental and Socio-economic Impacts of Shrimp-farming in Bangladesh; Wahab, M.A., Ed.; BARC Centre: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2003; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, J.; Koch, M.; Khoi, C.M.; Braun, G.; Sebesvari, Z.; Amelung, W. Land use change from permanent rice to alternating rice-shrimp or permanent shrimp in the coastal Mekong Delta, Vietnam: Changes in the nutrient status and binding forms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tho, N.; Vromant, N.; Hung, N.T.; Hens, L. Soil salinity and sodicity in a shrimp farming coastal area on the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gephart, J.A.; Troell, M.; Henriksson, P.J.G.; Beveridge, M.C.; Verdegem, M.; Metian, M.; Mateos, L.D.; Deutsch, L. The ‘seafood gap’ in the food-water nexus literature—Issues surrounding freshwater use in seafood production chains. Adv. Water Resourc. 2017, 110, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázár, A.N.; Clarke, D.; Adams, H.; Akanda, A.R.; Szabo, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Matthews, Z.; Begum, D.; Saleh, A.F.M.; Abedin, A.; et al. Agricultural livelihoods in coastal Bangladesh under climate and environmental change—A model framework. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebel, L.; Tri, N.H.; Saengnoree, A.; Pasong, S.; Buatama, U.; Thoa, L.K. Industrial transformation and shrimp aquaculture in Thailand and Vietnam: Pathways to ecological, social, and economic sustainability? AMBIO 2002, 31, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, A.R.; Bryan, E.; Ringler, C.; Ahmed, A. Rice productivity in Bangladesh: What are the benefits of irrigation? Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapan, M.S.H.; Gavin, M. A desert in the delta: Participatory assessment of changing livelihoods induced by commercial shrimp farming in Southwest Bangladesh. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, L.C.; Hoanh, C.T.; Le Page, C.; Bousquet, F.; Gajaseni, N. Facilitating dialogue between aquaculture and agriculture: Lessons from role-playing games with farmers in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Water Policy 2009, 11, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Osuna, F. The environmental impact of shrimp aquaculture: Causes, effects, and mitigating alternatives. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Han, N.H.; Cramb, R. Trends in rice-based farming systems in the Mekong Delta. In White Gold: The Commercialisation of Rice Farming in the Lower Mekong Basin; Cramb, R., Ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: Singapore, 2020; pp. 347–373. [Google Scholar]
- King, P.; Bird, J.; Haas, L. The Current Status of Environmental Criteria for Hydropower Development in the Mekong Region. A Literature Compilation; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boretti, A. Implications on food production of the changing water cycle in the Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.; Pittock, J.; Chapagain, A.; Dumaresq, D. Dams on the Mekong River: Lost fish protein and the implications for land and water resources. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, Y.N.; Burbano, M.; Roush, J.; Kang, H.; Sridhar, V.; Hyndman, D.W. A review of the integrated effects of changing climate, land use, and dams on Mekong River hydrology. Water 2018, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hecht, J.S.; Lacombe, G.; Arias, M.E.; Dang, T.D.; Piman, T. Hydropower dams of the Mekong River basin: A review of their hydrological impacts. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, N.H.; Cao, N.B. Damming the Mekong: Impacts in Vietnam and solutions. In Coasts and Estuaries, The Future; Wolanski, E., Day, J.W., Elliott, M., Ramachandran, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pierce, B.A. Constraints to the sustainability of cage aquaculture for resettlement from hydropower dams in Asia: An Indonesian case study. J. Environ. Devel. 1998, 7, 333–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, M.; Someth, P.; Salmivaara, A.; Kummu, M. Water-energy-food nexus in a transboundary river basin: The case of Tonle Sap Lake, Mekong River basin. Water 2015, 7, 5416–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskinen, M.; Guillaume, J.H.A.; Kattelus, M.; Porkka, M.; Räsänen, T.A.; Varis, O. The water-energy-food nexus and the transboundary context: Insights from large Asian rivers. Water 2016, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Middelkoop, H.; Erkens, G.; Stouthamer, E. Groundwater extraction may drown mega-delta: Projections of extraction-induced subsidence and elevation of the Mekong delta for the 21st century. Environ. Res. Commun. 2020, 2, 011005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Varis, O. Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Schmitt, R.J.; Carling, P.A.; Darby, S.; Arias, M.; Bizzi, S.; Castelletti, A.; Cochrane, T.A.; Gibson, S.; Kummu, M.; et al. Changing sediment budget of the Mekong: Cumulative threats and management strategies for a large river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuenzer, C.; Campbell, I.C.; Roch, M.; Leinenkugel, P.; Tuan, V.Q.; Dech, S. Understanding the impact of hydropower developments in the context of upstream-downstream relations in the Mekong river basin. Sustain. Sci. 2013, 8, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; He, D.; Wang, H. Environmental consequences of damming the mainstream Lancang-Mekong River: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 146, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VMNRE. Vietnam Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment Study on the Impacts of Mainstream Hydropower on the Mekong River; HDR, Inc.: Englewood, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Trung, B.H.; Tran, H.-D.; Lall, M.K.; Kakar, K.; Xuan, T.D. Impacts of mainstream hydropower dams on fisheries and agriculture in Lower Mekong Basin. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, K.R.; Morton, L.R. Polders, dikes, canals, rice, and aquaculture in the Mekong Delta. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 83A–89A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Käkönen, M. Mekong Delta at the crossroads: More control or adaptation. AMBIO 2008, 37, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredén, F. Impacts of Dams on Lowland Agriculture in the Mekong River Catchment; Lunds Universitets Naturgeografiska Institution-Seminarieuppsatser: Lund, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, I.N.B.L.; Kim, B.-K.; Yoon, I.-S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, T.-R. Salt tolerance in rice: Focus on mechanisms and approaches. Rice Sci. 2017, 14, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Duan, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhang, L.; Chai, Q.; Hu, X. Understanding land use/land cover dynamics and impacts of human activities in the Mekong Delta over the last 40 years. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, J.; Dumaresq, D.; Orr, S. The Mekong River: Trading off hydropower, fish, and food. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICEM. Strategic Environmental Assessment of Hydropower on the Mekong Mainstream. Summary of the Final Report; Mekong River Commission: Vientiane, Laos, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmsen, B. Progress, problems, and prospects of dam-induced displacement and resettlement in China. China Inf. 2011, 25, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, F.; Mohan, G.; Cook, S. China as a new shaper of international development: The environmental implications. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2013, 15, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, K.R.; Morton, L.R. Tonle Sap Lake and river and confluence with the Mekong River in Cambodia. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joffre, O.M.; Pant, J.; Somony, T.; Chantrea, B.; Viseth, H. Transforming Aquaculture in Cambodia through Introduction of Improved Tilapia; WorldFish: Penang, Malaysia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, O. Current status of sustainable agriculture in Cambodia. In Resource Enhancement and Sustainable Aquaculture Practices in Southeast Asia: Challenges in Responsible Production of Aquatic Species; Romana-Egua, R.R., Parado-Estepa, F.D., Salayo, N.D., Lebata-Ramos, J.H., Eds.; Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center: Tigbauan, Philippines, 2014; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gain, A.K.; Giupponi, C. Impact of the Farakka Dam on thresholds of the hydrologic flow regime in the lower Ganges River basin (Bangladesh). Water 2014, 6, 2501–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hennig, T. Damming transnational Ayeyarwady basin. Hydropower and the water-energy nexus. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 1232–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, X.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P. Recent evolution of the Irrawaddy (Ayeyarwady) delta and the impacts of anthropogenic activities: A review and remote sensing survey. Geomorphology 2020, 365, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.; Tian, F.; Zhu, T.; Zohidov, B.; Ni, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, H. Exploring synergies in the water-food-energy nexus by using an integrated hydro-economic optimization model for the Lancang-Mekong River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 137996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kautsky, N.; Berg, H.; Folke, C.; Larsson, J.; Troell, M. Ecological footprint for assessment of resource use and development limitations in shrimp and tilapia aquaculture. Aquacult. Res. 1997, 28, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Hasan, M.R.; Metian, M. Demand and Supply of Feed Ingredients from Farmed Fish. and Crustaceans; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, C.J.; Jackson, A.J. Global fishmeal and fish-oil supply: Inputs, outputs and markets. Fish. Biol. 2013, 83, 1046–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Hasan, M.R. Global synthesis of feeds and nutrients for sustainable aquaculture development. In Study and Analysis of Feeds and Fertilizers for Sustainable Aquaculture Development; Hasan, M.R., Hecht, T., De Silva, S.S., Tacon, A.G.J., Eds.; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tveterås, S.; Tveterås, R. The global competition for wild fish resources between livestock and aquaculture. J. Agric. Econ. 2010, 61, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Shan, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhongjie, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; et al. A revisit to fishmeal usage and associated consequences in Chinese aquaculture. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 10, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, M.; van Oel, P.R.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Increasing pressure on freshwater resources due to terrestrial feed ingredients for aquaculture production. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malcorps, W.; Kok, B.; Land, M.V.; Fritz, M.; Van Doren, D.; Servin, K.; Van Der Heijden, P.; Palmer, R.; Auchterlonie, N.A.; Rietkerk, M.; et al. The sustainability conundrum of fishmeal substitution by plant ingredients in shrimp feeds. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, J.P.; Mailloux, N.A.; Love, D.C.; Milli, M.C.; Cao, L. Feed conversion efficiency in aquaculture: Do we measure it correctly? Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Cobcroft, J.M.; Cole, A.; Condon, K. The future of aquatic protein: Implications for protein sources in aquaculture diets. One Earth 2019, 1, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, W.Y.; Man, Y.B.; Wong, M.H. Use of food waste, fish waste and food processing waste for China’s aquaculture industry: Needs and challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Yuan, X. The carp farming industry in China—An overview. In Species and System Selection for Sustainable Aquaculture; Leung, P., Lee, C., O’Bryen, P.J., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2007; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Verdegem, M.C.J.; Bosma, R.H.; Verreth, J.A. Reducing water use for animal production through aquaculture. Int. J. Water Resourc. Devel. 2006, 22, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, K.D. (Ed.) Rice-Fish. Culture in China. International Development Research Centre: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, C.H. Rice field ecology and fish culture—An overview. Hydrobiologia 1993, 259, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, D.C.; Edwards, P. Integrated Livestock-Fish. Farming Systems; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.V.; Sollows, J.D.; Mazid, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Hussain, M.G.; Dey, M.M. Economics and adoption patterns of integrated rice-fish farming in Bangladesh. In Rural Aquaculture; Edwards, P., Little, D.C., Demaine, H., Eds.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, R.K.; Verma, H.N.; Brahmanand, P.S. Performance evaluation of rice-fish integration system in rainfed medium land ecosystem. Aquaculture 2004, 230, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, D.C.; Surintaraseree, P.; Innes-Taylor, N. Fish culture in rainfed rice fields of northeast Thailand. Aquaculture 1996, 140, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.; Guttman, H. The ricefield catch and rural food security. In Rural Aquaculture; Edwards, P., Little, D.C., Demaine, H., Eds.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, M.M.; Spielman, D.J.; Haque, A.B.M.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Valmonte-Santos, R.A. Change and Diversity in Smallholder Rice-Fish. Systems. Recent Evidence from Bangladesh; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haroon, A.K.Y.; Pittman, K.A. Rice-fish culture: Feeding, growth and yield of two size classes of Puntius gonionotus Bleeker and Oreochromis spp. in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 1997, 154, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, B. An overview on desert aquaculture in Central Asia (Aral Sea Drainage Basin). In Aquaculture in Desert and Arid Lands, Development Constraints and Opportunities; Crespi, V., Lovatelli, A., Eds.; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Halwart, M.; Gupta, M.V. (Eds.) Culture of Fish in Rice Fields; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Uphoff, N. The System of Rice Intensification (SRI): IRC Newsletter No. 55, Using Alternative Cultural Practices to Increase Rice Production and Profitability from Existing Yield Potentials; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kunda, M.; Azim, M.E.; Wahab, M.A.; Dewan, S.; Roos, N.; Thilsted, S.H. Potential of mixed culture of freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) and self-recruiting small species mola (Amblypharyngodon mola) in rotational rice-fish/prawn culture systems in Bangladesh. Aquacult. Res. 2009, 39, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Ge, X. Freshwater prawn culture in China: An overview. Aquacult. Asia 2002, 7, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Giap, D.H.; Yi, Y.; Lin, C.K. Effects of different fertilization and feeding regimes on the production of integrated farming of rice and prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man). Aquacult. Res. 2005, 36, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesoemadinata, S.; Costa-Pierce, B.A. Development of rice-fish farming in Indonesia: Past, present and future. In Rice-Fish Research and Development in Asia; Dela Cruz, C.R., Lightfoot, B.A., Costa-Pierce, B.A., Carangal, V.R., Bimbao, M.P., Eds.; International Center for Living Aquatic Resources: Penang, Malaysia, 1992; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Wahab, M.A.; Thilsted, S.H. Integrated aquaculture-agriculture systems in Bangladesh: Potential for sustainable livelihoods and nutritional security of the rural poor. Aquacult. Asia 1992, 12, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.; Little, D.C.; Kabir, M.S.; Verdegem, M.J.C. Enhancing benefits from polycultures including tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) within integrated pond-dike systems: A participatory trial with households of varying socio-economic level in rural and peri-urban areas of Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2011, 314, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, D.K.; Phong, L.T.; Verdegem, M.; Duong, L.T.; Bosma, R.H.; Little, D.C. Integrated fresh water aquaculture, crop and livestock production in the Mekong delta, Vietnam: Determinants and the role of the pond. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, J.; Demaine, H.; Edwards, P. Assessment of the aquaculture subsystem in integrated agriculture-aquaculture systems in Northeast Thailand. Aquacult. Res. 2004, 35, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal-Lagarda, M.M.; Páez-Osuna, F.; Esquer-Méndez, J.L.; Guerrero-Monroy, I.; Del Vivar, A.R.; Félix-Gastelum, R. Integrated culture of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) with low salinity groundwater: Management and production. Aquaculture 2012, 366–367, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, L.; Van Dam, A.; Udo, H.; Van Mensvoort, M.; Tri, L.; Steenstra, F.; Van Der Zijpp, A. An agro-ecological evaluation of aquaculture integration into farming systems of the Mekong Delta. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, D.K.; Milstein, A.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Verreth, J.A.V. Food inputs, water quality and nutrient accumulation in integrated pond systems: A multivariate approach. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, H.; Lahoti, S.; Saito, O.; Mahalingam, A. Assessment of ecosystem services in homegarden systems in Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and Vietnam. Int. J. Agric. Sust. 2011, 5, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.; Byrd, K.A.; Pincus, L.; Naziri, D.; Yossa, R.; Thilsted, S. Integrating Fish., Tubers and Bananas in Food Systems: Opportunities and Constraints; WorldFish: Penang, Malaysia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, P.; Little, D.C.; Demaine, H. Issues in rural aquaculture. In Rural Aquaculture; Edwards, P., Little, D.C., Demaine, H., Eds.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 323–340. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, J.; Promthong, P.; Lin, C.K.; Demaine, H. Fertilisation of ponds with inorganic fertilisers: Low cost technologies for small-scale farmers. In Rural Aquaculture; Edwards, P., Little, D.C., Demaine, H., Eds.; CABI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle, K.; Zhong, G. Integrated Agriculture-Aquaculture in South. China. The Dike-Pond System of the Zhu Jiang Delta; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle, K.; Furtado, J.I.; Zhong, G.F.; Deng, H.Z. The mulberry dike-carp pond resource system of the Zhujiang (Pearl River) Delta, People’s Republic of China; I. Environmental context and system overview. Appl. Geog. 1983, 3, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.P. Environmental impact on the development of agricultural technology in China: The case of the dike-pond (‘jitang’) system of integrated agriculture-aquaculture in the Zhujiang Delta of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 60, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Min, Q.; Jiao, W.; Liu, C.; Yin, J. Integrated emergy and economic evaluation of Huzhou mulberry-dyke and fish-pond systems. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Dou, Y.Q.; Gui, Z.Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Y.-L.; Wang, W.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-S. Mulberry-base-fish-pond, the typical model of sericultural circular economy in southern China. Sci. Sericult. 2010, 36, 470–474. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Lou, L.; Liu, C.; Yu, Q. Jitang system: Research review and prospects. J. Nat. Resourc. 2018, 22, 709–720. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astudillo, M.F.; Thalwitz, G.; Vollrath, F. Modern analysis of an ancient integrated farming arrangement: Life cycle assessment of a mulberry dyke and pond system. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, T.; Ismukhanov, K.; Kamilov, B.; Umarov, P.D. Irrigation systems and their fisheries in the Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Management of Large Rivers for Fisheries; Wellcome, R.L., Petr, T., Eds.; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 223–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ismukhanov, K.; Mukhamedzhanov, V. The use of irrigation systems for sustainable production of agricultural and fish products in the Republic of Kazakhstan. In Fisheries in Irrigation Systems of Arid Asia; Petr, T., Ed.; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2004; pp. 101–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhiltsov, S.S.; Zhiltsova, M.S.; Medvedev, N.P.; Slizovskiy, D.Y. Water resources of Central Asia: Historical overview. In Water Resources in Central Asia: International Context; Zhiltsov, S.S., Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Semenov, A.V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 9–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidov, A.; Helming, K.; Balla, D. Impact of agricultural land use in Central Asia: A review. Agron. Sustain. Devel. 2016, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamilov, B. The use of irrigation systems for sustainable fish production: Uzbekistan. In Fisheries in Irrigation Systems of Arid Asia; Petr, T., Ed.; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2004; pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.; Rosen, M.R.; Saito, L.; Decker, D.L. The influence of irrigation water on the hydrology and lake water budgets of two small arid-climate lakes in Khorezm, Uzbekistan. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, C.H.; Halwart, M. Possibilities for the integration of fish farming into irrigation systems. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2000, 7, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gowing, J.W.; Mayilswami, C. Multiple-use management in a large irrigation system: An assessment of technical constraints to integrating aquaculture within irrigation canals. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, T.A.; Midlen, A.B. Fish. Production in Irrigation Canals, A Review; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang-Erlandsson, L.; van der Ent, R.J.; Gordon, L.J.; Savenije, H.H.G. Contrasting roles of interception and transpiration in the hydrological cycle. Part 1: Temporal characteristics over land. Earth. Syst. Dynam. 2014, 5, 441–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimov, B.; Kamilov, B.; Upare, M.; van Anrooy, R.; Bueno, P.; Shokhimardonov, D. Inland Capture Fisheries and Aquaculture in the Republic of Uzbekistan: Current Status and Planning; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Timirkhanov, S.; Chaikin, B.; Makhambetova, Z.; Thorpe, A.; van Anrooy, R. Fisheries and Aquaculture in the Republic of Kazakhstan: A review; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Karimov, B.K.; Matthies, M.; Kamilov, B.G. Unconventional water resources of agricultural origin and their re-utilization potential for development of desert land aquaculture in the Aral Sea basin. In The Global Water System in the Anthropocene; Bhaduri, A., Bogardi, J., Leentvaar, J., Marx, S., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kostianoy, A.B.; Kosarev, A.N. (Eds.) The Aral Sea Environment; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikov, Y.V.; Assylbekova, Z. The fisheries and aquaculture sector in Kazakhstan: Significant potential to be realized. Eurofish Mag. 2020, 3, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Badryzlova, N.; Koishybayeva, S.; Assylbekova, S.; Isbekov, K. Technology of formation of replacement-brood stock of pikeperch in conditions of fish farms in Kazakhstan. Eur. Asian J. BioSci. 2020, 14, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, N.A.; Pueppke, S.G.; Uderbayev, T. The current status and future of Central Asia’s fish and fisheries: Confronting a wicked problem. Water 2017, 9, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhiltsov, S.S.; Zonn, I.S.; Nogmova, A.S.; Shtol, V.V. Water resource policy in Kazakhstan. In Water Resources in Central Asia: International Context; Zhiltsov, S.S., Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Semenov, A.V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Wecker, B.; Karimov, B.; Kamilov, B.; Waller, U. Sustainable Aquaculture in Recirculating Systems, Feasibility Study for the Catchment Area of the Aral Sea; Institut für Umweltsystemforschung, Universität Osnabrück: Osnabrück, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, V.; Lovatelli, A. Global desert aquaculture at a glance. In Aquaculture in Desert and Arid Lands, Development Constraints and Opportunities; Crespi, V., Lovatelli, A., Eds.; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Crootof, A.; Mullabaev, N.; Saito, L.; Atwell, L.; Rosen, M.R.; Bekchonova, M.; Ginatullina, E.; Scott, J.; Chandra, S.; Nishonov, B.; et al. Hydroecological condition and potential for aquaculture in lakes of the arid region of Khorezm, Uzbekistan. J. Arid. Environ. 2015, 117, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.; Kaiser, B.O.; Lamers, J.P.A. Quantifying water volumes of small lakes in the inner Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia, and their potential for reaching food and water security. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 75, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, W.; Diffey, S.; Peter, T. Innovations in Fisheries Management for Kazakhstan; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- FAO, FAOLEX. Decree on Measures to Improve the Management System of the Fishing Industry; No. 2939; FAO, FAOLEX: Tashkent, Republic of Uzbekistan, 2017. (In Uzbek) [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell, R.S.; Nash, K.L.; Halpern, B.S.; Remenyi, T.; Corney, S.; Fleming, A.; Fulton, E.A.; Hornborg, S.; Johne, A.; Watson, R.A.; et al. Food production shocks across land and sea. Nat. Sust. 2019, 2, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullin, R.S.V.; Shehadeh, Z.X. (Eds.) Integrated Agriculture-Aquaculture Farming Systems; ICLARM: Manila, Philippines, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zajdband, A.D. Integrated agri-aquaculture systems. In Genetics, Biofuels and Local Farming Systems; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2011; pp. 87–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, M.; Xu, T. China’s water-saving irrigation management system: Policy, implementation, and challenge. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haylor, G.; Bhutta, M.S. The role of aquaculture in the sustainable development of irrigated farming systems in Punjab, Pakistan. Aquacult. Res. 2008, 28, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiltsov, S.S.; Zonn, I.S.; Kostianoy, G.; Semenov, A.K. Conclusions. In Water Resources in Central Asia: International Context; Zhiltsov, S.S., Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Semenov, A.V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, G. Conflict of interest between hydropower and irrigation in Central Asia. Its causes and ways of overcoming. Central Asia Cauc. 2010, 13, 59–72. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pullin, R.S.V. An overview of environmental issues in developing country agriculture. In Environment and Aquaculture in Developing Countries; Pullin, R.S.V., Rosenthal, H., Maclean, J.L., Eds.; ICLARM: Manila, Philippines, 1993; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tezzo, X.; Bush, S.R.; Oosterveer, P.; Belton, B. Food system perspective on fisheries and aquaculture development in Asia. Agric. Hum. Values 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, P.; Dey, M.M.; Sugunan, V.V. Fisheries and water productivity in tropical river basins: Enhancing food security and livelihoods by managing water for fish. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haylor, G.S. Fish production from engineered waters in developing countries. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture; Muir, J.E., Roberts, R.J., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1994; pp. 1–103. [Google Scholar]
- Intralawan, A.; Smajgl, A.; McConnell, W.; Ahlquist, D.B.; Ward, J.; Kramer, D.B. Reviewing benefits and costs of hydropower development evidence from the Lower Mekong River Basin. Wires Water 2019, 6, e1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pierce, B.A. Sustainable ecological aquaculture systems: The need for a new social contract for aquaculture development. Mar. Tech. Soc. J. 2010, 44, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.; Brugere, C.; Diedrich, A.; Ebeling, M.W.; Ferse, S.C.; Mikkelsen, E.; Agúndez, J.A.P.; Stead, S.M.; Stybel, N.; Troell, M. A revolution without people? Closing the people-policy gap in aquaculture development. Aquaculture 2015, 447, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, K.A. The problem with solutions: Development failures in Bangladesh and the interests they obscure. Ann. Amer. Assoc. Geog. 2020, 110, 1631–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Tran, D.D.; Dang, K.K.; Korbee, D. Land-use dynamics in the Mekong delta: From a national policy to livelihood sustainability. Sust. Devel. 2020, 28, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, S.R.; Belton, B.; Little, D.C.; Islam, M.S. Emerging trends in aquaculture value chain research. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toufique, K.A.; Gregory, R. Common waters and private lands: Distributional impacts of floodplain aquaculture in Bangladesh. Food Policy 2008, 33, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.S.; Morrissey, M.T. Biotechnology in aquaculture: Transgenics and polyploidy. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2007, 6, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, R.D.; Bean, T.P.; Macqueen, D.J.; Gundappa, M.K.; Jin, Y.H.; Jenkins, T.L.; Selly, S.L.C.; Martin, S.A.M.; Stevens, J.R.; Santos, E.M.; et al. Harnessing genomics to fast track genetic improvement in aquaculture. Nature Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, A.K.; Shamim, M.; Cruzado, K.; Soriano, G.; Ghatak, A.; Toleco, M.; Vikram, P. Role of biotechnology in rice production. In Rice Production Worldwide; Chauhan, B., Jabran, K., Mahajan, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 487–547. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson, P.J.G.; Belton, B.; Murshed-e-Jahan, K.; Rico, A. Measuring the potential for sustainable intensification of aquaculture in Bangladesh using life cycle assessment. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2958–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sears, L.; Caparelli, J.; Lee, C.; Pan, D.; Strandberg, G.; Vuu, L.; Lawell, C.-Y.C.L. Jevons’ Paradox and efficient irrigation technology. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pueppke, S.G.; Zhang, Q.; Nurtazin, S.T. Irrigation in the Ili River basin of Central Asia: From ditches to dams to diversion. Water 2018, 10, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumont, A.; Mayor, B.; López-Gunn, E. Is the rebound effect or Jevons paradox a useful concept for better management of water resources? Insights from the irrigation modernization process in Spain. Aquat. Proc. 2012, 1, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, L.; Lin, C.Y.C. Does efficient irrigation technology lead to reduced groundwater extraction? Empirical evidence. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 67, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Williams, J.; Perry, C.J.; Molle, F.; Ringler, C.; Steduto, P.; Udall, B.; Wheeler, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Garrick, D.; et al. The paradox of irrigation efficiency. Science 2018, 361, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fierro-Sañudo, J.F.; Rodriguez-Montes de Oca, G.A.; Páez-Osuna, F. Co-culture of shrimp with commercially important plants: A review. Rev. Aquacult 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barange, M.; Bahri, T.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Cochrane, K.L.; Funge-Smith, S.; Poulain, F. Impacts of Climate Change on Fisheries and Aquaculture: Synthesis of Current Knowledge, Adaptation and Mitigation Options; United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, G.K.; Gurney-Smith, H.J.; Flaherty, M.; Garber, A.F.; Forster, I.; Brewer-Dalton, K.; Knowler, D.; Marcogliese, D.J.; Chopin, T.; Moccia, R.D.; et al. Climate change and aquaculture: Considering adaptation potential. Aquacult. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 603–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, R.J. Innovations in plant genetics adapting agriculture to climate change. Curr. Opinion Plant Biol. 2020, 56, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gong, B. Response and adaptation of agriculture to climate change: Evidence from China. J. Devel. Econ. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, A.; Baumann, M.; Freitag, M.; Hölzel, N.; Hostert, P.; Kamp, J.; Müller, D.; Prischchepov, A.V.; Kuemmerle, T. Annual Landsat time series reveal post-Soviet changes in grazing pressure. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Oweis, T.; Steduto, P.; Bindraban, P.; Hanjra, M.A.; Kijne, J. Improving agricultural water productivity: Between optimism and caution. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, S.; Stentiford, G.; Leocadio, A.M.; Jeffery, K.R.; Metcalfe, J.D.; Katsiadaki, I.; Auchterlonie, N.A.; Mangi, S.C.; Pinnegar, J.K.; Ellis, T.; et al. Aquatic food security: Insights into challenges and solutions from an analysis of interactions between fisheries, aquaculture, food safety, human health, fish and human welfare, economy and environment. Fish. Fish. 2016, 17, 893–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, M.A.H.; Sikdar, M.M.H.; Mahbub Morshed Khan, A.B.M.; Alam, M.J. Poverty alleviation through aquaculture: An inquiry into some selected areas of rural Bangladesh. Haya Saudi J. Life Sci. 2019, 4, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
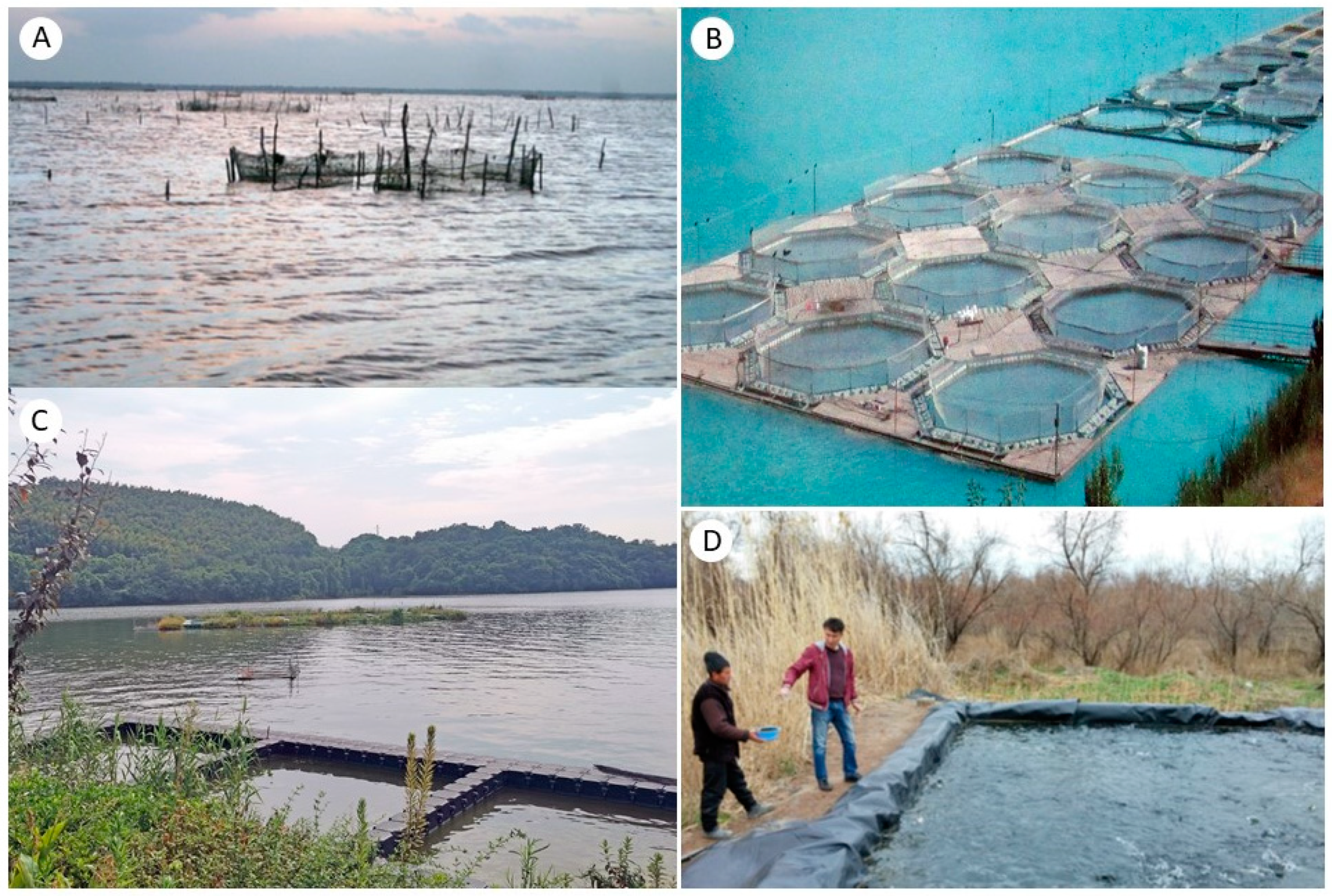



| System (examples) | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Open (Enclosures in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs) | Relies on natural processes Investment ranges from low to high Scalable, can be made intensive |
| Partially closed (Ponds, irrigation canals, flooded agricultural fields) | Suitable for smallholders Extensive to highly intensive Amenable to integrated agriculture-aquaculture (IAA) |
| Fully closed (Recirculating aquaculture facilities, hydroponic systems) | Complete environmental control High efficiency and productivity Requires significant investment and management |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pueppke, S.G.; Nurtazin, S.; Ou, W. Water and Land as Shared Resources for Agriculture and Aquaculture: Insights from Asia. Water 2020, 12, 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102787
Pueppke SG, Nurtazin S, Ou W. Water and Land as Shared Resources for Agriculture and Aquaculture: Insights from Asia. Water. 2020; 12(10):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102787
Chicago/Turabian StylePueppke, Steven G., Sabir Nurtazin, and Weixin Ou. 2020. "Water and Land as Shared Resources for Agriculture and Aquaculture: Insights from Asia" Water 12, no. 10: 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102787
APA StylePueppke, S. G., Nurtazin, S., & Ou, W. (2020). Water and Land as Shared Resources for Agriculture and Aquaculture: Insights from Asia. Water, 12(10), 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102787






